Calibration of Thermal Dissipation Probes for Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Plant Material and Sample Preparation
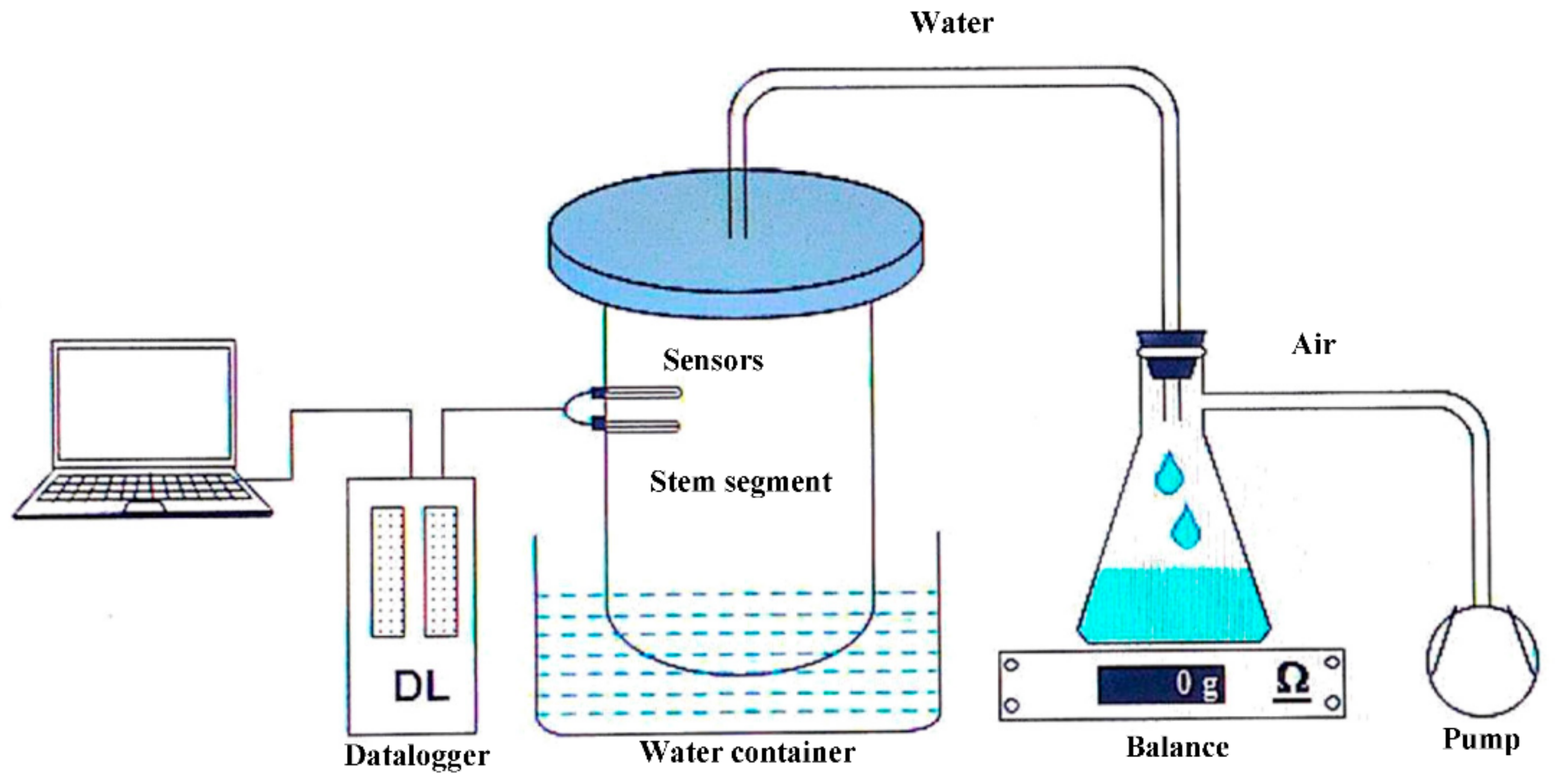
2.3. Thermal Dissipation Probes Method (TDP)
2.4. Laboratory Calibration
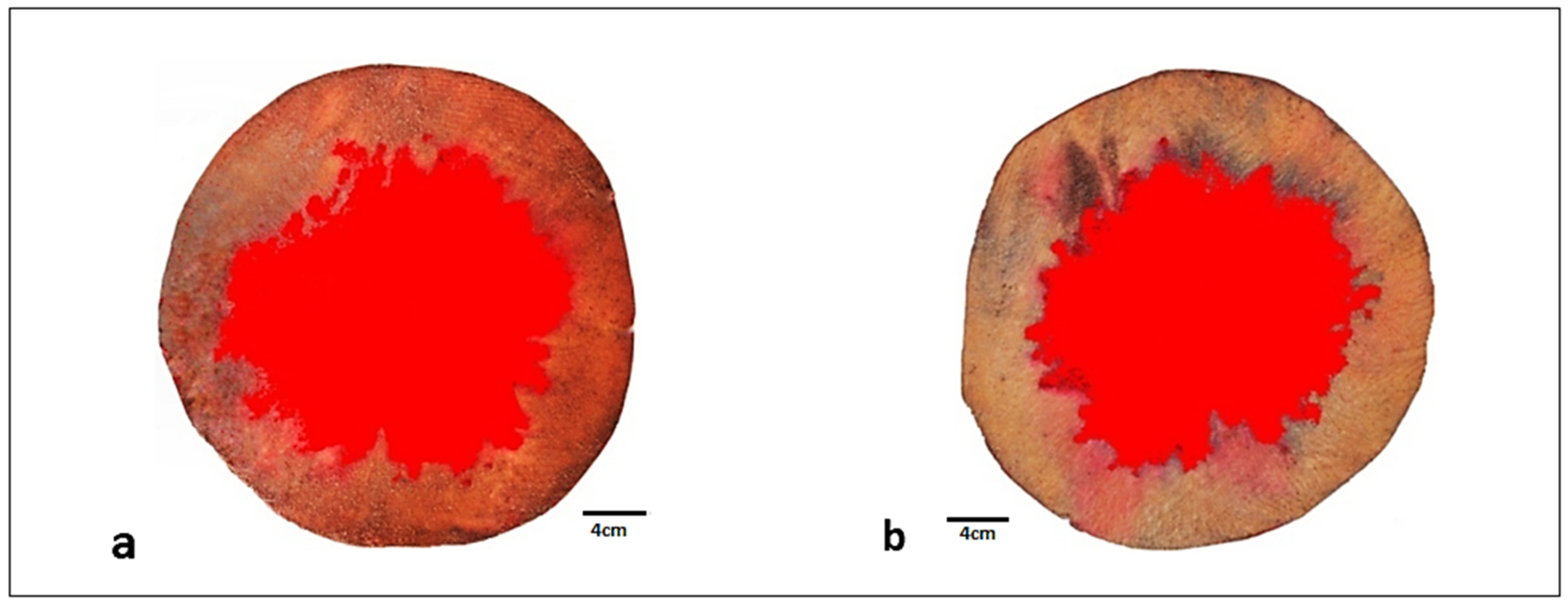
2.5. Conductive Area Determination
2.6. Error Calculations
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
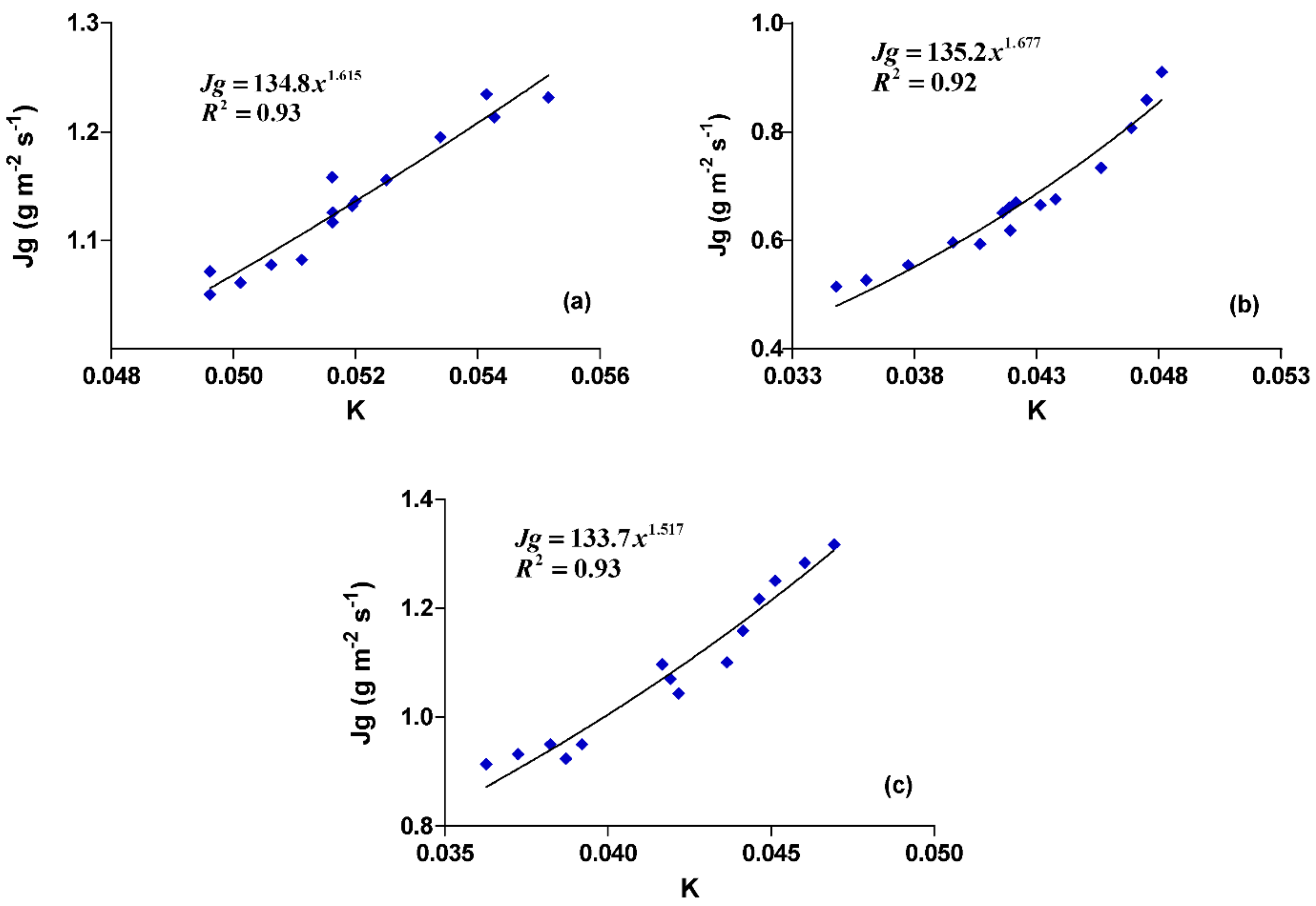
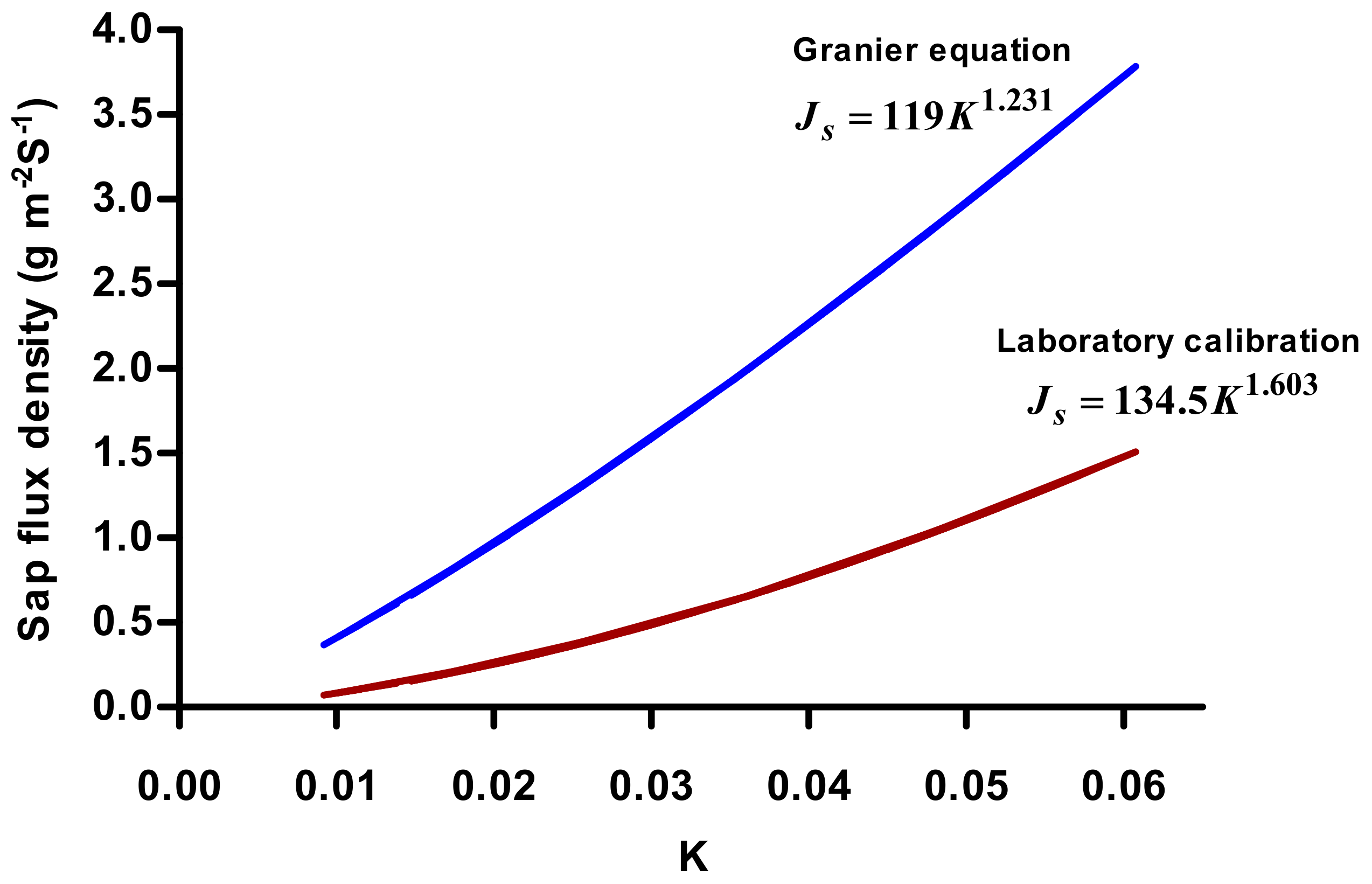
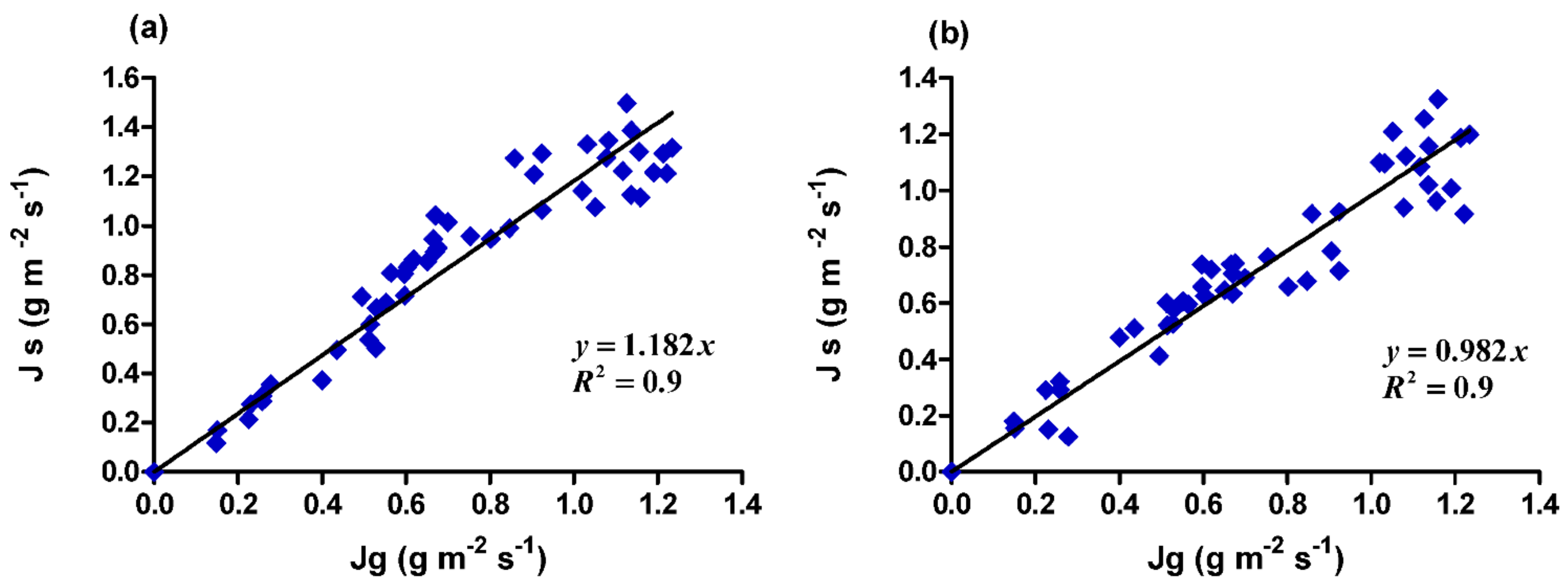
3.1. Calibration Experiment
3.2. Conductive Area
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Munier, P. Le Palmier-Dattier. Techniques Agricoles et Productions Tropicales; Maisonneuve & Larose: Paris, France, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- FAOSTAT. Agro-Statistics. Database; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2017. Available online: http://www.Fao.Org/Faostat (accessed on 19 March 2020).
- Bodian, A.; Elhoumaizi, M.A.; Ndir, K.N.; Hasnoui, A.; Nachtigall, M.; Wehling, P. Genetic diversity analysis of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) cultivars from Figuig oasis (Morocco) using SSR markers. J. Biodivers. Biopros. Dev. 2012, 2, 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Irrigated date palm production in the Near East. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Irrigation of Date Palm and Associated Crops, Damascus, Syria, 27–30 May 2007; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Cairo, Egypt, 2008; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.; Allen, S. Measurement of sap flow in plant stems. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tfwala, C.; Van Rensburg, L.; Bello, Z.; Green, S. Calibration of compensation heat pulse velocity technique for measuring transpiration of selected indigenous trees using weighing lysimeters. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 200, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, A. A new method for measuring the sap flux in the trunk of trees. Ann. For. Sci. 1985, 42, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, A. Evaluation of transpiration in a Douglas-fir stand by means of sap flow measurements. Tree Physiol. 1987, 3, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadezhdina, N.; Cermak, J.; Nadezhdin, V. Heat field deformation method for sap flow measurements. In Measuring Sap Flow in Intact Plants, Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop; Židlochovice, Czech Republic, 3–5 October 1998, IUFRO Publ.: Vienna, Austria; Mendel University: Brno, Czech Republic, 1998; pp. 72–92. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, D. Measurement of Sap Flow in Conifers by Heat Transport. Plant Physiol. 1958, 33, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, R.; Whitfield, D. A Numerical Analysis of Heat Pulse Velocity Theory and Practice. J. Exp. Bot. 1981, 32, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čermák, J.; Deml, M.; Penka, M. A new method of sap flow rate determination in trees. Biol. Plant. 1973, 15, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuratani, T. A Heat Balance Method for Measuring Water Flux in the Stem of Intact Plants. J. Agric. Meteorol. 1981, 37, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveras, I.; Llorens, P. Medium-term sap flux monitoring in a Scots pine stand: Analysis of the operability of the heat dissipation method for hydrological purposes. Tree Physiol. 2001, 21, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Aubrey, D.P.; Teskey, R.O. A simple calibration improved the accuracy of the thermal dissipation technique for sap flow measurements in juvenile trees of six species. Trees 2011, 26, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hultine, K.; Nagler, P.; Morino, K.; Bush, S.; Burtch, K.; Dennison, P.; Glenn, E.; Ehleringer, J. Sap flux-scaled transpiration by tamarisk (Tamarix spp.) before, during and after episodic defoliation by the saltcedar leaf beetle (Diorhabda carinulata). Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergeynst, L. Changes in temperature and stem water content evoke erroneous sap flux density estimates with Thermal Dissipation Probes. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Sap Flow, Volterra, Italy, 8–12 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Do, F.; Rocheteau, A. Influence of natural temperature gradients on measurements of xylem sap flow with thermal dissipation probes. 2. Advantages and calibration of a noncontinuous heating system. Tree Physiol. 2002, 22, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppe, K.; De Pauw, D.J.; Doody, T.M.; Teskey, R.O. A comparison of sap flux density using thermal dissipation, heat pulse velocity and heat field deformation methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Urban, L.; Zhao, P. Granier’s thermal dissipation probe (TDP) method for measuring sap flow in trees: Theory and practice. Acta Bot. Sin. 2004, 46, 631–646. [Google Scholar]
- Wullschleger, S.D.; Childs, K.W.; King, A.W.; Hanson, P.J. A model of heat transfer in sapwood and implications for sap flux density measurements using thermal dissipation probes. Tree Physiol. 2011, 31, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clearwater, M.; Meinzer, F.; Andrade, J.L.; Goldstein, G.; Holbrook, N.M. Potential errors in measurement of nonuniform sap flow using heat dissipation probes. Tree Physiol. 1999, 19, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandegehuchte, M. Measuring Sap Flow and Stem Water Content in Trees: A Critical Analysis and Development of a New Heat Pulse Method (Sapflow+). Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, R.; Liu, G.; Wen, M.; Horton, R.; Li, B.; Si, B. The effects of probe misalignment on sap flux density measurements and in situ probe spacing correction methods. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, S.E.; Hultine, K.R.; Sperry, J.S.; Ehleringer, J.R. Calibration of thermal dissipation sap flow probes for ring- and diffuse-porous trees. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedemann, A.; Marañón-Jiménez, S.; Rebmann, C.; Herbst, M.; Cuntz, M. An empirical study of the wound effect on sap flux density measured with thermal dissipation probes. Tree Physiol. 2016, 36, 1471–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyatos, R.; Granda, V.; Molowny-Horas, R.; Mencuccini, M.; Steppe, K.; Martinez-Vilalta, J. SAPFLUXNET: Towards a global database of sap flow measurements. Tree Physiol. 2016, 36, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Woo, K.; Liu, Z. Estimation of whole-plant transpiration of bananas using sap flow measurements. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-J.; Cohen, S.; Tanny, J.; Lemcoff, J.H.; Huang, G. Transpiration estimation of banana (Musa sp.) plants with the thermal dissipation method. Plant Soil 2008, 308, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrício, D.O.R.; Eliemar, C.; Sousa, D.E.F.; Silva, M.G.E. Sap flow in papaya plants: Laboratory calibrations and relationships with gas exchanges under field conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 110, 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, F.; Röll, A.; Hardanto, A.; Meijide, A.; Köhler, M.; Hendrayanto; Hölscher, D. Oil palm water use: Calibration of a sap flux method and a field measurement scheme. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Paço, T.; Ferreira, M.; Oliveira, M. Transpiration of a kiwifruit orchard estimated using the granier sap flow method calibrated under field conditions. Acta Hortic. 2008, 792, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, N.; Ferreira, M. Combination of sap flow and eddy covariance techniques to obtain long term transpiration in a pear orchard. In VII International Workshop on Sap Flow 846; International Society for Horticultural Science: Leuven, Belgium, 2008; pp. 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Na Ayutthaya, S.I.; Do, F.; Pannengpetch, K.; Junjittakarn, J.; Maeght, J.-L.; Rocheteau, A.; Cochard, H. Transient thermal dissipation method of xylem sap flow measurement: Multi-species calibration and field evaluation. Tree Physiol. 2009, 30, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubens, D.C.; Lucas, M.V.; Eusimio, F.F.J. Estimation of transpiration of the ‘Valencia’ orange young plant using thermal dissipation probe method. Eng. Agric. 2012, 32, 573–581. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Mei, T.-T.; Ni, G.-Y.; Yu, M.-H.; Zeng, X.-P. Application of thermal dissipation probe in the study of Bambusa chungii sap flow. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 979–984. [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, I.; Kanety, T.; Cohen, S. Inactive xylem can explain differences in calibration factors for thermal dissipation probe sap flow measurements. Tree Physiol. 2013, 33, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, G.L.; Hama, J.M.; Kluitenberg, G.J. A heat-pulse method for measuring sap flow in corn and sunflower using 3D-printed sensor bodies and low-cost electronics. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 246, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, M.C. Calibration of Sap Flow Techniques in Citrus Using the Stem Perfusion Method. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard, R.M.; Stape, J.; Ryan, M.; Almeida, A.C.; Rojas, J. Effects of irrigation on water use and water use efficiency in two fast growing Eucalyptus plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Niu, J.; Zhou, C.; Gu, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, P. Suppression of nighttime sap flux with lower stem photosynthesis in Eucalyptus trees. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 60, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roupsard, O.; Bonnefond, J.-M.; Irvine, M.; Berbigier, P.; Nouvellon, Y.; Dauzat, J.; Taga, S.; Hamel, O.; Jourdan, C.; Saint-André, L.; et al. Partitioning energy and evapo-transpiration above and below a tropical palm canopy. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2006, 139, 252–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renninger, H.J.; Phillips, N. Intrinsic and extrinsic hydraulic factors in varying sizes of two Amazonian palm species (Iriartea deltoidea and Mauritia flexuosa) differing in development and growing environment. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 1926–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellami, M.H.; Sifaoui, M.S. Estimating transpiration in an intercropping system: Measuring sap flow inside the oasis. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 59, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, O.; Shapira, O.; Cohen, S.; Tripler, E.; Schwartz, A.; Lazarovitch, N. Estimating sap flux densities in date palm trees using the heat dissipation method and weighing lysimeters. Tree Physiol. 2012, 32, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reyes-Acosta, J.L.; Vandegehuchte, M.W.; Steppe, K.; Lubczynski, M.W. Novel, cyclic heat dissipation method for the correction of natural temperature gradients in sap flow measurements. Part 2. Laboratory validation. Tree Physiol. 2012, 32, 913–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarinov, F.A.; Kucera, J.; Cienciala, E. The analysis of physical background of tree sap flow measurement based on thermal methods. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2005, 5, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.; Bond, B.J.; Jones, J.A.; Meinzer, F.C. Thermal-dissipation sap flow sensors may not yield consistent sap-flux estimates over multiple years. J. Tree Sci. 2010, 1, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, E.H.; Artog, G.D.; Black, T.A.; Yang, P.C.; Nesic, Z.; Zimmermann, R.; Neumann, H.H.; Blanken, P.D.; Hurdle, P.A.; Oren, R.; et al. Comparison of sap flow and eddy fluxes of water vapor from a boreal deciduous forest. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 28929–28937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.B.; Hanson, P.J.; Mulholland, P.J.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Wullschleger, S.D. A comparison of methods for determining forest evapotranspiration and its components: Sap-flow, soil water budget, eddy covariance and catchment water balance. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2001, 106, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, M.V.; Santiago, L.S. A comparison of sap flow measurements and potometry in two tropical lowland tree species with contrasting wood properties. Rev. Biol. Trop. 2014, 54, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, S.; Leuschner, C.; Link, R.M.; Coners, H.; Schuldt, B. Calibration and comparison of thermal dissipation, heat ratio and heat field deformation sap flow probes for diffuse-porous trees. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 244, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearsall, K.R.; Williams, L.E.; Castorani, S.; Bleby, T.M.; McElrone, A.J. Evaluating the potential of a novel dual heat-pulse sensor to measure volumetric water use in grapevines under a range of flow conditions. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 41, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cultivars | Circumference (cm) | Diameter (cm) | N * |
|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Assiane’ | 86.96 ± 0.95 | 27.69 ± 0.30 | 3 |
| ‘Tadmament’ | 85.16 ± 0.76 | 27.12 ± 0.24 | 3 |
| ‘Khalt’ | 94.83 ± 3.40 | 30.20 ± 1.08 | 3 |
| Cultivars | Conductive Area (cm2) | Sensors Depth (cm) | α (gm−2s−1) | β | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘Assiane’ | 330.66 ± 13.57 | 9 | 134.80 ± 0.66 *** | 1.615 ± 0.02 *** | 0.93 |
| ‘Tadmament’ | 302.33 ± 15.88 | 9 | 133.70 ± 0.48 *** | 1.517 ± 0.04 *** | 0.93 |
| ‘Khalt’ | 298.00 ± 26.96 | 9 | 135.20 ± 0.51 *** | 1.677 ± 0.03 *** | 0.92 |
| Mean | 310.33 ± 22.96 | 9 | 134.50 ± 0.57 *** | 1.603 ± 0.05 *** | 0.93 |
| SE | 7.65 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0 |
| Reference | Species | Technique | Calibration Method | α g/m3/s | β | Probes Lenght (mm) | Stem Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [7] | Pinus nigra, Pseudotsuga menziesii, Quercus pedunculata | TDP | Cut stem | 119 | 1.231 | 20 | 40–50 |
| [32] | Actinidia deliciosa | TDP | Cut tree Potometer | 57 63 | - | 10 20 | 10 |
| [30] | Carica papaya | TDP | Stem perfusion | 1531 | 1.910 | 30 | 55 |
| [34] | Mangifera indica, Heveabra siliensis, Citrus maxima | TDP | Cut stem | 772 778 749 | 1.414 | 20 | 43.5 46.8 51.4 |
| [16] | Tamarix spp. | TDP | Stem perfusion | 240 | 1.16 | 10 | 41.6 |
| [35] | Citrus sinensis | TDP | Stem perfusion | 594 | 1.231 | 10 | 25 |
| [37] | Malus domestica, Prunus persica, Diospyros kaki | TDP | Stem perfusion | 486 | 1.157 | 20 | 40–50 |
| [39] | Citrus limon Eureka | TDP | Stem perfusion | 184 | 1.33 | 30 | 50 |
| [41] | Eucalyptus grandis × urophylla | TDP | Cut stem | 304.46 | 1.606 | 20 | 134–145 |
| [42] | Cocos nucifera | TDP | Stem perfusion | 315 | 1.231 | 20 | 41 |
| [43] | Iriartea deltoidea | TDP | Cut stem | 192.3 | 1.3 | 10 | 50 |
| [31] | Elaeis guineesis Jacq. | TDP | Cut leaves | 134 | 1.6 | 12.5 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alla, F.; Jdaini, K.; M’hamdi, H.; Mechchate, H.; AlZain, M.N.; Alzamel, N.M.; Noman, O.; Mimouni, J.; Elhoumaizi, M.A. Calibration of Thermal Dissipation Probes for Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020107
Alla F, Jdaini K, M’hamdi H, Mechchate H, AlZain MN, Alzamel NM, Noman O, Mimouni J, Elhoumaizi MA. Calibration of Thermal Dissipation Probes for Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Horticulturae. 2022; 8(2):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020107
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlla, Fouzia, Kawtar Jdaini, Hanane M’hamdi, Hamza Mechchate, Mashail N. AlZain, Nurah M. Alzamel, Omar Noman, Jamal Mimouni, and Mohammed Aziz Elhoumaizi. 2022. "Calibration of Thermal Dissipation Probes for Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.)" Horticulturae 8, no. 2: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020107
APA StyleAlla, F., Jdaini, K., M’hamdi, H., Mechchate, H., AlZain, M. N., Alzamel, N. M., Noman, O., Mimouni, J., & Elhoumaizi, M. A. (2022). Calibration of Thermal Dissipation Probes for Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Horticulturae, 8(2), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8020107






