Exogenous Calcium on Calcium Accumulation, Uptake and Utilization in Tomato
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Conditions
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Indices and Methods
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Tomato Dry Matter Accumulation and Quality
3.1.1. Dry Matter Accumulation in Tomato
3.1.2. Tomato Fruit Quality
3.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Calcium Uptake and Distribution in Tomato
3.2.1. Calcium Concentration in Tomato Vegetative Organs
3.2.2. Proportion of Calcium Accumulation in Tomato Vegetative Organs
3.3. Effects of Different Treatments on Calcium Uptake, Utilization, and Yield in Tomato Plants
3.4. Correlation Analysis Between Indicators of Calcium Fertilizer Uptake and Utilization and Yield in Tomato Plants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patricia, A.; Demetrio, G.; Dolores, M.F.; García-Gomez, C.; Obrador, A. Both Zn biofortification and nutrient distribution pattern in cherry tomato plants are influenced by the application of ZnO nanofertilizer. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Ullah, I.; Rab, A.; Shah, S.T.; Ahmad, N.; Ahmad, I.; Ali, A.; Basit, A.; Bibi, F.; Ahmad, M. Foliar application of calcium improves growth, yield and quality of tomato cultivars. Pure Appl. Biol. 2020, 9, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadir, S.A. Fruit quality at harvest of “Jonathan” apple treated with foliarly-applied calcium chloride. J. Plant Nutr. 2005, 27, 1991–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, Y.; Nambeesan, S.U.; van der Knaap, E. Blossom-end rot: A century-old problem in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) and other vegetables. Mol. Hortic. 2022, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Tomizaki, R.; Watanabe, R.; Maruyama, H.; Shinano, T.; Urayama, M.; Kanayama, Y. Ionomic differences between tomato introgression line IL8–3 and its parent cultivar M82 with different trends to the incidence of blossom-end rot. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 287, 110266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, K.; Gilani, S.; Hussain, Z.; Ishaq, R.; Adeel, M.; Ilyas, N. Effect of salt stress on tomato plant and the role of calcium. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 43, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.Z.; Mele, M.A.; Baek, J.P.; Kang, H.-M. Cherry tomato qualities affected by foliar spraying with boron and calcium. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 57, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, B.; Tyerman, S.D.; Burton, R.A.; Gilliham, M. Fruit calcium: Transport and physiology. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemadac, A.; Jean-Baptiste, I.; Bertoni, G.; Morard, P. Changes in calcium contents during melon (Cucumis melo L.) fruit development. Sci. Hortic. 1996, 66, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazeta, L.; Lang, A.; Hall, A.J.; Volz, R.K.; Jameson, P.E. Causes and Effects of changes in xylem functionality in apple fruit. Ann. Bot. 2004, 93, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.H.; Liu, C.; Huang, M.L.; Liu, K.Z.; Yan, D.Y. Effects of foliar fertilization: A review of current status and future perspectives. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, M.N.; Azizah, M.; Phebe, D.; Puter, E.M.W.; Azhar, M. Preharvest Foliar Spray of Calcium Chloride on Growth, Yield, Quality, and Shelflife Extension of Different Lowland Tomato Varieties in Malaysia. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Pan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Shu, C.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W. Analysis of nutrients and volatile compounds in cherry tomatoes stored at different temperatures. Foods 2023, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Mahajan, M.; Jain, P. Non-spectrophotometric methods for the determination of Vitamin C. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 417, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ji, K. The role of abscisic acid in regulating cucumber fruit development and ripening and its transcriptional regulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 64, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fibiani, M.; Paolo, D.; Leteo, F. Influence of year, genotype and cultivation system on nutritional values and bioactive compounds in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzolf-Panek, M.; Kleiber, T.; Kaczmarek, A. Effect of increasing manganese concentration in nutrient solution on the antioxidant activity, vitamin C, lycopene and polyphenol contents of tomato fruit. Food Addit Contam A. 2017, 34, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhai, F.; Kok, F.J.; Jacobsen, E.; Yang, X. Iron and zinc deficiencies in China: What is a feasible and cost-effective strategy? Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Guo, F.; Yang, S.; Zou, J.; Wan, S. Increasing Calcium and Decreasing Nitrogen Fertilizers Improves Peanut Growth and Productivity by Enhancing Photosynthetic Efficiency and Nutrient Accumulation in Acidic Red Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Yang, T.; Luo, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, L.; Codling, E. Pre-harvest calcium application increases biomass and delays senescence of broccoli microgreens. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2014, 87, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepler, P.K. Calcium: A central regulator of plant growth and development. Plant Cell Online 2005, 17, 2142–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Deependra, Y.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A. Effect of Calcium on the Growth and Yield of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Biol. Forum. 2023, 15, 1162–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Rabbu, H.S.; Wahba, H.E.; Khalid, K.A. Effects of different methods of eggshells application on the productivity of sweet basil herb. J. Plant Nutr. 2024, 47, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Papadopoulos, A.P. Effects of Calcium and Magnesium on Plant Growth, Biomass Partitioning, and Fruit Yield of Winter Greenhouse Tomato. HortScience 2004, 39, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olle, M.; Williams, I.H. Physiological disorders in tomato and some methods to avoid them. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 92, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsons, A.; Osvalde, A.; Cekstere, G.; Āboliņa, L. Effects of Ca Sprays on Fruit Ca Content and Yield of Tomato Variety Susceptible to Blossom-End Rot. Plants 2023, 12, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyub, C.M.; Pervez, M.A.; Shaheen, M.R.; Ashraf, M.I.; Haider, M.W.; Hussain, S.; Mahmood, N. Assessment of various growth and yield attributes of tomato in response to pre-harvest applications of calcium chloride. Pak. J. Life Soc. Sci. 2012, 10, 102–105. [Google Scholar]
- Haleema, B.; Rab, A.; Hussain, S.A.; Sajid, M.; Arif, M.; Shah, S.T. Influence of Calcium Concentrations and Sources on the Fruit Quality of Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill) at Different Storage Conditions. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 1866–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.X.; Dong, Q.L.; You, C.X.; Zhai, H.; Hao, Y.J. Expression analysis and functionalcharacterization of apple MdVHP1 gene reveals its involvement in Na+, malate andsoluble sugar accumulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.N.S.; Subbarayappa, C.T.; Sathish, A.; Ramamurthy, V. Impact of Zinc Fertilization on Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Yield, Zinc use Efficiency, Growth and Quality Parameters in Eastern Dry Zone(EDZ) Soils of Karnataka, India. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2021, 33, 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Hu, X. Effects of different N, P, K and Ca levels on tomato yield, quality and fertiliser use efficiency. Plant Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, S.A.; Abdelrahman, S.Z.; Megahed, M.M.A.; Abdeldaym, E.A.; El-Mogy, M.M.; Abdelgawad, K.F. Extending Shelf Life and Maintaining Quality of Tomato Fruit by Calcium Chloride, Hydrogen Peroxide, Chitosan, and Ozonated Water. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navjot, S.; Gurcharan, S. Studies on Storage Behaviour of Peach cv. Earli Grande. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 2, 541–543. [Google Scholar]
- Haleema, B.; Shah, S.T.; Basit, A.; Hikal, W.M.; Arif, M.; Khan, W.; Said-Al Ahl, H.A.H.; Fhatuwani, M. Comparative effects ofcalcium, boron, and zinc inhibiting physiological disorders, improvingyield and quality of Solanum lycopersicum. Biology 2024, 13, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuna, A.L.; Kaya, C.; Ashraf, M.; Altunlu, H.; Yokas, I.; Yagmur, B. The effects of calcium sulphate on growth, membrane stability and nutrient uptake of tomato plants grown under salt stress. Environ. Experiment. Bot. 2007, 59, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirpour, M.; Khoshghalb, H.; Nemati, H.; Ramazani, M.; Rahimi, M. Foliar application of humic acid, calcium and boron on chemical characteristics and fruit quality of tomato. Agric. Biol. Res. 2018, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gholamnejad, S.; Haghighi, M.; Etemadi, N.; Shariatmadari, H. Fortification of tomato with Ca and its effects on the fruit quality, calcium status and nutraceutical values of tomato in different NO3:NH4 ratios. N. Z. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2020, 48, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sediqui, N.; Amin, M.W.; Dawlatzai, N.; Gulab, G.; Poyesh, D.S.; Terada, N.; Sanada, A.; Kamata, A.; Koshio, K. Elucidation of Shoot and Root Growth, Physiological Responses, and Quality Traits of Tomato (Solanum lycopersicon L.) Exposed to Elevated Calcium Carbonate Concentrations. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraslan, F.; Akbas, B.; Inal, A.; Tarakcioglu, C. Effects of foliar sprayed calcium sources on Tomato mosaic virus (ToMV) infection in tomato plants grown in greenhouse. Phytopathologica 2007, 35, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, M.; Liu, G.; Ma, F.; Bao, Z. Lignin Sulfonate-Chelated Calcium Improves Tomato Plant Development and Fruit Quality by Promoting Ca2+ Uptake and Transport. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.X.; Zhou, J.M.; Fan, X.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Duan, Z.Q.; Tang, C. Application methods of calcium supplements affect nutrient levels and calcium forms in mature tomato fruits. J. Plant Nutr. 2004, 27, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.; Montanha, G.S.; Agostinho, L.F.; Polezi, S.; Marques, J.P.R.; de Carvalho, H.W.P. Foliar calcium absorption by tomato plants: Comparing the effects of calcium sources and adjuvant usage. Plants 2023, 12, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheour, F.; Willemot, C.J.; Arul, Y.; Desjardins, J.; Makhlouf, P.M.; Gosselin, A. Effects of foliar application of CaCl2 on postharvest strawberry ripening. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1990, 115, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolong, T.; Mishra, S.; Barickman, C.; Sams, C. Impact of Supplemental Calcium Chloride on Yield, Quality, Nutrient Status, and Postharvest Attributes of Tomato. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, B. Effect of exogenous calcium on growth, nutrients uptake and plasma membrane H+-ATPase and Ca2+-ATPase activities in soybean(Glycine max) seedlings under simulated acid rain stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 165, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Wang, C.; Gao, Q.; Li, L.; Luan, S. Calcium spikes, waves and oscillations in plant development and biotic interactions. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Li, H.; Ren, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L. Calcium regulates growth and nutrient absorption in poplar seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 887098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Bi, A.Y.; Amombo, E.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, C.; Hu, T.; Fu, J. Exogenous calcium enhances the photosystem II photochemistry response in salt stressed tall fescue. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; An, H.; Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Liu, X. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorous addition on the ecological stoichiometry of plant-litter-soil in desert grassland. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 8773–8783. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Weng, X.H.; Zhou, Y.B.; Huo, Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Liu, L.Y.; Pei, J.B. Effects of exogenous calcium additions on the ecological stoichiometric characteristics of various organs and soil nutrients and their internal stability in Pinus tabuliformis. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1428011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivay, S.Y.; Kumar, D.; Prasad, R. Effect of zinc-enriched urea on productivity, zinc uptake and efficiency of an aromatic rice--wheat cropping system. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 81, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
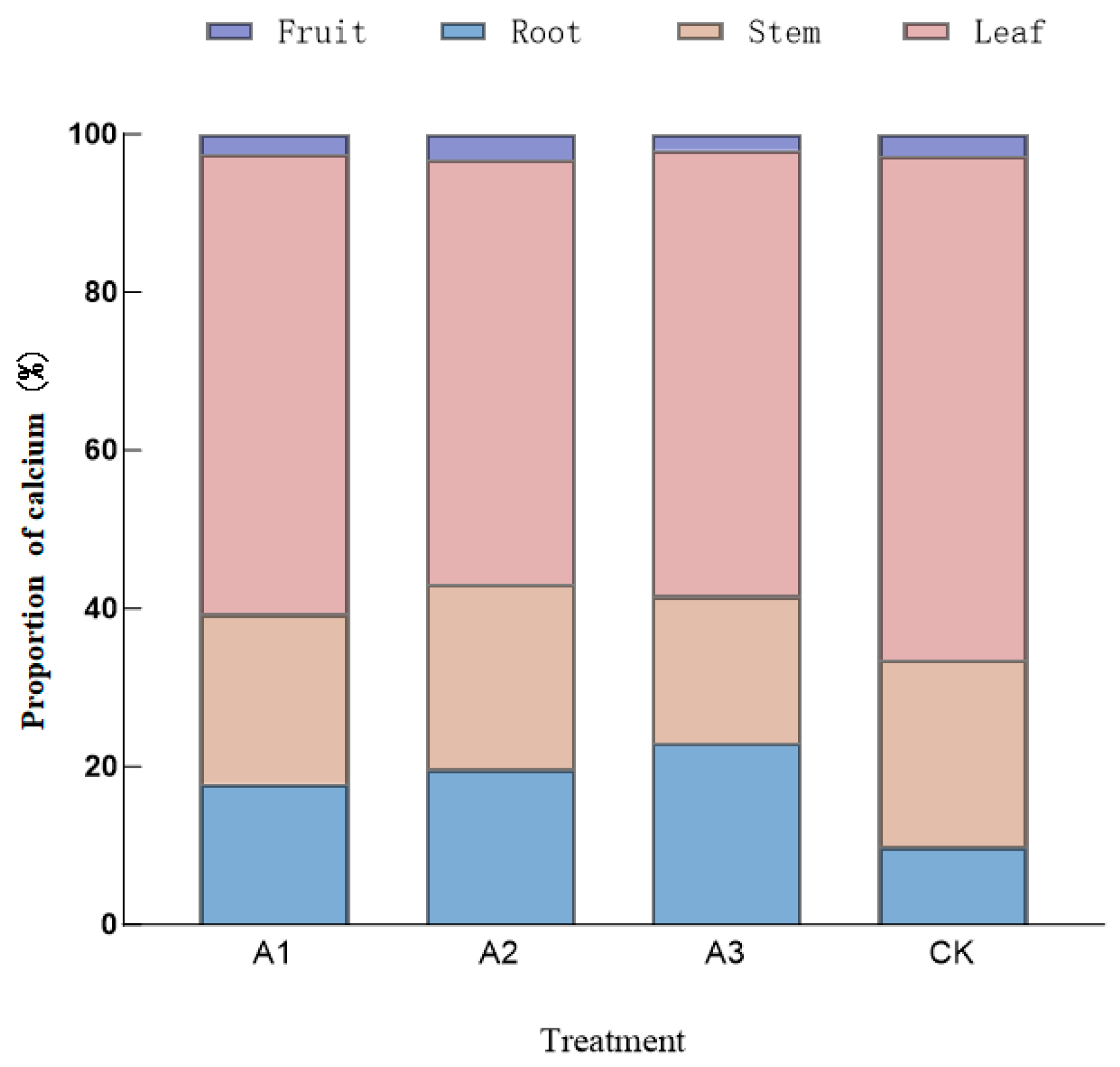
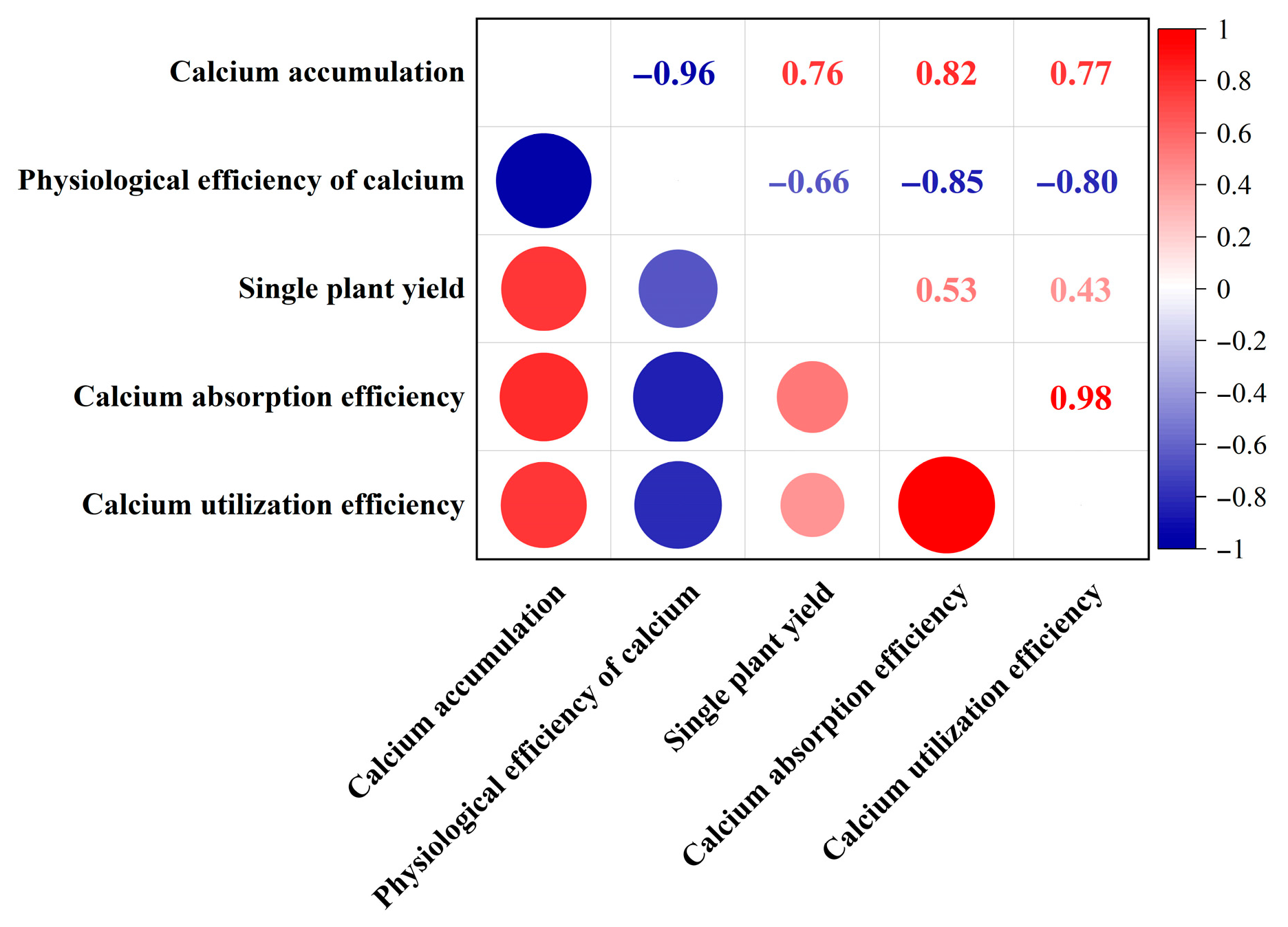
| Treatment | Root (g) | Stem (g) | Leaf (g) | Fruit (g) | Whole Plant (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 g (A1) | 6.39 ± 0.12 b | 61.91 ± 3.27 a | 55.6 ± 1.57 b | 258.04 ± 1.99 b | 381.94 ± 6.59 b |
| 6 g (A2) | 9.8 ± 0.61 a | 65.28 ± 2.35 a | 66.66 ± 2.04 a | 281.37 ± 12.16 a | 423.11 ± 13.39 a |
| 9 g (A3) | 5.9 ± 0.34 b | 55.57 ± 2.72 b | 48.42 ± 0.8 c | 240.03 ± 22.51 b | 349.92 ± 19.8 c |
| 0 g (CK) | 4.86 ± 0.67 c | 36.76 ± 1.11 c | 40.52 ± 0.17 d | 153.53 ± 1.17 c | 235.68 ± 2.26 d |
| Treatment | Soluble Protein (mg·g−1 FW) | Soluble Sugar (% FW) | Soluble Solid (% FW) | Vitamin C (mg·kg−1 FW) | Organic Acid (% FW) | Nitrate (ug·g−1 FW) | Lycopene (mg·kg−1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 g (A1) | 2.26 ± 1.79 ab | 2.32 ± 0.1 3 b | 3.63 ± 0.68 ab | 32.26 ± 2.29 a | 0.36 ± 0.09 ab | 23.93 ± 10.16 a | 5.89 ± 0.51 c |
| 6 g (A2) | 4.18 ± 0.81 a | 3.21 ± 0.42 a | 4.33 ± 0.4 a | 27.05 ± 2.27 b | 0.22 ± 0.02 c | 10.86 ± 6.67 ab | 22.85 ± 4.5 a |
| 9 g (A3) | 1.55 ± 0.92 b | 1.66 ± 0.1 b | 3.0 ± 0.1 b | 17.59 ± 1.56 c | 0.46 ± 0.04 a | 5.43 ± 3.67 b | 6.82 ± 0.86 c |
| 0 g (CK) | 3.25 ± 0.2 ab | 1.98 ± 0.68 b | 3.7 ± 0.2 ab | 23.48 ± 0.63 d | 0.32 ± 0.04 b | 13.85 ± 3.42 ab | 17.65 ± 2.93 b |
| Treatment | Root (mg·g−1) | Stem (mg·g−1) | Leaf (mg·g−1) | Fruit (mg·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 g (A1) | 20.4 ± 0.98 c | 24.6 ± 1.39 a | 66.22 ± 1.04 a | 2.85 ± 0.11 b |
| 6 g (A2) | 22.18 ± 1.06 b | 26.28 ± 1.11 a | 60.32 ± 0.89 c | 3.6 ± 0.43 a |
| 9 g (A3) | 26.33 ± 1.1 a | 21.3 ± 1.03 b | 64.46 ± 1.12 b | 2.25 ± 0.13 c |
| 0 g (CK) | 7.75 ± 0.21 d | 18.37 ± 1.06 c | 49.64 ± 0.92 d | 2.13 ± 0.01 c |
| Treatment | Calcium Accumulation (g/Plant) | Calcium Absorption Efficiency (%) | Calcium Utilization Efficiency (kg/kg) | Physiological Efficiency of Calcium (kg/kg) | Single Plant Yield (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 g (A1) | 6.07 ± 0.23 b | 100.65 ± 6.79 a | 127.31 ± 2.2 a | 62.94 ± 1.34 c | 4.28 ± 0.18 b |
| 6 g (A2) | 6.96 ± 0.07 a | 65.19 ± 1.46 b | 70.52 ± 2.23 b | 60.77 ± 1.86 c | 5.0 ± 0.11 a |
| 9 g (A3) | 5.0 ± 0.07 b | 21.62 ± 1.04 c | 38.88 ± 2.2 c | 70.02 ± 3.82 b | 3.93 ± 0.43 b |
| 0 g (CK) | 3.05 ± 0.03 b | - | - | 77.23 ± 0.34 a | 3.87 ± 0.29 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.; Xia, N.; Wang, W. Exogenous Calcium on Calcium Accumulation, Uptake and Utilization in Tomato. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080986
Wu C, Xia N, Wang W. Exogenous Calcium on Calcium Accumulation, Uptake and Utilization in Tomato. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080986
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chunyan, Nan Xia, and Wei Wang. 2025. "Exogenous Calcium on Calcium Accumulation, Uptake and Utilization in Tomato" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080986
APA StyleWu, C., Xia, N., & Wang, W. (2025). Exogenous Calcium on Calcium Accumulation, Uptake and Utilization in Tomato. Horticulturae, 11(8), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080986




