Pathogenic Fungi Diversity of ‘CuiXiang’ Kiwifruit Black Spot Disease during Storage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Measurement of Physiological Characteristics Data
2.2.1. Determination of Kiwifruit Firmness
2.2.2. Kiwifruit Ethylene Production Rate
2.2.3. Determination of Soluble Solid Content and Titratable Acid Content
2.2.4. Determination of Mineral Element Content
2.3. Observation of Scanning Electron Microscopy and Transmission Electron Microscope
2.3.1. Paraffin Sectioning
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Observation
2.3.3. Transmission Electron Microscope Observation
2.4. RNA Sequencing of Pulp Tissues during Storage
2.5. ITS Sequence and Bioinformatics Analysis of Fungal Communities on Fruit Surface
2.6. Laboratory Isolation, Purification, Identification, and Inoculation of Pathogenic Fungi
2.6.1. Isolation, Purification, and Identification of Pathogenic Fungus
2.6.2. Inoculation of Pathogenic Fungus
3. Results and Discussion
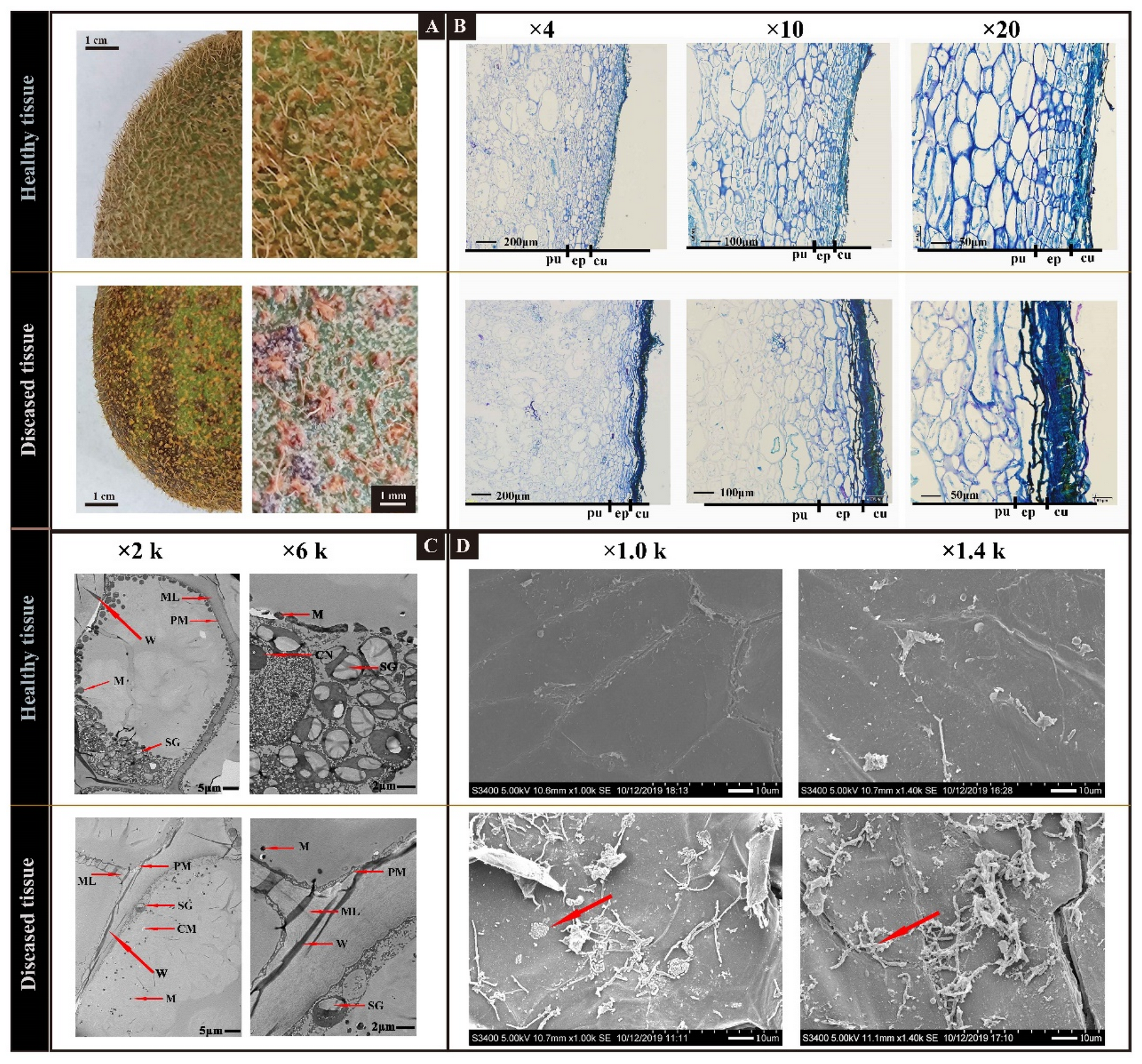
3.1. Black Spot Disease Symptom during Postharvest: Accelerating Softening of Fruit, Visioning Hyphae Attached to Fruit Skin and Exhibiting Cell Wall Structure Changes
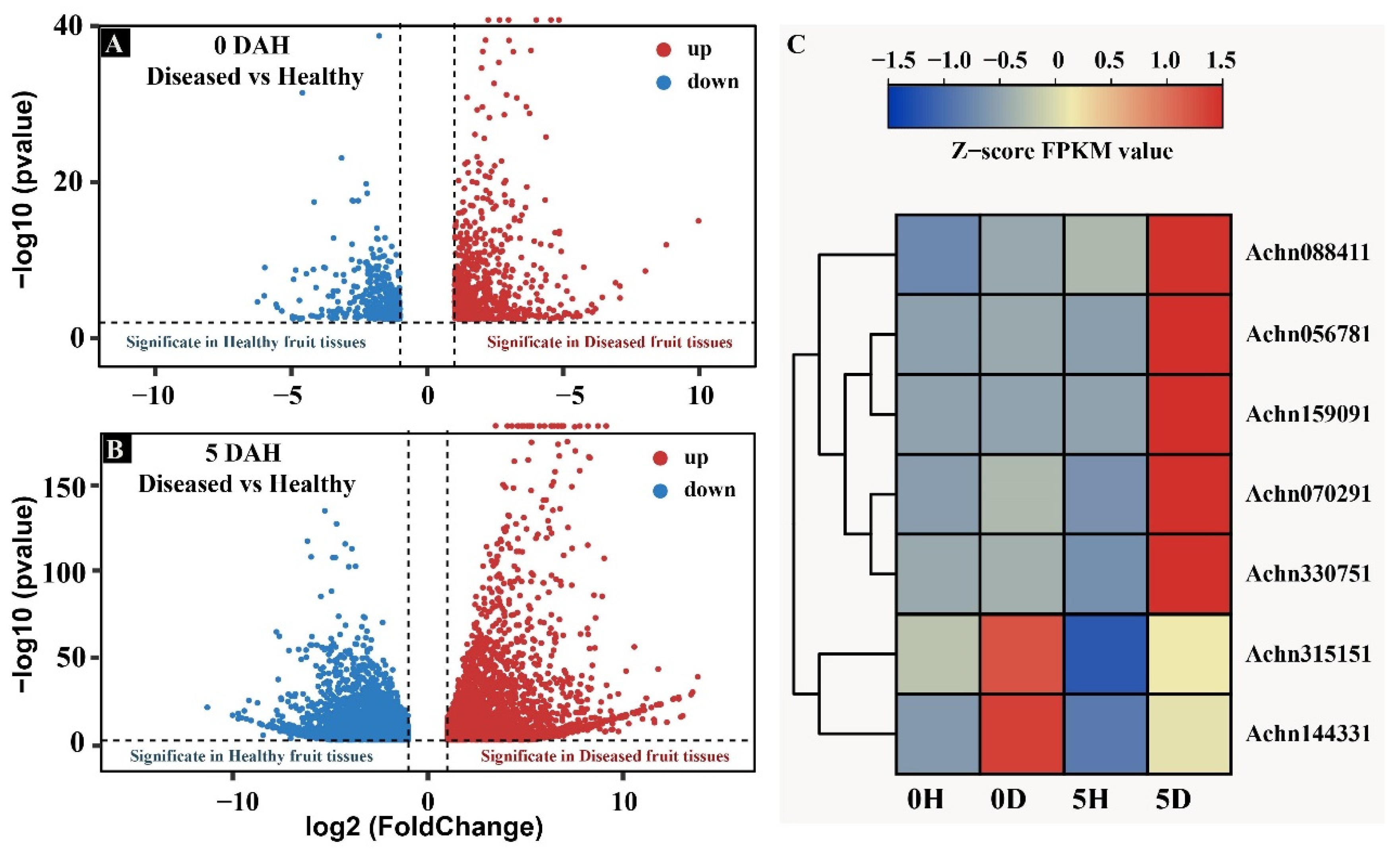
3.2. Transcription Influence of Black Spot Disease on Fruits: Cell Wall Modification and Pathogen Signals Genes Were Regulated
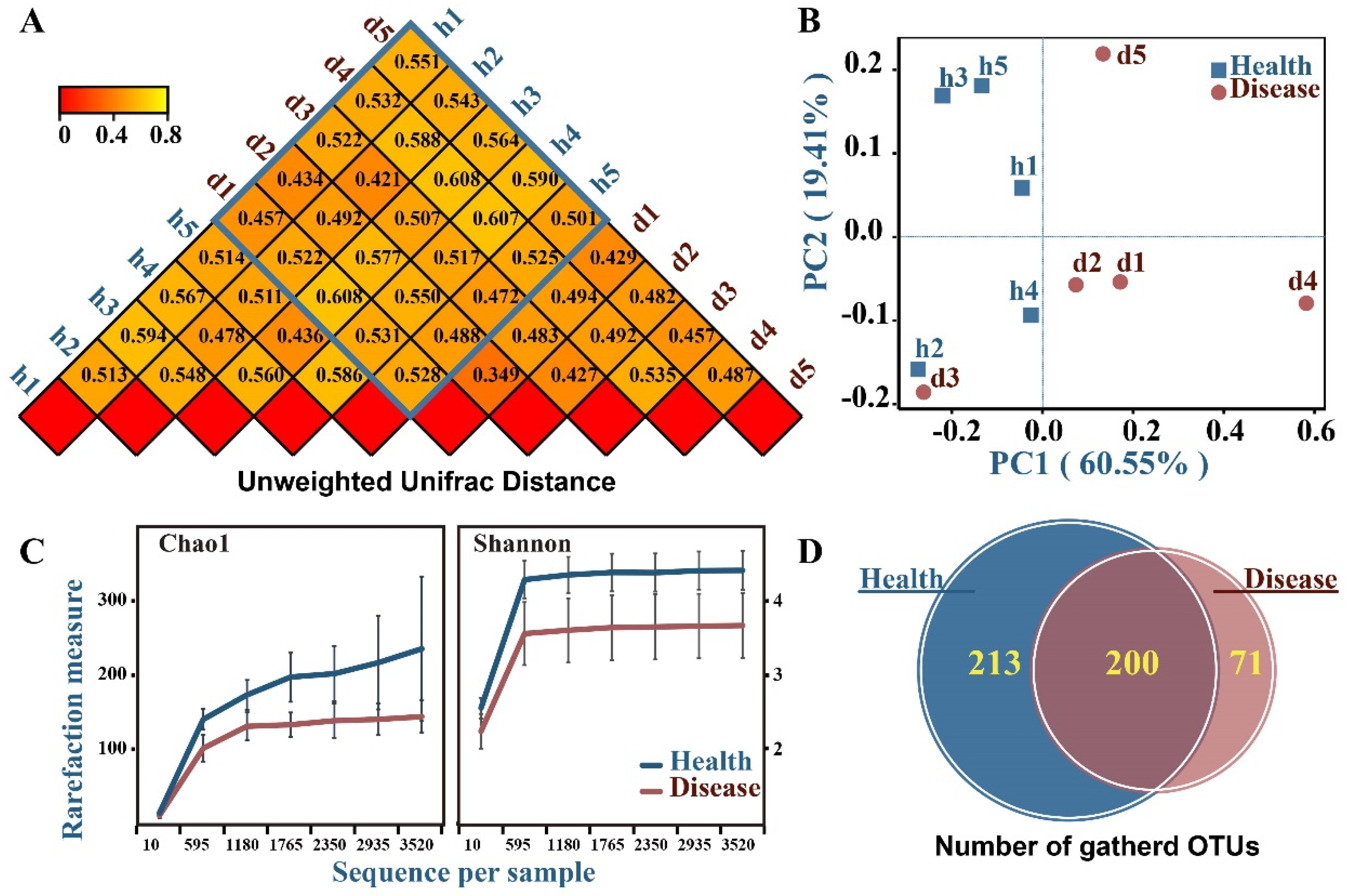
3.3. OTU Statistical Analysis of Fungal Community: The Species and Abundance of Microorganisms of Healthy Fruit Tissues Were Higher than That of Diseased Tissues
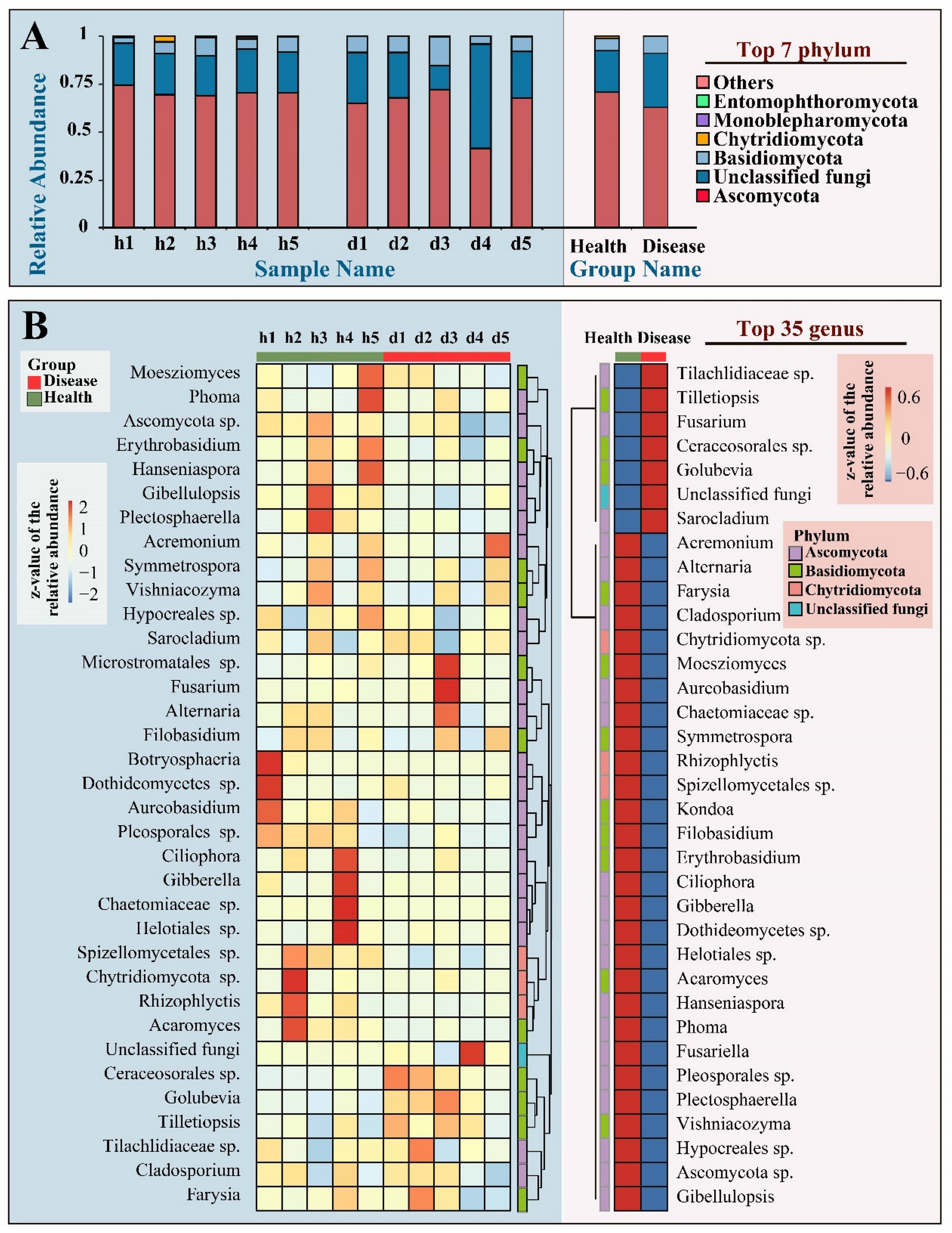
3.4. Prediction and Analysis of Pathogenic Fungi
3.5. Identification of Pathogenic Fungus
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, X.; Guo, D.; Wang, R.; Zhong, Y.; Fang, J. Development status and suggestions on Chinese ki-wifruit industry. J. Fruit Sci. 2020, 37, 754–763. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, Y.; He, P. Current Situation, Problems and Countermeasures of Kiwifruit Industry in China. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 69–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, A.-M.; Longeon, A.; Guyot, M. Fraxin and esculin: Two coumarins specific to Actinidia chinensis and A. deliciosa (kiwifruit). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2002, 30, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P. Formation reason and prevention and control measures of black spot in Cuixiang Kiwifruit fruit. Northwest Hortic. (Fruit Trees) 2015, 5, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Meng, J.; Chen, C. Kiwifruit ‘CuiXiang’ black spot prevention and control. J. Shanxi Fruit Trees 2019, 3, 84–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Wang, J.; Ren, P.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jin, P.; Zhang, F. Identification of the pathogen causing black spot on kiwifruit in Shaanxi Province. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2020, 50, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Prevention and control technology of black spot of Cuixiang ki-wifruit. Shaanxi Agric. Sci. 2016, 62, 125–126. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Chen, M.Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, Z.P.; Li, L.; Zhong, C.H. First Report of Didymella glomerata Causing Black Spot Disease of Kiwifruit in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, H.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhang, S.J.; Zhong, C.H. First Report of Nigrospora oryzae Causing Brown/Black Spot Disease of Kiwifruit in China. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-H.; Cheon, M.-G.; Kim, J.-W.; Kwack, Y.-B. Black Rot of Kiwifruit Caused by Alternaria alternata in Korea. Plant Pathol. J. 2011, 27, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikuhara, K.; Nakashima, C. Sooty spot of kiwifruit caused by Pseudocercospora actinidiae Deighton. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2008, 74, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, X. Identification and ITS Sequence Analysis of Gerbera Root Rot Pathogen. Plant Pathol. Bull. 2005, 5, 392–396. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Lin, S.; Jia, H.; Pan, Y.; Luo, H.; Deng, M. Study on microbial diversity and function prediction of Pekinensis bean juice based on 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing technology. Food Ind. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Janisiewicz, W.J.; Ii, W.M.J.; Peter, K.A.; Kurtzman, C.P.; Buyer, J. Yeasts associated with plums and their potential for controlling brown rot after harvest. Yeast 2014, 31, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Wisniewski, M.; Droby, S.; Schena, L. Spatial and compositional variation in the fungal communities of organic and conventionally grown apple fruit at the consumer point-of-purchase. Hortic. Res. 2016, 3, 16047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volschenk, Q.; Du Plessis, E.M.; Duvenage, F.J.; Korsten, L. Effect of postharvest practices on the culturable filamentous fungi and yeast microbiota associated with the pear carpoplane. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 118, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Pan, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, C. Isolation and identification of pathogenic fungi causing postharvest fruit rot of kiwifruit (Actinidia chinensis) in China. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 165, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboni, T.; Cannac, M.; Chiaramonti, N. Effect of cold storage and ozone treatment on physicochemical parameters, soluble sugars and organic acids in Actinidia deliciosa. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Polovka, M.; Suhaj, M.; Ham, K.-S.; Kang, S.G.; Park, Y.-K.; Arancibia-Avila, P.; Toledo, F.; Sánchez, M.R.; Gorinstein, S. The postharvest performance of kiwi fruit after long cold storage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahkoomahally, S.; Chaparro, J.X.; Beckman, T.G.; Sarkhosh, A. Influence of Rootstocks on Leaf Mineral Content in the Subtropical Peach cv. UFSun. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 55, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.S.; Lavorante, A.F.; Paim, A.P.S.; da Silva, M.J. Microwave-assisted digestion employing diluted nitric acid for mineral determi nation in rice by ICP OES. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.U.; Ma, Q.; Ahmad, B.; Hanif, M.; Zhang, Y. Histochemical and Microscopic Studies Pre-dict that Grapevine Genotype “Ju mei gui” is Highly Resistant against Botrytis cinerea. Pathogens 2020, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez Velasco, G.; Tydings, H.A.; Boyer, R.R.; Falkinham, J.O., III; Ponder, M.A. Characterization of interactions between Escherichia coli O157:H7 with epiphytic bacteria in vitro and on spinach leaf surfaces—ScienceDirect. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 153, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S. Bacterial community diversity on in-shell walnut surfaces from six representative provinces in China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.R.; Nagarajan, N.; Pop, M. Statistical Methods for Detecting Differentially Abundant Features in Clinical Metagenomic Samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, F.; Paolini, J.; Barboni, T.; Costa, J. Relationships between the leaf and fruit mineral compositions of Actinidia deliciosa var. Hayward according to nitrogen and potassium fertilization. Food Chem. 2013, 147, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarihami, H.; Cha, G.H.; Kim, J.G.; Kim, H.U.; Lee, M.; Kwack, Y.B.; Cho, J.G.; Kim, J. Effect of Preharvest Ca-chitosan Application on Postharvest Quality of ‘Garmrok’ Kiwifruit during Cold Storage. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2020, 38, 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Veraverbeke, E.; Verboven, P.; van Oostveldt, P.; Nicolai, B. Prediction of moisture loss across the cuticle of apple (Malus syl-vestris subsp. mitis (Wallr.)) during storage: Part 2. Model simulations and practical applications. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2003, 30, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.J. The Biochemistry and Structural Biology of Plant Cell Wall Deconstruction. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, K.; Bowen, J.; Allan, A.; Espley, R.; Karunairetnam, S.; Ferguson, I. Differential expression within the LOX gene family in ripening kiwifruit. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3825–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, G.; He, Z.; Yan, M.; Zou, M.; Jiang, J. Transcriptome analysis of Actinidia chinensis in response to Bot-ryosphaeria dothidea infection. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227303. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, Z.M.; Guzman, N.D.; Grace, E.; Moretto, M.; Sonego, P.; Engelen, K.; Zoli, L.; Moser, C.; Baraldi, E. Transcriptome Profiles of Strawberry (Fragaria vesca) Fruit Interacting with Botrytis cinerea at Different Ripening Stages. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, J.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, P.; Long, C.; Deng, B. Inhibitory activity of tea polyphenol and Hanseniaspora uvarum against Botrytis cinerea infections. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 51, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish, M.; Beuchat, L.; Suslow, T.; Harris, L.; Garrett, E.; Farber, J.; Busta, F. Methods to Reduce/Eliminate Pathogens from Fresh and Fresh-Cut Produce. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2003, 2, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, R.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, H. Compositional shifts in the fungal diversity of garlic scapes during postharvest transportation and cold storage. LWT 2019, 115, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghule, S.B.; Sawant, I.S.; Sawant, S.D.; Saha, S.; Devarumath, R.M. Isolation and identification of three new mycoparasites of Erysiphe necator for biological control of grapevine powdery mildew. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2019, 48, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Guo, J.H.; Cheng, Y.J.; Li, L.; Pu, L.; Wang, B.Q.; Deng, B.X.; Long, C.A. Control of gray mold of grape by Han-seniaspora uvarum and its effects on postharvest quality parameters. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, A.; Di Foggia, M.; Corbetta, M.; Baldo, D.; Ratti, C.; Baraldi, E. Biocontrol Activity and Plant Growth Promotion Exerted by Aureobasidium pullulans Strains. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 40, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
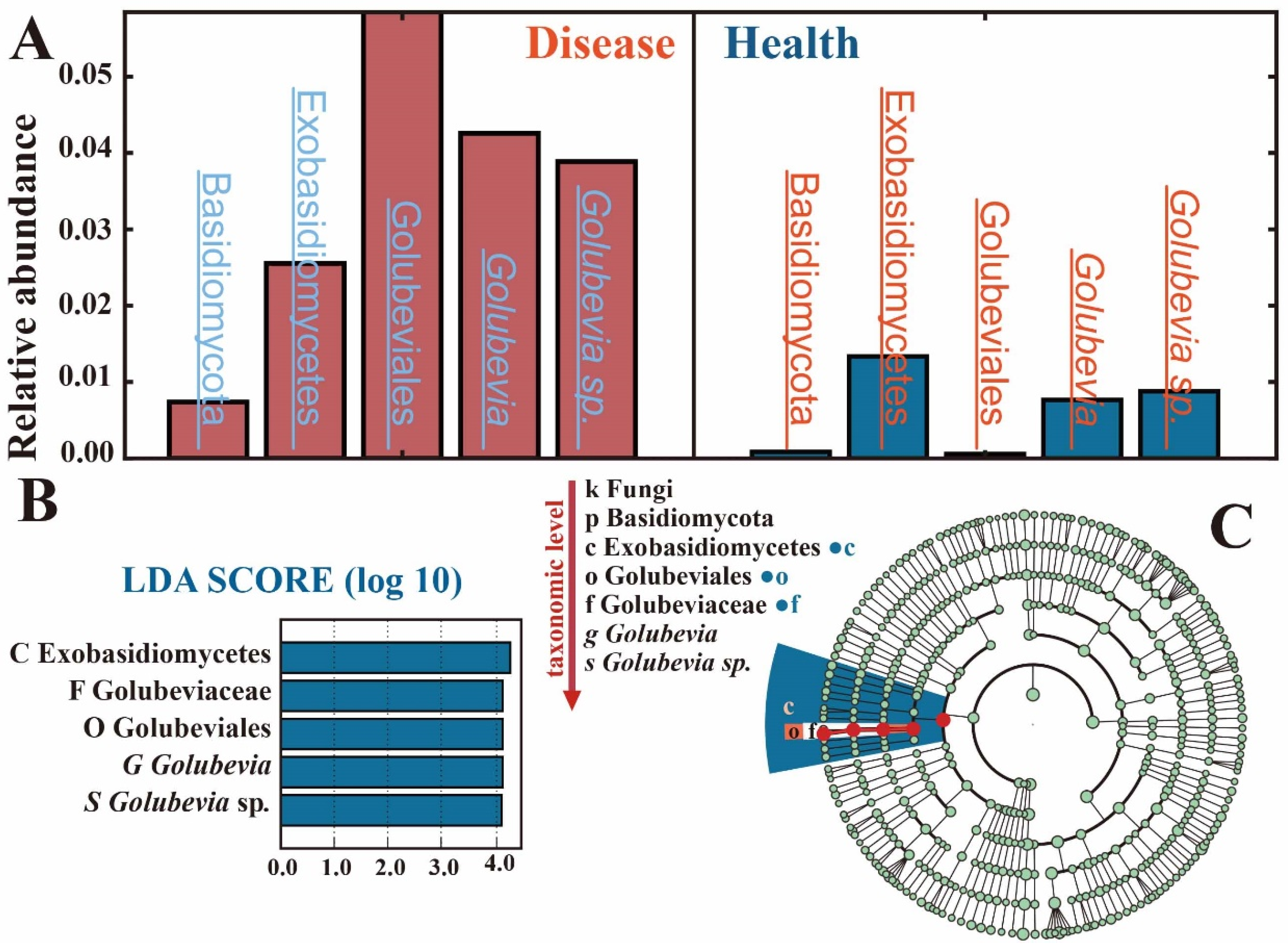
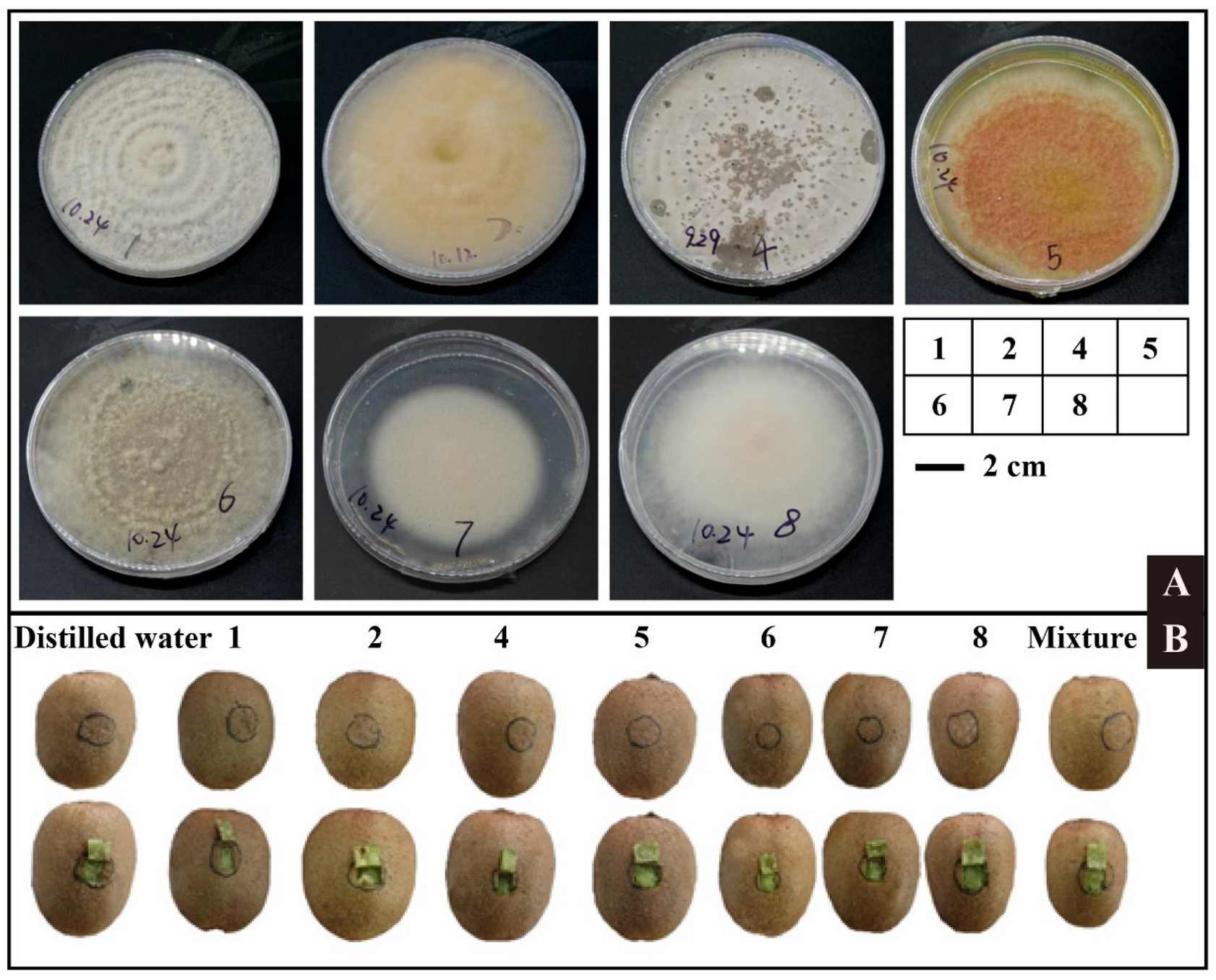
| Sample | Clean Reads | Total Bases | Average Length | Goods Coverage | OTU (97%) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 5593 | 3,822,534 | 683 | 0.993 | 146 |
| H2 | 6612 | 4,459,569 | 674 | 0.989 | 155 |
| H3 | 5899 | 4,027,333 | 682 | 0.988 | 178 |
| H4 | 6171 | 4,252,244 | 689 | 0.984 | 177 |
| H5 | 5688 | 3,888,406 | 683 | 0.977 | 170 |
| D1 | 6089 | 4,239,139 | 696 | 0.989 | 130 |
| D2 | 5993 | 4,142,348 | 691 | 0.988 | 132 |
| D3 | 6079 | 4,105,757 | 675 | 0.991 | 138 |
| D4 | 5899 | 4,358,927 | 738 | 0.99 | 93 |
| D5 | 6072 | 4,186,335 | 689 | 0.994 | 97 |
| Average health | 5992.6 | 4,090,017 | 682.2 | 0.9862 | 165.2 |
| Average disease | 6091.8 | 4,173,338 | 684.8 | 0.9854 | 162 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, C.; Peng, H.; Yin, W.; Li, R.; Liu, C.; Ren, X.; Ding, Y. Pathogenic Fungi Diversity of ‘CuiXiang’ Kiwifruit Black Spot Disease during Storage. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010013
Yang Y, Chen L, Wang C, Peng H, Yin W, Li R, Liu C, Ren X, Ding Y. Pathogenic Fungi Diversity of ‘CuiXiang’ Kiwifruit Black Spot Disease during Storage. Horticulturae. 2022; 8(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yaming, Lijuan Chen, Chenyu Wang, Honghui Peng, Weijie Yin, Rui Li, Cuihua Liu, Xiaolin Ren, and Yuduan Ding. 2022. "Pathogenic Fungi Diversity of ‘CuiXiang’ Kiwifruit Black Spot Disease during Storage" Horticulturae 8, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010013
APA StyleYang, Y., Chen, L., Wang, C., Peng, H., Yin, W., Li, R., Liu, C., Ren, X., & Ding, Y. (2022). Pathogenic Fungi Diversity of ‘CuiXiang’ Kiwifruit Black Spot Disease during Storage. Horticulturae, 8(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae8010013





