Identification and Quantification of Carotenoids in White and Yellow-Fleshed Peaches (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) by QTRAP+ LC-MS/MS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sampling
2.2. Detection and Quantification of Carotenoids
2.3. Metabolome Data Analysis
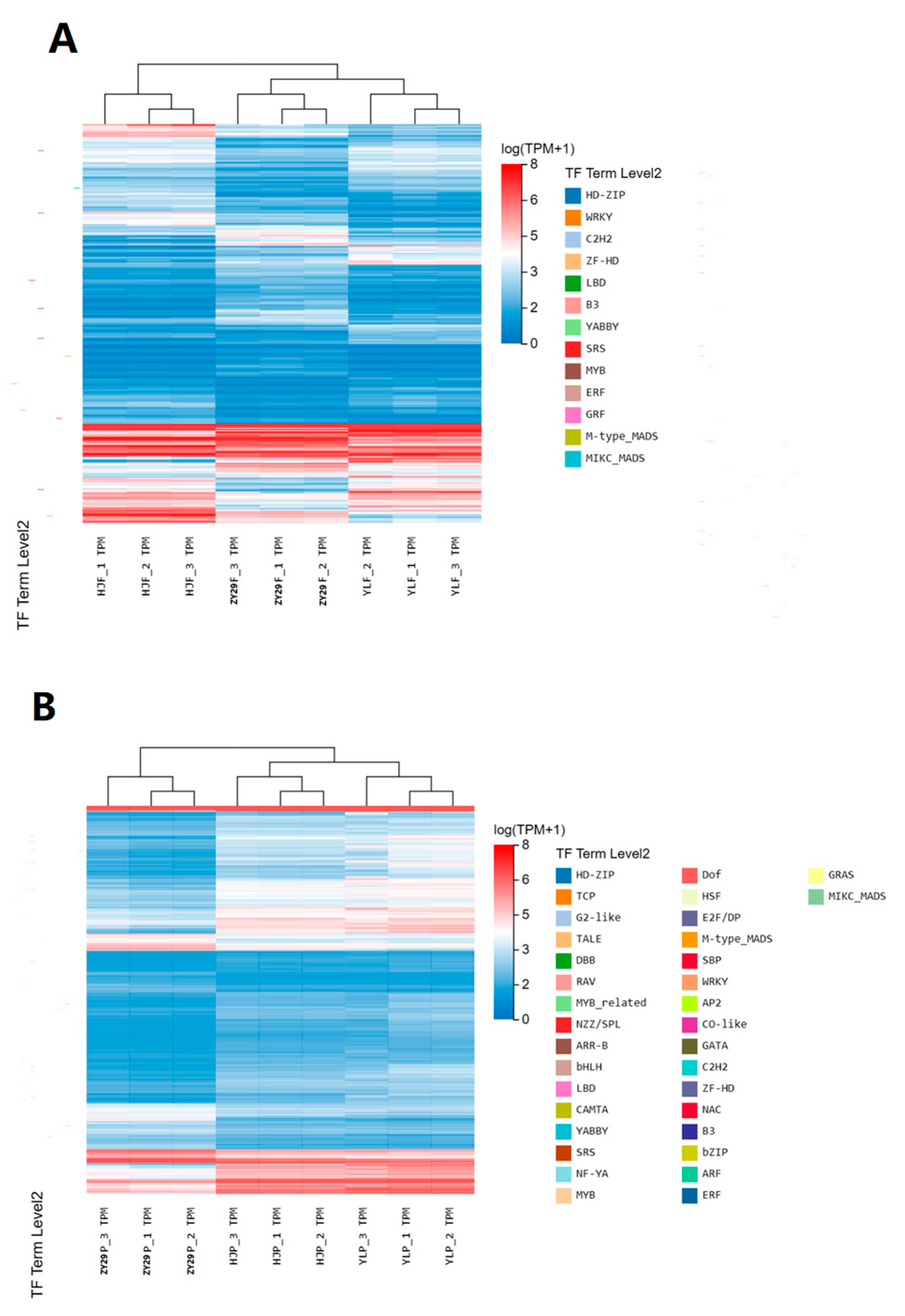
2.4. RNA-Seq Transcriptome Sequencing
2.5. Integration Analysis of the Metabolite and Transcriptome
2.6. qRT–PCR
3. Results
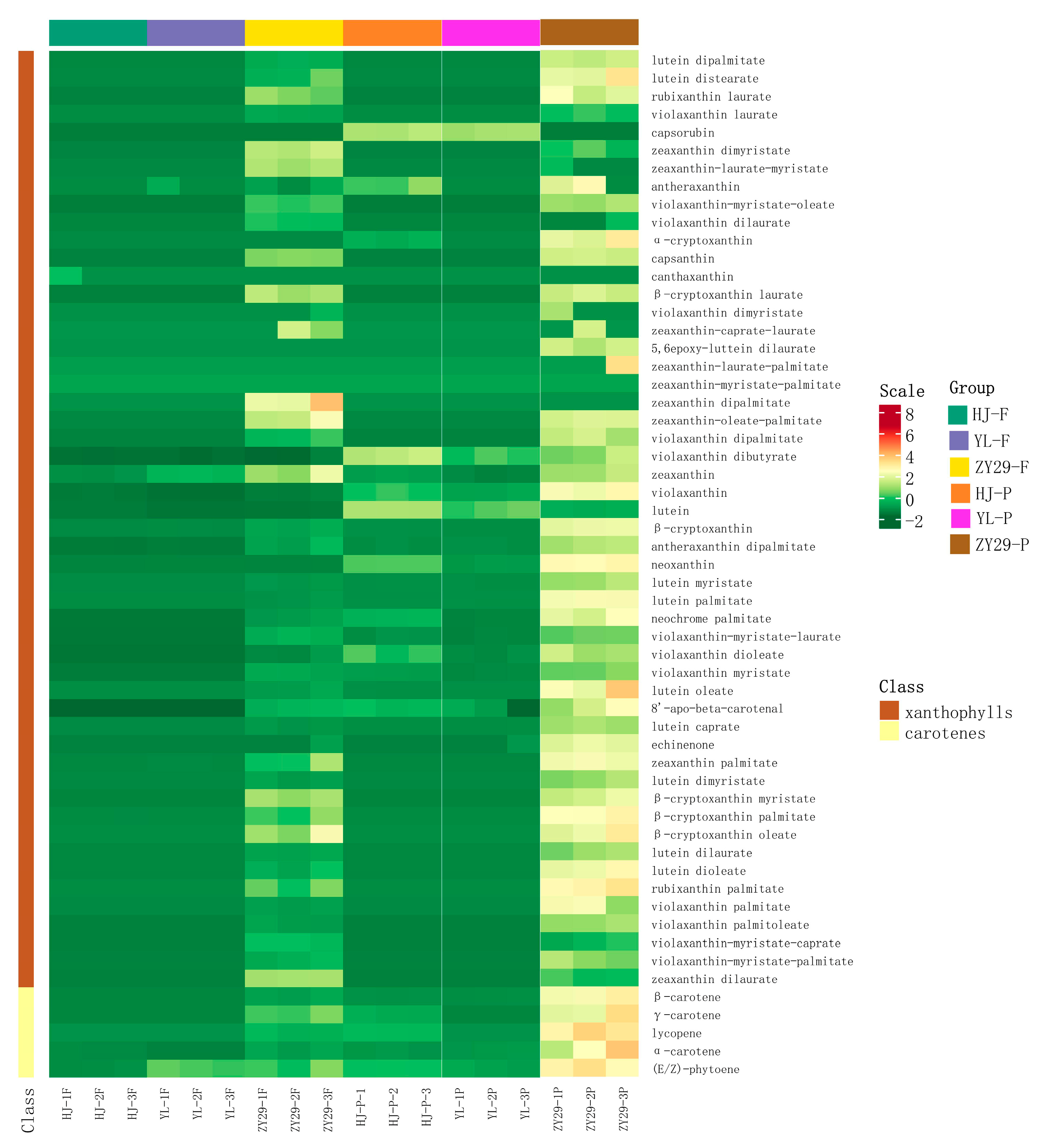
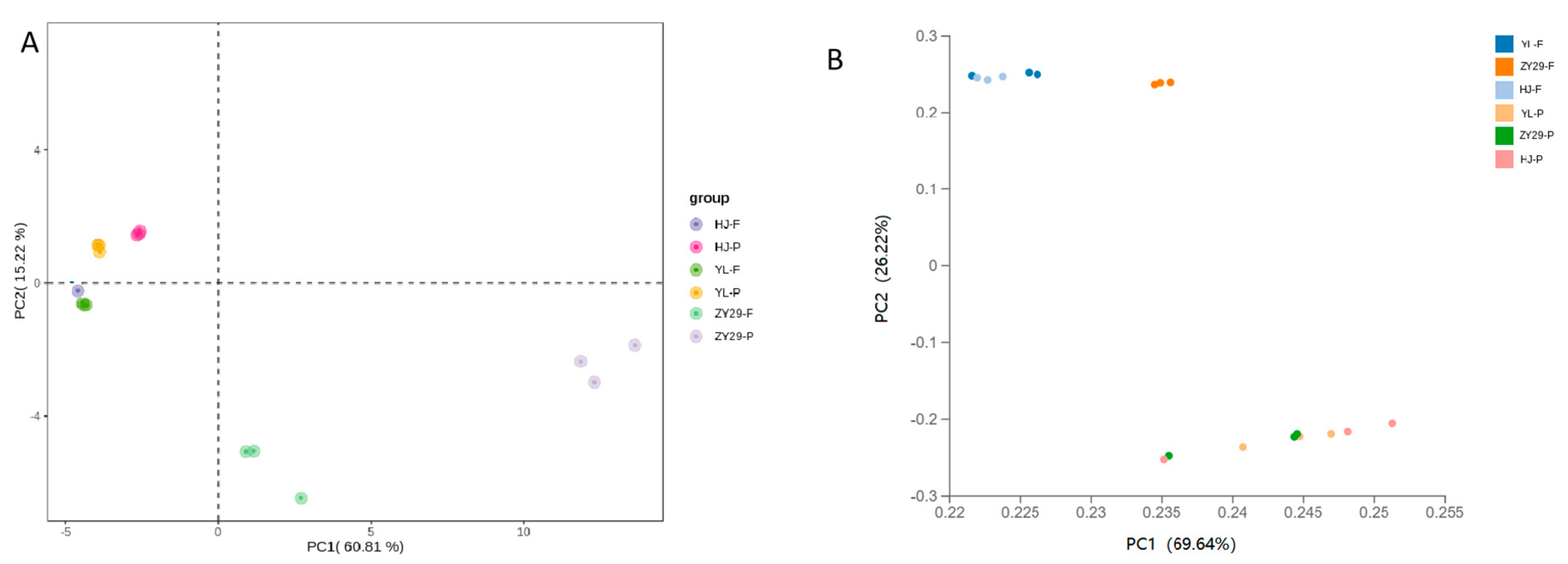
3.1. Transcriptome and Metabolome Analysis of Peach
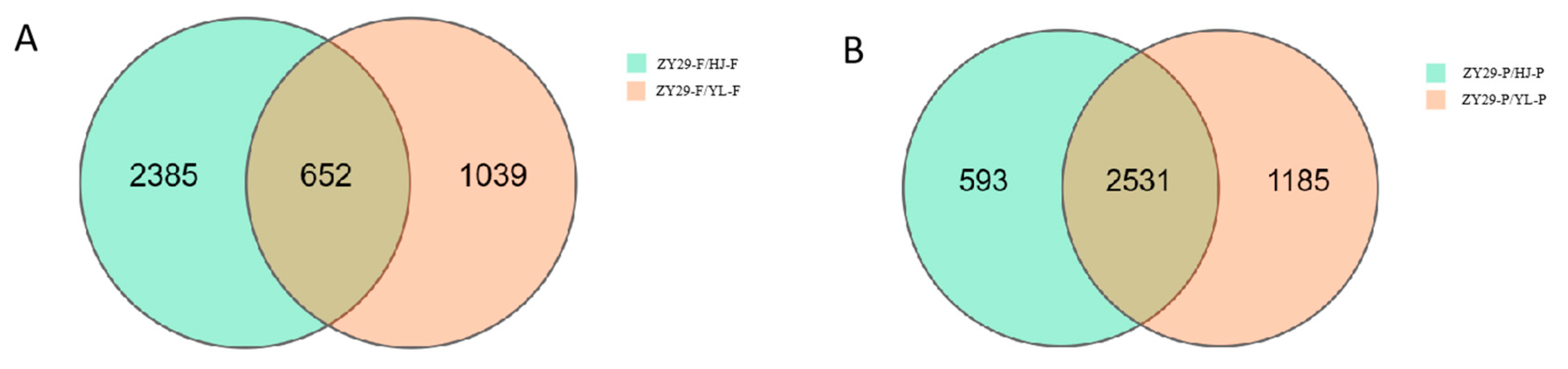
3.2. Identification of Differentially Expressed Unigenes
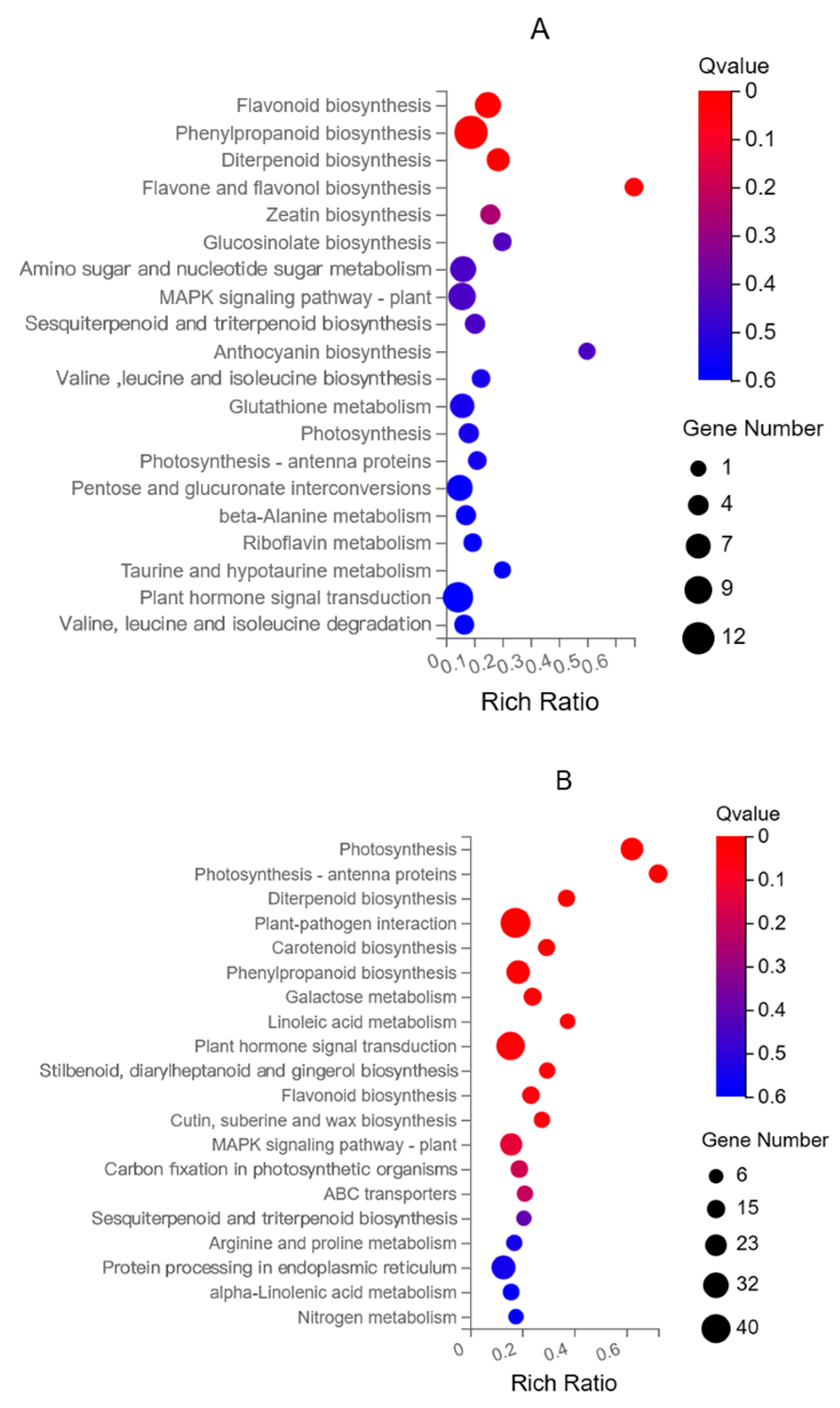
3.3. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of DEGs
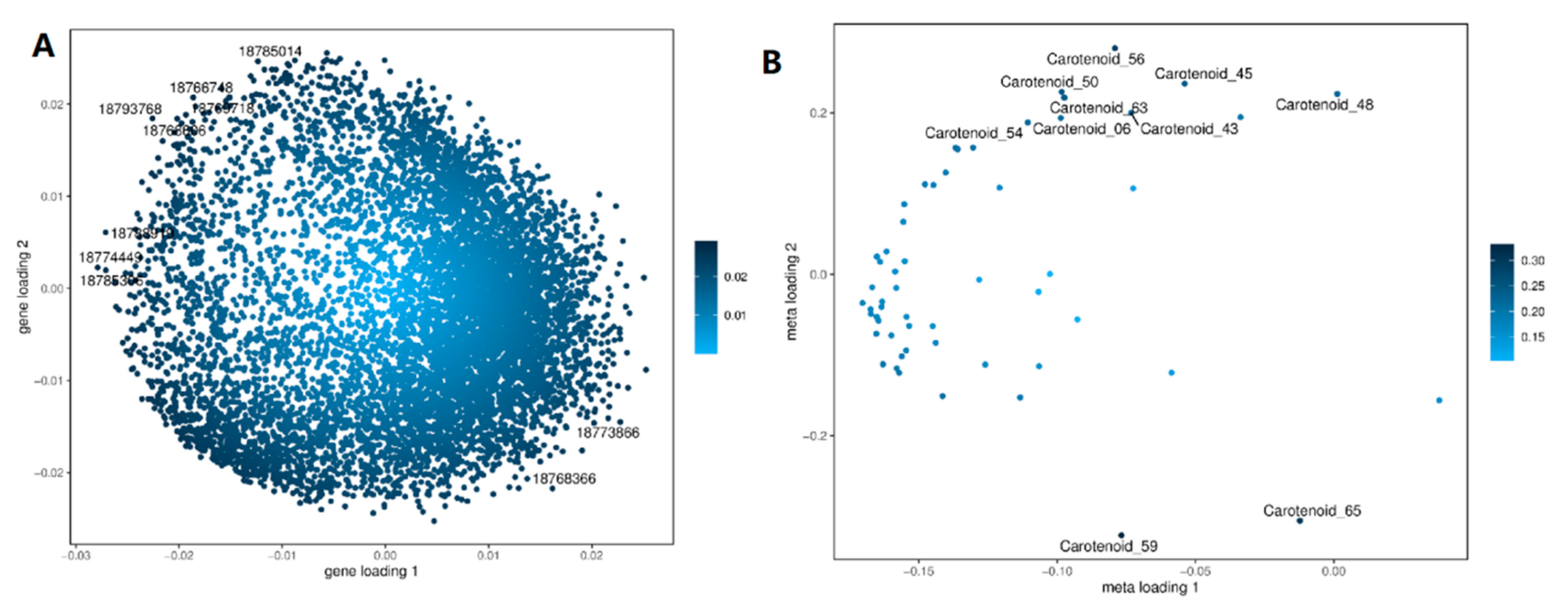
3.4. The Transcriptome and Metabolome Were Combined to Analyze the Metabolic Pathways Related to Peach Carotenoid
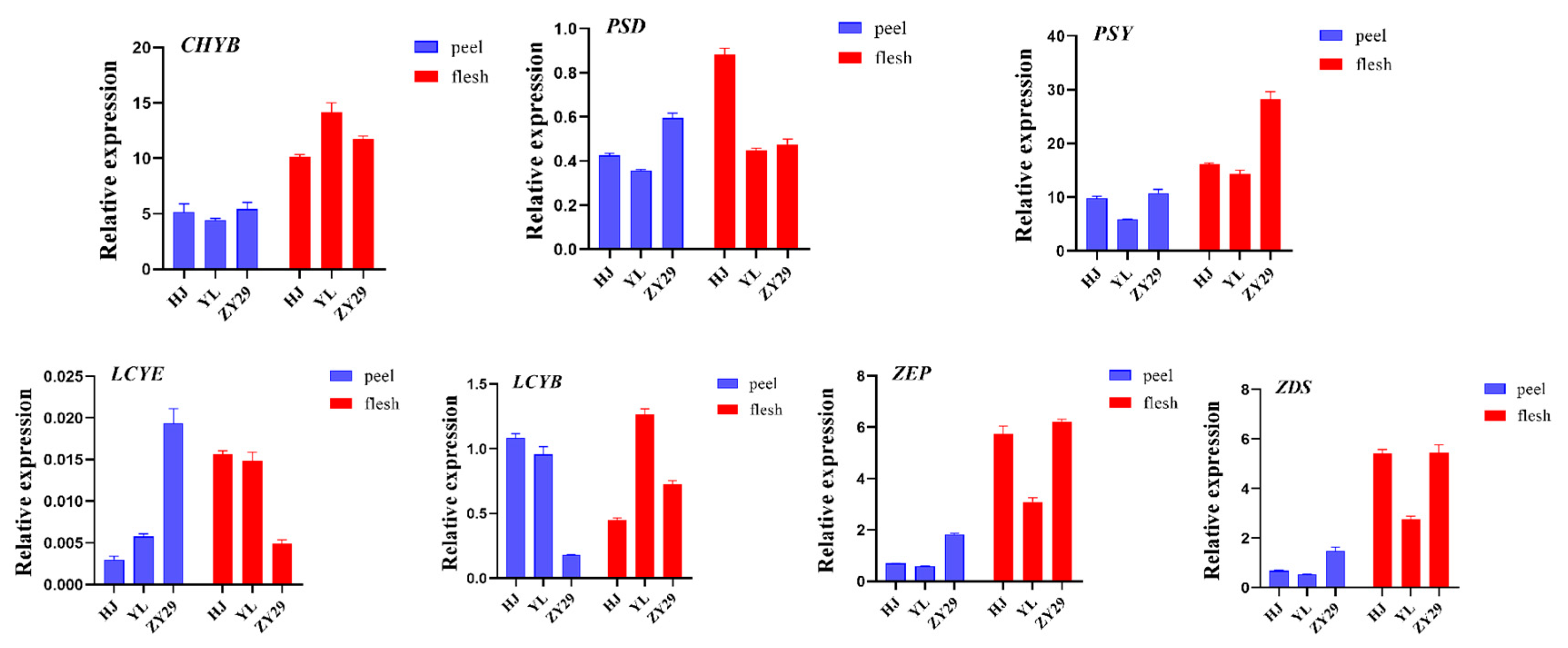
3.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gil, M.I.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant capacities, phenolic compounds, carotenoids, and vitamin C contents of nectarine, peach, and plum cultivars from California. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4976–4982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reig, G.; Iglesias, I.; Gatius, F.; Alegre, S. Antioxidant capacity, quality, and anthocyanin and nutrient contents of several peach cultivars [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] grown in Spain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6344–6357. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Cao, K.; Fang, W.; Zhu, G.; Chen, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Evaluation of phenolic components (anthocyanins, flavanols, phenolic acids, and flavonols) and their antioxidant properties of peach fruits. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 268, 109365. [Google Scholar]
- Auldridge, M.E.; McCarty, D.R.; Klee, H.J. Plant carotenoid cleavage oxygenases and their apocarotenoid products. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simkin, A.J.; Kapoor, L.; Doss, C.G.P.; Hofmann, T.A.; Lawson, T.; Ramamoorthy, S. The role of photosynthesis related pigments in light harvesting, photoprotection and enhancement of photosynthetic yield in planta. Photosynth. Res. 2022, 152, 23–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, N.; Alok, A.; Kumar, P.; Kaur, N.; Awasthi, P.; Chaturvedi, S.; Pandey, P.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Tiwari, S. CRISPR/Cas9 directed editing of lycopene epsilon-cyclase modulates metabolic flux for β-carotene biosynthesis in banana fruit. Metab. Eng. 2020, 59, 76–86. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, J.; Nageswaran, D.; Li, L. Carotenoid metabolism and regulation in horticultural crops. Hortic. Res. 2015, 2, 15036. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, M.; Yamano, Y.; Tode, C.; Wada, A. Carotenoid synthesis: Retrospect and recent progress. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 483, 224–228. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, P.D.; Enfissi, E.M.; Bramley, P.M. Genetic engineering of carotenoid formation in tomato fruit and the potential application of systems and synthetic biology approaches. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 483, 196–204. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Han, S.; Huo, Y.; Ma, G.; Sun, Z.; Li, H.; Hou, S.; Han, Y. Comparative metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals a coexpression network of the carotenoid metabolism pathway in the panicle of Setaria italica. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Al-Babili, S. Exploring the Diversity and Regulation of Apocarotenoid Metabolic Pathways in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 787049. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Lin, J.; Lin, H.; Hao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y. Dynamic change of the carotenoid metabolic pathway profile during oolong tea processing with supplementary LED light. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112839. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.H.; Akram, A.; Saeed, M.; ur Rahman, M.; ur Rehman, A.; Mansoor, S.; Amin, I. Establishment of Transcriptional Gene Silencing Targeting the Promoter Regions of GFP, PDS, and PSY Genes in Cotton using Virus-Induced Gene Silencing. Mol. Biotechnol. 2023, 65, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naing, A.H.; Song, H.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Lim, K.B.; Kim, C.K. Development of an efficient virus-induced gene silencing method in petunia using the pepper phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2019, 138, 507–515. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, K.; Du, Y.; Ren, Z.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Fu, J.; Ren, D.; et al. Mutations in the maize zeta-carotene desaturase gene lead to viviparous kernel. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174270. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Gao, Z. Characterization and Primary Functional Analysis of a Bamboo ZEP Gene from Phyllostachys edulis. DNA Cell Biol. 2017, 36, 747–758. [Google Scholar]
- Ronen, G.; Carmel-Goren, L.; Zamir, D.; Hirschberg, J. An alternative pathway to ε-carotene formation in plant chromoplasts discovered by map-based cloning of Beta and old-gold color mutations in tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Liang, M.; Shi, L.; Shao, J.; Song, C.; Bian, K.; Chen, W.; Yang, Z. Accumulation of carotenoids and expression of carotenogenic genes in peach fruit. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Fraser, P.D.; Enfissi, E.M.; Halket, J.M.; Truesdale, M.R.; Yu, D.; Gerrish, C.; Bramley, P.M. Manipulation of phytoene levels in tomato fruit: Effects on isoprenoids, plastids, and intermediary metabolism. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 3194–3211. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Gao, P.; Luan, F.; Liu, S. Identification and Characterization Roles of Phytoene Synthase (PSY) Genes in Watermelon Development. Genes 2022, 13, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, F.; Bar, E.; Mourgues, F.; Horváth, G.; Turcsi, E.; Giuliano, G.; Liverani, A.; Tartarini, S.; Lewinsohn, E.; Rosati, C. Study of ‘Redhaven’ peach and its white-fleshed mutant suggests a key role of CCD4 carotenoid dioxygenase in carotenoid and norisoprenoid volatile metabolism. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Falchi, R.; Vendramin, E.; Zanon, L.; Scalabrin, S.; Cipriani, G.; Verde, I.; Vizzotto, G.; Morgante, M. Three distinct mutational mechanisms acting on a single gene underpin the origin of yellow flesh in peach. Plant J. 2013, 76, 175–187. [Google Scholar]
- Phadungsawat, B.; Watanabe, K.; Mizuno, S.; Kanekatsu, M.; Suzuki, S. Expression of CCD4 gene involved in carotenoid degradation in yellow-flowered Petunia × hybrida. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 261, 108916. [Google Scholar]
- Adami, M.; De Franceschi, P.; Brandi, F.; Liverani, A.; Giovannini, D.; Rosati, C.; Dondini, L.; Tartarini, S. Identifying a carotenoid cleavage dioxygenase (ccd4) gene controlling yellow/white fruit flesh color of peach. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 2013, 31, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar]

| Sample Name | Raw Reads (M) | Clean Reads (M) | Clean Bases (M) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | Reads Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HJ-F-1 | 47.33 | 45.11 | 6.77 | 97.33 | 93.09 | 95.31 |
| HJ-F-2 | 47.33 | 44.81 | 6.72 | 97.37 | 93.19 | 94.67 |
| HJ-F-3 | 47.33 | 44.79 | 6.72 | 97.29 | 93.05 | 94.64 |
| HJ-P-1 | 47.19 | 45.07 | 6.76 | 97.22 | 91.47 | 95.51 |
| HJ-P-2 | 47.19 | 45.02 | 6.75 | 97.12 | 91.15 | 95.41 |
| HJ-P-3 | 45.44 | 43.83 | 6.57 | 97.28 | 91.59 | 96.46 |
| YL-F-1 | 47.19 | 45.12 | 6.77 | 97.2 | 91.41 | 95.61 |
| YL-F-2 | 47.19 | 45.12 | 6.77 | 97.23 | 91.46 | 95.63 |
| YL-F-3 | 47.19 | 44.66 | 6.7 | 97.27 | 91.57 | 94.64 |
| YL-P-1 | 44.06 | 42.71 | 6.41 | 95.03 | 89.03 | 96.93 |
| YL-P-2 | 47.33 | 45.43 | 6.81 | 94.94 | 88.82 | 96 |
| YL-P-3 | 43.9 | 42.11 | 6.32 | 94.56 | 88.01 | 95.91 |
| ZY29-F-1 | 47.19 | 45.32 | 6.8 | 97.19 | 91.34 | 96.04 |
| ZY29-F-2 | 47.19 | 45.33 | 6.8 | 97.22 | 91.42 | 96.06 |
| ZY29-F-3 | 47.19 | 45.07 | 6.76 | 97.19 | 91.37 | 95.51 |
| ZY29-P-1 | 47.33 | 45.49 | 6.82 | 94.91 | 88.78 | 96.12 |
| ZY29-P-2 | 47.33 | 45.3 | 6.8 | 95.06 | 89.06 | 95.72 |
| ZY29-P-3 | 44.97 | 43.01 | 6.45 | 95.03 | 89.03 | 95.64 |
| Sum | 839.87 | 803.3 | 120.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Jing, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W. Identification and Quantification of Carotenoids in White and Yellow-Fleshed Peaches (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) by QTRAP+ LC-MS/MS. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040376
Guo Y, Jing Y, Wang Q, Zhang W. Identification and Quantification of Carotenoids in White and Yellow-Fleshed Peaches (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) by QTRAP+ LC-MS/MS. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(4):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040376
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yanfei, Yonglin Jing, Qinghao Wang, and Wangshu Zhang. 2025. "Identification and Quantification of Carotenoids in White and Yellow-Fleshed Peaches (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) by QTRAP+ LC-MS/MS" Horticulturae 11, no. 4: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040376
APA StyleGuo, Y., Jing, Y., Wang, Q., & Zhang, W. (2025). Identification and Quantification of Carotenoids in White and Yellow-Fleshed Peaches (Prunus persica (L.) Batsch) by QTRAP+ LC-MS/MS. Horticulturae, 11(4), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040376






