Abstract
Grapevine sustainability is impacted by the timing of dormancy initiation and freezing tolerance in fall and winter and chilling fulfillment and bud break in the spring. These traits have genetic and local temperature contributing factors; therefore, this study was undertaken to develop an understanding of these characteristics in four recently developed cold climate cultivars. The cold hardiness and chilling fulfillment profiles were monitored in Brianna, Frontenac gris, La Crescent and Marquette using differential thermal analyses and bud break assays. Bud cold hardiness of all cultivars increased with the declining temperatures from November through February, after which the buds began to lose freezing tolerance. There were significant differences in cold hardiness and chilling fulfillment between cultivars during the endodormant and ecodormant period of winter. Marquette had the greatest freezing tolerance from early November through midwinter suggesting it has potential as a sentinel cultivar for comparisons of new cold climate selections. Brianna was slower to acclimate and deacclimated more rapidly than the other cultivars. Chilling fulfillment under natural field or constant 4 °C conditions showed no main effect differences for chilling accumulation condition; however, there were significant cultivar, condition, and time point interactions, indicating the cultivars differed in chilling fulfillment responses.
1. Introduction
Freezing injury is one of the most problematic issue impacting production of grapevine in Northern regions of the United States [1,2,3]. The freezing tolerance of grapevine species and cultivars varies considerably with Vitis riparia having the greatest reported tolerance of −40 °C [4,5]. The cultivars belonging to V. vinifera, have high grape quality; however, their winter freezing tolerance is reported to range between −10 °C and −26 °C [1,6,7]. Introduction of new cultivars since the 1980s, developed from complex interspecific hybrids of V. vinifera, V. riparia and V. labrusca, has resulted in new grape and wine production in the regions of the North Central and North Eastern states in the USA and Southern Canada [8,9]. These cold hardy wine grapes have been reported to survive temperatures from −25 °C to −38 °C in these regions; however, other reports indicate freezing injury can occur under less severe temperatures depending on the timing of the freeze event and the dormancy status of the vines [10]. South Dakota has winter temperatures that can reach −30 °C in some years [11]; however, it is noted that freezing injury can also occur in years with warmer winter temperatures. Typically, as temperatures decrease in fall and winter, the dormant buds survive increasingly negative temperatures, maintaining freezing tolerance at low mid-winter temperatures and then begin to deacclimate and lose freezing tolerance with increasing temperatures and chilling fulfillment [7,12,13]. Temperature conditions can fluctuate widely on a daily and weekly basis in a continental climate with potential sudden temperature drops after warming periods, which may contribute to freezing injury early or late in winter season.
Freezing tolerance is dynamic, rather than a fixed character in each cultivar and is affected by temperature fluctuations and bud dormancy status during the winter season [8,14]. Bud dormancy is typically divided into three stages with internal and external factors controlling the stage, paradormant (correlative inhibition during the growing season), endodormant (growth restriction factors are within the bud), and ecodormancy (chilling fulfilled, growth is limited by environmental conditions) [15]. The timing of subzero temperatures, intermittent winter warming temperatures, and the dormancy status of the buds may affect potential bud freezing damage. Sudden subzero temperature drops in early fall, as buds are entering dormancy, or in the spring when bud chilling requirement is fulfilled, can be damaging [8,16]. The transition from endodormancy to ecodormancy is driven by a genotype specific amount of exposure to hours of low temperature (0 to 7 °C) needed to achieve chilling fulfillment [17] and transition the vine to ecodormancy, followed by bud break with the increasing spring temperature [15]. Bud break assays can be used to estimate chilling requirement; however, these measures are frequently confounded with winter injury in grapevines [1]. Under non-injurious conditions, V. vinifera cultivars typically require 50–400 chilling hours (0 to 7 °C) while other species range between 250–2250 h [14]. To select cultivars suited for a region’s climatic conditions, it is important to understand the interaction of chilling fulfillment and rate of bud break [14]. In regions with early warming periods, it is important to maintain vine dormancy to avoid frost damage in the spring [14,18]. Cultivars with a greater chilling fulfilment requirement and slower deacclimation rates would be useful for avoiding spring freezes in a changing climate [16]. Sustainability of grapevines is dependent on the interaction of the grapevine’s response to local temperatures during acclimation and deacclimation periods, as well as the extreme winter low temperatures in a year. Therefore, the objective of this study was to provide baseline information on four interspecific grape cultivars freezing tolerance and chilling fulfillment patterns throughout the dormancy cycle in South Dakota, USA.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
Four cultivars with complex interspecific pedigrees were examined (Vitis International Variety Catalogue (VIVC) [19] variety number is listed in parenthesis: Brianna (VIVC 23260) [20], Frontenac gris (VIVC 23928) [21], La Crescent (VIVC 17632) [22], and Marquette (VIVC 22714) [23]. Cane samples of the grape cultivars were collected from bearing vines trained with bilateral low cordons and vertical shoot positioning at Tucker’s Walk commercial vineyard in Garretson, SD (lat. 43°43′2.901″ N, long. 96°30′10.155″ W) in USDA Plant Hardiness Zone 4b [24]. Canes were collected bi-weekly from 2 November 2017 to 23 March 2018 (year 1) and 7 November 2018 to 3 April 2019 (year 2) and 12 November 2019 to 11 March 2020 (year 3). Sample days are noted in Julian days for each dormancy season starting from 1 January of a given year through the next spring (next calendar year). Vines were sampled randomly across the vineyard cultivar block for each sampling time. A random cane (containing nodes 5–10 numbered from cane origin/base) was collected from each of five vines for one replicate. A total of five replicates were tested for freezing tolerance and dormancy status for each cultivar at each sampling time. To monitor controlled chilling fulfillment, 45 additional canes (one per vine, containing nodes 5–10 from cane origin/base) were collected from vines distributed across each cultivar block, on the first field sample date in November. Controlled chilling canes were cut into single nodes and nodes from each cane were placed in ziplock bags at 4 °C to fulfill chilling requirement.
2.2. Low Temperature Exotherms
Bud low temperature exotherms (LTEs) were determined using differential thermal analysis with a Keithley Multimeter Data Acquisition System (model 2700-DAQ-40; Keithley Instruments, Cleveland, OH, USA), a programmable freezer (Tenney Environmental Test Chamber, model T2C, Thermal Product Solutions, Williamsport, PA, USA) and thermoelectric modules (TEM) constructed as previously described by Mills et al. [7]. Five buds (one from each of the individual canes) were placed in a TEM and five replicates (five buds in each of five TEMs) were used for each cultivar. Temperature program was as described by Mills et al. [7] (1 h at 4 °C, followed by 4 °C/h temperature decline to −40 °C). LTEs representing the bud killing temperature were identified for each replicate [7,13].
2.3. Dormancy Status
Dormancy status was monitored for field collected and control chilled buds at two-week intervals using forcing assays. Dormancy status/bud break capacity was determined by placing a five cm long node section (sixth node from cane origin/base) in water at 22 °C and 24-h day length (n = 5). Bud phenological stage was monitored weekly using the modified E-L grapevine growth stage and E-L stage 4 (green tip visible) was considered bud break [25]. Chilling was considered fulfilled when 50% of bud reached E-L stage 4 within 4 weeks [14]. After four weeks, buds that did not break were cut longitudinally to determine viability (green = alive, brown = dead). Chilling hours were calculated as hours of exposure to temperatures between 0 °C and 7 °C in field or controlled conditions [26]. Chilling hour accumulation for the field condition was calculated from 1 October to the sample time by using hourly temperature data from the Garretson station of South Dakota Mesonet [11]. Chilling hour accumulation for the controlled chilling treatment was calculated by adding the field chilling hours from 1 October to the collection date for controlled treatment and adding hours accumulated in 4 °C controlled refrigeration cooler (24 chilling hours/day) until sample date for bud break assay. The buds in controlled chilling treatment accumulated chilling hours more quickly than under field conditions; therefore, four accumulated chilling hour groups (200–500, 501–700, 701–900 and >901 (922 to 1538 and 917 to 1629 chilling hours in field and controlled conditions, respectively) were used to compare the field and controlled condition responses. The resulting experimental design was a three-way factorial with two chilling treatments, four cultivars and four chilling periods.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Freezing
Descriptive analysis was conducted using psych library in R [27]. Correlation analysis was performed between cultivar LTEs and mean minimum temperature of the week prior to sample collection using stats library in R [28]. Influence of cultivar, sampling time (in Julian days), dormant season, and their interaction effects on LTEs were assessed by a linear model (lm function) applied in the stats package in R software [28]. Seven models (one model for each of the three seasons, two models for first two seasons, two models for all seasons) were built to check cultivar, sampling time, season main effect, and cultivar by sampling time, cultivar by season or cultivar by sampling time and season interactions. The most appropriate model to describe the current experimental data was selected by model adequacy. In addition, each model’s residual was checked for normality assumptions. Freezing tolerance plots were plotted using ggplot2 in R [29].
2.4.2. Dormancy Status
Chilling fulfillment descriptive analysis was performed using psych library in R [27]. The effect of cultivar (4), chilling accumulation method (natural or controlled), chilling hour accumulation group (200–500, 501–700, 701–900, and >901 chilling hours), season (3) and their interactions on bud break growth stages were assessed by ANOVA using stats package in R [28]. A model that included all main effects and interaction effects was tested for normality assumptions.
3. Results
3.1. Dormant Season Temperature Variation 2017–2020
The three winter seasons had different low temperature severity (Figure 1). The 2017/18 to 2018/19 dormant seasons show wide fluctuation minimum hourly temperatures in Garretson, SD. The 2017/18 and 2018/19 winters were similar with the exception that the lowest temperatures occurred later in 2018/19. Temperatures below −15 °C typically do not occur until late November or early December in South Dakota, as noted by the first temperature below −15 °C in 2017/18 and 2018/19 temperatures (7 December 2017, Julian day 342 and 29 December 2019, Julian day 364). However, in 2019/2020 a −18 °C occurred very early (7 November 2019, Julian day 312). In this three- year period, the lowest temperatures occurred most frequently in January and the March temperatures were the most variable ranging from −11 to −29 °C. Mean monthly temperatures were similar for the three seasons, emphasizing the need to track daily temperatures (Supplementary Table S1).
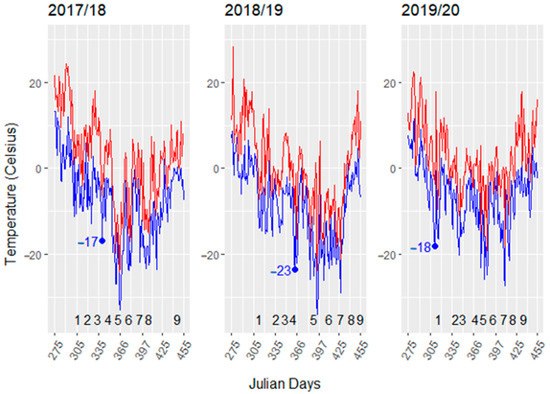
Figure 1.
Dormant season temperatures for 2017 to 2020. The daily maximum and minimum temperatures are indicated by red and blue lines, respectively. Numbers from 1 to 9 indicate tissue sampling time in each dormant season. The blue dot indicates the first date that the minimum temperature was below −15 °C in each dormant season. The first day of each month for a dormant season (November through April) are 305, 335, 366, 398, 426, and 457 Julian days, respectively.
3.2. Bud Freezing Tolerance Differs between Seasons and Cultivars
Cultivar, sampling time, season, and cultivar by sampling time interactions were significant (Supplementary Table S2). The cultivar LTEs were lower in 2017/18 than the 2018/19 and 2019/20 dormant seasons (Figure 2). The earlier colder temperatures in 2017/18 winter season are reflected in lower LTEs in all cultivars (Supplementary Table S3). Minimum LTEs varied by the winter season, occurring 29 January in 2017/18, 3 March in 2018/19 and 28 February in 2019/20. Buds began to deacclimate after January in 2017/18 and in mid-March in 2018/19 and 2019/20 (Figure 2, Supplementary Table S3). Brianna and Marquette had consistently lower LTEs in mid-winter than other cultivars; however, Brianna appeared to deacclimate more rapidly with higher LTEs in March (Supplementary Table S3). Marquette had greater over all freezing tolerance with a consistently lower mean LTEs in November and March than the other cultivars (Figure 2, Supplementary Table S3).
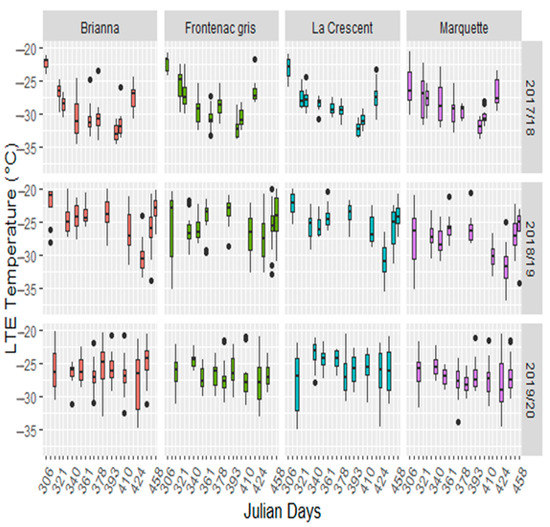
Figure 2.
Low temperature exotherms for Brianna, Frontenac gris, La Crescent, and Marquette across the 2017/18, 2018/19 and 2019/20 dormant seasons.
The LTEs showed a parallel profile to the minimum temperatures in 2017/18 and 2018/19. In 2018/19, the lowest temperatures and lowest LTEs were skewed towards February in contrast to 2017/18 (Figure 1 and Figure 2). There was little change in LTEs throughout 2019/20 after the early −18 °C freezing temperature. There were significant correlations between cultivar LTEs and the mean minimum temperature of the seven days prior to sampling in 2017/18 and 2018/19 (Table 1). There were no significant correlations between temperature and LTEs in the 2019/20 season (Table 1). The early −18 °C temperature in the 2019/20 season resulted in bud damage that occurred before sample collection was started; thereby, limiting the cultivar LTEs fluctuation with local temperature. Minimum temperature and LTEs correlations were strongest for the 2017/18 season in all cultivars, when tested across seasons the correlations decrease and are significantly impacted by the 2019/20 year. Modeling the contribution of cultivar, sampling time, season, and their interactions showed the complexity of grapevine bud freezing tolerance and its interactions with environmental changes (Table 2). All models showed significant environment (sampling time or season) main effects. Complex models showed significant cultivar environment interactions and increased model complexity did not violate normality assumptions. Cultivar was a significant contributor to LTEs in 2017/18 and 2018/19, but not in 2019/20 (Table 2, models 1–3), suggesting that primary bud damage occurred with the early −18 °C in 2019/2020. Comparison of complex models (cultivar, sampling time, season, and cultivar by sampling time and/or season interactions) for the first two seasons with that of all three seasons further supports presence of earlybud damage, as cultivar was not a significant contributor when all three seasons were included (Table 2, bottom row). This indicated that timing of acclimation initiation as well as extreme low temperatures early in the dormant season are important factors in freezing tolerance.

Table 1.
Pearson correlation coefficient between cultivar low temperature exotherms and mean seven-day minimum temperature prior to sampling in 2017/18, 2018/19, and 2019/20 winter seasons.

Table 2.
Modeling cultivar, sampling time, season, and cultivar by sampling time and/or season interaction contributions to the low temperature exotherms.
3.3. Bud Dormancy Release Showed Significant Cultivar by Treatment or Season Interactions
The controlled and natural field chilling conditions showed similar bud break phenology across cultivars in each chilling hour accumulation group and the major effect of chilling condition was not significant (Figure 3, Supplementary Table S4). Cultivar differences in bud break stage are noted for the four chilling periods (200–500, 501–700, 701–900, >901). The main effects for cultivar, chilling hour accumulation group, and season were significant. The two-way interaction effects of cultivar, chilling hour accumulation group, and the season and chilling condition and the cultivar and season interactions were significant indicating cultivar and seasonal components (Supplementary Table S4). Brianna required lower chilling hour accumulation as evidenced by the advanced E-L phenology stage in comparison to other cultivars (Table 3). Frontenac gris and La Crescent chilling fulfillment response was similar and intermediate to Brianna and Marquette. Freezing injury to the primary bud meristem can cause delay in bud break and it is noted that La Crescent had a lower bud break phenology stage under natural conditions (Table 3) as well as less negative mean LTEs (Supplementary Table S4), suggesting a delayed break in response to freezing injury. In this study the specific impact of prior freezing damage to primary buds, resulting in delays in bud break, could not be definitively determined as emerging shoots were not differentiated as arising from the primary or secondary bud meristems in the assay.
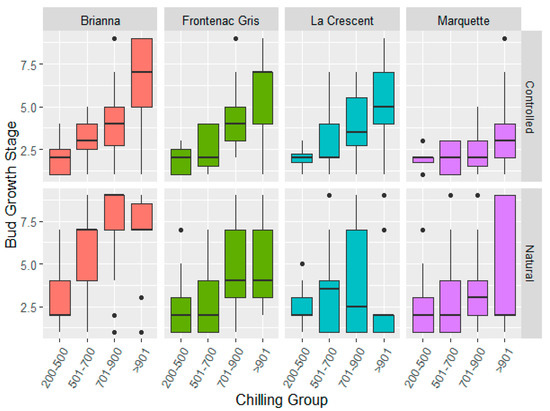
Figure 3.
Cultivar bud break changes in response to similar chilling hour groups in controlled and natural chilling hour accumulation conditions in 2017/18, 2018/19, and 2019/20 dormant seasons.

Table 3.
Bud phenology stage determined after 4 weeks forcing for Brianna, Frontenac gris, La Crescent, and Marquette for 200–500, 501–700, 701–900, or >901 chilling hour accumulation in controlled (4 °C) and natural field conditions.
4. Discussion
Grapevine bud freezing tolerance increases from October to February with decreasing and subzero freezing temperatures [30]. Typically, the maximum freezing tolerance occurs in January and then begins to decrease with increasing temperatures in February or March [31,32,33]. Interspecific cultivars are reported to have a wide range of inherent cold hardiness and winter survival characteristics [2,33]. The results of this study showed the complex interactions of the grapevine cultivar freezing tolerance and bud dormancy phenotype in response to changing temperatures. Sampling time and season influenced bud freezing tolerance in interspecific cultivars and data modeling predicted factors influencing bud freezing tolerance across years with varying field conditions. Differing field temperatures impacted LTEs (temperatures of bud injury due to intracellular freezing) at the various sampling times; however, differences between cultivars were consistent from year to year. As shown for other grape cultivars, in mild winters, LTEs are less negative than in colder winters [8,13]. This can be seen in the LTEs for Brianna averaging −24.7 °C and −26 °C in 2018/19 and 2019/20, respectively. January is generally considered the period of the dormant season when vines will be at their maximum freezing tolerance. The muscadine cultivars Carlos and Summit were maximally hardy in January [34]. In V. vinifera cultivars and hybrids Vignole and St. Vincent the bud cold hardiness correlates with the recent cold temperatures [35]. In this study, the lowest cultivar LTEs occurred in January in 2018 and 2020; however, in 2019 the lowest LTEs occurred in March in conjunction with field temperatures approaching −30 °C.
The influence of local temperatures at different times in the dormant season have been reported for several cultivars [35]. For example, Chardonnay was found to be more freezing tolerant than Cabernet Sauvignon; however, Chardonnay is noted to transition to ecodormancy and break bud earlier than Cabernet Sauvignon [36]. Similar responses are apparent in this study, including inherent cultivar difference in freezing tolerance. Marquette was more freezing tolerant than Brianna in 2018/19 and 2019/20. In contrast, in 2017/2018 Marquette and Brianna showed similar freezing tolerance throughout the dormant season. The temperature profiles from this three year period emphasizes the need for cultivars that acclimate quickly and have moderate to slow deacclimation characteristics [35]. In 2019/20, there was an early atypical low temperature in November that appeared to damage primary buds and resulted in little change in freezing tolerance during the rest of the season. Brianna appeared to deacclimate more rapidly, whereas Marquette has a slower deacclimation profile. The bud break phenology at different chilling hours suggest that Brianna requires lower chilling than the other three cultivars, which indicates that although it is a cold hardy grape it may be susceptible to injury in late winter due to rapid bud break [14].
Long term sustainability of cultivars is influenced by their ability to acclimate with changing dormant season temperatures. La Crescent and Marquette were identified as suitable cultivars for Wisconsin [37]. In contrast, La Crescent had a higher survival rate than Marquette in Vermont [38]. Marquette had more than 90% bud survival in a six year study in Iowa and the primary bud injury was lower than that of Brianna, Frontenac Gris, and La Crescent [39]. Brianna had greater primary bud kill than La Crescent and Marquette [40]. In this study, Brianna is noted as a cold hardy cultivar; however, it has the potential risk of early bud break due to a lower chilling requirement. Marquette was a superior cultivar in South Dakota for freezing tolerance and higher chilling requirement than Brianna, Frontenac gris, and La Crescent.
A relationship between the loss of freezing tolerance and greater chilling accumulation in grapevines has been reported [41]. Thus potential differences in cultivar chilling fulfillment requirements should be considered when choosing cultivars for specific regions as it may contribute to long term sustainability [1]. Increasing temperatures or warming periods in late winter and early spring can trigger deacclimation and promote bud break, therefore, early chilling fulfillment and early break can put cultivars at risk to freezing stress [6,18]. In this study, Brianna showed increased bud break at lower chilling hour accumulation than the other cultivars and Brianna also had higher LTEs in the corresponding timeframes suggesting that chilling fulfillment may decrease freezing tolerance stability and negatively influence long term sustainability. It is of note that the controlled chilling and natural field chilling produced a similar bud break phenology. This makes it possible to avoid the confounding factor of primary bud injury on bud break phenology. Damage of the primary bud frequently delays bud break with the secondary bud emerging more slowly than a healthy primary bud. It is not possible to separate out prior freezing damage in natural conditions on the rate of bud break in the forcing assays without destructively viewing the bud. Thus, collection of materials shortly after leaf drop and testing bud break phenology over a series of chilling hours can be used to provide chilling requirement information for new cultivars without the confounding factor of freezing injury. Additional study of controlled chilling and controlled non-lethal freezing acclimation conditions would be needed to determine specific interactions between freezing tolerance and chilling accumulation.
5. Conclusions
Grapevine bud freezing tolerance is a critical factor in sustainable grape production; however, the results of this study indicate the importance of determining both freezing tolerance and chilling requirements of new cultivars to identify their potential success in northern cold climate regions. All cultivars showed distinct acclimation and chilling fulfilment characteristics, with Marquette exhibiting the greatest freezing tolerance in early and mid-winter. There was a positive correlation between the 7-day minimum temperature average and LTEs in 2017/18 and 2018/19. Modeling the potential contribution of factors (cultivar, sampling time, and season) to LTEs indicated that in dormant seasons with a gradual decrease in fall to winter temperatures (2017/18 and 2018/19) all main factors and their interactions contributed to LTEs. In 2019/20 an early low temperature of −18 °C resulted in major bud damage and contributed to limited changes in LTEs in response to low temperature in mid-winter. This early low temperature injury emphasized the need for early acclimating cultivars in Northern Central Plains and that very early low temperature extremes can cause damage in cold hardy interspecific cultivars. There is also a risk associated with early deacclimation as noted in Brianna due to its lower chilling requirement than found in the other cold hardy cultivars. Marquette had a greater chilling requirement than Brianna, La Crescent, and Frontenac gris. The chilling fulfilment studies indicated that main effect of natural accruing and constant controlled environment temperatures showed similar bud break stage results; however, there were significant interactions between cultivar and treatment and season indicating greater complexity to the chilling fulfillment trait.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2311-7524/7/1/4/s1, Table S1. Mean monthly maximum and minimum temperatures during the dormant seasons of 2017/18, 2018/19 and 2019/20. Table S2. ANOVA for cultivar, sampling time, season, and interaction effects on LTEs. Table S3. Mean bud LTEs for Brianna, Frontenac gris, La Crescent, and Marquette during the dormant seasons of 2017/18, 2018/19 and 2019/20. Table S4. ANOVA for controlled and natural chilling on grapevine bud break across three seasons.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.F., T.Y.; Methodology A.F., T.Y. and D.A.; Data curation T.Y. and D.A.; Formal analysis and manuscript development T.Y. and D.A.; Review and Editing A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the South Dakota Research Station through multistate Project 3AR668.
Acknowledgments
David and Sue Greenlee of Tucker’s Walk Vineyard and winery, Garretson, SD, for allowing us to sample vines.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fennell, A. Freezing tolerance and injury in grapevines. J. Crop. Improv. 2004, 10, 201–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svyantek, A.; Köse, B.; Stenger, J.; Auwarter, C.; Hatterman-Valenti, H. Cold-Hardy Grape Cultivar Winter Injury and Trunk Re-Establishment Following Severe Weather Events in North Dakota. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabadal, T. Winter Injury to Grapevines and Methods of Protection (E2930); Michigan State University: East Lansing, MI, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pierquet, P.; Stushnoff, C. Relationship of low temperature exotherms to cold injury in Vitis riparia Michx. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1980, 31, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pierquet, P.; Stushnoff, C.; Burke, M. Low temperature exotherms in stem and bud tissues of Vitis riparia Michx [North America]. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1977, 102, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lipe, W.N.; Baumhardt, L.; Wendt, C.; Rayburn, D. Differential thermal analysis of deacclimating Chardonnay and Cabernet Sauvignon grape buds as affected by evaporative cooling. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1992, 43, 355–361. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, L.J.; Ferguson, J.C.; Keller, M. Cold-hardiness evaluation of grapevine buds and cane tissues. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2006, 57, 194–200. [Google Scholar]
- Londo, J.P.; Kovaleski, A.P. Characterization of wild North American grapevine cold hardiness using differential thermal analysis. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2017, 68, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.G. Grapevine Breeding Programs for the Wine Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hemstad, P.; Luby, J.J. Utilization of Vitis riparia for the development of new wine varieties with resistance to disease and extreme cold. In Proceedings of the VII International Symposium on Grapevine Genetics and Breeding, Montpellier, France, 6 July 1998; pp. 487–496. [Google Scholar]
- Mesonet at SDSTATE. Available online: https://www.sdstate.edu/mesonet (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Ferguson, J.C.; Moyer, M.M.; Mills, L.J.; Hoogenboom, G.; Keller, M. Modeling dormant bud cold hardiness and budbreak in twenty-three Vitis genotypes reveals variation by region of origin. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2014, 65, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.C.; Tarara, J.M.; Mills, L.J.; Grove, G.G.; Keller, M. Dynamic thermal time model of cold hardiness for dormant grapevine buds. Ann. Bot. 2011, 107, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londo, J.P.; Johnson, L.M. Variation in the chilling requirement and budburst rate of wild Vitis species. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 106, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, G.; Early, J.; Martin, G.; Darnell, R. Endo-, para-, and ecodormancy: Physiological terminology and classification for dormancy research. HortScience 1987, 22, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Londo, J.; Kovaleski, A.P. Deconstructing cold hardiness: Variation in supercooling ability and chilling requirements in the wild grapevine Vitis riparia. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2019, 25, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchigami, L.; Weiser, C.; Kobayashi, K.; Timmis, R.; Gusta, L. A degree growth stage (GS) model and cold acclimation in temperate woody plants. Plant cold hardiness and freezing stress. Mech. Crop. Implic. 1982, 2, 93–116. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, M.; Fuhrer, J.; Holzkämper, A. Changing risk of spring frost damage in grapevines due to climate change? A case study in the Swiss Rhone Valley. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2018, 62, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, E.; Sudharma, K.N.; Ganesch, A.; Brühl, U.; Hundemer, M.; Kecke, S.; Mahler-Ries, A.; Marx, G.; Schreiber, T.; Walk, M.; et al. 30 years VIVC—Vitis International Variety Catalogue. In Proceedings of the XI International Conference on Grapevine Breeding and Genetics, Beijing, China, 28 July–2 August 2014; Available online: www.vivc.de (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Okie, W. Register of new fruit and nut varieties. HortScience 2004, 39, 1509–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luby, J.; Hemstad, P. Grape plant named ‘Frontenac gris’. U.S. Patent Application No. 10/775,435, 25 April 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Okie, W. Register of new fruit and nut varieties list 41. HortScience 2002, 37, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemstad, P.; Luby, J. Grapevine plant named ‘Marquette’. U.S. Patent Application No. 11/580,356, 16 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- USDA. United States Department of Agriculture. USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Available online: https://mauroseed.com/pages/usda-planting-zone-map?gclid=Cj0KCQiAlZH_BRCgARIsAAZHSBlLbpQSJzHpikz5SGDi1FCbvorASxtrspMSoGrDJjBSCyaiENEtRSUaAgawEALw_wcB (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Coombe, B.G. Growth stages of the grapevine: Adoption of a system for identifying grapevine growth stages. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 1995, 1, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokoozlian, N. Chilling Temperature and Duration Interact on the Budbreak of ‘Perlette’ Grapevine Cuttings. HortScience 1999, 34, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelle, W. Psych: Procedures for Psychological, Psychometric, and Personality Research; Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, T.K.; Cook, M.K. Seasonal deacclimation patterns of three grape cultivars at constant, warm temperature. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1992, 43, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, T.; Moore, J. Cold hardiness in grape cultivar development. Fruit Var. J. 1991, 45, 26–28. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, T.F.; Moore, J.; George, M.F. Primary bud hardiness of four genotypes of grapes in Arkansas. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1991, 116, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.K.; Cook, M.K. Cold hardiness of dormant buds of grape cultivars: Comparison of thermal analysis and field survival. HortScience 1994, 29, 1453–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.R.; Wolf, T.K.; Warren, M.K. Thermal Analysis of Dormant Buds of Two Muscadine Grape Cultivars and of Vitis labrusca L.‘Mars’. HortScience 1996, 31, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanliang Gu, S.; Shufu Dong, S.; Jianqiang Li, J.; Susanne Howard, S. Acclimation and deacclimation of primary bud cold hardiness in ‘Norton’, ‘Vignoles’ and ‘St. Vincent’grapevines. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragin, J.; Serpe, M.; Keller, M.; Shellie, K. Dormancy and cold hardiness transitions in winegrape cultivars Chardonnay and Cabernet Sauvignon. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 2017, 68, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atucha, A.; Hedtcke, J.; Workmaster, B.A. Evaluation of cold-climate interspecific hybrid wine grape cultivars for the upper Midwest. J. Am. Pomol. Soc 2018, 72, 80–93. [Google Scholar]
- Berkett, L.P.; Bradshaw, T.L.; Kingsley-Richards, S.L.; Cromwell, M.L. 2008 Grape Bud Survival on Eight Winegrape Cultivars in Vermont. In Proceedings of the 2nd Annual National Viticulture Research Conference, University of California-Davis, Davis, CA, USA, 9–11 July 2008; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Domoto, P.A.; Nonnecke, G.R.; Hannan, J.M.; Portz, D.N.; Riesselman, L.B.; Havlovic, B.J.; Howell, N.P.; Pecinovsky, K.T.; Van Dee, K. 2003 Wine Grape Cultivar Trial Performance; RFR A1039; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Domoto, P.A.; Nonnecke, G.R.; Tabor, P.; Riesselman, L.B. Cold Hardy Wine Grape Cultivar Trial; RFR A1214; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kovaleski, A.P.; Reisch, B.I.; Londo, J.P. Deacclimation kinetics as a quantitative phenotype for delineating the dormancy transition and thermal efficiency for budbreak in Vitis species. AoB Plants 2018, 10, ply066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).