Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Growth and Physiological Metabolism in Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Experimental Design
- (1)
- CK: standard calcium concentration (4 mmol/L Ca(NO3)2)
- (2)
- CK+Q: 4 mmol/L Ca(NO3)2 + B. amyloliquefaciens QST713
- (3)
- LCa: low calcium concentration (0.4 mmol/L Ca(NO3)2)
- (4)
- LCa+Q: 0.4 mmol/L Ca(NO3)2 + B. amyloliquefaciens QST713
- (5)
- 0Ca: calcium-free (0 mmol/L Ca(NO3)2)
- (6)
- 0Ca+Q: 0 mmol/L Ca(NO3)2 + B. amyloliquefaciens QST713
2.2. Determination of Experimental Indexes
2.2.1. Measurement of Cucumber Growth Parameters
2.2.2. Measurement of Photosynthetic and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Characteristics in Cucumber Leaves
2.2.3. Measurement of Carbohydrate Content in Cucumber Leaves
2.2.4. Determination of Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Parameters in Cucumber Leaves
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cucumber Growth
3.2. Photosynthetic Performance in Cucumber Leaves
3.2.1. Photosynthetic Pigments in Cucumber Leaves
3.2.2. Photosynthetic Parameters in Cucumber Leaves
3.2.3. Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters in Cucumber Leaves
3.3. Carbohydrate Metabolism in Cucumber Leaves
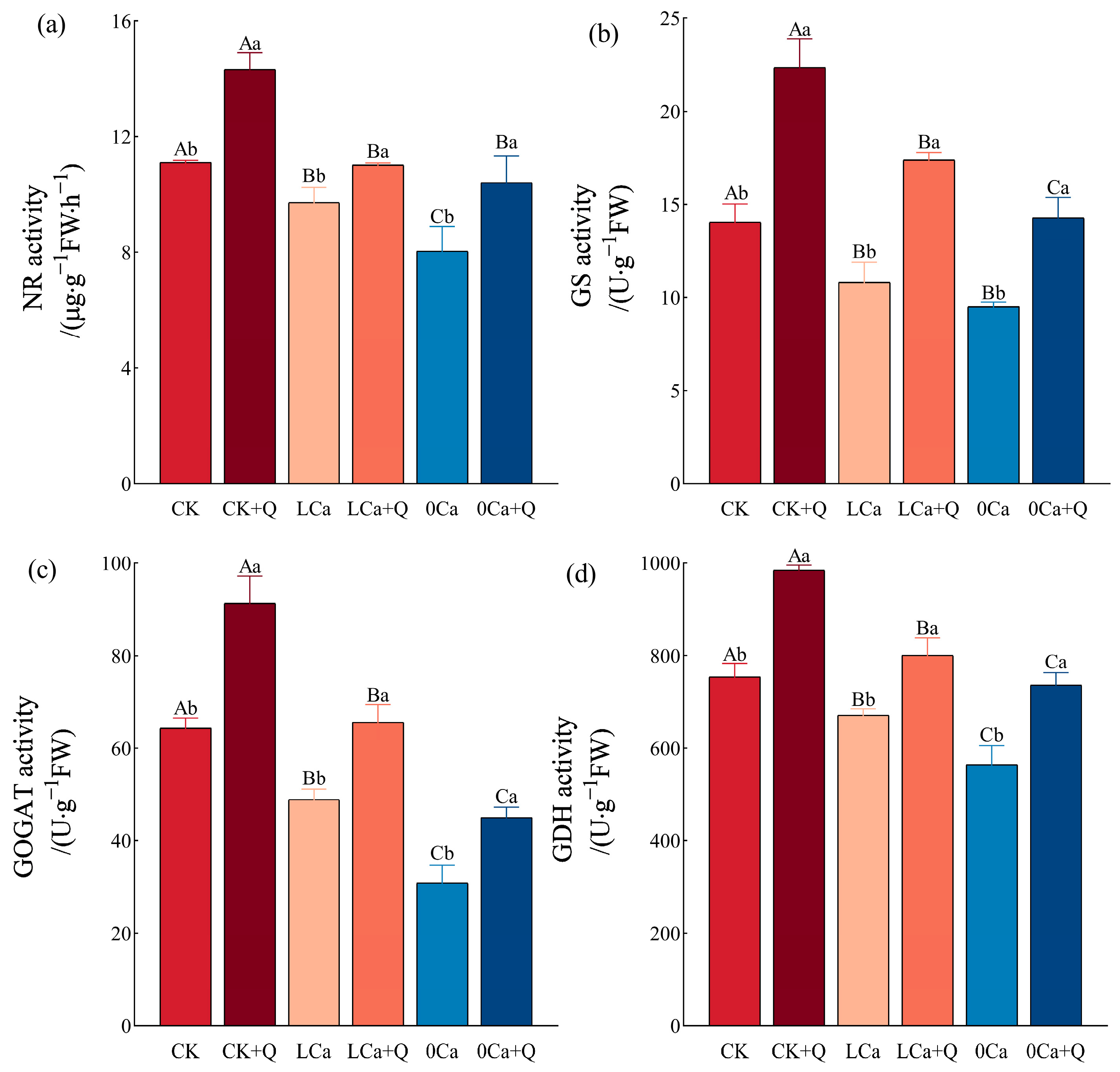
3.4. Nitrogen Metabolism in Cucumber Leaves
3.4.1. Nitrogenous Compounds in Cucumber Leaves
3.4.2. Key Nitrogen Metabolism Enzymes in Cucumber Leaves
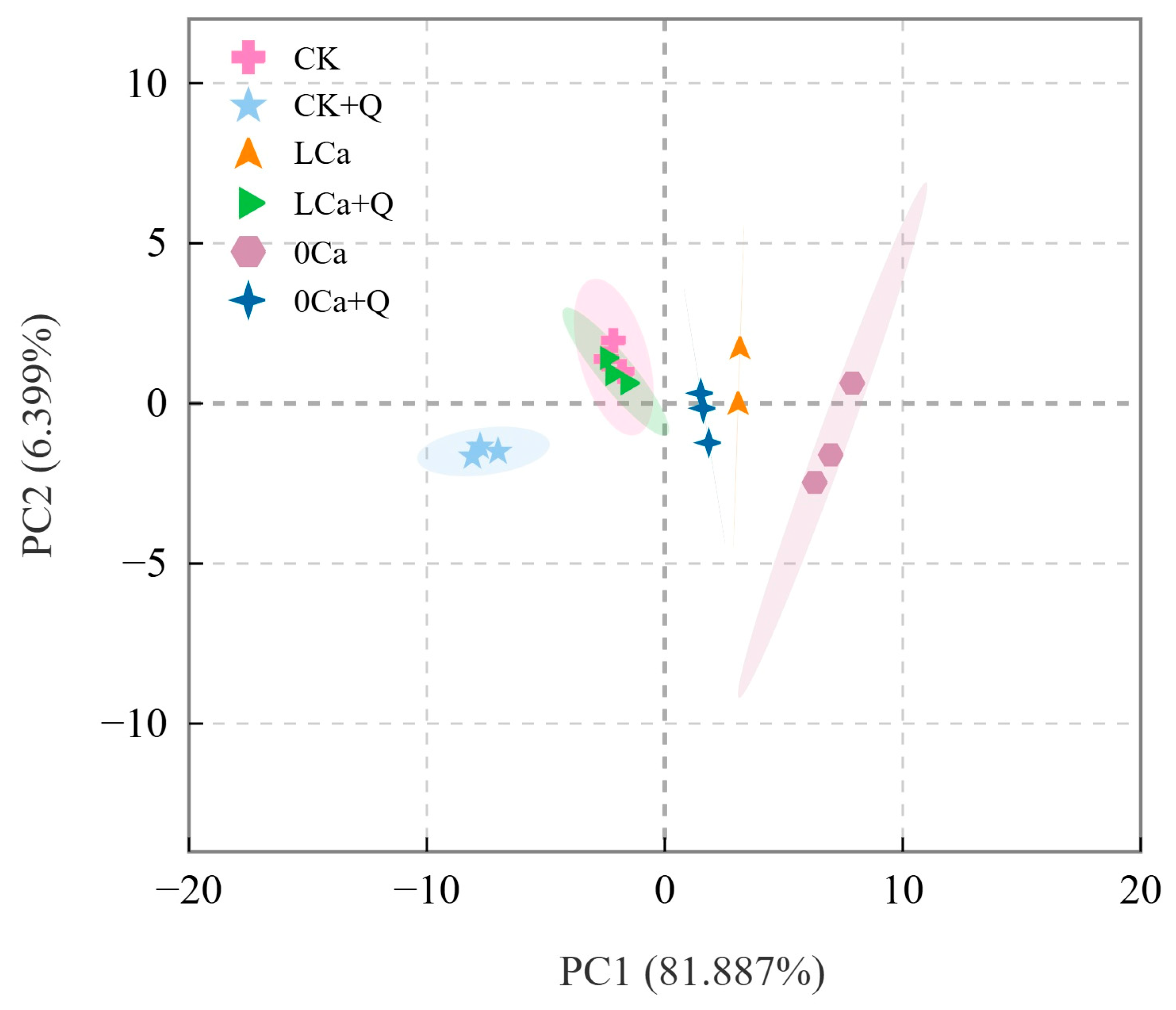
3.5. Principal Component Analysis of Growth, Photosynthesis, and Carbon–Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Parameters in Cucumber
3.6. Comprehensive Evaluation of Growth, Photosynthesis, and Carbon–Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Parameters in Cucumber Under Different Treatments
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of B. amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Cucumber Growth Under Low-Calcium Stress
4.2. Effects of B. amyloliquefaciens QST713 on the Photosynthetic Fluorescence Characteristics of Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress
4.3. Effects of B. amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Carbohydrate Metabolism in Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress
4.4. Effects of B. amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Nitrogen Metabolism in Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress
4.5. Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, Y.H.; Li, W.Q.; Ma, D.H. Present status, problems and development tendency of cucumber production in China. J. Tianjin Agric. Sci. 2003, 3, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.D. Effects of Excessive Application of Chemical Fertilizer on Calcium Accumulation and Change in Continuous Cropping Cucumber Plants and Soil in Solar Greenhouse. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang Agricultural University, Shenyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Yuan, S.K.; Cui, A.H.; Shu, G.A.; Zhou, X.Y.; Ma, C.S. Symptoms of calcium deficiency in facility-cultivated cucumbers and comprehensive prevention and control technology. China Cucurbits Veg. 2019, 32, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.H.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.D.; Niu, R.S.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Qi, L.F. Solar greenhouse cucumber winter and spring stubble precision water and fertilizer cultivation technology. China Cucurbits Veg. 2019, 32, 64–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepler, P.K. Calcium: A central regulator of plant growth and development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 2142–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.S.; Chen, J.J.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.P.; Chen, H.C.; He, Y. Microanalysis characteristics and physiological of peanut pods and plant biochemical responses under Ca stress. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 23, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Lang, D.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, X.H. Response of carbon and nitrogen metabolism and secondary metabolites to drought stress and salt stress in plants. J. Plant Biol. 2019, 62, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Liu, C.L.; Xu, X.X.; Xing, Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Lyu, M.X.; Feng, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Qin, H.H.; Jiang, H.; et al. Effects of Magnesium on nitrate uptake and sorbitol synthesis and translocation in apple seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 2023, 196, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, T.D. The end game(s) of photosynthetic carbon metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2024, 195, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.; Iqbal, A. Phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria as alternative of chemical fertilizer for growth and yield of Triticum aestivum (Var. Galaxy 2013). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1400–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.S.; Ma, Y.; Rocha, I.; Carvalho, M.F.; Vosátka, M.; Freitas, H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi are an alternative to the application of chemical fertilizer in the production of the medicinal and aromatic plant Coriandrum sativum L. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2016, 79, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, A.I.; Bopape, F.L.; Sanger, L.K. Microbial Inoculants as Agents of Growth Promotion and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkovic, S.; Beskoski, V.; Karabegovic, I. Microbial fertilizers: A comprehensive review of current findings and future perspectives. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2018, 16, e09R01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamford, N.P.; Felix, F.; Oliveira, W.; Silva, E.; Carolina, S.; Arnaud, T.; Freitas, A.D. Interactive effectiveness of microbial fertilizer enriched in N on lettuce growth and on characteristics of an Ultisol of the rainforest region. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 247, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.M.; Farag, M.A.; Hu, C.H.; Reddy, M.S.; Kloepper, J.W.; Paré, P.W. Bacterial volatiles induce systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatima, T.; Arora, N.K. Pseudomonas entomophila PE3 and its exopolysaccharides as biostimulants for enhancing growth, yield and tolerance responses of sunflower under saline conditions. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 244, 126671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, C.M.; Farag, M.A.; Hu, C.H.; Reddy, M.S.; Wei, H.X.; Paré, P.W.; Kloepper, J.W. Bacterial volatiles promote growth in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4927–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Mechanism of Enhanced Plant Salt Tolerance by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Doctor’s Thesis, Nanjing Agricultural University, Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; He, G.S.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.F.; Lu, L.; Peng, G.X.; Tan, Z.Y. Effects of amylase producing thermophilic Bacillus strains on starch degradation in tobacco during flue-curing. Acta Tabacaria Sinica 2017, 23, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, D.A.; Maroon, M.; Schrader, L.E.; Youngs, V.L. Rapid colorimetric determination of nitrate in plant tissue by nitration of salicylic acid. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 1975, 6, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorzano, L. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1969, 14, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, J.A.; Matos, J.C.; Cecatto, V.M.; Viegas, R.A.; Oliveira, J.T. Nitrate reductase activity, distribution, and response to nitrate in two contrasting Phaseolus species inoculated with Rhizobium spp. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2001, 46, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.F.; Peng, S.B.; Peng, X.X.; Chavez, A.Q.; Bennett, J. Response of glutamine synthetase isoforms to nitrogen sources in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Plant Sci. 1997, 125, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Chi, W.; Kuang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Ku, M.S.; Cho, D. Photosynthetic characteristics and tolerance to photo-oxidation of transgenic rice expressing C(4) photosynthesis enzymes. Photosynth. Res. 2002, 72, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debouba, M.; Maâroufi-Dghimi, H.; Suzuki, A.; Ghorbel, M.H.; Gouia, H. Changes in growth and activity of enzymes involved in nitrate reduction and ammonium assimilation in tomato seedlings in response to NaCl stress. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadak, M.S.; Hanafy, R.S.; Elkady, F.M.A.M.; Mogazy, A.M.; Abdelhamid, M.T. Exogenous calcium reinforces photosynthetic pigment content and osmolyte, enzymatic, and non-enzymatic antioxidants abundance and alleviates salt stress in bread wheat. Plants 2023, 12, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Lv, W.H. Effect of exogenous calcium on potato morphological characters, physiological index, yield and quality traits. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2015, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.H.; Tang, X.F.; Yu, W.J.; Liao, Y.; Huang, W.H.; Qin, R.Y. Effects of different calciumlevels on photosynthesis and protective enzyme activities of melonleaves. Guihaia 2005, 25, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Hu, Y.G.; Zeng, Z.H.; Qian, X.; Ren, C.Z.; Guo, L.C.; Wang, C.L. Effect of bio-fertilizer on oat (Avena sativa L.) nitrogen accumulation and photosynthetic physiology. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 28, 2586–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Li, D.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, P. Effects of organic bio-bacterial manure on nutrient uptake and photosynthetic characteristics of continuous cropping flue-cured tobacco. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Yue, D.D.; Li, G.J.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.Y.; Zhen, J.; Zhao, J.J.; Chen, G.C.; Yang, J.X.; Mu, Q. Effects of Bacillus subtilis on physiological and biochemical indexes of winter wheat. Henan Sci. 2020, 38, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.F.; Lin, M.Z.; Chen, C.X.; Lei, X.L. Effects of Paenibacillus polymyxa S960 on the growth and photosynthetic physiological characteristics of tomato. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2018, 40, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, H.D.; Fang, K.; Xu, Q.M. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HM618 on the growth and physiological characteristics of wheat seedlings under salt stress. J. Tianjin Agric. Sci. 2020, 26, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annick, M.; Elisabeth, P.; Gérard, T. Osmotic adjustment, gas exchanges and chlorophyll fluorescence of a hexaploid triticale and its parental species under salt stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2004, 161, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Fan, L.L.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, L.; He, T.Y.; Rong, J.D.; Zheng, Y.S. Effects of different application rates of biological bacteria fertilizer on the growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Bambusa tuldoides during shooting period. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2018, 39, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.L.; Yuan, Z.S.; Jiang, T.Y.; Zhu, X.R.; Chen, R.Y.; Zhang, G.F. Effects of different microbial agents on the chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Cinnamomum camphora. Prot. For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 11, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, V.; Ricard, B.; Raymond, P.; Saglio, P.H. The Role of sugars, hexokinase, and sucrose synthase in the determination of hypoxically induced tolerance to anoxia in tomato roots. Plant Physiol. 1997, 114, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.; Li, C.C.; Sung, J.M. Carbohydrate metabolism enzymes in CO2-enriched developing rice grains of cultivars varying in grain size. Physiol. Plant. 1994, 90, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veierskov, B.; Meravý, L. Changes in carbohydrate composition in wheat and pea seedlings induced by calcium deficiency. Plant Physiol. 1985, 79, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.F.; Gao, X.Q.; Qi, M.F.; Li, T.L. Effect of calcium on production and accumulation of photosythate in toma to under low night temperature stress. Jiangsu J. Agr. Sci. 2012, 28, 828–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Lv, Y.H.; Li, H.Y.; Deng, S.Y.; Chen, J.J. Advances on regulatory mechanism and index of carbon-nitrogen metabolism in flue-cured tobacco. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2018, 45, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.R.; Wu, Q.X.; Cao, J.W.; Wu, X.L.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Sun, M.H. Effects of different nitrogen forms ratios on root growth and activities of key enzymes in nitrogen metabolism in Ormosia henryi prain seedlings. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2024, 33, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horchani, F.; Hajri, R.; Aschi-Smiti, S. Effect of ammonium or nitrate nutrition on photosynthesis, growth, and nitrogen assimilation in tomato plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2010, 173, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.Y.; Wu, L.H.; Tao, Q.N. Research advances on GS/GOGAT cycle in higher plant. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2001, 7, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, Y.C.; Chen, X.S.; Li, M.J.; Guo, F.; Gao, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Li, C.Y. Effects of nitrogen application rates on enzyme activities related to carbon and nitrogen metabolism, yield and quality of peanut in chernozem. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2024, 46, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Ikeda, M.; Yamada, Y. Effect of the supply of potassium, calcium, and magnesium on the absorption, translocation, and assimilation of ammonium- and nitrate-nitrogen in wheat plants. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1987, 33, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.E.; Paulsen, G.M. Nitrogen assimilation and protein synthesis in wheat seedlings as affected by mineral nutrition. II. micronutrients. Plant Physiol. 1969, 44, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Teraoka, K.; Kawasaki, T. Repression of nitrate reductase in cucumber leaves caused by calcium deficiency. Plant Cell Physiol. 1980, 21, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, R.; Bilal, S.; Imran, M.; Khan, A.L.; Alosaimi, A.A.; Al-Shwyeh, H.A.; Almahasheer, H.; Rehman, S.; Lee, I.J. Amelioration of heavy metal stress by endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens RWL-1 in rice by regulating metabolic changes: Potential for bacterial bioremediation. Biochem J. 2019, 476, 3385–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, Z.X.; Ma, X.Q.; Qu, F.; Hu, X.H. Effects of two microbial agents on yield, quality and rhizosphere environment of autumn cucumber cultured in organic substrate. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 3077–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
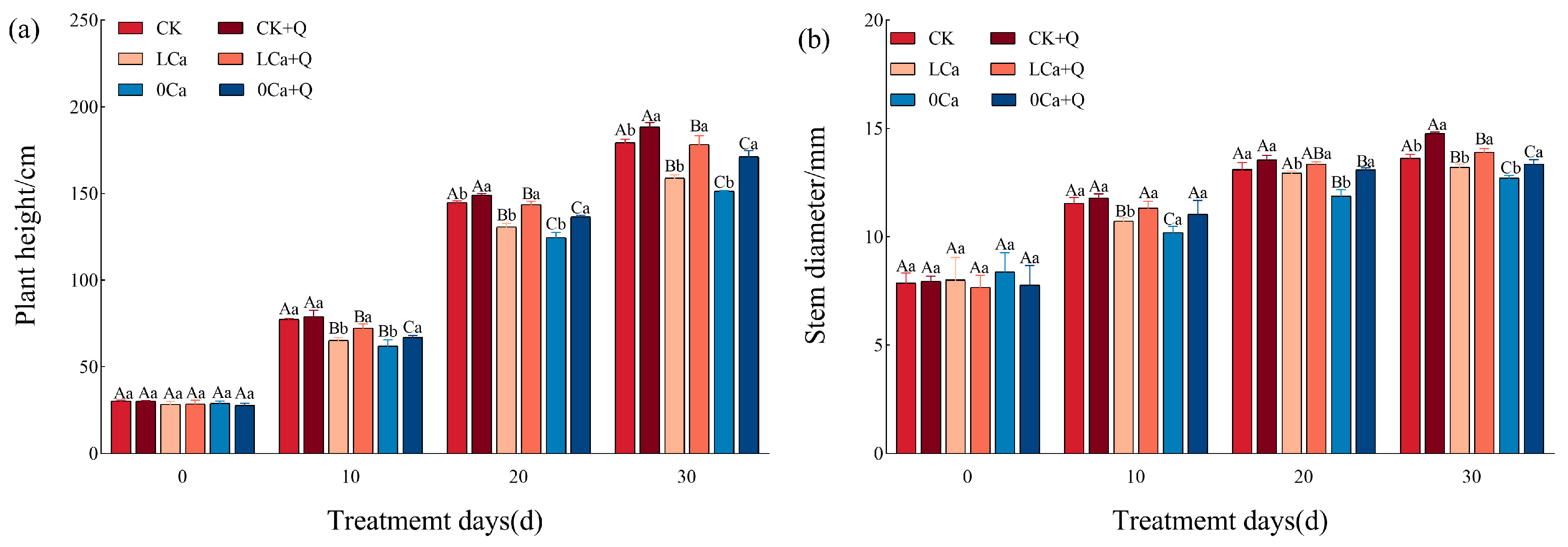

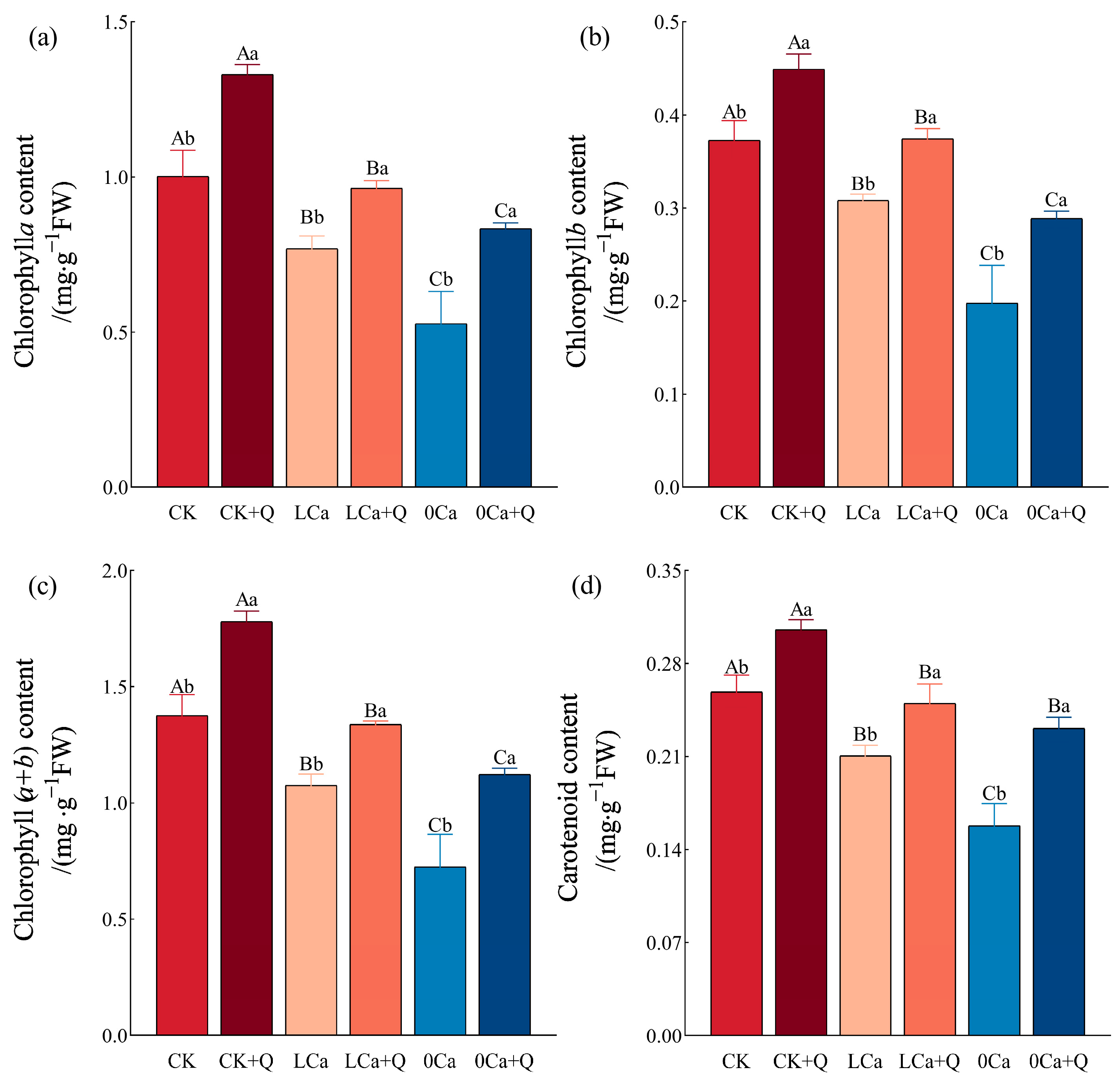
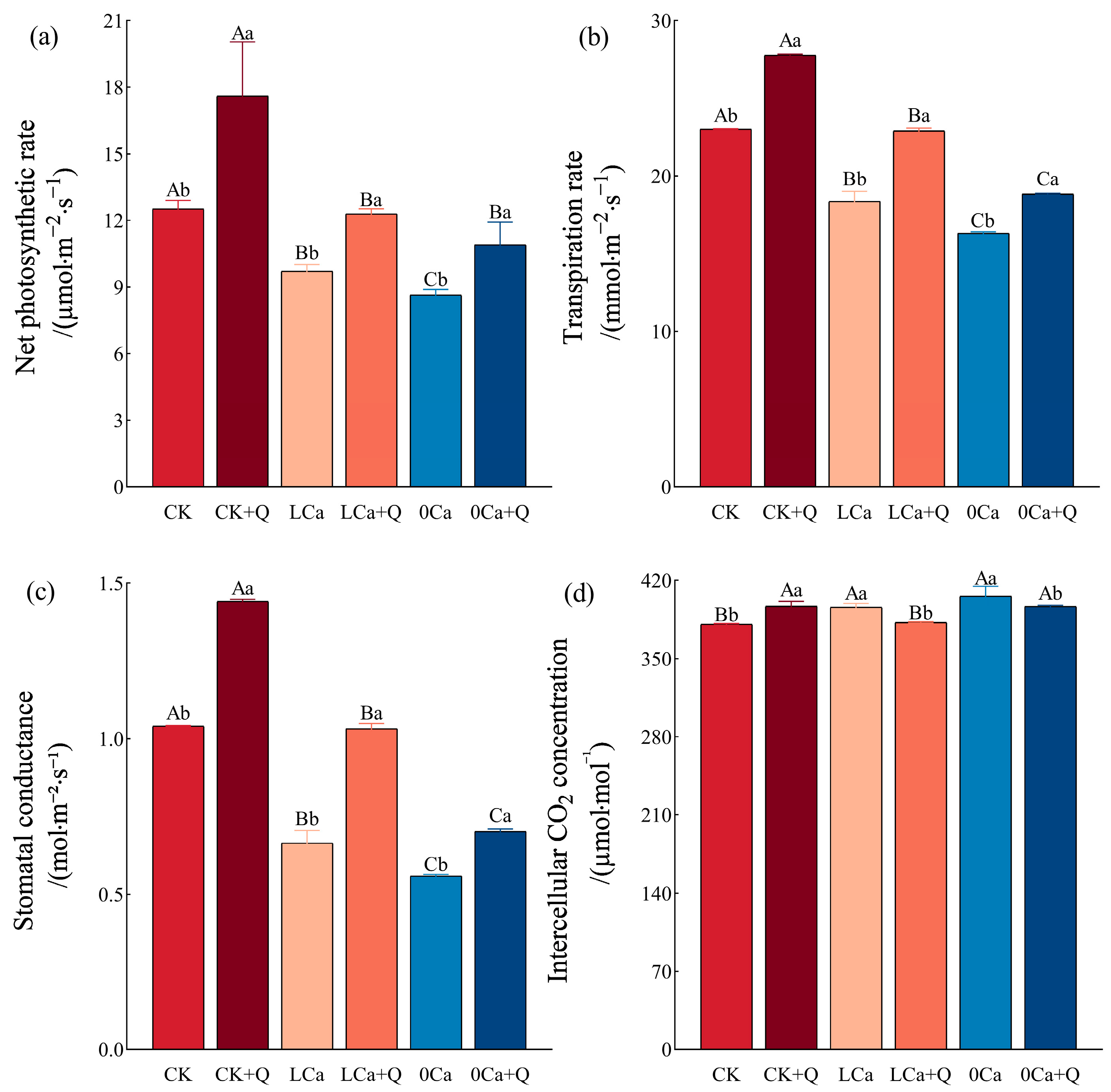
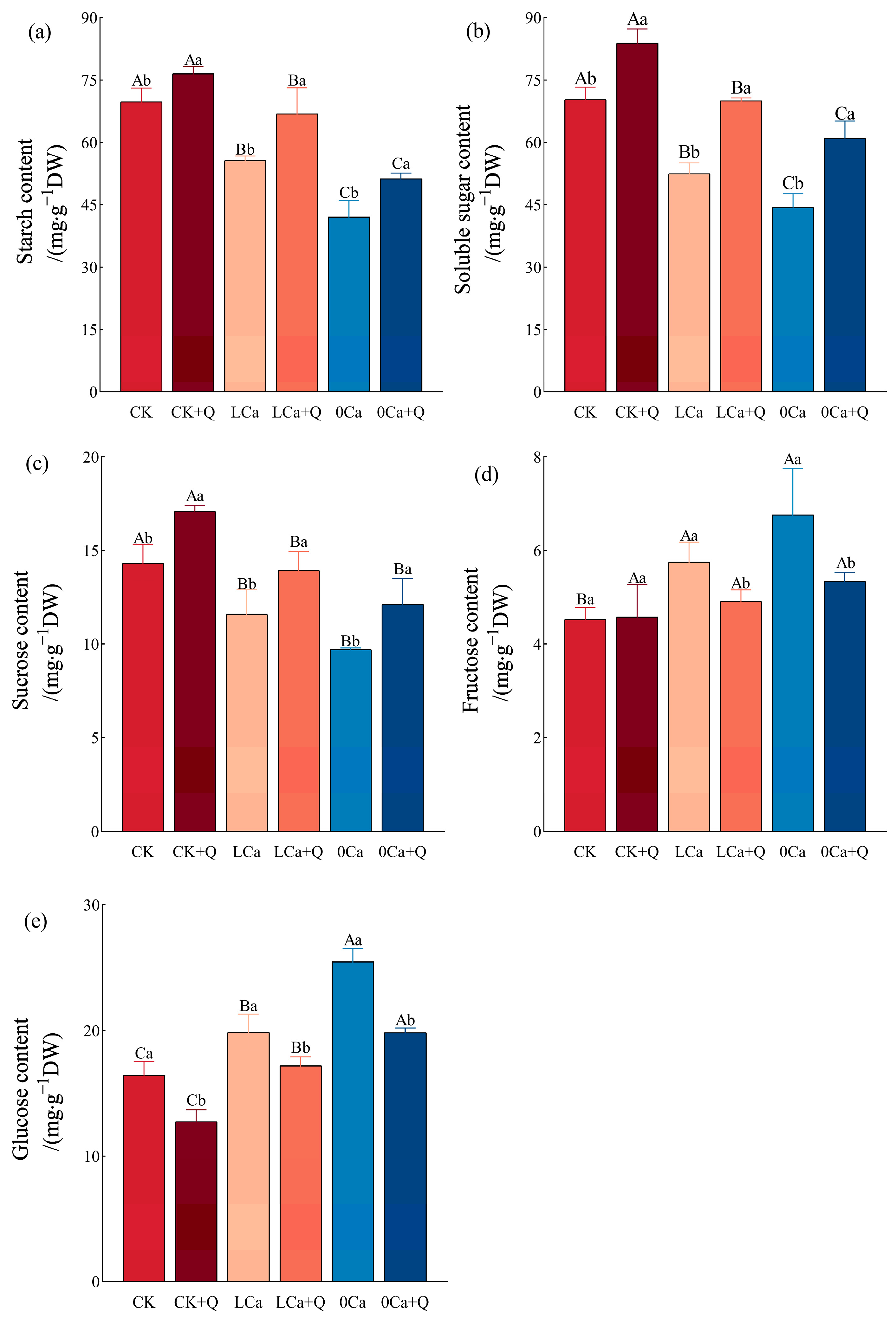


| Treatments | Ca2+ (mg·g−1 DW) | Mg2+ (mg·g−1 DW) | K+ (mg·g−1 DW) | Na+ (mg·g−1 DW) | K+/Na+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 14.54 ± 0.49 Aa | 9.01 ± 0.06 Aa | 50.55 ± 1.00 Aa | 0.19 ± 0.01 Aa | 263.01 ± 12.85 Aa |
| CK+Q | 15.46 ± 0.44 Aa | 9.16 ± 0.10 Aa | 51.24 ± 0.28 Aa | 0.18 ± 0.01 Aa | 280.77 ± 13.63 Aa |
| LCa | 10.95 ± 0.22 Bb | 8.58 ± 0.01 Aa | 48.19 ± 0.98 Aa | 0.21 ± 0.00 Aa | 233.15 ± 1.20 Ab |
| LCa+Q | 13.12 ± 0.31 Ba | 8.89 ± 0.23 ABa | 50.00 ± 1.78 Aa | 0.19 ± 0.00 ABb | 258.61 ± 8.56 Aa |
| 0Ca | 8.76 ± 0.12 Cb | 7.23 ± 0.17 Bb | 39.00 ± 0.80 Bb | 0.17 ± 0.00 Ba | 230.23 ± 12.17 Ab |
| 0Ca+Q | 10.11 ± 0.13 Ca | 8.58 ± 0.15 Ba | 45.18 ± 0.93 Ba | 0.17 ± 0.01 Ba | 271.49 ± 5.70 Aa |
| Treatments | Fv/Fm | ΦPSII | ETR | qP | NPQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.82 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.67 ± 0.00 Ab | 56.98 ± 0.08 Ab | 0.88 ± 0.00 Ab | 0.14 ± 0.01 Ca |
| CK+Q | 0.82 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.70 ± 0.00 Aa | 59.14 ± 0.05 Aa | 0.92 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.14 ± 0.03 Ba |
| LCa | 0.82 ± 0.01 Aa | 0.63 ± 0.00 Bb | 53.84 ± 0.13 Bb | 0.86 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.23 ± 0.00 Ba |
| LCa+Q | 0.83 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.66 ± 0.00 Ba | 56.27 ± 0.33 Ba | 0.86 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.17 ± 0.01 ABb |
| 0Ca | 0.83 ± 0.00 Aa | 0.64 ± 0.01 Bb | 54.00 ± 1.06 Bb | 0.86 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.32 ± 0.01 Aa |
| 0Ca+Q | 0.82 ± 0.01 Aa | 0.66 ± 0.01 Ba | 55.95 ± 0.54 Ba | 0.87 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.20 ± 0.00 Ab |
| Principal Component | Eigenvalues | Contribution Rates/% | Cumulative Contribution Rates/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.928 | 81.887 | 81.887 |
| 2 | 1.792 | 6.399 | 88.286 |
| 3 | 1.047 | 3.738 | 92.024 |
| Index | Principal Component 1 | Principal Component 2 | Principal Component 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plant height | 0.957 | −0.122 | 0.012 |
| Stem diameter | 0.960 | 0.092 | 0.125 |
| chlorophyll a | 0.982 | 0.108 | −0.051 |
| chlorophyll b | 0.968 | −0.075 | −0.030 |
| chlorophyll (a+b) | 0.986 | 0.063 | −0.046 |
| Carotenoid | 0.975 | −0.042 | −0.051 |
| Pn | 0.928 | 0.176 | −0.050 |
| Tr | 0.983 | 0.036 | 0.062 |
| Gs | 0.973 | 0.076 | 0.052 |
| Ci | −0.448 | 0.824 | −0.088 |
| Fv/Fm | −0.058 | 0.520 | 0.753 |
| ΦPSⅡ | 0.889 | 0.280 | −0.236 |
| ETR | 0.891 | 0.277 | −0.234 |
| qP | 0.682 | 0.548 | −0.440 |
| NPQ | −0.880 | 0.320 | 0.025 |
| Starch | 0.933 | −0.223 | 0.096 |
| Soluble sugar | 0.977 | 0.033 | 0.097 |
| Sucrose | 0.950 | 0.013 | 0.103 |
| Fructose | −0.818 | 0.119 | 0.164 |
| Glucose | −0.956 | 0.172 | 0.034 |
| NO3−-N | 0.942 | −0.012 | 0.150 |
| NH4+-N | −0.954 | 0.202 | 0.045 |
| Soluble protein | 0.956 | −0.160 | 0.057 |
| Free amino acid | 0.920 | 0.024 | 0.112 |
| NR | 0.938 | 0.092 | 0.080 |
| GS | 0.928 | 0.152 | 0.136 |
| GOGAT | 0.973 | −0.022 | 0.064 |
| GDH | 0.952 | 0.070 | 0.088 |
| Treatments | Factor Scores | Comprehensive Score F | Ranking | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | |||
| CK | 0.490 | −0.179 | −1.299 | 0.341 | 3 |
| CK+Q | 1.102 | 1.496 | 0.581 | 1.020 | 1 |
| LCa | −0.473 | −0.561 | −0.248 | −0.432 | 4 |
| LCa+Q | 0.922 | −0.914 | 0.319 | 0.708 | 2 |
| 0Ca | −1.588 | 1.523 | 0.618 | −1.180 | 6 |
| 0Ca+Q | −0.652 | 0.563 | 0.817 | −0.467 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Han, L.; Li, B. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Growth and Physiological Metabolism in Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091131
Zhang L, Guo Y, Zhou X, Wang S, Han L, Li B. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Growth and Physiological Metabolism in Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(9):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091131
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Li, Yan Guo, Xufeng Zhou, Shiyan Wang, Lingjuan Han, and Bin Li. 2025. "Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Growth and Physiological Metabolism in Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress" Horticulturae 11, no. 9: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091131
APA StyleZhang, L., Guo, Y., Zhou, X., Wang, S., Han, L., & Li, B. (2025). Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 on Growth and Physiological Metabolism in Cucumber Under Low-Calcium Stress. Horticulturae, 11(9), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091131





