Abstract
A field experiment was conducted in 2023 and 2024 in Beijing, China, to investigate effects of soil water stress, applied before the fruit ripening stage, on the fruit total soluble solid accumulation and cracking of jujube trees. The experiment consisted of two variation factors: (a) irrigation levels (MDI and SDI, applied 80% and 50% of the irrigation volume, respectively) and (b) growth stages (stage 1, before the fruit enlargement stage, and 2, before the fruit ripening stage). The two irrigation levels were applied at each growth stage in a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement, plus a control treatment receiving 100% irrigation volume, resulting in five treatments per replicate. The findings indicated that pre-enlargement stage water stress enhanced the accumulation of total soluble solid content within fruits, which subsequently promoted faster fruit growth in from the early- to mid-August period. However, by late August, both the total soluble solid content and fruit growth rates had declined, thereby mitigating the risk of fruit cracking. During the fruit enlargement stage, the fruit total soluble solid content in SDI-2 increased by approximately 24% by the end of August compared to the control, leading to lower osmotic potential and higher turgor pressure during the following ripening stage. As skin growth ceased, high turgor pressure caused fruit cracking at the following ripening stage. The SDI-2 treatment demonstrated a fruit cracking rate approximately 1.5 times higher than that of the control. Pearson correlation analysis also indicated that fruit cracking was positively correlated with total soluble solids accumulated in August. Meanwhile, the yield of SDI-2 was reduced about 18%. Therefore, the adequate soil moisture during the fruit enlargement stage was crucial to minimize jujube fruit cracking and economic losses. Meanwhile, the deficit irrigation applied during the pre-enlargement stage could effectively conserve water resources and mitigate the occurrence of extensive jujube fruit cracking.
1. Introduction
Jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.), native to China, has been cultivated for more than 4000 years and is widely favored by consumers due to its rich nutritional content and delicious, juicy taste [1,2]. Therefore, the jujube trees are widely planted in Hebei, Xinjiang, Shanxi, Shaanxi, Shandong, Ningxia, Yunnan, and Beijing in China [3,4]. However, the susceptibility of jujube fruits to cracking had led to considerable economic losses for farmers and has severely hindered the development of the jujube industry in China [5].
Fruit cracking, as a physiological disorder, is affected by many factors, such as the external environment, mineral nutrients, fruit load, cuticle layer structure, fruit size, rootstock, and variety, but most researchers have indicated that pre-harvest rainfall has a significant impact on fruit cracking [6,7,8,9]. The study on the grapes [10] and apricots [11] has also shown that the fruit cracking is associated with the intense precipitation during the rapid fruit enlargement stages. During the fruit enlargement stage, the precipitation is absorbed by the roots and fruits, increasing the fruit turgor pressure and resulting in cracking over the fruit skin [6,9].
Therefore, fruit cracking is collectively influenced by water availability and the rate of water absorption by the fruit. In general, osmotic adjustment can regulate water content in plant cells and promote water uptake [12,13]. Following the intense precipitation, the excessively high fruit-soluble solid content within the fruit accelerates water absorption due to the osmotic adjustment, exacerbating the occurrence of fruit cracking [14,15,16]. Accordingly, during the fruit’s cracking-susceptible stage, the fruit soluble solid content plays a critical role in influencing the occurrence of fruit cracking.
In fact, during the initial stages of fruit development, many orchards around the world commonly face the challenge of drought stress [17,18,19]. Such aridity often leads to a degree of soil water stress in both fields and orchards. Notably, the fruit-sugar and -soluble solid content are often elevated due to soil water stress [20]. The drought stress may stimulate the accumulation of total soluble solids within fruits, as the total soluble solids play a role in regulating osmotic pressure of plant cells [20]. The studies on pears have also reported that the osmotic adjustment during the period of water stress could facilitate the transfer of solutes from the leaves to fruits, leading to an accumulation of sugars in the fruits [21]. The similar results were also reported by Francaviglia et al. [22] and Arji et al. [23]. Although the drought-induced enhancement of sugar content improves fruit quality, it is potentially associated with an increased risk of fruit cracking [24,25]. The osmotic stress-related water uptake and increase in fruit volume result in an excessive turgor pressure, which increases the peel area and leads to fruit cracking [25,26,27,28]. A study on sweet cherries concluded that the sugar content increased osmotic pressure and water uptake in the fruit, resulting in fruit cracking [15,29]. Similar results were also reported by Considine [30] and Zhang et al. [31] on grapes.
For this reason, during the early growth stage of jujube fruits, drought conditions lead to elevated soluble solid and sugar content within the fruits. During the ripening phase, exposure to continuous rainfall leads to rapid water absorption by the fruits, driven by osmotic adjustment caused by high soluble solid content. This results in elevated internal turgor pressure, potentially worsening the occurrence of fruit cracking. Extensive research has predominantly attributed severe fluctuations in water availability as the principal factor contributing to fruit cracking [32,33]. An escalation in the severity of fruit cracking has been observed in the pear orchards subjected to rapid transitions from dry to saturated soil conditions following intense rainfall events [34,35,36,37]. Therefore, by regulating the soil moisture in orchards during the dry season, it is possible to control the fruit sugar content to some extent. This may help prevent the fruits from rapidly absorbing large amounts of water and expanding excessively after the rainy season begins, thereby mitigating the risk of fruit cracking. Seo et al. [36] and Krajewski et al. [38] also suggested that effective orchard floor management practices should be implemented to minimize rapid fluctuations in soil water content, which helps mitigate fruit cracking in susceptible cultivars. However, the studies investigating the influences of soil moisture during the early growth phase of jujube trees on accumulation of soluble solid content within the jujube fruit, along with its subsequent effects on fruit development and cracking, are still relatively scarce.
In northern China, although precipitation is predominantly concentrated between July and September, certain extreme years may experience prolonged drought events during July and August. Although such climatic phenomena occurred infrequently, their occurrence can significantly exacerbate fruit cracking in jujube and, in severe cases, lead to complete crop failure in some orchards. Furthermore, in recent years, greenhouse cultivation of jujube had been widely adopted in provinces such as Shaanxi, Shanxi, and Shandong to promote early ripening of fruits and enhance economic benefits. To accelerate fruit maturation, farmers typically cease irrigation between one and two months prior to ripening. These practices have collectively resulted in excessively dry soil conditions in orchards during the pre-ripening stage of jujube fruits, which undoubtedly increases the risk of fruit cracking. Therefore, the objective of this research was to evaluate the effects of deficit irrigation applied before the fruit enlargement stage on the fruit growth, total soluble solids accumulation, and cracking of jujube trees.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Location of Study Area
From May 2023 to October 2024, the field experiments were conducted in the experimental orchard of the Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences (Beijing, China, 39°95′ N, 116°03′ E). The experimental site was characterized by a continental monsoon climate, featuring an average annual precipitation of 600 mm and a mean annual temperature of 12.8 °C.
2.2. Experimental Design
Ten-year-old jujube trees (Ziziphus jujube Mill.‘Jing39’) were planted under simple rain shelters (with plastic film roofs) that were 4.5 m in height. Tree spacing was 4 m between rows and 3 m within rows (833 trees per hectare). The jujube trees were irrigated with two driplines (QC.1630020, Qicheng Huanya Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) located 1 m away from and on both sides of the tree rows. The drip irrigation pipe featured a working pressure range of 0.5–3.5 bar, 1 mm wall thickness, 14 mm inner diameter, 2 L·h−1 emitter flow rate, 0.3 m emitter spacing, and ±10% manufacturing coefficient of variation. The field capacity and the permanent wilting point of the soil were 27% and 9% (v/v), respectively.
The growing stage of jujube trees (Ziziphus jujube Mill.‘Jing39’) was divided into the slow fruit growth stage (from late May to late July), fruit enlargement stage (August), and fruit ripening stage (from early September July to harvest). The experiment consisted of two variation factors: (a) irrigation levels, including moderate (MDI) and severe deficit irrigation (SDI), applied 80% and 50% of the irrigation volume, respectively, and (b) growth stages, including stage 1 (before the fruit enlargement stage) and 2 (before the fruit ripening stage). The two irrigation levels were applied at each growth stage in a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement (Table 1), plus a control treatment receiving 100% irrigation volume, resulting in five treatments per replicate. The deficit irrigation treatments were irrigated with 100% irrigation volume during non-water stress stages. Jujube trees are highly resistant to water stress [39,40], so the irrigation of the control was initiated when the soil water content at a 30 cm depth dropped below 60% of the field capacity [40,41,42,43,44] and ceased when it surpassed 90% of the field capacity [40,42,43,44,45,46]. The irrigation amount of each treatment is shown in Table 2. A randomized design was adopted, and each treatment was replicated 3 times. Each irrigation plot consisted of 12 trees in 3 rows, with the 2 sample trees located in the middle and 10 guard trees located surrounding sample trees. Each treatment consisted of 6 samples trees and 30 guard trees.

Table 1.
Experimental design.

Table 2.
The irrigation amount of each treatment in 2023 and 2024.
2.3. Measurements
The soil water content at 30 cm depths were monitored by the time-domain reflectometer (TDR-CS655, Campbell SCI Co., Ltd., Salt Lake City, UT, USA) once a week throughout the experimental period. One-probe per replicate was placed beneath the driplines at a 30 cm depth.
In early June in two experimental years, between three and five shoots per replication per treatment were labeled in the south part of the canopy, and the shoot lengths were measured with a measuring tape in late September. Fruit fresh weight and total soluble solid content were measured at intervals from seven to ten days from late June to late September. Five fruits per replication per treatment were harvested by hand to measure each fruit fresh weight with an electronic scale. And then the total soluble solid content of each fruit was measured using a digital refractometer (PR1 ATAGO Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The fresh fruit weight and total soluble solids content were measured with five repetitions per replicates.
At the harvest stage, two sample trees were hand-harvested for each replication (six sample trees per treatment), and the fruits from each tree were weighed using an electronic scale. The fresh yield of each sampled tree was measured and recorded separately. The incidence of fruit cracking per replication of each treatment was assessed at seven-day intervals from mid-August to harvest. The fruit cracking ratio (%) was calculated as the percentage of the number of cracked fruits relative to the total number of sampled fruits.
2.4. Data Analysis
Analysis of variance, Pearson correlation analysis, and mapping were performed by statistical analysis software (OriginPro 2021). Differences between means were analyzed using the Tukey tests at significant level of P0.05.
3. Results
3.1. The Soil Water Status
The soil volume water content in the control maintained a relatively higher level (Figure 1), as compared with the water stress treatments, which indicated that less or no water stress. The soil volumetric water content in deficit irrigation treatments was markedly lower than that in the control during the water stress stages. Subsequently, the soil volumetric water content under DI treatment was gradually restored due to full irrigation.
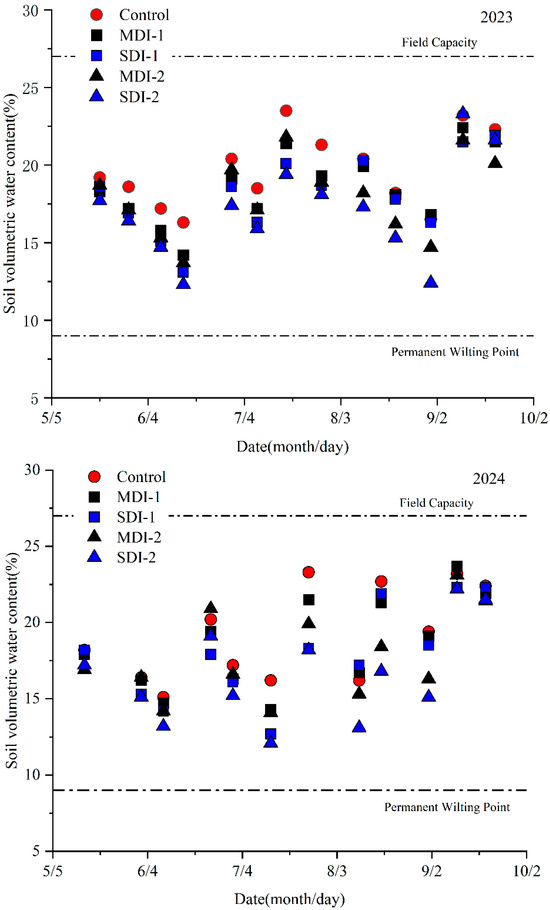
Figure 1.
The effects of deficit irrigation applied different growing stages on soil water status in two experimental years.
3.2. The Shoot Growth, Fruit Growth, and Yield
The vegetative growth was restricted by the water stress. Compared to the control, the final shoot extension of MDI-1 and SDI-1 was reduced by 9% and 13% in 2023, and by 7% and 17% in 2024 (Figure 2), respectively. The deficit irrigation applied before the fruit ripening stage exerted a more pronounced effect on the shoot growth of the jujube trees (Figure 2). The final shoot length of MDI-2 and SDI-2 was decreased by 16% and 24% in 2023, and by 12% and 24% in 2024, respectively, compared to the control.
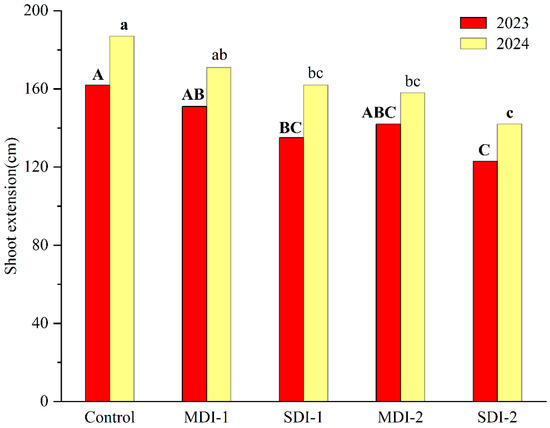
Figure 2.
The effects of deficit irrigation applied different growing stages on shoot length of jujube trees in two experimental years. Note: Different capital and small letters next to bars indicate significant differences at the p = 0.05 level in 2023 and 2024, respectively.
Prior to August, the jujube fruit grew slowly at a rate less than 0.3 g/day, while during the August, the fruit experienced rapid growth, reaching approximately 60% of its final fruit weight at this stage, and then the fruit growth nearly ceased (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The fruit growth of MDI-1 was slightly reduced compared to the control, suggesting that the moderate deficit irrigation applied during slow fruit growth stage had no inhibitory effect on fruit development. But significant differences in fruit weight between the SDI-1 and control were observed. Following the restoration of the full irrigation, MDI-1 and SDI-1 treatments exhibited a higher fruit growth rate compared to the control; however, this trend ceased in late August. The fruit growth during the fruit enlargement stage was negatively impacted by deficit irrigation, especially with the SDI-2 treatment significantly reducing fruit growth compared to the control.
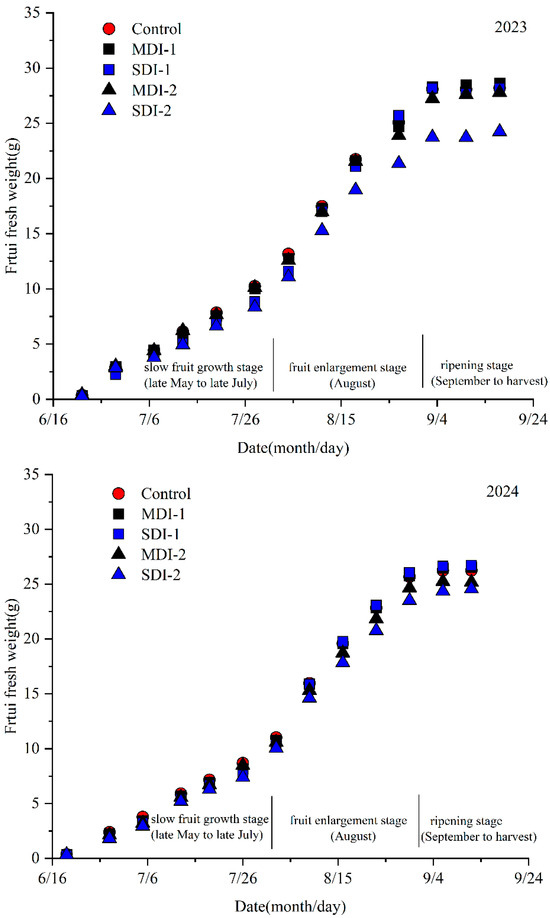
Figure 3.
The effects of deficit irrigation applied different growing stages on jujube fruit fresh weight in two experimental years.
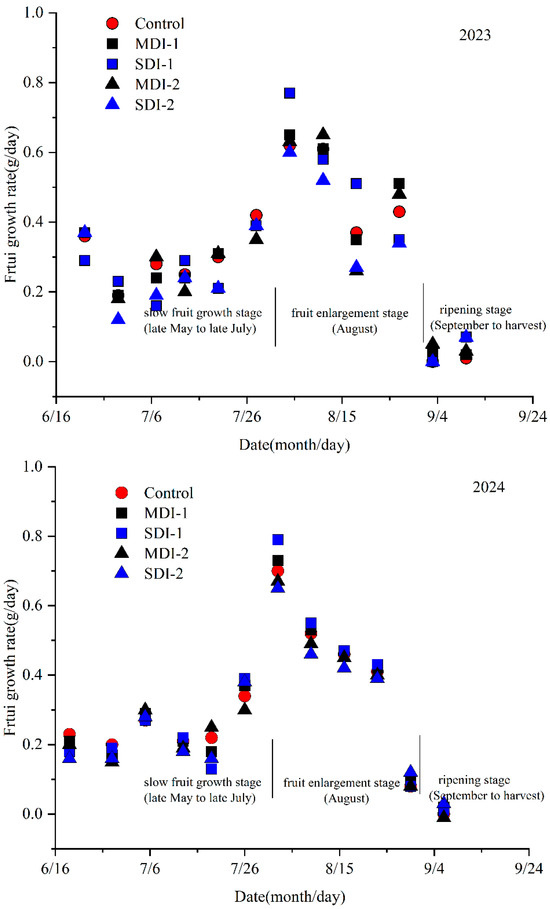
Figure 4.
The effects of deficit irrigation applied different growing stages on jujube fruit growth rate in two experimental years.
There were no significant differences among MDI-1, SDI-1, and the control treatment (Figure 5), suggesting that the deficit irrigation applied before the fruit enlargement stage had no negative impacts on the final fruit yield of jujube trees. Similarly, the fruit yield in MDI-2 was comparable to that of the control. However, a marked reduction in yield was observed in SDI-2. The final fruit yield of SDI-2 decreased by 17% and 20% in 2023 and 2024, respectively, compared to the control, with the reduction in 2023 being statistically significant.
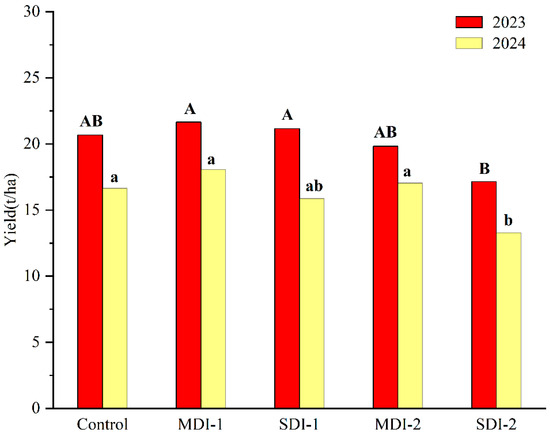
Figure 5.
The effects of deficit irrigation applied different growing stages on jujube fruit fresh yield in two experimental years. Note: Different capital and small letters next to bars indicate significant differences at the p = 0.05 level in 2023 and 2024, respectively.
3.3. The Accumulation of Fruit Total Soluble Solids
The fruit total soluble solid content was improved by the deficit irrigation (Figure 6). Prior to August, the fruit soluble solid content was increased by the moderate and severe deficit irrigation treatments, but the differences were not significant among the moderate deficit irrigation treatment and the control. After the resumption of full irrigation, the difference in total soluble solid content in the fruits of MDI-1 and SDI-1 treatments compared to the control gradually diminished, and this discrepancy virtually disappeared by the end of August. During the fruit enlargement stage, the higher total soluble solid contents in MDI-2 and SDI-2 were observed, where the total soluble solid content of SDI-2 increased by 26% and 22% at the end of August in 2023 and 2024, respectively, compared to the control.
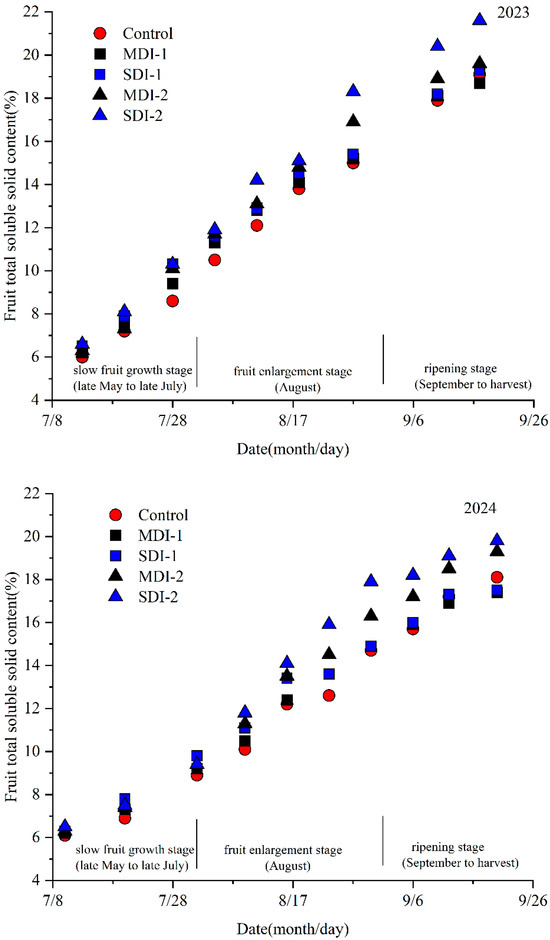
Figure 6.
The effects of deficit irrigation applied different growing stages on jujube fruit total soluble solid content in two experimental years.
3.4. The Fruit Cracking
The final fruit cracking ratio of the control maintained 20% in two consecutive experimental years. Deficit irrigation applied prior to the fruit enlargement stage, whether moderate or severe, did not significantly influence the fruit cracking ratio (Figure 7). However, deficit irrigation applied during the fruit enlargement stage exerted a greater impact on fruit cracking compared to other growth stages of jujube trees. In 2023 and 2024, SDI-2 exhibited 1.7-fold and 1.6-fold higher fruit cracking rates, respectively, compared to the control, with significant differences observed. Meanwhile, MDI-2 also showed 75% and 59% increases in cracking rates for the respective years, though the result was not significant in 2024.
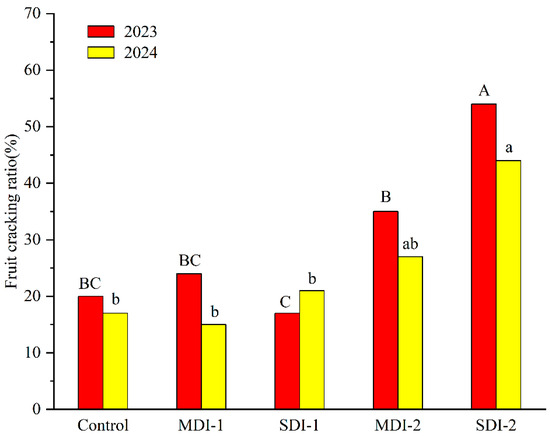
Figure 7.
The effects of deficit irrigation applied different growing stages on final jujube fruit cracking ratio in two experimental years. Note: Different capital and small letters next to bars indicate significant difference at the p = 0.05 level in 2023 and 2024, respectively.
Pearson correlation analysis indicated that the final fruit cracking ratio was significantly and positively correlated with the total soluble solids accumulated in August, as well as with the final total soluble solid content (Figure 8). However, the analysis revealed no significant correlation between final fruit cracking ratio and total soluble solids accumulated before August.
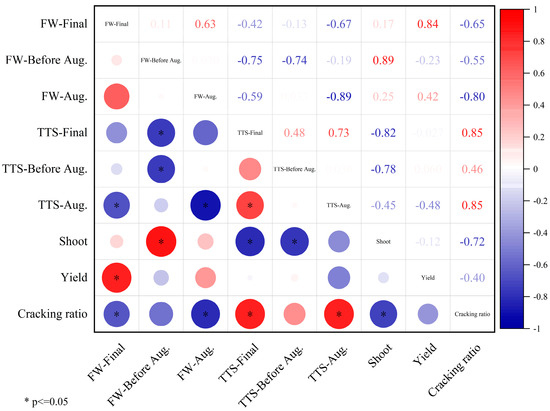
Figure 8.
Heat map for correlation analysis of various parameters. Note: * 0.05-significant correlation. FW-Final means the final fruit fresh weight; FW-Before Aug. means mass increment of the fruit before August; FW-Aug. means mass increment of the fruit during August; TTS-Final means the final fruit soluble solid content; TTS-Before Aug. means the fruit total soluble solids accumulated before August; TTS-Aug. means the fruit total soluble solids accumulated during August; Shoot means the final shoot extension; Yield means the final fruit fresh yield; Cracking ratio means the final fruit cracking ratio.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Effects of Deficit Irrigation on the Shoot and Fruit Growth of Jujube Trees
The vegetative growth of fruit trees is very sensitive to the deficit irrigation; in general, the shoot extension is inhibited by the deficit irrigation [47,48,49]. The leaf photosynthetic rates are reduced by the deficit irrigation, which results in insufficient nutrient supply for the shoot growth. Additionally, the abscisic acid generated in roots is transferred to shoots, which negatively impacts the vegetative growth [50]. Excessive vegetative growth consumed more soil nutrients and water, resulting in the negatively effects on the fruits’ growth and final yield. Thus, implementing appropriate water regulation during the vigorous growth period of shoots can effectively prevent the inefficient utilization of soil nutrients and water in the orchard.
The moderate deficit irrigation applied before fruit enlargement stage had no significantly negative effects on the growth of fruits (Figure 3 and Figure 4). During this stage, the fruit exhibited a diminutive volume and a retarded growth rate, with a concomitantly low demand for nutrients and water to sustain its development. Consequently, the deficit irrigation applied at this stage predominantly inhibited vegetative growth of jujube trees, exerting a relatively minor impact on the growth of fruits. Moreover, the photosynthetic assimilates were translocated from source organs (leaves or shoots) to sink organs (fruits), enabling the persistence of photosynthetic activity and sustaining fruit development under drought stress [21,51,52]. However, significant reductions in fruit weight were observed in SDI-1 at the end of July, compared to the control. This indicated that severe deficit irrigation had led to insufficient supply of nutrients and water, thereby adversely affecting fruit growth. During the following full irrigation, obviously rapidly growth rates were observed in the SDI-1 treatments, as compared with the control. This was primarily due to the high sugar content within the fruits, which created a strong osmotic potential, driving the rapid uptake of water by the fruits. A similar phenomenon was observed by Behboudian et al. [51]. However, compared to SDI-1, the growth rate of MDI-1 in August was relatively slower, which may be attributed to the lower accumulation of soluble solids in MDI-1.
During August, the jujube fruit growth rate exhibited an obvious acceleration compared to the preceding period. The jujube fruit growth was significantly restricted by the deficit irrigation applied in this stage. After full irrigation applied in the next fruit ripening stage, the growth of jujube fruit had nearly ceased. Therefore, during the fruit enlargement stage, it was essential to ensure adequate water supply to the jujube trees to facilitate the normal growth and development of the jujube fruits.
In two experimental years, no significant impacts of the deficit irrigation applied before the fruit enlargement stage on the final fruit yield were observed (Figure 5). From June to July, the fruit grew slowly, the moderate deficit irrigation applied during this stage had no negative effects on the final fruit yield. Despite a significant reduction in fruit growth of SDI-1 before August, compensation occurred during the subsequent fruit enlargement stage, preserving the final fruit yield, the similar results were reported by Wu et al. [21]. However, the severe deficit irrigation applied during the fruit enlargement stage reduced the final fruit yield, with particularly significantly differences observed between the control and SDI-2 in 2024. The fruit grew rapidly during the August, thereby insufficient supply of water and nutrients resulted in the inhibition of fruit growth, ultimately impacting the fruit yield.
4.2. The Effects of Deficit Irrigation on the Accumulation of Total Soluble Solids in Jujube Fruits
The total soluble solid content was improved by the deficit irrigation. The vegetative growth was significantly inhibited by the water stress, which maintained more photosynthetic assimilates and other nutrients accumulated in the fruits [21]. Multiple studies have also demonstrated that deficit irrigation induces soluble sugar accumulation as part of osmoregulation in plants [53,54]. Kapur et al. [55] reported that elevated fructose, glucose, and sucrose levels were observed in drought-stressed strawberry fruits, and similar results were concluded by Abdou et al. [56]. Additionally, the water deficit can increase the conversion of starch to sugar and result in sugars accumulating in fruit [53,57,58]. Moreover, Thomas et al. [59] further demonstrated that water deficit upregulates the expression of genes associated with sugar metabolism. As the primary storage tissues for sugars, the jujube fruits consequently accumulated higher levels of sugars. Moreover, the abscisic acid, induced by the soil water stress, could increase the transport rate of photosynthetic assimilates from leaves to fruits, thereby improving the fruit total soluble solid content [60,61]. Therefore, the significantly higher fruit total soluble solid content was observed in SDI-1 in late July. However, due to the small fruit volume and relatively low accumulation rate of total soluble solids, the total soluble solid content levels in the fruit were not significantly increased by moderate deficit irrigation treatment before August. In the following rapid fruit expansion period, the total soluble solid content in MDI-1 and SDI-1 showed a progressive decline relative to the control, suggesting that the application of full irrigation diluted the soluble solids accumulated in the fruits of the two treatments. Because MDI-2 and SDI-2 underwent deficit irrigation from late May to August, there was a disparity in the total soluble solid content between these treatments, and the control expanded during the fruit enlargement stage. Furthermore, since this stage was characterized by rapid sugar accumulation in jujube fruits, the deficit irrigation further promoted total soluble solid accumulation.
4.3. The Effects of Deficit Irrigation on the Final Fruit Cracking
The severe deficit irrigation applied before the fruit ripening stage (SDI-2) significantly increased the fruit cracking rate. The fruit total soluble solid content was significantly increased by the severe deficit irrigation applied before the fruit ripening stage. Increased total soluble solid content in fruits elevates the osmotic pressure [62,63], representing a key drought protection strategy [64,65,66]. Yooyongwech et al. [67] also concluded that sugars play a key role in plants under deficit irrigation by adjusting their osmotic potential. The higher osmotic pressure facilitates the translocation of water into the fruit interior, thereby enhancing the turgor pressure of the pulp in the following fruit ripening stage [32,68,69,70,71]. However, the epidermal growth of the jujube fruit had ceased at this stage, and the excessively high internal turgor pressure induced the cracking of the fruit skin. In comparison with SDI-2, MDI-2 exerted a markedly smaller effect on the accumulation of total soluble solids within the fruit, potentially explaining why the fruit cracking ratio in MDI-2 was substantially lower than that in SDI-2 (Figure 7). Correlation analysis also revealed a significant positive correlation between the fruit cracking ratio and the total soluble solids accumulated in August (Figure 8). This suggested that the accumulation of the total soluble solids, driven by the deficit irrigation applied during the fruit enlargement stage, significantly influenced the fruit cracking ratio.
There were no significant differences in fruit cracking ratio among the MDI-1, SDI-1 and control. Although the jujube fruit expansion rate of MDI-1 and SDI-1 were relatively higher than that of the control in early August, this trend was not sustained and disappeared by late August. The fruit underwent rapid expansion in August, during which the fruit skin maintained synchronous growth with the pulp. Furthermore, the fruit volume remained relatively limited in early to mid August, thereby mitigating the risk of fruit cracking induced by rapid growth. Additionally, the fruit total soluble solid content within fruits under SDI-1 was significantly higher than that of the control, no significant differences were observed between the two treatments by late August, as the soluble solids were subsequently diluted by the following full irrigation applied. Therefore, the total soluble solids accumulated before August did not exhibit a significant correlation with the final fruit cracking ration (Figure 8), indicating that deficit irrigation applied during slow growth period of fruits did not exacerbate the fruit cracking phenomenon in jujube. However, the study on the satsuma mandarin [28], lemon [72] indicated that the fruit cracking mainly occurs during the fruit enlargement stage, these differences may be attributed to species characteristics.
5. Conclusions
In summary, while the deficit irrigation applied prior to the fruit enlargement stage enhanced the total soluble solids content and expansion rates of jujube fruits in early August, this effect was transient and did not extend into the fruit maturation stage. Although the fruit underwent rapid expansion during August, the fruit skin maintained synchronous growth with the pulp. Thus, the deficit irrigation applied prior to the fruit enlargement stage did not increase the risk of jujube fruit cracking. The fruits’ soluble solid content were significantly improved by the severe deficit irrigation applied during the fruit enlargement stage, resulted in higher total soluble solid content and turgor pressure in the pulp during the following fruit ripening stage. At this stage, the growth of the fruit skin nearly ceased. Therefore, the cracking rates were increased by 59–75% in severe deficit irrigation (50% of the control irrigation volume) applied during the fruit enlargement stage, as compared with the control. Therefore, during the rapid fruit expansion stage of jujube, it was essential that the soil water content at a 30 cm depth be maintained between 60% and 90% of the field capacity to prevent the increase in fruit cracking risk. While this study provided valuable insights for optimizing irrigation practices to mitigate fruit cracking in jujube, further investigation is necessary to study the interactive effects of irrigation regimes with other agronomic practices, particularly mineral elements’ application, on fruit cracking susceptibility.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and Q.P.; methodology, Y.W., Z.Z. and Q.P.; investigation, Y.W., D.L. and Y.Z.; resources, Q.P; data curation, Z.Z., Y.W., D.L. and Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W.; writing—review and editing, Y.W., Z.Z., D.L. and Q.P.; supervision, Y.Z., D.L., Z.Z. and Q.P.; funding acquisition, Y.W. and Q.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Youth Foundation of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, project number: QNJJ202227; the Science and Technology Innovation Capacity Building Program of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, project number: KJCX20240317 and KJCX20230118.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Yang, W.; Kang, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, M.; Chen, G. Effect of salicylic acid treatment on antioxidant capacity and endogenous hormones in winter jujube during shelf life. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.; Kou, X.; Xue, Z. Storage quality prediction of winter jujube based on particle swarm optimization-backpropagation-artificial neural network (PSO-BP-ANN). Sci. Hortic. 2024, 331, 112789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Jiang, F.; Li, S.; Xu, N.; Li, D.; Wu, C. Design and experiment of vibratory harvesting mechanism for Chinese hickory nuts based on orthogonal eccentric masses. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 156, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, C.; Feng, J.; Qiao, Y. Vibration response characteristics of Jujube trees based on finite element method and structure-from-motion. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 331, 113125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shan, G. The Chinese Jujube; Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Measham, P. Rain-Induced Fruit Cracking in Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.); School of Agricultural Science, University of Tasmania: Tasmania, Australia, 2011; p. 170. [Google Scholar]
- Meland, M.; Kaiser, C.; Christensen, J.M. Physical and chemical methods to avoid fruit cracking in cherry. AgroLife Sci. J. 2014, 3, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Tian, C.; Zhou, X.G.; Li, L. A proposed systemic modeling software for jujube fruit cracking. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, B.; Bektas, E.; Aglar, E.; Karakaya, O.; Gun, S. Cracking and quality attributes of jujube fruits as affected by covering and pre-harvest Parka and GA3 treatments. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.J.; Hardie, W.J.; Rogiers, S.Y. Changes in susceptibility of grape berries to splitting are related to impaired osmotic water uptake associated with losses in cell vitality. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2010, 16, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülșen, Y.; Dumanoğlu, H.; Kunter, B. Fruit cracking in some turkish apricot cultivars. Acta Hortic. 1995, 384, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuzunaga-Rosas, J.; González-Orenga, S.; Calone, R.; Rodríguez-Heredia, R.; Asaff-Torres, A.; Boscaiu, M.; Ibáñez-Asensio, S.; Moreno-Ramón, H.; Vicente, O. Use of a biostimulant to mitigate the effects of excess salinity in soil and irrigation water in tomato plants. Plants 2023, 12, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, A.; Muhammad, M.; Munir, A.; Abdi, G.; Zaman, W.; Ayaz, A.; Khizar, C.; Reddy, S.P.P. Role of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Regulating Growth, Enhancing Productivity, and Potentially Influencing Ecosystems under Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. Plants 2023, 12, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.V. Rain-induced cracking of sweet cherries: Its causes and prevention. In Cherries: Crop Physiology, Production and Uses; Webster, A.D., Looney, N.E., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 1996; pp. 297–327. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, D.G. Rain-cracking of ‘Royal Ann’ sweet cherries: Fruit physiological relationships, water temperature, orchard treatments, and cracking index. Acta Hortic. 1998, 468, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, S.; Schouten, R.; Silva, A.P.; GonçalveS, B. Sweet cherry fruit cracking mechanisms and prevention strategies: A review. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 240, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, R.S.N.; de Assis Figueiredo, F.A.M.M.; Martins, A.O.; da Silva de Deus, B.C.; Ferraz, T.M.; de Assis Gomes, M.M.; de Sousa, E.F.; Glenn, D.M.; Campostrini, E. Partial rootzone drying (PRD) and regulated deficit irrigation (RDI) effects on stomatal conductance, growth, photosynthetic capacity, and water-use efficiency of papaya. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 183, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çolak, Y.B.; Yazar, A. Evaluation of crop water stress index on Royal table grape variety under partial root drying and conventional deficit irrigation regimes in the Mediterranean Region. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 224, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossad, A.; Scalisi, A.; Lo Bianco, R. Growth and water relations of field-grown ‘Valencia’ orange trees under long-term partial rootzone drying. Irrig. Sci. 2018, 36, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Tao, H.; Fan, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, Y. Effects of soil water stress on fruit yield, quality and their relationship with sugar metabolism in ‘Gala’ apple. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 258, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Huang, X. Yield and growth of mature pear trees under water deficit during slow fruit growth stages in sparse planting orchard. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 164, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francaviglia, D.; Farina, V.; Avellone, G.; Bianco, R.L. Fruit yield and quality responses of apple cvars Gala and Fuji to partial rootzone drying under Mediterranean conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 151, 556–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arji, I.; Hassany, B.; Ghamarnia, H. The effects of water stress on apple qualities and quantities (Golden delicious variety). J. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 29, 610–620. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Duan, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, D.; Hu, H.; Xie, J. Transcriptome analysis of atemoya pericarp elucidates the role of polysaccharide metabolism in fruit ripening and cracking after harvest. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, M.; Tang, W.; Wu, S.; Zhang, K.; Yang, G. Effect of nordihydroguaiaretic acid on grape berry cracking. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.V. Cracking in Cherries: IV. Physiological Studies of the Mechanism of Cracking. Acta Agric. Scand. 1972, 22, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekse, L.; Bjerke, K.L.; Vangdal, E. Fruit cracking in sweet cherries-an integrated approach. In Proceedings of the IV International Cherry Symposium, Richland, WA, USA, 24–29 June 2001; pp. 471–474. [Google Scholar]
- Measham, P.F.; Bound, A.; Gracie, J.; Wilson, S.J. Incidence and type of cracking in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) are affected by genotype and season. Crop Pasture Sci. 2009, 60, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, G.; Hajagos, A.; Ghasemi, S.; Végvári, G. Fruit quality analysis of two new promising Hungarian sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars on different rootstocks. Acta Aliment. 2012, 41, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, J.A. Physical aspects of fruit growth: Cuticular fracture and fracture patterns in relation to fruit structure in Vitis vinifera. J. Hortic. Sci. 1982, 57, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Song, P.; Li, G.; Wang, E.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, F.; Yang, J. Exogenous application of nutrient elements effectively reduces grape cracking and improves fruit quality. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 319, 112157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, G.; Wen, M.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, Y. Mechanisms and Management Strategies for Satsuma Mandarin Fruit Cracking. Agronomy 2025, 15, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Study on Fruit Cracking Characteristic and Preventive Technigues of Zizyphus jujuba Mll.cv.Lingwu Changzao in Protected Cultivation. Master’s Thesis, Ningxia University, Yinchuan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.H.; Lee, B.; Gu, M.; Lee, U.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Jung, S.K.; Choi, H.S. Course of fruit cracking in ‘Whansan’ pears. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.J.; Sawant, S.S.; Lee, B.; Kim, K.; Song, J.; Choi, E.D. Mechanisms driving fruit cracking in ‘Sinhwa’ pears (Pyrus pyrifolia Nakai) and effect of foliar fertilizer application on fruit quality. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 332, 113232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.J.; Sawant, S.S.; Song, J. Fruit Cracking in Pears: Its Cause and Management-A Review. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Zhou, X.; Tong, C.; Zhang, D. The Physiological and Molecular Mechanisms of Fruit Cracking Alleviation by Exogenous Calcium and GA3 in the Lane Late Navel Orange. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, A.; Ebert, T.; Schumann, A.; Waldo, L. Pre-Harvest Fruit Splitting of Citrus. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Du, T.; Kang, S.; Li, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, M.; Li, Z. Relationship between stable carbon isotope discrimination and water use efficiency under regulated deficit irrigation of pear-jujube tree. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Du, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Guo, J. Effects of regulated deficit irrigation at different growth stages on greenhouse pear-jujube quality. Trans. CSAE 2009, 25, 32–38, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Cui, N.; Du, T.; Gong, D.; Hu, X.; Zhao, L. Response of sap flux and evapotranspiration to deficit irrigation of greenhouse pear-jujube trees in semi-arid northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 194, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Fei, L.; Huang, D.; Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Cai, Y. Coupling effects of irrigation and nitrogen levels on yield, water and nitrogen use efficiency of surge-root irrigated jujube in a semiarid region. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Kang, S.; Wang, M.; Pang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. Effect of regulated deficit irrigation on water use efficiency and fruit quality of pear-jujube tree in greenhouse. Trans. CSAE 2006, 22, 37–43, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z. Transcriptomic analyses provide new insights into jujube fruit quality affected by water deficit stress. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 291, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Cao, H.X.; Xue, W.K.; Liu, X. Effects of the combination of mulching and deficit irrigation on the soil water and heat, growth and productivity of apples. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, S. Mulching broad ridges with a woven polypropylene fabric increase the growth and yield of young pear trees ‘Yuluxiang’ in the North China Plain. Hortic. Plant J. 2023, 9, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santesteban, L.G.; Miranda, C.; Royo, J.B. Regulated deficit irrigation effects on growth, yield, grape quality and individual anthocyanin composition in Vitis vinifera L. cv ‘Tempranillo’. Agric Water Manag. 2011, 98, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, P.; Pérez-Pérez, J.G.; del Amor, F.M.; Martinez-Cutillas, A.; Dodd, I.C.; Botía, P. Partial root zone drying exerts different physiological responses on field-grown grapevine (Vitis vinifera cv. Monastrell) in comparison to regulated deficit irrigation. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 41, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, W. Does partial root-zone drying have advantages over regulated deficit irrigation in pear orchard under desert climates? Sci. Hortic. 2020, 262, 109099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Effects of Drought Stress on Photosynthetic Characteristics and Endogenous Hormone Levels in the Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas). Horticulturae 2025, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboudian, M.H.; Lawes, G.S.; Griffiths, K.M. The influence of water deficit on water relations, photosynthesis and fruit growth in Asian pear (Pyrus serotina Rehd.). Sci. Hortic. 1994, 60, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Du, T.; Li, F.; Tong, L.; Kang, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Li, Z. Response of vegetative growth and fruit development to regulated deficit irrigation at different growth stages of pear-jujube tree. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laribi, A.; Palou, L.; Intrigliolo, D.; Nortes, P.; Rojas-Argudo, C.; Taberner, V.; Bartual, J.; Pérez-Gago, M.B. Effect of sustained and regulated deficit irrigation on fruit quality of pomegranate cv. ‘Mollar De Elche’ at harvest and during cold storage. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoalinotto, B.H.; Polyzos, N.; Liava, V.; Mandim, F.; Pires, T.C.S.P.; Añibarro-Ortega, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Dias, M.I.; Barros, L.; Petropoulos, S.A. The Effect of Cropping System and Irrigation Regime on the Plant Growth and Biochemical Profile of Cichorium spinosum. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapur, B.; Karaca, C.; Sarıda¸s, M.A.; Ağçam, E.; Çeliktopuz, E.; Kargı, S.P. Enhancing secondary compounds in strawberry fruit through optimized irrigation and seaweed application. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 324, 112609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdou, N.M.; Roby, M.H.H.; AL-Huqail, A.A.; Elkelish, A.; Sayed, A.A.S.; Alharbi, B.M.; Mahdy, H.A.A.; Abou-Sreea, A.I.B. Compost Improving Morphophysiological and Biochemical Traits, Seed Yield, and Oil Quality of Nigella sativa under Drought Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.F.; Ajaj, R.; Abd El-Khalek, A.F.; Alam-Eldein, S.M.; Gaballah, M.S.; Athar, H.u.R.; Hatterman-Valenti, H.M. Effects of deficit irrigation on growth, yield, and quality of pomegranate (Punica granatum) grown in semi-arid conditions. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, M.; Ramezanian, A.; Eshghi, S.; Sarkhosh, A. Chilling and heat requirement of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) trees grown under sustained deficit irrigation. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 263, 109117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Beena, R.; Laksmi, G.; Soni, K.B.; Swapna, A.; Viji, M.M. Changes in sucrose metabolic enzymes to water stress in contrasting rice genotypes. Plant Stress 2022, 5, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobasshi, K.; Gemma, H.; Iwahori, S. Sugar accumulation in peach fruit as affected by abscisic acid (ABA) treatment in relation to some sugar metabolizing enzymes. J. Jpn. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1999, 68, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Ge, S.; Jing, Y. Effects of exogenous ABA on translocation of photosynthate to fruit of Fuji apple during late stage of fruit rapid-swelling. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Asif, M.; Kamran, A. Plant Breeding for Water-Limited Environments. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, S.; Sun, C.; Du, J.; Ji, W.; Cao, G.; Wang, Z. Effects of straw returning on drought tolerance and growth status of maize under drought stress in the cold and arid regions of northern China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; He, J.; Ai, L. Physiological factors associated with interspecific variations in drought tolerance in centipedegrass. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Gupta, A.K.; Kaur, N. Effect of water deficit on carbohydrate status and enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in seedlings of wheat cultivars. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 44, 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Dong, D.; Wang, S. Sugar Metabolism and Transport in Response to Drought–Rehydration in Poa pratensis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yooyongwech, S.; Samphumphuang, T.; Tisarumb, R.; Theerawitaya, C.; Cha-um, S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) improved water deficit tolerance in two different sweet potato genotypes involves osmotic adjustments via soluble sugar and free proline. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 198, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichert, H.; Jagemann, C.V.; Peschel, S.; Knoche, M.; Neumann, D.; Erfurth, W. Studies on Water Transport through the Sweet Cherry Fruit Surface: VIII. Effect of Selected Cations on Water Uptake and Fruit Cracking. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2004, 129, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekse, L. Fruit cracking mechanisms in sweet cherries (Prunus avium L.)—A review. Acta Hortic. 1998, 468, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanayama, Y. Sugar metabolism and fruit development in the tomato. Hortic. J. 2017, 86, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachma, D.F.; Munyanont, M.; Maeda, K.; Lu, N.; Takagaki, M. Estimation of harvest time based on cumulative temperatures to produce high-quality cherry tomatoes in a plant factory. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, N.; Singh, H. Fruit cracking in lemon cv. Punjab Baramasi in relation to developmental physiology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 92, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).