Comparative Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Tissue- and Species-Specific Differences in the Abundance of Dammarane-Type Ginsenosides in Three Panax Species
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
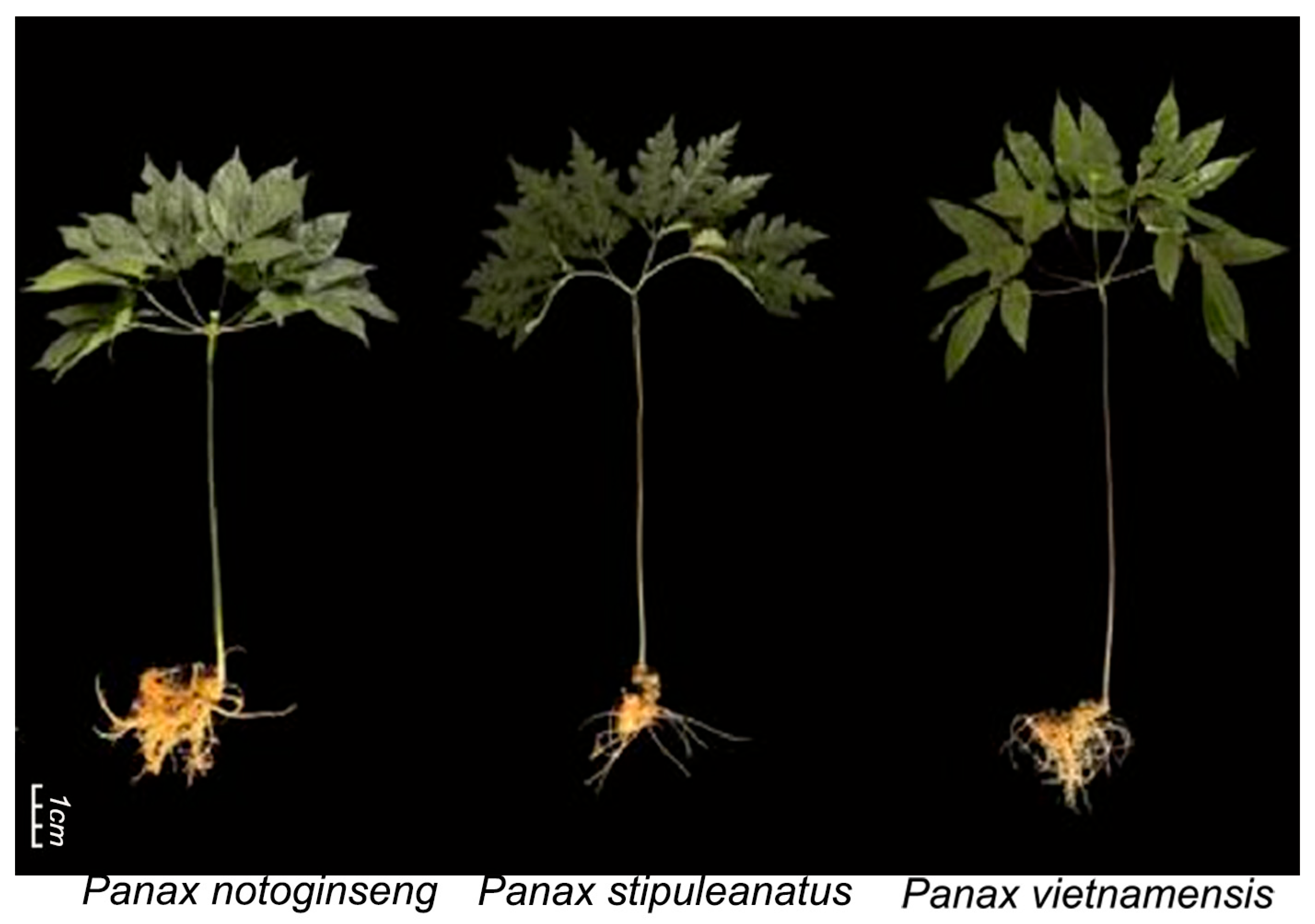
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Untargeted LC-MS Profiling of Metabolites
3. Results
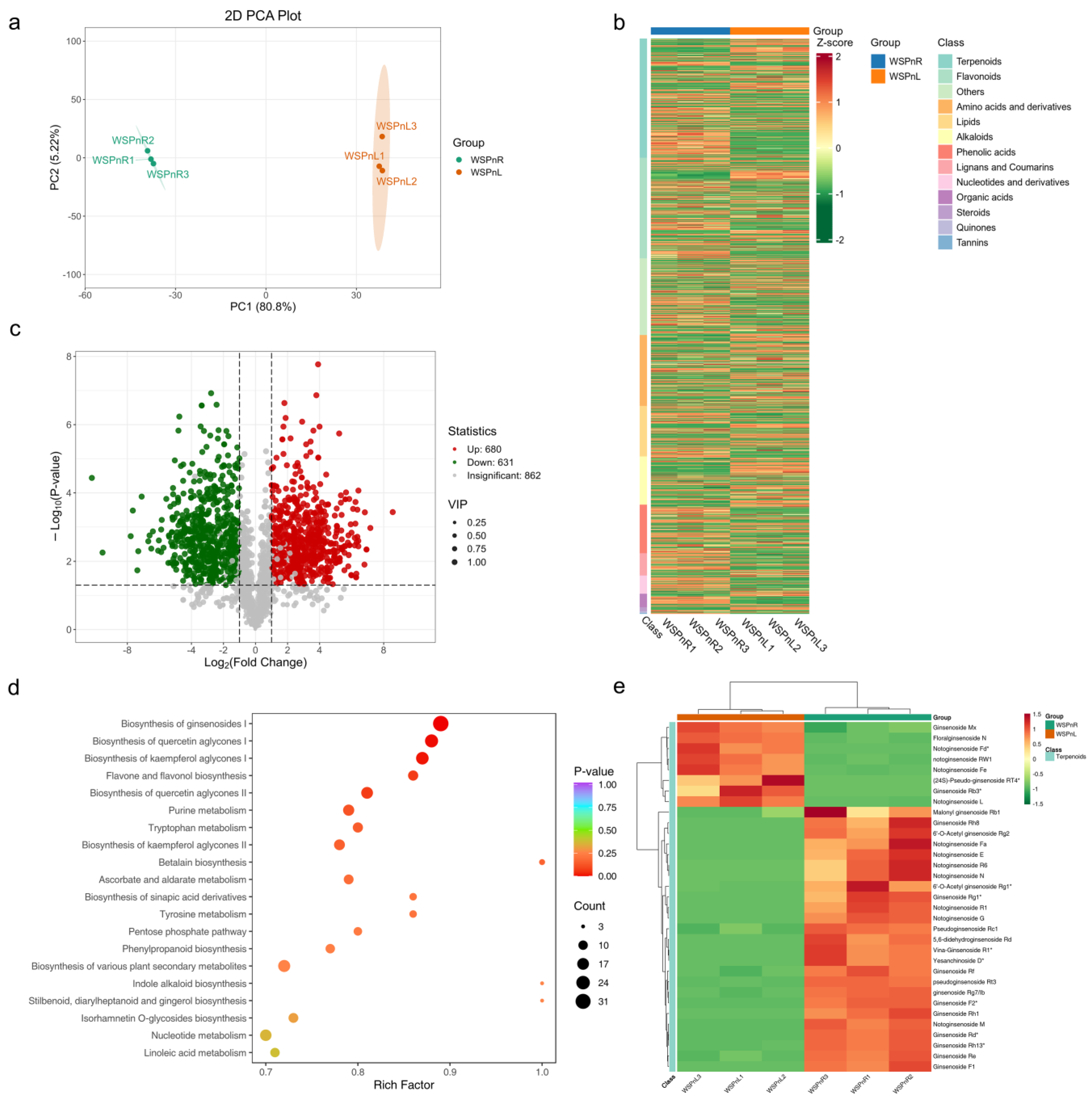
3.1. Metabolite Profiling of Potential Saponin-Related Metabolites in the Root and Leaf of P. notoginseng
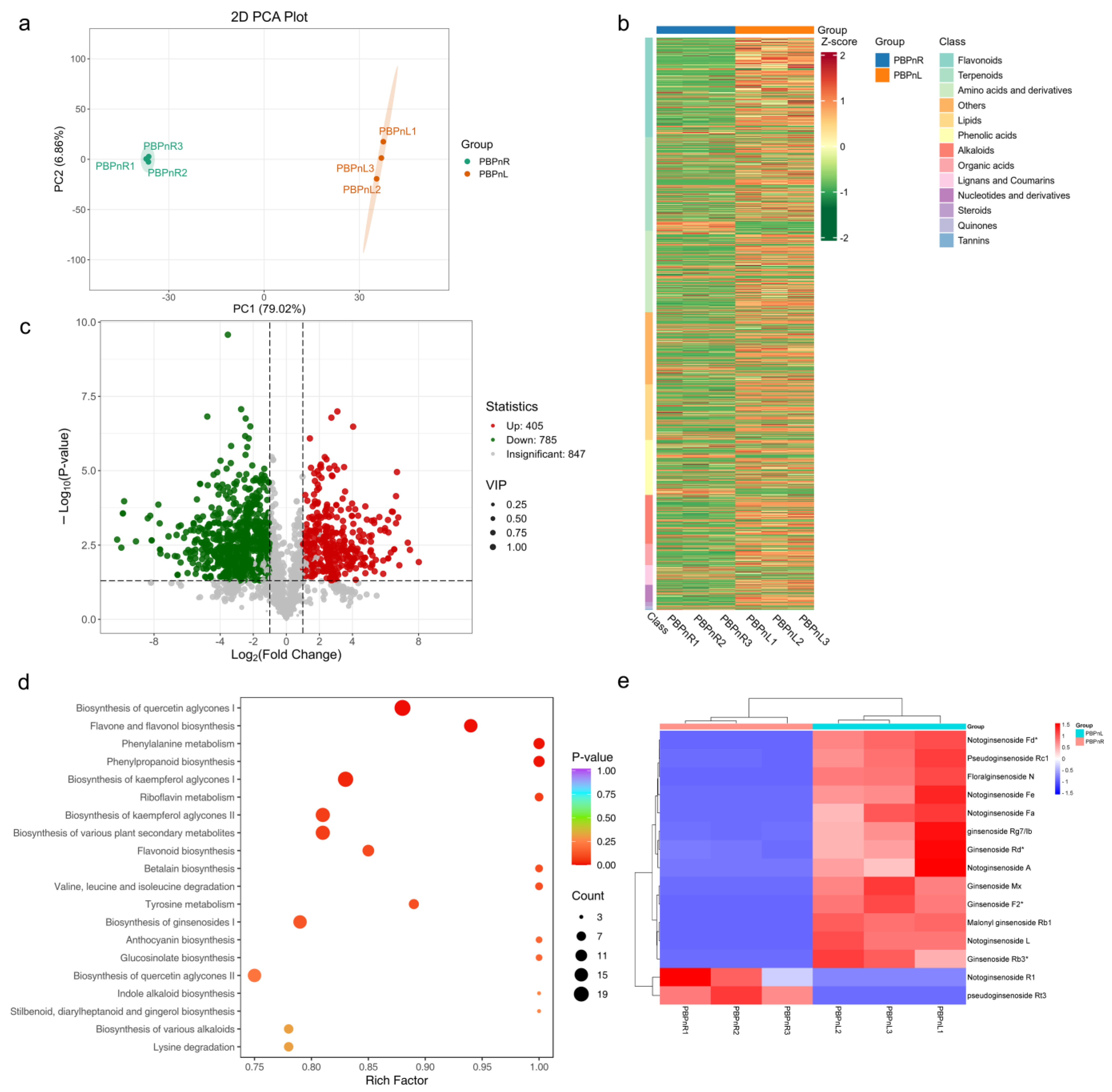
3.2. Metabolite Profiling of Potential Saponin-Related Metabolites in the Root and Leaf of P. stipuleanatus
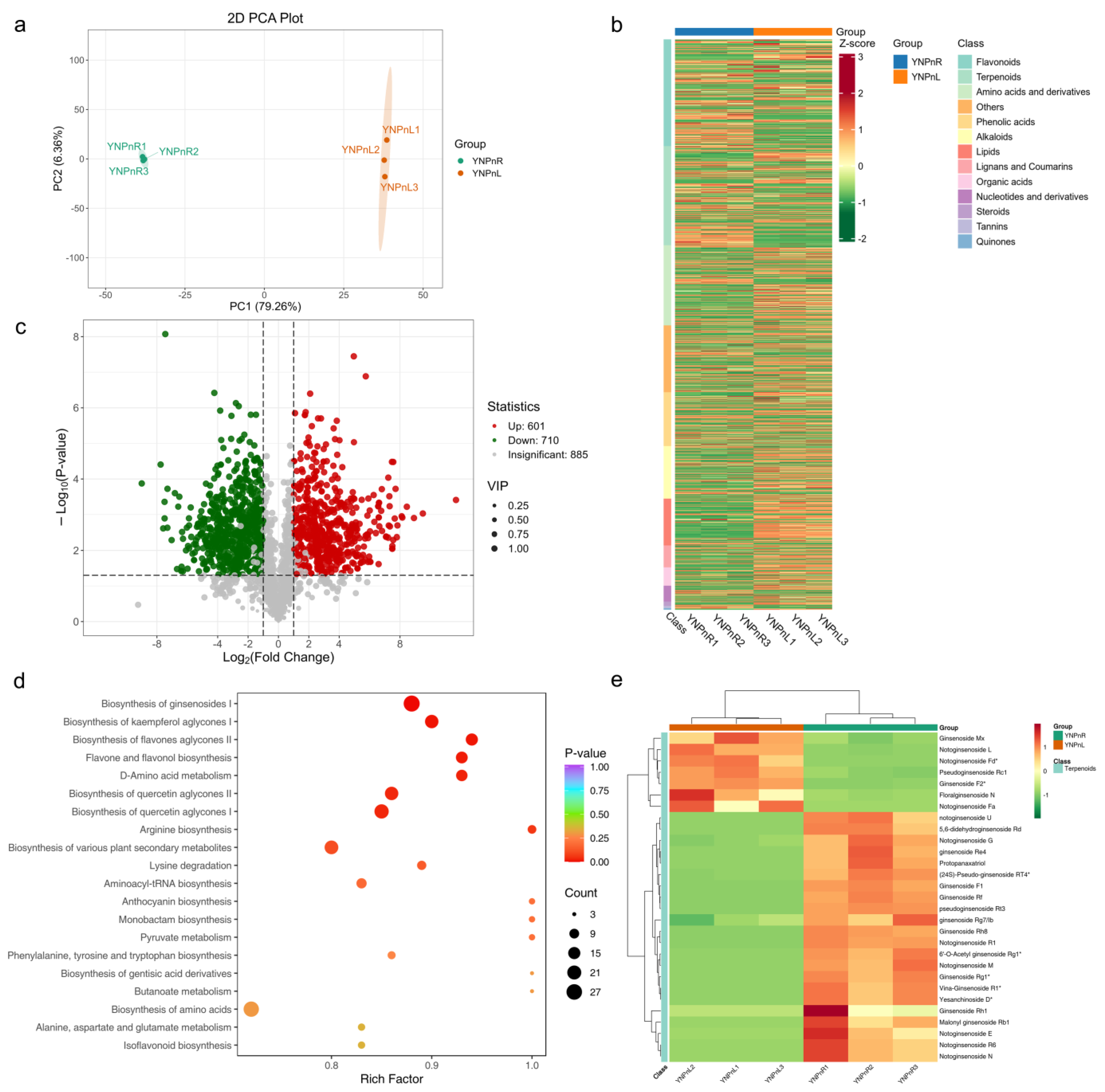
3.3. Metabolite Profiling of Potential Saponin-Related Metabolites in the Root and Leaf of P. vietnamensis
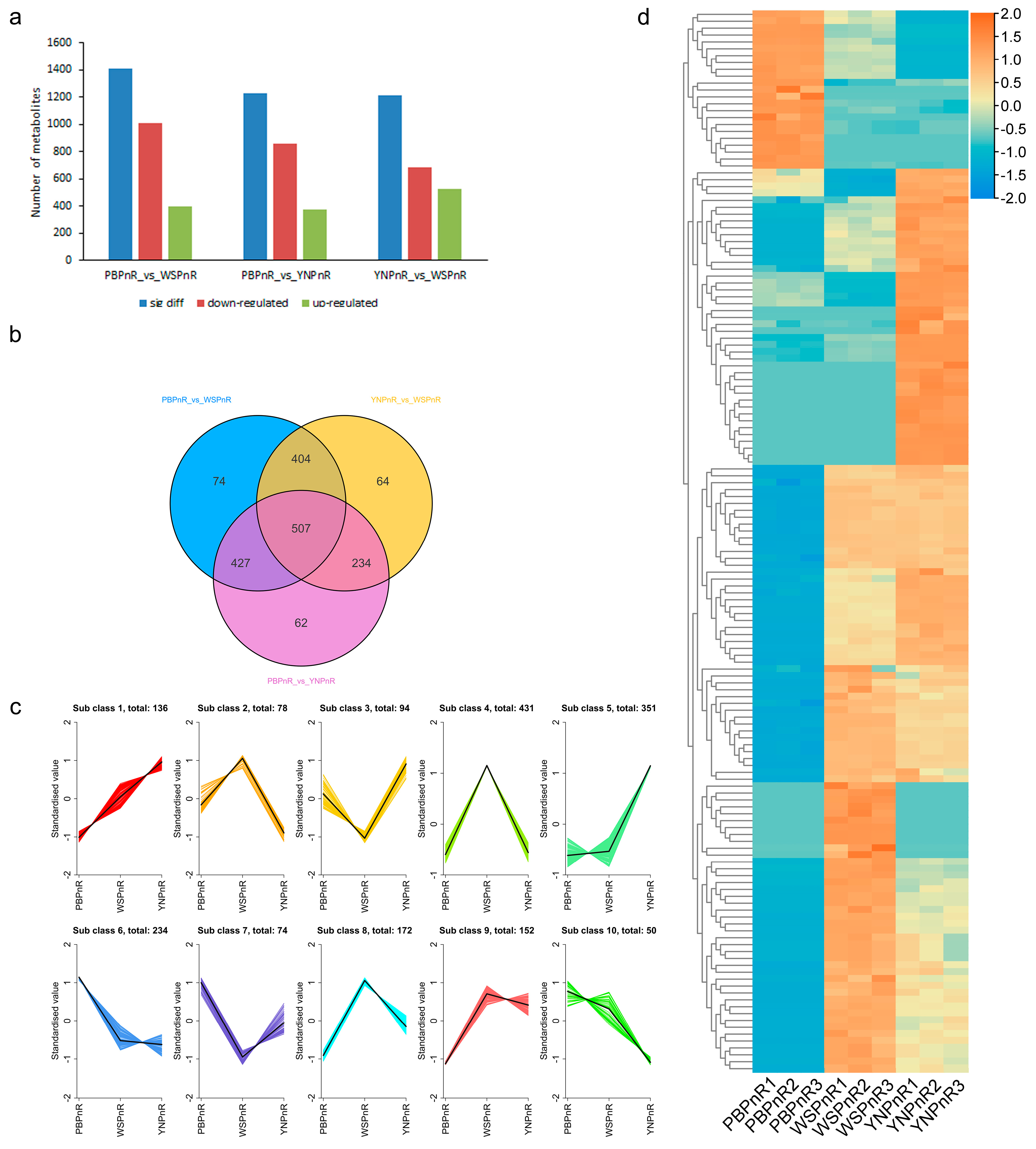
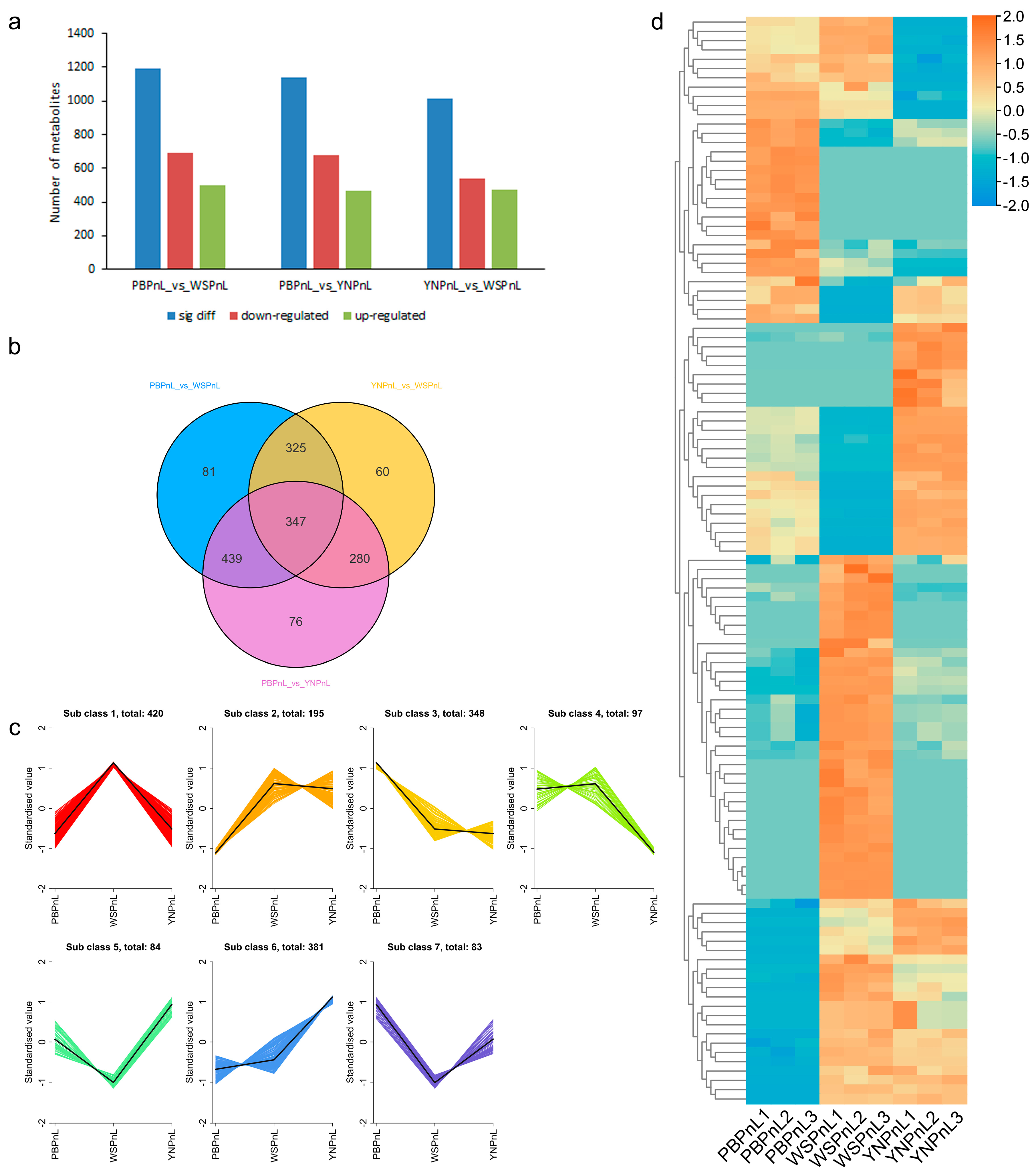
3.4. Comparison of Differential Metabolites in the Root of Three Panax Species
3.5. Comparison of Differential Metabolites in the Leaves of Three Panax Species
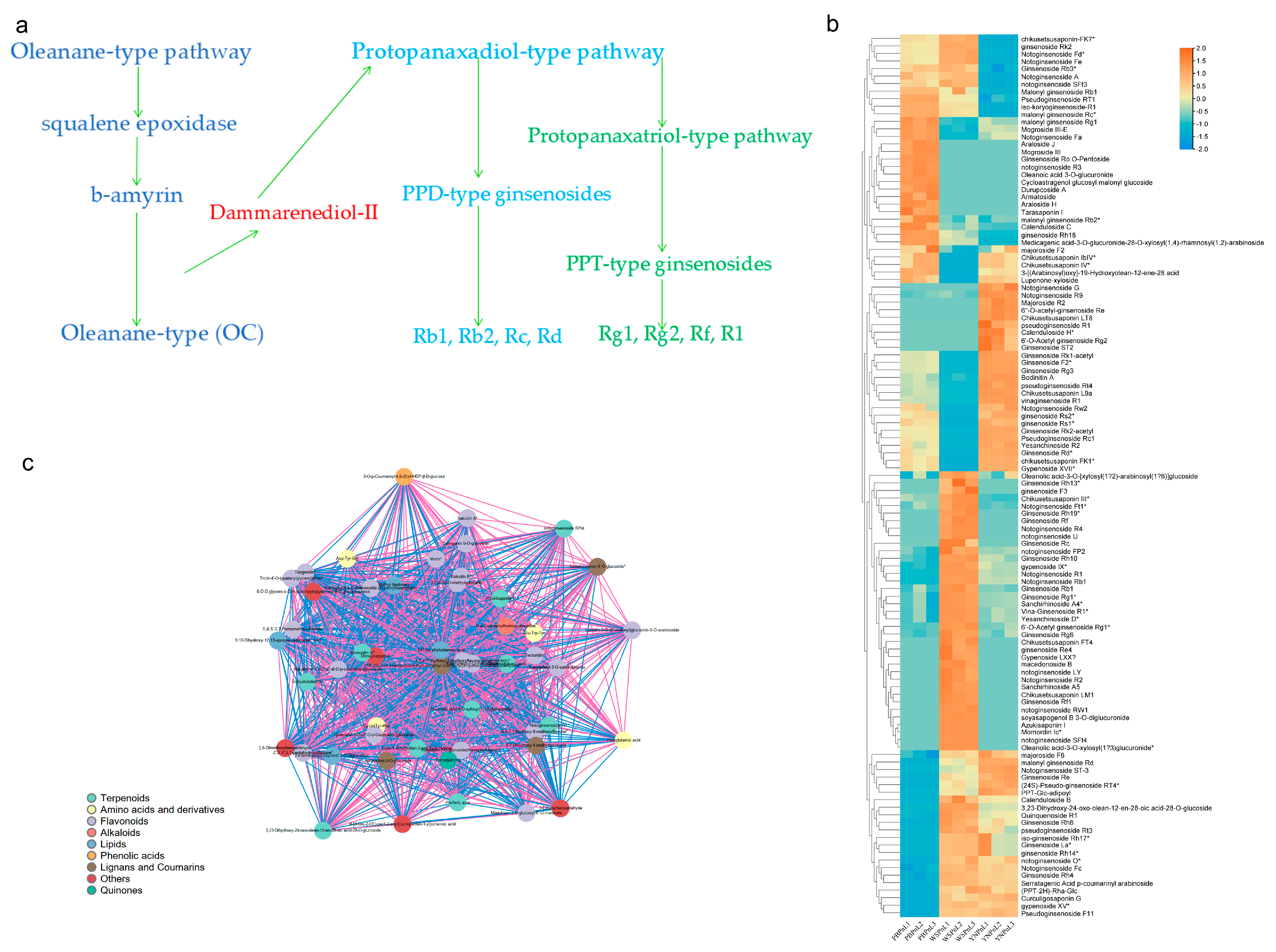
3.6. Regulatory Network of Metabolites of the Triterpene Saponins Biosynthesis Pathway in P. stipuleanatus Leaf
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W.-Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.-Y.; Ye, M.; Guo, D.-A. Saponins in the genus Panax L. (Araliaceae): A systematic review of their chemical diversity. Phytochemistry 2014, 106, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanilla, V.; Kool, A.; Nguyen Nhat, L.; Nong Van, H.; Le Thi Thu, H.; De Boer, H. Phylogenomics and barcoding of Panax: Toward the identification of ginseng species. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jee, H.-S.; Chang, K.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, K.-T.; Paik, H.-D. Morphological characterization, chemical components, and biofunctional activities of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolium, and Panax notoginseng roots: A comparative study. Food Rev. Int. 2014, 30, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Ryu, J.H. Ginseng in traditional herbal prescriptions. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Jayakodi, M.; Lee, S.C.; Choi, B.S.; Jang, W.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.H.; Waminal, N.E.; Lakshmanan, M.; van Nguyen, B. Genome and evolution of the shade-requiring medicinal herb Panax ginseng. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 1904–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Tabassum, N.; Uddin, M.R.; Park, S.U. Ginseng: A miracle sources of herbal and pharmacological uses. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2016, 16, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, L.; Liu, H.; Wu, H.; Zhang, E.; Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z. Platelet P2Y12 receptors are involved in the haemostatic effect of notoginsenoside Ft1, a saponin isolated from P anax notoginseng. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, F.-R.; Wang, Y.-Z. Traditional uses, chemical diversity and biological activities of Panax L. (Araliaceae): A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 112792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.W.; Wong, A.S.-T. Pharmacology of ginsenosides: A literature review. Chin. Med. 2010, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.L.; Kim, C.-E.; Jung, K.; Kang, K.S. Beneficial effects of Panax ginseng for the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases: Past findings and future directions. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahid, F.; Khan, T.; Subhan, F.; Khan, M.; Kim, Y. Ginseng pharmacology: Multiple molecular targets and recent clinical trials. Drugs Future 2010, 35, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.S.; Song, M.-Y.; Yim, S.-V.; Lee, S.-E.; Park, K.-S. Global analysis of ginsenoside Rg1 protective effects in β-amyloid-treated neuronal cells. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, G.; Gong, J.; Lu, F.; Diao, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, K.; Tian, J.; Liu, J. Ginseng for Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Su, H.; Xu, P.; Qi, H.; Zhao, D.; Li, X. Panax ginseng clinical trials: Current status and future perspectives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H. Cardiovascular diseases and Panax ginseng: A review on molecular mechanisms and medical applications. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.G.; Sun, H.X.; Ye, Y.P. Ginsenoside Rd from Panax notoginseng is cytotoxic towards HeLa cancer cells and induces apoptosis. Chem. Biodivers. 2006, 3, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, K.-S.; Yi, Y.-S.; Son, Y.-J.; Jeong, D.; Sung, N.Y.; Aravinthan, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, J.Y. Comparison of anticancer activities of Korean Red Ginseng-derived fractions. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.-J.; Shang, J.-H.; Wang, D.; Zhu, H.-T.; Yang, C.-R.; Zhang, Y.-J. Research of panax spp. in kunming institute of botany, CAS. Nat. Prod. Bioprospecting 2018, 8, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Koh, H.-L.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, H.-T.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Yang, C.-R. Chemical and morphological variations of Panax notoginseng and their relationship. Phytochemistry 2013, 93, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Dong, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, F.; Cheng, R.; Xu, R.; Chen, S. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses revealed the distribution of saponins in Panax notoginseng. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Luo, H.; Sun, C.; Yang, T.-J.; Dong, L.; Huang, L.; Chen, S. Expression profiling of the triterpene saponin biosynthesis genes FPS, SS, SE, and DS in the medicinal plant Panax notoginseng. Gene 2014, 533, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Sun, C.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Niu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Xu, H.; Li, C. Analysis of the transcriptome of Panax notoginseng root uncovers putative triterpene saponin-biosynthetic genes and genetic markers. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralampidis, K.; Trojanowska, M.; Osbourn, A.E.J.H. Biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in plants. Hist. Trends Bioprocess. Biotransform. 2002, 75, 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Rohmer, M.; Schwender, J. Two independent biochemical pathways for isopentenyl diphosphate and isoprenoid biosynthesis in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 1997, 101, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Basu, S.; Yang, Z.; Deb, A.; Hu, M. Bioavailability challenges associated with development of saponins as therapeutic and chemopreventive agents. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 1885–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, X.; Hu, Y.; Fan, X. Chemical constituents of Panax ginseng and Panax notoginseng explain why they differ in therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.-H.; Kim, D.-Y.; Woo, S.; Lee, H.-K.; Oh, S.-R. An approach for simultaneous determination for geographical origins of Korean Panax ginseng by UPLC-QTOF/MS coupled with OPLS-DA models. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Yi, T.; Qin, M.; Liang, Z. Chemical differentiation and quality evaluation of commercial asian and american ginsengs based on a UHPLC–QTOF/MS/MS metabolomics approach. Phytochem. Anal. 2015, 26, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Wei, F.; Yuan, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Chen, S. Integrated chemical and transcriptomic analysis reveals the distribution of protopanaxadiol-and protopanaxatriol-type saponins in Panax notoginseng. Molecules 2018, 23, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.; Zuo, C.; Song, N.; Zhu, S.; Wu, J. Transcriptome analysis of 1-and 3-year-old Panax notoginseng roots and functional characterization of saponin biosynthetic genes DS and CYP716A47-like. Planta 2019, 249, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.-W.; Wang, C.-Z.; Yuan, C.-S. Isolation and analysis of ginseng: Advances and challenges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 467–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Yang, F.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, X. Chemical characteristics for different parts of Panax notoginseng using pressurized liquid extraction and HPLC-ELSD. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 41, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.B.; Li, S.p.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, Y.T. Chemical characteristics of three medicinal plants of the Panax genus determined by HPLC-ELSD. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Fan, Y.; Rao, Z.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Qi, X.; Wang, L. Comparative investigation on metabolite changes in ‘wu mi’production by Vaccinium bracteatum Thunb. leaves based on multivariate data analysis using UPLC–QToF–MS. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Lian, W.; Li, T.; Fan, Y.; Rao, Z.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Qi, X. Metabolomics approach reveals discriminatory metabolites associating with the blue pigments from Vaccinium bracteatum thunb. leaves at different growth stages. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 147, 112252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; He, S.; Meng, J.; Lu, Y.; Shi, H.; Liu, C.; Hao, B.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, S. Integrated metabolome and transcriptome analyses reveal the molecular mechanism underlying dynamic metabolic processes during taproot development of Panax notoginseng. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-T.; Yang, D.; Sun, M.-J.; Wei, F.-G.; Li, S.-Y.; Di, X.; Li, N.; Song, H.-P.; Zhang, H.; Kang, T.-G. Integrated transcriptomic and targeted-metabolomic analysis reveal the co-upregulation and mechanism of saponin and starch biosynthesis in the underground parts of Panax notoginseng induced by inflorescence removal. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 226, 120643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Zuo, T.; Li, W.; Jia, L.; Wang, X.; Qian, Y.; Guo, D.; Yang, W.J.A.; Chemistry, B. In-depth profiling, characterization, and comparison of the ginsenosides among three different parts (the root, stem leaf, and flower bud) of Panax quinquefolius L. by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7817–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Garran, T.A.; Luo, Y.; Cheng, M.; Ren, M.; Zhou, X. Untargeted Metabolomic Analysis and Chemometrics to Identify Potential Marker Compounds for the Chemical Differentiation of Panax ginseng, P. quinquefolius, P. notoginseng, P. japonicus, and P. japonicus var. major. Molecules 2023, 28, 2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Cheng, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Gao, M.; Ma, J.; Cui, X. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis of Panax Notoginseng root: Mechanistic insights into the effects of flower bud removal on yield and phytochemical composition. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 223, 120138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yin, N.; Mao, Y.; Sun, F.; Chen, S.; Hu, R.; Liu, X.; Shang, G. Metabolite profiling and transcriptome analysis provide insight into seed coat color in Brassica juncea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Clowers, B.H.; Moore, R.J.; Zink, E.M. Signature-discovery approach for sample matching of a nerve-agent precursor using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, XCMS, and chemometrics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR: An R package for flexible and reproducible analysis of metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4313–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; He, Z.; Bi, X.; Xu, W.; Wei, T.; Wu, S.; Hu, S. Transcriptomic profiling reveals MEP pathway contributing to ginsenoside biosynthesis in Panax ginseng. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudone, L.; Motiekaityte, V.; Vainoriene, R.; Zymone, K.; Marksa, M.; Janulis, V. Phytochemical Profiles of Alpine Plant Horminum pyrenaicum L. during Phenological Growth Stages. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Yue, H.; Xiu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S. Accumulation characteristics and correlation analysis of five ginsenosides with different cultivation ages from different regions. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yuan, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xu, M.; Wei, D.; Wu, D.; Wan, J.; Mei, S.; Cui, T.; et al. New dammarane-type triterpenoid saponins from Panax notoginseng saponins. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Deng, H.; Shu, T.; Xu, M.; Su, L.; Li, H. Study on chemical constituents of Panax notoginseng leaves. Molecules 2023, 28, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ke, Z.; Chen, S.; Li, M.; Fan, W.; Wu, H.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Z. Cardioprotective effect of stem-leaf saponins from panax notoginseng on mice with sleep deprivation by inhibiting abnormal autophagy through PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 694219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Guo, X.-X.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.-X.; He, J.-H.; Xu, T.-R.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X.-M. Converting ginsenosides from stems and leaves of Panax notoginseng by microwave processing and improving their anticoagulant and anticancer activities. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40471–40482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-K.; Xiong, J.; Shen, Y. Two new dammarane-type triterpenoids from the stems and leaves of Panax notoginseng. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 23, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, D.; Xiang, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. New 20 (S)-protopanaxadiol type saponins from the leaves of Panax notoginseng and their potential anti-inflammatory activities. Steroids 2020, 162, 108696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.T.; Van, T.T.H.; Hung, L.V.; Van Khiem, N.; Mai, L.Q.; Xuyen, D.T.; Oanh, P.T.; Van Hai, D.; Dien, N.D.; Nhut, D.T. Bioactive compounds and biological activities of Vietnamese ginseng (Panax Vietnamensis Ha et Grushv.). In Bioactive Compounds in the Storage Organs of Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Yoon, Y.C.; Jung, C.W.; Kim, T.H.; Wang, Q.; Cho, W.; Yang, T.-J.; Van Le, T.H.; Cho, C.J.; Kim, J.H. Development of a leaf metabolite-based intact sample distinguishing algorithm for the three varieties of Panax Vietnamensis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.T.; Ghimeray, A.K.; Vu, N.T.; Jeong, Y.-H. Quantitative estimation of ginsenosides in different ages of Panax vietnamensis and their anti-proliferation effects in hela cells. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 12, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.T.; Hieu, N.N.; Hiep, D.H.; Anh, N.T.H.; Ngan, D.T.; Tung, P.H.T.; Thuong, P.T.; Tung, N.H. Dammarane-Type Saponins from the Leaves of Vietnamese Ginseng (Panax vietnamensis Ha & Grushv.) and Their Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition In Vitro and In Silico. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 22, e202401329. [Google Scholar]
- Van Le, T.H.; Lee, G.J.; Vu, H.K.L.; Kwon, S.W.; Nguyen, N.K.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Ginseng saponins in different parts of Panax vietnamensis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 63, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; Tezuka, Y.; Tran, Q.; Kadota, S. Chemical constituents and biological activities of Vietnamese medicinal plants. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2003, 3, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tran, Q.; Adnyana, I.K.; Tezuka, Y.; Harimaya, Y.; Saiki, I.; Kurashige, Y.; Tran, Q.K.; Kadota, S. Hepatoprotective effect of majonoside R2, the major saponin from Vietnamese ginseng (Panax vietnamensis). Planta Medica 2002, 68, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Phuong, T.T. Vietnamese Ginseng (Panax vietnamensis Ha and Grushv.): Phylogenetic, Phytochemical, and Pharmacological Profiles. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2019, 13, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deyholos, M.K.; Peng, L.; Jia, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Z. Wild Panax vietnamensis and Panax stipuleanatus markedly increase the genetic diversity of Panax notoginseng (Araliaceae) revealed by start codon targeted (SCoT) markers and ITS DNA barcode. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 66, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, P.-P.; Li, L.-X.; He, Q.-M.; Pan, J.; Li, X.-L.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Y.; Qu, Y. Identification and quantification of oleanane triterpenoid saponins and potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities from the roots and rhizomes of Panax stipuleanatus. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. Two new saponins of oleanolic acid from the underground part of Panax stipuleanus Tsai et Feng. Acta Bot. Yunnanica 1985, 7, 103–108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Xie, W.; He, S.; Sun, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Ginsenoside Rb1 as an anti-diabetic agent and its underlying mechanism analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, L.-L.; Xie, R.F.; Lam, W.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Jiang, Z.-L.; Cheng, Y.-C. Chemosynthesis pathway and bioactivities comparison of saponins in radix and flower of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) FH Chen. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 201, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, C.; Santangelo, R. Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius: From pharmacology to toxicology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 107, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Ding, Y.; Kim, J.-A.; Yang, S.-Y.; Boo, H.-J.; Kang, H.-K.; Nguyen, M.C.; Kim, Y.-H. Polyacetylenes from Panax stipuleanatus and their cytotoxic effects on human cancer cells. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3513–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, S.; Gong, Y.; Deng, S.; Dou, Y.; Wang, J.; Sam, H.V.; Chen, X.; He, X.; Shi, R. Comparative Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Tissue- and Species-Specific Differences in the Abundance of Dammarane-Type Ginsenosides in Three Panax Species. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080916
He S, Gong Y, Deng S, Dou Y, Wang J, Sam HV, Chen X, He X, Shi R. Comparative Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Tissue- and Species-Specific Differences in the Abundance of Dammarane-Type Ginsenosides in Three Panax Species. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(8):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080916
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Shu, Ying Gong, Shuangfei Deng, Yaquan Dou, Junmin Wang, Hoang Van Sam, Xingliang Chen, Xiahong He, and Rui Shi. 2025. "Comparative Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Tissue- and Species-Specific Differences in the Abundance of Dammarane-Type Ginsenosides in Three Panax Species" Horticulturae 11, no. 8: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080916
APA StyleHe, S., Gong, Y., Deng, S., Dou, Y., Wang, J., Sam, H. V., Chen, X., He, X., & Shi, R. (2025). Comparative Metabolomic Analysis Reveals Tissue- and Species-Specific Differences in the Abundance of Dammarane-Type Ginsenosides in Three Panax Species. Horticulturae, 11(8), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11080916






