Genome-Wide Survey and Expression Analysis of the Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) Gene Family in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Investigation of bZIP Genes Family in Eggplant and Other Plant Species
2.2. Phylogenetic Characterization of bZIP Gene Family
2.3. Phylogenetic, Motif Composition, Gene Structure, and Physicochemical Analysis of SmbZIP Proteins
2.4. Chromosome Distribution, Gene Duplication, and Synteny Analysis of SmbZIPs in Eggplant
2.5. Promoter Analysis of SmbZIP Genes
2.6. Prediction of the SmbZIPs Protein-Protein Interaction Network
2.7. Plant Materials, Growth Conditions, and Stress Treatments
2.8. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
3. Results
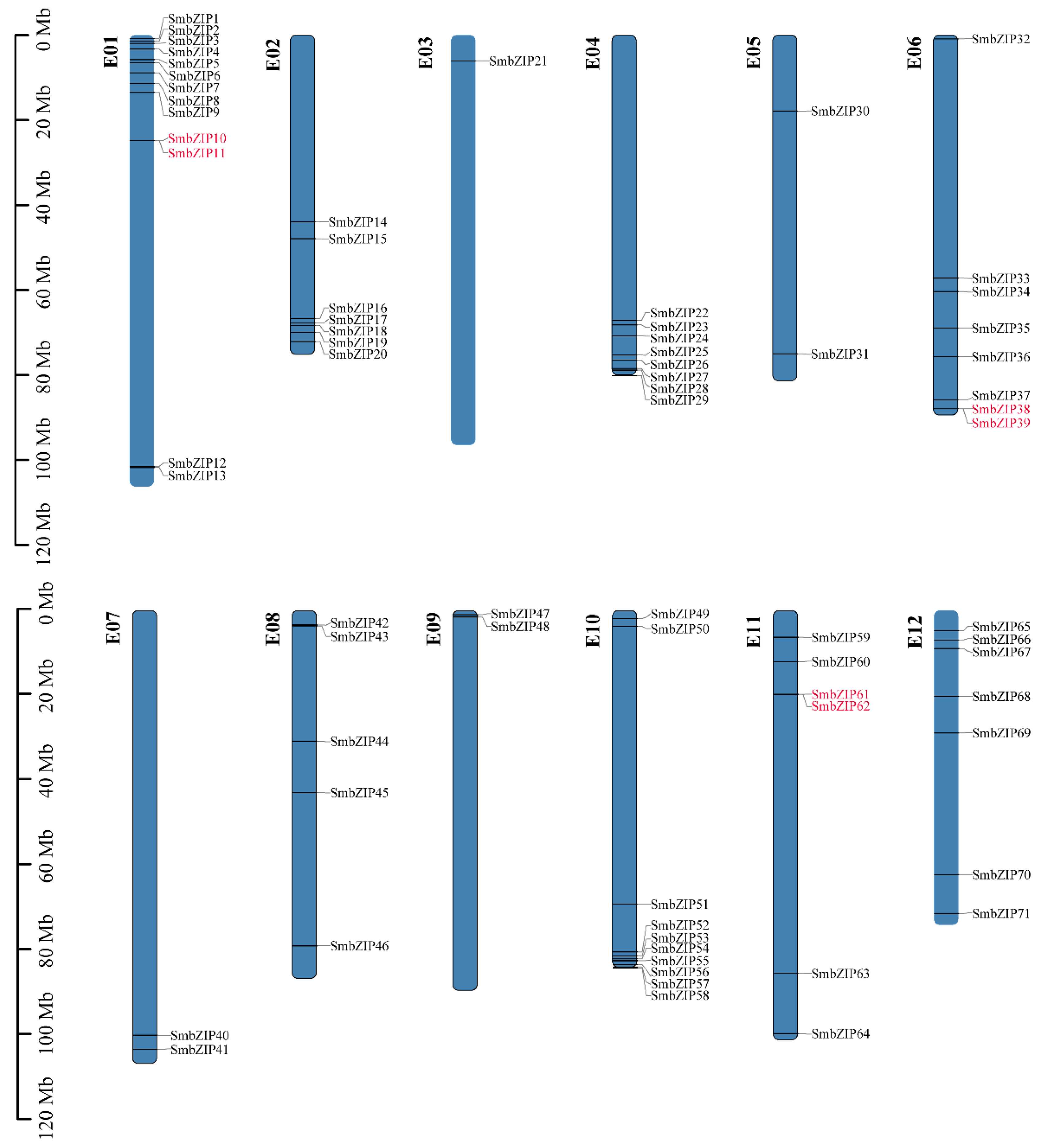
3.1. Identifcation and Chromosome Distribution of the SmbZIP Gene Family in Eggplant
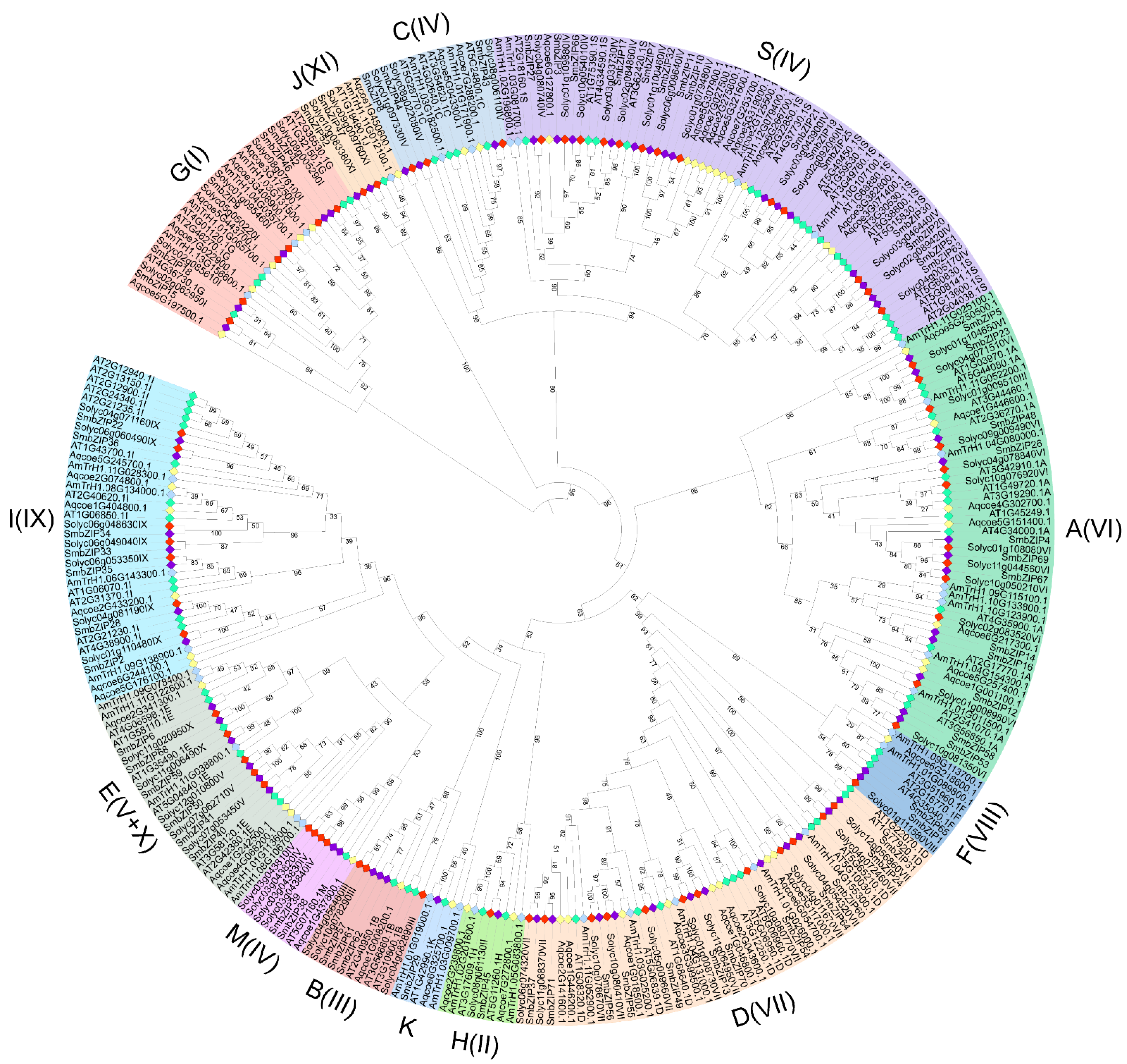
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of SmbZIP Gene Family and Comparative Analyses
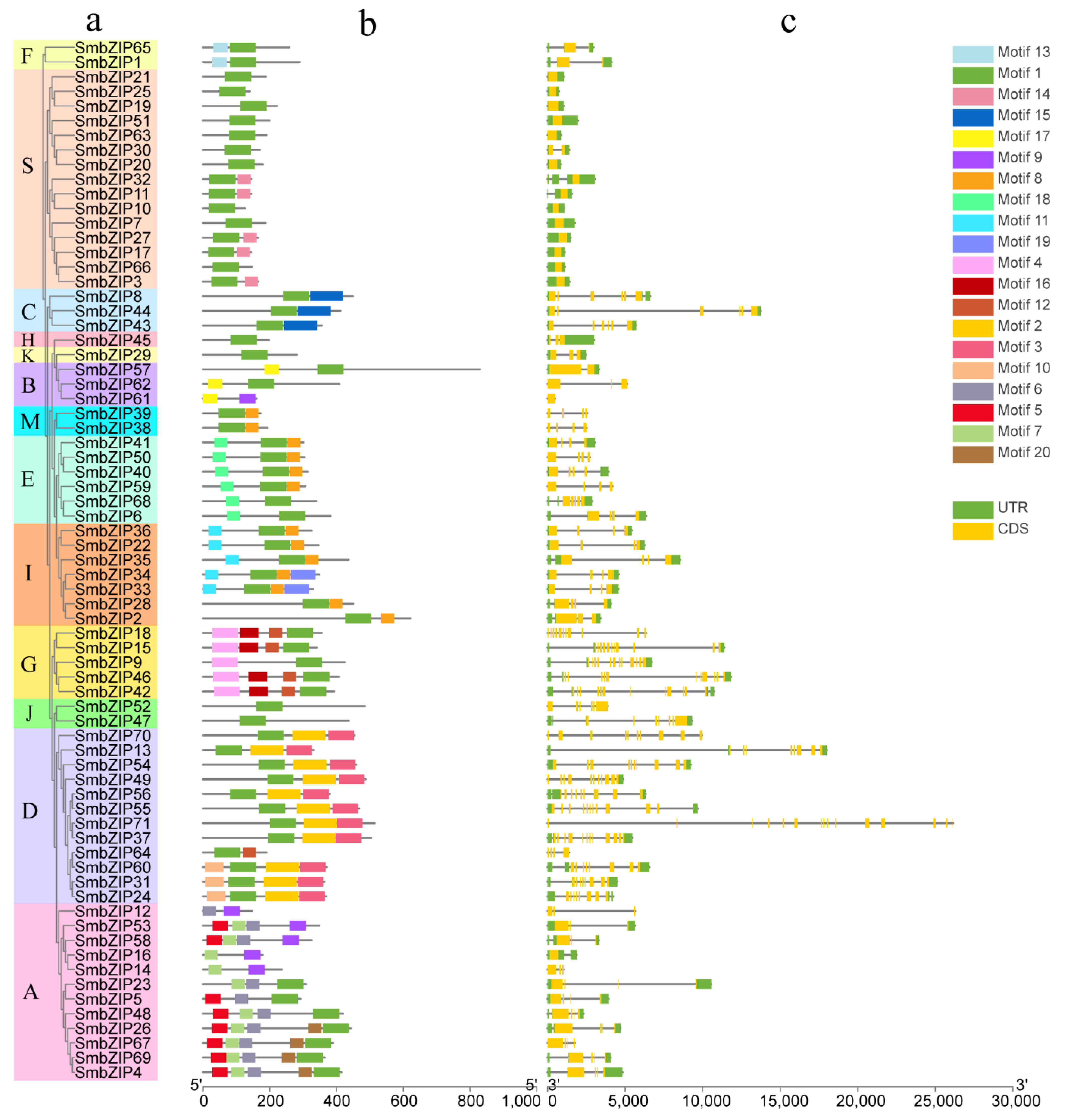
3.3. Gene Structure and Protein Motif Analysis of bZIP Gene Family in Eggplant
3.4. Gene Collinearity, Duplication, and Ka/Ks Analysis of SmbZIPs
3.5. Promoter Analysis of SmbZIP Family Genes
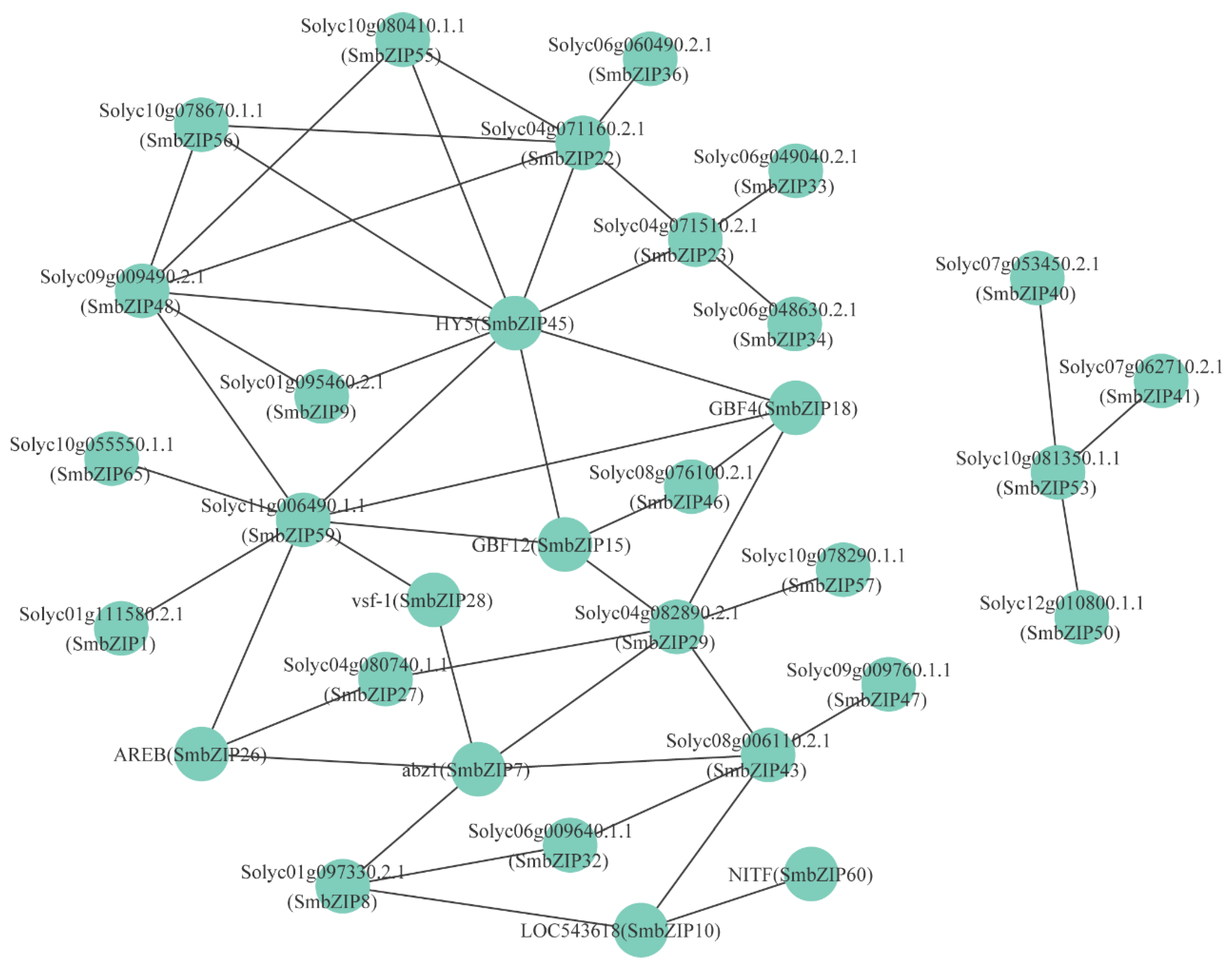
3.6. Interaction Network of bZIP Proteins in Eggplant
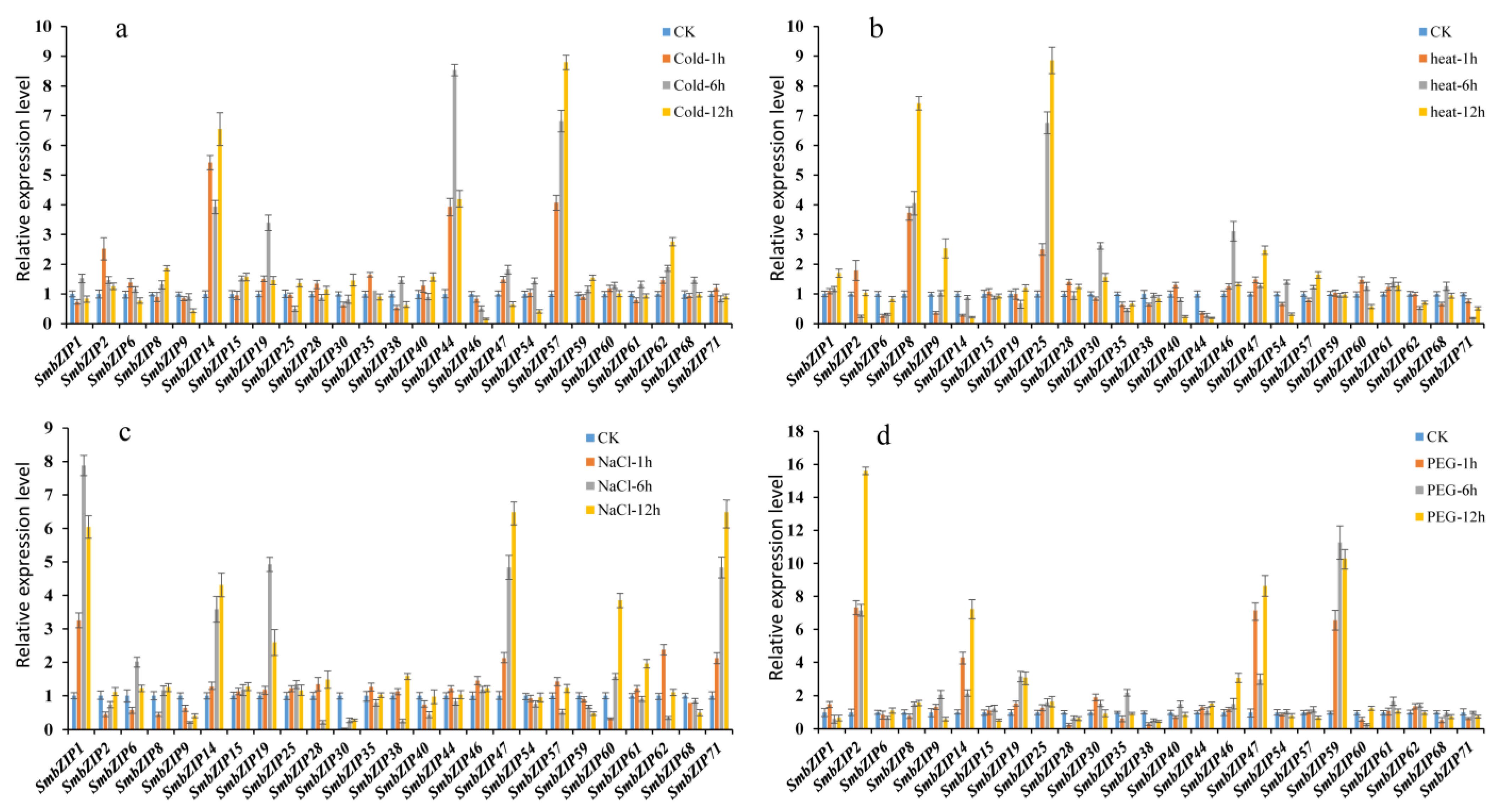
3.7. Expression Pattern of SmbZIPs under Stresses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitchell, P.J.; Tjian, R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science 1989, 245, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, H.C. Transcription factors 1: bZIP proteins. Protein Profile 1995, 2, 101–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jakoby, M.; Weisshaar, B.; Droge-Laser, W.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Tiedemann, J.; Kroj, T.; Parcy, F. bZIP transcription factors in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suckow, M.; Schwamborn, K.; Kisters-Woike, B.; Von Wilcken-Bergmann, B.; Muller-Hill, B. Replacement of invariant bZip residues within the basic region of the yeast transcriptional activator GCN4 can change its DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4395–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Renshaw-Gegg, L.; Miller, L.; Guiltinan, M.J. Bipartite determinants of DNA-binding specificity of plant basic leucine zipper proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landschulz, W.H.; Johnson, P.F.; McKnight, S.L. The leucine zipper: A hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science 1988, 240, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, T.; Foster, R.; Chua, N.H. Plant bZIP protein DNA binding specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 1993, 230, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenberger, T.E.; Brandl, C.J.; Struhl, K.; Harrison, S.C. The GCN4 basic region leucine zipper binds DNA as a dimer of uninterrupted α helices: Crystal structure of the protein-DNA complex. Cell 1992, 71, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, D.; Jia, L.; Huang, X.; Ma, G.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, A.; Guan, M.; Lu, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Structural Analysis of bZIP Transcription Factor Genes in Brassica napus. Genes 2017, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shi, H.; Guo, M.; Chai, M.; He, Q.; Yan, M.; Cao, D.; Zhao, L.; Cai, H.; et al. Evolutionary and expression analyses of soybean basic Leucine zipper transcription factor family. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Chen, S.; Yao, W.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP gene family in poplar. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Xia, J.; Jiang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Yu, J.; Cang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of bZIP Gene Family and Resistance of TaABI5 (TabZIP96) under Freezing Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhawan, A.; Jain, M.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Genomic survey and gene expression analysis of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor family in rice. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröge-Laser, W.; Snoek, B.L.; Snel, B.; Weiste, C. The Arabidopsis bZIP transcription factor family-an update. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2018, 45, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, N.; Chen, F.; Cai, B.; Dal Santo, S.; Tornielli, G.B.; Pezzotti, M.; Cheng, Z.M. Genome-wide analysis and expression profile of the bZIP transcription factor gene family in grapevine (Vitis vinifera). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CAO, X.; Ming, C.; XU, Z.; CHEN, Y.; LI, L.; YU, Y.; LIU, Y. Isolation and functional analysis of the bZIP transcription factor gene TaABP1 from a Chinese wheat landrace. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 1580–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilay, G.H.; Castro, P.H.; Guedes, J.G.; Almeida, D.M.; Campilho, A.; Azevedo, H.; Aarts, M.G.M.; Saibo, N.J.M.; Assuncao, A.G.L. Rice F-bZIP transcription factors regulate the zinc deficiency response. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 3664–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Ran, Q.; Xie, G.; Wang, B.; Fang, S.; Chu, J.; Zhang, J. ZmbZIP4 contributes to stress resistance in maize by regulating ABA synthesis and root development. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, T.F.; Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.Z.; Wei, W.L.; Xu, Z.S. The Soybean bZIP Transcription Factor Gene GmbZIP2 Confers Drought and Salt Resistances in Transgenic Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gan, Z.; Gao, M.; Lv, J.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, S. Group-C/S1 bZIP heterodimers regulate MdIPT5b to negatively modulate drought tolerance in apple species. Plant J. 2021, 107, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Yu, Y.; Dong, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Du, F.; Xia, C.; Ni, Z.; Kong, X.; Zhang, L. The bZIP transcription factor TabZIP15 improves salt stress tolerance in wheat. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, Y.; Furihata, T.; Abe, H.; Yoshida, R.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Arabidopsis basic leucine zipper transcription factors involved in an abscisic acid-dependent signal transduction pathway under drought and high-salinity conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11632–11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Delaney, T. Over-expression of TGA5, which encodes a bZIP transcription factor that interacts with NIM1/NPR1, confers SAR-independent resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana to Peronospora parasitica. Plant J. 2002, 32, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Cho, J.I.; Han, M.; Ahn, C.H.; Jeon, J.S.; An, G.; Park, P.B. The ABRE-binding bZIP transcription factor OsABF2 is a positive regulator of abiotic stress and ABA signaling in rice. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.; Tang, N.; Yang, J.; Peng, L.; Ma, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Xiong, L. Feedback Regulation of ABA Signaling and Biosynthesis by a bZIP Transcription Factor Targets Drought-Resistance-Related Genes. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2810–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plazas, M.; Andujar, I.; Vilanova, S.; Hurtado, M.; Gramazio, P.; Herraiz, F.J.; Prohens, J. Breeding for chlorogenic acid content in eggplant: Interest and prospects. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2013, 41, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Hu, T.; Hu, H.; Bao, C. A high-quality chromosome-level genome assembly reveals genetics for important traits in eggplant. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Khedkar, S.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D458–D460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yang, D.C.; Meng, Y.Q.; Jin, J.; Gao, G. PlantRegMap: Charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1104–D1113. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Meng, D.; Li, M.; Cheng, L. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bZIP gene family in apple (Malus domestica). Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloglu, M.C.; Eldem, V.; Hajyzadeh, M.; Unver, T. Genome-wide analysis of the bZIP transcription factors in cucumber. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Qi, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, W.; Wang, Y. Genome-wide identification, expression profiling, and SSR marker development of the bZIP transcription factor family in Medicago truncatula. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 61, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, L.G.G.; Riaño-Pachón, D.M.; Schrago, C.G.; Vicentini dos Santos, R.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Vincentz, M. The role of bZIP transcription factors in green plant evolution: Adaptive features emerging from four founder genes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Fu, F.; Zhang, H.; Song, F. Genome-wide systematic characterization of the bZIP transcriptional factor family in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Vanitha, J.; Ramachandran, S.; Jiang, S. Genome-wide Expansion and Expression Divergence of the Basic Leucine Zipper Transcription Factors in Higher Plants with an Emphasis on Sorghum. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 212–231. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, L.; Fu, M.; Liao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Ye, J. Genome-wide characterization of bZIP gene family identifies potential members involved in flavonoids biosynthesis in Ginkgo biloba L. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Paterson, A.H. PGDD: A database of gene and genome duplication in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D1152–D1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Cui, P.; Wu, S.; Ai, C.; Hu, N.; Li, A.; He, B.; Shao, X. The nearly complete genome of Ginkgo biloba illuminates gymnosperm evolution. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, D.B.; Sessa, E.B.; Wolf, P.G.; Heo, K.; Barbazuk, W.B.; Soltis, P.S.; Soltis, D.E. The C-Fern (Ceratopteris richardii) genome: Insights into plant genome evolution with the first partial homosporous fern genome assembly. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notredame, C.; Higgins, D.G.; Heringa, J. T-Coffee: A novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2-a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Wong, G.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator: Calculating Ka and Ks through model selection and model averaging. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2006, 4, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Roychoudhury, A. Abscisic-acid-dependent basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors in plant abiotic stress. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensing, S.A.; Lang, D.; Zimmer, A.D.; Terry, A.; Salamov, A.; Shapiro, H.; Nishiyama, T.; Perroud, P.-F.; Lindquist, E.A.; Kamisugi, Y. The Physcomitrella genome reveals evolutionary insights into the conquest of land by plants. Science 2008, 319, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Yin, H.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S. Different modes of gene duplication show divergent evolutionary patterns and contribute differently to the expansion of gene families involved in important fruit traits in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Paterson, A.H. Genome and gene duplications and gene expression divergence: A view from plants. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1256, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeling, M. Bias in plant gene content following different sorts of duplication: Tandem, whole-genome, segmental, or by transposition. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.E.; Chen, E.Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, F.G. Genome-wide analysis of GRAS transcription factor gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Luo, X.; Wu, M.; Wei, L.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression of GRAS gene family members in cassava. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Su, L.; Gao, H.; Jiang, X.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ren, F. Genome-wide characterization of bHLH genes in grape and analysis of their potential relevance to abiotic stress tolerance and secondary metabolite biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Han, P.; Liu, H.; Gong, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, B.; Liu, A.; Xu, L. Genome-wide investigation of bHLH genes and expression analysis under different biotic and abiotic stresses in Helianthus annuus L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Gao, L. Genome-wide analysis of WRKY genes and their response to hormone and mechanic stresses in carrot. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, H.; Zhong, X.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Kang, J. Identification and expression profiling analysis of NBS–LRR genes involved in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. conglutinans resistance in cabbage. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, Z. Different scales of gene duplications occurring at different times have jointly shaped the NBS-LRR genes in Prunus species. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chai, Z.; Lin, P.; Huang, C.; Huang, G.; Xu, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors in sugarcane (Saccharum spontaneum L.). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chao, J.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Song, D.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, G. Systematic analysis of the bZIP family in tobacco and functional characterization of NtbZIP62 involvement in salt stress. Agronomy 2021, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Quan, S.; Niu, J.; Guo, C.; Kang, C.; Liu, J.; Yuan, X. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification, Expression and Duplication Analysis of bZIP Family Genes in Juglans regia L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, Q.; Dong, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bZIP transcription factors, and functional analysis in response to drought and cold stresses in pear (Pyrus breschneideri). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, L.D. The Ka/Ks ratio: Diagnosing the form of sequence evolution. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
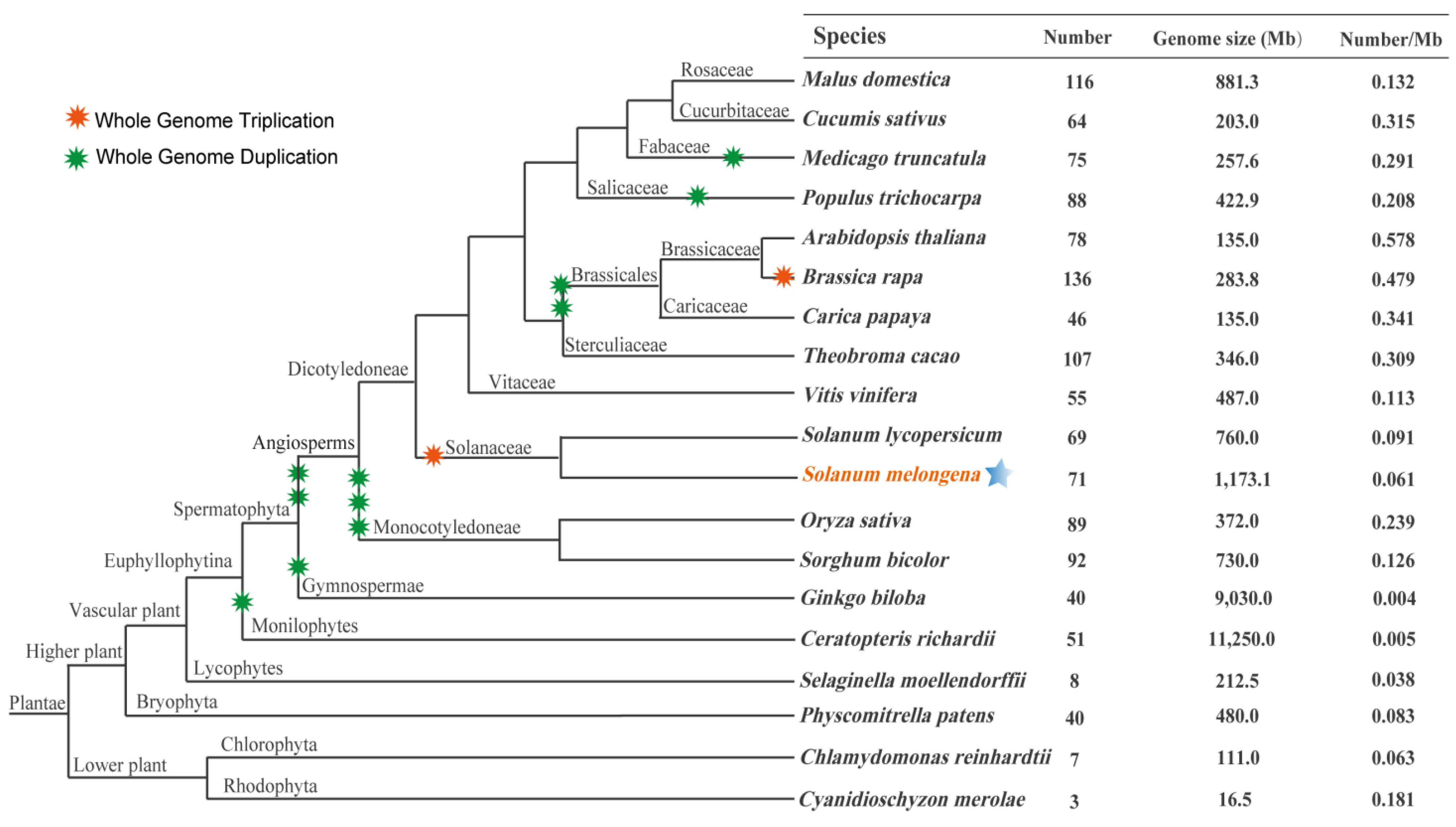

| Species | Number of Genes Included | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (VI) | B (III) | C (IV) | D (VII) | E (V + X) | F (VIII) | G (I) | H (II) | I (IX) | J (XI) | K | M (IV) | S (IV) | Total | |
| Eggplant | 12 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 6 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 15 | 71 |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | 13 | 3 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 17 | 78 |
| Solanum lycopersicum | 12 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 13 | 69 |
| Aquigelia coerulea | 7 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 49 |
| Amborella trichopoda | 8 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 4 | 39 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Yao, G.; Tang, Y.; Lu, X.; Qiao, X.; Wang, C. Genome-Wide Survey and Expression Analysis of the Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) Gene Family in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121153
Li Y, Yao G, Tang Y, Lu X, Qiao X, Wang C. Genome-Wide Survey and Expression Analysis of the Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) Gene Family in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Horticulturae. 2022; 8(12):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121153
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yan, Guoxin Yao, Yafang Tang, Xudong Lu, Xiu Qiao, and Cheng Wang. 2022. "Genome-Wide Survey and Expression Analysis of the Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) Gene Family in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.)" Horticulturae 8, no. 12: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121153
APA StyleLi, Y., Yao, G., Tang, Y., Lu, X., Qiao, X., & Wang, C. (2022). Genome-Wide Survey and Expression Analysis of the Basic Leucine Zipper (bZIP) Gene Family in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Horticulturae, 8(12), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8121153





