An Integrated Analysis of WRKY Genes in Autotetraploid Bupleurum chinense: Evolution, Stress Response, and Impact on Saikosaponin Biosynthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Sequence Retrieval
2.3. Identification and Characterization of WRKY in B. chinense
2.4. Classification of BcWRKYs
2.5. Chromosomal Locations, Phylogenetic and Collinearity Analysis for BcWRKYs Genes
2.6. Analysis of the Expression Profiles of WRKYs in B. chinense Based on RNA-Seq
2.7. Expression Profiling of BcWRKYs and Saikosaponin Biosynthetic Genes Under Abiotic Stress by qRT-PCR
2.8. Determination of Saikosaponin Contents
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of BcWRKY Genes
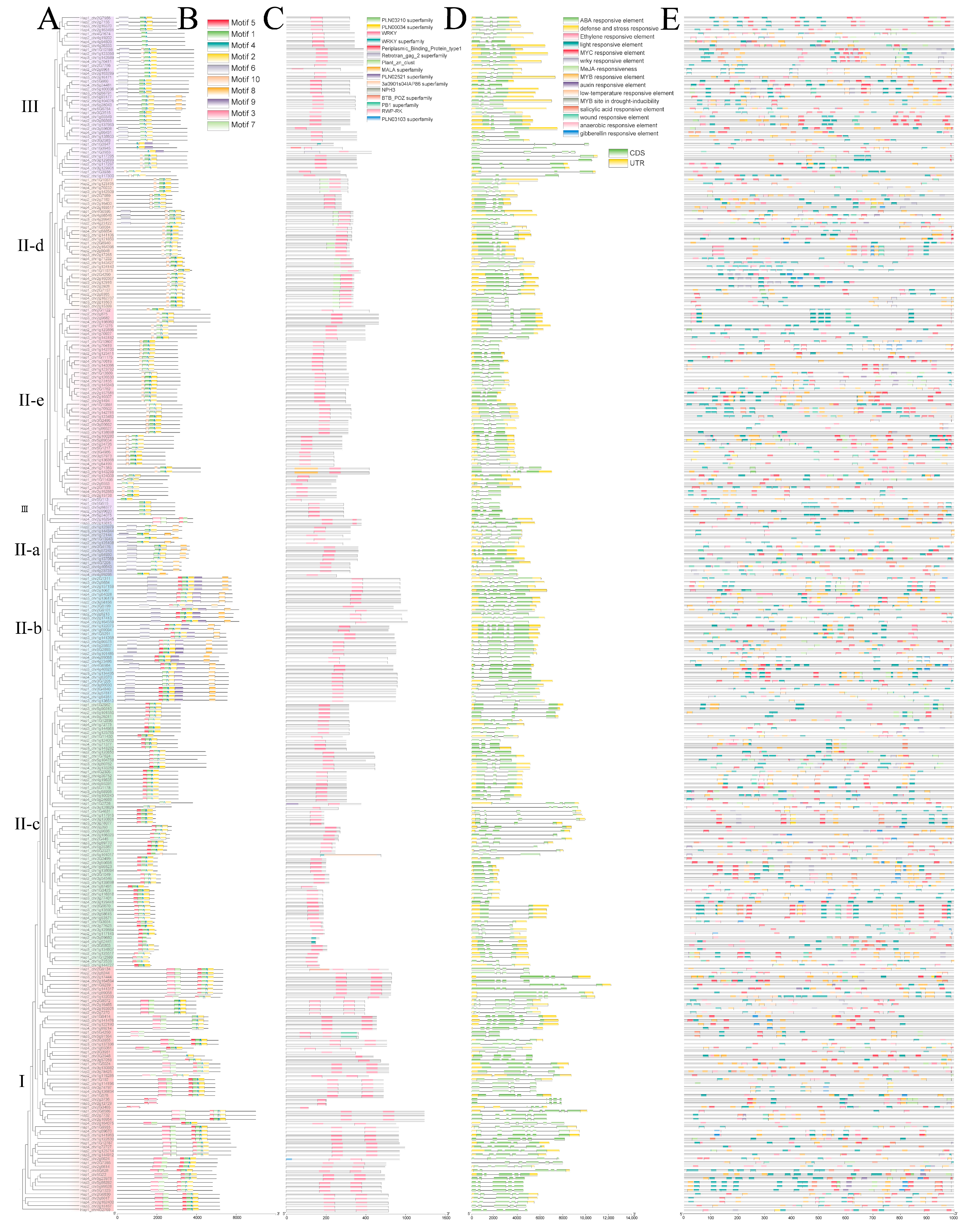
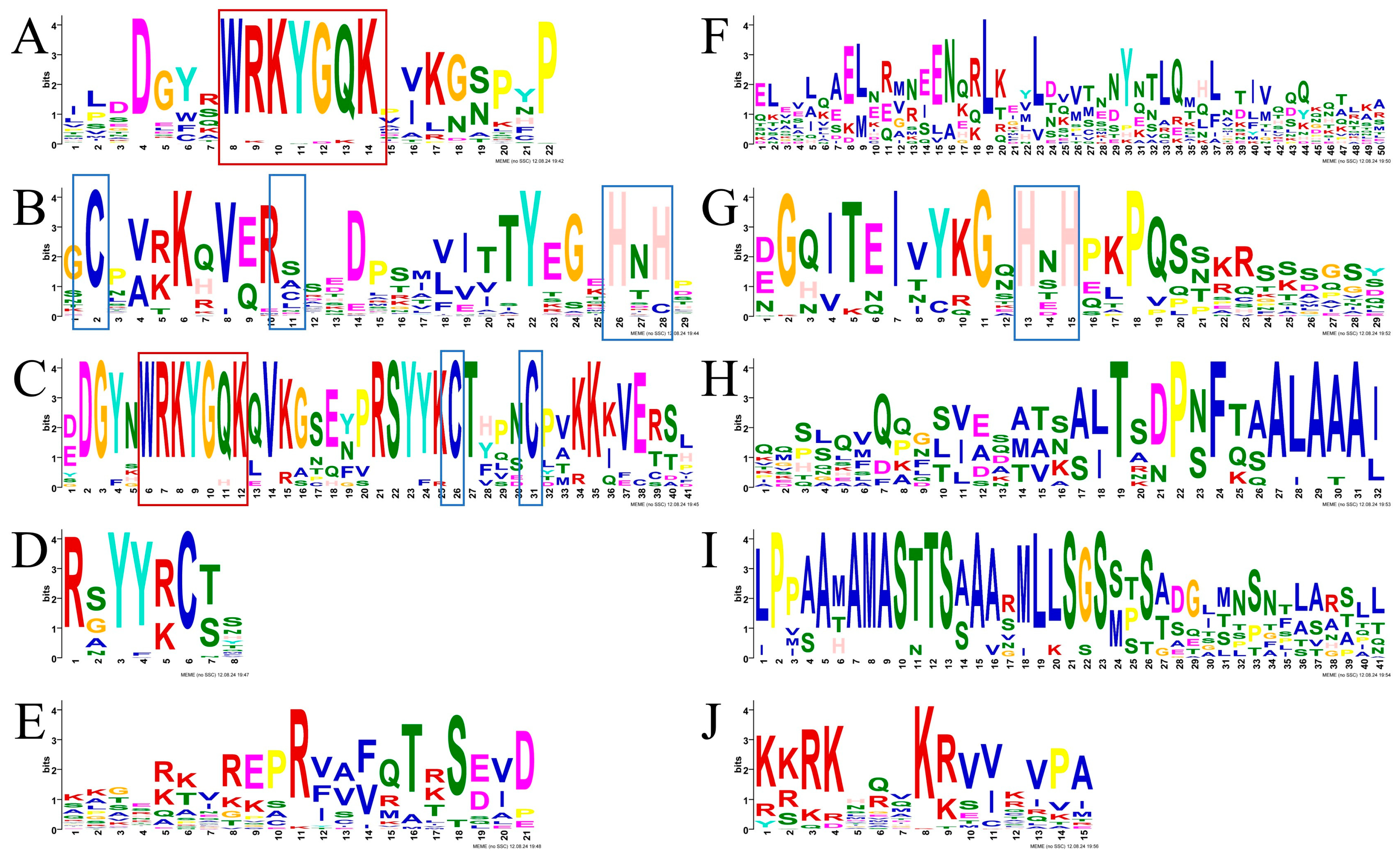
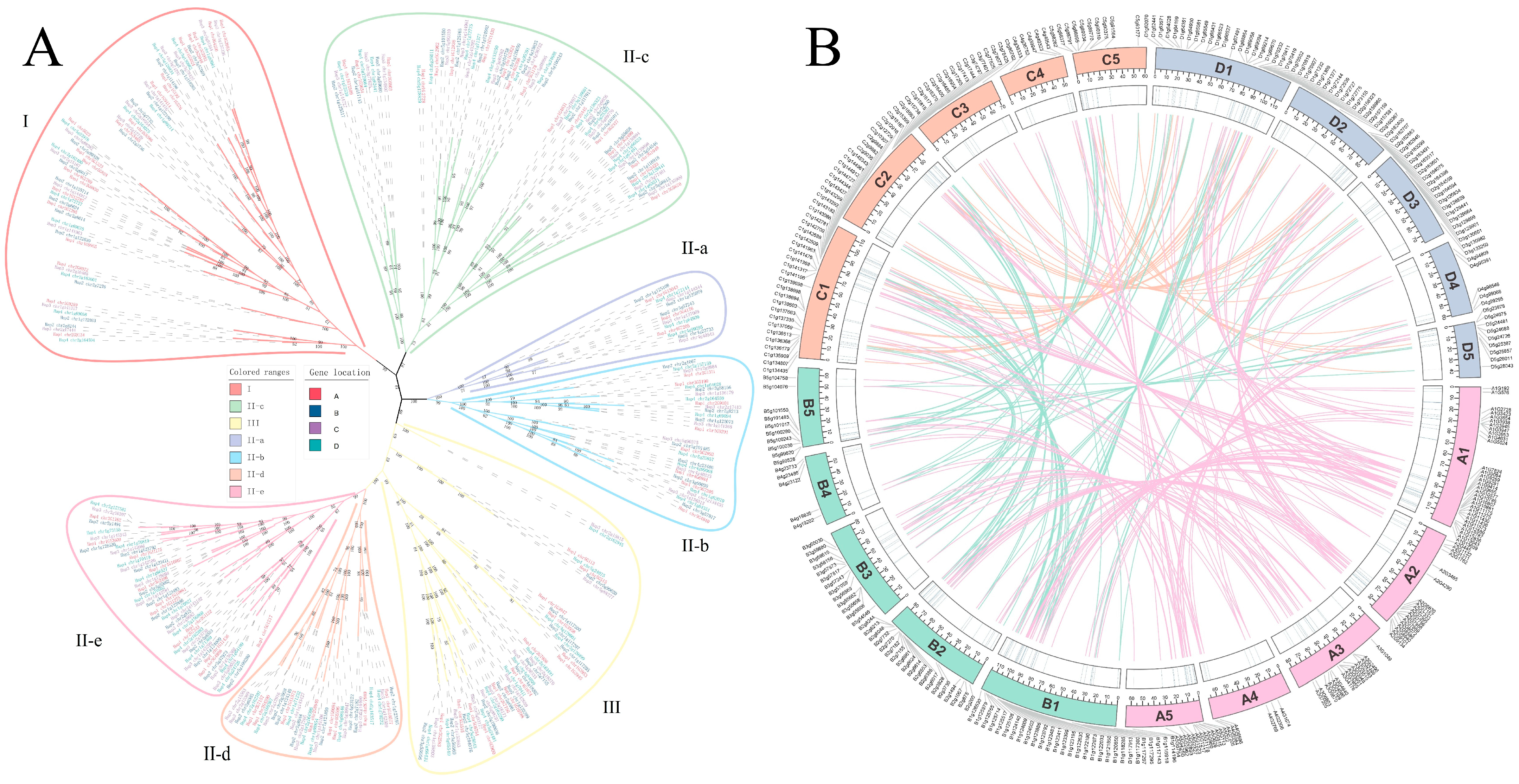
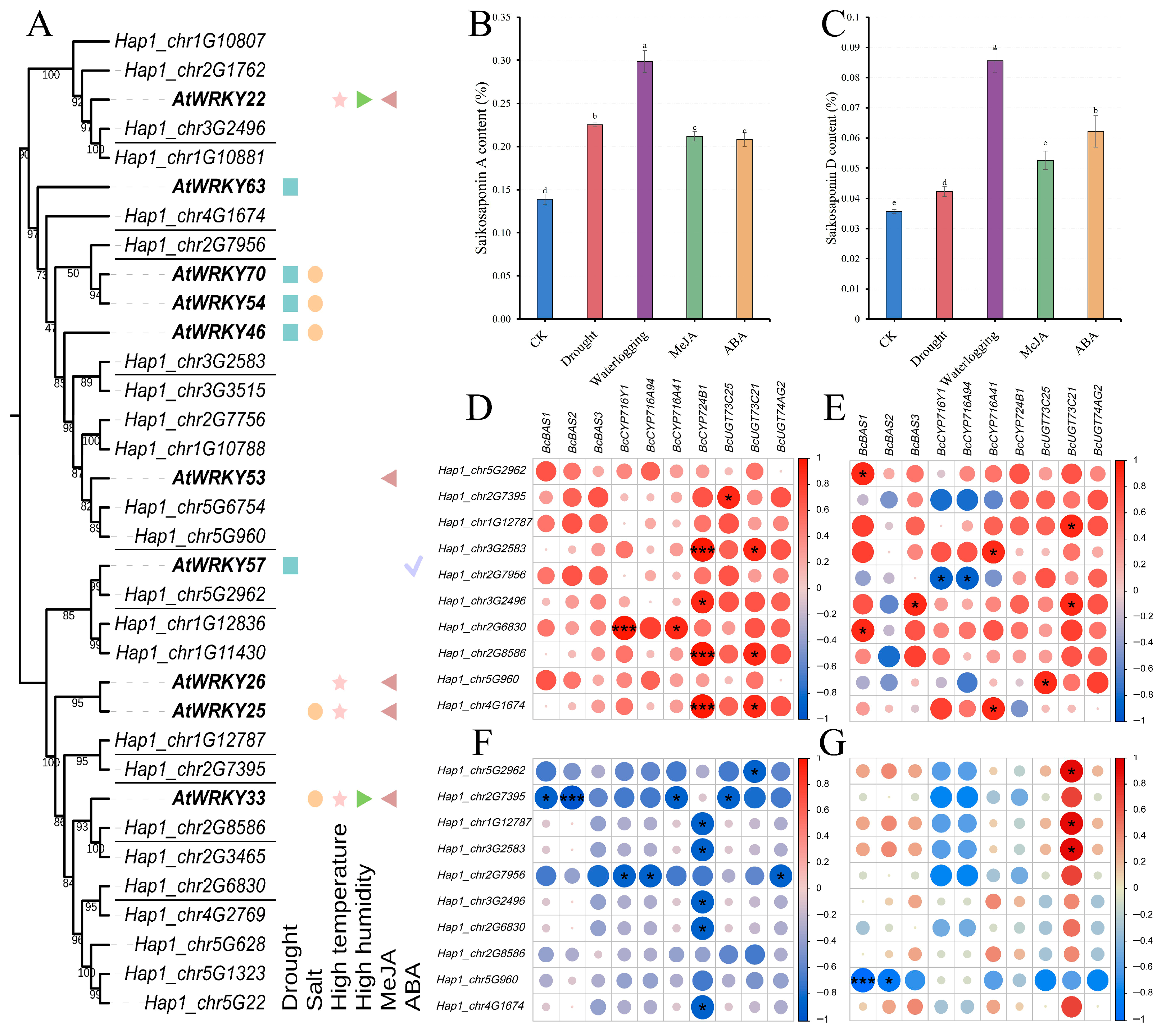
3.2. Phylogenetic Classification and Conserved Domain Analysis
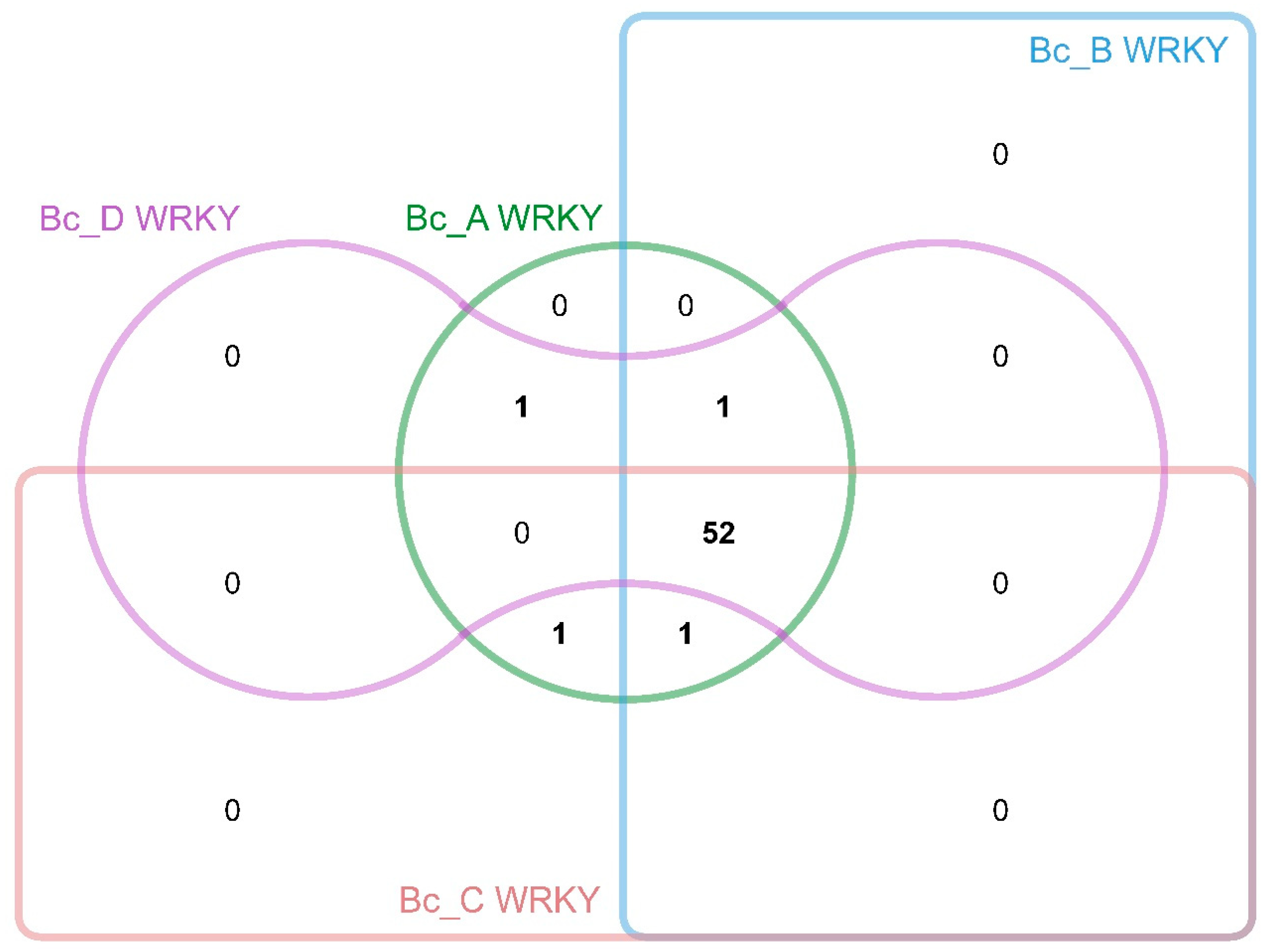
3.3. Chromosomal Distribution and Gene Duplication Patterns
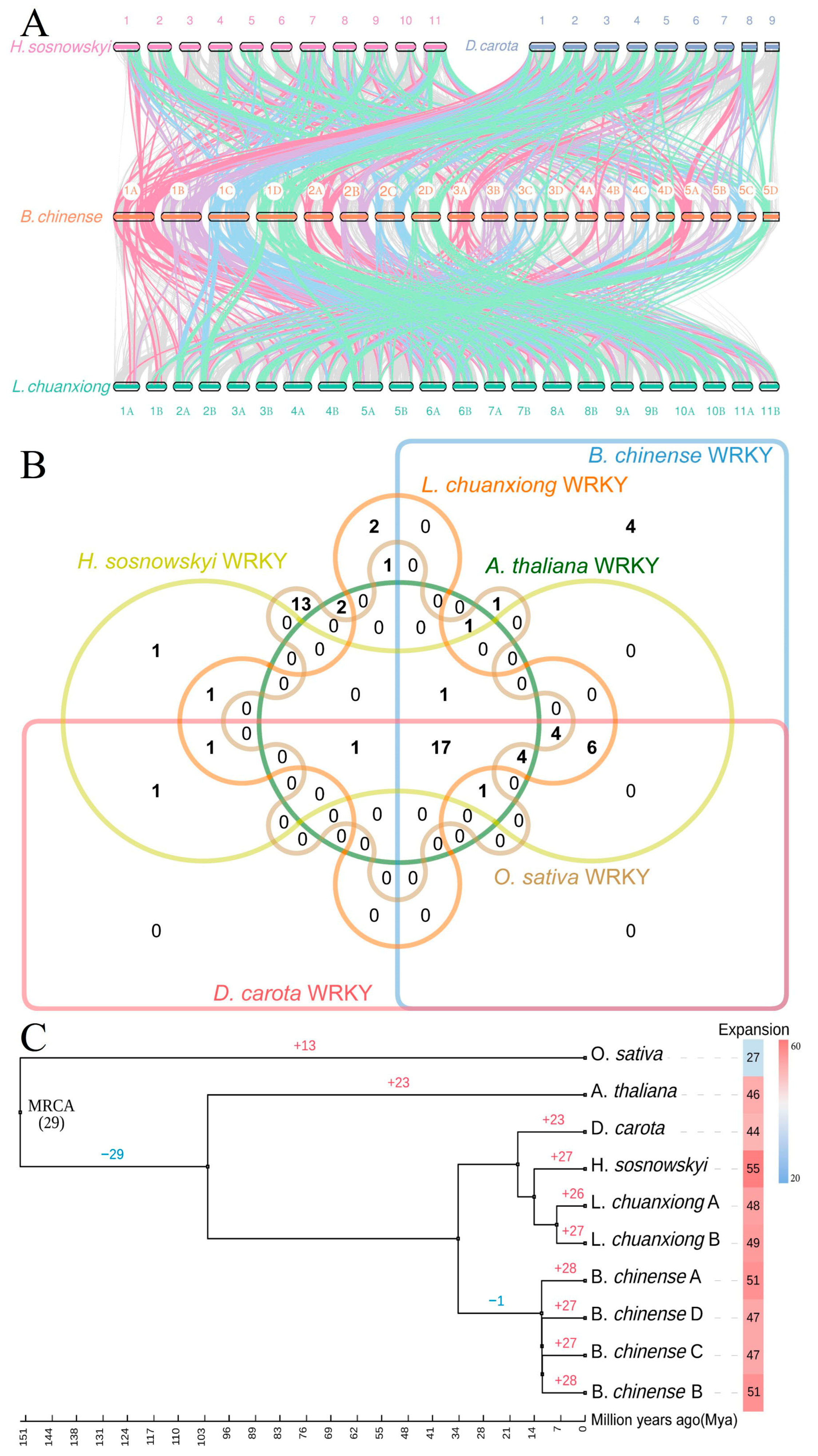
3.4. Comparative Genomics and Evolutionary Dynamics of BcWRKYs in Apiaceae Family
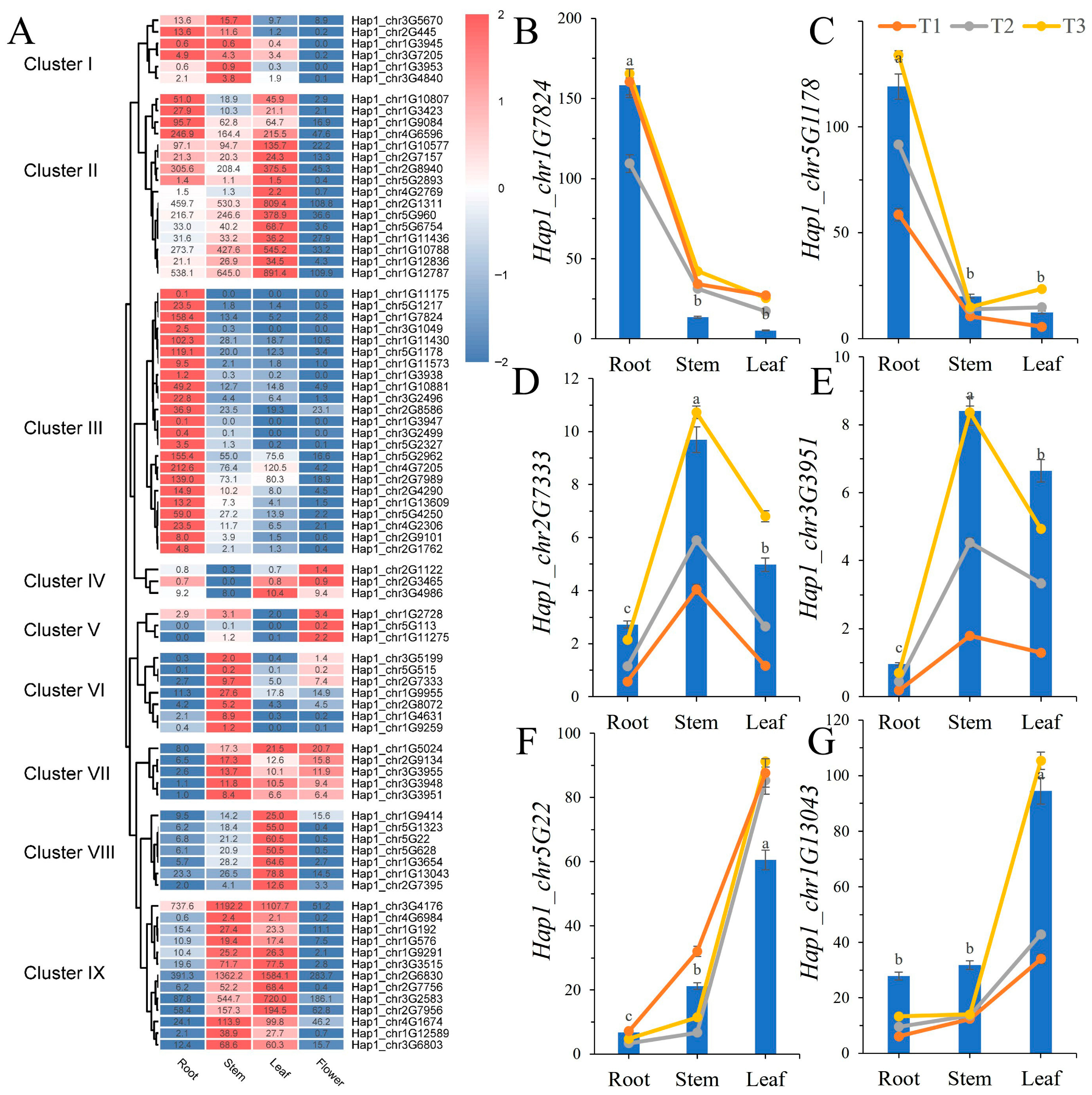
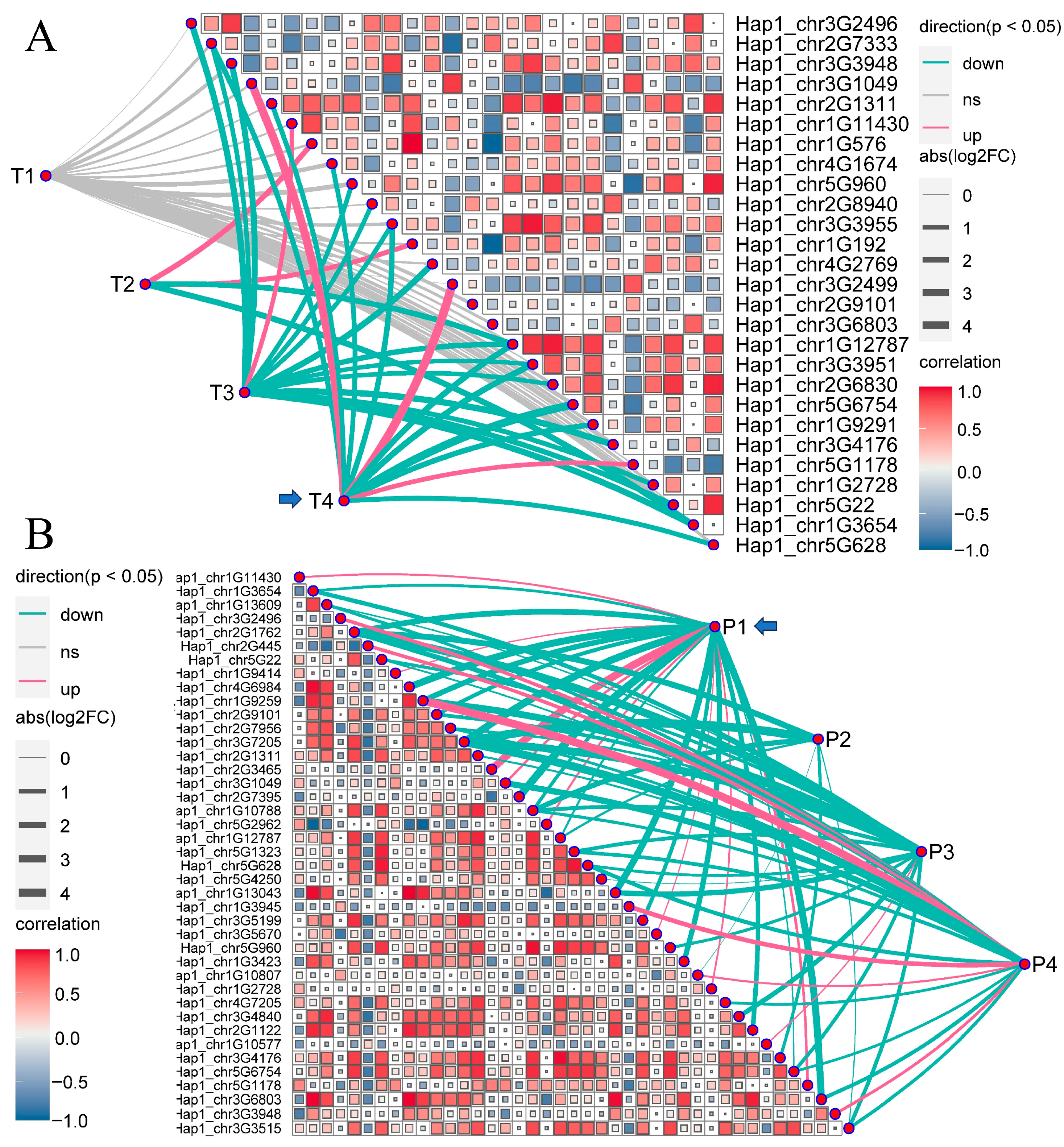
3.5. Expression Profiles of BcWRKY Genes in B. chinense by RNA-Seq Analysis
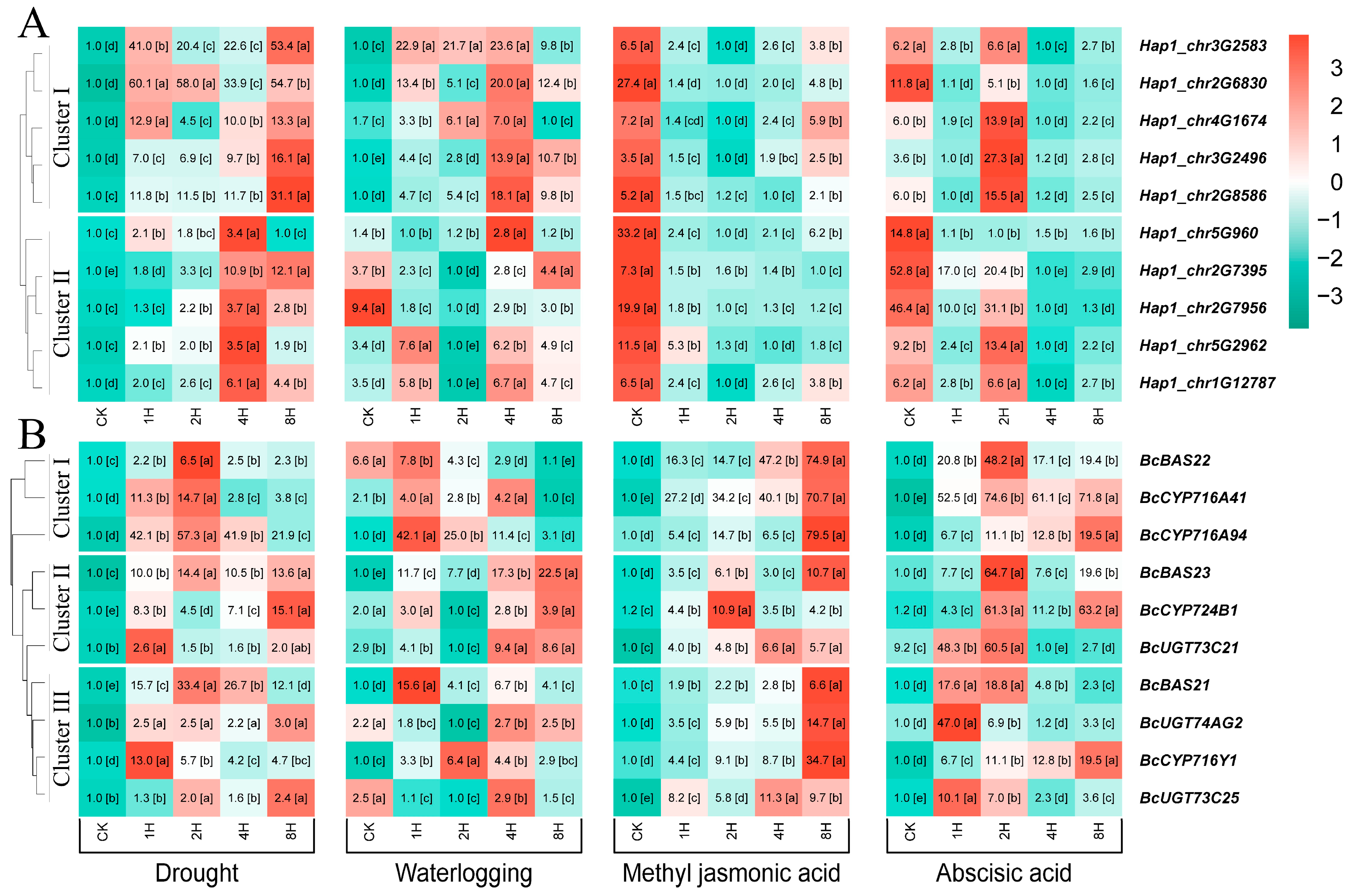
3.6. Transcriptome-Based Expression Patterns of BcWRKY Genes in Abiotic Stress
3.7. Expression Profile of BcWRKY Genes Under Abiotic Stresses Treatment
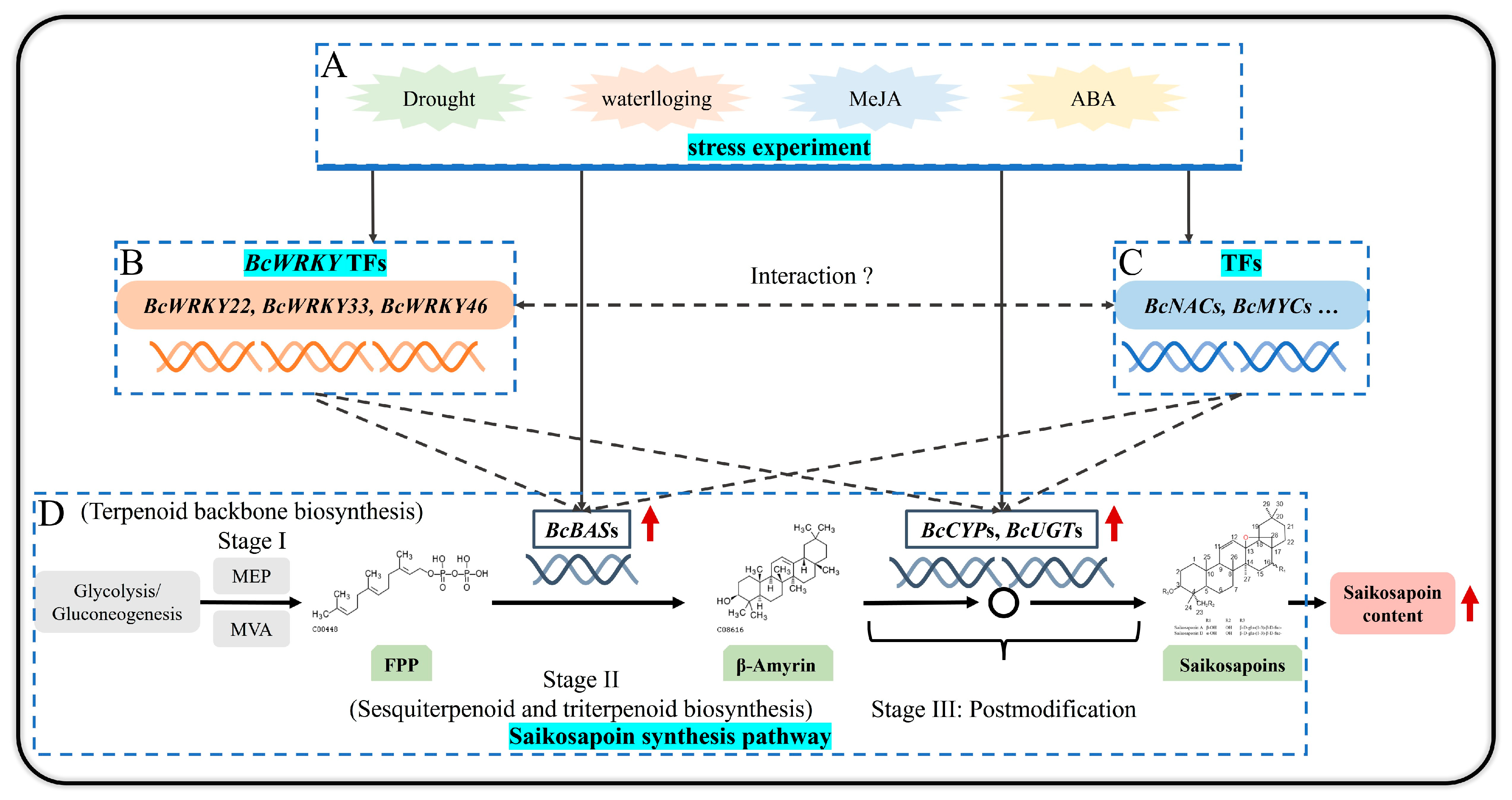
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Gene ID | Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′→3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hap1_chr1G12787 | BcWRKY33-2 | TCATCCCAAGCCTCAGTCAAC | TGCAGCAGAATCCATTTGCC |
| Hap1_chr2G8586 | BcWRKY33-1 | TTGATGATGGATACCGCTGGAG | AGCCTGCATTTGTGCACTTG |
| Hap1_chr2G6830 | BcWRKY33 | ACAACCCCGGAAAATTCTGC | TTGCCTCGGGTTCATTTTCC |
| Hap1_chr2G7956 | BcWRKY70 | AGCTATTGTGAAGGCTGCAC | AGATTTGGGTTGCGAAGTGC |
| Hap1_chr2G7395 | BcWRKY33-3 | AGCAGCCACTCTTTGAACAG | ATGTTGGTGCCCTCAAACTG |
| Hap1_chr3G2583 | BcWRKY46 | TAATGCACAAGGCTGCTTGG | TGGTTCTGAGCCTTGTTTGC |
| Hap1_chr3G2496 | BcWRKY22 | ACCAAATTGCTCTGCTTCGG | AAGGCGTATCGGAAGACCAC |
| Hap1_chr4G1674 | BcWRKY63 | AAGATGAGCTCGTCTGTGGTG | TTTGTTGCTTGGCACCCTTG |
| Hap1_chr5G960 | BcWRKY53 | AGACAACGGAGTGGAAAGTTCC | TGTGGCGCAACAACTTTGAG |
| Hap1_chr5G2962 | BcWRKY57 | TTGCCTGAAAAGTCGACAGC | TCGCTCTTGGTCACAAATGC |
| Hap1_chr1G5366 | BcBAS21 | TGGCACTGTGACAGCAATAC | ACCACATTTTCGCTGGATGC |
| Hap1_chr1G5523 | BcBAS22 | TGATGGTGGTTGGGGAGAAAG | AAACCCATTGTTGCCCATGC |
| Hap1_chr1G5343 | BcBAS23 | ATGCCAAGAACCTTGTTCGG | TGGCTCAAGCACTTGTTTGG |
| Hap1_chr5G3928 | BcCYP716Y1 | GGTTGCGCAAAAACATGGTG | AGGTCTCGCAATTCCAATGC |
| Hap1_chr3G7452 | BcCYP716A94 | AACCCACAGAAACGCAGAAG | TTTCCAGGGCACATTCTTGG |
| Hap1_chr1G5524 | BcCYP716A41 | AACTGCATCAGCCACACAAG | AAAGCACAAGCAGAGCTAGC |
| Hap1_chr2G8480 | BcCYP724B1 | AATTCCATCCGGTTGGCAAG | GAAACTGAGAGGCATGAGCATG |
| Hap1_chr1G9521 | BcUGT73C25 | TGGACCGCTAAAGTTGCATG | TGTCCGAAACGCCAACATTC |
| Hap1_chr1G9522 | BcUGT73C21 | TGTTTGCTCACCATGGCATG | CCTCAGCTGCTGGAAAATCAAG |
| Hap1_chr3G5569 | BcUGT74AG2 | ATGTTTCGTGTCCCATTGCG | ACACCCCAAACTTGTTCCAC |
References
- Eulgem, T.; Rushton, P.J.; Robatzek, S.; Somssich, I.E. The WRKY Superfamily of Plant Transcription Factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluttenhofer, C.; Yuan, L. Regulation of Specialized Metabolism by WRKY Transcription Factors. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinerson, C.I.; Rabara, R.C.; Tripathi, P.; Shen, Q.J.; Rushton, P.J. The Evolution of WRKY Transcription Factors. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rushton, P.J.; Somssich, I.E.; Ringler, P.; Shen, Q.J. WRKY Transcription Factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Pang, S.; Lu, Z.; Jin, B. Function and Mechanism of WRKY Transcription Factors in Abiotic Stress Responses of Plants. Plants 2020, 9, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY Transcription Factors and Plant Defense Responses: Latest Discoveries and Future Prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, L.H.; Fischer, N.M.; Harter, K.; Kohlbacher, O.; Wanke, D. Elucidating the Evolutionary Conserved DNA-Binding Specificities of WRKY Transcription Factors by Molecular Dynamics and in Vitro Binding Assays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 9764–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-H.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Xie, P.; Gu, C.; Li, K.; Wang, D.-C.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Fan, Z.-H.; Wang, C.-J.; Wang, Y.-P.; et al. Transcription Factors WRKY70 and WRKY11 Served as Regulators in Rhizobacterium bacillus Cereus AR156-Induced Systemic Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae Pv. Tomato DC3000 in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arraño-Salinas, P.; Domínguez-Figueroa, J.; Herrera-Vásquez, A.; Zavala, D.; Medina, J.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Meneses, C.; Canessa, P.; Moreno, A.A.; Blanco-Herrera, F. WRKY7, -11 and -17 Transcription Factors Are Modulators of the bZIP28 Branch of the Unfolded Protein Response during PAMP-Triggered Immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2018, 277, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Bai, X.; Wang, X.; Chu, C. OsWRKY71, a Rice Transcription Factor, Is Involved in Rice Defense Response. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 164, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, Y.; Xie, L.; Hao, X.; Liu, H.; Qin, W.; Wang, C.; Yan, X.; Wu-Zhang, K.; Yao, X.; et al. AaWRKY17, a Positive Regulator of Artemisinin Biosynthesis, Is Involved in Resistance to Pseudomonas syringae in Artemisia annua. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, D.; Zhao, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, X. Group IIc WRKY Transcription Factors Regulate Cotton Resistance to Fusarium oxysporum by Promoting GhMKK2-Mediated Flavonoid Biosynthesis. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Cai, S.; Haughn, G.; Page, J.E. Three Novel Transcription Factors Involved in Cannabinoid Biosynthesis in Cannabis sativa L. Plant Mol. Biol. 2021, 106, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Cao, X.; Mi, Y.; Sun, W.; Meng, X.; Chen, W.; Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of WRKY Gene Family in High-CBD Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Identification of the WRKY Genes Involved in Abiotic Stress Responses and Regulation Cannabinoid Accumulation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, M.L.; Wink, M. Genus Bupleurum: A Review of Its Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Modes of Action. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Guo, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, L.; Wei, J.; Xiao, P. A Comprehensive Review on Traditional and Modern Research of the Genus Bupleurum (Bupleurum L., Apiaceae) in Recent 10 Years. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.-L.; Cai, X.; Hu, Z.-H.; Ni, X.-L. Localization and Dynamic Change of Saikosaponin in Root of Bupleurum chinense. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, P.; Chen, H.; Hou, D. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Insights into the Molecular Mechanism Underlying the Effect of MeJA Treatment on the Biosynthesis of Saikosaponins in Bupleurum chinense DC. Life 2023, 13, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, C.; Han, W.-J.; Zhu, C.-R.; Wei, J.-H. Recent Progress in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2021, 22, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Qiao, L.; Su, X.; Ji, B.; Dong, C. Drought Stress Stimulates the Terpenoid Backbone and Triterpenoid Biosynthesis Pathway to Promote the Synthesis of Saikosaponin in Bupleurum chinense DC. Roots. Molecules 2022, 27, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gao, K.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wei, J.; Sui, C. Identification of WRKY Transcription Factors Related to Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Adventitious Roots of Bupleurum chinense. Chin. Herb. Med. 2017, 9, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Jin, J.; Gao, G. PlantRegMap: Charting Functional Regulatory Maps in Plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1104–D1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayers, E.W.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Canese, K.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; Funk, K.; Kelly, C.; Kim, S.; et al. Database Resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D20–D26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A Comparative Platform for Green Plant Genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, B.; Chen, X.; Hou, Z.; Guo, M.; Li, C.; Sun, W.; Ji, J.; Zang, L.; Yang, S.; Fan, P.; et al. Haplotype-Phased Genome Unveils the Butylphthalide Biosynthesis and Homoploid Hybrid Origin of Ligusticum chuanxiong. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadj6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnuco, I.A.; Revuelta, M.V.; Bondino, H.G.; Brun, M.; Ten Have, A. HMMER Cut-off Threshold Tool (HMMERCTTER): Supervised Classification of Superfamily Protein Sequences with a Reliable Cut-off Threshold. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The Conserved Domain Database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Jeffryes, M.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The HMMER Web Server for Protein Sequence Similarity Search. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2017, 60, 3.15.1–3.15.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artimo, P.; Jonnalagedda, M.; Arnold, K.; Baratin, D.; Csardi, G.; de Castro, E.; Duvaud, S.; Flegel, V.; Fortier, A.; Gasteiger, E.; et al. ExPASy: SIB Bioinformatics Resource Portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W597–W603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple Sequence Alignment with High Accuracy and High Throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An Upgraded Gene Feature Visualization Server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “One for All, All for One” Bioinformatics Platform for Biological Big-Data Mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing Large Minimum Evolution Trees with Profiles Instead of a Distance Matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A Tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Suleski, M.; Craig, J.M.; Kasprowicz, A.E.; Sanderford, M.; Li, M.; Stecher, G.; Hedges, S.B. TimeTree 5: An Expanded Resource for Species Divergence Times. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Jiao, B.; Yang, Y.; Shan, L.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Xi, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. WGDI: A User-Friendly Toolkit for Evolutionary Analyses of Whole-Genome Duplications and Ancestral Karyotypes. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.K.; Vanderpool, D.; Fulton, B.; Hahn, M.W. CAFE 5 Models Variation in Evolutionary Rates among Gene Families. Bioinformatics 2021, 36, 5516–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, B.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, P.; Hou, D.; Zhao, J.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis to Reveal Major Genes of Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum chinense. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Gao, Z.; Sui, C.; Ji, H.; Jiang, J.; Xinwei, G.; Wei, J. Transcriptome Profiling of Bupleurum Chinense DC. Root Provides New Insights into the Continuous Inflorescence Removal Induced Improvements to Root Growth and Saikosaponin Biosynthesis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 160, 113085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A Fast Spliced Aligner with Low Memory Requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The R package Rsubread is easier, faster, cheaper and better for alignment and quantification of RNA sequencing reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A Scaling Normalization Method for Differential Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3—New Capabilities and Interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.-C.; Sui, C.; Chen, G.-D.; Tang, Z.-K.; Yang, C.-M.; Hou, D.-B.; Wei, J.-H. Validation of Reference Genes for Expression Analysis in Three Bupleurum Species. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulker, B.; Somssich, I.E. WRKY Transcription Factors: From DNA Binding towards Biological Function. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, J.; Chang, X.; Dong, N.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Zha, L.; Gui, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of the WRKY Gene Family Reveals Abiotic Stress Response Mechanisms in Platycodon grandiflorus. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 257, 128617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-Y.; Feng, K.; Hou, X.-L.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Z.-S.; Wang, G.-L.; Liu, J.-X.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.-S. The Genome Sequence of Celery (Apium graveolens L.), an Important Leaf Vegetable Crop Rich in Apigenin in the Apiaceae Family. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelkunov, M.I.; Shtratnikova, V.Y.; Klepikova, A.V.; Makarenko, M.S.; Omelchenko, D.O.; Novikova, L.A.; Obukhova, E.N.; Bogdanov, V.P.; Penin, A.A.; Logacheva, M.D. The Genome of the Toxic Invasive Species Heracleum sosnowskyi Carries an Increased Number of Genes despite Absence of Recent Whole-Genome Duplications. Plant J. 2024, 117, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, J.; Li, N.; Yu, J.; Meng, F.; Wei, C.; Liu, C.; Chen, W.; Nie, F.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Deciphering the High-Quality Genome Sequence of Coriander That Causes Controversial Feelings. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H. The WRKY Gene Family Members in Panax quinquefolius L.: Identification, Evolution, and Expression Analysis in Response to Rusty Root Rot Disease. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2025, 66, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hua, X.; Zhong, W.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ming, R.; Zhang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profile Analysis of WRKY Family Genes in the Autopolyploid Saccharum spontaneum. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Gala, J.; Higuera, J.-J.; Rodríguez-Franco, A.; Muñoz-Blanco, J.; Amil-Ruiz, F.; Caballero, J.L. A Comprehensive Study of the WRKY Transcription Factor Family in Strawberry. Plants 2022, 11, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, M.-Y.; Xu, Z.-S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.-S. Genome-Wide Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors and Their Response to Abiotic Stress in Celery (Apium graveolens L.). Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Gao, L. Genome-Wide Analysis of WRKY Genes and Their Response to Hormone and Mechanic Stresses in Carrot. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, R.; Wang, G.; Wan, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factors Involved in Abiotic Stress and ABA Response in Caragana korshinskii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Cao, H.; Xiu, H.; Luo, T.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Luo, Z. Transcriptomics-Based Identification of WRKY Genes and Characterization of a Salt and Hormone-Responsive PgWRKY1 Gene in Panax ginseng. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Hou, X.; Zeng, Y.; Jia, D.; Li, Q.; Gu, Y.; Miao, H. Genome-Wide Identification and Comprehensive Analysis of WRKY Transcription Factor Family in Safflower during Drought Stress. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Tan, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Han, Z. Phylogenetic Analysis and Drought-Responsive Expression Profiles of the WRKY Transcription Factor Family in Maize. Agri Gene 2017, 3, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolkowski, I.; Wanke, D.; Birkenbihl, R.P.; Somssich, I.E. Studies on DNA-Binding Selectivity of WRKY Transcription Factors Lend Structural Clues into WRKY-Domain Function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 68, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Z. Transcription Factor WRKY Complexes in Plant Signaling Pathways. Phytopathol. Res. 2025, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Han, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, C.; Guo, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F.; Huo, Q.; Zhao, W.; Guo, Z.; et al. Phosphorylation and Ubiquitination of OsWRKY31 Are Integral to OsMKK10-2-Mediated Defense Responses in Rice. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 2391–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Cai, W.; Shen, L.; Cao, J.; Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Guan, D.; He, S. A CaCDPK29-CaWRKY27b Module Promotes CaWRKY40-Mediated Thermotolerance and Immunity to Ralstonia solanacearum in Pepper. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 1843–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Niu, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, M.; Wu, Q.; Song, J.; Sun, C.; et al. Discovery of WRKY Transcription Factors through Transcriptome Analysis and Characterization of a Novel Methyl Jasmonate-Inducible PqWRKY1 Gene from Panax quinquefolius. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2013, 114, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, T.; Gao, Y.; Gao, S.; Hao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Transcriptional Regulatory Mechanism of Triterpenoid Saponin Biosynthesis in Soapberry (Sapindus mukorossi Gaertn.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7095–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.-W.; Xu, Y.-H.; Yu, C.-C.; Lv, F.-F.; Tang, X.-L.; Gao, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, J.-H. WRKY44 Represses Expression of the Wound-Induced Sesquiterpene Biosynthetic Gene ASS1 in Aquilaria sinensis. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, P.; Hou, D. Molecular Cloning, Functional Characterization and Expression of the β-Amyrin Synthase Gene Involved in Saikosaponin Biosynthesis in Bupleurum chinense DC. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2023, 32, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, T.; Pollier, J.; Almagro, L.; Buyst, D.; Van Montagu, M.; Pedreño, M.A.; Martins, J.C.; Thevelein, J.M.; Goossens, A. Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Sapogenins and Saponins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Using a C-16α Hydroxylase from Bupleurum falcatum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, C.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Jin, Y.; Xie, C.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Bupleurum chinense Focusing on Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis of Saikosaponins. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Tpye | Chr1 | Chr2 | Chr3 | Chr4 | Chr5 | Summary | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alleles | 1 | 7 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 35 |
| 2 | 7 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 14 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 4 | |
| 4 | 25 | 16 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 57 | |
| Gene locus | 40 | 22 | 17 | 7 | 24 | 110 | |
| Gene number | 124 | 73 | 42 | 22 | 42 | 303 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Mo, C.; Chen, W.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, M.; Zhao, J.; Yu, Z.; Xin, C.; Yu, M.; et al. An Integrated Analysis of WRKY Genes in Autotetraploid Bupleurum chinense: Evolution, Stress Response, and Impact on Saikosaponin Biosynthesis. Horticulturae 2026, 12, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae12010102
Mo C, Chen W, Wei Z, Li Y, Wang X, Yan M, Zhao J, Yu Z, Xin C, Yu M, et al. An Integrated Analysis of WRKY Genes in Autotetraploid Bupleurum chinense: Evolution, Stress Response, and Impact on Saikosaponin Biosynthesis. Horticulturae. 2026; 12(1):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae12010102
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Chuanxin, Wenshuai Chen, Zhen Wei, Yuchan Li, Xueling Wang, Mingyue Yan, Jun Zhao, Zeru Yu, Chao Xin, Ma Yu, and et al. 2026. "An Integrated Analysis of WRKY Genes in Autotetraploid Bupleurum chinense: Evolution, Stress Response, and Impact on Saikosaponin Biosynthesis" Horticulturae 12, no. 1: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae12010102
APA StyleMo, C., Chen, W., Wei, Z., Li, Y., Wang, X., Yan, M., Zhao, J., Yu, Z., Xin, C., Yu, M., & Chen, H. (2026). An Integrated Analysis of WRKY Genes in Autotetraploid Bupleurum chinense: Evolution, Stress Response, and Impact on Saikosaponin Biosynthesis. Horticulturae, 12(1), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae12010102






