Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium under Heat Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Treatment
2.2. Identification and Sequence Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in C. lavandulifolium
2.3. Chromosomal Location, Gene Duplication, and Synteny Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Gene Structures, Motifs, and Conserved Domains
2.6. Promoter Sequence Analysis of ClHSP70 Family
2.7. qRT-PCR
3. Results
3.1. Identification of ClHSP70 Genes in C. lavandulifolium
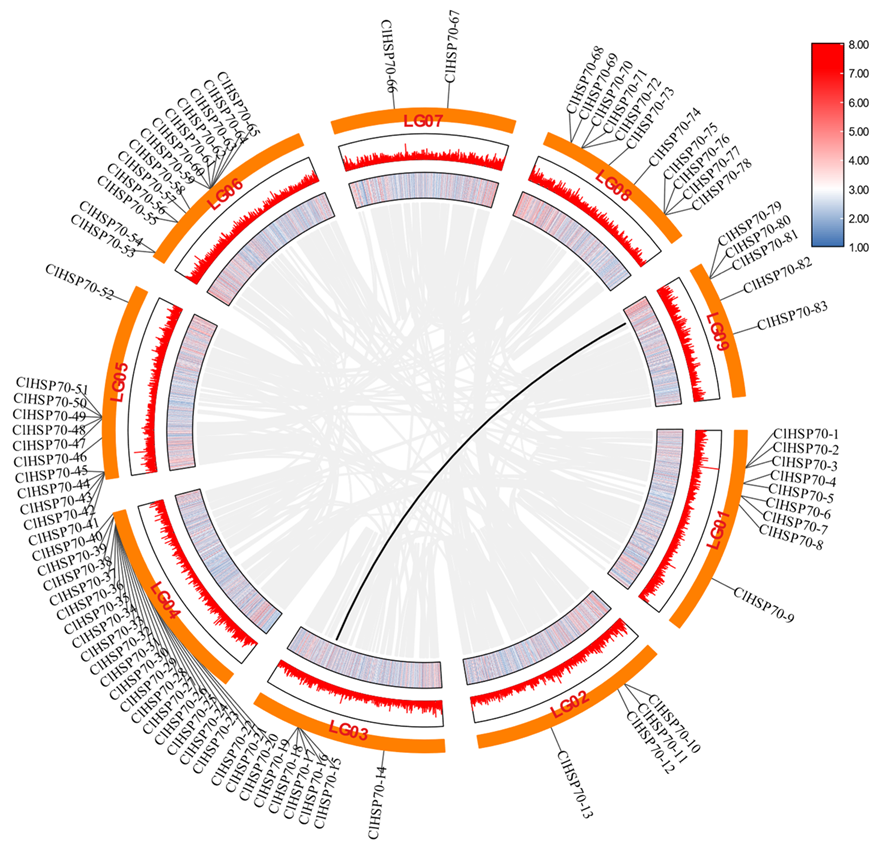
3.2. Chromosomal Localization and Collinearity Analysis of ClHSP70 Genes
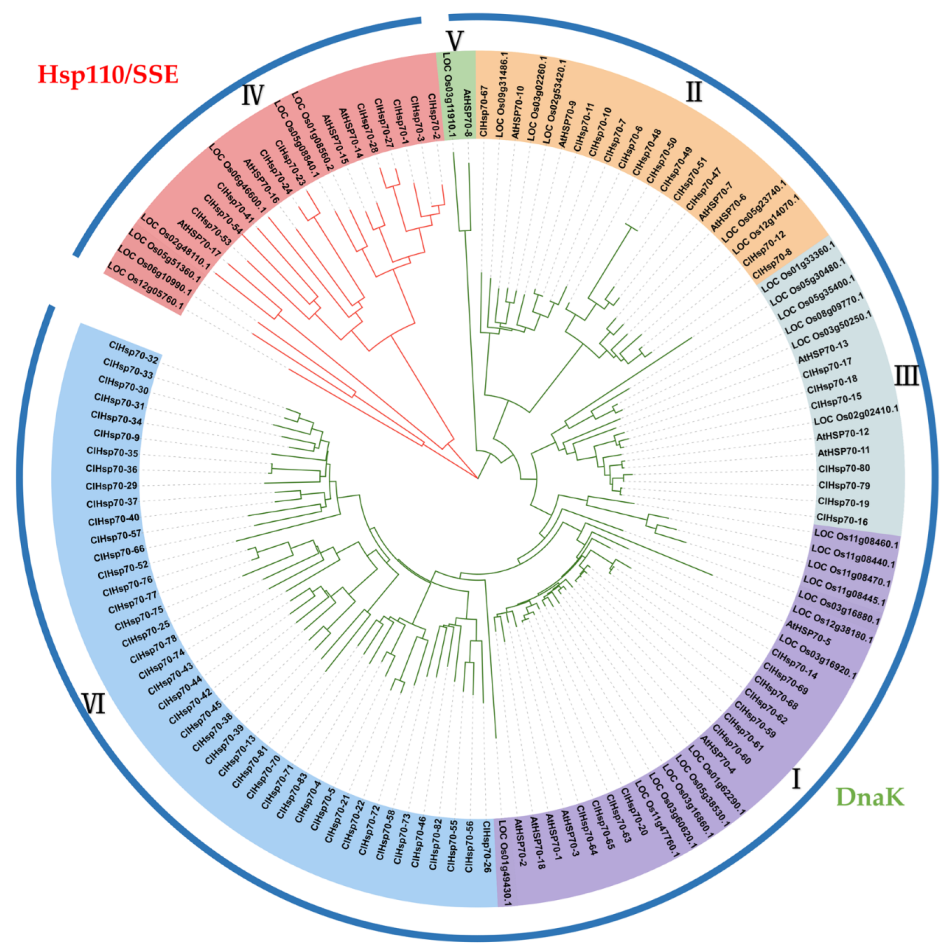
3.3. Phylogenetic Relationship ClHSP70 Genes
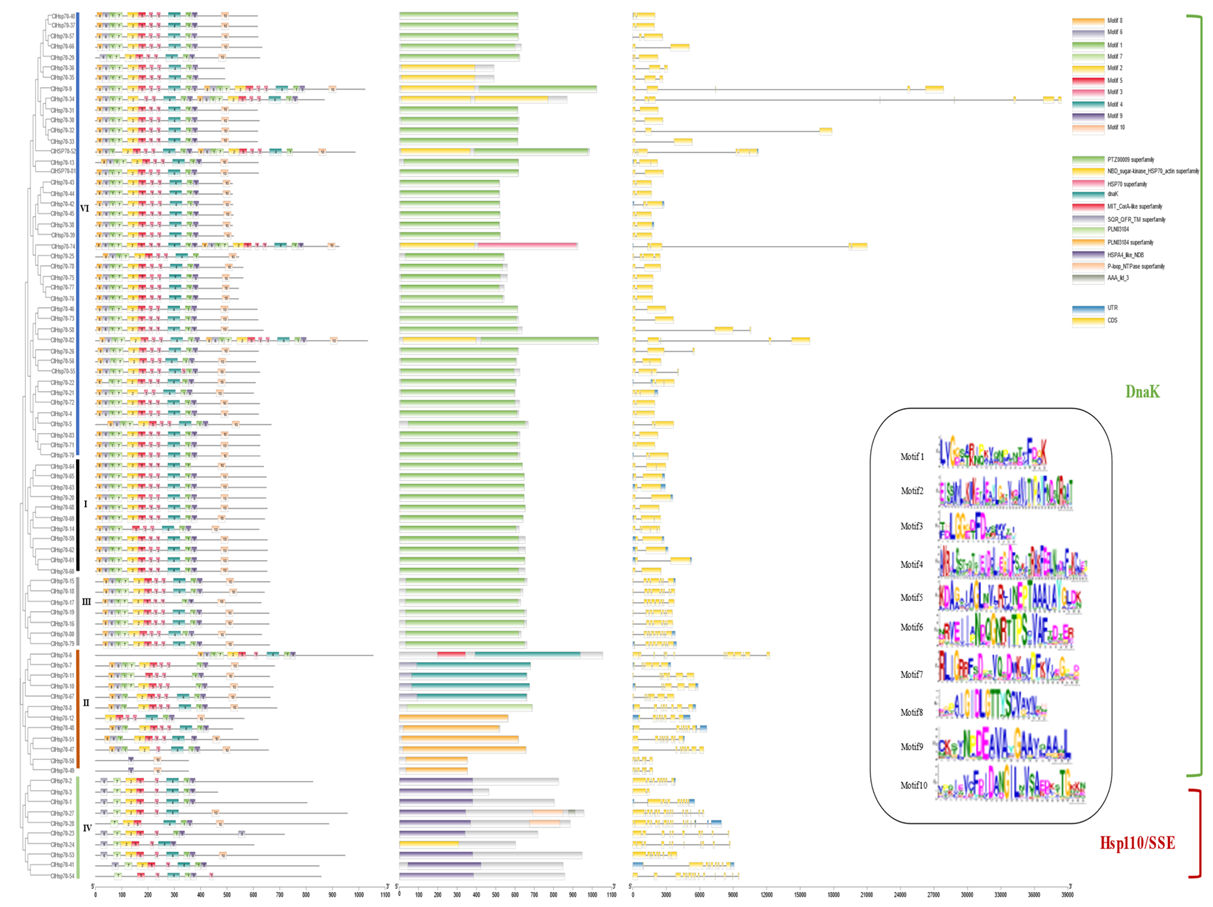
3.4. Conserved Motif, Gene Structure, and Domain Analysis of ClHSP70s
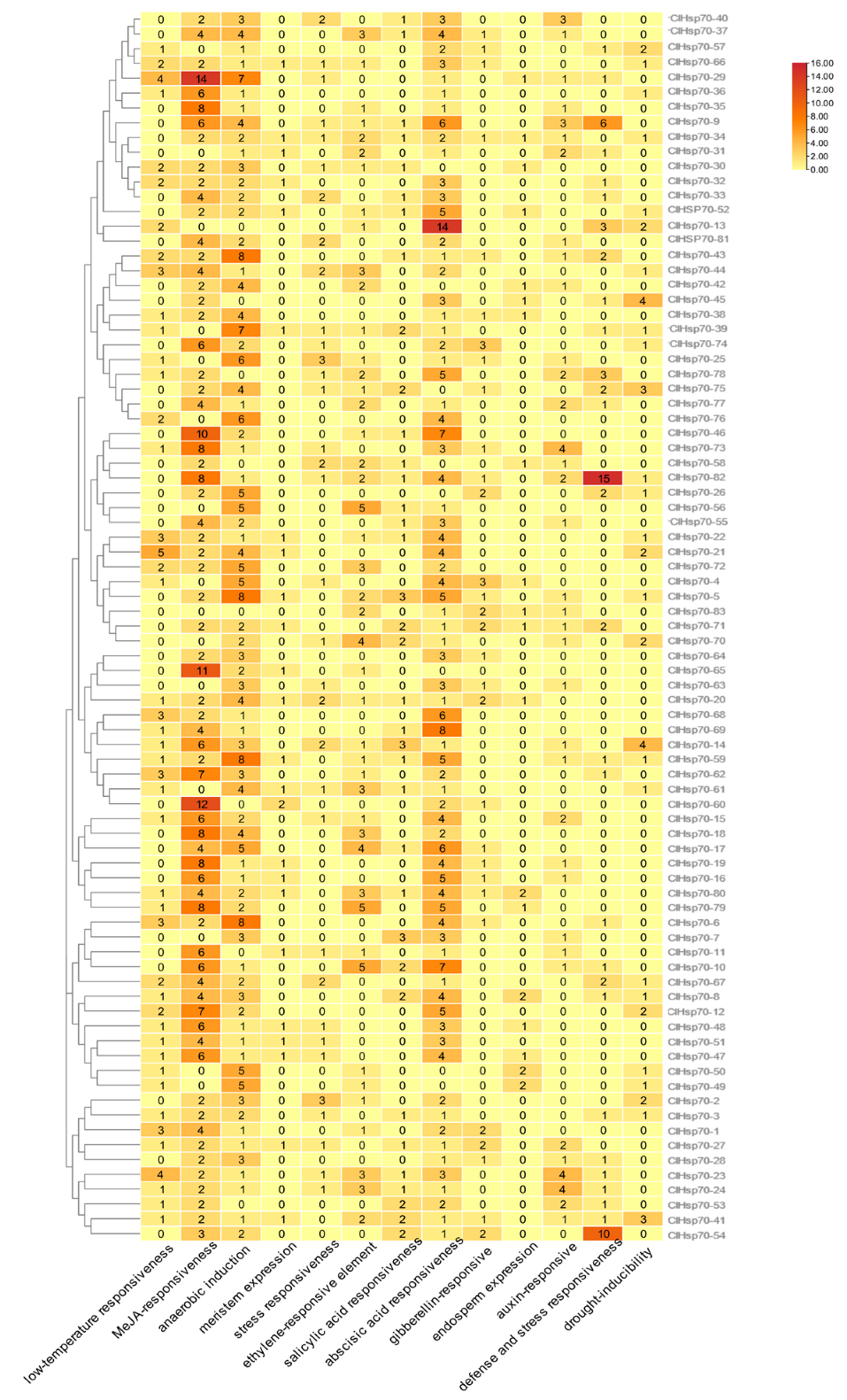
3.5. cis-Element and CpG Island Analysis of the ClHSP70 Genes in C. lavandulifolium
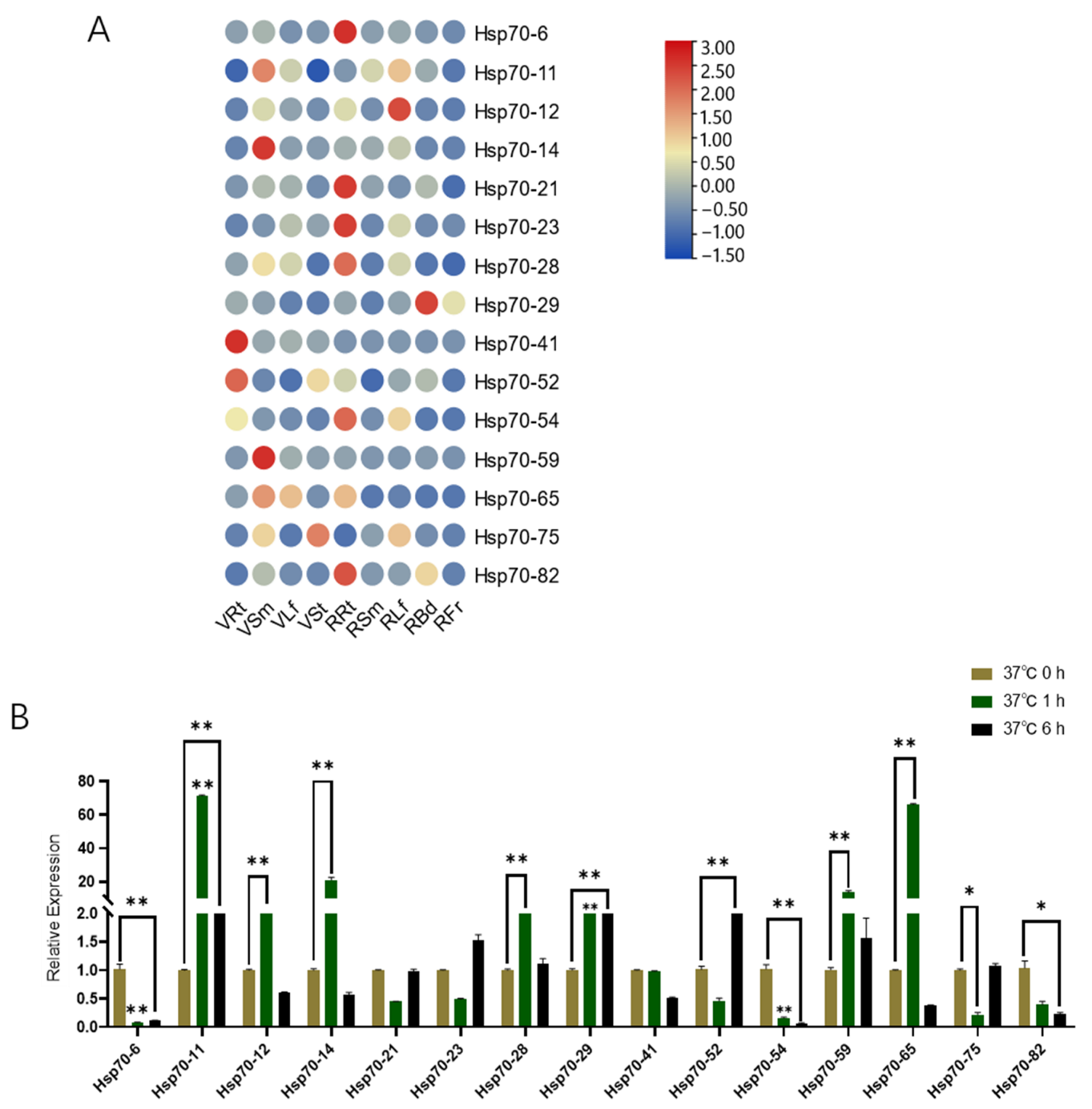
3.6. qRT-PCR Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sukiran, N.L.; Ma, J.C.; Ma, H.; Su, Z. ANAC019 is required for recovery of reproductive development under drought stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 99, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ul Haq, S.; Khan, A.; Ali, M.; Khattak, A.M.; Gai, W.X.; Zhang, H.X.; Wei, A.M.; Gong, Z.H. Heat Shock Proteins: Dynamic Biomolecules to Counter Plant Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.L.; Brown, C. Plasticity of the Hsp90 chaperone machine in divergent eukaryotic organisms. Cell Stress Chaperone 2009, 14, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.G.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, M.R.; Malek, M.A.; Latif, M.A. Expression of target gene Hsp70 and membrane stability determine heat tolerance in chili pepper. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2015, 140, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedonks, N.; Xu, J.; Peters, J.L.; Park, S.; Rieu, I. Multi-Level Interactions Between Heat Shock Factors, Heat Shock Proteins, and the Redox System Regulate Acclimation to Heat. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.G.; Rafii, M.Y.; Martini, M.Y.; Yusuff, O.A.; Ismail, M.R.; Miah, G. Molecular analysis of Hsp70 mechanisms in plants and their function in response to stress. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2017, 33, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, E.R. The evolution, function, structure, and expression of the plant sHSPs. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.L.; Wang, J.S.; Liu, H.C.; Chen, R.W.; Meyer, Y.; Barakat, A.; Delseny, M. Genomic analysis of the Hsp70 superfamily in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell Stress Chaperones 2001, 6, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovic, Z.; Broadley, S.A.; Shomura, Y.; Bracher, A.; Hartl, F.U. Molecular chaperones of the Hsp110 family act as nucleotide exchange factors of Hsp70s. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 2519–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genevaux, P.; Georgopoulos, C.; Kelley, W.L. The Hsp70 chaperone machines of Escherichia coli: A paradigm for the repartition of chaperone functions. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 840–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, R.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Mayer, M.P.; Bukau, B. The Hsp70 chaperone network. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 665–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampinga, H.H.; Craig, E.A. The HSP70 chaperone machinery: J proteins as drivers of functional specificity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.Y.; Lee, S.; Cyr, D.M. Mechanisms for regulation of Hsp70 function by Hsp40. Cell Stress Chaperones 2003, 8, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermann, J.P.; Jiang, J.; Cuellar, J.; Llorca, O.; Wang, L.; Gimenez, L.E.; Jin, S.; Taylor, A.B.; Demeler, B.; Morano, K.A.; et al. Structure of the Hsp110: Hsc70 nucleotide exchange machine. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polier, S.; Dragovic, Z.; Hartl, F.U.; Bracher, A.W. Structural basis for the cooperation of Hsp70 and Hsp110 chaperones in protein folding. Cell 2008, 133, 1068–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-J.J.; Seo, Y.-S.S. Heat shock proteins: A review of the molecular chaperones for plant immunity. Plant Pathol. J. 2015, 31, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berka, M.; Kopecká, R.; Berková, V.; Brzobohatý, B.; Černý, M. Regulation of heat shock proteins 70 and their role in plant immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 1894–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, D.Y.; Guy, C.L. Physiological and molecular assessment of altered expression of Hsc70-1 in Arabidopsis. Evidence for pleiotropic consequences. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.-H.; Guo, J.; Ding, K.; Wang, S.-J.; Zhang, H.; Dai, X.-W.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Govers, F.; Huang, L.-L.; Kang, Z.-S. Characterization of a wheat HSP70 gene and its expression in response to stripe rust infection and abiotic stresses. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.-H.; Gho, H.-J.; Nguyen, M.X.; Kim, S.-R.; An, G. Genome-wide expression analysis of HSP70 family genes in rice and identification of a cytosolic HSP70 gene highly induced under heat stress. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2013, 13, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.K.; Kundnani, P.; Grover, A. Functional analysis of Hsp70 superfamily proteins of rice (Oryza sativa). Cell Stress Chaperones 2013, 18, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, L.D.; Cagna, G.; Stuttmann, J.; Wirthmüller, L.; Betsuyaku, S.; Witte, C.P.; Bhat, R.; Pochon, N.; Colby, T.; Parker, J.E. Interaction between SGT1 and cytosolic/nuclear HSC70 chaperones regulates Arabidopsis immune responses. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 4061–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, A.; Zhu, X.; Chen, F.; Gao, H.; Jiang, J.; Chen, S. A chrysanthemum heat shock protein confers tolerance to abiotic stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5063–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungkunz, I.; Link, K.; Vogel, F.; Voll, L.M.; Sonnewald, S.; Sonnewald, U. AtHsp70-15-deficient Arabidopsis plants are characterized by reduced growth, a constitutive cytosolic protein response and enhanced resistance to TuMV. Plant J. 2011, 66, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shi, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, S.; Aharoni, A.; Shi, J.; Xu, J. Arabidopsis HSP70-16 is required for flower opening under normal or mild heat stress temperatures. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.K.; Dong, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, H.Y.; Xing, G.J.; Li, Q.Y.; Dong, Y.S. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling under heat and drought treatments of HSP70 gene family in soybean (Glycine max L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Xing, M.; Liu, X.; Fang, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lv, H. Genome-wide analysis of HSP70 family genes in cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) reveals their involvement in floral development. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzade, K.P.; Kale, S.S.; Chavan, N.R.; Hatzade, B. Genome-wide analysis of Hsp70 and Hsp100 gene families in Ziziphus jujuba. Cell Stress Chaperones 2021, 26, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, J.H.; Ma, X.; Zhai, Y.F.; Gong, Z.H.; Lu, M.H. Genome-wide analysis of the Hsp70 family genes in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) and functional identification of CaHsp70-2 involvement in heat stress. Plant Sci. 2016, 252, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, W.; Sheng, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, K.; Jiang, J.; Fang, W.; Guan, Z.; et al. Over-expression of chrysanthemum CmDREB6 enhanced tolerance of chrysanthemum to heat stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, C.; Gao, Q.; Xu, P.; Pu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, Y.; Hong, L.; et al. The chrysanthemum lavandulifolium genome and the molecular mechanism underlying diverse capitulum types. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, N.; Hausman, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Evers, D. Housekeeping gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 2907–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Løvdal, T.; Lillo, C. Reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in tomato subjected to nitrogen, cold, and light stress. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 387, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, A.; Yakovlev, I.; Strauss, S. Validating internal controls for quantitative plant gene expression studies. Plant. Biol. 2004, 4, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, C.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Shan, H.; Luo, H.; Guan, Z.; Chen, F. Reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR in Chrysanthemum subjected to biotic and abiotic stress. Mol. Biotechnol. 2011, 49, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub Khan, M.; Dongru, K.; Yifei, W.; Ying, W.; Penghui, A.; Zicheng, W. Characterization of WRKY Gene Family in Whole-Genome and Exploration of Flowering Improvement Genes in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 861193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.K.; Choi, Y.J. A nuclear-localized HSP70 confers thermoprotective activity and drought-stress tolerance on plants. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Barrientos, M.; Hermosa, R.; Cardoza, R.E.; Gutiérrez, S.; Nicolás, C.; Monte, E. Transgenic expression of the Trichoderma harzianum hsp70 gene increases Arabidopsis resistance to heat and other abiotic stresses. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ma, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Lü, J.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, C.Z.; Hong, B.; Gao, J. Control of chrysanthemum flowering through integration with an aging pathway. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Ding, Y.; Jin, J.; Song, A.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Fang, W.; Jiang, J. Physiological and Transcripts Analyses Reveal the Mechanism by Which Melatonin Alleviates Heat Stress in Chrysanthemum Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 673236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; He, M.; Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, S.; Zhou, Y. Overexpression of Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium ClCBF1 in Chrysanthemum morifolium ‘White Snow’ improves the level of salinity and drought tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, S.; Furuta, M.; Imamoto, N. Hikeshi, a nuclear import carrier for HSP70s, protects cells from heat shock-induced nuclear damage. Cell 2012, 149, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudi, M.; Chen, J.; Lou, Q. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Heat Shock Protein 70 (HSP70) Gene Family in Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) Rootstock under Drought Stress Suggested the Potential Role of these Chaperones in Stress Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, M.E.; Moen, A.; Bousset, L.; Egge-Jacobsen, W.; Kernstock, S.; Melki, R.; Falnes, P.Ø. Identification and characterization of a novel human methyltransferase modulating Hsp70 protein function through lysine methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 27752–27763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.S.; Shimazu, T.; Toyokawa, G.; Daigo, Y.; Maehara, Y.; Hayami, S.; Ito, A.; Masuda, K.; Ikawa, N.; Field, H.I.; et al. Enhanced HSP70 lysine methylation promotes proliferation of cancer cells through activation of Aurora kinase B. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Han, X.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, L.J.; Chen, S.; Fang, W.; Chen, F.; Jiang, J. Transcriptome analysis reveals chrysanthemum flower discoloration under high-temperature stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1003635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, H.; Khurana, N.; Agarwal, P.; Khurana, P. Heat shock factors in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Genome-wide expression analysis during reproductive development and abiotic stress. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2011, 286, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Rong, M.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Xu, Y.; Wei, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of HSP70 Gene Family in Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg. Genes 2021, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.F.; Yu, S.W.; Shu, L.B.; Wu, J.H.; Wu, A.Z.; Luo, L.J. Expression profile analysis of 9 heat shock protein genes throughout the life cycle and under abiotic stress in rice. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Shang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Q.; Hong, S.; Gu, C. Physiological and transcriptional responses to heat stress and functional analyses of PsHSPs in tree peony (Paeonia suffruticosa). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 926900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, W.; Qian, Y.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the Hsf and Hsp70 gene families in maize. Gene 2021, 770, 145348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| NO. | HSP70 Gene | Island # | Start | End | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ClHSP70-11 | 1 | −51 | −302 | 251bp |
| 2 | ClHSP70-12 | 2 | −532 | −633 | 102bp |
| −1719 | −1933 | 215bp | |||
| 3 | ClHSP70-15 | 1 | −230 | −364 | 135bp |
| 4 | ClHSP70-16 | 1 | −1691 | −1861 | 171bp |
| 5 | ClHSP70-19 | 1 | −1677 | −1841 | 165bp |
| 6 | ClHSP70-28 | 1 | −180 | −467 | 288bp |
| 7 | ClHSP70-29 | 1 | −358 | −472 | 115bp |
| 8 | ClHSP70-40 | 1 | −1422 | −1591 | 170bp |
| 9 | ClHSP70-46 | 2 | −625 | −791 | 167bp |
| −1496 | −1627 | 132bp | |||
| 10 | ClHSP70-47 | 1 | −1407 | −1515 | 109bp |
| 11 | ClHSP70-48 | 1 | −1391 | −1507 | 117bp |
| 12 | ClHSP70-51 | 1 | −1391 | −1455 | 121bp |
| 13 | ClHSP70-52 | 1 | −168 | −456 | 271bp |
| 14 | ClHSP70-53 | 1 | −332 | −434 | 102bp |
| 15 | ClHSP70-60 | 1 | −861 | −995 | 135bp |
| 16 | ClHSP70-61 | 1 | −1582 | −1701 | 120bp |
| 17 | ClHSP70-65 | 3 | −257 | −487 | 231bp |
| −736 | −858 | 123bp | |||
| −1450 | −1550 | 101bp | |||
| 18 | ClHSP70-72 | 1 | −692 | −833 | 142bp |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, M.; Hu, R.; Song, A.; Guan, Z.; Chen, F.; Jiang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium under Heat Stress. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020238
Yin M, Hu R, Song A, Guan Z, Chen F, Jiang J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium under Heat Stress. Horticulturae. 2023; 9(2):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020238
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Mengru, Rongqian Hu, Aiping Song, Zhiyong Guan, Fadi Chen, and Jiafu Jiang. 2023. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium under Heat Stress" Horticulturae 9, no. 2: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020238
APA StyleYin, M., Hu, R., Song, A., Guan, Z., Chen, F., & Jiang, J. (2023). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of HSP70 Gene Family in Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium under Heat Stress. Horticulturae, 9(2), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae9020238









