Water Use and Yield Responses of Chile Pepper Cultivars Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Reverse Osmosis Concentrate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Set Up
2.2. Saline Irrigation Treatments
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Salinity-Yield Response Equations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
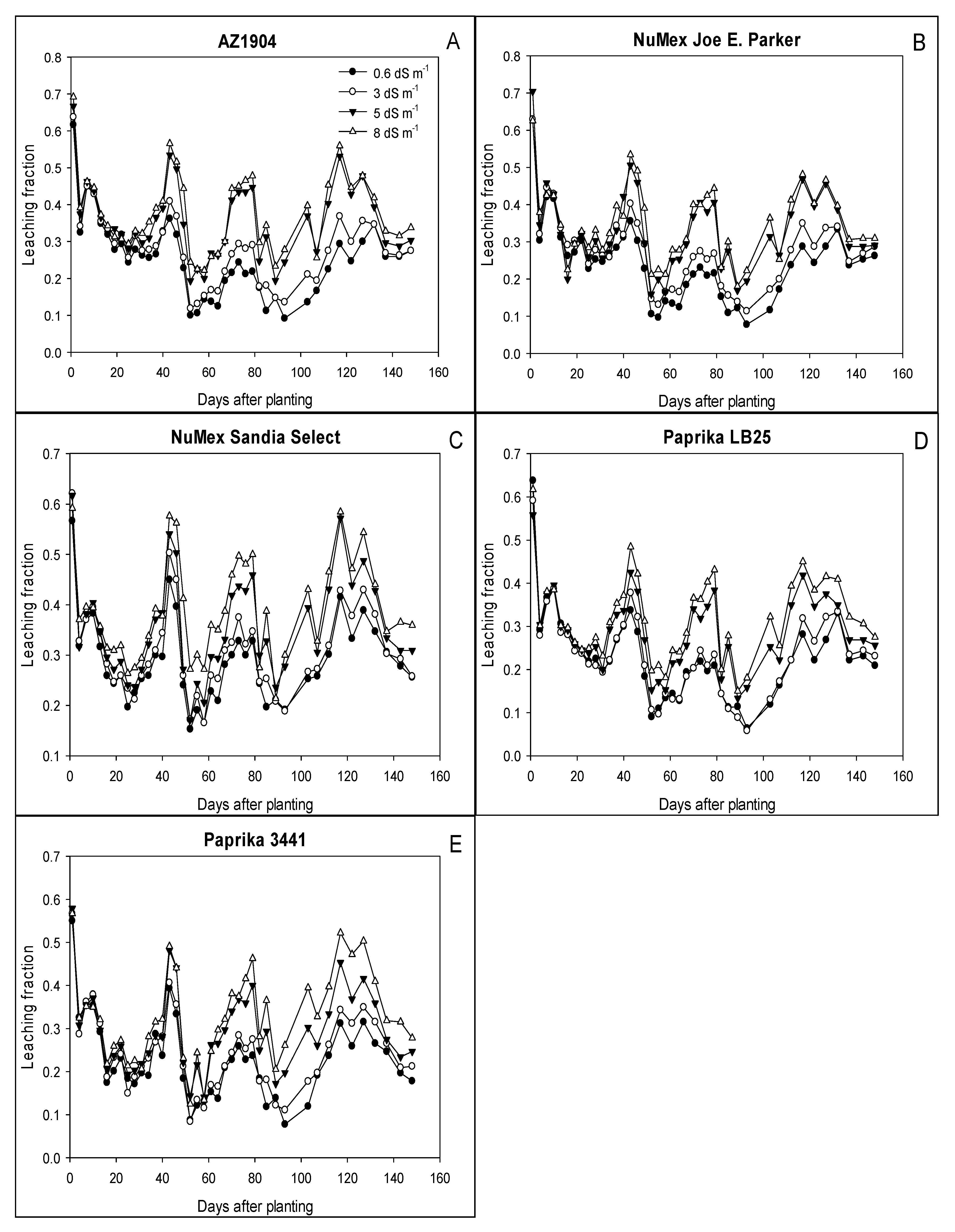
3.1. Leaching Fraction over Growing Season
3.2. Water Balance
3.3. Water Use Efficiency
3.4. Accumulation of Mg2+, Ca2+ and Na+ Cations in Soil
3.5. Yield Responses to Root-Zone Salinity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neill, M.P.; Dobrowolski, J.P. Water and agriculture in a changing climate. HortScience 2011, 46, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Saini, R.K.; Singh, S.; Sharma, S.P. Potential of integrating biochar and deficit irrigation strategies for sustaining vegetable production in water-limited regions: A review. HortScience 2019, 54, 1872–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J. Increasing agricultural water use efficiency to meet future food production. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 82, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternak, D.; De Malach, Y. Irrigation with brackish water under desert conditions X. Irrigation management of tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum Mills) on desert sand dunes. Agric. Water Manag. 1995, 28, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayars, J.E.; Schoneman, R.A. Irrigating field crops in the presence of saline groundwater. Irrig. Drain. 2006, 55, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbs, B.J.; Boghici, R.N.; Hayes, M.E.; Ashworth, J.B.; Hanson, A.N.; Samani, Z.A.; Kennedy, J.F.; Creel, R.J. Transboundary Aquifers of the El Paso/Ciudad Juarez/Las Cruces Region; Contract Report; Texas Water Development Board, Austin & New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 1997; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Flores, A.M.; Shukla, M.K.; Daniel, D.; Ulery, A.L.; Schutte, B.J.; Picchioni, G.A.; Fernald, S. Evapotranspiration changes with irrigation using saline groundwater and RO concentrate. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 131, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Russo, D.; Silber, A.; Or, D. Balancing water scarcity and quality for sustainable irrigated agriculture. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3419–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankarla, V.; Shukla, M.; VanLeeuwen, D.; Schutte, B.; Picchioni, G. Growth, evapotranspiration, and ion uptake characteristics of alfalfa and triticale irrigated with brackish groundwater and desalination concentrate. Agronomy 2019, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.F.; Shukla, M.K.; Stringam, B.; Picchioni, G.A.; Gard, C. Irrigation with brackish water changes evapotranspiration, growth and ion uptake of halophytes. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, E.P.; Brown, J.J.; Blumwald, E. Salt tolerance and crop potential of halophytes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 227–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Läuchli, A.; Epstein, E. Plant responses to saline and sodic conditions. Agric. Salin. Assess. Manag. 1990, 71, 113–137. [Google Scholar]
- Läuchli, A.; Grattan, S. Plant growth and development under salinity stress. In Advances in Molecular Breeding toward Drought and Salt Tolerant Crops; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Katerji, N.; Van Hoorn, J.; Hamdy, A.; Mastrorilli, M. Salinity effect on crop development and yield, analysis of salt tolerance according to several classification methods. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 62, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nass, U. Quick Stats; USDA-NASS: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V.; Hoffman, G.J. Crop salt tolerance—Current assessment. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1977, 103, 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Chartzoulakis, K.; Klapaki, G. Response of two greenhouse pepper hybrids to NaCl salinity during different growth stages. Sci. Hortic. 2000, 86, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.; Garrido, C.; Carvajal, M.; Martinez, V. Yield and fruit quality of pepper plants under sulphate and chloride salinity. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2002, 77, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornillon, P.; Palloix, A. Influence of sodium chloride on the growth and mineral nutrition of pepper cultivars. J. Plant Nutr. 1997, 20, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Rodriguez, D.S.; Crosby, K.; Leskovar, D.; Jifon, J. Rapid screening for relative salt tolerance among chile pepper genotypes. HortScience 2010, 45, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktas, H.; Abak, K.; Cakmak, I. Genotypic variation in the response of pepper to salinity. Sci. Hortic. 2006, 110, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattan, S.; Grieve, C. Salinity-mineral nutrient relations in horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 1998, 78, 127–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.T.; Grieve, C.M. Mineral nutrition, growth, and germination of Antirrhinum majus L.(snapdragon) when produced under increasingly saline conditions. HortScience 2008, 43, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baath, G.S.; Shukla, M.K.; Bosland, P.W.; Steiner, R.L.; Walker, S.J. Irrigation water salinity influences at various growth stages of Capsicum annuum. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shani, U.; Dudley, L. Field studies of crop response to water and salt stress. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripler, E.; Ben-Gal, A.; Shani, U. Consequence of salinity and excess boron on growth, evapotranspiration and ion uptake in date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L., cv. Medjool). Plant Soil 2007, 297, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Shukla, M.K.; Bosland, P.W.; Steiner, R.L. Physiological responses of greenhouse-grown drip-irrigated chile pepper under partial root zone drying. HortScience 2015, 50, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavlak, R.G.; Horneck, D.A.; Miller, R.O. Plant, Soil, and Water Reference Methods for the Western Region; Western Rural Development Center: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Hoffman, G.F. Analysis of crop salt tolerance data. In Soil Salinity under Irrigation: Processes and Management; Ecology studies; Shainberg, I., Shalhevet, J., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 258–271. [Google Scholar]
- Institute, S. Base SAS 9.4 Procedures Guide; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Grothendieck, G. Non-linear regression with brute force. R package nls2. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=nls2 (accessed on 30 December 2019).
- Acosta-Motos, J.; Ortuño, M.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.; Hernandez, J. Plant responses to salt stress: Adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Gal, A.; Ityel, E.; Dudley, L.; Cohen, S.; Yermiyahu, U.; Presnov, E.; Zigmond, L.; Shani, U. Effect of irrigation water salinity on transpiration and on leaching requirements: A case study for bell peppers. Agric. Water Manag. 2008, 95, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, J.M.N. Irrigation with saline water: Benefits and environmental impact. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhantana, P.; Lazarovitch, N. Evapotranspiration, crop coefficient and growth of two young pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) varieties under salt stress. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaee, M.; Schmidhalter, U. Water integration by plants root under non-uniform soil salinity. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 27, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, X.; Lei, J.; Li, S.; Hill, R.; Zhao, Y. The effects of soil salt crusts on soil evaporation and chemical changes in different ages of Taklimakan Desert Shelterbelts. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2013, 13, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Karaki, G.N. Growth of mycorrhizal tomato and mineral acquisition under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 2000, 10, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtseven, E.; Kesmez, G.; Ünlükara, A. The effects of water salinity and potassium levels on yield, fruit quality and water consumption of a native central anatolian tomato species (Lycopersiconesculantum). Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina-Sánchez, A.; Romero-Aranda, R.; Cuartero, J. Plant water uptake and water use efficiency of greenhouse tomato cultivars irrigated with saline water. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, B.; Grattan, S.R.; Fulton, A. Agricultural salinity and drainage. In University of California Irrigation Program; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Kandiah, A.; Marshali, A.M. The Use of Saline Waters for Crop Production; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, E.V.; Poss, J.A.; Hoffman, G.J. Salt tolerance of plants. Appl. Agric. Res. 1986, 1, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- De Pascale, S.; Ruggiero, C.; Barbieri, G.; Maggio, A. Physiological responses of pepper to salinity and drought. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2003, 128, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Genuchten, M.T.; Gupta, S. A reassessment of the crop tolerance response function. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1993, 41, 730737. [Google Scholar]
- Ehret, D.; Redmann, R.; Harvey, B.; Cipywnyk, A. Salinity-induced calcium deficiencies in wheat and barley. Plant Soil 1990, 128, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, G.R.; Spurr, A.R. Salt reponses of lettuce to salinity. II. Effect of calcium on growth and mineral status. J. Plant Nutr. 1986, 9, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañero, F.J.; Martínez-Ballesta, M.C.; Teruel, J.A.; Carvajal, M. New evidence about the relationship between water channel activity and calcium in salinity-stressed pepper plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, D. Calcium regulation in plant cell and his role in signalling. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 1995, 46, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| EC dS m−1 | Ion Concentration (meq/L) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Ca | Na | K | Cl | SO4 | ||
| Tap water | 0.6 | 0.75 (0.01) | 2.28 (0.01) | 2.73 (0.37) | 0.15 (0.01) | 1.64 (0.07) | 1.58 (0.02) |
| Well 1 | 3 | 8.65 (0.01) | 11.90 (0.38) | 8.94 (0.18) | 0.16 (0.00) | 11.91 (0.05) | 18.70 (0.79) |
| Well 2 | 5 | 15.24 (0.28) | 17.60 (2.08) | 19.04 (1.92) | 0.21 (0.02) | 16.86 (1.72) | 38.78 (3.56) |
| RO conc. | 8 | 25.81 (0.16) | 29.43 (2.69) | 33.51 (2.96) | 0.37 (0.06) | 31.23 (5.04) | 67.15 (7.43) |
| Treatment | Deep Percolation (cm) | Change in Storage (cm) | Evapotranspiration (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity (S; dS m−1) | |||
| 0.6 | 25.06 d | 1.56 a | 76.99 a |
| 3 | 28.06 c | 1.48 ab | 74.07 b |
| 5 | 33.26 b | 1.42 bc | 68.93 c |
| 8 | 36.73 a | 1.34 c | 65.55 d |
| LSD (0.05) | 1.36 | 0.09 | 1.37 |
| Cutivars (C) | |||
| AZ 1904 | 32.55 b | 1.42 a | 69.65 c |
| NuMex Joe E. Parker | 30.80 c | 1.45 a | 71.37 b |
| NuMex Sandia Select | 34.77 a | 1.50 a | 67.34 d |
| LB 25 | 27.56 d | 1.45 a | 74.60 a |
| 3441 | 28.22 d | 1.43 a | 73.97 a |
| LSD (0.05) | 1.52 | 0.11 | 1.53 |
| C X S | NS | NS | NS |
| Piecewise Linear Function | |||||
| a (dS m−1) | b (dS m−1)−1 | r2 | RSS | N | |
| AZ1904 | 1.19 | 0.044 | 0.88 | 0.21 | 32 |
| NuMex Joe E. Parker | 1.04 | 0.045 | 0.90 | 0.24 | 32 |
| Numex Sandia Select | 1.12 | 0.045 | 0.89 | 0.25 | 32 |
| Paprika LB25 | 1.33 | 0.046 | 0.85 | 0.25 | 32 |
| Paprika 3441 | 1.09 | 0.038 | 0.89 | 0.17 | 32 |
| All cultivars | 1.10 | 0.043 | 0.87 | 1.18 | 160 |
| Sigmoid non-linear function | |||||
| c50 (dS m−1) | p | r2 | RSS | N | |
| AZ1904 | 12.22 | 2.110 | 0.89 | 0.18 | 32 |
| NuMex Joe E. Parker | 11.61 | 1.633 | 0.91 | 0.19 | 32 |
| Numex Sandia Select | 10.75 | 1.262 | 0.89 | 0.32 | 32 |
| Paprika LB25 | 12.01 | 1.761 | 0.87 | 0.16 | 32 |
| Paprika 3441 | 13.55 | 1.537 | 0.90 | 0.12 | 32 |
| All cultivars | 12.11 | 1.618 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 160 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baath, G.S.; K. Shukla, M.; Bosland, P.W.; Walker, S.J.; Saini, R.K.; Shaw, R. Water Use and Yield Responses of Chile Pepper Cultivars Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Horticulturae 2020, 6, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6020027
Baath GS, K. Shukla M, Bosland PW, Walker SJ, Saini RK, Shaw R. Water Use and Yield Responses of Chile Pepper Cultivars Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Horticulturae. 2020; 6(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaath, Gurjinder S., Manoj K. Shukla, Paul W. Bosland, Stephanie J. Walker, Rupinder K. Saini, and Randall Shaw. 2020. "Water Use and Yield Responses of Chile Pepper Cultivars Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Reverse Osmosis Concentrate" Horticulturae 6, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6020027
APA StyleBaath, G. S., K. Shukla, M., Bosland, P. W., Walker, S. J., Saini, R. K., & Shaw, R. (2020). Water Use and Yield Responses of Chile Pepper Cultivars Irrigated with Brackish Groundwater and Reverse Osmosis Concentrate. Horticulturae, 6(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6020027






