Abstract
Eucommia ulmoides Oliver is a unique tertiary relict tree species in China belonging to the Eucommia family and genus. It is a traditional and precious Chinese medicinal herb with anti-tumor, antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and bidirectional blood pressure regulation effects. Eucommia ulmoides mainly grows in temperate regions of China, but due to its sensitivity to low-temperatures, it is difficult to introduce into new regions. To study the role of Eucommia ulmoides lipocalin in plants. This investigation was conducted utilizing gene cloning, bioinformatics analysis, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), subcellular localization, and stable genetic transformation to transfer EuTIL1 into Nicotiana tabacum Xanthi. The wild-type transgenic vector and EuTIL1 tobacco were cold-treated, and the corresponding protective enzyme activity and cold-induced gene expression levels were measured to analyze the functions of the genes. In this study, the full-length of the temperature-induced lipocalin gene (EuTIL1) cDNA was cloned from the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides using the rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) method. The sequence analysis showed that the full-length cDNA of EuTIL1 was 917 bp and encodes a protein of 188 aa residues, which is a member of the Lipocalin-2 family. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that EuTIL1 was found in the plasma membrane. The transgenic tobacco lines expressing EuTIL1 under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter had increased tolerance to cold compared to wild-type (WT) plants. The average water loss rate of EuTIL1 transgenic plants was 12.4%, the average conductivity at 24 h was 55.11%, and the malondialdehyde content at 24 h was significantly lower than that of wild-type plants. The maximum soluble sugar (SS) content, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, peroxidase (POD) activity, and catalase activity of EuTIL1 plants after low-temperature treatment were 22.03 mg/g, 726.87 U/g, 1283.94 U/g, and 356.84 U/g, respectively, which are significantly higher than those of the wild-type. Meanwhile, in the EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco plants, the expression of the NtDREB1, NtDREB2, NtDREB4, and NtCOR15a elevated under the low-temperature treatment condition. In conclusion, our study demonstrates that EuTIL1 is a gene involved in the cold-stress response and has the potential to enhance cold tolerance in plants, providing a potential molecular basis for the study of Eucommia ulmoides introduction and serving as a candidate gene for evaluating cold-tolerant plants.
1. Introduction
Eucommia ulmoides Oliver is a unique tertiary relict tree species in China belonging to the Eucommia family and genus. It is a traditional and precious Chinese medicinal herb with antitumor, antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and bidirectional blood pressure regulation effects [1]. The stem, leaf, and peel cells of Eucommia ulmoides contain rubber that has dual rubber and plastic characteristics and is known as Eucommia gum; it is used in a variety of industries, including construction, national defense, transportation, and medicine [2]. Eucommia ulmoides mainly grows in temperate regions of China, but due to its sensitivity to low temperatures, it is difficult to introduce into new regions. Eucommia ulmoides is mostly found in the Qinling Mountains, south of the Yellow River, north of the Five Ridges, west of the Yellow Sea, and east of the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau. The temperature in Northeast China is relatively low and is not suited for the growth of this plant, making the northeast an unsuitable habitat. Ji’an City is located on the southern slope of Changbai Mountain in Jilin Province. Eucommia ulmoides has been introduced there since 1997, but multiple introduction experiments have failed due to cold currents [3]. In 2018, Eucommia ulmoides was introduced to several areas of Liaoning Province, namely in Jinzhou, Fushun, and Tieling, but suffered freezing injuries that prevented it from surviving the winter, with all of the plants perishing. This proved that Eucommia ulmoides was unsuitable for growing in severely cold climates [4]. Although most studies have shown that Eucommia ulmoides has stress-resistant growth characteristics, there is not much research on cold resistance [5]. Therefore, this study was based on the establishment of a transcriptome sequencing and whole-genome annotation database for Eucommia ulmoides in the early stages [6].
Lipocalins are a class of extracellular proteins widely present in animals, plants, and microorganisms [7]. Due to their ability to bind various hydrophobic small-molecule substances, such as arachidonic acid, bilirubin, steroid hormones, and cholesterol, they have multiple functions, such as regulating cell growth and metabolism, responding to environmental changes to improve stress resistance, and binding to cell surface receptors to affect plant immune responses [5,8,9,10]. Chrysanthemum DgTIL1 interacts with DgnsLTP, and the DgTIL1 protein can promote peroxidase (POD) gene expression and increase POD activity to reduce the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby improving the cold resistance of transgenic DgnsLTP chrysanthemums [11]. In Siberian spruce, the temperature-induced lipocalins increased by 3.87 times after cold treatment [12]. The overexpression of MfTIL1 in alfalfa induces the expression of cold response genes, such as the CBF transcription factor and the NtCOR15a gene, improving the cold tolerance of transgenic plants [13]. Expression analyses by quantitative real-time PCR showed that the expression of wheat (Triticum aestivum) lipocalins and lipocalin-like proteins is associated with an abiotic stress response and is correlated with the plant’s capacity to develop freezing tolerance [10]. According to some studies, temperature-induced lipocalin of Arabidopsis, AtTIL, is crucial for both acquired and basic heat tolerance, suggesting that it can increase the resistance of Arabidopsis to oxidative stress. The combined roles of AtTIL and AtCHL (chloroplast lipocalin) lipocalins can lengthen the life of seeds [14]. Plant temperature-induced lipocalins and lipoprotein-like proteins are tissue-specific and exhibit transcript accumulation under temperature stress, both of which imply that they may act as protective mechanisms against temperature extremes [15].
To study the functional role of Eucommia ulmoides lipocalins in cold tolerance, the full-length cDNA of EuTIL1 was cloned by RACE technology; an overexpression vector was created; and the coding sequence of Eucommia ulmoides lipocalin gene EuTIL1 was compared, analyzed, and identified. This study cloned a novel lipocalin gene from Eucommia ulmoides and analyzed its structure. After cold treatment of transgenic tobacco, the water loss rate, relative conductivity, protective enzyme activity, and the expression levels of genes related to CBF/DREB transcription factors were measured to determine whether this protein can improve plant cold resistance. Thus, we established the groundwork for further investigation into the molecular mechanisms underlying the role of the lipocalins in Eucommia ulmoides in plant stress resistance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
The plant materials used in this experiment are the Huazhong No. 12 Eucommia ulmoides seeds (purchased from Shanxi Yuncheng Huimin Seedling Seed Company, Shanxi, China). Collect young stems, leaves, and samara from female plants. The tender stems, bark, leaves, and flowers of the male plants are all from adult Eucommia ulmoides trees grown in the plant-planting base of the Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology, Guizhou University. N. benthamiana was used as the recipient for the visualization of the subcellular localization of the protein. Nicotiana tabacum Xanthi seeds were preserved in the Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology, Guizhou University. Immediately freeze the collected materials in liquid nitrogen and store them at −80 °C for future experiments. Each test was repeated three times.
The strain of Escherichia coli DH5 α, Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 strain, and initial vector pH737 were stored in the Agricultural Biotechnology Research Institute of Guizhou University, and pCAMBIA1300-35S-EGFP was purchased empty from Wuhan Transduction Biology Company (Wuhan, China).
2.2. Experimental Method
2.2.1. Total RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, and qRT-PCR Analysis
Total RNA extraction from ‘in the leaves of the seedlings of Eucommia ulmoides No. 12 after 15 days of seed germination’ was performed via the application of an RNA pure Plant Kit (Kangwei Century, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The purity and concentration of RNA samples were detected using an ultramicro ultraviolet spectrophotometer (Implen N60, Gmbh, Munich, Germany). Single-strand cDNA was synthesized using a Revert Aid First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. 2 × RealStar Green Fast Mixture (GenStar, Beijing, China) was used for qRT-PCR according to the manufacturers’ protocols (two-step approach). Using cDNA as the template, a real-time PCR kit and the 2−ΔΔCt method were used to calculate the relative expression [16]. The EuActin gene was used as the internal control gene in Eucommia ulmoides [17]. The Nt18S gene was used as the internal control gene in Nicotiana tabacum cv Xanthi [18]. Each test was repeated three times.
2.2.2. Gene Cloning
This study used comparison analysis with the transcriptome sequencing and genome wide annotation database of Eucommia ulmoides to obtain the full-length sequence of the gene encoding the temperature-induced lipocalin EuTIL1 coding sequence. An Ultrapure RNA Kit (Kangwei Century, Beijing, China) was used to extract the total RNA of Eucommia ulmoides seedling leaves according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RACE cloning was performed using a SMARTer RACE 5′/3′ Kit (TaKaRa, Shiga, Otsu, Japan) to convert RNA into 5′/3′-RACE-ready cDNA according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The GSP1- and GSP2-specific primers were designed according to the requirements of the SMARTer RACE 5′/3′ Kit (Table S1). The following amplification protocol was utilized: denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s; annealing at 65 °C for 30 s; extension at 72 °C for 3 min; and storage at 12 °C. After electrophoresis using 1.2% agarose gel, the single target band was recovered using a gel recovery kit (TaKaRa) and then recombined with PUC19-T by homologous recombination. After transforming DH5α competent cells, blue and white spots were screened on Luria–Bertani (LB) medium containing 100 mg/Lampicillin (Amp). Positive single colonies were verified by colony PCR and then sent to Beijing Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China) for sequencing.
An Ultrapure RNA Kit (Kangwei Century) was used to extract total RNA from the leaves of Eucommia ulmoides, and the RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a ReverAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific, Vilnius, Lithuania). The EuTIL1-F and EuTIL1-R primers were designed according to the full-length cDNA sequence of EuTIL1 (Table S1). The CDS was amplified by high-fidelity DNA polymerase using cDNA as template. After double enzyme digestion, the CDS was ligated into PUC19-T vectors by T4 DNA ligase. After the transformation of DH5α competent cells, a selective culture was conducted onto the LB medium supplemented with 100 mg/L Amp. Positive colonies with Amp resistance were identified by colony PCR, and the bacterial liquid was sent to Beijing Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for sequencing.
2.2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
Following sequencing, bioinformatics software was used to examine the EuTIL1 clone’s cDNA sequence and predict protein for its physical and chemical characteristics, functions, and phylogeny. After using the ExPASy program to examine the physicochemical characteristics of proteins (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 15 July 2023), ProtScale (https://web.expasy.org/protscale/, accessed on 15 July 2023) was used to examine the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of proteins, and the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) CD-Search tool (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd/, accessed on 15 July 2023) was used for that structural analysis of the conservative domain. Protein phosphorylation sites were analyzed using the NetPhos tool (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/, accessed on 15 July 2023). The signal peptide sequence can be predicted using the Web tool SignalP (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/, accessed on 15 July 2023). The protein transmembrane region was predicted using TMHMM server software v2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/ accessed on 15 July 2023). SWISS-MODEL (https://swissmodel.expasy.org, accessed on 15 July 2023) was used to examine the protein’s three-dimensional structure, and NetNGlyc-1.0, a Web application (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk, accessed on 15 July 2023), was used to examine the locations of protein glycosylation. Comparing the amino acid sequences of EuTIL1 to those of Arabidopsis thaliana, Bauhinia variegata, Cucurbita argyrosperma subsp., Catharanthus roseus, Vitis vinifera, Solanum lycopersicum, Nicotiana tabacum, Populus tremuloides, Gossypium arboreum, and Prunus armeniaca will provide useful information. Comparative analysis was performed between the TIL amino acid sequence and that of other plants. The phylogenetic tree of temperature-induced lipocalins was built using the neighbor-joining feature of the Mega 6 program.
2.2.4. Carrier Construction
The pSH737-35S-EuTIL1 recombinant plasmid was created using EuTIL1 after it had been purified, and the target gene fragment amplified by PCR was recovered. Following identification, it was validated as being accurate and transferred to receptive cells DH5α. After Km (100 mg/L) was used to screen the responsive cells, positive colonies were chosen for PCR verification, the target bands were confirmed, and they were then delivered to Qingke Biological for sequencing. By using the freeze–thaw technique, the isolated plasmid was added to A. tumefaciens GV3101 for standby.
The entire length of the EuTIL1 gene ORF was amplified using gene-specific primers EuTIL1-F/R1 (restriction sites KpnI and BamHI) and connected to the starting vector pCAMBIL1300-35S-EGFP. This process resulted in the creation of the expression vector for the EuTIL1-EGFP fusion. The recombinant plasmid pCAMBIL1300-35S-EuTIL1-EGFP was obtained and transformed into A. tumefaciens GV3101 for standby after the accuracy of the sequencing was verified. The building procedure was followed exactly as described before.
2.2.5. Agrobacterium-Mediated Transformation and Identification of Nicotiana tabacum Xanthi
Tobacco genetic transformation was accomplished using the Agrobacterium-mediated leaf-disk technique. Activate and cultivate Agrobacterium GV3101 containing the plant overexpression vector pSH737-35S-EuTIL1. Positive single colonies were selected and transferred to 20 mL of LB liquid medium containing 100 mg/L kanamycin and 20 mg/L rifampicin, followed by being incubated at 28 °C with shaking at 200 rpm until the OD600 value reached approximately 0.6. The bacteria were collected, suspended in MS liquid medium, and allowed to incubate for 2–3 h.
Under aseptic conditions in an ultra-clean table, healthy leaves from well-cultured sterile Nicotiana tabacum Xanthi seedlings were carefully excised into 1 cm × 1 cm sized leaves (avoiding the veins as much as possible) using sterilized knives. The prepared Nicotiana tabacum Xanthi leaves were subsequently immersed in a prepared agrobacterium solution for approximately 6 min, during which the solution was continuously agitated to ensure optimal contact with the leaves. After completion, excess bacterial solution was removed using sterile filter paper, and the leaves were rinsed 2–3 times with sterile water.
Subsequently, the leaves were placed on sterile filter paper to dry. A Murashige–Skoog medium containing 1 mg/L 6-benzylamino purine (6-BA) + 0.1 mg/L 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) was kept in the dark for a period of 3 d. Co-cultured Nicotiana tabacum cv Xanthi leaves were then placed onto a culture medium containing MS + 2.0 mg/L 6-benzylamino purin (6-BA) + 0.1 mg/L 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) + 50 mg/L kanamycin + 100 mg/L timentin and transferred to a normal-light condition, and the culture medium was changed approximately once every 10 d. The adventitious buds presenting excellent growth were excised and transferred to a differentiation culture medium containing MS + 2.0 mg/L NAA+ 100 mg/L kanamycin (Kan) + 300 mg/L timentin (Tim). For rooting, the adventitious buds were cultured in a 1/2MS + 100 mg/L Kan + 300 mg/L Tim medium until they developed 2–3 leaves and reached sufficient height. Once the root system became adequately grown, the cap of the culture bottle was loosened, and sterile water was added for a period of 3–4 d under low-light conditions. Prior to transplanting the seedlings into small plastic pots, the medium on the roots was carefully cleaned, and the seedlings were covered with transparent glass or plastic containers for a period of 10 d after transplantation. This step aimed to maintain a high-ambient humidity, allowing the seedlings to gradually adapt to the new environment.
Transgenic tobacco plants were confirmed using the β-glucuronidase (GUS) histochemical staining method. The DNA from tobacco leaves was extracted using a DNA extraction kit, and transgenic tobacco was identified using 35S/EuTIL1-147R PCR with specific primers. When analyzing the outcomes, we utilized 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis.
2.2.6. Gene Expression Analysis in Eucommia ulmoides
From April to October of 2022, samples of male and female plants of Eucommia ulmoides were grown in the field for 17 y in the experimental base and were collected, including young stem bark, young leaves, and male flowers, along with the radicle, hypocotyl, and cotyledon of the tissue culture seedlings of Eucommia ulmoides with 30 d of germination, which were frozen with liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C. The RNA of the above Eucommia ulmoides samples was extracted with an RNA pure plant (DNase I) kit and a high-capacity cDNA reverse transcription kit reverse was used to obtain cDNA. These cDNAs were used for qRT-RCR analysis. The method is shown in Section 2.2.1.
2.2.7. Subcellular Localization Analysis
To construct the protein localization vector pCAMBIA1300-35S-EuTIL1- EGFP, the EuTIL1 coding sequence without stop codon fused with GFP was inserted into the binary vector pCAMBIA1300. Then, the vector was introduced into the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101. Transient expression was performed using the leaves of N. benthamiana according to the method of Li [19]. The GFP fluorescence signal was observed using a laser confocal microscope (Leica TCS SP8 STED, Wetzlar, Lahn-Dill-Kreis, Germany) under excitation at 488 nm.
2.2.8. Water Loss Rate and Electrical Conductivity of Blades Treated at Low Temperature (4 °C) for 24 h
According to the phenotype observation above, tobacco leaves began to wilt after 24 h of low-temperature treatment. So, in this study, three lines of EuTIL1 transgenic plants and empty vector plants, wild type plants, were selected, and cold-temperature stress (4 °C) was applied to them for 24 h. The moisture content of the plant was determined by the drying and weighing method [20]. The tobacco plant’s third leaf from top to bottom was selected after being treated at 4 °C for 24 h, and the leaves were then desiccated in an oven at 105 °C for 15 min. After that, the oven’s temperature was changed to 80 °C in order to dry the material to a constant weight, and its water content was estimated as follows:
Water content = [(fresh weight at 0 h − dry weight)/fresh weight at 0 h] × 100%.
The water loss rate of the leaves was measured by the gravimetric method. The plant was treated at 4 °C for 24 h, and the third leaf from top to bottom was selected and weighed. The leaves were then dried, weighed, and the rate of water loss was calculated as follows:
Water loss rate = [fresh weight at 0 h − fresh weight at 24 h)/fresh weight at 0 h] × 100%.
The cold treatment conditions for tobacco were the same as above. The third leaves of transgenic tobacco, wild-type, and empty vector plants were collected and cut into small pieces; 0.1 g of the leaves was weight and placed in a clean test tube containing 10 mL of deionized water. After soaking for 12 h, R1 was measured using a conductivity meter (LE730, METTLER TOLEDO, Shanghai, China). After boiling water for 30 min, R2 was measured.
Electrical conductivity rate = R1/R2 × 100%
2.2.9. Determination of Physiological and Biochemical Indexes
Measure the levels of catalase activities (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and soluble sugar (SS) in three lines of wild type, empty vector, and the third to last leaf of EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco plants that were exposed to 4 °C for 0 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h (6–8 leaf stage). Measure catalase activities using a spectrophotometer [21]. Measure superoxide dismutase activity using the method of reducing nitrogen blue tetrazole with superoxide anion [22]. Measure peroxidase activity using visible spectrophotometry [23]. The content of malondialdehyde was measured using the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) method. The measurement of soluble sugar content was performed using anthrone colorimetry [24]. Each test was repeated three times.
2.2.10. Analysis of Gene Expression in Response to Low-Temperature Stress
Low-temperature stress: Low-temperature treatment was applied to wild-type, empty vector, and transgenic tobacco plants in the 6–8 leaf stage. The leaves were collected at 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80 °C. The low-temperature response genes NtDREB1, NtDREB2, NtDREB4, NtCOR15a, and EuTIL1 were chosen for a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR study after the RNA was extracted and inverted into cDNA. Using cDNA as the template, a real-time PCR kit and the 2−ΔΔCt method were used to calculate the relative expression [16]. The Nt18S gene was used as the internal control gene [4]. The primer sequence is located in Table S1 of the supplementary. Each test was repeated three times.
2.2.11. Data Statistics and Analysis
All data shown as mean ± standard error of means was analyzed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Duncan’s test, using IBM SPSS Statistics 25 software (IBM Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA). Differences among means of plant lines and treatments were evaluated by Duncan’s test at 0.05 probability level, and GraphPad Prism 9.0 was used for mapping.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. EuTIL1 Gene Cloning and Bioinformatics Analysis
The electrophoresis results demonstrated that RACE amplification was used to extract the EuTIL1 gene’s 5′ and 3′ ends (Figure S1a,b). The cloning outcome revealed that EuTIL1 has an overall length of 897 bp, which includes a 567 bp open reading frame, a 103 bp 5′UTR, a 227 bp 3′UTR, and a 20 bp tail of PloyA. The tail signal AATAAA sequence was found between positions 695-701, the start codon ATG between positions 104 and 106, and the stop codon TAA between positions 668 and 670 (Figure S1c).
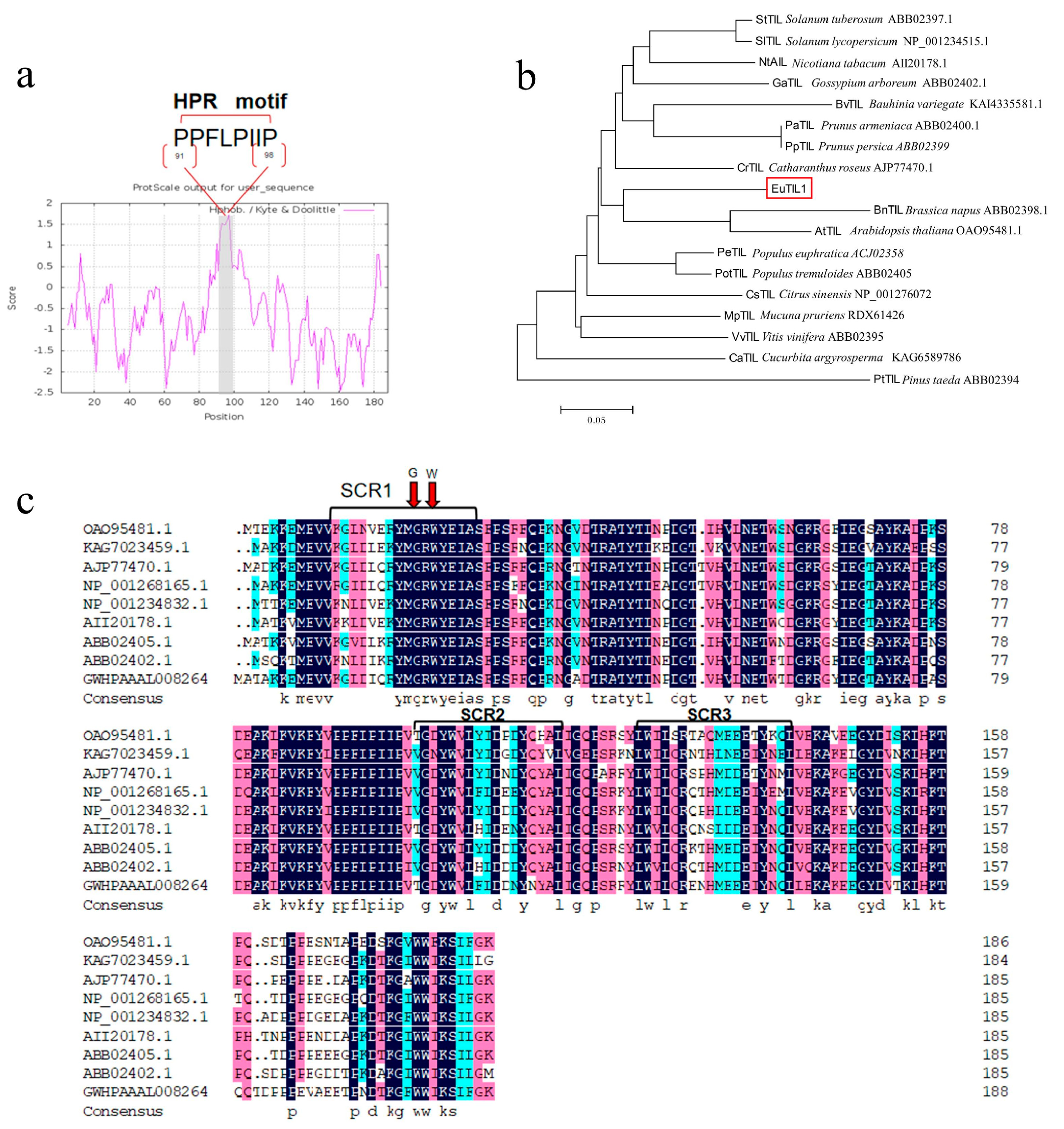
Utilizing this as a template, the particular primers EuTIL1-forward and EuTIL1-reverse were utilized for PCR amplification, and 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis was performed to identify a single brilliant band (Figure S1d). Upon sequencing, the ORF sequence of this gene was found to be 567 bp, encoding a total of 188 aa. This outcome is in line with what was anticipated. The theoretical relative molecular mass is 21.864 kDa and the isoelectric point is 5.49. The instability coefficient of the molecular formula, C996H1504N256O290S5, is 39.96, which is <40. With an aliphatic index of 69.52 and an average hydrophilicity–hydrophobicity value of −0.686, it is expected that the protein encoded by EuTIL1 is stable. A brief hydrophobic proline-rich motif (HPR) can be found in this hydrophilic protein between amino aa 91 and 98 (Figure 1a). This motif can interact with the cell membrane, thus binding to the cell membrane. It has three conserved domains, SCR1, SCR2, and SCR3, which are exclusive to Lipocalin-2. It is a member of the Lipocalin-2 family (Figure 1b), which has 15 phosphorylation sites; however, it lacks a transmembrane domain and signal peptide. The results showed that the cloned gene had high homology with the above plants, with a maximum of 77.96%, indicating that the cloned gene was most likely the temperature-induced lipocalin gene and was named EuTIL1. According to the evolutionary tree, Eucommia ulmoides shares a genetic ancestor with Catharanthus roseus, Arabidopsis, and Brassica napus (Figure 1c).
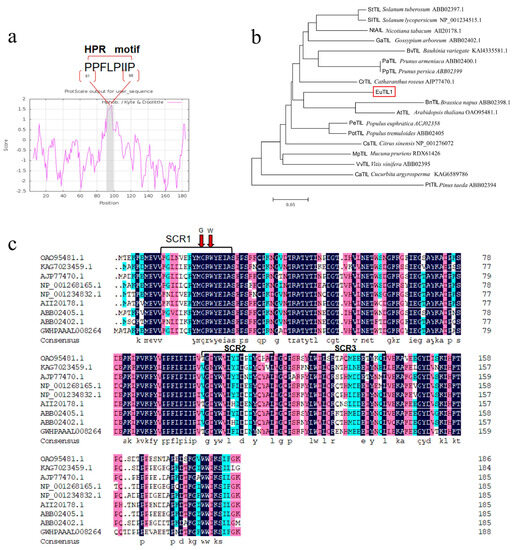
Figure 1.
HPR structural analysis of EuTIL1, construction of EuTIL1 phylogenetic tree, and multiple sequence alignment of EuTIL1 with other species. (a) Hydrophilicity analysis of EuTIL1 protein. Note that the gray part (aa 91–98) in the figure is a short hydrophobic proline-rich motif (HPR). (b) Phylogenetic tree of EuTIL1 protein and other species by using neighbor-joining (NJ). Note that the red box is E. lipocalins. (c) Alignment analysis of the conserved regions of lipocalins between EuTIL1 and other species. The red arrow represents the stable amino acids C and W in the conserved domain.
3.2. EuTIL1 Gene Spatiotemporal Expression in Eucommia ulmoides Plants
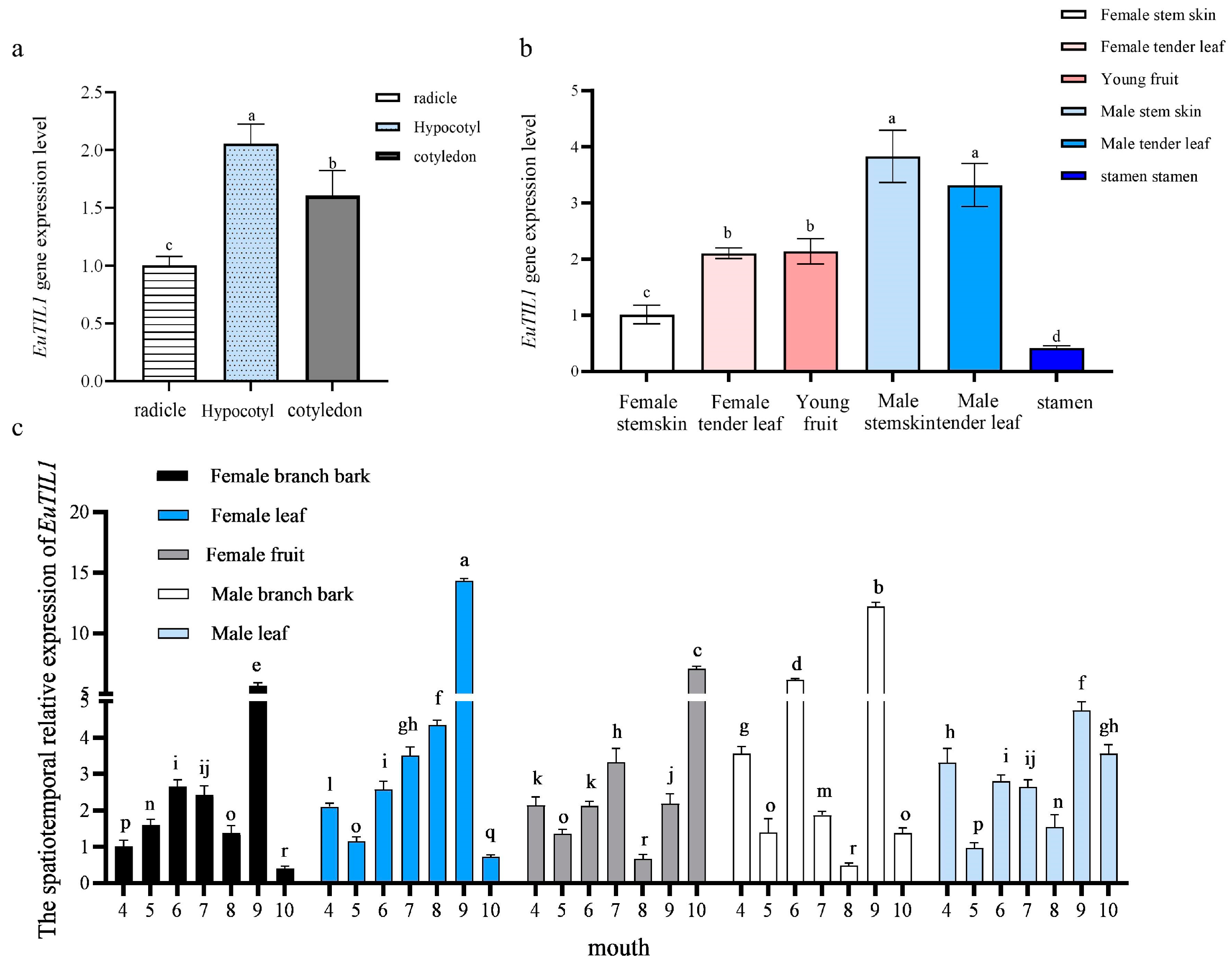
The EuTIL1 gene is expressed in the radicle, hypocotyl, and cotyledon of Eucommia ulmoides seedlings when they are grown at 25 °C (16 h day, 8 h night). The expression level in the hypocotyl and cotyledon is higher, 2.05- and 1.60-fold that of the radicle, respectively (Figure 2a).
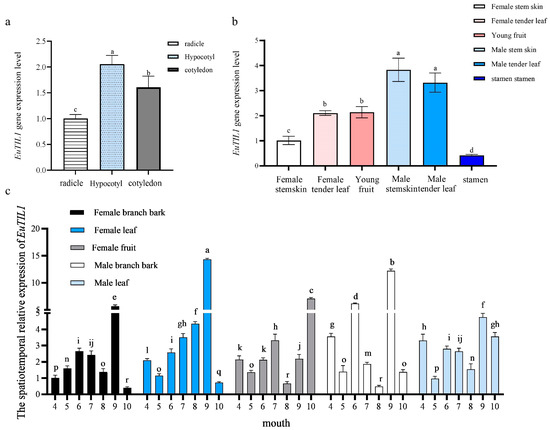
Figure 2.
EuTIL1 gene Spatiotemporal expression in Eucommia ulmoides plants. (a) Analysis of relative expression of EuTIL1 gene in different tissues of Eucommia ulmoides seedlings. (b) Analysis of relative expression of EuTIL1 gene in different tissues of Eucommia ulmoides. (c) Analysis of relative expression of EuTIL1 gene in different tissues and different stages of adult Eucommia ulmoides. Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
It is expressed in the tender stem bark, tender leaves, young fruits, and male flowers of adult Eucommia ulmoides. The stamens and all other sections of the male plant have an expression level that is much higher than that of the female plant, which is 3.83-fold higher in the male stem bark and 3.29-fold higher in all other areas of the male plant (Figure 2b). In comparison with other months, September had a significantly greater expression of the EuTIL1 gene. The patterns of expression varied from month to month, and the expression in the female plant stem bark exhibited a pattern of first rising then decreasing, then rising and then falling, with the expression peaks occurring in June and September, respectively. Young female plant leaves displayed an overall pattern of first rising then dropping in the middle of April and October and peaking in September. The expression of samara did not change significantly from April to September and reached its peak in October. From April through October, the amount of male plant stem bark that was expressed varied significantly, fluctuated, and peaked in September. A general tendency of first declining, then increasing, and then declining again was visible in the expression of male tender leaves between April and October, reaching its peak value in September (Figure 2c).
3.3. Subcellular Localization Analysis of EuTIL1
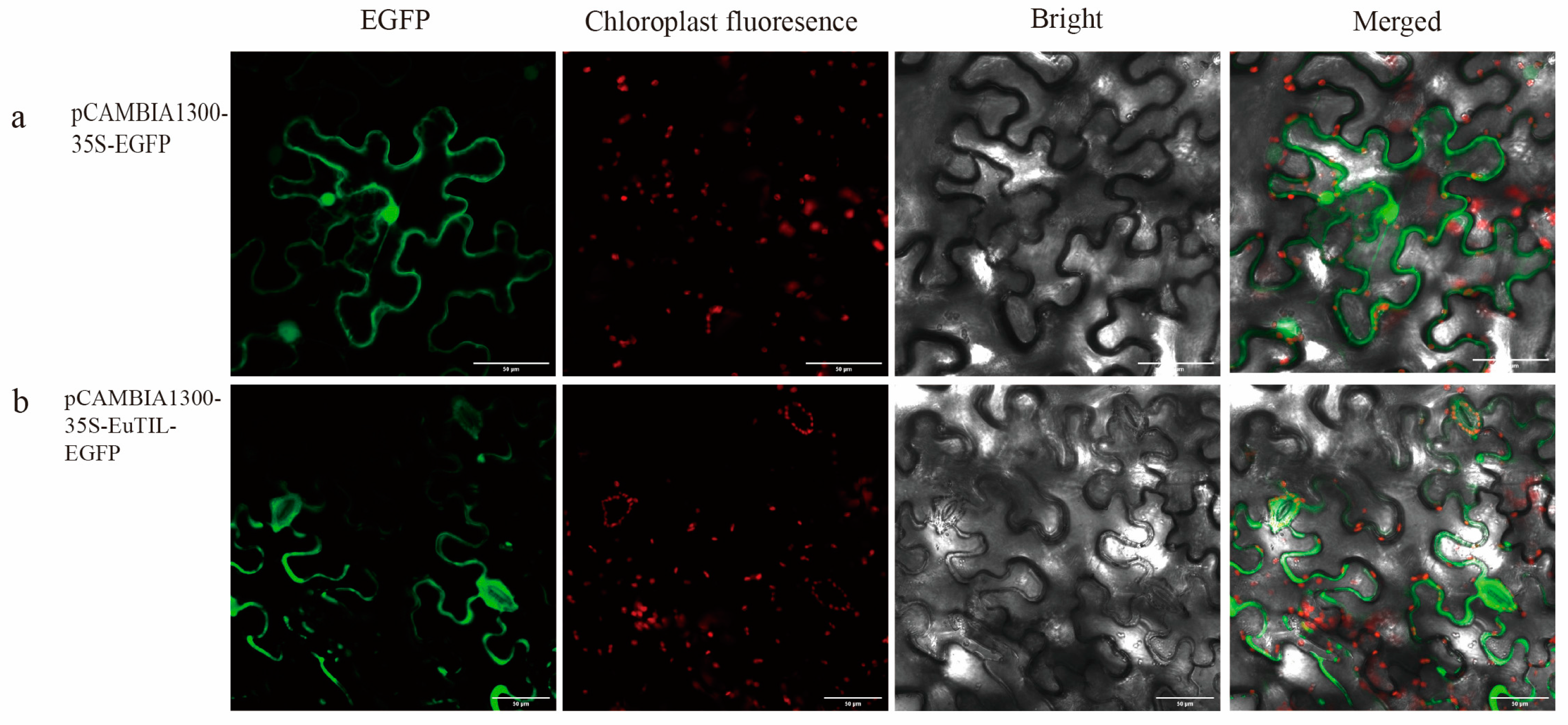
To determine the subcellular localization of EuTIL1, the pCAMBIA1300-35S-EuTIL1-EGFP construct was transiently expressed in leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana. The result showed that the EuTIL1 protein was located on the plasma membrane and guard cell (Figure 3).
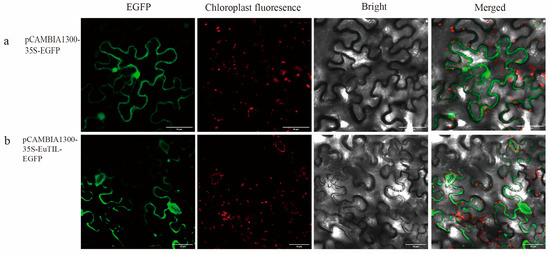
Figure 3.
Subcellular localization of EuTIL1. (a). is the subcellular localization map of pCAMBIA1300-35S-EGFP. (b) is the subcellular localization map of pCAMBIA1300-35S-EuTIL1-EGFP.
3.4. Effect of EuTIL1 on Cold Resistance of Tobacco
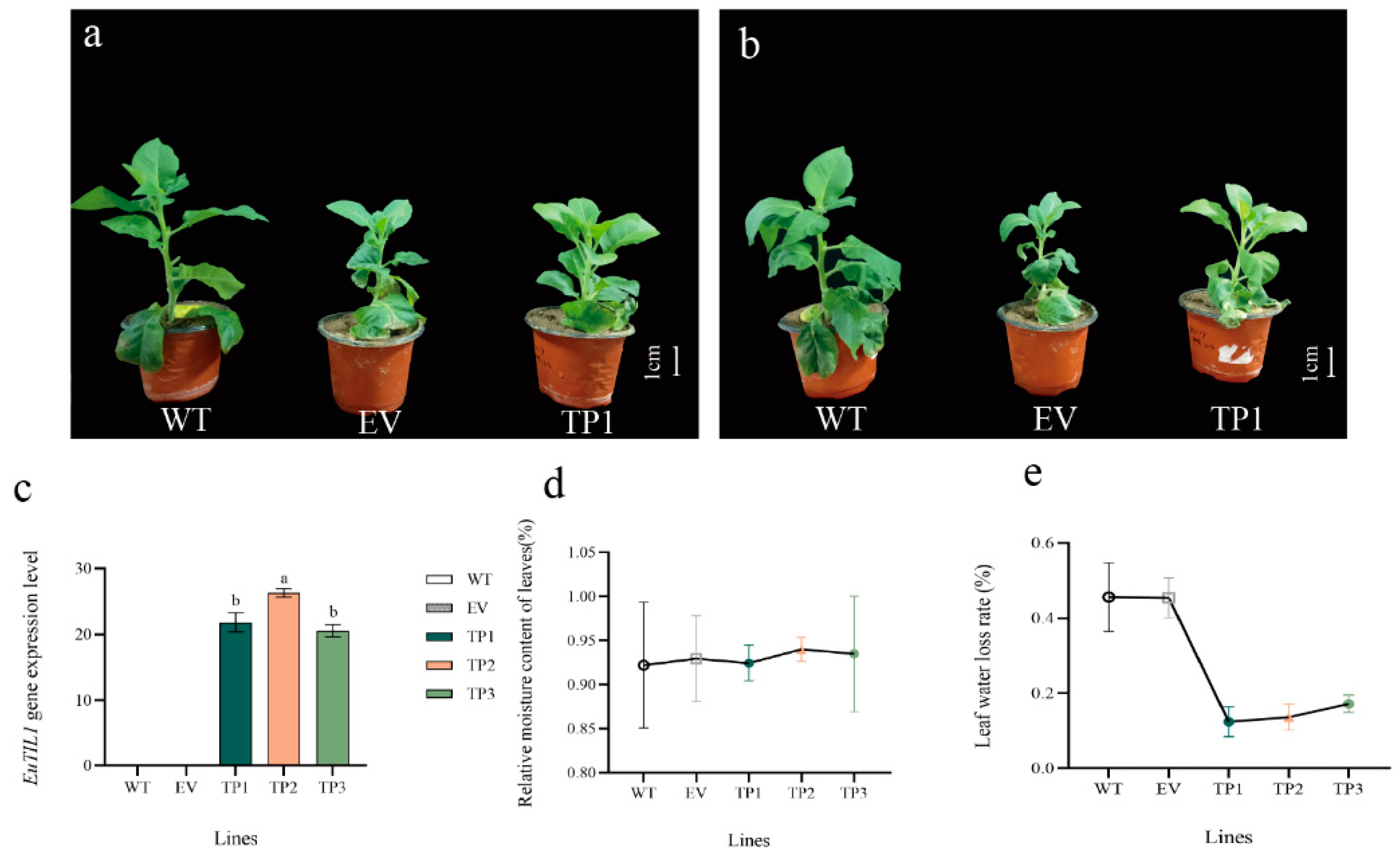
The construction of overexpression vector pSH737-35S-EuTIL1 can be seen in Figure 2. The agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of Nicotiana tabacum Xanthi (Figure S3a–d) was completed using the vector pSH737-35S-EuTIL1, which overexpresses the EuTIL1 gene (Figure S3). Using GUS histochemical analysis (Figure S3e) and PCR amplification verification, 35 transgenic tobacco plants were obtained (Figure S3f).
The third leaves of wild-type tobacco plants, empty-vector-transformed tobacco plants, and EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco plants withered to a considerable extent from top to bottom after 24 h at 4 °C, with EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco leaves showing less withering than wild-type leaves (Figure 4b). The leaf weight of EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco leaves, empty-vector-transformed tobacco, and wild-type tobacco leaves from the three lines did not differ significantly after being treated at 4 °C for 0 h (Figure 4c), nor did the relative water content of leaves of the three lines (Figure 4d). The EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco leaves, the empty vector tobacco leaves, and the wild-type tobacco leaves of the three lines all exhibited some water loss after being exposed to 4 °C for 24 h. The water loss rate of the wild-type peaked at 45.4%, while the water loss rate of tobacco with empty vectors was 39.3%. The three EuTIL1 transgenic lines of EuTIL1 had water loss rates of 10.8%, 14.6%, and 20.8%, respectively (Figure 4d). This suggests that the overexpression of the EuTIL1 gene can increase the ability of cells to attach to water, hence reducing the rate of water loss in leaves and improving the ability of tobacco to withstand cold temperatures.
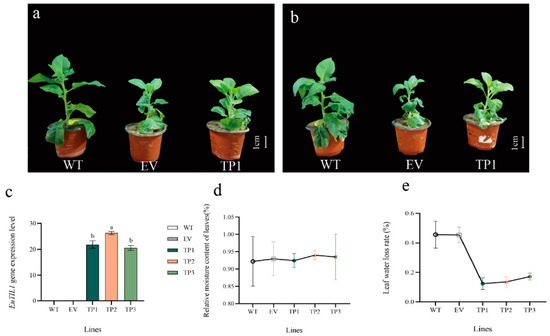
Figure 4.
Phenotypic observation of tobacco under cold stress, analysis of expression levels in transgenic tobacco, and moisture loss rate and relative moisture content of tobacco after low-temperature treatment. (a) Tobacco phenotype at 25 °C. (b) Tobacco phenotype at 4 °C. (c) The expression level of EuTIL1 in wild-type, empty vector, and transgenic lines (TP1, TP2, and TP3). (d) Relative moisture content of tobacco. (e) Leaf water loss rate. Note: WT, wild-type tobacco; EV, empty-body-converted tobacco; TP1, TP2, and TP3, respectively, are the transgenic tobacco line 1, line 2, and line 3. Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05). The bar is 1 cm.
3.4.1. Electrical Conductivity of Low-Temperature-Treated Tobacco
The relative conductivity of the leaves of the transgenic tobacco plants exposed to low temperature (4 °C) for 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h exhibited a tendency to increase at first and subsequently decrease with the length of exposure. The conductivity of the wild-type and empty vector lines increases with time. EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco leaves had significantly lower conductivity than wild-type and empty vector tobacco leaves (Figure 5). According to the findings, wild-type and empty vector plants had less cold resistance and were more prone to low-temperature harm. The tobacco plants that were transgenic for the EuTIL1 gene were more resistant to cold damage than the wild-type ones.
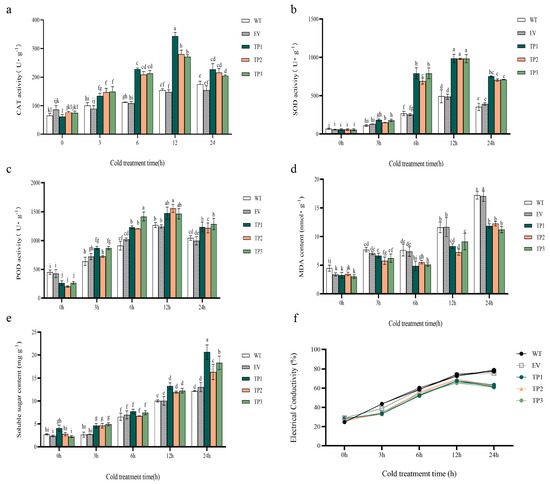
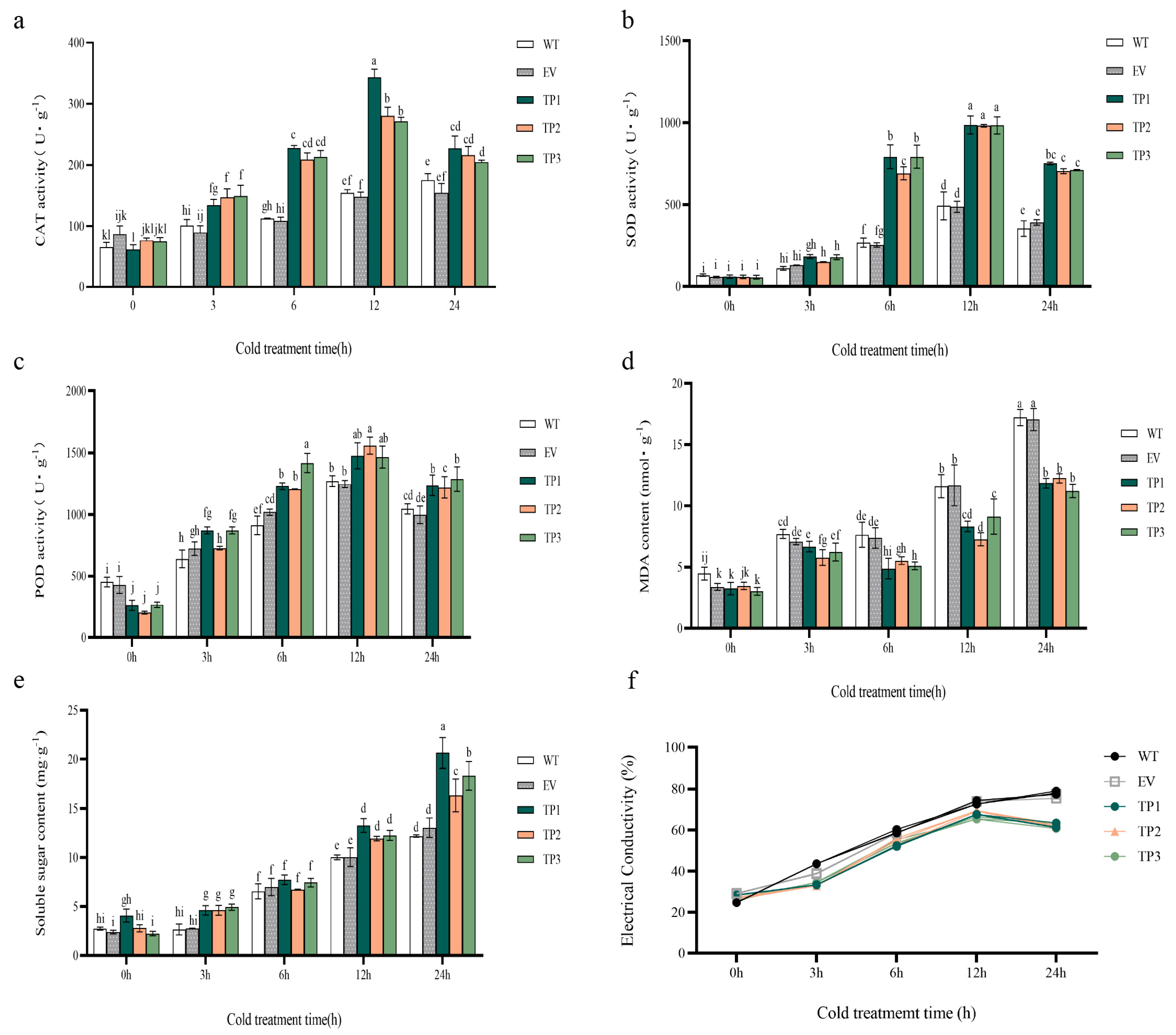
Figure 5.
Effect of low temperature treatment on physiological indexes of wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic plants. (a) Catalase activities. (b) Superoxide dismutase activity. (c) Peroxidase activity. (d) Malondialdehyde content. (e) Soluble sugar content. (f) Electrical conductivity of tobacco leaves treated with low temperature. WT, wild tobacco; EV, empty-vector-converted tobacco; TP, EuTIL1 transgenic plants. Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
3.4.2. Effect of EuTIL1 on the Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes and MDA Content
The findings demonstrated a tendency of first increasing and subsequently lowering superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase activities (CAT) in wild-type tobacco, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic plants. The activities of catalase activities, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase in EuTIL1 transgenic plants significantly increased at four time points after low-temperature treatment and were higher than those of wild-type and empty vector plants. These activities peaked at 12 h of treatment: 298.07 U/g, 1002.54 U/g, and 1333.86 U/g. The levels were 1.93-, 2.01-, 2.07-, 2.23-, and 1.05-, 1.07-fold more potent than those of tobacco plants of the wild-type and empty vector lines (Figure 5a–c). It is suggested that catalase activities, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase may participate in the process of cold resistance of transgenic EuTIL1 tobacco. At 0 h, the malondialdehyde (MDA) content of EuTIL1 transgenic plants was slightly lower than that of wild-type and empty vector plants. As the low-temperature treatment progressed, the malondialdehyde content of EuTIL1 transgenic plants increased, peaking at 11.71 nmol/g at 24 h. The content was significantly less (p < 0.05) than those of empty vector plants (16.188 nmol/g) and wild-type plants (17.106 nmol/g) (Figure 5d). It has been hypothesized that overexpressing the EuTIL1 gene can lower the rate of lipid peroxidation and lessen damage to the membranes of plant cells.
At various time gradients, transgenic tobacco’s soluble sugar (SS) content in EuTIL1 transgenic plants is higher than that of wild-type and empty vector plants. The accumulation of soluble sugar content increased with the length of the low-temperature treatment, reaching its peak after 24 h at 18.44 mg/g, 12.19 mg/g, and 13.04 mg/g, respectively (Figure 5e). This shows that the overexpression of the EuTIL1 gene can promote soluble sugar accumulation, raise the protoplasm concentration in plant cells, improve the control of osmotic pressure, reduce intracellular water loss and freezing, maintain the integrity of the membrane system, and improve plant cell resistance to cold.
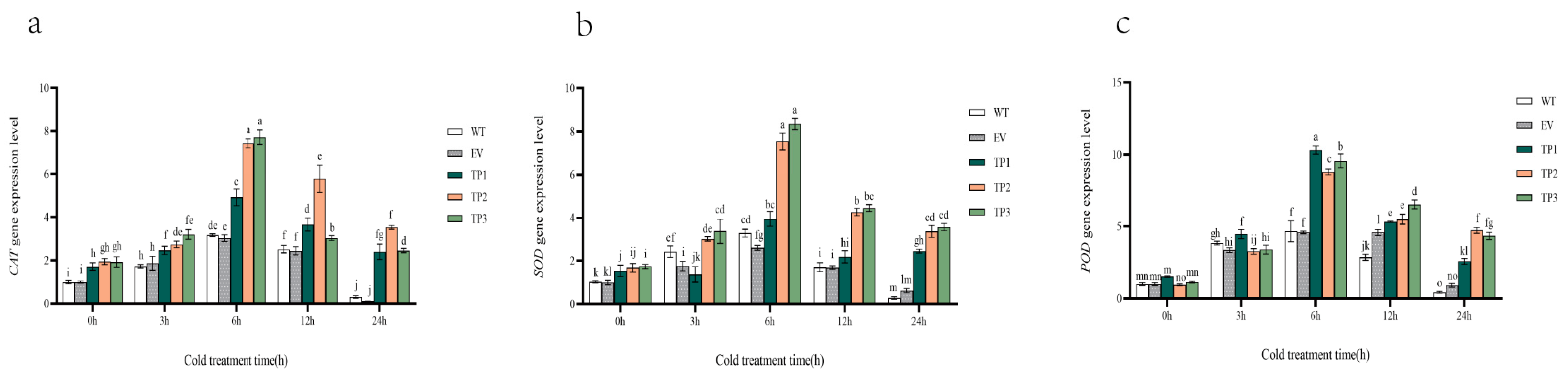
Quantitative real-time PCR was used to examine the expression of the protective enzyme activity genes catalase activities, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase in wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic plants exposed to 4 °C for 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h. During cold treatment, the expression of these three protective enzyme activity genes displayed a general trend of first increasing and then dropping, reaching its peak at 6 h. During 0 h of cold treatment, EuTIL1 transgenic plants had slightly higher levels of catalase activities, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase gene expression than the wild-type and empty vector plants. The expression of catalase activities, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase considerably increased in wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic plants after 6 h of cold stress. Compared to wild-type and EuTIL1 transgenic plants, the expression of catalase activities was considerably higher in empty vector plants (Figure 6a). At 1.92- and 2.54-fold that of wild-type and empty vector, respectively, EuTIL1 transgenic plants’ expression of superoxide dismutase was noticeably higher than that of wild-type and empty vector plants (Figure 6b). At 2.10- and 2.20-fold that of wild-type and empty vector, respectively, the peroxidase expression of EuTIL1 transgenic plants was noticeably higher than that of wild-type and empty vector plants (Figure 6c). After 6 h, the catalase activities, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase expression levels in wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic quickly dropped.
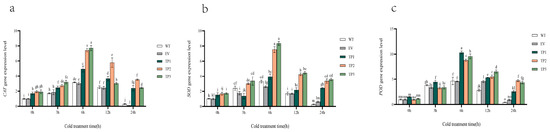
Figure 6.
Analysis of relative expression of catalase activities, superoxide dismutase, peroxidase genes in tobacco during temperature treatment. (a) Catalase activities gene expression. (b) Superoxide dismutase gene expression. (c) Peroxidase gene expression. WT, wild tobacco; EV, empty-vector-converted tobacco; TP, EuTIL1 transgenic plants. Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
3.4.3. Effect of EuTIL1 on Expression Level of Cold-Induced Genes in Tobacco Plants
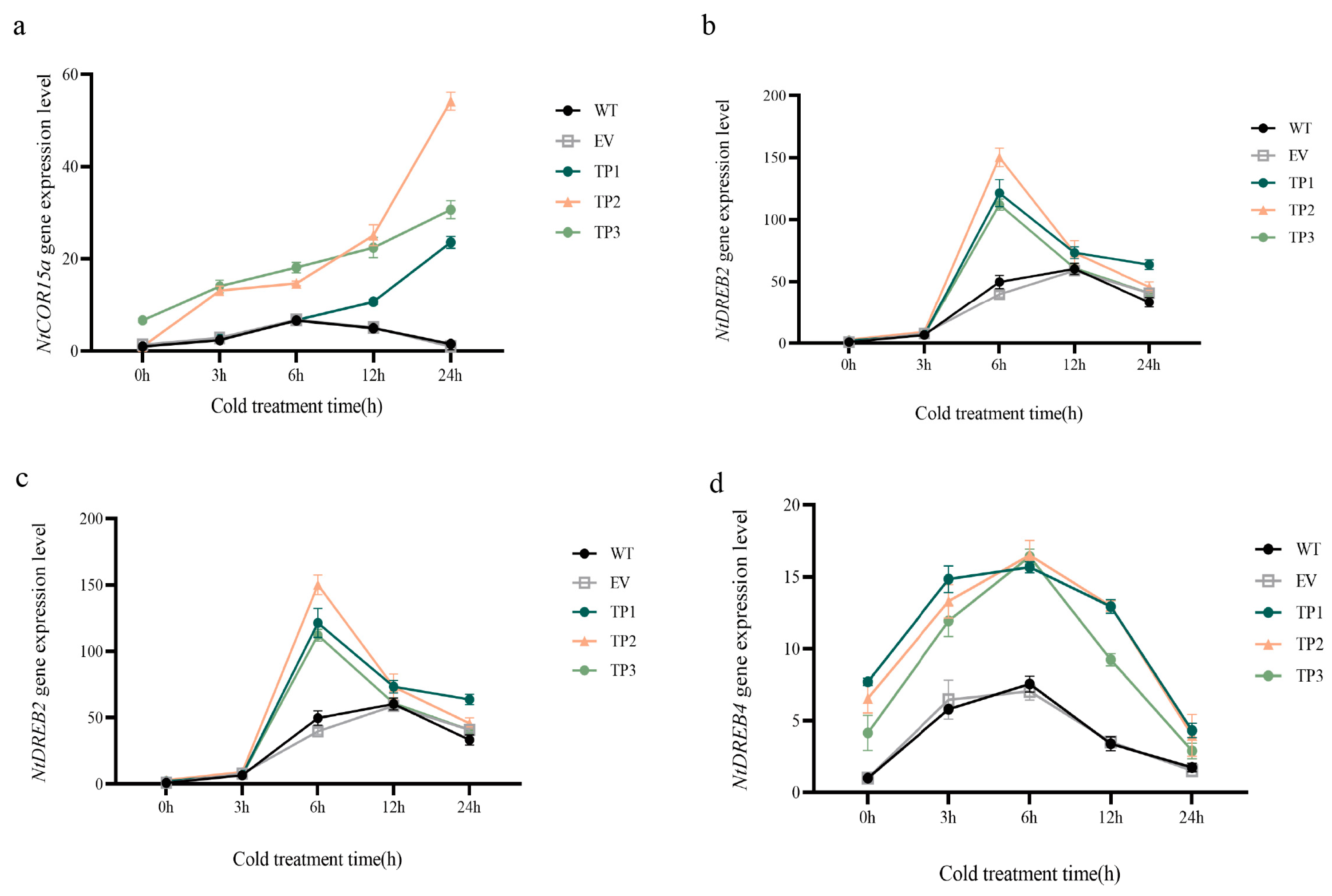
In wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic plants treated at 4 °C for 0, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h, the expression levels of the EuTIL1 gene, low-temperature-responsive CBF transcription factors (NtDREB1, NtDREB2, and NtDREB4), and the cold-inducible gene NtCOR15a were examined. NtDREB2 and NtDREB4 expression levels in EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco plants were higher than those in wild-type and empty vector plants, respectively, after being exposed to 4 °C for 0 h. In comparison to wild-type and empty vector plants, there was no appreciable variation in the expression level of NtDREB1 in EuTIL1 transgenic plants after being exposed to 4 °C for 0 h. The NtDREB1 gene’s expression peaked in wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic plants 6 h after being exposed to low temperatures. In comparison to wild-type and empty vector plants, the expression level in EuTIL1 transgenic plants was noticeably higher. The expression of NtDREB2 and NtDREB4 under the low-temperature treatment tended to increase initially before declining, peaking at 6 h. The expression of NtDREB2 and NtDREB4 in EuTIL1 transgenic plants was significantly higher than that in wild-type and empty vector plants (p < 0.05). Transcription levels began to decrease after 12 h of low-temperature treatment. After exposure to low temperatures for 24 h, NtCOR15a gene expression in wild-type and empty vector plants first increased and subsequently declined. The peak value of expression was at 6 h. At increasing low-temperature treatment times, NtCOR15a gene expression in EuTIL1 transgenic plants rose. It peaked at 24 h and was substantially higher than in wild-type and empty vector (p < 0.05). This suggests that low-temperature induction can increase the sensitivity of the cold-responsive gene NtDREB1 to low temperature, thereby increasing its expression level. The overexpression of the EuTIL1 gene increased DREB2, DREB4, and NtCOR15a expression in transgenic plants, further improving the activity of protective enzymes, improving tobacco’s ability to scavenge ROS, and improving tobacco’s tolerance to a low temperature (Figure 7).
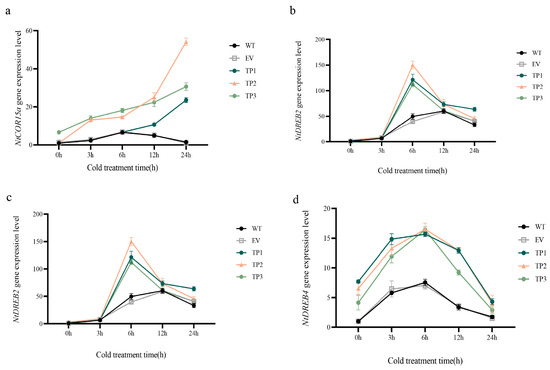
Figure 7.
Expression levels of cold-induced genes in tobacco. (a) Expression amount of the NtCOR15a gene. (b) NtDREB1 gene expression. (c) NtDREB2 gene expression. (d) NtDREB4 gene expression. Note: WT, wild-type tobacco plants; EV, empty vector plants; TP: EuTIL1 transgenic plants. Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
Temperature is one of the most important environmental factors affecting plant growth and development. Eucommia ulmoides is mainly distributed in the central and western regions of China. Due to its sensitivity to temperature, the introduction of Eucommia ulmoides in the Northeast region has failed. In order to further improve the introduction rate of Eucommia ulmoides in Northeast China, it is very important to study and improve its tolerance to low temperatures. In our study, we successfully cloned a temperature-induced lipocalin gene from Eucommia ulmoides. The bioinformatics analysis results indicated that the EuTIL1-encoded protein contains 188 amino acid residues. EuTIL1 is highly related to the amino acid sequences of temperature-induced lipocalins in species such as Arabidopsis and Brassica napus. It has three typical structural domains, SCR1, SCR2, and SCR3, and is a member of the Lipocalin-2 family, which is consistent with the research results of Flower, Charon, and others. Therefore, it is inferred that it is a temperature-induced lipocalin gene of Eucommia ulmoides [5,9,10].
EuTIL1 is expressed in different parts of Eucommia ulmoides, indicating that EuTIL1 participates in the growth and development processes of Eucommia ulmoides and plays an important role. The fruit of Eucommia ulmoides matures from April to September. During this period, the expression of EuTIL1 in the bark and leaves of the female plant was higher than that in April. It is speculated that the fruit of Eucommia ulmoides high in nutrients. Both the leaves and stems need photosynthesis to synthesize organic substances and transport them to the fruit for storage. Therefore, the expression level of EuTIL1 from April to September gradually increased and may be induced by a variety of stress factors during this period. Because the sensitivity of different parts of the body to the environment is not consistent, it shows different expression patterns. Winter arrives in the middle of October, which causes the abscisic acid level to rise, the leaves to fall, and plant metabolism to slow down. As a result, EuTIL1 translation started to gradually decline.
Studies have shown that lipocalins bind to the cytoplasmic membrane in two ways. The first is through their C-terminal, which contains a presumed cleavage site that can be anchored to the plasma membrane by accepting GPI [3,10]. The second is to bind the HPR motif in the amino acid residues to specific receptors on the cell surface, thereby fixing it onto the surface of the cell membrane [25]. It has been reported that AtTIL does not contain any recognizable membrane targeting or transmembrane motif signals. Similar to human ApoD protein, the HPR motif is located between the fifth and sixth β folds and interacts with the plasma membrane [5,26,27]. The results indicate that the EuTIL1 protein contains an HPR motif at 91–98 amino acids, but further validation is needed to determine whether the protein interacts with the plasma membrane through the HPR motif. In this study, the protein was localized at the plasma membrane and guard cells of tobacco epidermal cells. The location of the EuTIL1 protein was not consistent with the predicted location of nuclei, cell walls, and chloroplasts, but it was consistent with the observations of other Lipocalin-2 family genes, such as AtTIL, PeuTIL, MfTIL1, and DgTIL1 [11,13,26,27,28,29,30]. As for why EuTIL1 is located in the guard cells of the mesophyll epidermis, it remains to be studied.
Here, we successfully introduced EuTIL1 into Nicotiana tabacum Xanthi to achieve stable conversion. The low-temperature treatment of wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco plants was used to observe changes in plant morphology and analyze the changes in protective enzyme activity in the plant. The expression of cold-induced genes was measured to analyze their gene function. Low-temperature stress causes obvious damage to plants, including wilting, discoloration, drying of leaf edges, accelerated aging, incomplete ripening, and even death [31,32]. In this study, leaf wilting occurred in wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco plants treated with low temperatures for 24 h, and the leaf water loss rate and electrical conductivity of EuTIL1 transgenic tobacco plants were significantly lower than those of wild-type and empty vector plants. The conductivity of leaves reflects the degree of damage to plant cell membranes. The higher the conductivity, the greater the degree of damage to the cell membrane and the higher the ion permeability. The overexpression of the EuTIL1 gene can improve membrane stability and reduce ion leakage to protect cell water content. Under normal growth conditions, plants maintain a dynamic balance of their own ROS content. Once subjected to low-temperature stress, a large amount of ROS is produced, leading to lipid peroxidation [33,34]. As a key enzyme in the antioxidant enzyme system, superoxide dismutase can clear a large amount of ROS in the body, playing a protective role in plants [35,36]. In this study, the content of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase, and catalase activities in EuTIL1 transgenic plants showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing during 24 h of cold treatment, and was significantly higher than that of wild-type and empty vector transgenic plants. The EuTIL1 gene can promote the production of a large amount of antioxidant enzymes in plants to eliminate ROS produced in the body, maintain plant life activities, and improve plant tolerance to stress. Low temperature stress causes membrane lipid peroxidation and the accumulation of malondialdehyde content in plants, and the increase in malondialdehyde content indicates damage to plant cell membranes [37,38,39]. In this study, the malondialdehyde content in EuTIL1 transgenic plants first increased and then decreased, while the malondialdehyde content in wild-type and empty vector transgenic plants gradually increased. This indicates that the EuTIL1 gene can stabilize cell membrane structures, reduce membrane lipid peroxidation, reduce cell membrane damage, and improve plant cold resistance.
Soluble sugars are important organic osmoregulation substances. Under cold stress, the increase in soluble sugars in plant cells can regulate cell permeability and freezing point, enhancing plant cold resistance. In this study, the soluble sugar content in EuTIL1 transgenic plants increased with increasing duration of the low-temperature treatment, reaching its maximum value at 24 h. This indicates that tobacco can rapidly increase the soluble sugar content in its cells after being subjected to low-temperature stress to increase the permeability of cells, thereby reducing cell damage and enhancing plant cold resistance.
In order to adapt to cold environments, the expression of thousands of genes in plants are altered, and metabolic pathways also undergo changes [40,41,42]. The CBF transcription factor is a key gene that regulates cold response genes and cold adaptation. In Arabidopsis, the CBF transcription factor regulates the expression of 12% of the cold-induced genes [40,43]. NtDREB1, NtDREB2, and NtDREB4 are used as cold response marker genes in tobacco [44]. During the cold adaptation process of Arabidopsis, CBF transcription factors can regulate the expression of the AtCOR15a gene [45]. In this study, NtDREB1, NtDREB2, NtDREB4, and NtCOR15a genes were induced to be expressed in wild-type, empty vector, and EuTIL1 transgenic plants after 3 h of low-temperature treatment, and their expression levels in EuTIL1 transgenic plants were significantly higher than those of wild-type and empty vector plants. This is consistent with the research results of He in alfalfa [13]. The EuTIL1 gene is a cold response gene, which is overexpressed in tobacco and can activate the cold signaling pathway that is dependent on CBFs/DREB transcription factors. At the same time, it regulates the expression of the cold-induced gene NtCOR15a, enhancing the cold resistance of tobacco.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, we found that EuTIL1 was induced by low-temperature treatment and plays an important role in various tissues of Eucommia ulmoides. The overexpression of the EuTIL1 gene can reduce cell dehydration rate, electrical conductivity, and malondialdehyde content. It also enhanced the cold resistance of transgenic tobacco by increasing superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase activities, and soluble sugar content to reduce membrane damage and maintain ion homeostasis. The EuTIL1 gene is a cold response gene, which is overexpressed in tobacco and can activate the cold signaling pathway that is dependent on CBFs/DREB transcription factors. At the same time, it regulates the expression of the cold-induced gene NtCOR15a, enhancing the cold resistance of tobacco. These results indicate that EuTIL1 has potential for use in improving plant stress tolerance.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae9090950/s1, Figure S1: EuTIL1 gene full length, CDS cloning.; Figure S2: Construction process of expression vector pSH737-35S-EuTIL1; Figure S3: Tobacco genetic transformation process and GUS staining and PCR identification. Table S1: Primer sequences used for quantitative RT-PCR and gene cloning the accession numbers of the analyzed genes.
Author Contributions
D.Z. conceptual proposal and experimental design of the article, revision of the manuscript, finalization of the version to be published, agreement to take responsibility for the accuracy and authenticity of the entire research content. X.W. experimental design of the article, focusing on data collection, analysis, or interpretation; Revise the manuscript, agree to take responsibility for the accuracy and authenticity of the entire research content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (“863” Program), grant number 2013AA102605-05, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences Talent Special Project (No. 2022-02), and by Talent Base for Germplasm Resources Utilization and Innovation of Characteristic Plant in Guizhou (grant number RCJD2018–14).
Data Availability Statement
The Eucommia whole genome database and transcriptome database can be consulted with corresponding authors. All data in this study could be found in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the colleagues that helped with the development of different parts of this manuscript and Key Laboratory of Mountain Plant Resources Protection and Germplasm Innovation of the Ministry of Education and Guizhou Plant Conservation Technology Center, Guizhou Key Laboratory for providing equipment and technical support for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, C.; Guo, F.F.; Xiao, J.P.; Wei, J.Y.; Tang, L.Y.; Yang, H.J. Research advances in chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of different parts of Eucommia ul-moides. Chin. Pharm. J. 2020, 45, 479–512. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Peng, P.; Peng, F.; Dong, J. Natural Polymer Eucommia Ulmoides Rubber: A Novel Material. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 3797–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganfornina, M.D.; Sánchez, D.; Bastiani, M.J. Lazarillo, a new GPI-linked surface lipocalin, is restricted to a subset of neurons in the grasshopper embryo. Development 1995, 121, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.P.; You, W.Z.; LI, L.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jia, C.J. Current situation and development proposal of Eucommia ulmoides introduction in Liaoning. Liaoning For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 05, 58–59. [Google Scholar]
- Charron, J.B.; Ouellet, F.; Pelletier, M.; Danyluk, J.; Chauve, C.; Sarhan, F. Identification, expression, and evolutionary analyses of plant lipocalins. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.G.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zhao, D.; Lv, L.T.; Liu, S.H.; Song, L.; Dong, X.; Feng, Y. Transcriptome data assembly and gene function annotation of female and male plants in Eucom-mia ulmoides. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 2015, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Lareyre, J.J.; Sánchez, D.; Gutierrez, G.; Araki, Y.; Matusik, R.J.; Orgebin-Crist, M.C. Molecular evolution of epididymal lipocalin genes localized on mouse chromosome 2. Gene 2004, 339, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, D.R. Structural relationship of streptavidin to the calycin protein superfamily. FEBS Lett. 1993, 333, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, D.R.; North, A.C.; Sansom, C.E. The lipocalin protein family: Structural and sequence overview. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, J.B.F.; Breton, G.; Badawi, M.; Sarhan, F. Molecular and structural analyses of a novel temperature stress-induced lipocalin from wheat and Arabidopsis. FEBS Lett. 2002, 517, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.X.; Liao, X.Q.; Yang, X.H.; Luo, Y.C.; Lin, P.; Zeng, Q.H. Lysine crotonylation of DgTIL1 at K72 modulates cold tolerance by enhancing DgnsLTP stability in chrysanthemum. Plant Biotechnol. J. (PBJ) 2020, 19, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellsen, T.D.; Shiryaeva, L.; SchraDer, W.P.; Strimbeck, G.R. Proteomics of extreme freezing tolerance in Siberian spruce (Picea obovata). J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.Y.; Sambe, M.A.N.; Zhuo, C.L.; Tu, Q.H.; Guo, Z.F. A temperature induced lipocalin gene from Medicago falcata (MfTIL1) confers tolerance to cold and oxidative stress. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 87, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Fung, R.W.M.; Liu, H.; Hsu, C.; Charng, Y. Temperature-induced lipocalin is required for basal and acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Su, W. Advances in the study of chemical constituents and pharmacology of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Zhong Yao Cai 2003, 26, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kenneth, S.T.L. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using RT-qPCR pdf. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, C.; Mayumi, G.; Yoshihisa, N.; Koichiro, G. Selection of Housekeeping Genes for Transgene Expression Analysis in Eucommia ulmoides Oliver Using Real-Time RT-PCR. J. Bot. 2010, 2010, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Ran, X.; Zhao, D.G. Transgenic Tobacco with EuAFP1.2 Gene Improves Fungal Disease Resistance. Genom. Appl. Biol. 2022, 40, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. Infiltration of Nicotiana benthamiana Protocol for Transient Expression via Agrobacterium. Bio-Protocol 2011, 2011, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryd, C.F.M. The determination of moisture in tobacco. Anal. Anal. J. R. Soc. Chem. A Mon. Int. Publ. Deal. All Branches Anal. Chem. 1951, 76, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avi-Dor, Y.; Lipkin, R. A spectrophotometric method for the determination of reduced glutathione. J. Biol. Chem. 1958, 233, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masayasu, M.; Hiroshi, Y. A simplified assay method of superoxide dismutase activity for clinical use. Clin. Chim. Acta 1979, 92, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuveni, R. Peroxidase Activity as a Biochemical Marker for Resistance of Muskmelon (Cucumis melo) to Pseudoperonospora cubensis. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, B.; Roel, M. An Improved Colorimetric Method to Quantify Sugar Content of Plant Tissue. J. Exp. Bot. 1993, 44, 1627–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Gras, F.; Boronat, A. A hydrophobic proline-rich motif is involved in the intracellular targeting of temperature-induced lipocalin. Plant Mol. Biol. 2015, 88, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R.E. The bacterial lipocalins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1482, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugière, S.; Kowalski, S.; Ferro, M.; Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Miras, S.; Salvi, D.; Ravanel, S.; D’hérin, P.; Garin, J.; Bourguignon, J.; et al. The hydrophobic proteome of mitochondrial membranes from Arabidopsis cell suspensions. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1693–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkley, T.P.; Hester, S.; Shadforth, I.P.; Runions, J.; Weimar, T.; Hanton, S.L.; Griffin, J.L.; Bessant, C.; Brandizzi, F.; Hawes, C.; et al. Mapping the Arabidopsis organelle proteome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6518–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eubel, H.; Meyer, E.H.; Taylor, N.L.; Bussell, J.D.; O’Toole, N.; Heazlewood, J.L.; Castleden, I.; Small, I.D.; Smith, S.M.; Millar, A.H. Novel proteins, putative membrane transporters, and an integrated metabolic network are revealed by quantitative proteomic analysis of Arabidopsis cell culture peroxisomes. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1809–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Ogiala, A.; Carsjens, C.; Diekmann, H.; Fayyaz, P.; Herrfurth, C.; Feussner, I.; Polle, A. Temperature-induced lipocalin (TIL) is translocated under salt stress and protects chloroplasts from ion toxicity. J. Plant Physiol. 2014, 171, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, D.; Chong, K. Cold signaling in plants: Insights into mechanisms and regulation. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Feng, S.; Yu, X.; Zhou, A. Morphological and physiological responses of Dianthus spiculifolius high wax mutant to low-temperature stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 275, 153762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, M.; Kandlbinder, A.; Golldack, D.; Dietz, K.J. Oxidative stress and ozone: Perception, signalling and response. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H. Cryopreservation of seeds of blue waterlily (Nymphaea caerulea) using glutathione adding plant vitrification solution, PVS+. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.14201. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.G.; She, X.P. The Generation and the Role of Hydrogen Peroxide in Plant. J. Lianyungang Norm. Coll. 2010, 04, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Mittler, R.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweł, S.; Wardas, M.; Niedworok, E.; Wardas, P. Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad. Lek. 2004, 57, 453–455. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, P.; Entazari, M.; Ebrahimi, A.; Ahmadizadeh, M.; Vannozzi, A.; Palumbo, F.; Barcaccia, G. Exogenous EBR Ameliorates Endogenous Hormone Contents in Tomato Species under Low-Temperature Stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yang, Z.; Wu, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Nie, S. Enhanced brassinosteroid signaling via the overexpression of SlBRI1 positively regulates the chilling stress tolerance of tomato. Plant Sci. 2022, 320, 111281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.; Thomashow, M.F. Arabidopsis Transcriptome Profiling Indicates That Multiple Regulatory Pathways Are Activated during Cold Acclimation in Addition to the CBF Cold Response Pathway. Imp. Coll. Lond. 2002, 14, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasensky, J.; Jonak, C. Drought, salt, and temperature stress-induced metabolic rearrangements and regulatory networks. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, F.; Sun, Z.; Ni, Z.; Iqbal, S.; Gu, X. Exogenous Melatonin Improves Cold Tolerance of Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) through Modulation of DREB/CBF-COR Pathway and Antioxidant Defense System. Horticulture 2022, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.; Catalá, R.; Salinas, J. The CBFs: Three arabidopsis transcription factors to cold acclimate. Plant Sci. 2011, 180, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steponkus, P.L.; Uemura, M.; Joseph, R.A.; Gilmour, S.J.; Thomashow, M.F. Mode of action of the COR15a gene on the freezing tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14570–14575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.S.; Wilhelm, K.S.; Thomashow, M.F. The 5′-region of Arabidopsis thaliana cor15a has cis-acting elements that confer cold-, drought- and ABA-regulated gene expression. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 24, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).