Functional Analysis of SmMYB39 in Salt Stress Tolerance of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatments
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis of SmMYB39
2.3. Subcellular Localization
2.4. SmMYB39 Transcriptional Activation Activity Validation
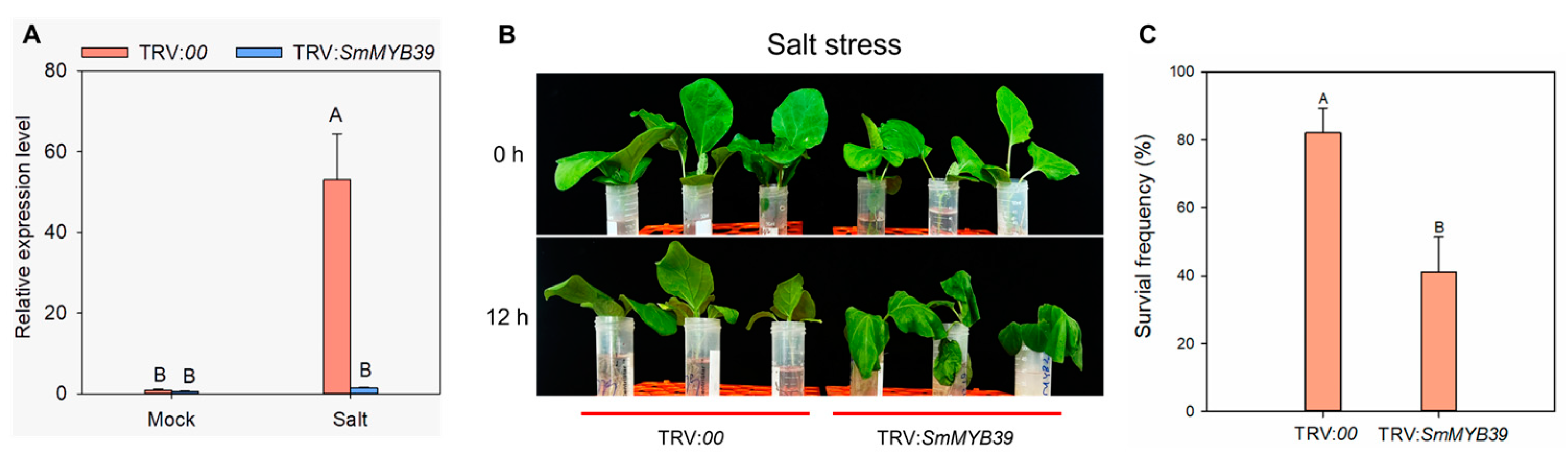
2.5. Functional Analysis of SmMYB39 Based on VIGS Method
2.6. qRT-PCR Assay
2.7. Statistical Calculations
3. Results
3.1. Expression Patterns of SmMYB39 in Response to Salt Stress
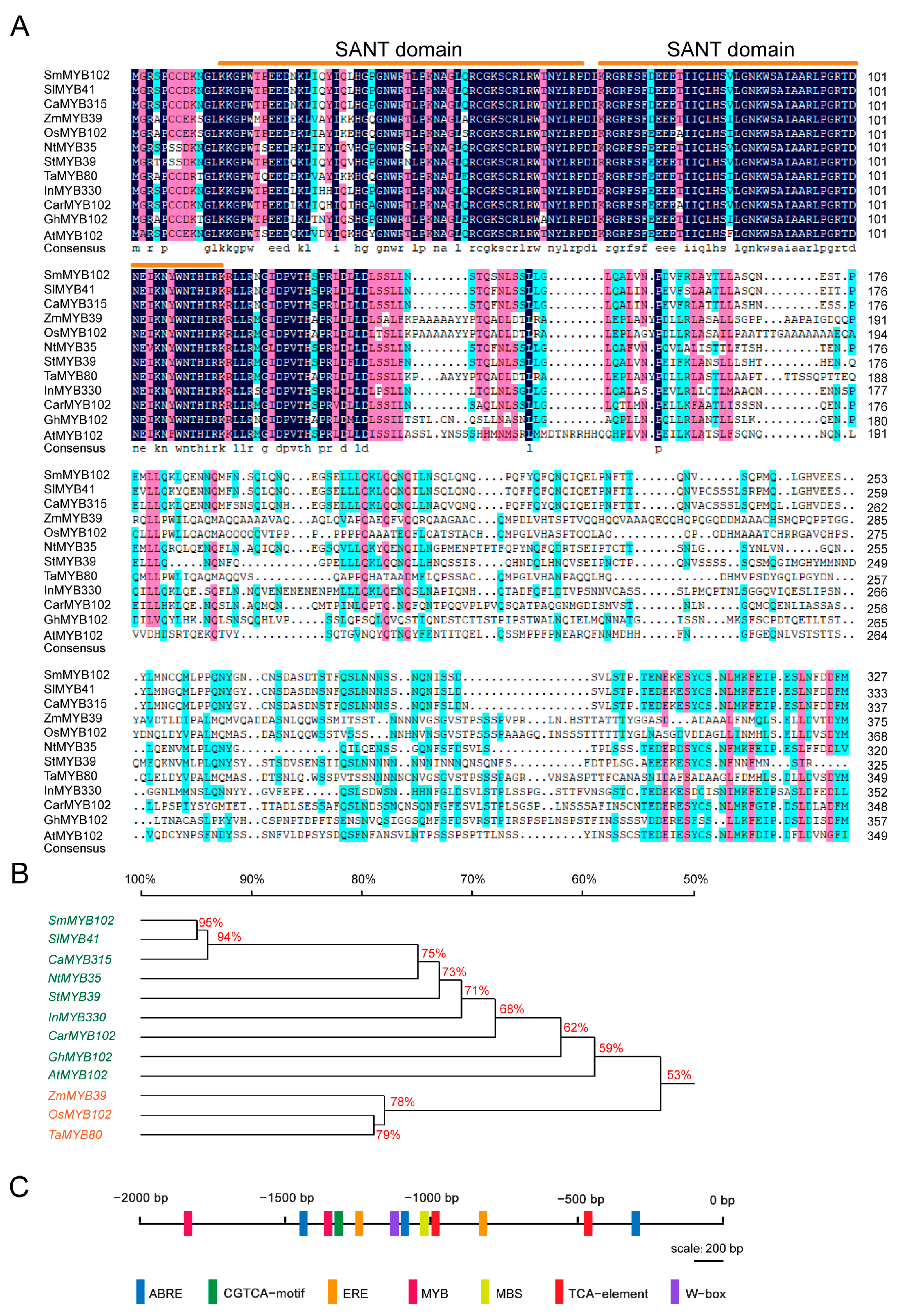
3.2. Sequence, Phylogenetic and Promoter Analysis of SmMYB39
3.3. Nuclear Localization of SmMYB39
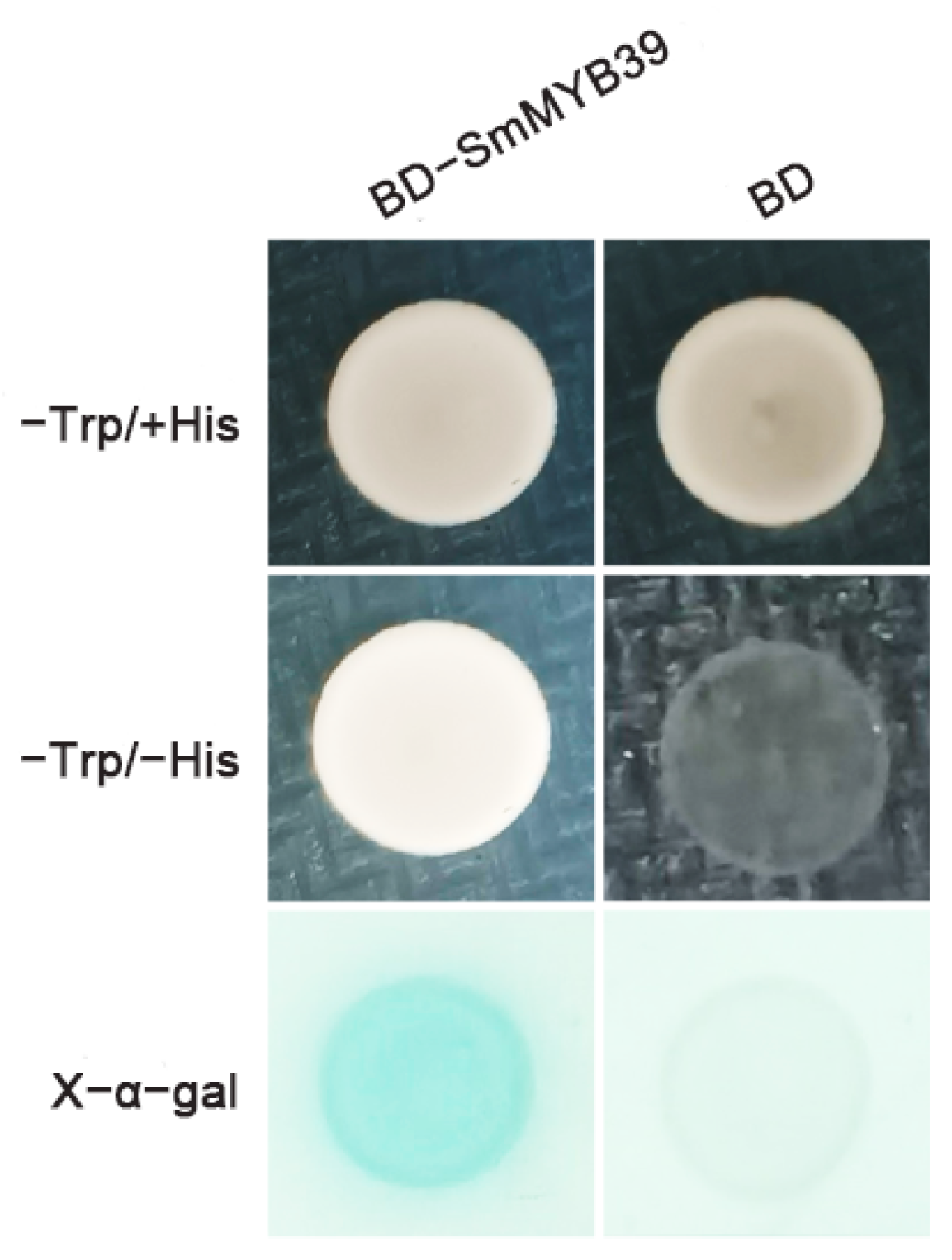
3.4. SmMYB39 Exhibits Transcriptional Activation Activity

3.5. Silencing of SmMYB39 Reduced Eggplant Tolerance to Salt Stress
3.6. Analysis Interaction Network of SmMYB39 in Eggplant
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Behera, T.K.; Krishna, R.; Ansari, W.A.; Aamir, M.; Kumar, P.; Kashyap, S.P.; Pandey, S.; Kole, C. Approaches Involved in the Vegetable Crops Salt Stress Tolerance Improvement: Present Status and Way Ahead. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 787292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Sun, H.; Xue, J.; Yan, D.; Liu, Y.; Gui, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Acceleration of soil salinity accumulation and soil degradation due to greenhouse cultivation: A survey of farmers’ practices in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannachi, S.; Signore, A.; Mechi, L. Alleviation of Associated Drought and Salinity Stress’ Detrimental Impacts on an Eggplant Cultivar (‘Bonica F1’) by Adding Biochar. Plants 2023, 12, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisuria, H.J.; Dhaduk, H.L.; Kumar, S.; Sakure, A.A.; Thounaojam, A.S. Physiological and gene expression responses involved in teak (Tectona grandis L.) seedlings exposed to osmotic and salt stressors. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 4875–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambawat, S.; Sharma, P.; Yadav, N.R.; Yadav, R.C. MYB transcription factor genes as regulators for plant responses: An overview. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 2013, 19, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranz, H.D.; Denekamp, M.; Greco, R.; Jin, H.; Leyva, A.; Meissner, R.C.; Petroni, K.; Urzainqui, A.; Bevan, M.; Martin, C.; et al. Towards functional characterisation of the members of the R2R3-MYB gene family from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosinski, J.A.; Atchley, W.R. Molecular evolution of the Myb family of transcription factors: Evidence for polyphyletic origin. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 46, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubos, C.; Stracke, R.; Grotewold, E.; Weisshaar, B.; Martin, C.; Lepiniec, L. MYB transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilaud, T.; Koering, C.E.; Binet-Brasselet, E.; Ancelin, K.; Pollice, A.; Gasser, S.M.; Gilson, E. The telobox, a Myb-related telomeric DNA binding motif found in proteins from yeast, plants and human. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, N.W.; Griffiths, A.G.; Cousins, G.R.; Verry, I.M.; Williams, W.M. Anthocyanin leaf markings are regulated by a family of R2R3-MYB genes in the genus Trifolium. N. Phytol. 2015, 205, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, O.; Okada, Y.; Ando, H.; Guedj, M.; Higashijima, S.; Shimazaki, T.; Chino, N.; Okano, H.; Okamoto, H. Comparative functional genomics revealed conservation and diversification of three enhancers of the isl1 gene for motor and sensory neuron-specific expression. Dev. Biol. 2005, 278, 587–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.S.; Agarwal, P.; Gupta, K.; Agarwal, P.K. Molecular characterization of an MYB transcription factor from a succulent halophyte involved in stress tolerance. AoB Plants 2015, 7, plv054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.X.; Qin, L.J.; Zhao, D.G. Overexpression of the OsIMP Gene Increases the Accumulation of Inositol and Confers Enhanced Cold Tolerance in Tobacco through Modulation of the Antioxidant Enzymes’ Activities. Genes 2017, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Meng, S.; Xiang, Z.; Yang, G.; He, N. An R1R2R3 MYB Transcription Factor, MnMYB3R1, Regulates the Polyphenol Oxidase Gene in Mulberry (Morus notabilis). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Chini, A.; Fernandez-Barbero, G.; Chico, J.M.; Gimenez-Ibanez, S.; Geerinck, J.; Eeckhout, D.; Schweizer, F.; Godoy, M.; Franco-Zorrilla, G.M.; et al. The Arabidopsis bHLH transcription factors MYC3 and MYC4 are targets of JAZ repressors and act additively with MYC2 in the activation of jasmonate responses. Plant Cell. 2011, 23, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Schrader, A. TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA 1-Dependent Regulation of Flavonoid Biosynthesis. Plants 2017, 6, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Dai, X.; Zhang, W.H. A R2R3-type MYB gene, OsMYB2, is involved in salt, cold, and dehydration tolerance in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2541–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; Xu, W.; Ahmed, N.; Yu, A.; Wang, Z.; Liu, A. Changes and Associations of Genomic Transcription and Histone Methylation with Salt Stress in Castor Bean. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, R.; Yang, X.; Ju, Q.; Li, W.; Lu, S.; Tran, L.P.; Xu, J. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor AtMYB49 modulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis by modulating the cuticle formation and antioxidant defence. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1925–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L.; Shi, Q.; Ren, Z. SlMYB102, an R2R3-type MYB gene, confers salt tolerance in transgenic tomato. Plant Sci. 2020, 291, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Zhao, E.; Liu, R.; Yang, X. Transcriptome Analysis of Eggplant under Salt Stress: AP2/ERF Transcription Factor SmERF1 Acts as a Positive Regulator of Salt Stress. Plants 2022, 11, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, L. An MYB-family transcription factor with suber powers. Plant J. 2020, 102, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Yang, S.; Yang, F.; Guan, D.; He, S. CaCBL1 Acts as a Positive Regulator in Pepper Response to Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.S.; Hwang, I.S.; Hwang, B.K. Requirement of the cytosolic interaction between PATHOGENESIS-RELATED PROTEIN10 and LEUCINE-RICH REPEAT PROTEIN1 for cell death and defense signaling in pepper. Plant Cell. 2012, 24, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, S.; Yang, T.; Liang, J.; Wen, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, L.; Tang, Q.; et al. Pepper CabZIP63 acts as a positive regulator during Ralstonia solanacearum or high temperature-high humidity challenge in a positive feedback loop with CaWRKY40. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 2439–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Niu, N.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Xue, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Zhao, J. Virus-Induced Gene Silencing (VIGS) in Chinese Jujube. Plants 2023, 12, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Chu, X.; Liu, H.; Ding, X.; Lu, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; et al. SlMYB1 regulates the accumulation of lycopene, fruit shape, and resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhac282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.H.; Zhang, S.Z.; Wang, R.K.; Zhang, R.F.; Hao, Y.J. Genome wide analysis of the apple MYB transcription factor family allows the identification of MdoMYB121 gene confering abiotic stress tolerance in plants. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.F.; Cara, B.; Perez-Martin, F.; Pineda, B.; Egea, I.; Flores, F.B.; Fernandez-Garcia, N.; Capel, J.; Moreno, V.; Angosto, T.; et al. The tomato mutant ars1 (altered response to salt stress 1) identifies an R1-type MYB transcription factor involved in stomatal closure under salt acclimation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhou, X.; Hou, X.; Yang, G.; Meng, J.; Luan, Y. Tomato MYB49 enhances resistance to Phytophthora infestans and tolerance to water deficit and salt stress. Planta 2018, 248, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Dong, N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Expression of a wheat MYB gene in transgenic tobacco enhances resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum, and to drought and salt stresses. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2011, 11, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.B.; Luan, Y.S.; Yin, Y.L. SpMYB overexpression in tobacco plants leads to altered abiotic and biotic stress responses. Gene 2014, 547, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefsbol, T.O. Handbook of Epigenetics: The New Molecular and Medical Genetics, 2nd ed.; An Imprint of Elsevier; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Cui, R.; Wang, D.; Huang, H.; Rui, C.; Malik, W.A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; Liu, X.; et al. Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses elucidate key salt-responsive biomarkers to regulate salt tolerance in cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Tian, M.; Gao, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Yang, W. Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis identifies candidate genes involved in jasmonic acid-mediated salt tolerance of alfalfa. Peer J. 2023, 11, e15324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Ansari, M.W.; Kaula, B.C.; Rao, Y.R.; Al Meselmani, M.; Siddiqui, Z.H.; Kumar, S.B.; Rani, V.; Sarkar, A.; Rakwal, R.; et al. Regulation of ethylene metabolism in tomato under salinity stress involving linkages with important physiological signaling pathways. Plant Sci. 2023, 334, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adavi, S.; Pandesha, P.H.; Jagadhesan, B.; Jha, S.K.; Chinnusamy, V.; Sathee, L. Nitrate supply regulates tissue calcium abundance and transcript level of Calcineurin B-like (CBL) gene family in wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 199, 107724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.X.; Ren, X.L.; Qi, X.T.; Yang, Z.M.; Feng, X.L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.-J.; Liang, P.; Jiang, Q.-Y.; Yang, W.-J.; et al. Evolution of the CBL and CIPK gene families in Medicago: Genome-wide characterization, pervasive duplication, and expression pattern under salt and drought stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, I.; Eckhardt, M. An enzymatic fluorimetric assay for determination of N-acetylaspartate. Anal. Biochem. 2023, 667, 115083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.K.; Wu, M.F.; Cui, S.; Wagner, D. Roles and activities of chromatin remodeling ATPases in plants. Plant J. 2015, 83, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Jung, C.; Cheong, J.J. Chromatin remodeling for the transcription of type 2C protein phosphatase genes in response to salt stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 141, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liang, X.; Lin, M.; Lan, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Yan, H. Comprehensive analysis of MAPK gene family in Populus trichocarpa and physiological characterization of PtMAPK3-1 in response to MeJA induction. Physiol. Plant. 2023, 175, e13869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Z.; Shen, L.; He, J.; Du, L.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X. Functional Analysis of SmMYB39 in Salt Stress Tolerance of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Horticulturae 2023, 9, 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080848
Jiang Z, Shen L, He J, Du L, Xia X, Zhang L, Yang X. Functional Analysis of SmMYB39 in Salt Stress Tolerance of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Horticulturae. 2023; 9(8):848. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080848
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Zheng, Lei Shen, Jie He, Lihui Du, Xin Xia, Longhao Zhang, and Xu Yang. 2023. "Functional Analysis of SmMYB39 in Salt Stress Tolerance of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.)" Horticulturae 9, no. 8: 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080848
APA StyleJiang, Z., Shen, L., He, J., Du, L., Xia, X., Zhang, L., & Yang, X. (2023). Functional Analysis of SmMYB39 in Salt Stress Tolerance of Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Horticulturae, 9(8), 848. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9080848




