Effects of Drought Stress on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Idesia polycarpa Maxim
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
2.2. Design of the Experiment
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Measurement of Growth Indexes
2.5. Photosynthetic Characteristics and Photosynthetic Pigment Indexes
2.6. Physiological and Biochemical Indexes
2.7. Root System Indexes and Leaf Anatomy
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
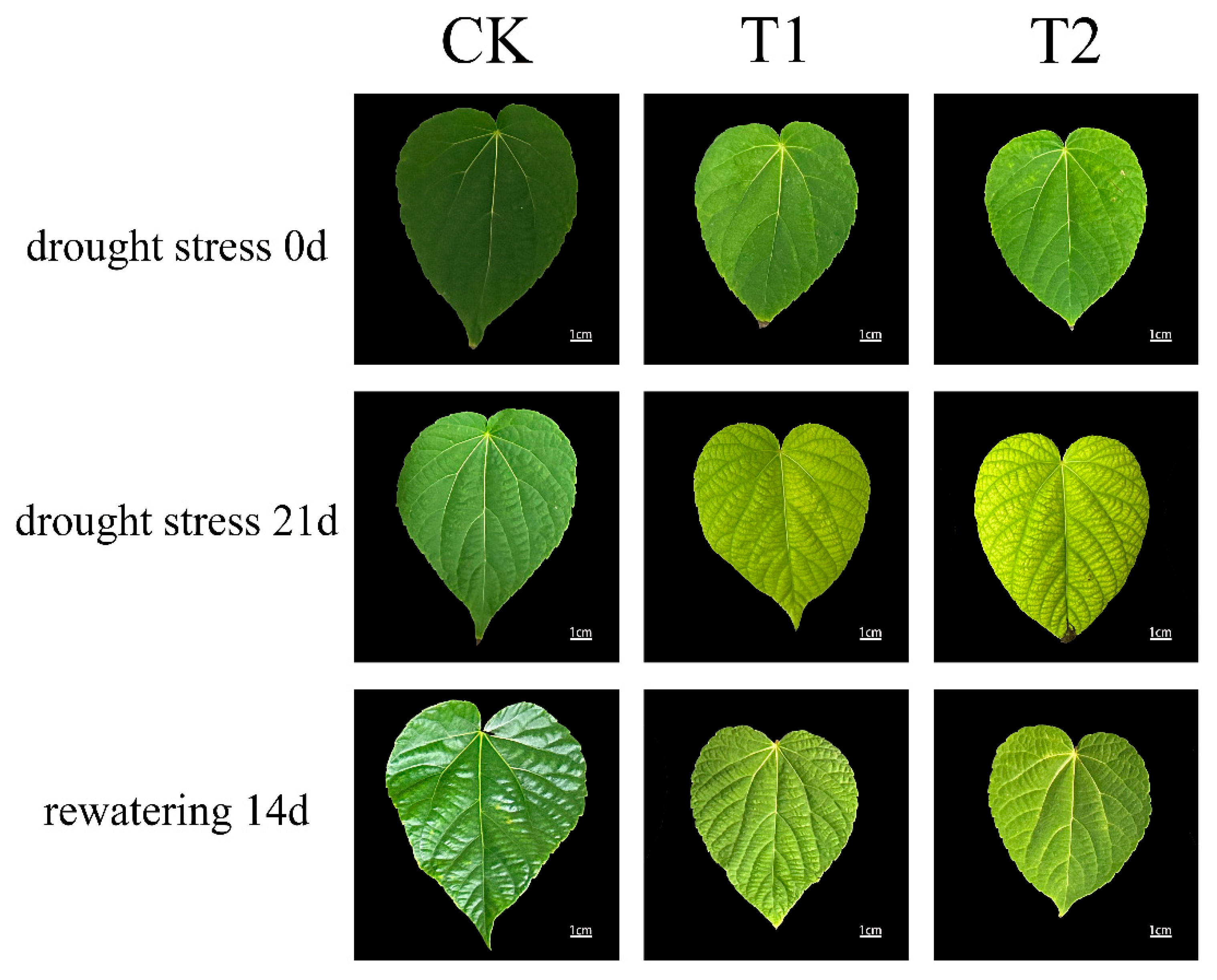
3.1. Effects of Drought Stress on Leaf Phenotypic Characteristics of I. polycarpa Seedlings
3.2. Effects of Drought Stress on Photosynthetic Pigment Content in Leaves of I. polycarpa Seedlings
3.3. Effects of Drought Stress on Plant Growth of I. polycarpa Seedlings
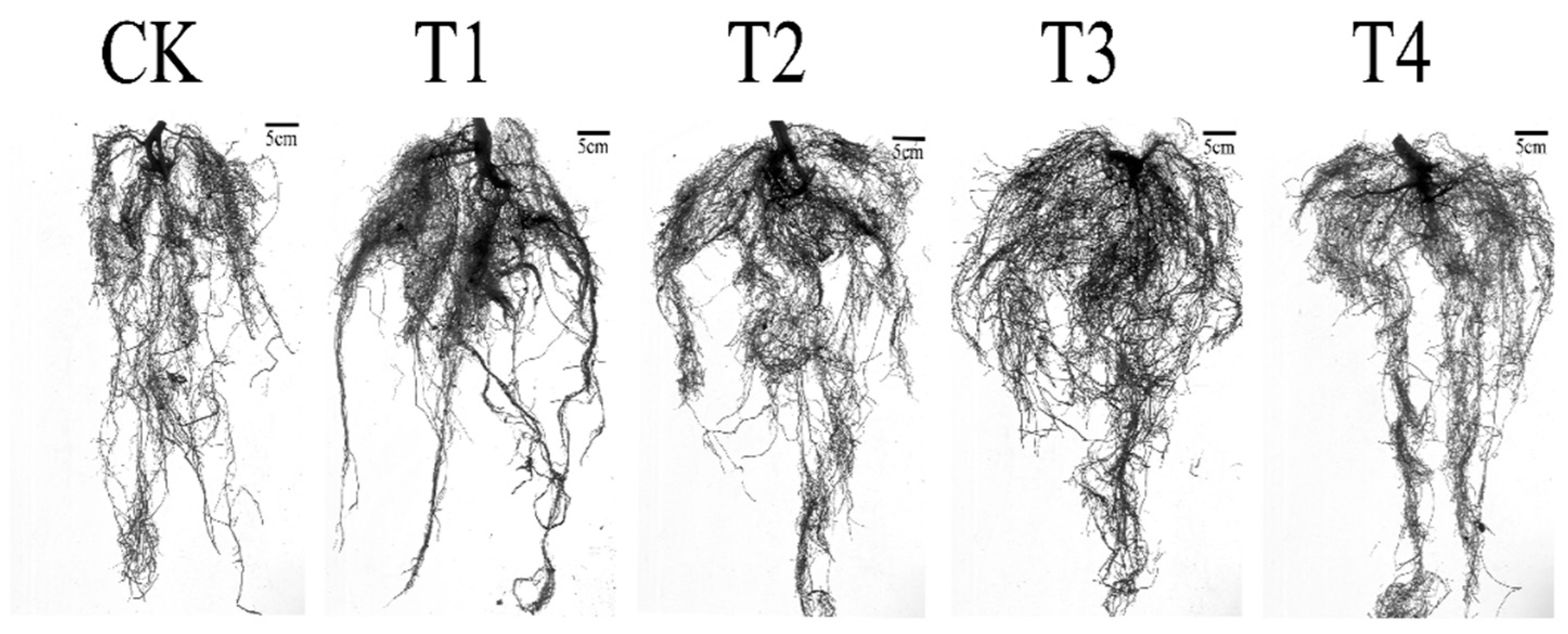
3.4. Effects of Drought Stress on Root Growth of I. polycarpa Seedlings
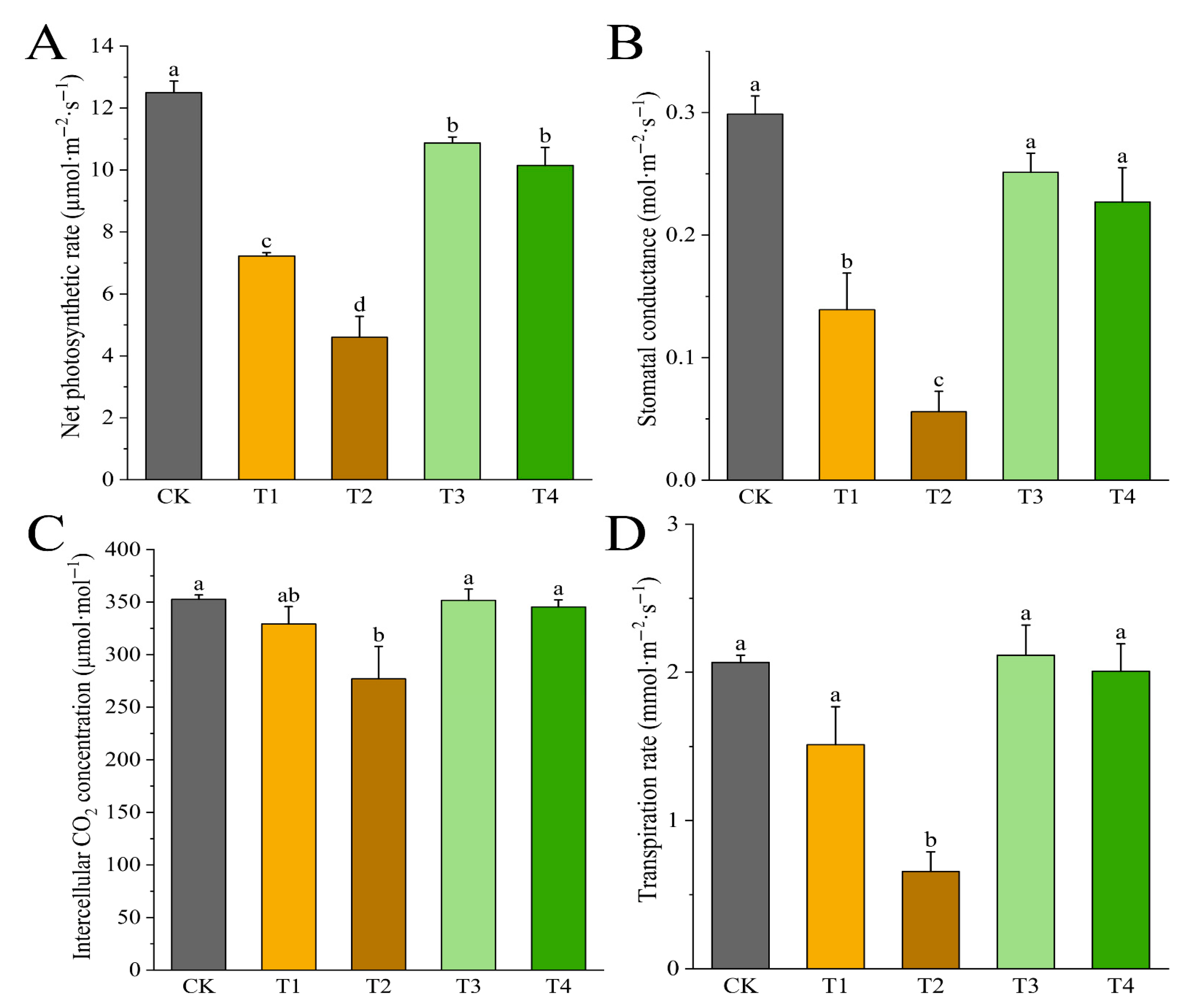
3.5. Effects of Drought Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics of I. polycarpa Seedlings
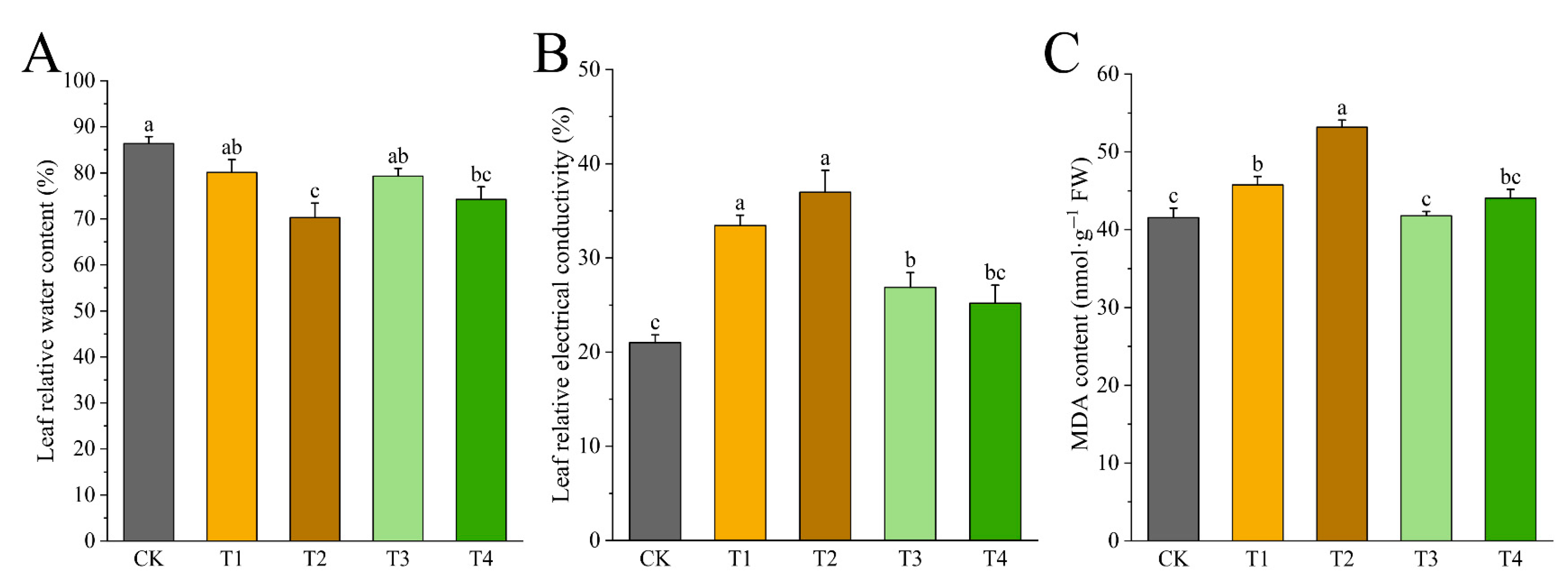
3.6. Effects of Drought Stress on LRWC, REC, and MDA Content of I. polycarpa Seedling Leaves
3.7. Effects of Drought Stress on Activities of Antioxidant Enzymes of I. polycarpa Seedling Leaves
3.8. Effects of Drought Stress on the Osmoregulatory Substances of I. polycarpa Seedlings’ Leaves
3.9. Effects of Drought Stress on Endogenous Hormones of I. polycarpa Seedling Leaves
3.10. Effects of Drought Stress on the Leaf Anatomy of I. polycarpa Seedling Leaves
3.11. Correlation Analysis
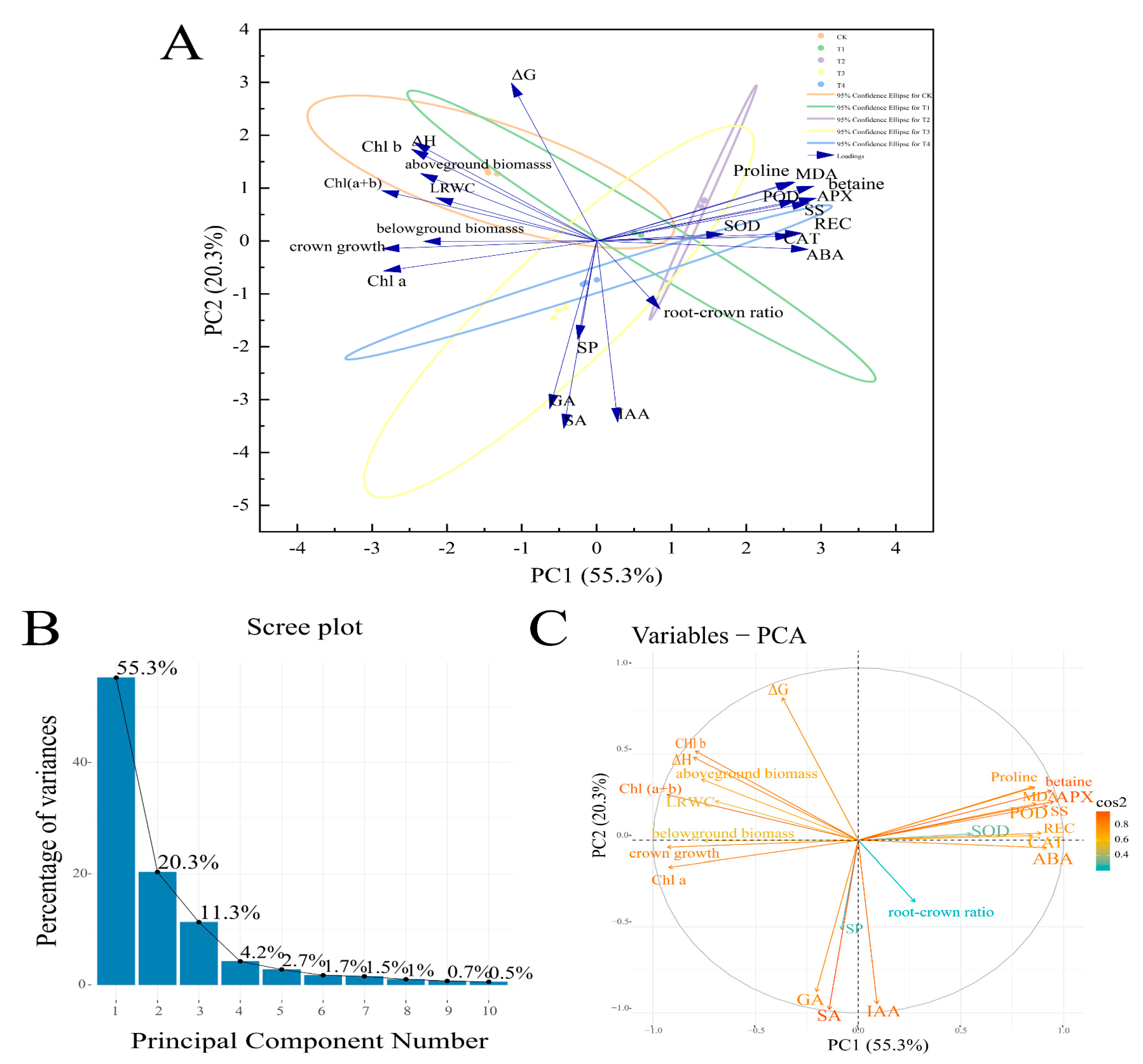
3.12. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RWC | Soil relative water content |
| LRWC | Leaf relative water content |
| REC | Leaf relative electrical conductivity |
References
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Song, M.; Wang, N.; Fan, P.; Wu, P.; Cui, K.; Zheng, P.; Du, N.; Wang, H.; et al. Physiological Responses of Robinia pseudoacacia and Quercus acutissima Seedlings to Repeated Drought-Rewatering under Different Planting Methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 760510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Qin, R.X.; Shi, Q.L.; Jie, Z.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ma, W.; Li, J.R. Response of Chinese Cabbage Seedlings to Drought Stress and Rehydration. Plant Physiol. J. 2023, 59, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanè, C.; Siah, S.; Cafaro, V.; Cosentino, S.L.; Corinzia, S.A. Potential Impact of Drought and Rewatering on Plant Physiology and Fruit Quality in Long-Shelf-Life Tomatoes. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hura, T.; Hura, K.; Ostrowska, A. Drought-Stress Induced Physiological and Molecular Changes in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zheng, W.; Zou, X.X. The Influence of Drought Stress on Rhododendron ovatum on Morphology and Physiological Indexes. J. Fujian For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 48, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Yang, M.M.; Kong, D.S.; Zhang, Y.J. Effect of Drought Stress on Lipid Peroxidation, Osmotic Adjustment and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of Leaves and Roots of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Seedling. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 65, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, W.; Ullah, S.; Ali, S.; Idrees, M.; Khan, M.N.; Ali, K.; Khan, A.; Ali, M.; Younas, F.; Ali, B. Effect of Exogenous Alpha-Tocopherol on Physio-Biochemical Attributes and Agronomic Performance of Lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) under Drought Stress. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Li, Y.T.; Huang, Y.R.; Zhang, J. Effects of Drought Stress on Endogenous Hormones in Potted Seedlings of Ulmus pumila ‘Jinye’. J. West China For. Sci. 2021, 50, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Xu, W.N.; Su, Y.; Zhang, B. Changes in Leaf Morphology and Anatomical Structure of Seedlings of Alfalfa and Medicago falcata L. under Drought Stress. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2023, 38, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.M.; Shen, Y.B.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X.B. Research Progress on Idesia polycarpa. J. Jiangsu For. Sci. Technol. 2023, 50, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Deng, W.F.; Lu, X.Y.; Niu, C.T.; Tian, H.; Li, Z. Research Progress in the Development and Utilization of Idesia polycarpa. Non-Wood For. Res. 2023, 41, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.S.; Zhou, B.C.; Cao, J. Development and Utilization of the Woody Oilseed Tree Species Idesia polycarpa. Hubei For. Sci. Technol. 2017, 46, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.W.; Wang, X.S.; Yang, F.B.; Yang, X.G.; Yang, W.; Diao, R.J.; Wang, X.; Cui, J.; Zhou, F. Fast Extraction and Precise Determination of Chlorophyll. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2016, 51, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.P. Plant Physiology Lab Guide; China Agricultural University Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leon, J.A.D.; Borges, C.R. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress in Biological Samples Using the Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 159, e61122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Shen, J.; He, Z.; Lai, H. Effects of Exogenous Abscisic Acid on the Physiological and Biochemical Responses of Camellia oleifera Seedlings under Drought Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirova, A.; Dossymbetova, S.; Rysbayeva, Y.; Usenbekov, B.; Tolegen, A.; Ydyrys, A. Multiple Plant Regeneration from Embryogenic Calli of Paulownia tomentosa (Thunb.) Steud. Plants 2022, 11, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Ma, R. A Method to Improve Sample Preparation for Observing Epidermis of Highly Lignified Leaf. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2012, 47, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought Stress Impacts on Plants and Different Approaches to Alleviate Its Adverse Effects. Plants 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tang, W.; Chen, L.; Li, Z. Physiological and Biochemical Effects of Exogenous Calcium on Camellia oleifera Abel under Drought Stress. Forests 2023, 14, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Liu, Y.J.; Li, B. Effect of Drought Stress and Rewatering on Physiological Characteristics of Delphinium grandiflorum Seedling. North. Hortic. 2015, 9, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, P.; Wu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Cen, Y.; Lu, H.J. Effects of Drought-Rehydration on Photosynthetic Capacity, Chlorophyll Fluorescence, and Microstructure of Cyclobalanopsis glauca Seedling Leaves in Karst Area of Northwest Guangxi. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2024, 44, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.L.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Si, J.H.; Yu, T.F. An Overview of Stomatal and Non-Stomatal Limitations to Photosynthesis of Plants. Arid Zone Res. 2018, 35, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.N.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.X.; Cao, H.; Long, J.L. Effects of Drought and Rewatering on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Chlorophyll Fluorescence of Trachycarpus fortunei Seedlings. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2021, 41, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.J.; Zhang, M.; Dong, Q.; Duan, H.C.; Cha, X.F.; Chen, Y. Mechanism of Exogenous Calcium Alleviating Drought Stress Damage to Fraxinus malacophylla Seedlings. Plant Physiol. J. 2024, 60, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Chung, Y.S.; Lee, E.; Tripathi, P.; Heo, S.; Kim, K.-H. Root Response to Drought Stress in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, K.; Moghaddam, M.; Farhadi, N.; Pirbalouti, A.G. Morphological, Physiological and Phytochemical Responses of Mexican Marigold (Tagetes minuta L.) to Drought Stress. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 284, 110116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Response Mechanism of Plants to Drought Stress. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Liu, P.F.; Wang, L.; Du, L.Y.; Qing, J.; Du, Q.X.; Du, H.Y. Effect of Drought Stress and Rewatering on Physiological Characteristics of Eucommia ulmoides Seedling. Plant Physiol. J. 2021, 57, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y. Exogenous Melatonin Improves Seedling Health Index and Drought Tolerance in Tomato. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 77, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denaxa, N.K.; Damvakaris, T.; Roussos, P.A. Antioxidant Defense System in Young Olive Plants against Drought Stress and Mitigation of Adverse Effects through External Application of Alleviating Products. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 259, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Bano, A.; Fazal, A. Recent Methods of Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 82, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Ma, C.; Liu, J.; Dong, S. Effects of Different Drought Degrees on Physiological Characteristics and Endogenous Hormones of Soybean. Plants 2022, 11, 2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Meng, P.P.; Lyu, Q.H.; Li, S.; Qi, R.L.; Zhang, H.R. Comprehensive Evaluation of Drought Resistance and Screening of Drought Resistance Identification Indicators in Chrysanthemum morifolium Seedling Stage. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 10, 1942–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

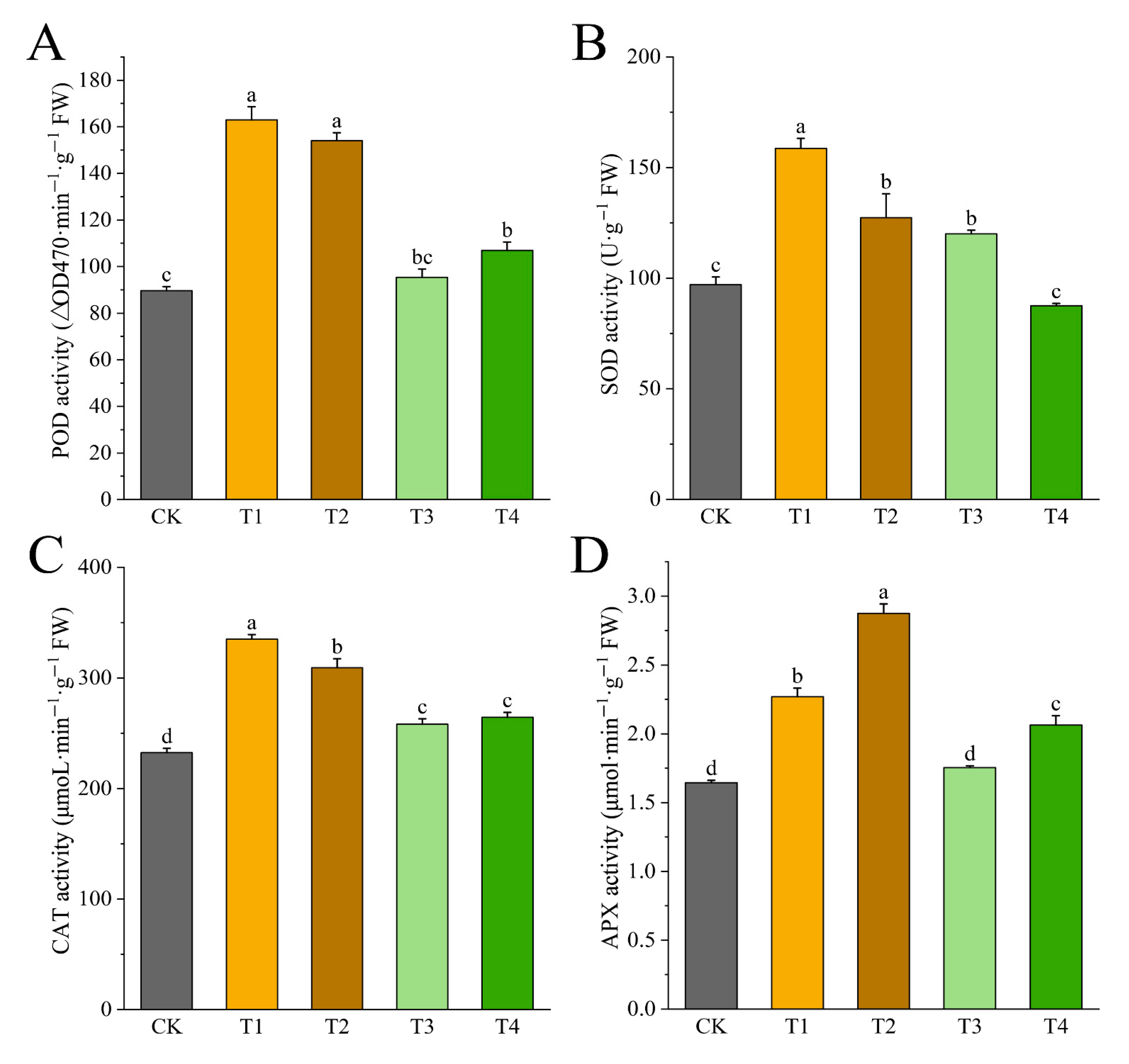

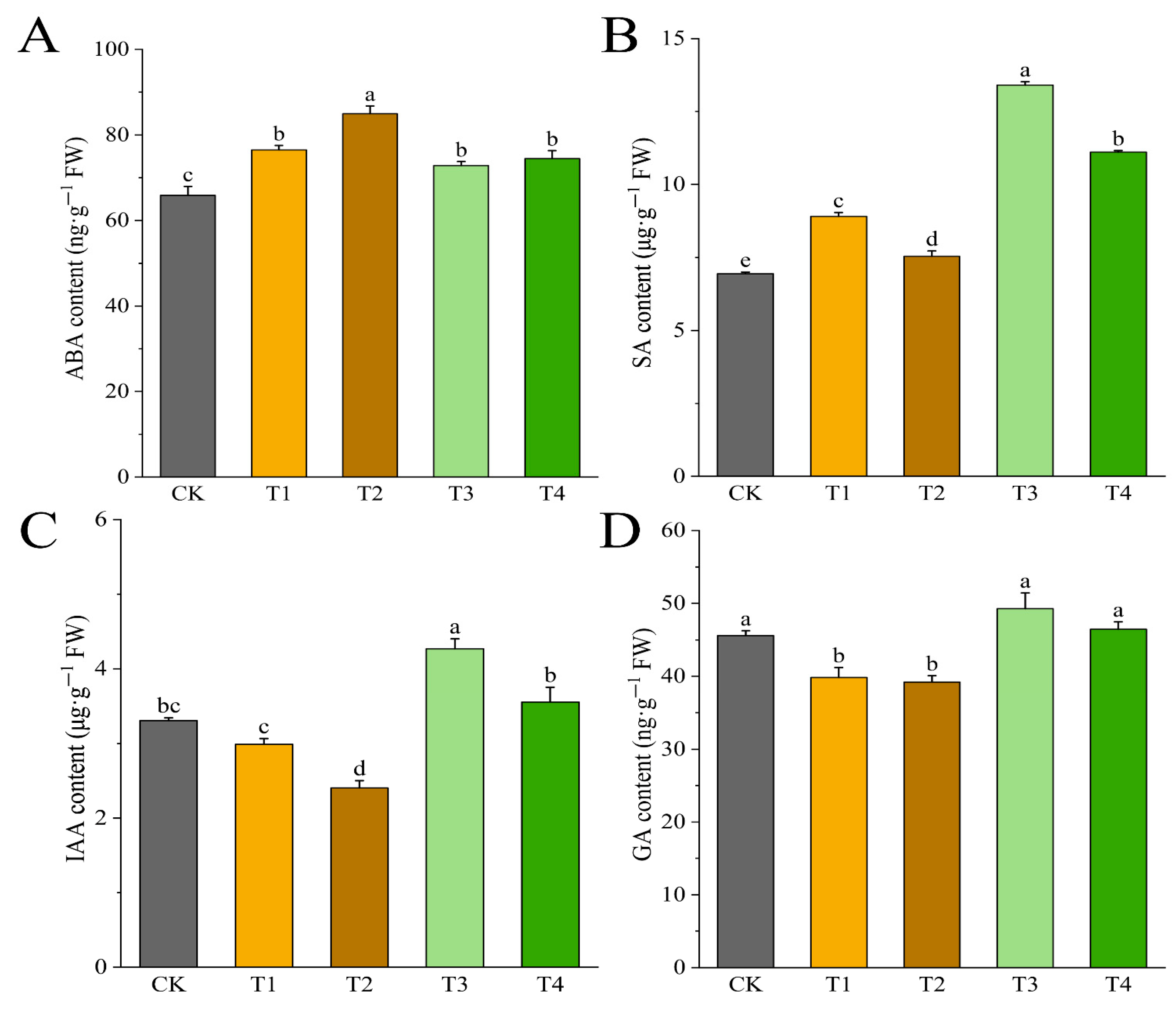
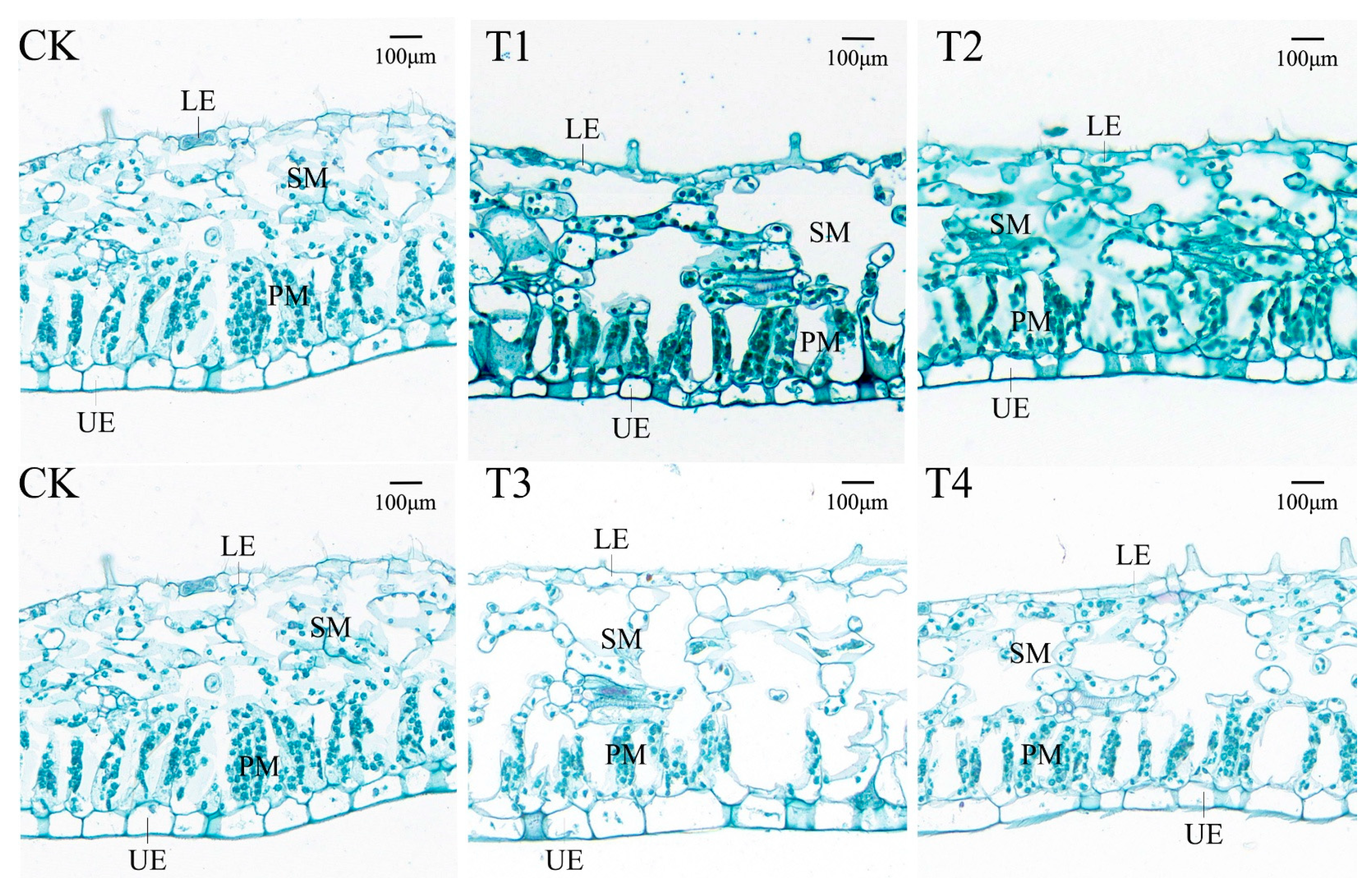
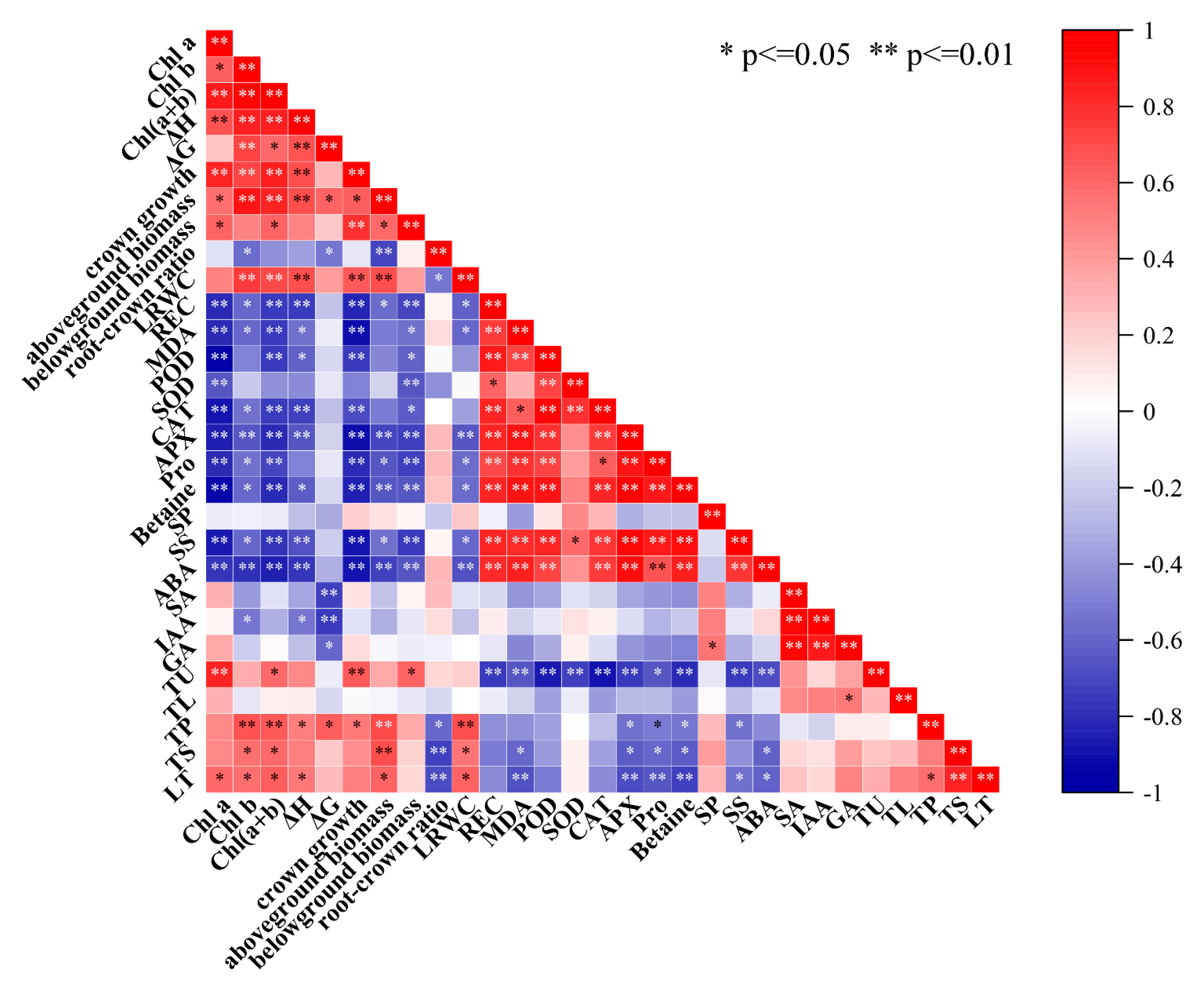
| Treatment | Chlorophyll a Content (mg·g−1 FW) | Chlorophyll b Content (mg·g−1 FW) | Chlorophyll (a + b) Content (mg·g−1 FW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1.882 ± 0.001 a | 2.161 ± 0.082 a | 4.042 ± 0.082 a |
| T1 | 0.948 ± 0.004 c | 1.044 ± 0.094 b | 1.992 ± 0.091 c |
| T2 | 0.907 ± 0.017 c | 0.526 ± 0.038 d | 1.433 ± 0.055 d |
| T3 | 1.741 ± 0.086 a | 0.956 ± 0.139 bc | 2.696 ± 0.224 b |
| T4 | 1.499 ± 0.121 b | 0.688 ± 0.104 cd | 2.188 ± 0.225 bc |
| Treatment | ΔH (cm) | ΔG (mm) | Crown Growth (cm) | Aboveground Biomass (g) | Belowground Biomass (g) | Root–Crown Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.90 ± 0.15 a | 2.66 ± 0.29 a | 6.82 ± 1.00 a | 51.80 ± 5.72 a | 43.82 ± 1.66 a | 0.87 ± 0.10 c |
| T1 | 0.83 ± 0.41 b | 1.18 ± 0.26 bc | −0.92 ± 0.16 bc | 33.51 ± 1.61 bc | 33.07 ± 1.44 b | 0.99 ± 0.03 bc |
| T2 | 0.73 ± 0.18 b | 1.42 ± 0.06 b | −9.02 ± 0.27 d | 21.24 ± 1.98 c | 26.42 ± 2.32 b | 1.25 ± 0.06 b |
| T3 | 1.47 ± 0.44 b | 0.77 ± 0.06 cd | 0.92 ± 0.19 c | 34.42 ± 3.86 b | 34.19 ± 2.19 b | 1.01 ± 0.11 bc |
| T4 | 1.13 ± 0.22 b | 0.47 ± 0.05 d | 2.56 ± 0.80 b | 24.64 ± 4.16 bc | 42.69 ± 3.85 a | 1.79 ± 0.16 a |
| Treatment | Root Length (cm) | Root Surface Area (cm 2) | Root Volume (cm 3) | Root Tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1923.44 ± 14.41 bc | 955.24 ± 20.94 a | 39.07 ± 2.11 a | 1119.0 ± 48.5 c |
| T1 | 2873.54 ± 228.60 a | 946.86 ± 26.38 a | 22.53 ± 0.85 c | 1613.7 ± 113.8 ab |
| T2 | 2165.50 ± 71.36 b | 645.79 ± 24.28 c | 14.91 ± 1.92 d | 1685.7 ± 29.8 ab |
| T3 | 1764.77 ± 123.61 bc | 827.66 ± 50.09 b | 33.45 ± 0.91 ab | 1877.7 ± 141.1 a |
| T4 | 1664.69 ± 81.47 c | 863.47 ± 15.04 ab | 31.85 ± 2.49 b | 1408.0 ± 47.1 bc |
| Treatment | TU (μm) | TL (μm) | TP (μm) | TS (μm) | LT (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.07 ± 0.90 b | 7.83 ± 0.38 b | 60.07 ± 1.34 a | 76.70 ± 2.16 a | 154.40 ± 3.99 a |
| T1 | 11.53 ± 0.99 a | 6.40 ± 0.56 b | 56.23 ± 2.09 abc | 72.87 ± 1.73 ab | 145.97 ± 0.75 b |
| T2 | 12.40 ± 0.72 a | 8.33 ± 1.28 ab | 51.60 ± 2.22 bc | 66.90 ± 0.69 b | 138.00 ± 2.79 bc |
| T3 | 19.50 ± 1.02 b | 11.47 ± 1.33 a | 57.10 ± 0.51 ab | 77.13 ± 3.59 a | 158.37 ± 1.03 a |
| T4 | 19.53 ± 1.55 b | 7.27 ± 0.73 b | 51.33 ± 1.44 c | 67.67 ± 2.72 b | 137.40 ± 2.08 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Yin, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, S.; Niu, Z.; Wu, L.; Chen, C. Effects of Drought Stress on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070834
Lu X, Yin Y, Yang M, Zhang S, Niu Z, Wu L, Chen C. Effects of Drought Stress on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(7):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070834
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xiaoyu, Yian Yin, Maolin Yang, Shucheng Zhang, Zhangtai Niu, Lingli Wu, and Chan Chen. 2025. "Effects of Drought Stress on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Idesia polycarpa Maxim" Horticulturae 11, no. 7: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070834
APA StyleLu, X., Yin, Y., Yang, M., Zhang, S., Niu, Z., Wu, L., & Chen, C. (2025). Effects of Drought Stress on the Growth and Physiological Characteristics of Idesia polycarpa Maxim. Horticulturae, 11(7), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11070834






