BSA-Seq-Based Discovery of Functional InDel Markers for Seed Size Selection in Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Phenotypic Trait Evaluation and Analysis
2.3. BSA-Seq Analysis
2.3.1. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3.2. Data Processing, Alignment, Variant Calling, and Linkage Analysis
2.3.3. Gene Functional Annotation
2.4. InDel-PCR Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Variation Analysis of Six Fruit Quality Traits
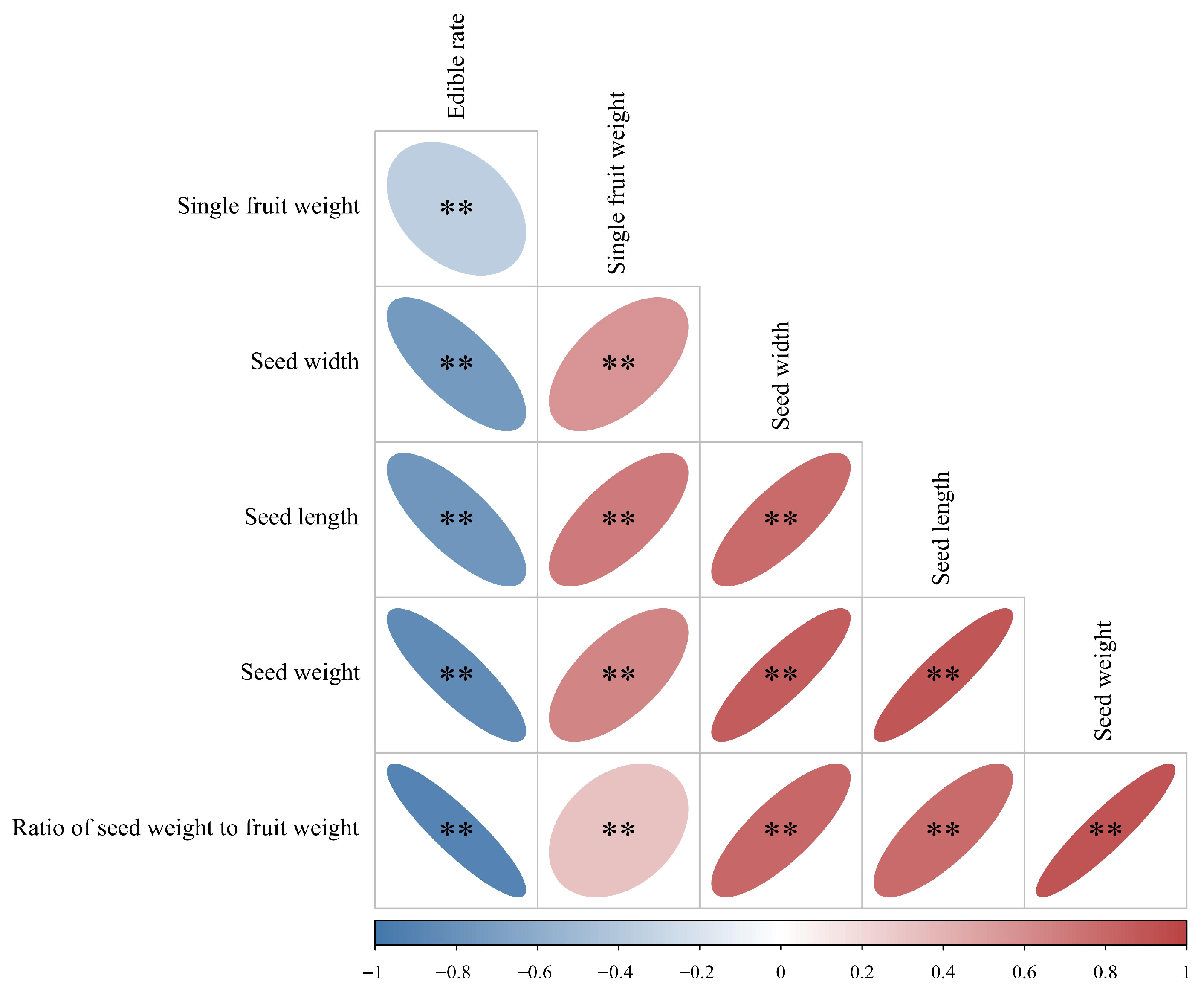
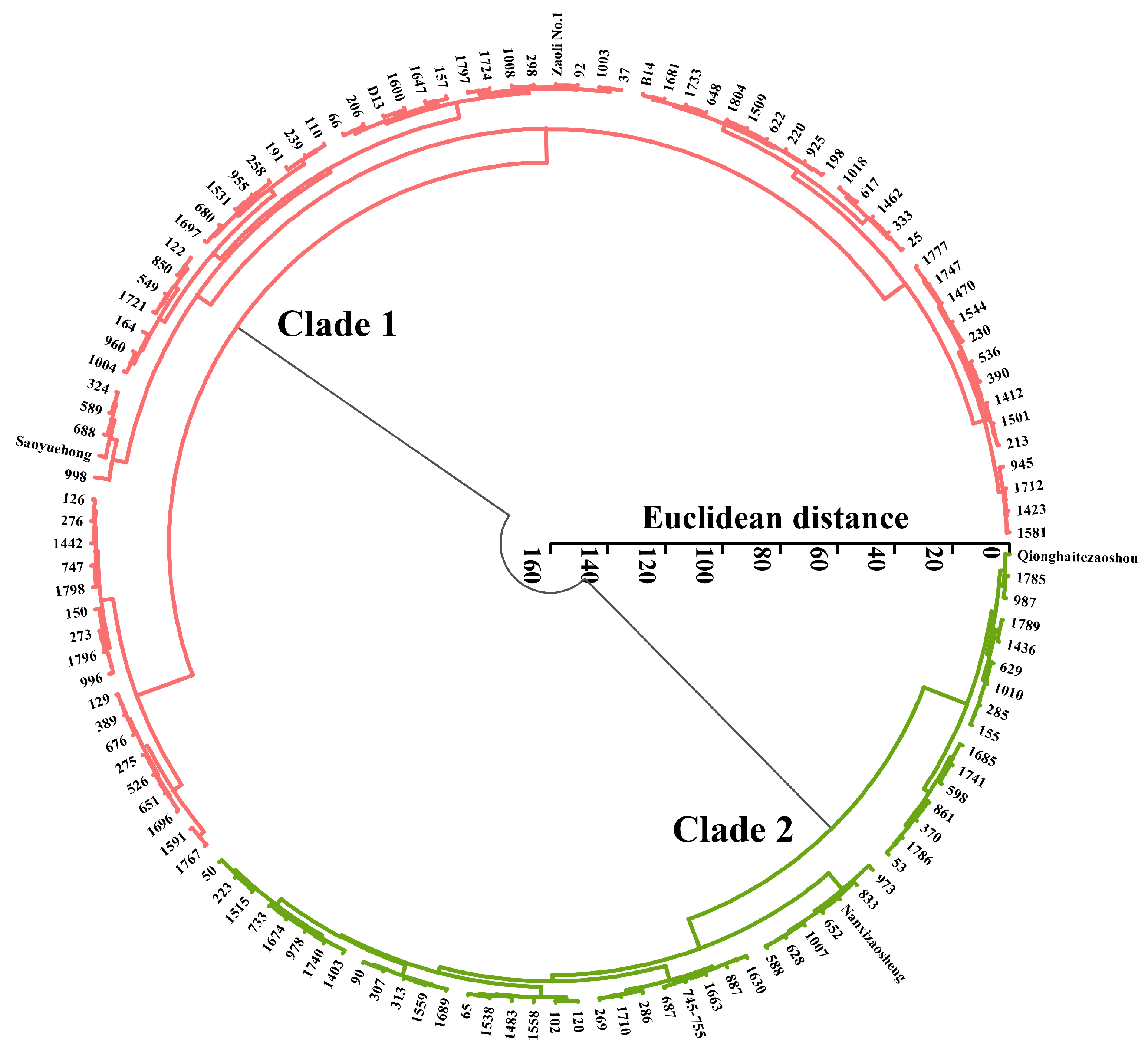
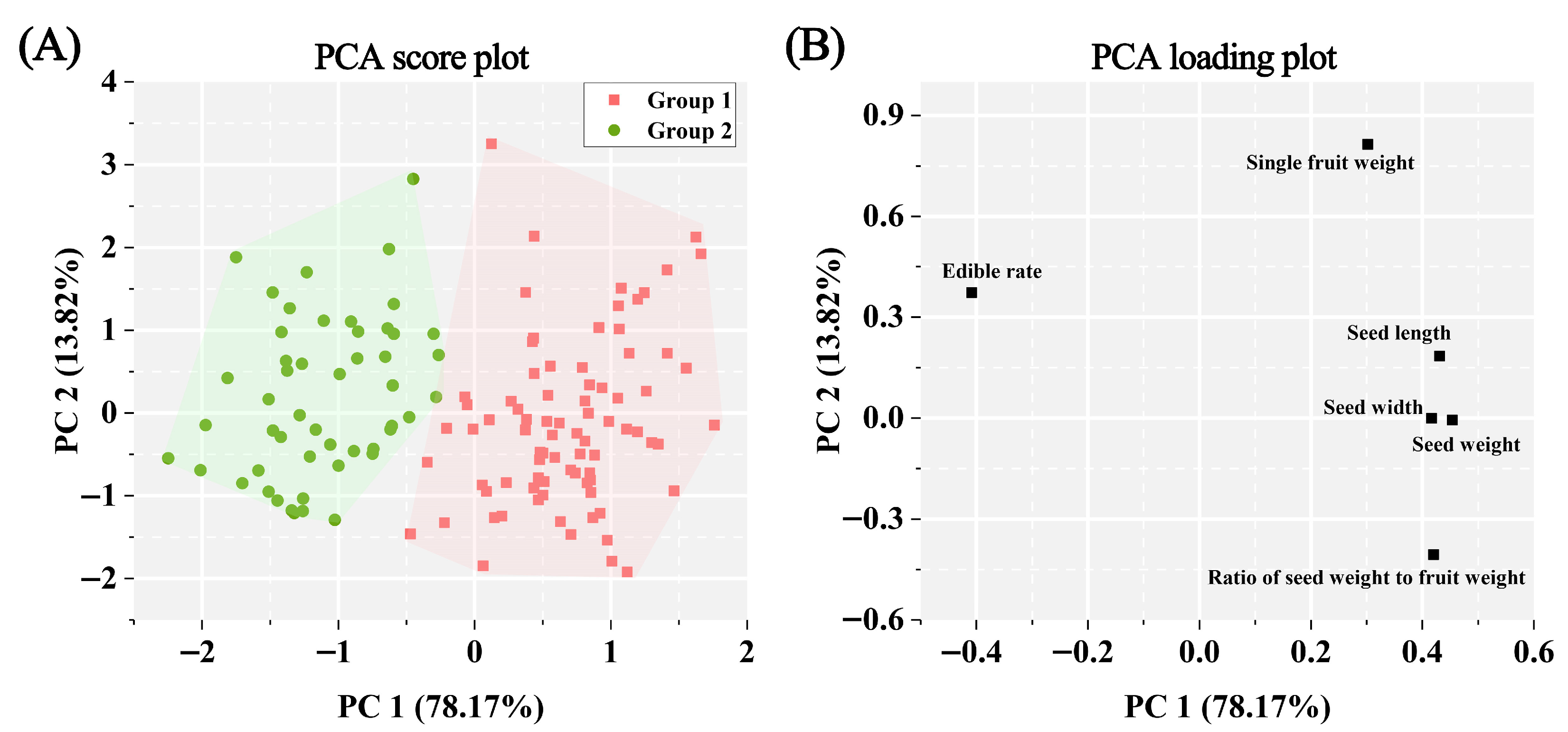
3.2. Correlation, Cluster, and PCA Analyses of Phenotypic Traits
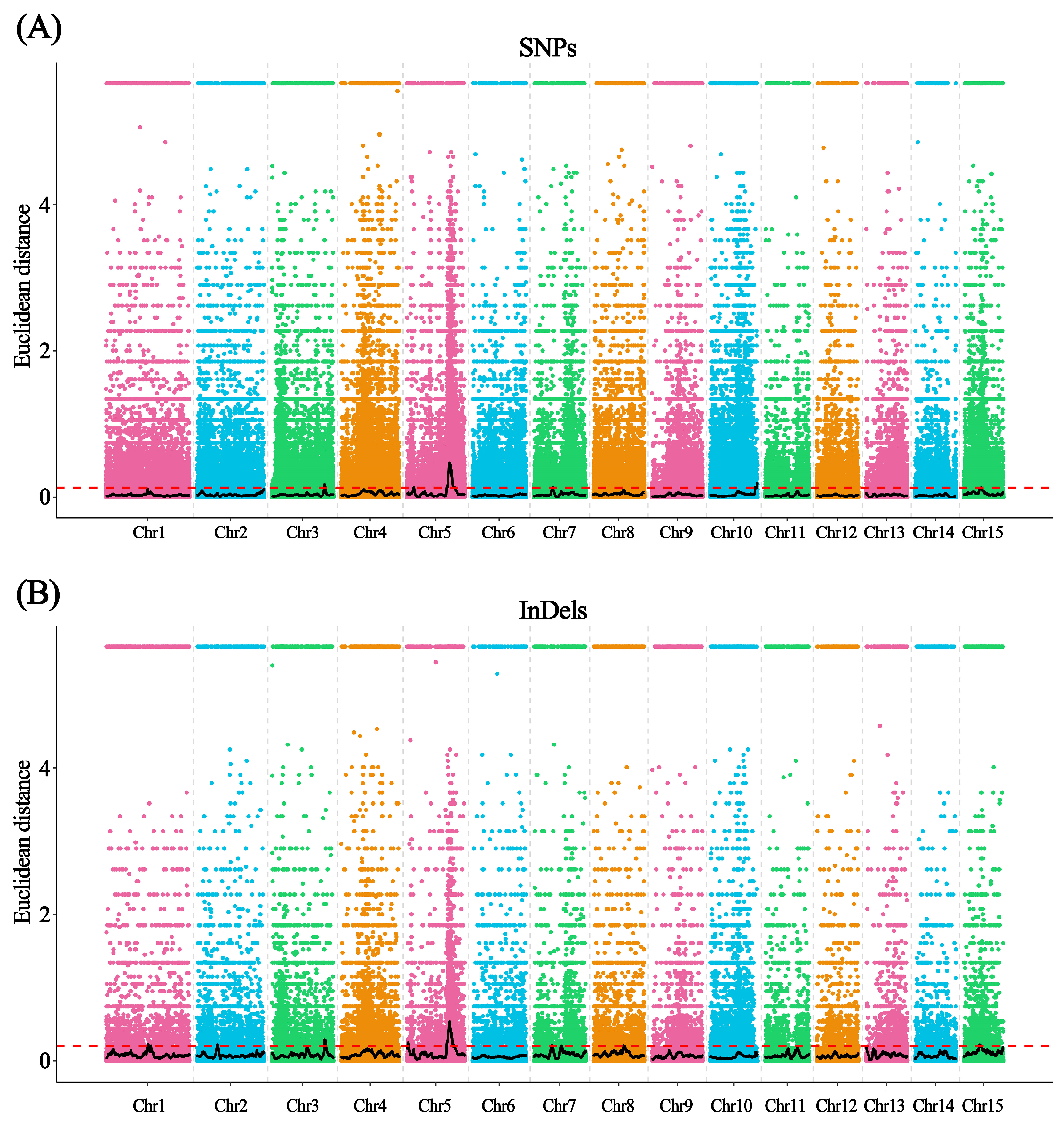
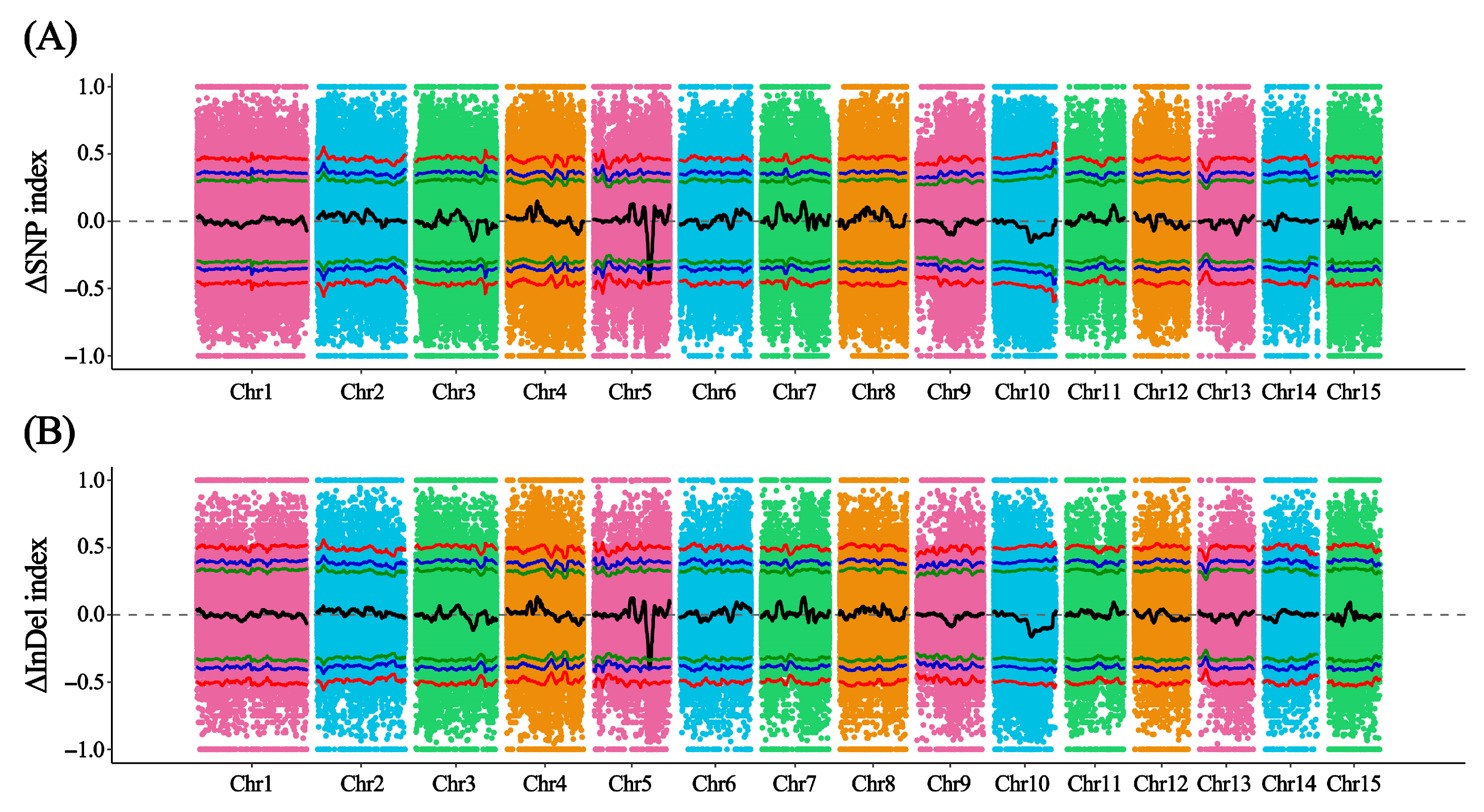
3.3. BSA-Seq Analysis of the AS and NS Phenotypic Pools
3.4. Gene Annotation in the BSA Target Region
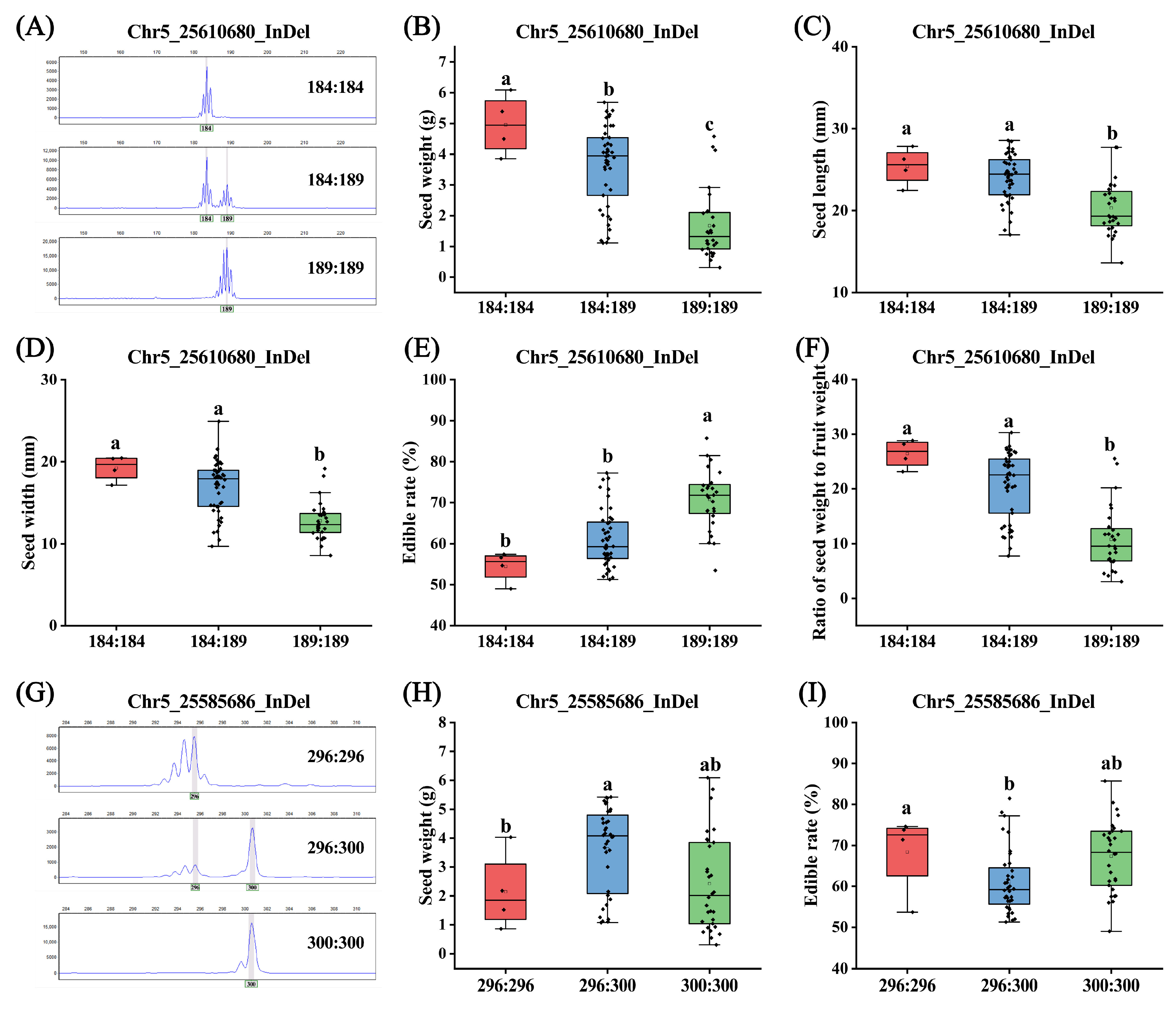
3.5. Development and Validation of InDel Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, D.; Huang, S.; Xiang, X. Analysis of guangdong litchi production situation in 2022. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2022, 49, 130–137. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, X.; Caiqin, L.; Wangjin, L.; Juan, D.; Zehuai, W.; Jianguo, L. 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase 1 (hmg1) is highly associated with the cell division during the early stage of fruit development which determines the final fruit size in litchi chinensis. Gene 2012, 498, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xia, R.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Y. The gras gene family and its roles in seed development in litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Yin, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Li, J. Increased DNA methylation of the splicing regulator sr45 suppresses seed abortion in litchi. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, C.; Ma, X.; Xia, R.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Ying, P.; Peng, M.; Wang, J.; Shi, C.; et al. Knox protein knat1 regulates fruitlet abscission in litchi by repressing ethylene biosynthetic genes. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 4069–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, J.; Jing, X.; Khan, F.S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Y. Genome-wide identification of litchi spl gene family and expression analysis in pericarp anthocyanin biosynthesis. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Zhao, M.; Huang, Q.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Molecular characterization and functional roles of nac transcription factors in regulating chlorophyll degradation during litchi fruit ripening. Sci. Hortic. 2025, 341, 113975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lin, S.; Huang, R.; Jiang, Y.; Duan, X. Lcnac13 physically interacts with LcR1MYB1 to coregulate anthocyanin biosynthesis-related genes during litchi fruit ripening. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Peng, H.; Chen, H.; Hu, F.; Lai, B.; Wei, Y.; Ma, W.; Li, H.; et al. Development of molecular markers based on the promoter difference of lcft1 to discriminate easy- and difficult-flowering litchi germplasm resources and its application in crossbreeding. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, A.K.; Singh, S.P.; Gupta, Y.; Gurjar, A.K.S.; Mantri, S.S.; Tuli, R. Transcriptional changes during ovule development in two genotypes of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) With contrast in seed size. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Hu, F.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, H. Aberrant seed development in Litchi chinensis is associated with the impaired expression of cell wall invertase genes. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.; Ma, X.; Rahman, M.Z.; Yang, M.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, H. Thermo-sensitive sterility and self-sterility underlie the partial seed abortion phenotype of litchi chinensis. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 247, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xiao, Z.; Bao, X.; Yang, X.; Fang, J.; Xiang, X. Identifying litchi (Litchi chinensis sonn.) Cultivars and their genetic relationships using single nucleotide polymorphism (snp) markers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e135390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhou, M.; Normand, F.; Bahorun, T.; Hormaza, J.I. Fingerprinting and analysis of genetic diversity of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) Accessions from different germplasm collections using microsatellite markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Kanzaki, S.; Triest, L.; Hormaza, I.; Kuk, N.J.; Ming, R.; Bousquet, J.; Khasa, D.; Van Damme, P. Analysis of genetic diversity of lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) And wild forest relatives in the sapindaceae from vietnam using microsatellites. Genet. Resour. Crop Ev. 2019, 66, 1653–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.K.; Singh, S.P.; Tuli, R. Amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting to identify genetic relatedness among lychee cultivars and markers associated with small-seeded cultivars. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2014, 139, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Cheng, J.; Mei, Z.; Zhao, L.; Wei, C.; Fu, S.; Khan, M.A.; Fu, J. Genetic analysis of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) In southern China by improved random amplified polymorphic dna (RAPD) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Long, Y.; Khan, M.A.; Wei, C.; Fu, S.; Fu, J. Development and significance of rapd-scar markers for the identification of Litchi chinensis Sonn. By improved RAPD amplification and molecular cloning. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 18, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, J.; Hu, G. Construction of high-density SNP genetic maps and QTL mapping for dwarf-related traits in litchi chinensis sonn. J. Integr. Agr. 2021, 20, 2900–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, P.; Li, F.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Hong, J.; et al. Litchi40k v1.0: A cost-effective, flexible, and versatile liquid SNP chip for genetic analysis and digitalization of germplasm resources in litchi. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Feng, J.; Xiang, X.; Wang, J.; Salojarvi, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Two divergent haplotypes from a highly heterozygous lychee genome suggest independent domestication events for early and late-maturing cultivars. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Feng, J.; Chen, J.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Mai, Y.; Huang, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Shi, F.; et al. Comprehensive genomic and phenotypic analyses reveal the genetic basis of fruit quality in litchi. Genome Biol. 2025, 26, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonsungsan, P.; Nganga, M.L.; Lieberman, M.C.; Amundson, K.R.; Stewart, V.; Plaimas, K.; Comai, L.; Henry, I.M. A k-mer-based bulked segregant analysis approach to map seed traits in unphased heterozygous potato genomes. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2024, 14, jkae035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, L.; Brown, S.; Xu, K. Dwarf tree habit is a recessive phenotype independent of the dominant columnar growth in scion apples and controlled by multiple genomic loci and their epistatic interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2025, 14, eraf372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, L.; Niu, L.; Cui, G.; Wei, B.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z. Fine mapping of the gene controlling the weeping trait of Prunus persica and its uses for mas in progenies. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, T.; Chen, L.; Wang, E.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, D.; Guo, L.; Hou, X. Hmgr regulates floral fragrance through terpene synthesis pathway in Paeonia suffruticosa. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 224, 120418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasimuddin, M.; Misra, S.; Li, H.; Aluru, S. Efficient Architecture-Aware Acceleration of Bwa-Mem for Multicore Systems, 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The sequence alignment/map format and samtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The genome analysis toolkit: A mapreduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, snpeff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; Iso-2; Iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.T.; Demarest, B.L.; Bisgrove, B.W.; Gorsi, B.; Su, Y.; Yost, H.J. Mmappr: Mutation mapping analysis pipeline for pooled RNA-seq. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, H.; Abe, A.; Yoshida, K.; Kosugi, S.; Natsume, S.; Mitsuoka, C.; Uemura, A.; Utsushi, H.; Tamiru, M.; Takuno, S.; et al. Qtl-seq: Rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of dna from two bulked populations. Plant J. 2013, 74, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruitt, K.D.; Tatusova, T.; Maglott, D.R. Ncbi reference sequences (refseq): A curated non-redundant sequence database of genomes, transcripts and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Galperin, M.Y.; Natale, D.A.; Koonin, E.V. The cog database: A tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. Swiss-prot protein sequence database and its supplement trembl in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. Kegg: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. Tassel: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, N.; Pandey, S.K.; Pandey, S.D.; Nath, V. Genetic diversity and grouping of litchi genotypes based on 83 qualitative and quantitative traits. Erwerbsobstbau 2023, 65, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Cai, C.; Wang, L.; Fu, D.; Ou, L. Morphological diversity within litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) Based on leaf and branch traits. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 207, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Meng, H.; Chen, B.; Xie, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Yan, J.; Cai, J.; Yang, S.; Jiang, B.; et al. Identification of candidate genes controlling cucumber hypocotyl elongation under low light stress based on BSA-seq and RNA-seq. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 337, 113488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Ren, L.; Qi, F.; Wang, H.; Yu, S.; Sun, Z.; Huang, B.; Han, S.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; et al. Bsa-seq approach identified candidate region and diagnostic marker for chilling tolerance of high oleic acid peanut at germination stage. Agronomy 2023, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Jiao, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, X. Qtl-seq analysis of the seed size trait in grape provides new molecular insights on seedlessness. J. Integr. Agr. 2022, 21, 2910–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, I.A. Seed storage oil mobilization. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santner, A.; Calderon-Villalobos, L.I.A.; Estelle, M. Plant hormones are versatile chemical regulators of plant growth. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Geng, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, H.; Yang, W. Association and genetic identification of loci for four fruit traits in tomato using indel markers. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Zhu, Q.; Jia, X.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, S.; Wang, S.; Shan, N.; Sun, J.; et al. Genome-wide development of indel-ssrs and association analysis of important agronomic traits of taro (Colocasia esculenta) in China. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 13347–13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Song, J.; Qiao, C.; Duan, K.; Feng, P.; Kong, W.; Bai, T.; Zhu, C.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Genome-wide association studies of salt-tolerance-related traits in rice at the seedling stage using indel markers developed by the genome re-sequencing of japonica rice accessions. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, A.; Gupta, A.; Mahalaxmi, M.; Aykkal, R.; Singh, T.R.; Arunachalam, V. Tools, resources and databases for snps and indels in sequences: A review. Int. J. Bioinform. Res. Appl. 2014, 10, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Li, Z.; Huang, S.; Tao, J.; Shi, Y.; Chen, A.; Li, J.; Tang, H.; Chang, L.; Deng, Y.; et al. Genome-wide development of insertion-deletion (Indel) markers for cannabis and its uses in genetic structure analysis of Chinese germplasm and sex-linked marker identification. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
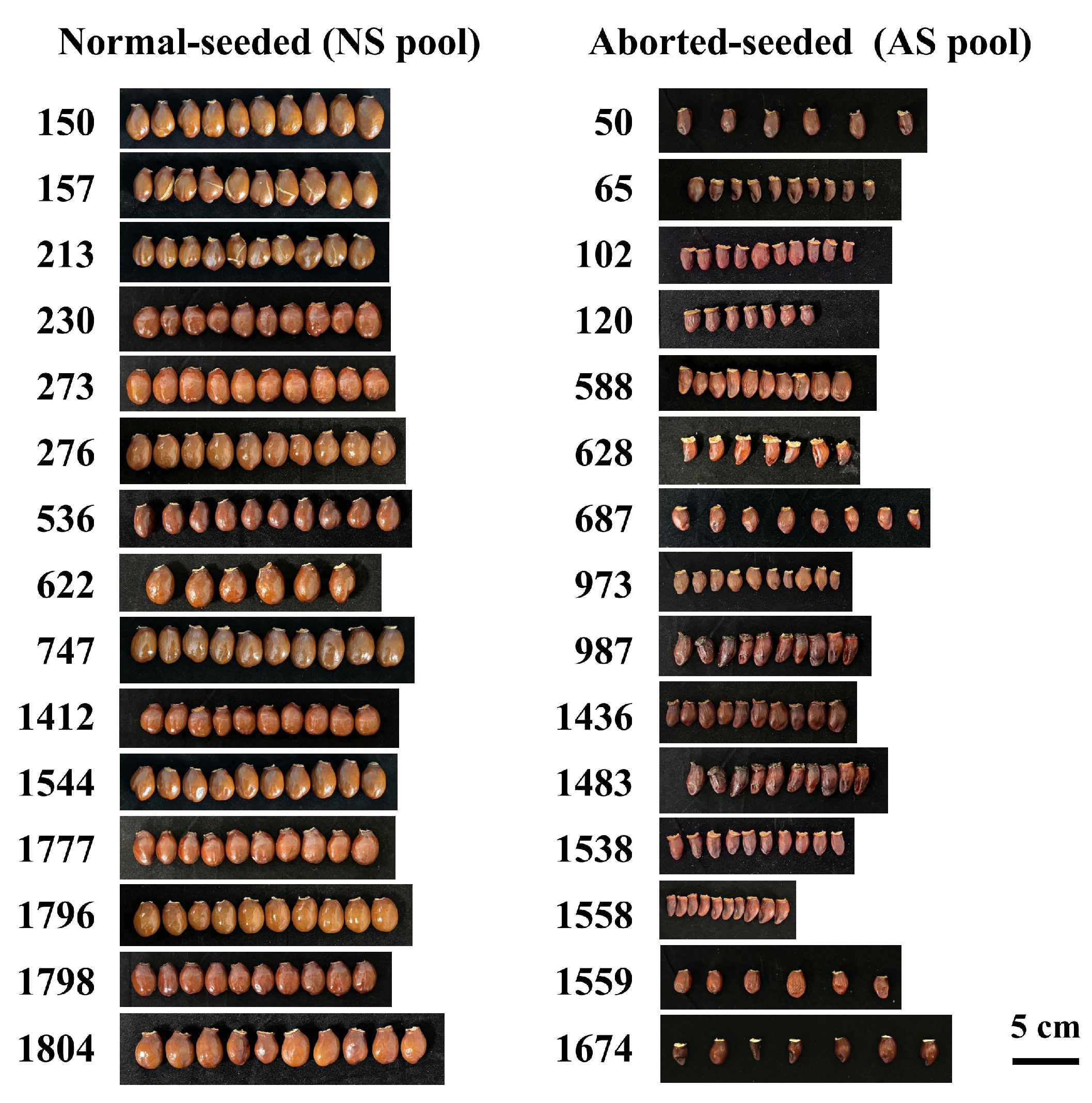
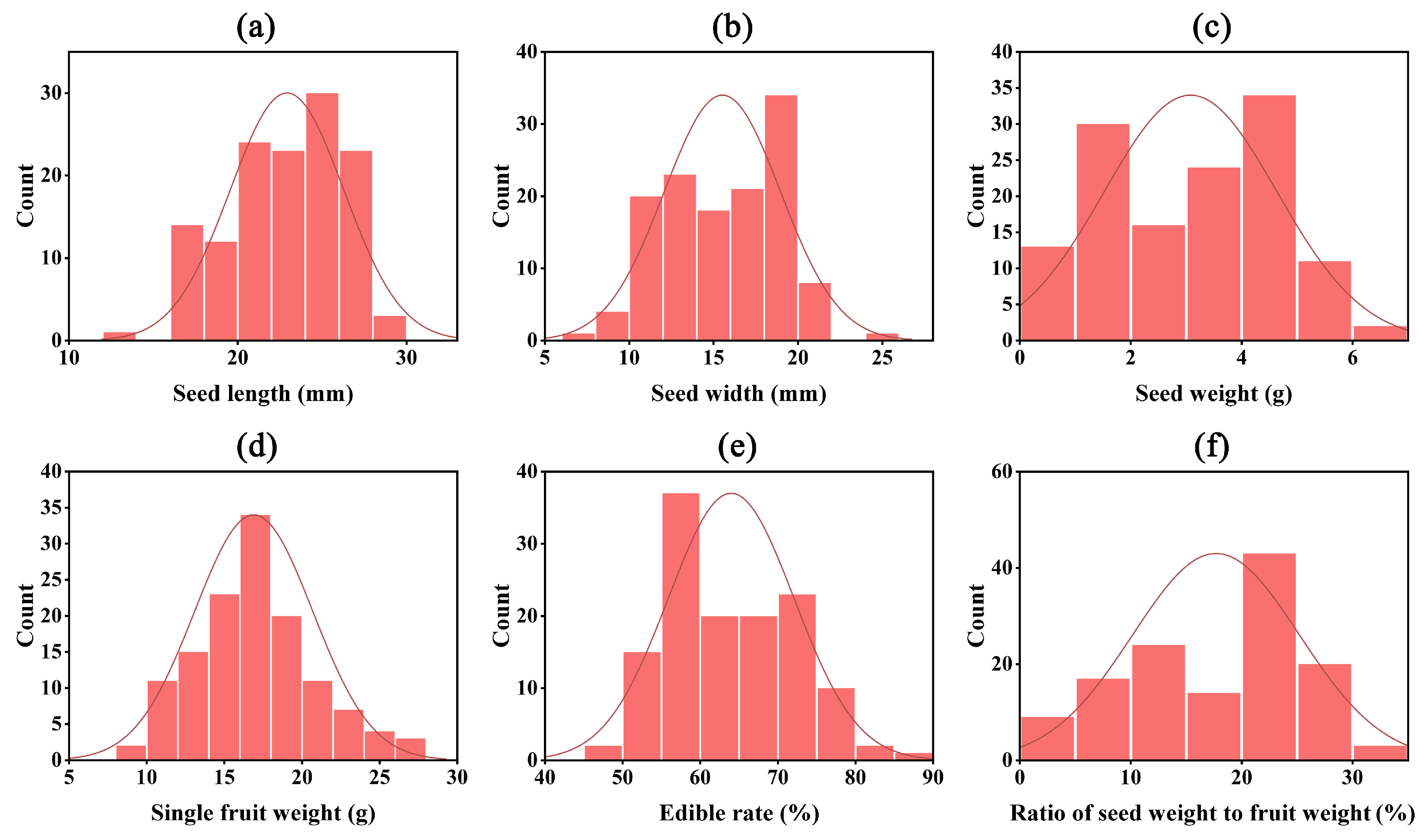
| Trait | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single fruit weight (g) | 9.07 | 26.53 | 16.91 | 3.80 | 0.26 | −0.01 | 0.22 |
| Seed weight (g) | 0.31 | 6.39 | 3.09 | 1.56 | −0.08 | −1.22 | 0.50 |
| Seed length (mm) | 13.61 | 29.55 | 22.94 | 3.37 | −0.35 | −0.70 | 0.15 |
| Seed width (mm) | 7.61 | 24.92 | 15.52 | 3.44 | −0.06 | −0.84 | 0.22 |
| Edible rate (%) | 49.00 | 85.72 | 63.97 | 8.07 | 0.38 | −0.74 | 0.13 |
| Ratio of seed weight to fruit weight (%) | 3.04 | 31.70 | 17.72 | 7.50 | −0.26 | −1.18 | 0.42 |
| Trait | Loci | p-Value | Permutation p-Value | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ratio of seed weight to fruit weight | Chr5_25610680_InDel | 5.42 × 10−8 | 0.001 | 35.54% |
| Seed weight | Chr5_25610680_InDel | 4.17 × 10−7 | 0.001 | 32.22% |
| Seed width | Chr5_25610680_InDel | 9.36 × 10−6 | 0.001 | 26.79% |
| Edible rate | Chr5_25610680_InDel | 6.11 × 10−5 | 0.001 | 23.29% |
| Seed length | Chr5_25610680_InDel | 8.77 × 10−5 | 0.001 | 22.60% |
| Edible rate | Chr5_25585686_InDel | 5.49 × 10−4 | 0.001 | 18.94% |
| Seed weight | Chr5_25585686_InDel | 6.30 × 10−4 | 0.001 | 18.66% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.; Ju, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, F. BSA-Seq-Based Discovery of Functional InDel Markers for Seed Size Selection in Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091079
Yan T, Ju Y, Chen Z, Yang M, Wang X, Wang L, Zhou Y, Hu F. BSA-Seq-Based Discovery of Functional InDel Markers for Seed Size Selection in Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Horticulturae. 2025; 11(9):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091079
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Tingting, Yutong Ju, Zhe Chen, Mingchao Yang, Xianghe Wang, Lin Wang, Yiwei Zhou, and Fuchu Hu. 2025. "BSA-Seq-Based Discovery of Functional InDel Markers for Seed Size Selection in Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.)" Horticulturae 11, no. 9: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091079
APA StyleYan, T., Ju, Y., Chen, Z., Yang, M., Wang, X., Wang, L., Zhou, Y., & Hu, F. (2025). BSA-Seq-Based Discovery of Functional InDel Markers for Seed Size Selection in Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.). Horticulturae, 11(9), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11091079







