The Influence of Red and Blue Light Ratios on Growth Performance, Secondary Metabolites, and Antioxidant Activities of Centella asiatica (L.) Urban
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Light Treatment Instrument
2.3. Measurement of Growth Parameters
2.4. Analysis of Triterpene Glycoside Content
2.5. Analysis of Total Phenol and Total Flavonoid Content
2.6. Measurement of Antioxidant Activities
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Light Conditions on Growth Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Light Conditions on Triterpene Glycoside Content
3.3. Effect of Light Conditions on TPC, TFC, and Antioxidant Activities
3.4. Correlations between Triterpene Glycosides, TPC, TFC, and Antioxidant Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sritongkul, J.; Srilaong, V.; Uthairatanakij, A.; Kanlayanarat, S.; Chalermglin, P. Effect of light intensity on chemical composition of asiatic pennywort (Centella asiatica L. Urban). Acta Hortic. 2009, 837, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, K.; Kays, S. Asiatic Pennywort [Centella asiatica (L.) Urb.]: A little-known vegetable crop. Horttechnology 1996, 6, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devkota, A.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Comai, S.; Innocenti, G.; Jha, P.K. Centella asiatica (L.) urban from Nepal: Quali-quantitative analysis of samples from several sites, selection of high terpene containing populations for cultivation. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Verma, R.; Gupta, M.; Ram, M.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, S. Screening of genetic resources of the medicinal-vegetable plant Centella asiatica for herb and asiaticoside yields under shaded and full sunlight conditions. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menglan, S.; Fading, P.; Zehui, P.; Watson, M.F.; Cannon, J.F.; Holmes-Smith, I.; Kljuykov, E.V.; Phillippe, L.R.; Pimenov, M.G. Apiaceae (Umbelliferae). Flora China 2005, 14, 1–205. [Google Scholar]
- Srithongkul, J.; Kanlayanarat, S.; Srilaong, V.; Uthairatanakij, A.; Chalermglin, P. Effects of light intensity on growth and accumulation of triterpenoids in three accessions of Asiatic pennywort (Centella asiatica (L.) Urb.). J. Food Agric. Environ. 2011, 9, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Bylka, W.; Znajdek-Awizen, P.; Studzinska-Sroka, E.; Brzezinska, M. Centella asiatica in cosmetology. Postepy. Dermatol. Alergol. 2013, 30, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, A.; Dall’ Acqua, S.; Jha, P.K.; Innocenti, G. Variation in the active constituents in Centella asiatica grown in different habitats in Nepal. Bot. Orient.: J. Plant Sci. 2010, 7, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Singh, D.R.; Banu, V.S.; Avinash, N. Functional constituents (micronutrients and phytochemicals) and antioxidant activity of Centella asiatica (L.) Urban leaves. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 61, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plengmuankhae, W.; Tantitadapitak, C. Low temperature and water dehydration increase the levels of asiaticoside and madecassoside in Centella asiatica (L.) Urban. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2015, 97, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafat, A.; Philip, K.; Muniandy, S. A novel source of bioactive compounds: Endophytic bacteria isolated from Centella asiatica. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.; Rasik, A.M.; Jain, G.M.; Shankar, R.; Kulshrestha, D.K.; Dhawan, B.N. In vitro and in vivo wound healing activity of asiaticoside isolated from Centella asiatica. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.T.; Kurup, R.; Johnson, A.J.; Chandrika, S.P.; Mathew, P.J.; Dan, M.; Baby, S. Elite genotypes/chemotypes, with high contents of madecassoside and asiaticoside, from sixty accessions of Centella asiatica of south India and the Andaman Islands: For cultivation and utility in cosmetic and herbal drug applications. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 32, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, E. Plant production in a closed plant factory with artificial lighting. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Light in Horticultural Systems, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 15–18 October 2012; pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kozai, T. Resource use efficiency of closed plant production system with artificial light: Concept, estimation and application to plant factory. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2013, 89, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adil, M.; Ren, X.; Jeong, B.R. Light elicited growth, antioxidant enzymes activities and production of medicinal compounds in callus culture of Cnidium officinale Makino. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 196, 111509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, A.; Jha, P.K. Effects of different light levels on the growth traits and yield of Centella asiatica. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2010, 5, 226–230. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.S.; Arya, M.; Mahadevappa, P.; Gridhar, P. Influence of photoperiod on growth, bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in callus cultures of Basella rubra L. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 209, 111937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naznin, M.T.; Lefsrud, M.; Gravel, V.; Azad, M.O.K. Blue light added with red LEDs enhance growth characteristics, pigments content, and antioxidant capacity in lettuce, spinach, kale, basil, and sweet pepper in a controlled environment. Plants 2019, 8, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poudel, P.R.; Kataoka, I.; Mochioka, R. Effect of red-and blue-light-emitting diodes on growth and morphogenesis of grapes. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2008, 92, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.-H.; Oh, M.-M. Growth, photosynthetic and antioxidant parameters of two lettuce cultivars as affected by red, green, and blue light-emitting diodes. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2015, 56, 639–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watcharatanon, K.; Ingkaninan, K.; Putalun, W. Improved triterpenoid saponin glycosides accumulation in in vitro culture of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst with precursor feeding and LED light exposure. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 134, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Yu-Xin, T.; Qi-Chang, Y. Optimal control of environmental conditionds affecting lettuce plant growth in a controlled environment with artificial lighting: A review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 130, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, E.; Jaafar, H.Z.; Ghasemzadeh, A.; Ibrahim, M.H. Light intensity effects on production and antioxidant activity of flavonoids and phenolic compounds in leaves, stems and roots of three varieties of Labisia pumila Benth. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Guo, B. Effects of light intensity on the growth, photosynthetic characteristics, and flavonoid content of Epimedium pseudowushanense B.L. Guo. Molecules 2016, 21, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Effects of light intensity and temperature on the photosynthesis characteristics and yield of lettuce. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.-X.; Xu, Z.-G.; Liu, X.-Y.; Tang, C.-M.; Wang, L.-W.; Han, X.-l. Effects of light intensity on the growth and leaf development of young tomato plants grown under a combination of red and blue light. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 153, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kang, C.; Kaiser, E.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, T. Red/blue light ratios induce morphology and physiology alterations differently in cucumber and tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, S.; Gu, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Ye, N. Exploration of the effects of different blue light intensities on flavonoid and lipid metabolism in tea plants via transcriptomics and metabolomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Zou, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Wang, Y. The combination of blue and red LED light improves growth and phenolics acid contents in Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 158, 112959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.-S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurshid, R.; Ullah, M.A.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Drouet, S.; Shah, M.; Zaeem, A.; Hameed, S.; Hano, C.; Abbasi, B.H. Lights triggered differential accumulation of antioxidant and antidiabitic secondary metabolites in callus culture of Eclipta alba L. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagnari, F.; Mattia, C.D.; Galieni, A.; Santarelli, V.; D’Egidio, S.; Pagnani, G.; Pisante, M. Light quantity and quality supplies sharply affect growth, morphological, physiological and quality traits of basil. Indus. Crop. Prod. 2018, 122, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.-S.; Chung, I.-M.; Hwang, M.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Yu, C.Y.; Ghimire, B.K. Application of light-emitting diodes for improving the nutritional quality and bioactive compound levels of some crops and medicinal plants. Molecules 2021, 26, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.-H.; Oh, M.-M. Leaf shape, growth, and antioxidant phenolic compounds of two lettuce cultivars grown under various combinations of blue and red light-emitting diodes. HortScience 2013, 48, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Van Labeke, M.-C. Long-term effects of red-and blue-light emitting diodes on leaf anatomy and photosynthetic efficiency of three ornamental plants. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Ho, T.-T.; Lee, H.; Jung, G.; Kim, Y.E.; Jeong, C.-S.; Park, S.-Y. Enhanced biosynthesis of triterpenoids in Centella asiatica hairy root culture by precursor feeding and elicitation. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 14, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.R.; Lee, J.G. Ripening-dependent changes in antioxidants, color attributes, and antioxidant activity of seven tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cultivars. J. Anal. Method Chem. 2016, 2016, 5498618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, Y.K.; Bhandari, S.R.; Jo, J.S.; Song, J.W.; Cho, M.C.; Yang, E.Y.; Lee, J.G. Response of salt stress in lettuce: Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, phytochemical contents, and antioxidant activities. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, S.R.; Cho, M.-C.; Lee, J.G. Genotypic variation in carotenoid, ascorbic acid, total phenolic, and flavonoid contents, and antioxidant activity in selected tomato breeding lines. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 57, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johkan, M.; Shoji, K.; Goto, F.; Hashida, S.-N.; Yoshihara, T. Blue light-emitting diode light irradiation of seedlings improves seedling quality and growth after transplanting in red leaf lettuce. HortScience 2010, 45, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-G.; Oh, S.-S.; Cha, S.-H.; Jang, Y.-A.; Kim, S.-Y.; Um, Y.-C.; Cheong, S.-R. Effects of red/blue light ratio and short-term light quality conversion on growth and anthocyanin contents of baby leaf lettuce. J. Bio-Environ. Con. 2010, 19, 351–359. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lu, W.; Tong, Y.; Yang, Q. Leaf morphology, photosynthetic performance, chlorophyll fluorescence, stomatal development of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) exposed to different ratios of red light to blue light. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puttarak, P.; Panichayupakaranant, P. Factors affecting content of pentacyclic triterpenes in Centella asiatica raw materials. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 1508–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunjumon, R.; Johnson, A.J.; Remadevi, R.K.S.; Baby, S. Assessment of major centelloside ratios in Centella asiatica accessions grown under identical ecological conditions, bioaconversion clues and identification of elite lines. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Advances in flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Mazur, A.; Scalbert, A. Polyphenols and prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2005, 16, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; Agrawal, S.B. Effects of supplemental ultraviolet-B radiation on growth and physiology of Acorus calamus L. (sweet flag). Acta. Biol. Cracov. Ser. Bot. 2009, 51, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, B.; Shang, X.; Fang, S.; Li, Q.; Fu, X.; Su, J. Integrated effects of light intensity and fertilization on growth and flavonoid accumulation in Cyclocarya paliurus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6286–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugosz-Grochowska, O.; Wojciechowska, R.; Kruczek, M.; Habela, A. Supplemental lighting with LEDs improves the biochemical composition of two Valerianella locusta (L.) cultivars. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2017, 58, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekar, C.B.; Carey, E.E.; Zhao, X.; Oh, M.-M. Health-promoting phytochemicals in fruits and vegetables: Impact of abiotic stresses and crop production practices. Funct. Plant Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 3, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.Q.; Wu, Y.J.; Tang, R.H.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Cashmore, A.R. The C termini of Arabidopsis cryptochromes mediate a constitutive light response. Cell 2000, 103, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasad, A.; Mathur, A.K.; Mathur, A. Advances and emerging research trends for modulations of centelloside biosynthesis in Centella asiatica (L.) Urban—A review. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 141, 111768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.-L.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Kuang, L.; Li, H.-B. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant capacities of selected Chinese medicinal plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2362–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
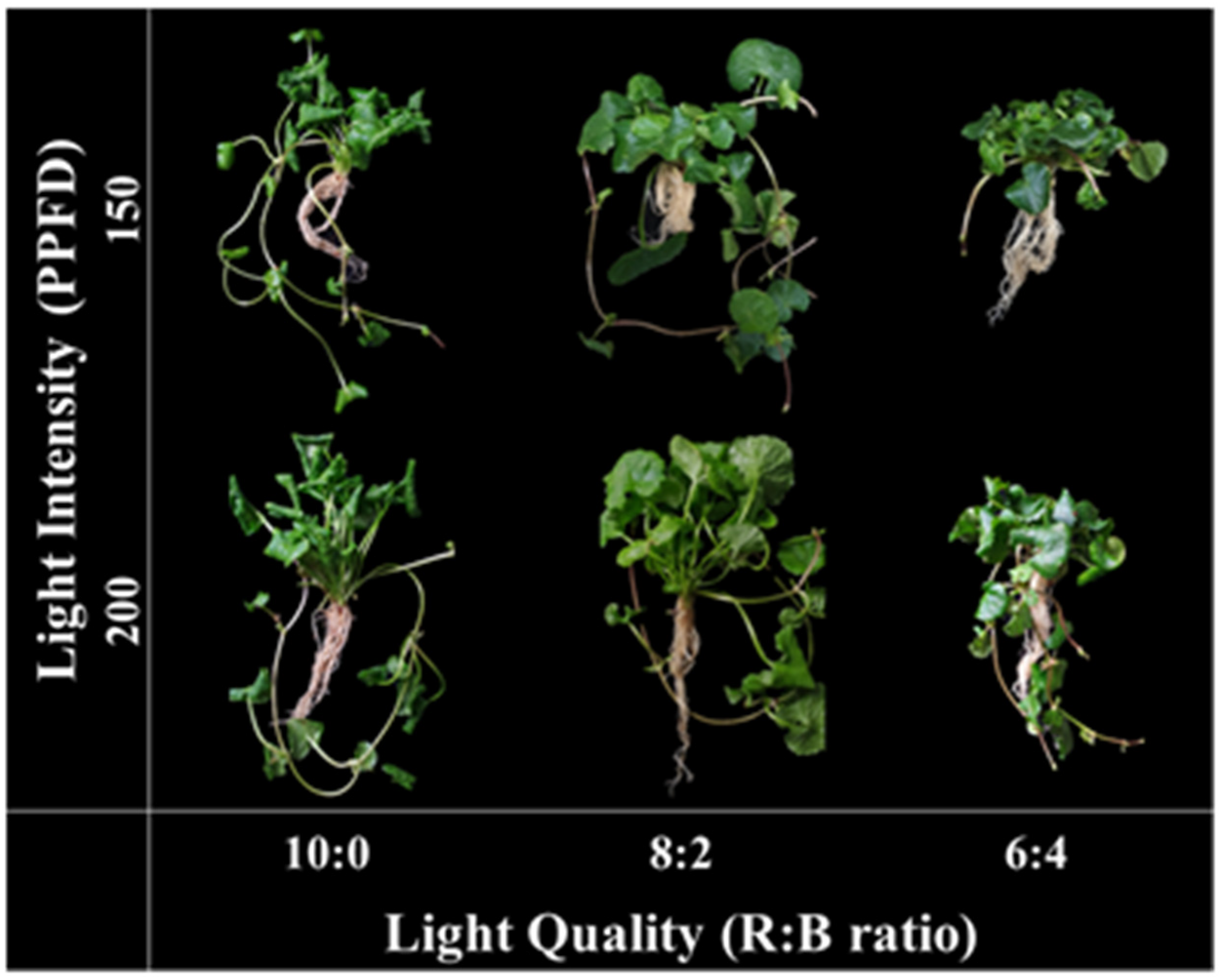
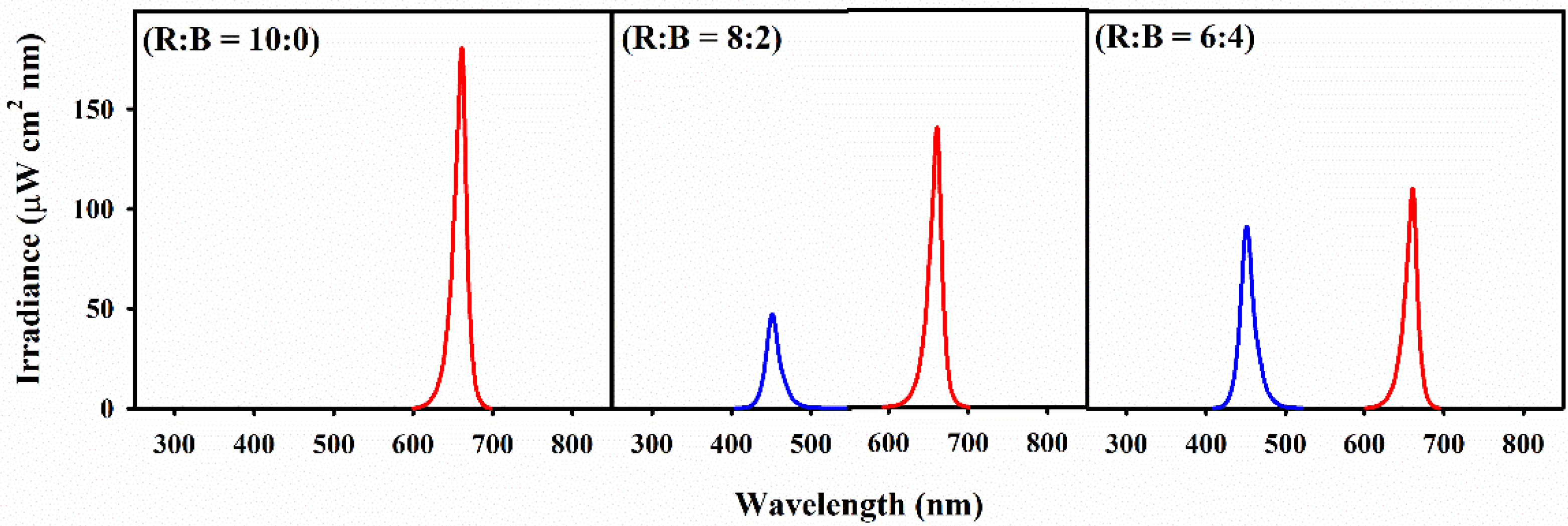

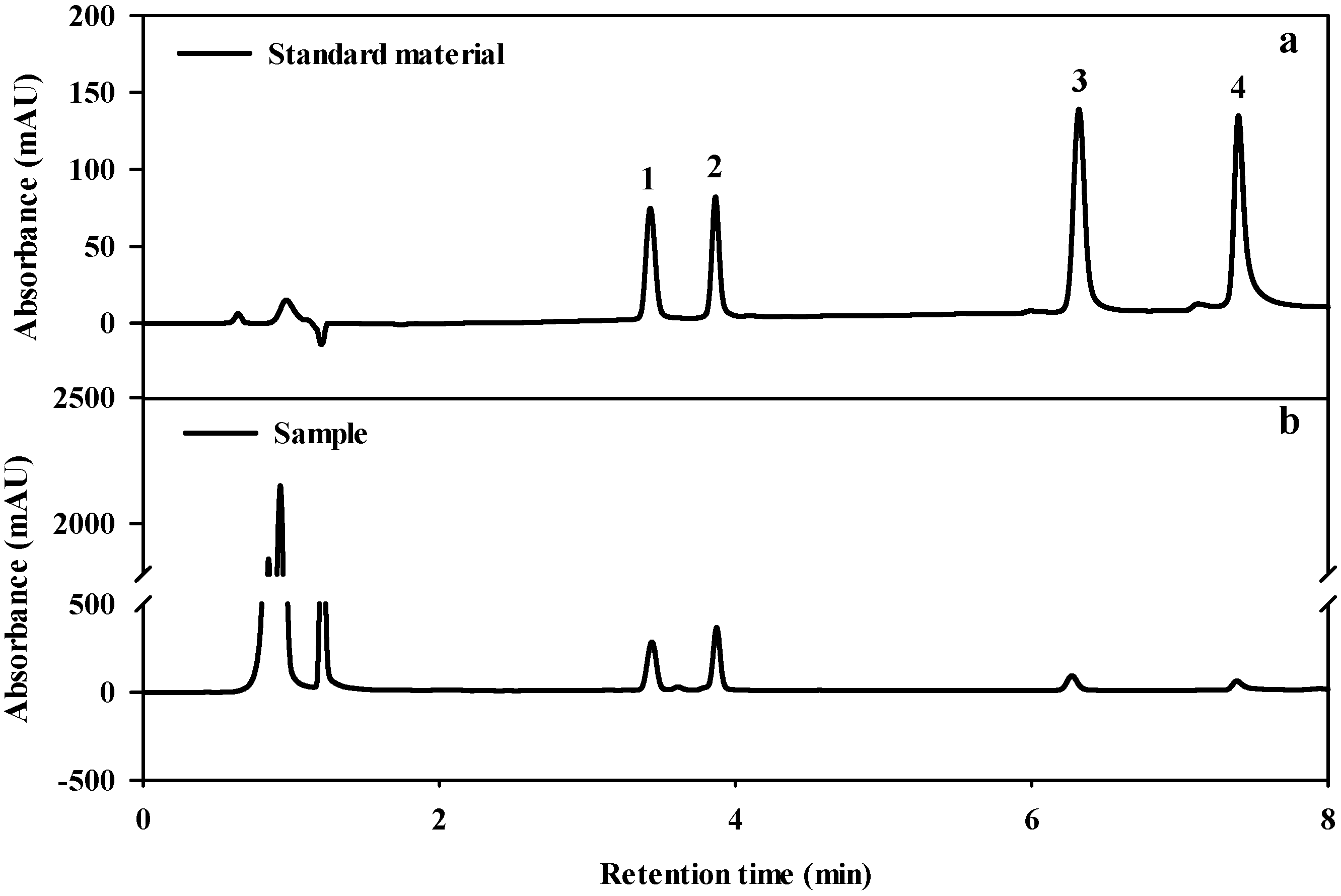


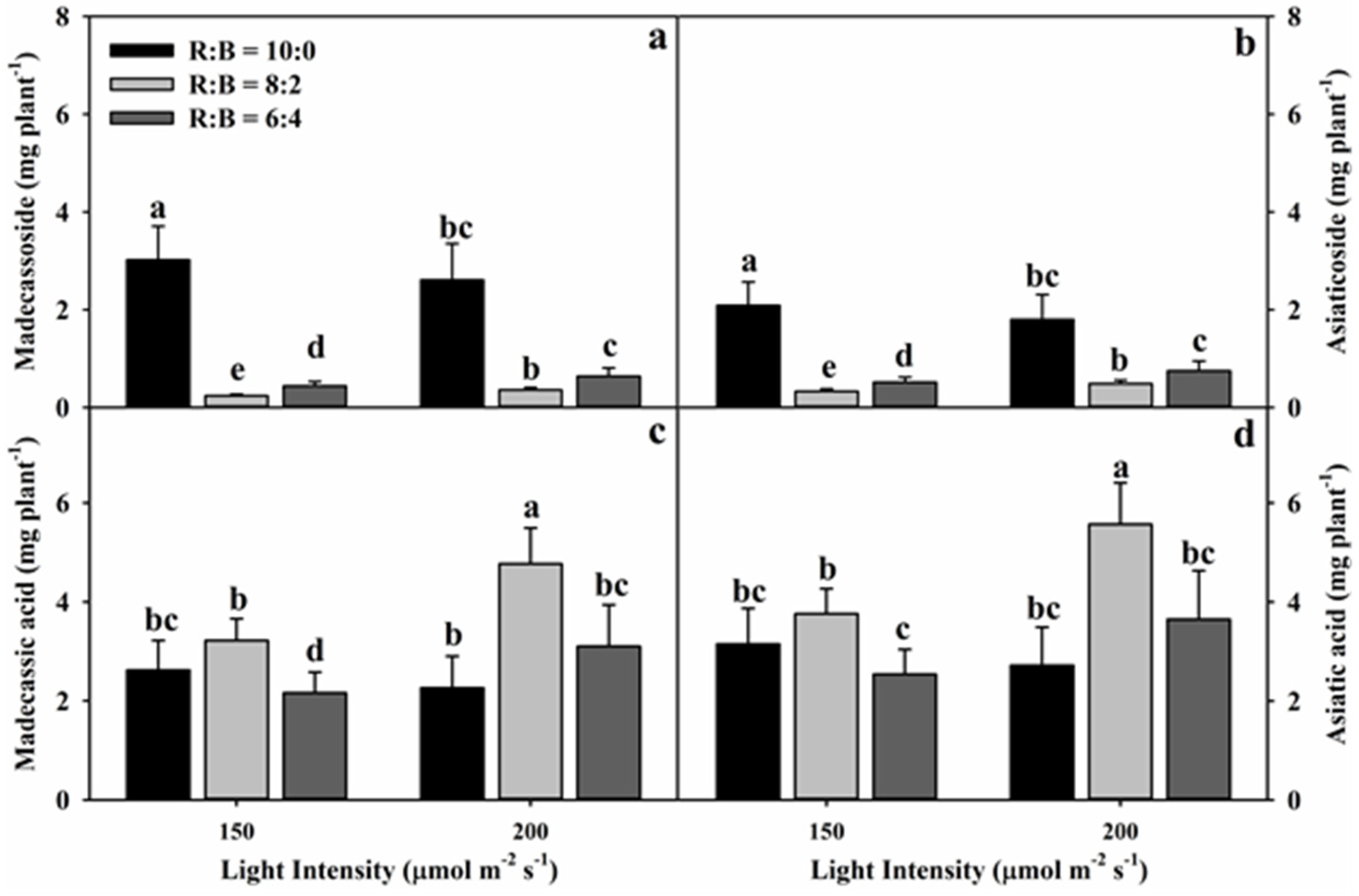
| Light Intensity (μmol m−2 s−1) | Light Quality (R:B) | Whole Plant | Leaf | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petiole Length (cm) | Root Length (cm) | Fresh Weight (g) | Dry Weight (g) | Length (g) | Width (g) | Fresh Weight (g) | Dry Weight (g) | ||
| 150 | 10:0 | 8.4 ± 1.7 z b y | 12.0 ± 2.0 a | 8.19 ± 1.54 a | 0.92 ± 0.19 ab | 4.2 ± 0.4 b | 4.8 ± 0.3 bc | 3.93 ± 0.63 a | 0.51 ± 0.12 ab |
| 8:2 | 6.0 ± 1.7 c | 13.8 ± 1.5 a | 5.57 ± 0.62 bc | 0.74 ± 0.09 bc | 4.0 ± 0.6 bc | 4.8 ± 0.6 bc | 2.78 ± 0.41 b | 0.39 ± 0.05 bc | |
| 6:4 | 5.5 ± 1.7 c | 12.9 ± 1.5 a | 4.35 ± 1.10 c | 0.62 ± 0.14 c | 3.6 ± 0.5 bc | 4.3 ± 0.9 c | 1.97 ± 0.19 c | 0.31 ± 0.06 c | |
| 200 | 10:0 | 7.5 ± 1.4 bc | 12.3 ± 0.6 a | 6.78 ± 1.59 ab | 0.76 ± 0.21 bc | 3.9 ± 0.4 bc | 5.3 ± 0.5 b | 4.11 ± 0.87 a | 0.44 ± 0.12 abc |
| 8:2 | 11.2 ± 1.7 a | 13.6 ± 1.9 a | 7.34 ± 0.69 ab | 1.02 ± 0.15 a | 5.5 ± 0.8 a | 6.3 ± 0.7 a | 3.92 ± 0.54 a | 0.58 ± 0.09 a | |
| 6:4 | 5.4 ± 1.4 c | 14.1 ± 3.5 a | 6.24 ± 1.38 b | 0.82 ± 0.21 abc | 3.4 ± 0.4 c | 4.4 ± 0.5 c | 3.26 ± 0.84 b | 0.45 ± 0.12 abc | |
| Parameter | Light Intensity (L) | Light Quality (Q) | L × Q | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | Significance | F-Value | Significance | F-Value | Significance | |
| Madecassoside z | 719.00 | *** | 338.50 | *** | 335.00 | *** |
| Asiaticoside | 1076.30 | *** | 114.70 | *** | 253.90 | *** |
| Madecassic acid | 194.34 | *** | 12.40 | ** | 39.98 | *** |
| Asiatic acid | 195.78 | *** | 12.80 | ** | 39.51 | *** |
| Total | 0.13 | NS | 13.35 | *** | 2.80 | NS |
| ABTS | 1062.98 | *** | 414.32 | *** | 83.21 | *** |
| FRAP | 318.23 | *** | 79.40 | *** | 27.69 | *** |
| TPC | 319.50 | *** | 95.90 | ** | 41.46 | *** |
| TFC | 521.16 | *** | 155.68 | ** | 54.16 | *** |
| Light Intensity (μmol m−2 s−1) | Light Quality (R:B) | ABTS (μmol TE g−1 DW) | FRAP (μmol TE g−1 DW) | Total Phenol (mg GAE g−1 DW) | Total Flavonoid (mg CE g−1 DW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 150 | 10:0 | 46.31 ± 0.46 z d y | 26.57 ± 2.07 d | 6.36 ± 0.22 d | 3.62 ± 0.71 d |
| 8:2 | 46.74 ± 5.68 d | 27.16 ± 2.08 d | 6.66 ± 0.48 d | 4.20 ± 0.28 d | |
| 6:4 | 74.76 ± 3.77 c | 43.61 ± 3.16 c | 8.53 ± 0.61 c | 6.92 ± 0.23 c | |
| 200 | 10:0 | 80.07 ± 4.08 c | 52.28 ± 3.38 c | 9.18 ± 0.33 c | 7.89 ± 0.36 c |
| 8:2 | 99.18 ± 2.24 b | 76.01 ± 4.20 b | 12.57 ± 0.36 b | 11.41 ± 1.11 b | |
| 6:4 | 163.47 ± 4.40 a | 120.18 ± 12.95 a | 19.06 ± 1.61 a | 19.59 ± 1.16 a |
| Parameter | A | Ma | Aa | TTC | ABTS | FRAP | TPC | TFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | 0.995 *** | −0.983 *** | −0.983 *** | 0.426 | 0.711 * | 0.744 * | 0.733 * | 0.738 * |
| A | −0.994 *** | −0.994 *** | 0.314 | 0.758 * | 0.788 * | 0.778 * | 0.782 * | |
| Ma | 1.000 *** | −0.158 | −0.825 * | −0.851 ** | −0.843 ** | −0.846 ** | ||
| Aa | −0.158 | −0.826 * | −0.852 ** | −0.843 ** | −0.846 ** | |||
| TTC | −0.481 | −0.432 | −0.451 | −0.444 | ||||
| ABTS | 0.999 *** | 0.999 *** | 0.999 *** | |||||
| FRAP | 1.000 *** | 1.000 *** | ||||||
| TPC | 1.000 *** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, J.W.; Bhandari, S.R.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, J.G. The Influence of Red and Blue Light Ratios on Growth Performance, Secondary Metabolites, and Antioxidant Activities of Centella asiatica (L.) Urban. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070601
Song JW, Bhandari SR, Shin YK, Lee JG. The Influence of Red and Blue Light Ratios on Growth Performance, Secondary Metabolites, and Antioxidant Activities of Centella asiatica (L.) Urban. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(7):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070601
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Jae Woo, Shiva Ram Bhandari, Yu Kyeong Shin, and Jun Gu Lee. 2022. "The Influence of Red and Blue Light Ratios on Growth Performance, Secondary Metabolites, and Antioxidant Activities of Centella asiatica (L.) Urban" Horticulturae 8, no. 7: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070601
APA StyleSong, J. W., Bhandari, S. R., Shin, Y. K., & Lee, J. G. (2022). The Influence of Red and Blue Light Ratios on Growth Performance, Secondary Metabolites, and Antioxidant Activities of Centella asiatica (L.) Urban. Horticulturae, 8(7), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8070601







