The Effect of the Calcination Time on the Microstructure and Properties of MnZn Ferrite Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. X-ray Analysis
3.2. BET and Particle Size Analysis
3.3. Spectral Analysis
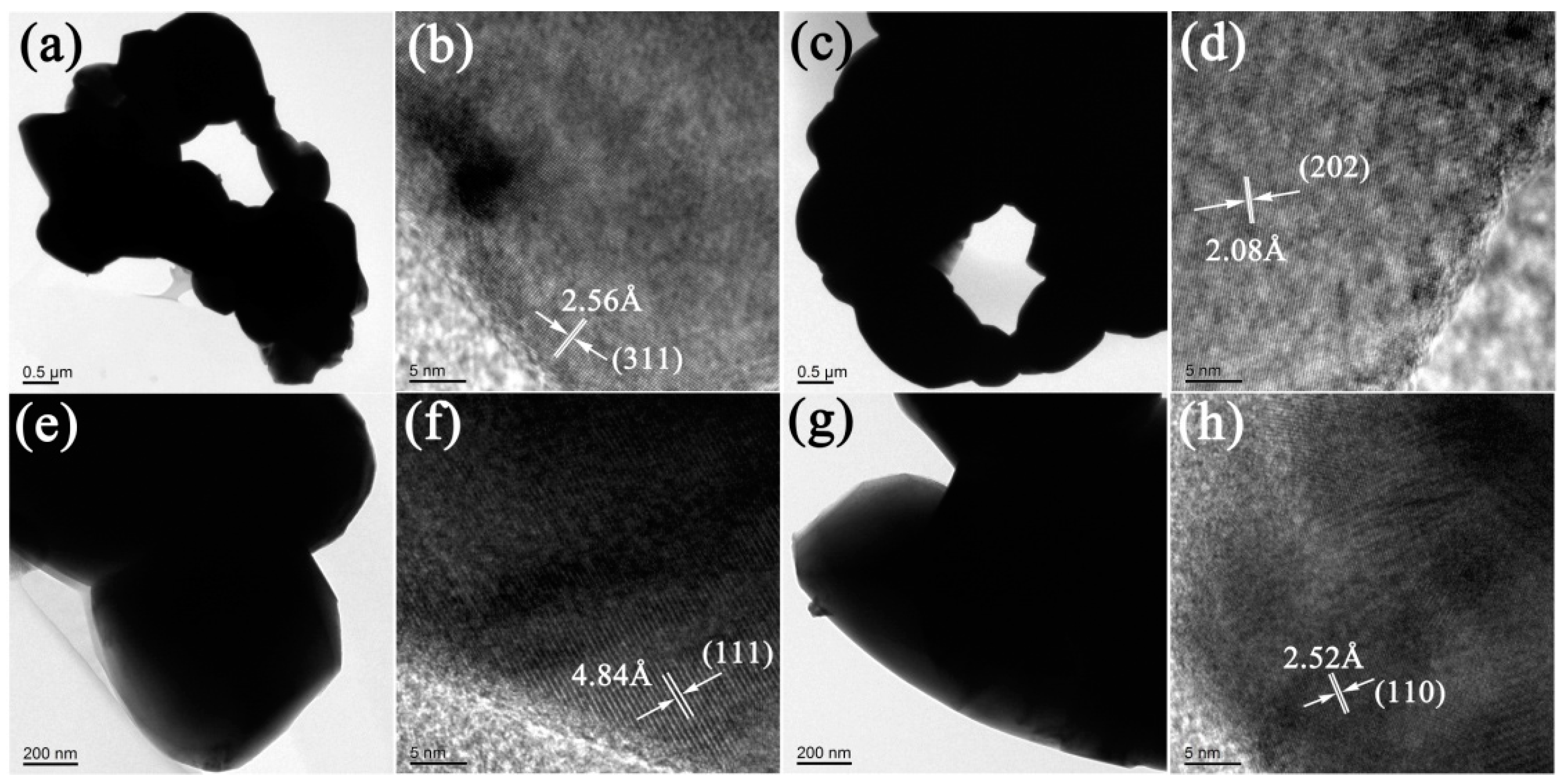
3.4. Electron Microscopic Analysis
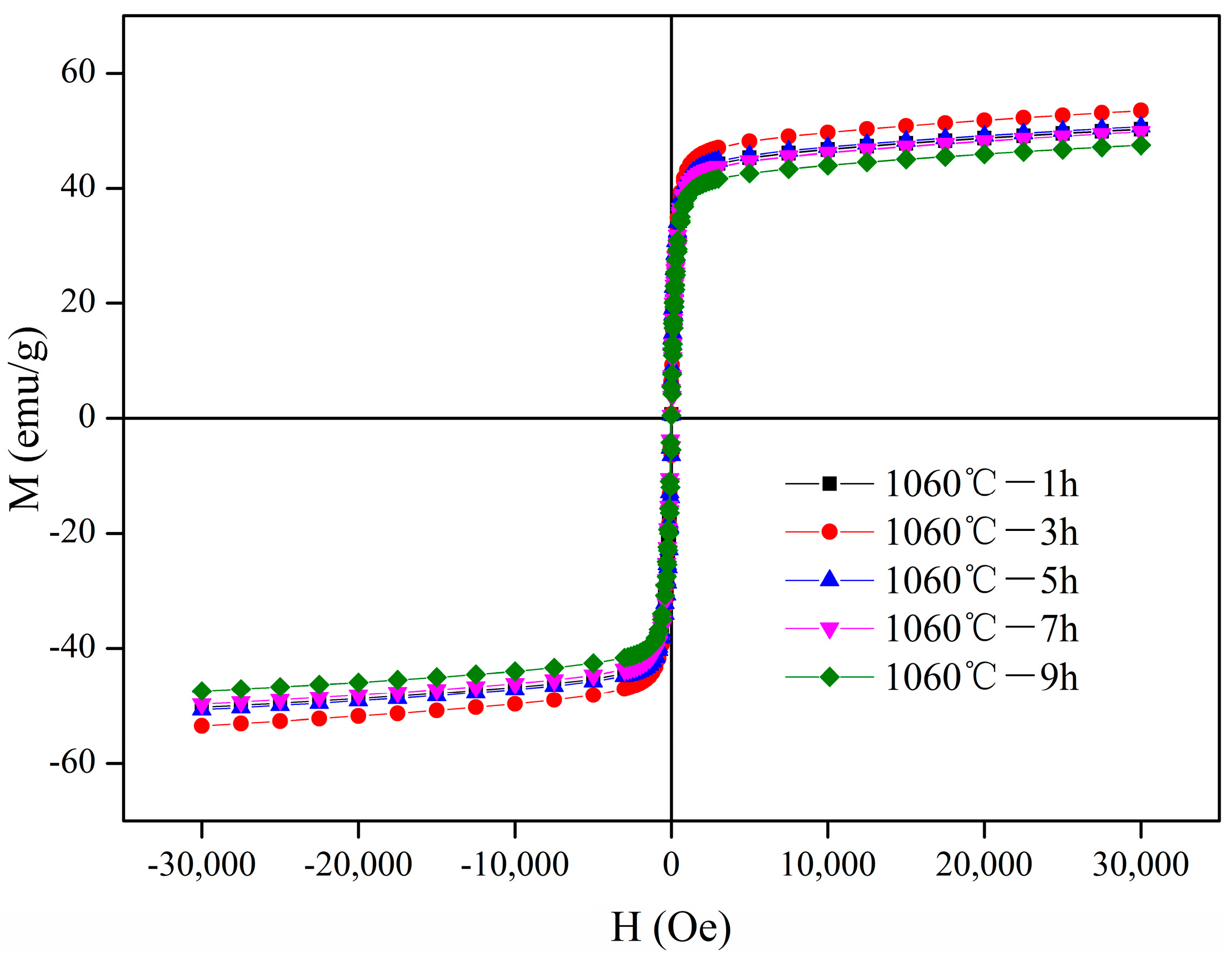
3.5. Magnetic Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yi, S.; Bai, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hussain, A.; Jin, J.; Yan, M. Development of high-temperature high-permeability MnZn power ferrites for MHz application by Nb2O5 and TiO2 co-doping. Ceram. Int. 2019, 46, 8935–8941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ma, D.; Sun, B.; Xu, X.; Quan, W.; Xiao, Z.; Zhai, Y. A high-performance magnetic shield with MnZn ferrite and Mu-metal film combination for atomic sensors. Materials 2022, 15, 6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakaloudi, V.; Zaspalis, V. Synthesis of a low loss Mn–Zn ferrite for power applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 400, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yu, Z.; Sun, K.; Guo, R.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Wu, C.; Lan, Z. Ultra-low core losses at high frequencies and temperatures in MnZn ferrites with nano-BaTiO3 additives. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 821, 153573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yi, S.; Wu, C.; Bai, G.; Yan, M. Correlating the microstructure and magnetic properties of MnZn power ferrites via Co2O3 and MoO3 co-doping for MHz applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 538, 168324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Prakash, G.; Ozturk, A.B.; Saghazadeh, S.; Sohail, M.F.; Seo, J.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A. Evolution and clinical translation of drug delivery nanomaterials. Nano Today 2017, 15, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.C.; Guo, X.J.; Zou, S.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Liu, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, K.X. Improving soft magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrite by rare earth ions doping. AIP Adv. 2017, 8, 047807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadu, A.V.; Jagtap, S.V.; Chaudhari, G.N. Chaudhari, Studies on the preparation and ethanol gas sensing properties of spinel Zn0.6Mn0.4Fe2O4 nanomaterials. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sertkol, M. Impact of Cd2+ substitution on the structural and magnetic peculiarities of MnZn nanospinel ferrites. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2022, 101, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Luo, F. Preparation and characterization of fibrous MnZn ferrite via a water-assisted solvothermal method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 571, 170563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y. Tuning the structural and magnetic properties of MnZn nano-ferrites synthesized under a high magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 495, 165832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Ju, B.K.; Chun, M.P. Characterization and synthesis of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by thermal decomposition. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2020, 21, S28–S32. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, F.; Lahiri, B.; Ranoo, S.; Philip, J. Effect of Zn substitution on the AC induction heating properties of ZnxMn1-xFe2O4 (x=0.1–0.9) nanoparticles prepared using microwave assisted synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 33462–33473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Fan, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, P.; Yan, H. The influence of modification route on the properties of W-0.3 wt% Y2O3 powder and alloy prepared by nano-in-situ composite method. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 774, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J. Research progress of nano-in-situ composite high-performance fine-grained tungsten matrix composites. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Powder Metallurgy and Cross-Strait Seminar on Powder Metallurgy Technology, Wuhan, China, 9–12 September 2015; p. 328. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Fan, J.; Han, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Song, K.; Zhang, C. Preparation and characterization of Mn–Zn ferrites via nano-in-situ composite method. Solid State Sci. 2019, 98, 106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Fan, J.; Liu, T.; Han, Y.; Zhang, H. Calcination induced phase transformation in MnZn ferrite powders. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 814, 152307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Fan, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Yin, F.; Han, Y.; Liu, T. Microstructure and magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite powders prepared by nano-in-situ composite method. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Fan, J. Research on the surfactant-assisted synthesis of MnZn ferrite precursor powders. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D. The Researech of SHS Method for the Preparation of Ferrites; Sichuan University: Chendu, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Grau-Crespo, R.; Al-Baitai, A.Y.; Saadoune, I.; Leeuw, N.H.D. Vacancy ordering and electronic structure of γ-Fe2O3 (maghemite): A theoretical investigation. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2010, 22, 255401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babay, S.; Mhiri, T.; Toumi, M. Synthesis, structural and spectroscopic characterizations of maghemite γ-Fe2O3 prepared by one-step coprecipitation route. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1085, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, D.L.; McCarthy, G.J. X-ray Powder Data for an Industrial Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3). Powder Diffr. 1988, 3, 104–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelm, K.; Mader, W. The Symmetry of Ordered Cubic γ-Fe2O3 Investigated by TEM. Z. Naturforschung B 2006, 61, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.S.; Masoudpanah, S.; Amiri, H.; Yousefzadeh, M. Magnetic properties of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles obtained by SHS and sol-gel autocombustion techniques. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 6713–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Yang, H.-B.; Pan, D.-A.; Wang, H.; Tian, J.-J.; Zhang, S.-G.; Wang, X.-F.; Volinsky, A.A. Heat treatment effects on microstructure and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrite powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleknejad, Z.; Gheisari, K.; Raouf, A.H. Structure, microstructure, magnetic, electromagnetic, and dielectric properties of nanostructured Mn–Zn ferrite synthesized by microwave-induced urea–nitrate process. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2016, 29, 2523–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyshova, I.; Hochella, M., Jr.; Madden, A. Size-dependent structural transformations of hematite nanoparticles. 1. Phase transition. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 1736–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamritski, I.; Burns, G. Infrared- and Raman-Active Phonons of Magnetite, Maghemite, and Hematite: A Computer Simulation and Spectroscopic Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 4965–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Qin, X.F.; Meng, Y.F.; Guo, Z.L.; Yang, L.X.; Ming, Y.F. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2013, 16, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Qi, L.; Gao, S.; Jian, K.S. Arsenic (III,V) removal from aqueous solution by ultrafine α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles synthesized from solvent thermal method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, K.; Lenggoro, I.W. Preparation of nanoparticles via spray route. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagdi, A.R.; Solanki, N.P.; Carvalho, F.E.; Meena, S.S.; Bhatt, P.; Pullar, R.C.; Jotania, R.B. Influence of Mg substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of X-type bariumzinc hexaferrites Ba2Zn2-xMgxFe28O46. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 741, 377–391. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Xxa, B.; Nwa, B.; Jza, B.; Jing, Y.; Wla, B.; Liang, Q.; Wei, C.; Jla, B.; Hui, H.A. Low temperature sintered MnZn ferrites for power applications at the frequency of 1 MHz. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 5924–5930. [Google Scholar]





| Samples | Crystallite Size (nm) | Particle Size (μm) | SBET (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 63.4 | 16.1 | 0.23 |
| 3 h | >100 | 14.0 | 0.33 |
| 5 h | 92.0 | 21.6 | 0.19 |
| 7 h | 93.9 | 28.4 | 0.14 |
| 9 h | 88.0 | 32.2 | 0.16 |
| Samples | Ms (emu/g) | Mr (emu/g) | Hc (Oe) | Mr/Ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 50.31 | 5.97 | 27.54 | 0.12 |
| 3 h | 53.49 | 6.50 | 28.03 | 0.12 |
| 5 h | 50.72 | 6.51 | 28.23 | 0.13 |
| 7 h | 49.81 | 5.04 | 28.68 | 0.10 |
| 9 h | 47.49 | 5.56 | 28.68 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Bai, L.; Fan, J. The Effect of the Calcination Time on the Microstructure and Properties of MnZn Ferrite Powders. Magnetochemistry 2024, 10, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10100068
Xu Z, Zhao W, Bai L, Fan J. The Effect of the Calcination Time on the Microstructure and Properties of MnZn Ferrite Powders. Magnetochemistry. 2024; 10(10):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10100068
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhanyuan, Wei Zhao, Lichun Bai, and Jinglian Fan. 2024. "The Effect of the Calcination Time on the Microstructure and Properties of MnZn Ferrite Powders" Magnetochemistry 10, no. 10: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10100068
APA StyleXu, Z., Zhao, W., Bai, L., & Fan, J. (2024). The Effect of the Calcination Time on the Microstructure and Properties of MnZn Ferrite Powders. Magnetochemistry, 10(10), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry10100068





