Bioactive Components and Color Variation Mechanism Among Three Differently Colored Peppers Based on Transcriptomics and Non-Targeted Metabolomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
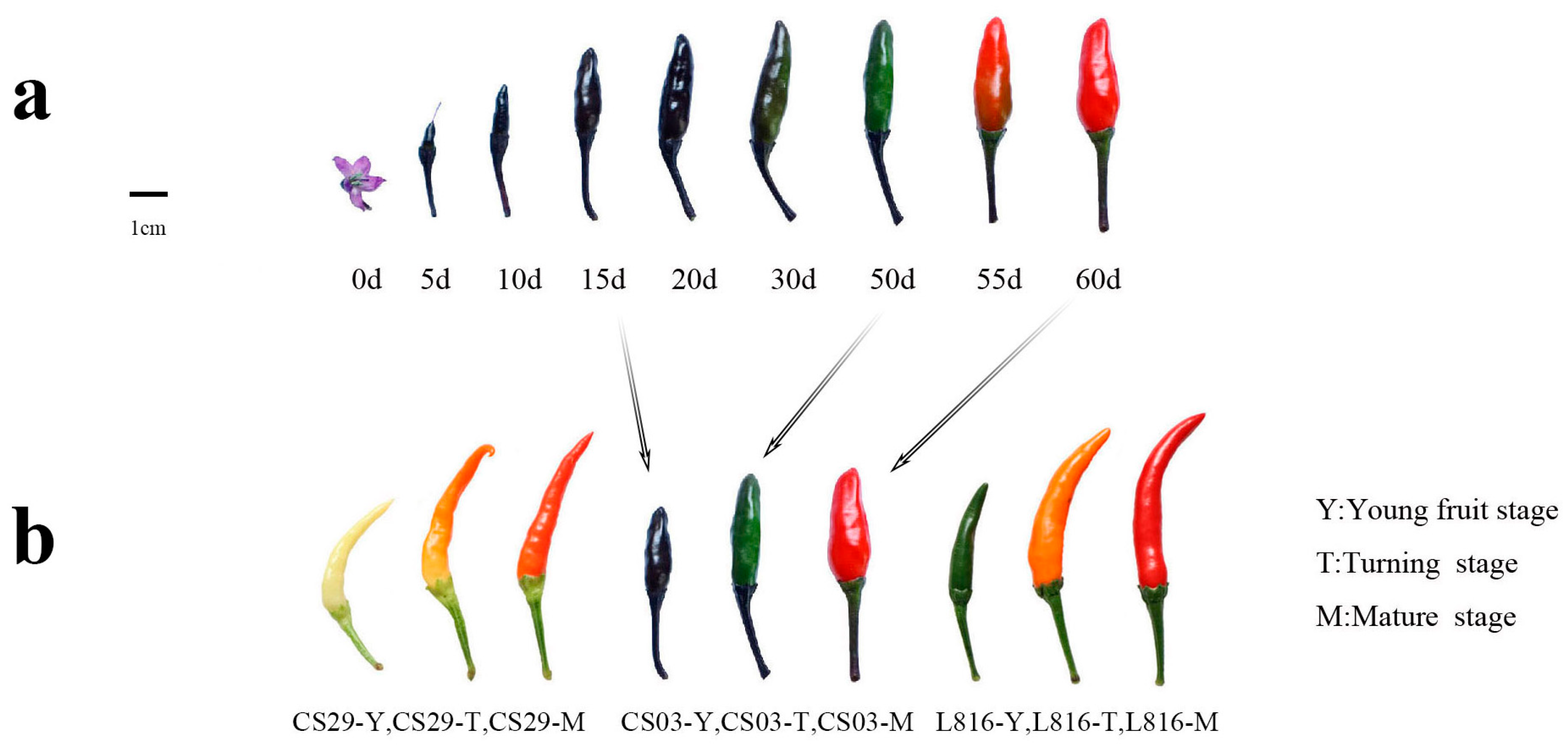
2.1. Pepper Materials
2.2. Extraction and Identification of Total Chlorophyll, Carotenoids, and Anthocyanins
2.3. Non-Targeted Metabolomics
2.4. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.5. Combined Analysis of Transcriptomics and Non-Targeted Metabolomics
2.6. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR
3. Results
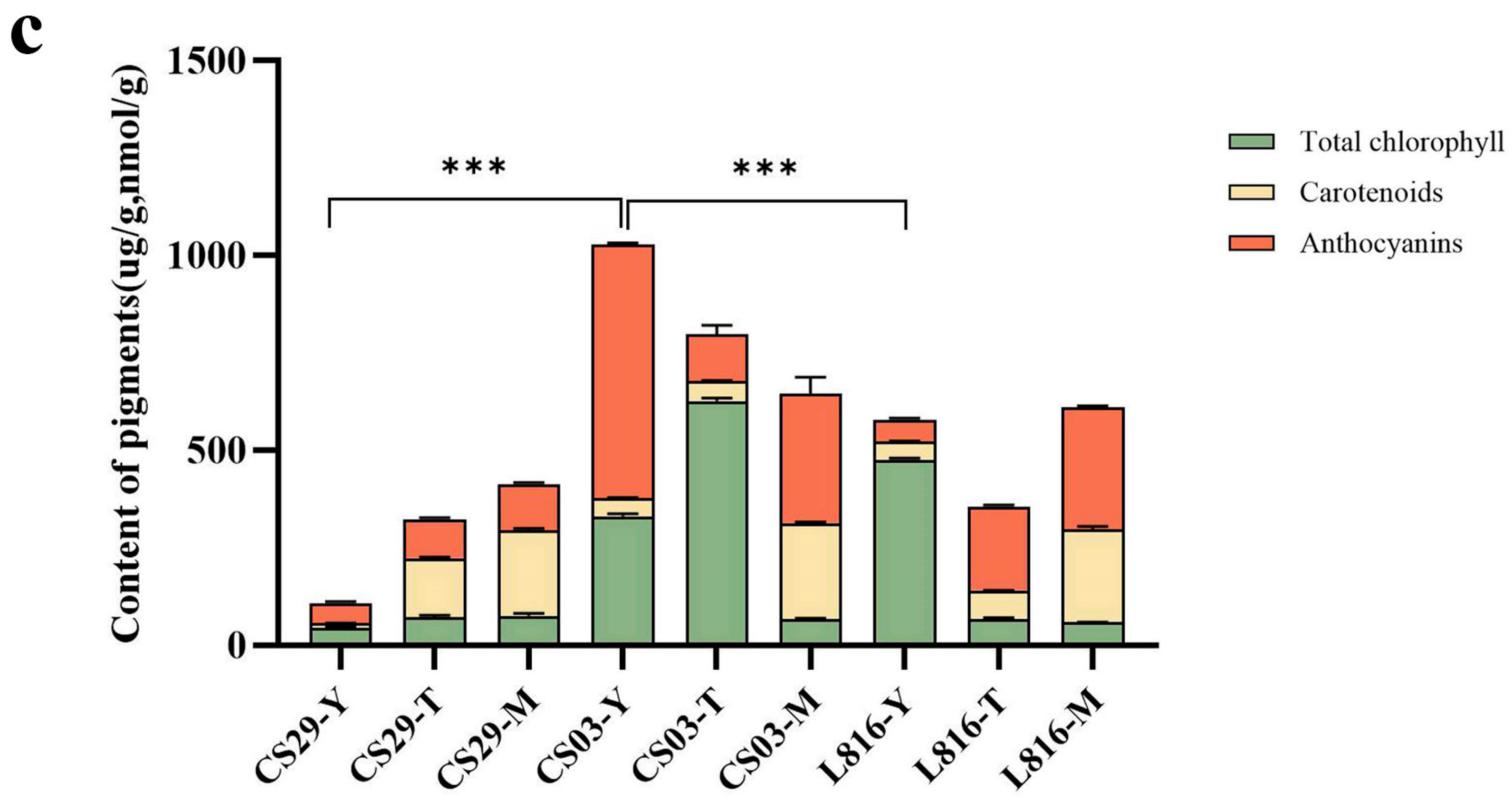
3.1. Contents of Total Chlorophyll, Carotenoids, and Anthocyanins
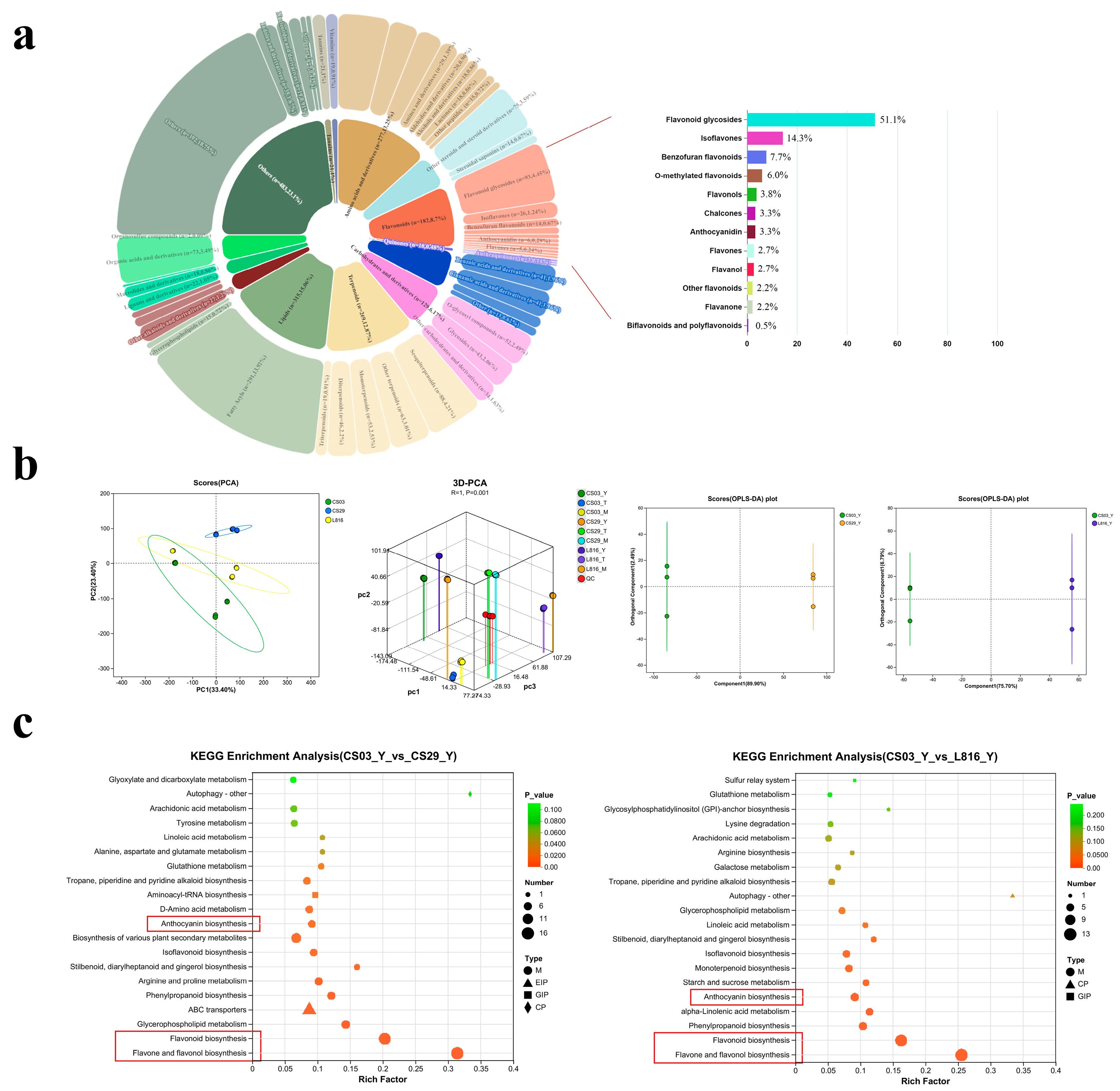
3.2. Differentially Accumulated Metabolites in Peppers
3.3. Cluster Analysis of Common Flavonoids
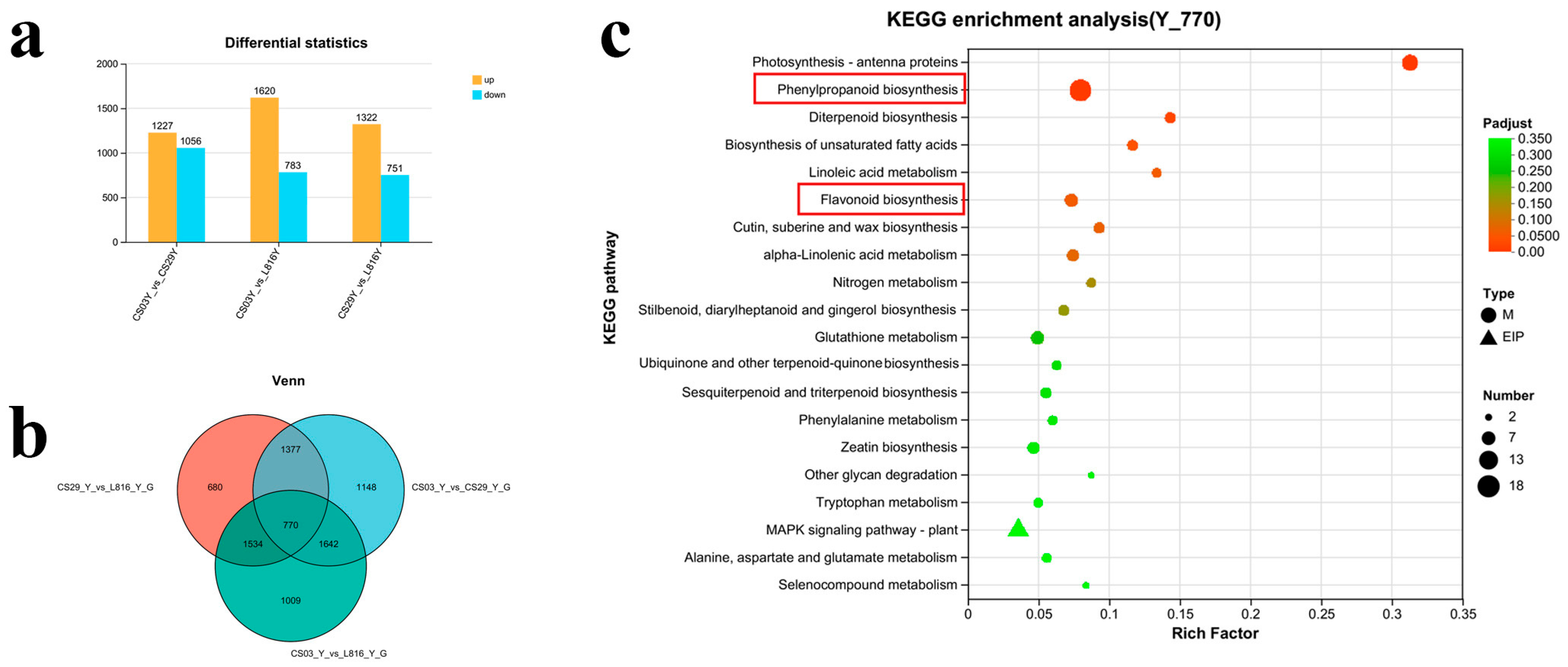
3.4. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in Chili Peppers During Young Fruit Stage
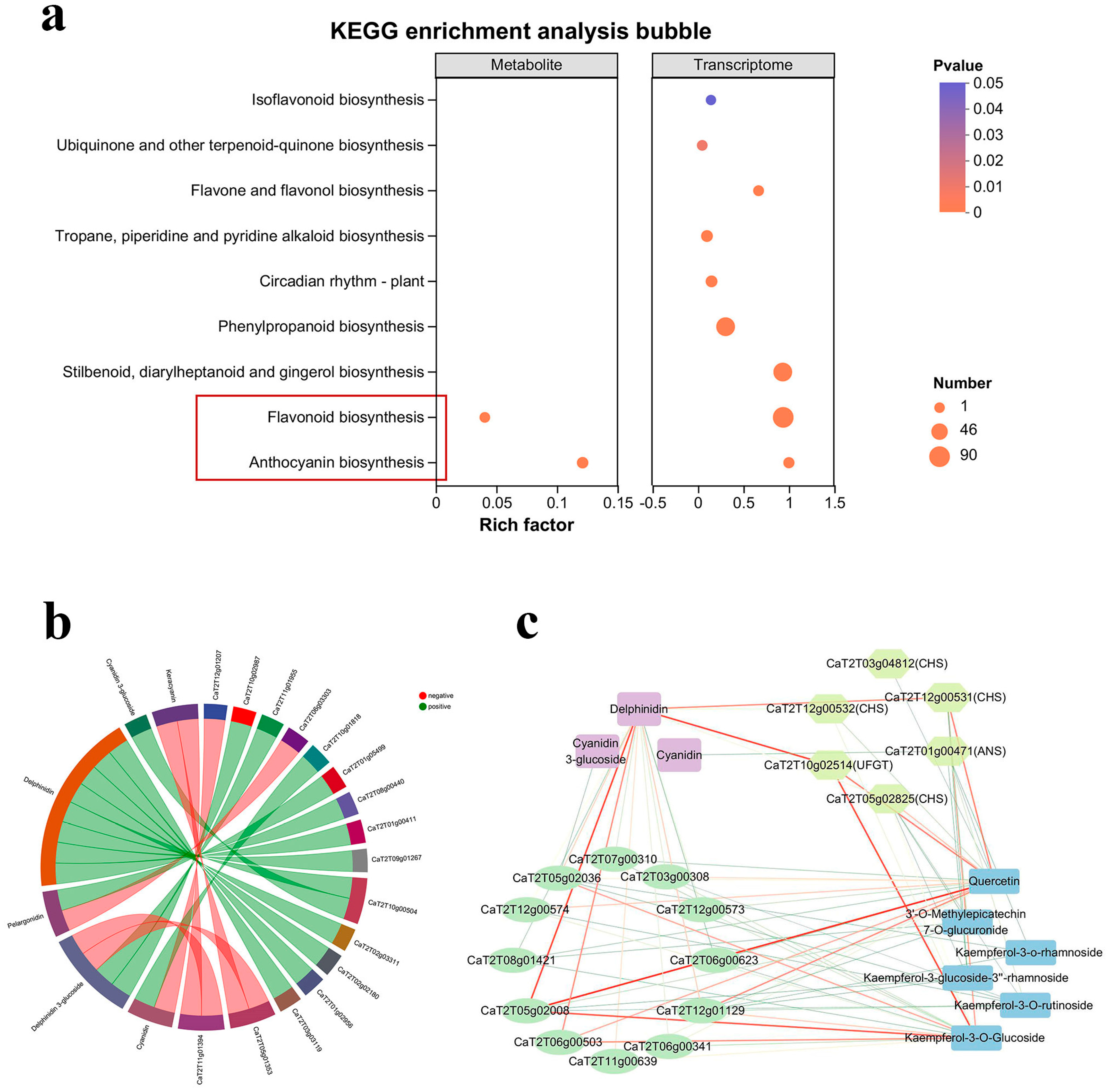
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Transcriptome and Metabolome
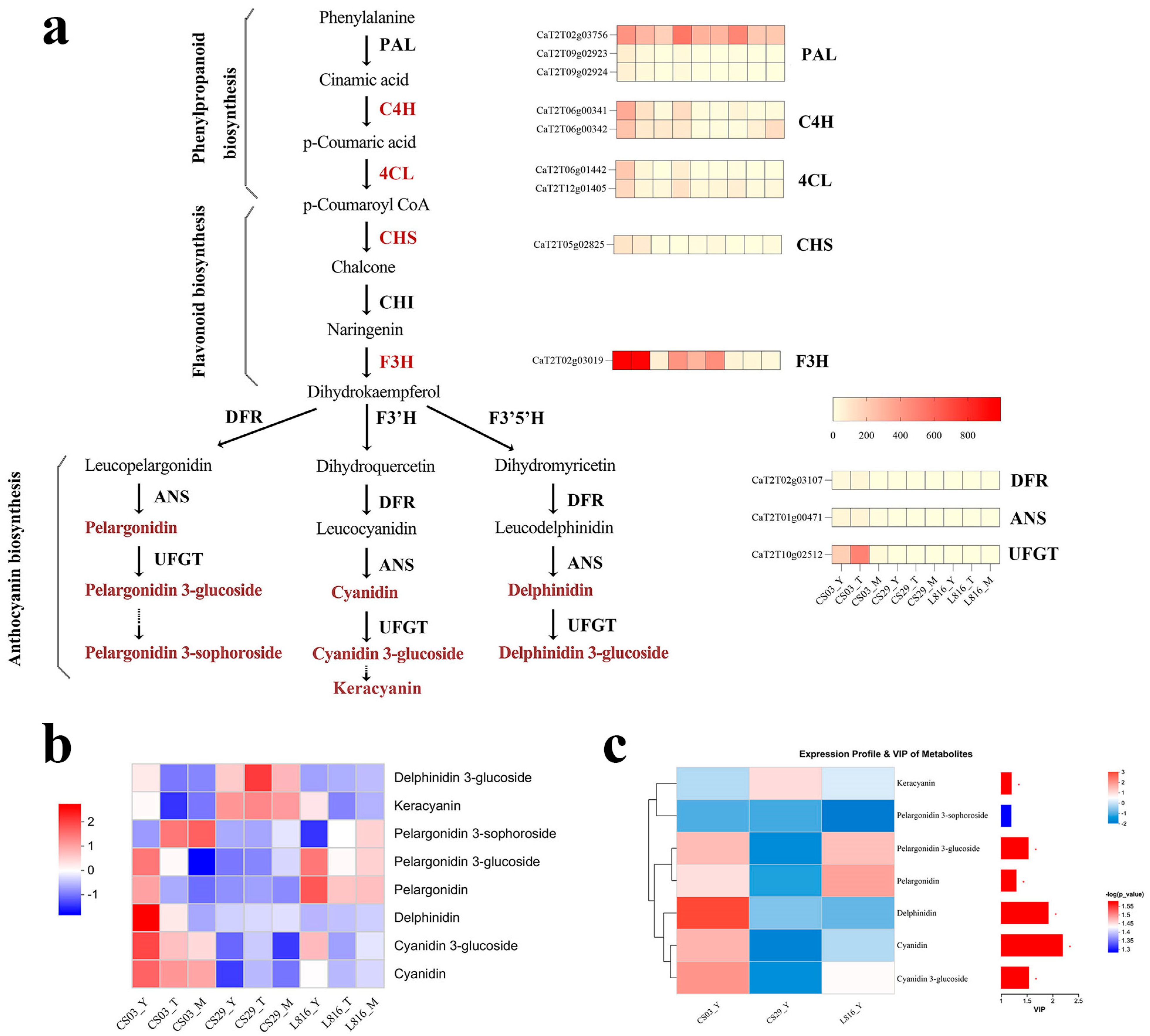
3.6. Relationship Between Structural Genes and Metabolites in Anthocyanin Synthesis Pathway
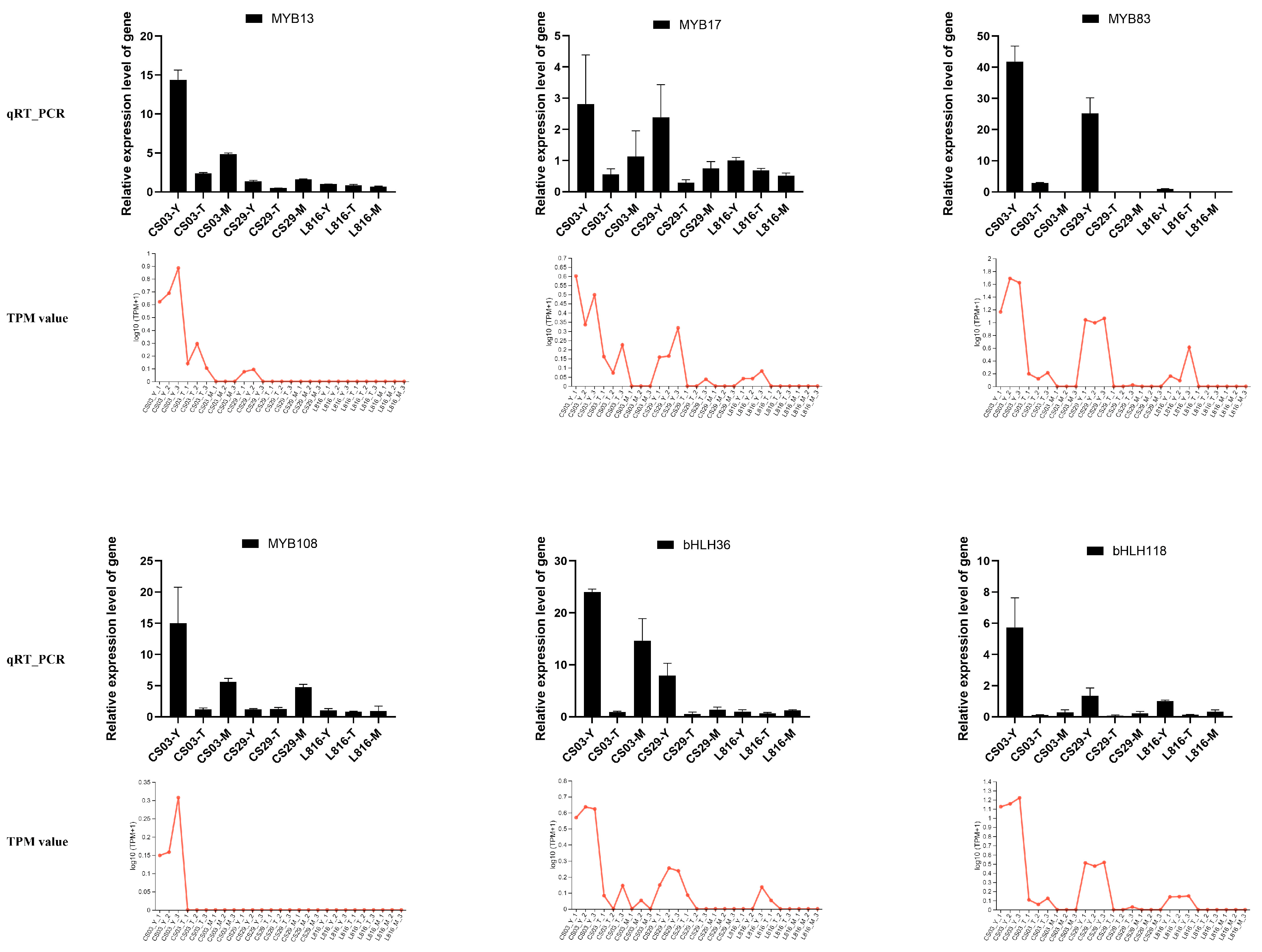
3.7. Prediction and Family Analysis of Transcription Factors in Peppers
4. Discussion
4.1. The Purple Color of Pepper CS03 Is Related to the Content of Anthocyanins
4.2. Key Structural Genes and Transcription Factors Involved in Anthocyanin Synthesis in Pepper CS03
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grotewold, E. The genetics and biochemistry of floral pigments. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Rivera, M.G.; Ochoa-Alejo, N. Chili Pepper Carotenoids: Nutraceutical Properties and Mechanisms of Action. Molecules 2020, 25, 5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Yoon, Y.; Yoon, H.; Park, H.M.; Song, S.; Yeum, K.J. Dietary Anthocyanins against Obesity and Inflammation. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Paramás, A.M.; Ayuda-Durán, B.; Martínez, S.; González-Manzano, S.; Santos-Buelga, C. The Mechanisms Behind the Biological Activity of Flavonoids. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6976–6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepiniec, L.; Debeaujon, I.; Routaboul, J.M.; Baudry, A.; Pourcel, L.; Nesi, N.; Caboche, M. Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.B.; Choe, J.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Jang, H.H. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities in Relation to the Flavonoids Composition of Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Antioxidants 2020, 9, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, T.A.; Cornish, E.C. Genetics and Biochemistry of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tikunov, Y.; Schouten, R.E.; Marcelis, L.F.M.; Visser, R.G.F.; Bovy, A. Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Degradation Mechanisms in Solanaceous Vegetables: A Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Begum, R.F.; Singh, A.S.; Chitra, V. Anthocyanin as a therapeutic in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review of preclinical evidences. Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 76, 101595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, X.; Ge, L.; Cao, F.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Antitumor, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of kaempferol and its corresponding glycosides and the enzymatic preparation of kaempferol. PLoS ONE 2018, 3, e0197563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Saeed, F.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Umair Arshad, M.; Khan, H.; et al. Kaempferol: A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisah, Y.; Jalil, J.; Yunos, N.M.; Zainalabidin, S. Cardioprotective Properties of Kaempferol: A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tan, T.; Jia, Y.; Xie, Q.; Chen, G. Correction to Anthocyanin Accumulation and Transcriptional Regulation of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Purple Pepper. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 12152–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M.; Liang, R.; Wang, J.; Qu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Y.; He, G.; Yang, Y.; Yang, P.; Xu, L.; et al. Multifaceted roles of LhWRKY44 in promoting anthocyanin accumulation in Asiatic hybrid lilies (Lilium spp.). Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; He, X.; Dong, Y.; Sun, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Lakshmanan, P.; et al. Comparative metabolomics reveals complex metabolic shifts associated with nitrogen-induced color development in mature pepper fruit. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1319680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karppinen, K.; Lafferty, D.J.; Albert, N.W.; Mikkola, N.; McGhie, T.; Allan, A.C.; Afzal, B.M.; Häggman, H.; Espley, R.V.; Jaakola, L. MYBA and MYBPA transcription factors co-regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in blue-coloured berries. N. Phytol. 2021, 232, 1350–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, A.H.; Kim, C.K. Roles of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in horticultural plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 98, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, R.; Miao, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J.; Pang, X.; Wan, H. Pigment Biosynthesis and Molecular Genetics of Fruit Color in Pepper. Plants 2023, 12, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Tao, Y.; Gao, L.; Liang, H.; Tang, D.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Gmitter, F.G., Jr.; Li, C. An Integrated Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal the Regulation Mechanisms of Flavonoid Biosynthesis in a Purple Tea Plant Cultivar. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 880227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Luo, M.; Liu, X.Q.; Hao, L.Y.; Zhu, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.Y. MYB-1 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in Magnolia wufengensis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 217, 109283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, K.; Chen, M.; Liu, S.; Chen, G.; Cao, B.; Cao, F.; et al. Coexpression network analysis reveals an MYB transcriptional activator involved in capsaicinoid biosynthesis in hot peppers. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, L.; Xi, D.; Li, X.; Gao, L.; Miao, L.; Luo, Y.; Tian, M.; Zhu, H. Methyl jasmonate-induced bHLH42 mediates tissue-specific accumulation of anthocyanins via regulating flavonoid metabolism-related pathways in Caitai. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, e14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; Li, S.; Wang, L. The combination of DNA methylation and positive regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis by MYB and bHLH transcription factors contributes to the petal blotch formation in Xibei tree peony. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, X. Sichuan Southwest Pepper Germplasm Resources. Chin. Veg. 1997, 31–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sui, Y.; Qian, C.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Hu, N.; Cao, Y. Analysis of Summer Fruit Setting Rate and Main Photosynthetic Characteristics of Purple Chili. J. Hortic. 2011, 38, 77–86. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Razola-Díaz, M.D.C.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; López de Andrés, J.; Voltes-Martínez, A.; Zamora, A.; Pérez-Molina, G.M.; Castro, D.J.; Marchal, J.A.; Verardo, V. Evaluation of Phenolic Compounds and Pigments Content in Yellow Bell Pepper Wastes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Q.; Sun, L.; Shen, H. Identification of the Regulatory Genes of UV-B-Induced Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Pepper Fruit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, W.; Ou, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, X. Integrative analysis of metabolome and transcriptome reveals the mechanism of color formation in pepper fruit (Capsicum annuum L.). Food Chem. 2020, 306, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Qiu, H.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, A.; Xu, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Metabolomics and transcriptomics analyses provide insights into the dynamic of metabolites and the molecular mechanisms of natural pigment formation of different color-transition types of red Pepper (Capsicum). Sci. Hortic. 2025, 342, 114062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, Z.; Bedő, J.; Pápai, B.; Tóth-Lencsés, A.K.; Csilléry, G.; Szőke, A.; Bányai-Stefanovits, É.; Kiss, E.; Veres, A. Ripening-Induced Changes in the Nutraceutical Compounds of Differently Coloured Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Breeding Lines. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashina, T. Contribution to flower colors of flavonoids including anthocyanins: A review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K. Chemical and biological study of flavonoid-related plant pigment: Current findings and beyond. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2024, 88, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, M.; Hirabuchi, A.; Goto, F.; Nishizaki, Y.; Uesugi, S.; Watanabe, A.; Tasaki, K.; Washiashi, R.; Sasaki, N. Production of yellow-flowered gentian plants by genetic engineering of betaxanthin pigments. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadilova, E.; Stintzing, F.C.; Carle, R. Anthocyanins, colour and antioxidant properties of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) and violet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) peel extracts. Z. Naturforsch C J. Biosci. 2006, 61, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Holland, T.M.; James, B.D.; Cherian, L.J.; Aggarwal, N.T.; Leurgans, S.E.; Bennett, D.A.; Schneider, J.A. Pelargonidin and Berry Intake Association with Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathology: A Community-Based Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 88, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.; Liu, R.H.; Tang, J. Effect of processing on phenolic antioxidants of fruits, vegetables, and grains—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 887–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhera, D.; Capaldi-Phillips, E.D. A review of visual cues associated with food on food acceptance and consumption. Eat. Behav. 2014, 15, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Q.; Zhou, X.-L.; Lyu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, L.; Shen, S.-K. Anthocyanin accumulation underlies petal blotch coloration in Rhododendron rex and its medicinal potential. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 224, 120335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; Feng, K.; Que, F.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. A MYB transcription factor, DcMYB6, is involved in regulating anthocyanin biosynthesis in purple carrot taproots. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Yan, L. Anthocyanins accumulation analysis of correlated genes by metabolome and transcriptome in green and purple peppers (Capsicum annuum). BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, Y.; Hua, W.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Deng, M. Bioactive Components and Color Variation Mechanism Among Three Differently Colored Peppers Based on Transcriptomics and Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060638
Mo Y, Hua W, Cheng H, Zhang R, Li P, Deng M. Bioactive Components and Color Variation Mechanism Among Three Differently Colored Peppers Based on Transcriptomics and Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(6):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060638
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Yunrong, Wei Hua, Hong Cheng, Ruihao Zhang, Pingping Li, and Minghua Deng. 2025. "Bioactive Components and Color Variation Mechanism Among Three Differently Colored Peppers Based on Transcriptomics and Non-Targeted Metabolomics" Horticulturae 11, no. 6: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060638
APA StyleMo, Y., Hua, W., Cheng, H., Zhang, R., Li, P., & Deng, M. (2025). Bioactive Components and Color Variation Mechanism Among Three Differently Colored Peppers Based on Transcriptomics and Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Horticulturae, 11(6), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11060638





