A Potassium Phosphite Solution as a Dual-Action Strategy Against Bean Anthracnose: Antifungal Activity and Defense Gene Priming
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C. lindemuthianum Isolate
2.2. Effect of Potassium Phosphite Solution on C. lindemuthianum Under In Vitro Conditions
2.3. Inoculum Increase and Pathogenicity Test
2.4. Effect of Potassium Phosphite Solution on Anthracnosis Disease
2.5. Effect of the Potassium Phosphite Solution on Defense Gene Expression
3. Results
3.1. Effect of the Potassium Phosphite Solution on C. lindemuthianum
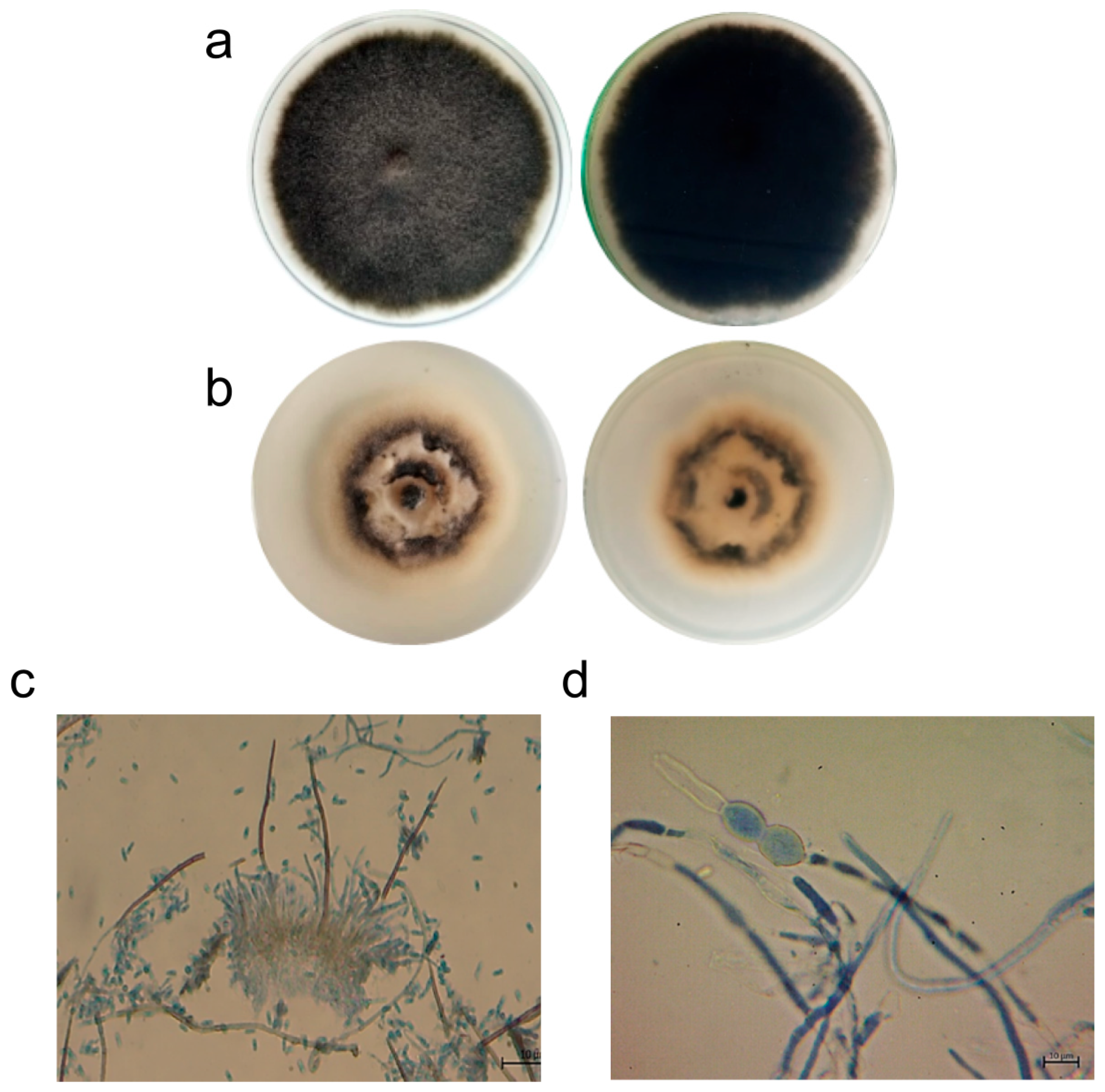
3.1.1. Effect on C. lindemuthianum Morphology
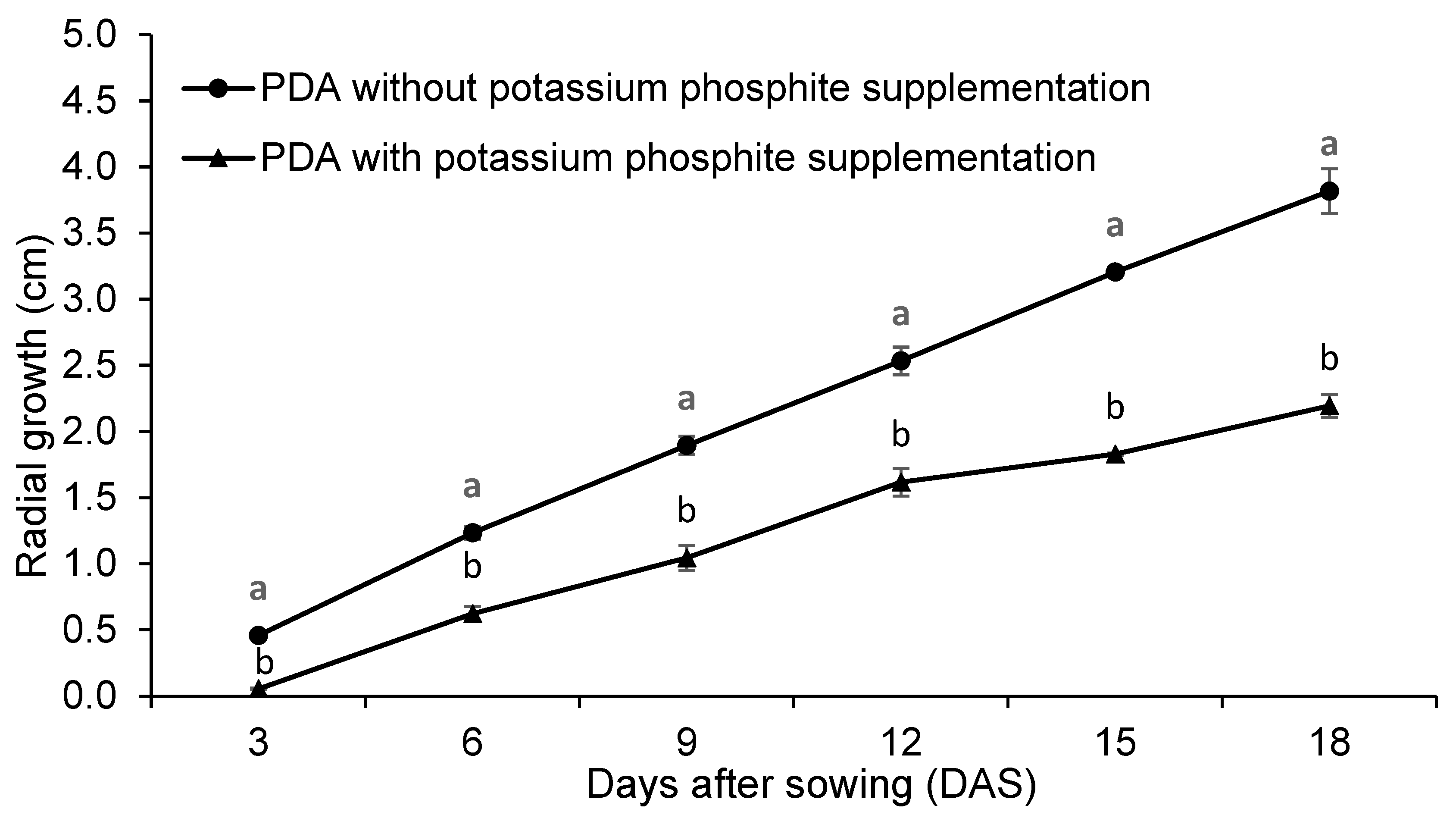
3.1.2. Effect on C. lindemuthianum Growth Rate and Conidia Germination
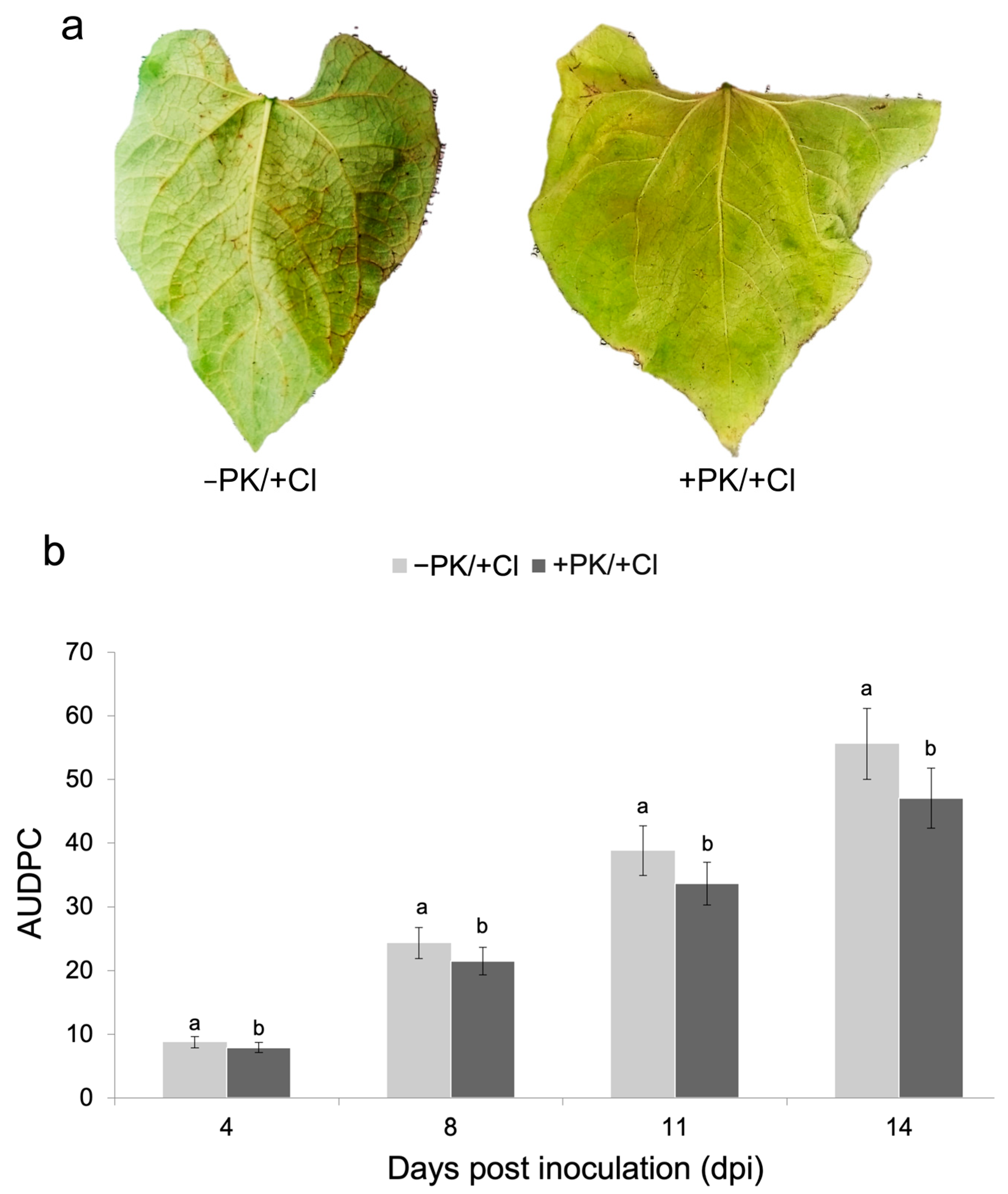
3.2. Effect of Potassium Phosphite Solution on Bean Anthracnose
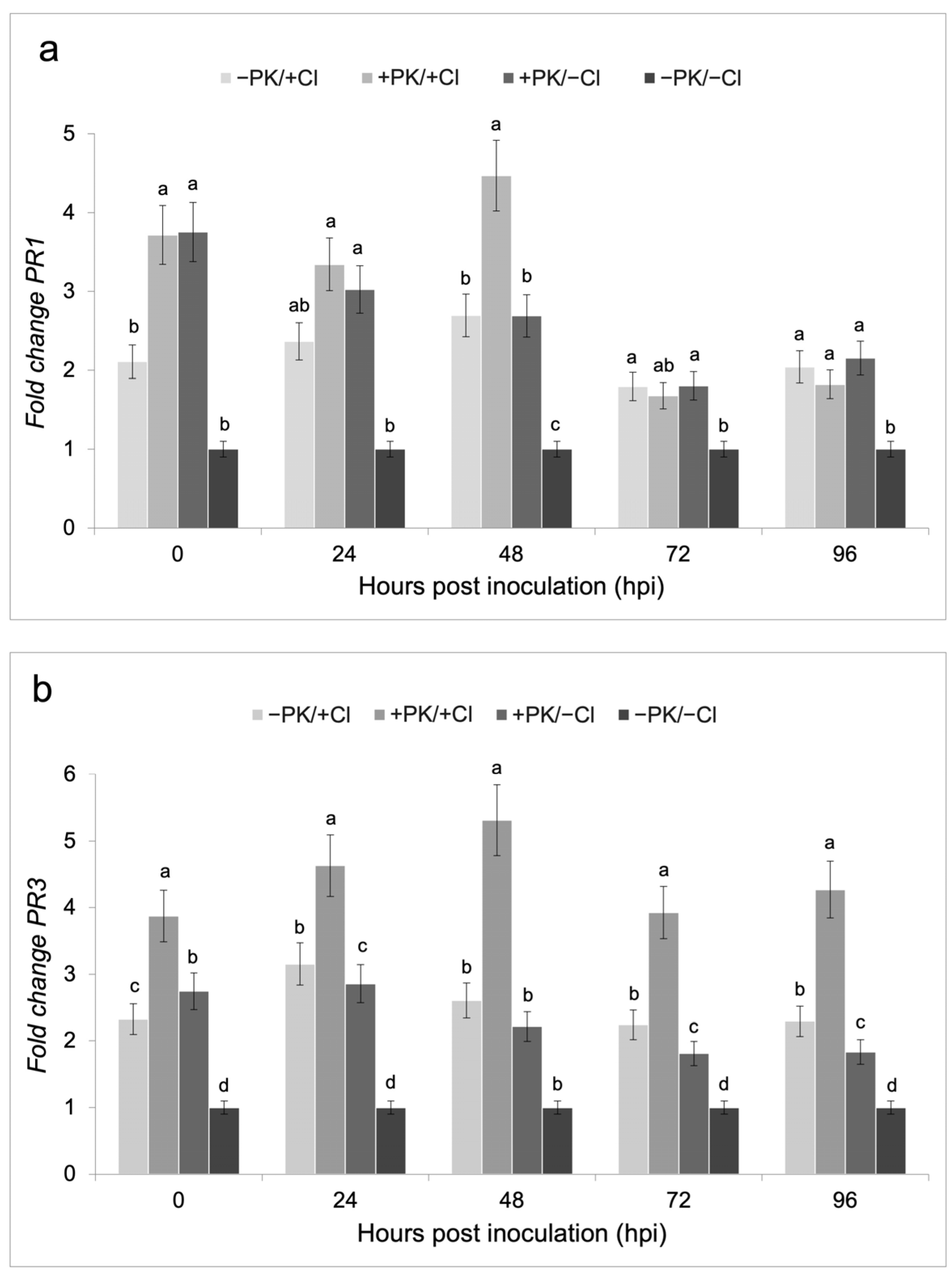
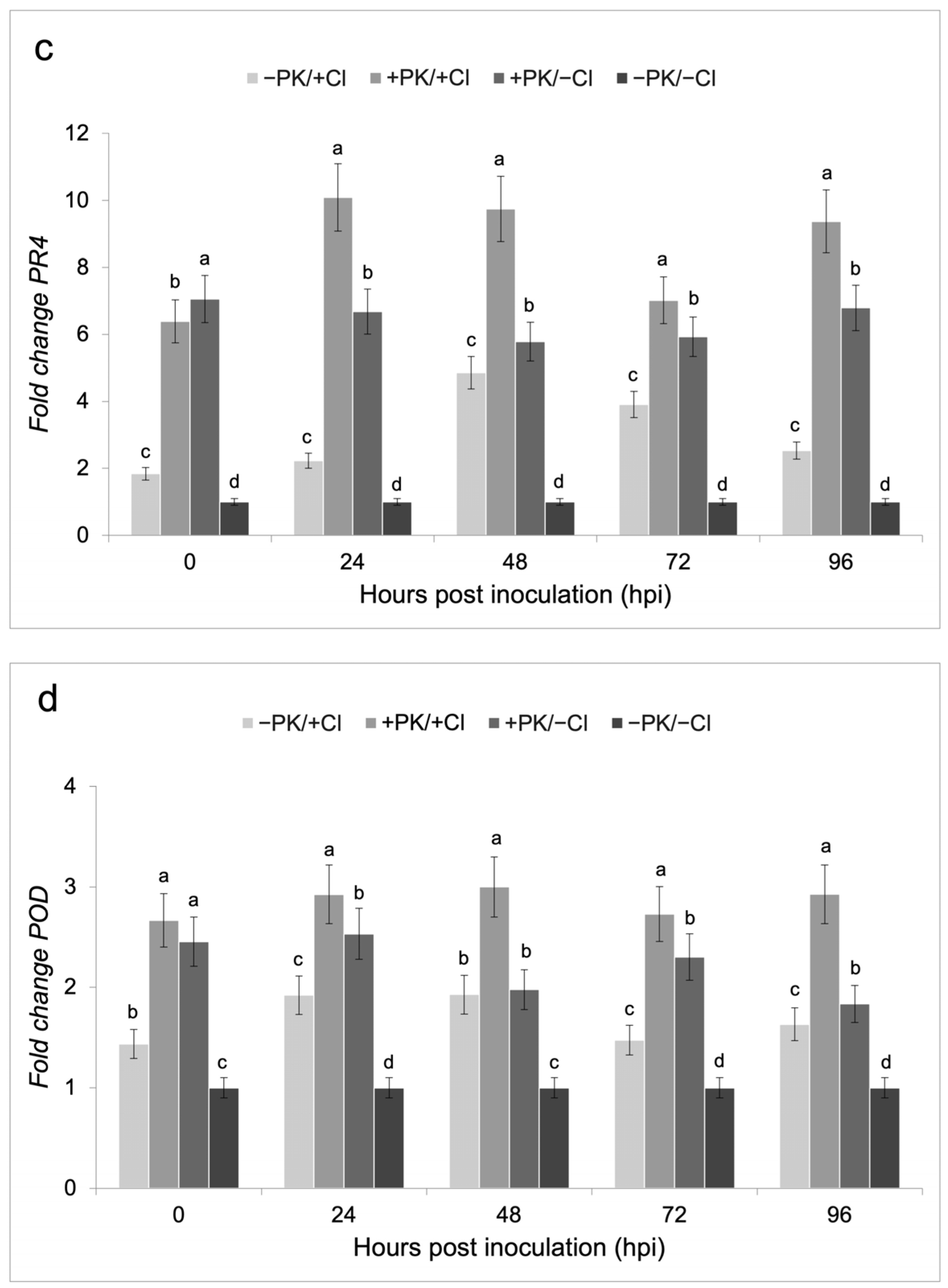
3.3. Defense Gene Expression on Bean Plants Treated with the Potassium Phosphite Solution and Infected with C. lindemuthianum
4. Discussion
4.1. Antifungal Effect of the Potassium Phosphite Solution on C. lindemuthianum
4.2. Reduction in Bean Anthracnose Induced by the Potassium Phosphite Solution
4.3. Induction of Defense Gene Expression by the Potassium Phosphite Solution
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahmanzadeh, A.; Khahani, B.; Taghavi, S.M.; Khojasteh, M.; Osdaghi, E. Genome-wide meta-QTL analyses provide novel insight into disease resistance repertoires in common bean. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.; Salgotra, R.K.; Damm, U.; Rajeshkumar, K.C. Phylogeny and pathogenicity of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum causing anthracnose of Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Bhaderwah-Rajmash from northern Himalayas, India. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, N.; Nabi, A.; Fayaz, T.; Lateef, I.; Nisa, Q.; Bashir, A.; Rashid, Z.; Shah, M.D.; Itoo, H.; Shah, R.A.; et al. Pathogenically altered Colletotrichum lindemuthianum transformants help in understanding the biochemical defense and colonization dynamics in Phaseolus vulgaris. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 129, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, A.; Lateef, I.; Nisa, Q.; Banoo, A.; Rasool, R.S.; Shah, M.D.; Ahmad, M.; Padder, B.A. Phaseolus vulgaris-Colletotrichum lindemuthianum pathosystem in the post-genomic era: An update. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.L.; Moreno, H.L.A.; Correia, H.L.N.; Santana, M.F.; Queiroz, M.V. Colletotrichum: Species complexes, lifestyle, and peculiarities of some sources of genetic variability. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Zapata, S.P.; Castaño-Zapata, J. In vitro effect of four fungicides on Colletotrichum gloeosporioides causing anthracnosis on the Red Globe grape variety. Rev. Acad. Colomb. Cienc. Exactas. Fis. Nat. 2020, 44, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.A.; Cheng, Y.; Aslam, M.; Jakada, B.H.; Wai, M.H.; Ye, K.; He, X.; Luo, T.; Ye, L.; Dong, C.; et al. ROS and oxidative response systems in plants under biotic and abiotic stresses: Revisiting the crucial role of phosphite triggered plants defense response. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 631318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmer, A.; Pastor, V.; Gamir, J.; Flors, V.; Mauch-Mani, B. The ’prime-ome’: Towards a holistic approach to priming. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achary, V.M.M.; Ram, B.; Manna, M.; Datta, D.; Bhatt, A.; Reddy, M.K.; Agrawal, P.K. Phosphite: A novel P fertilizer for weed management and pathogen control. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, L.; Aanderson, J.; Aryamaseh, N.; Shearer, B.; McComb, J.; Hardy, G.E.S.; O’Brien, P.A. Phosphite primed defence responses and enhanced expression of defence genes in Arabidopsis thaliana infected with Phytophthora cinnamomi. Plant Pathol. 2011, 60, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, J.L.; Schlegel, A.J. Review of phosphite as a plant nutrient and fungicide. Soil Syst. 2021, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.; Reeve, W.; Van Der Hoek, M.; Williams, N.; McComb, J.; O’Brien, P.A.; Hardy, G.E.S.J. Defining the phosphite-regulated transcriptome of the plant pathogen Phytophthora cinnamomi. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2010, 284, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.H.G.; De Resende, M.L.V.; Monteiro, A.C.A.; Junior, P.M.R.; Botelho, D.M.S.; Silva, B.M. Potassium phosphites in the protection of common bean plants against anthracnose and biochemical defence responses. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 66, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, H.E.; Rivero, R.; Hoyos, C.L. Manual de Prácticas de Fitopatología General; Facultad de Ciencias Agrarias Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Bogotá, Colombia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, N.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, K.S. Mitogen-activated protein kinase CsPMK1 is essential for pepper fruit anthracnose by Colletotrichum scovillei. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 770119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, G.; Jara, C.E.; Mosquera, G. Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Enfermedad antracnosis. In Guías Prácticas de Laboratorio Para el Manejo de Patógenos del Frijol; Castellanos, G., Jara, C.E., Mosquera, G., Eds.; Alliance Bioversity International—CIAT: Palmira, Colombia, 2011; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, G.; González, S.; Royero, W.; González, A. Morphological and transcriptional analysis of Colletotrichum lindemuthianum race 7 during early stages of infection in common bean. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2024, 47, e20220263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza-Padilla, M.C.; Rodriguez-Arevalo, K.A.; Rincon-Rivera, L.J.; Gonzalez-Almario, A. Co-52 resistance allele contributes to induce basal defense against Colletotrichum lindemuthianum race 7. Pesqui. Agropecu. Trop. 2022, 52, e71746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schoonhoven, A.; Pastor-Corrales, M.A. Standard System for the Evaluation of Bean Germplasm; Alliance Bioversity International—CIAT: Palmira, Colombia, 1987; pp. 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shaner, G.; Finney, R.E. The effect of nitrogen fertilization on the expression of slow-mildewing resistance in knox whetl. Phytopathology 1977, 67, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga-Gomez, C.; Gonzalez-Almario, A. Evaluation of defense genes expression and the virulence factor Cac1 in Phaseolus vulgaris and Colletotrichum lindemuthianum interaction. Agron. Colomb. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, L.; Valdebenito-Sanhueza, R.M.; Stadnik, M.J. Evaluation of potassium phosphite formulations against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in vitro and for post-infection control of Glomerella leaf spot in apple. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2010, 35, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogoshi, C.; Abreu, M.S.; Silva, B.M.; Neto, H.S.; Ribeiro-Junior, P.M.; Resende, M.L.V. Potassium phosphite: A promising product in the management of diseases caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in coffee plants. Biosci. J. 2013, 29, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Gadaga, S.J.C.; Abreu, M.S.; De Resende, M.L.V.; Junior, P.M.R. Phosphites for the control of anthracnose in common bean. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2017, 52, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueira, E.P.P.; Kuhn, O.J.; Martinazzo-Portz, T.; Stangarlin, J.R.; Pereira, M.D.P.; Lampugnani, C. Histochemical changes induced by Trichoderma spp. and potassium phosphite in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in response to the attack by Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Semin. Ciênc. Agrár. 2020, 41, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, M.; Schmulling, T. Stress priming, memory, and signalling in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 42, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yañez-Juarez, M.G.; Lopez-Orona, C.A.; Ayala-Tafoya, F.; Partida-Ruvalcaba, L.; Velasquez-Alcatraz, T.J.; Medina-Lopez, R. Los fosfitos como alternativa para el manejo de problemas fitopatológicos. Rev. Mex. Fitopatol. 2018, 36, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Wu, J. Global transcriptome analysis reveals resistance genes in the early response of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) to Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Ramezani, F.; Rahmani, F.; Dehestani, A. Exogenous potassium phosphite application improved PR-protein expression and associated physiobiochemical events in cucumber challenged by Pseudoperonospora cubensis. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, B.; Vashi, R.; Rajput, K.; Joshi, R. Plant chitinases and their role in plant defense: A comprehensive review. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 159, 110055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Diaz, J.C.; Laugé, R.; Delannoy, E.; Huguet, S.; Paysant-Le Roux, C.; Gratias, A.; Geffroy, V. Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of the effects of infection with the hemibiotrophic fungus Colletotrichum lindemuthianum on common bean. Plants 2022, 11, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, B.; Lin, M.; Chen, G.; Ding, X.; Weng, Q.; Chen, Q. Phosphite-induced reactive oxygen species production and ethylene and ABA biosynthesis, mediate the control of Phytophthora capsici in pepper (Capsicum annuum). Funct. Plant Biol. 2016, 43, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshraghi, L.; Anderson, J.P.; Aryamanesh, N.; McComb, J.A.; Shearer, B.; Hardy, G. Defence signalling pathways involved in plant resistance and phosphite-mediated control of Phytophthora cinnamomi. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Aguilar, K.; Hernandez-Chavez, J.L.; Alvarez-Venegas, R. Priming of seeds with INA and its transgenerational effect in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants. Plant Sci. 2021, 305, 110834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novaes, M.; Debona, D.; Fagundes-Nacarath, I.; Brás, V.; Rodrigues, F. Physiological and biochemical responses of soybean to white mold affected by manganese phosphite and fluazinam. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2018, 41, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, F.W.; Faquin, V.; Da Silva-Lobato, A.K.; Avila, P.A.; Marques, D.J.; Silva-Guedes, E.M.; Yuen-Tan, D.K. Effect of phosphite supply in nutrient solution on yield, phosphorus nutrition and enzymatic behavior in common bean (’Phaseolus vulgaris’. L.) plants. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 713–722. [Google Scholar]
- Mofidnakhaei, M.; Abdossi, V.; Dehestani, A.; Pirdashti, H.; Babaeizad, V. Potassium phosphite affects growth, antioxidant enzymes activity and alleviates disease damage in cucumber plants inoculated with Pythium ultimum. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2016, 49, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipini, R.B.; Boneti, J.I.; Katsurayama, Y.; Neto, A.C.R.; Veleirinho, B.; Maraschin, M.; Piero, R. Apple scab control and activation of plant defence responses using potassium phosphite and chitosan. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 145, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Mycelial Growth Rate (cm/Day) | Growth Inhibition Percentage (%) | Conidial Germination Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDA without supplementation | 0.22 a | - | 49.44 a |
| PDA supplemented with potassium phosphite | 0.14 b | 42.39 | 25.78 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saldarriaga-Gómez, C.; Paez-Monroy, P.N.; González-Almario, A. A Potassium Phosphite Solution as a Dual-Action Strategy Against Bean Anthracnose: Antifungal Activity and Defense Gene Priming. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050462
Saldarriaga-Gómez C, Paez-Monroy PN, González-Almario A. A Potassium Phosphite Solution as a Dual-Action Strategy Against Bean Anthracnose: Antifungal Activity and Defense Gene Priming. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(5):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050462
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaldarriaga-Gómez, Catalina, Paula Natalia Paez-Monroy, and Adriana González-Almario. 2025. "A Potassium Phosphite Solution as a Dual-Action Strategy Against Bean Anthracnose: Antifungal Activity and Defense Gene Priming" Horticulturae 11, no. 5: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050462
APA StyleSaldarriaga-Gómez, C., Paez-Monroy, P. N., & González-Almario, A. (2025). A Potassium Phosphite Solution as a Dual-Action Strategy Against Bean Anthracnose: Antifungal Activity and Defense Gene Priming. Horticulturae, 11(5), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11050462






