Identifying Primary Ecological Drivers and Regional Suitability for High-Quality Diospyros kaki ‘Taishuu’
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Materials
2.2. Metabolomic Analysis Method
2.3. Electronic Tongue-Mediated Analysis
2.4. Texture Analysis
2.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
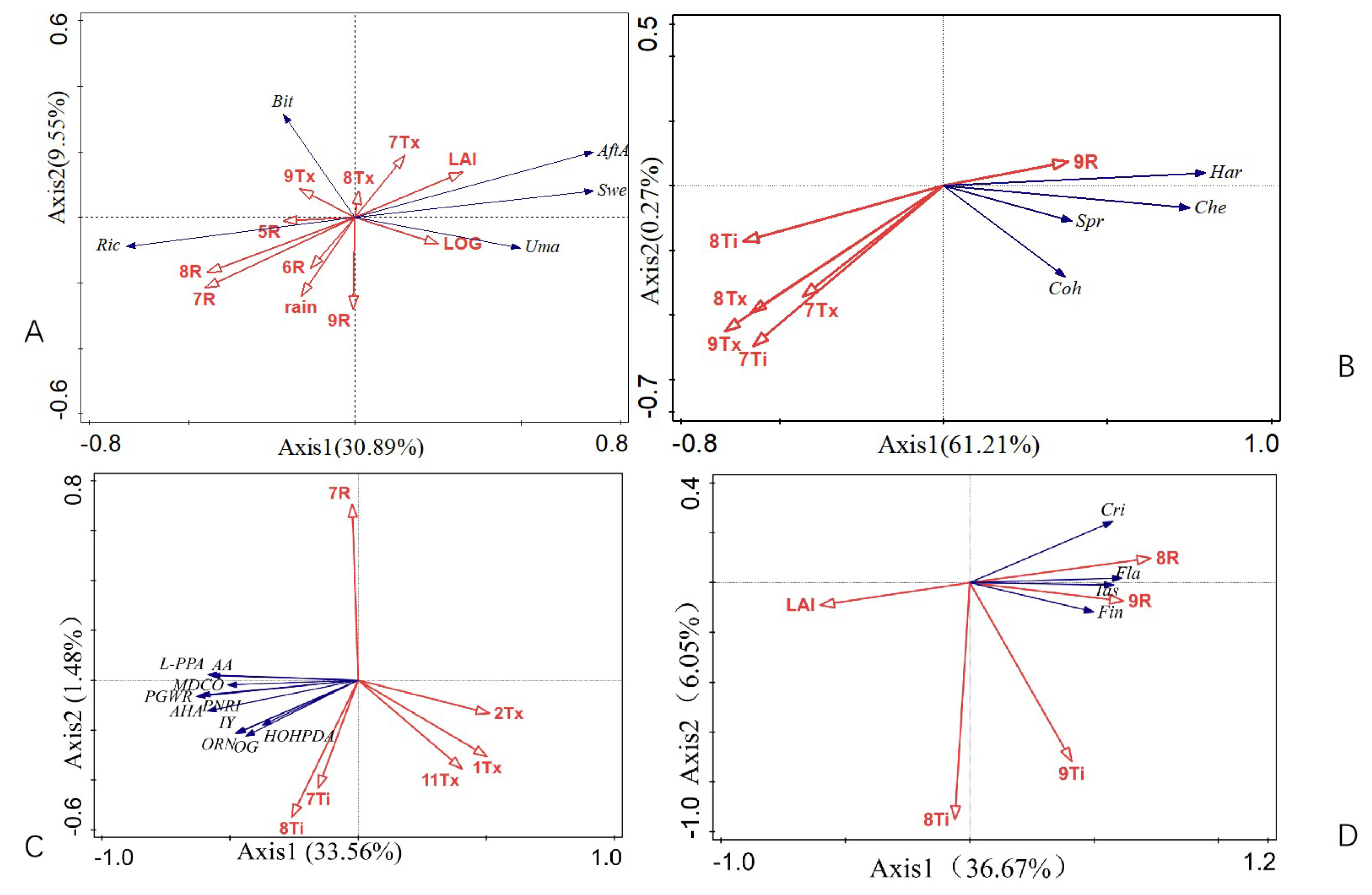
3.1. Regionalization Results of Ecological Adaptation and the Main Ecological Driving Factors
3.2. Fruit Qualities of Different Levels of Cultivation Suitability
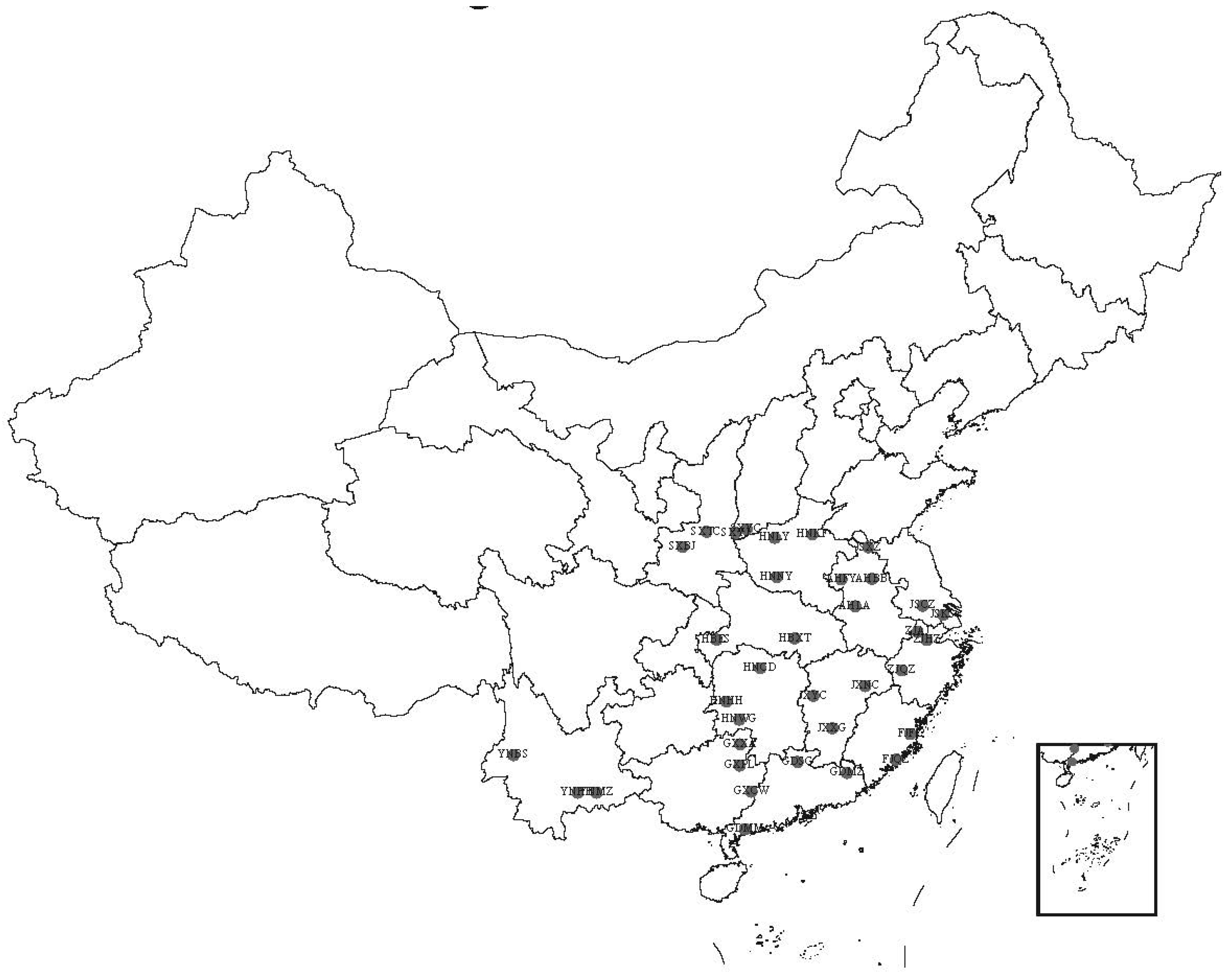
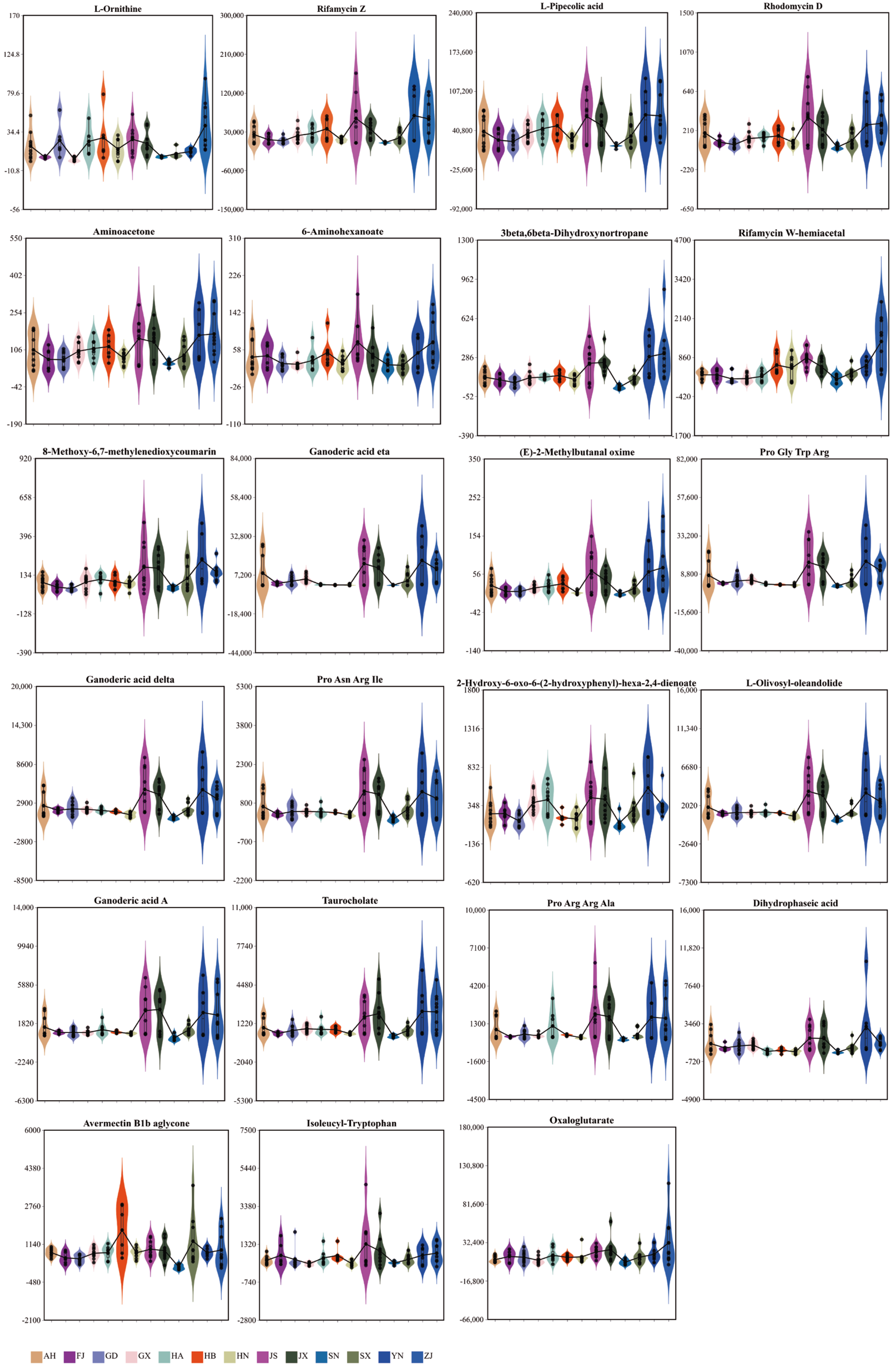
3.3. Fruit Quality of Different Provinces
3.4. The Main Factors Influencing Fruit Mouthfeel Properties
3.5. Adaptability Zoning Results Based on Sensory Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Geographical Trends of Mouthfeel Properties from Different Cultivation Regions
4.2. The Main Influencing Factors for Mouthfeel Properties
4.3. Zoning for High-Quality D. kaki ‘Taishuu’
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adaskaveg, J.A.; Blanco-Ulate, B. Targeting ripening regulators to develop fruit with high quality and extended shelf life. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2023, 179, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, H.; Yamada, M.; Kurihara, A.; Lwanami, H. New Japanese persimmon cultivar ‘Taishuu’. Bull. Nati Inst. Fruit Tree Sci. 2021, 35, 57–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.F. The current situation of sweet persimmon and the introduction of cultivation technology of Taiqiu. J. Zhejiang Agric. Sci. 2023, 64, 1909–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.C.; Zhang, Q.L.; Xu, L.Q.; Guo, D.Y.; Luo, Z.R. Recent developments in deastringency mechanism of persimmon fruit. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2016, 9, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.X.; Wang, J.F.; Gong, B.C.; Chen, Y.; Shi, H.Z.; Zhang, Q.L. A preliminary analysis on the suitable climatic and ecological region for introducing Japanese sweet persimmon. For. Res. 2000, 13, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.Y. Climatic regionalization of non astringent persimmon introduction cultivated area. Yunnan For. Sci. Technol. 1998, 3, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kafkaletou, M.; Christopoulos, M.V.; Tsaniklidis, G.; Papadakis, I.; Ioannou, D.; Tzoutzoukou, C.; Tsantili, E. Nutritional value and consumer-perceived quality of fresh goji berries (Lycium barbarum L. and L. chinense L.) from plants cultivated in Southern Europe. Fruits 2018, 73, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyotte, B.; Bowen, A.J.; Banks, T.L. Mapping the sensory perception of apple using descriptive sensory evaluation in a genome wide association study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Lee, J.W.; Bae, G.S.; Moon, B.K. Evaluation of umami taste in Hanwoo with different feed sources by chemical analysis, electronic tongue analysis, and sensory evaluation. Food Chem. 2023, 20, 100889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoz-Redondo, J.; Puertas, B.; Pereira-Caro, G.; Ordóñez-Díaz, J.; Ruiz-Moreno, M.J.; Cantos-Villar, E.; Moreno-Rojas, J.A. A statistical workflow to evaluate the modulation of wine metabolome and its contribution to the sensory attributes. Fermentation 2021, 7, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, W.C.; Park, S.J.; Lee, M.J.; Park, S.H.; Min, S.G.; Ku, K.M. Seasonal variation of metabolites in Kimchi cabbage: Utilizing metabolomics based machine learning for cultivation season and taste discrimination. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2024, 65, 981–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Zheng, M.P.; Yang, H.C.; Zhang, J.M.; Li, Y.C.; Wang, G.J.; Tian, J.J.; Zhang, K.; Xia, Y.; Li, Z.F.; et al. The effect of broad bean diet on structure, flavor and taste of fresh grass carp: A comprehensive study using E-nose, E-tongue, TPA, HS-SPME-GC-MS and LC-MS. Food Chem. 2024, 436, 137690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, Q.H.; Yan, E.D.; Chen, R.H.; Yan, F.T.; Lai, X.F.; Zhang, Z.B.; Chen, Z.Z.; Li, Q.; et al. Metabolomics and electronic tongue reveal the effects of different storage years on metabolites and taste quality of Oolong Tea. Food Control 2023, 152, 109847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Liao, B.; Li, J.W.; Liu, H.L.; Liu, Z. Pollen donor affects the taste and aroma compounds in ‘Cuixiang’ and ‘Xuxiang’ kiwifruit. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 314, 111945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.L.; Ren, J.C.; Yan, A.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Xu, H.Y.; Sun, L. Effects of trellis systems on the vegetative growth and fruit quality of muscat-flavored table grapes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, P.; Boonen, M.; Bylemans, D.; Melis, A.; Delm, T.; Vendel, I.; Hertog, M.L.A.; Vandendriessche, H.J. Optimization of the irrigation schedule in field-grown strawberry results in higher water use efficiency and improved taste quality. Acta Hortic. 2022, 1335, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB33/T 2500-2022; The Technical Regulation of Cultivation for Non-astringent Persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.). Zhejiang Provincial Administration for Market Regulation: Hangzhou, China, 2022.
- Yue, Z.H.; Gong, B.C.; Cheng, W.Q.; Wu, K.Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Liu, C.Y.; Xu, Y. Identification of main metabolites correlated with the sensory attributes of Diospyros kaki. cv. “Taishuu” through a large-scale comprehensive analysis by sensory evaluation, electronic tongue and metabolomics. LWT 2024, 195, 115834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.Q.; Xu, Y.; Wu, K.Y.; Zhao, X.M.; Gong, B.C. Comparison of three comprehensive evaluation methods to evaluate the quality of persimmon fruit. J. Nanjing For. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2023, 47, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 10221-2012; Sensory Analysis Methodology—General Introduction. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of China, AQSIQ: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Qin, A.L.; Liu, B.; Guo, Q.S.; Bussmann, R.W.; Ma, F.Q. Maxent modeling for predicting impacts of climate change on the potential distribution of Thuja sutchuenensis Franch., an extremely endangered conifer from southwestern China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 10, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gong, B.C.; Liu, C.Y.; Xu, Y. Effects of long-term sod culture management on soil fertility, enzyme activities, soil microorganisms, and fruit yieldand quality in “Jiro” sweet persimmon orchard. Plants 2024, 13, 1537. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.; Lee, Y. Instrumental analysis or human evaluation to measure the appearance, smell, flavor, and physical properties of food. Foods 2023, 12, 3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.B.; Jiang, S.Y.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W. T Cultural regionalization for Notopterygium incisum based on 3S technology platform Ⅱ. Evaluation for quality suitability for N. incisum based on collocated Cokriging. J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2017, 42, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar]
- Soneji, J.R.; Nageswara-Rao, M. (Eds.) Breeding and Health Benefits of Fruit and Nut Crops; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-272-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Li, X.M.; Zhu, Y.N.; He, W.L.; Bai, Q.F. Ecological climate suitability division for citrus in Southern Shaanxi based on GIS. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2011, 32, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.M.; He, T.F.; Zhang, B.Y.; Xie, Z.Y. Ecological suitability investigation of the northern margin of citrus production area in China. Chin. Citrus 1982, 2, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Lin, J.; Yang, K.; Yang, F.; Huling, C.; Chen, T.; Lichun, L.; Line, L.; Chen, F. Construction and application of climate quality evaluation model for indian jujube. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2021, 32, 443–455. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Tang, G.N.; Li, R. Study of Land Geological Background of Distinctive Agricultural Products in Zhejiang Province; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.L.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.X.; Du, Y.P. The aroma difference of ‘Muscat’ grape in Penglai, Pingdu and Dongying of Shandong Province. Chin. Fruit 2021, 2, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.C.; Huang, Z.Y.; Gao, M. Relationship between climatic characteristics and planting suitability of main cash crops in Yunnan. J. Meteorol. Res. Appl. 2021, 3, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.N.; Zheng, W.; Lu, Z.M. Differences in fruit quality of Dawuxing loquat from seven production regions. J. Northwest. Agric. For Univ. (Nat. Sci.). 2023, 52, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.L.; Yang, F. Evaluation and comparation of fruit quality of pomegranate cultivars in China. Storage Process 2015, 15, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tharaga, P.C. Sweet cherry yield, fruit quality and water productivity under rainfed conditions in eastern Free State. Acta Hortic. 2022, 1348, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccheri, M.; Vecchi, P.D.; Ughini, V.; Eccher, T.; Cortellino, G. Quality and nutritional properties of ready-to-eat blackberry from different cultivars and pedoclimatic conditions. Acta Hortic. 2018, 1194, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galdón, B.R.; Rodríguez, C.T.; Rodríguez, E.R.; Romero, C.D. Organic acid contents in onion cultivars (Allium cepa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6512–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwieterman, M.L. Metabolite Analysis, Environmental Factors, and a Transgenic Approach to Understanding Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) Flavor. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Florida, Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, C.Y.; Gong, B.C.; Yang, X.; Wu, K.Y.; Yue, Z.H.; Xu, Y. Analysis of the correlation between persimmon fruit-sugar components and taste traits from germplasm evaluation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakatos, L.; Biniak-Pieróg, M.; Zyromski, A. Effect of night and day temperature on the cover colour and quality parameters of apple. J. Water Land Dev. 2012, 16, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.F.; Wu, R.Y.; Ni, J.P.; Teng, Y.W. High temperature alters sorbitol metabolism in Pyrus pyrifolia leaves and fruit flesh during late stages of fruit enlargement. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. 2013, 138, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Gong, B.C.; Wu, K.Y.; Fei, X.Q. Studies on reproductive law and precocity and prolificacy of non-astringent persimmon. For. Res. 1996, 9, 461–468. [Google Scholar]
- Harada, H.; Itamura, H.; Taira, S.; Zheng, G.H. Natural removal of astringency in PCNA persimmon fruit cv. ‘Jiro’ grown in some different districts of Japan. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1990, 58, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.P.; Zheng, Z.M.; Liang, H.N.; Li, B. Relationship between activity of alcohol dehydrogenase and soluble tannin in persimmon. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2009, 35, 741–746. [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyama, E.; Shibasaki, T.; Kawabe, H.; Mukai, J.; Uchida, T. Bitterness suppression of BCAA solutions by L-Ornithine. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1288–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Sun, B.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Zhong, W.; Yin, J.; Hu, C.; He, D.; Wang, X. Effects of different amino acid enzymatic preparations on the quality and flavor of fragrant rapeseed oil. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.T.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.J. Recent advances in research on flavor substances in tomato fruit and their influential factors. Food Sci. 2023, 144, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Hossain, D.; Perry, P.L.; Ren, J.C.; Yan, A.L.; Liu, Z.H.; Xu, H.Y.; Sun, L. Characterization of volatile and aroma-impact compounds in persimmon (Diospyros kaki L. var. Triumph) fruit by GC-MS and GC-O analyses. Flavour Fragr. J. 2012, 27, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muna, E.M.A. Study of Quality Characteristics, Aroma Components and Gene Expression of Alcohol Acyltransferase (DkAA T1) of Persimmon Fruits. Ph.D. Thesis, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Missang, C.E.; Maingonnat, J.F.; Renard, C.M.; Audergond, R.C. Apricot cell wall composition: Relation with the intra-fruit texture heterogeneity and impact of cooking. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.V.; Burity, H.A.; Martinez, C.R.; Chanway, C.P. Drought stress response on some key enzymes of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp.) nodule metabolism. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Dong, L.; Li, R.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, J.W.; Ji, S.J. Low temperature conditioning prevents loss of aroma-related esters from ‘Nanguo’ pears during ripening at room temperature. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 100, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.S.; Sicher, R.C.; Lary, D.; Strem, M.D.; Natarajan, S.; Bailey, B.A. The drought response of Theobroma cacao (cacao) and the regulation of genes involved in polyamine biosynthesis by drought and other stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 46, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R.G.; Sutherland, P.W.; Johnston, S.L.; Johnston, S.L.; Gunaseelan, K.; Hallett, I.C.; Mitra, D.; Brummell, D.A.; Schröder, R.; Johnston, J.W.; et al. Down-regulation of POLYGALACTURONASE1 alters firmness, tensile strength and water loss in apple (Malus× domestica) fruit. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P. Transcriptome Analysis of Melon (Cucumis melo L.) Fruit with Different Texture During Ripening and Study on XTH Genes. Master’ Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.Z.; Hu, Y.L.; Zhou, B.Y.; Yao, Q.; Hu, Z.Q. Effect of soil moisture on cell-wall metalbolism of pericarp in citrus. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2008, 28, 486–492. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.X. Brittleness Character Evaluation System and the Formation Mechanism of Melon Pulp. Master’ Thesis, Hangzhou Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.L.; Zhang, G.L.; Lv, X.L.; Gong, R.G.; Luo, N.; Hu, Q. Cell wall enzyme activity, cell ultrastructure and fruit quality of Robertson Navel orange grown in three different habitats. J. Fruit Sci. 2006, 23, 670–675. [Google Scholar]
- Roeck, A.D.; Duvetter, T.; Fraeye, U.; Plancken, I.V.; Sila, D.N.; Loey, A.V.; Hendrickx, M. Effect of high-pressure/high-temperature processing on chemical pectin conversions in relation to fruit and vegetable texture. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, A.; Zheng, G.H.; Yonemori, K. Growth and ripening of persimmon fruit at controlled temperatures during growth stage III. Hortscience 1991, 26, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilkah, S.; David, I.; Lazar, M.; Itzhak, S.; Winer, L. The effect of high tempterre on fruit of ‘Triumph’ persimmon. Acta Hortic. 2013, 996, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagnachew, S.; Teketay, D.; Demissew, S. The Effects of monthly rainfall and temperature on flowering and fruiting intensities vary within and among selected woody species in northwestern ethiopia. Forests 2023, 14, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.K.; Yang, Z.Q. Effect of day and night temperature difference on fruit quality of tomato and its simulation models. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2017, 6, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.Y.; Han, W.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.Q. The difference in temperature between day and night affects the strawberry soluble sugar content by influencing the photosynthesis, respiration and sucrose phosphatase synthase. Hortic. Sci. 2021, 48, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpin, G.J.; Carolina, C.A. Use of artificial saliva for evaluation of instrumental texture of expanded snacks: Part II–correlations between sensory characteristics and instrumental properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 975–984. [Google Scholar]
- Coltri, P.P.; Pinto, H.S.; de Medeiros, Y.O.; Hashimoto, K.S.; Di Blasio, G.C.; Alfonsi, E.L.; Ribeiro do Valle Gonçalves, R.; Monteiro Alfonsi, E. Software for agriculture climate risk management focused in smallholders. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, P.; Wang, H.L.; Yuan, W. Problems on introducing fine sweet persimmon varieties in northern persimmon-planted area, China. J. China Agric. Univ. 2003, 8, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, I.; Lee, S. Impact of climate on yield of sweet persimmon in Gyeongsangnam-province, South Korea. J. Clim. Res. 2017, 12, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Jeon, K.S.; Kim, T.C. Analysis of air temperature factors related to difference of fruit characteristics according to cultivating areas of persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.). J. Bio-Environ. Control 2008, 17, 124–131. [Google Scholar]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Liu, C.; Jiang, X.; Xu, Y. Identifying Primary Ecological Drivers and Regional Suitability for High-Quality Diospyros kaki ‘Taishuu’. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080984
Yang X, Liu C, Jiang X, Xu Y. Identifying Primary Ecological Drivers and Regional Suitability for High-Quality Diospyros kaki ‘Taishuu’. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080984
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xu, Cuiyu Liu, Xibing Jiang, and Yang Xu. 2025. "Identifying Primary Ecological Drivers and Regional Suitability for High-Quality Diospyros kaki ‘Taishuu’" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080984
APA StyleYang, X., Liu, C., Jiang, X., & Xu, Y. (2025). Identifying Primary Ecological Drivers and Regional Suitability for High-Quality Diospyros kaki ‘Taishuu’. Horticulturae, 11(8), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080984





