Managing the Microbiome on the Surface of Tomato Fruit by Treatment of Tomato Plants with Non-Thermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma During Cultivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Cultivation and Experimental Protocol
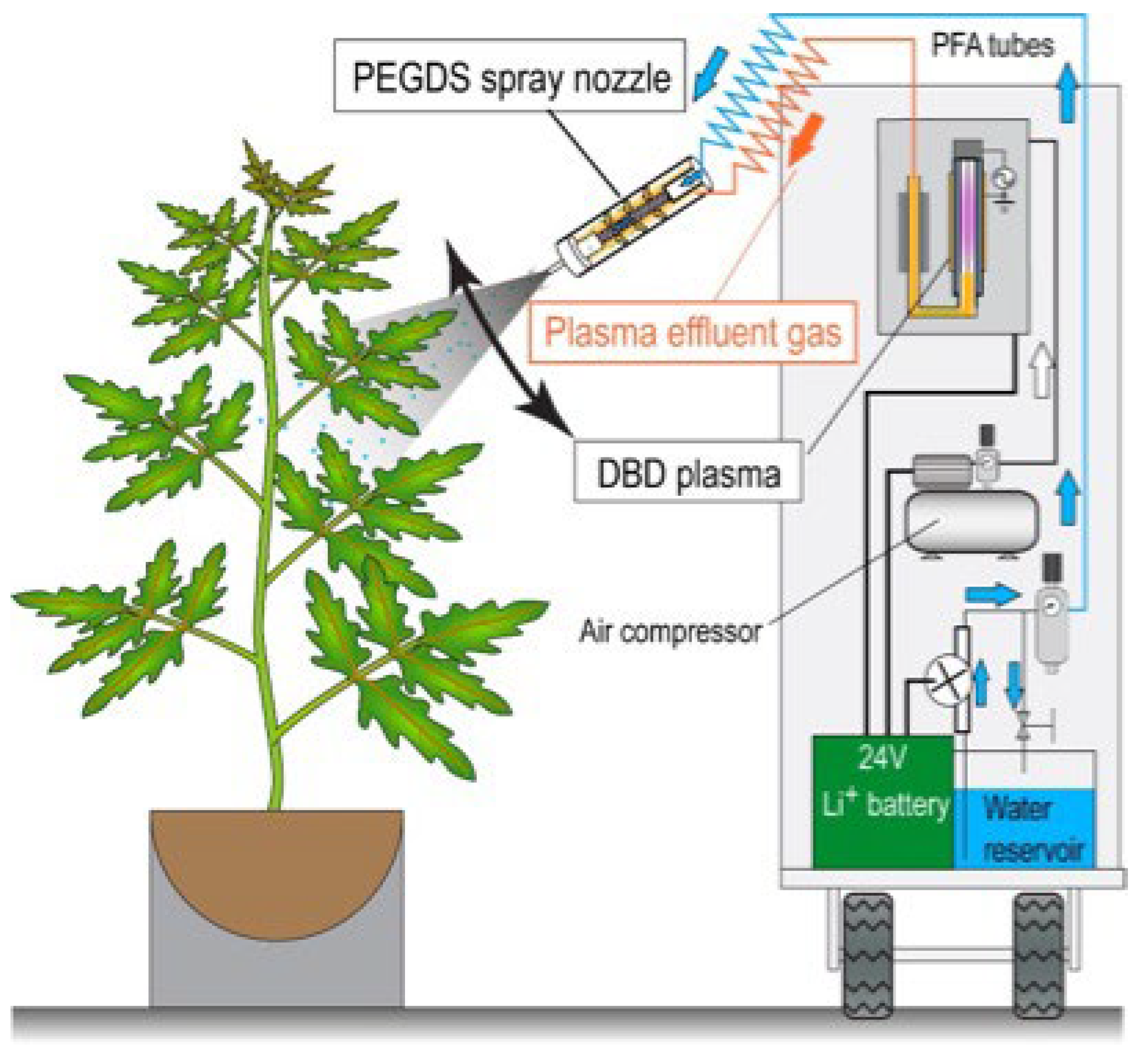
2.2. Plasma Treatment
2.3. Analysis of Plant Growth
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Analysis of the Microbial Community on the Surface of Tomato Fruits
3. Results
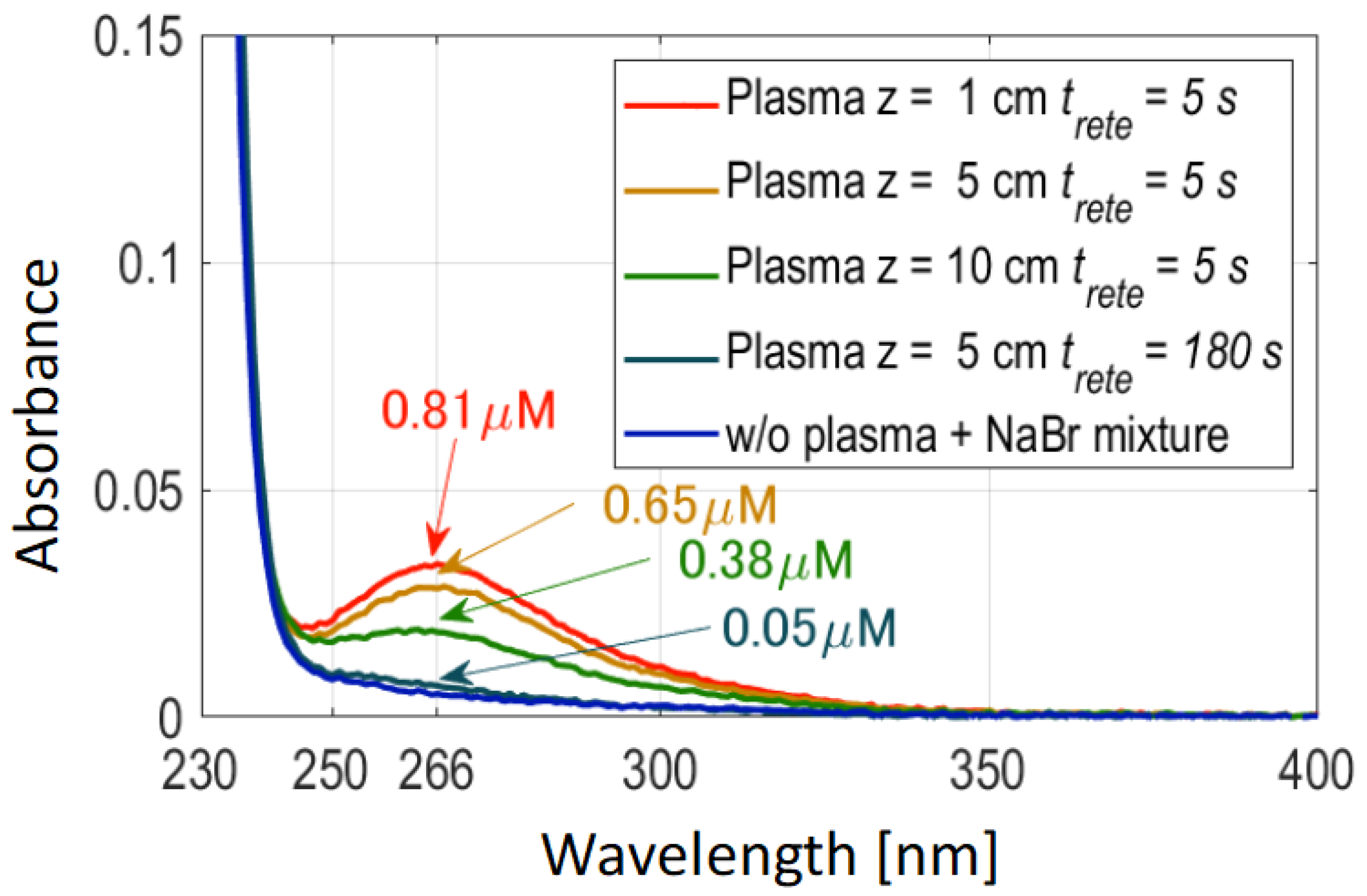
3.1. Analysis of Air Plasma Effluent Gas and Liquid-Phase O3
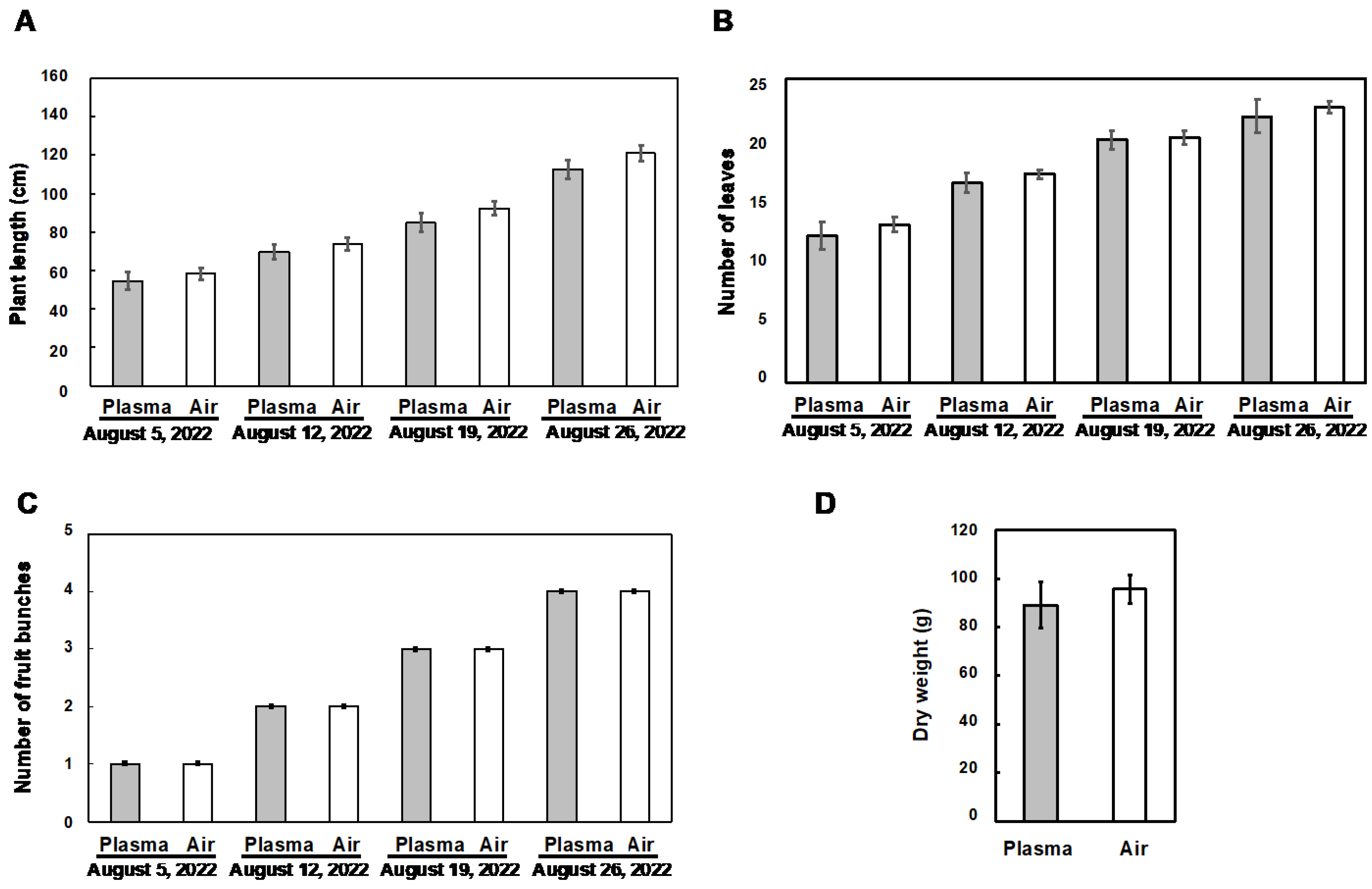
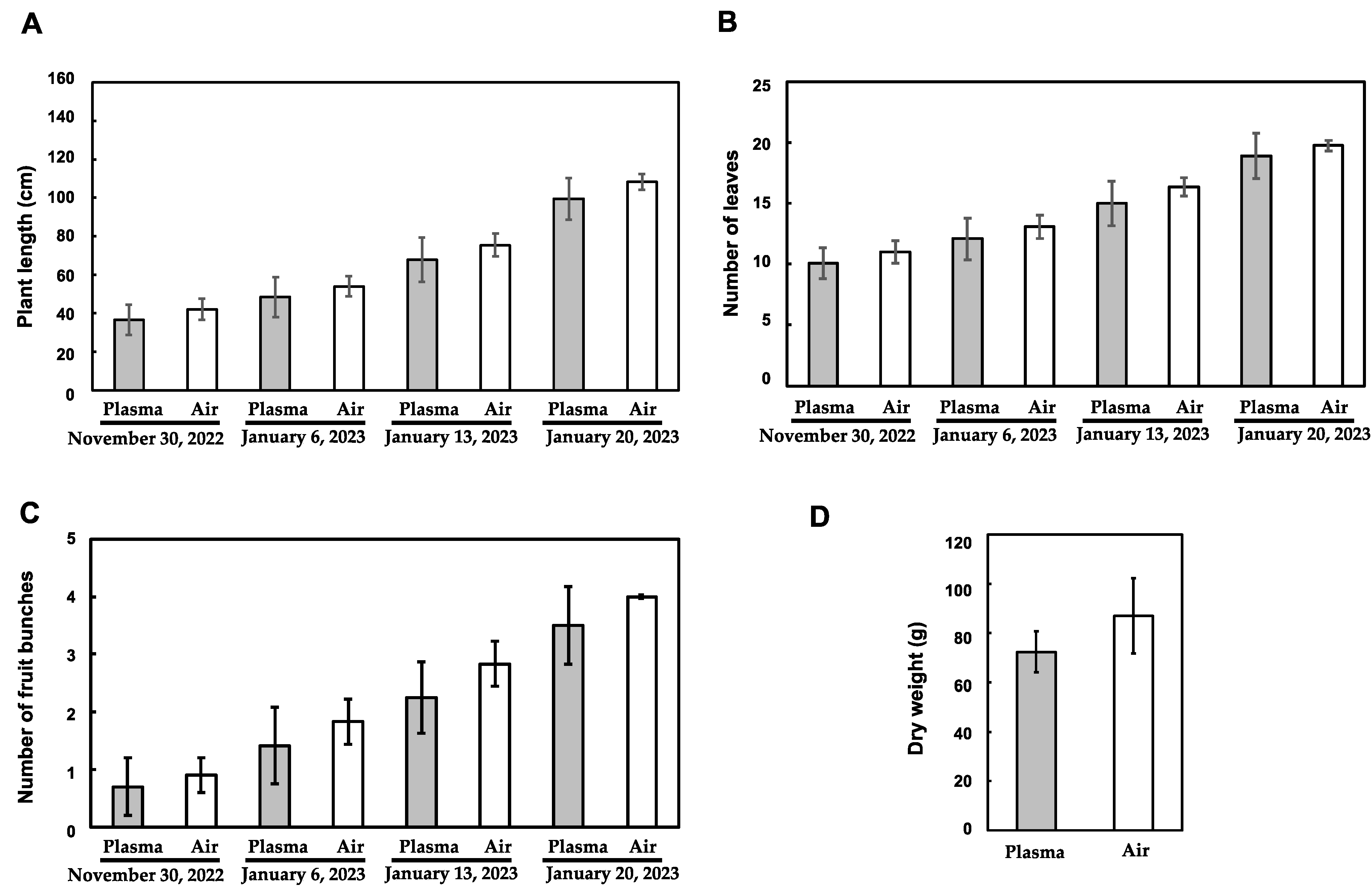
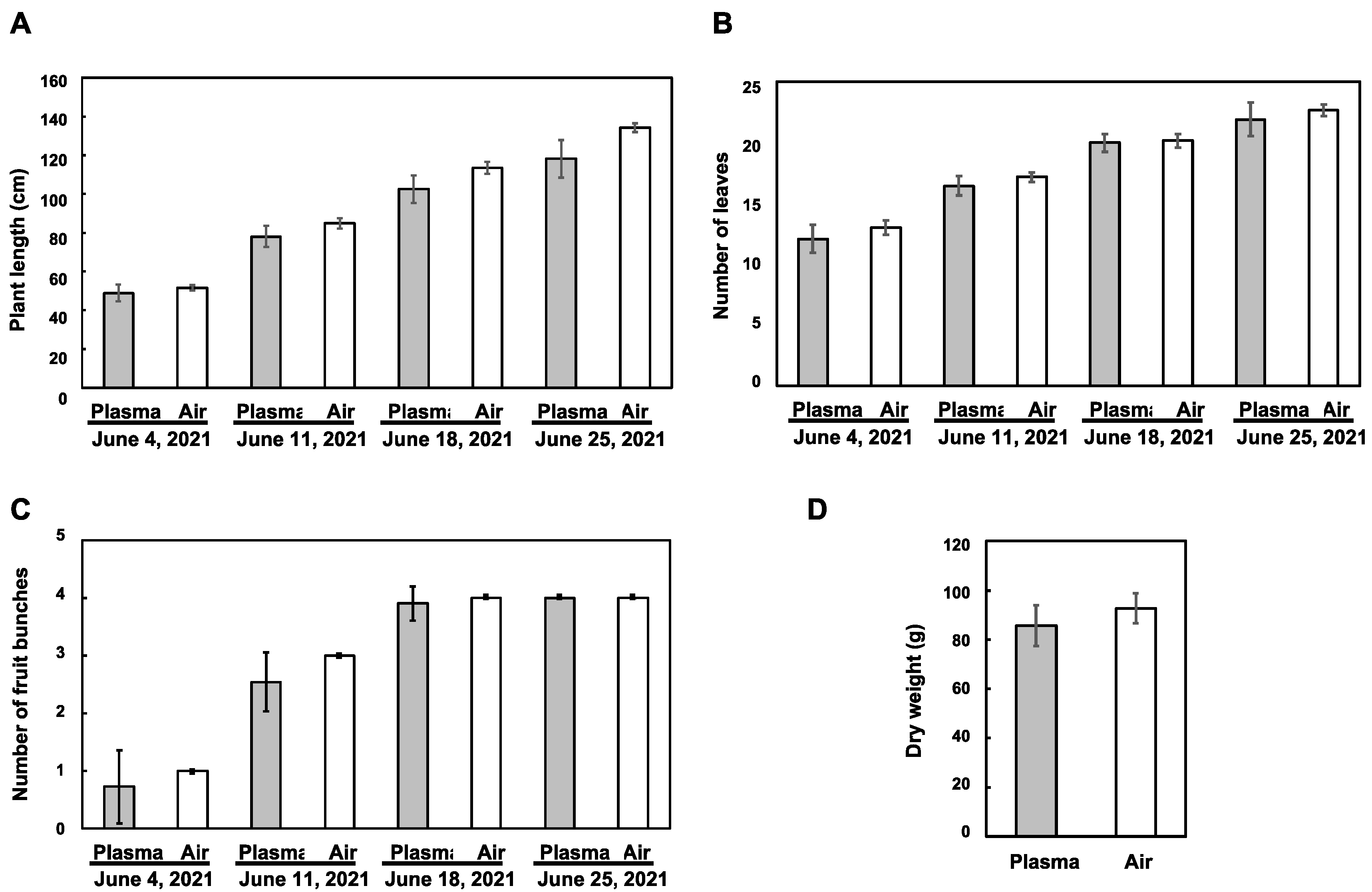
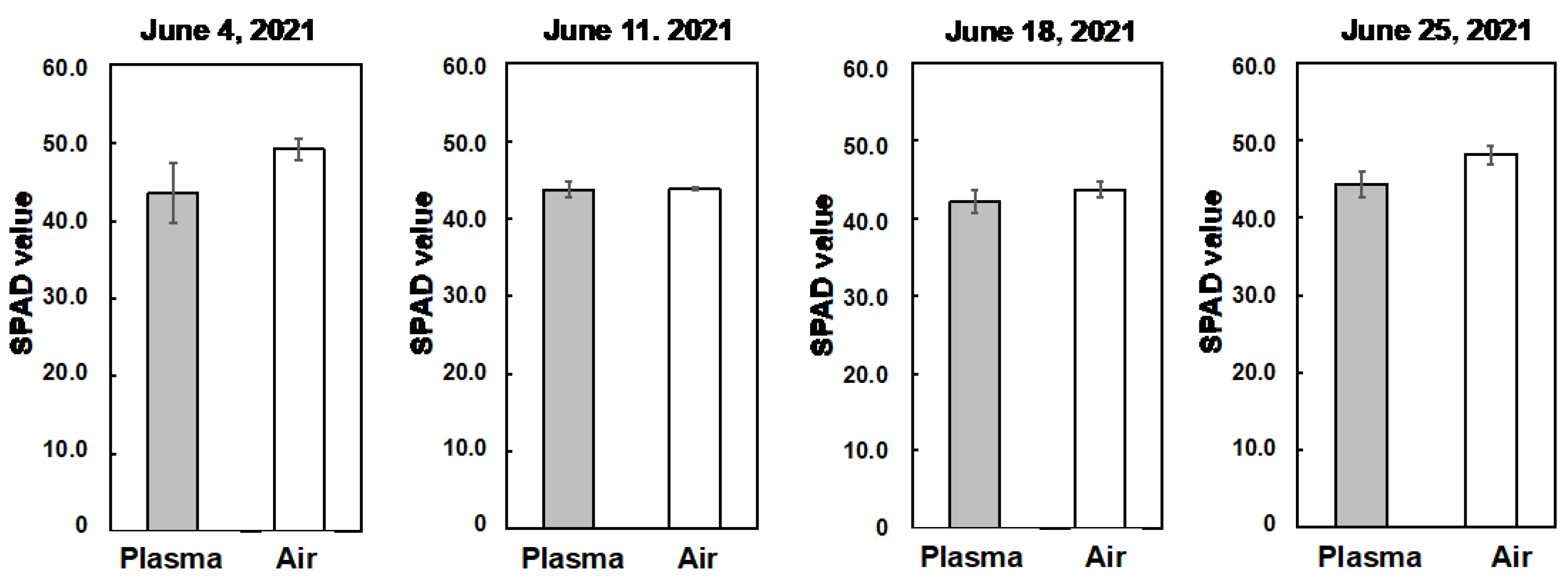
3.2. Influence of the Plasma Treatment on the Vegetative Growth of Tomato Plants
3.3. Influence of the Plasma Treatment on the Reproductive Growth of Tomato Plants
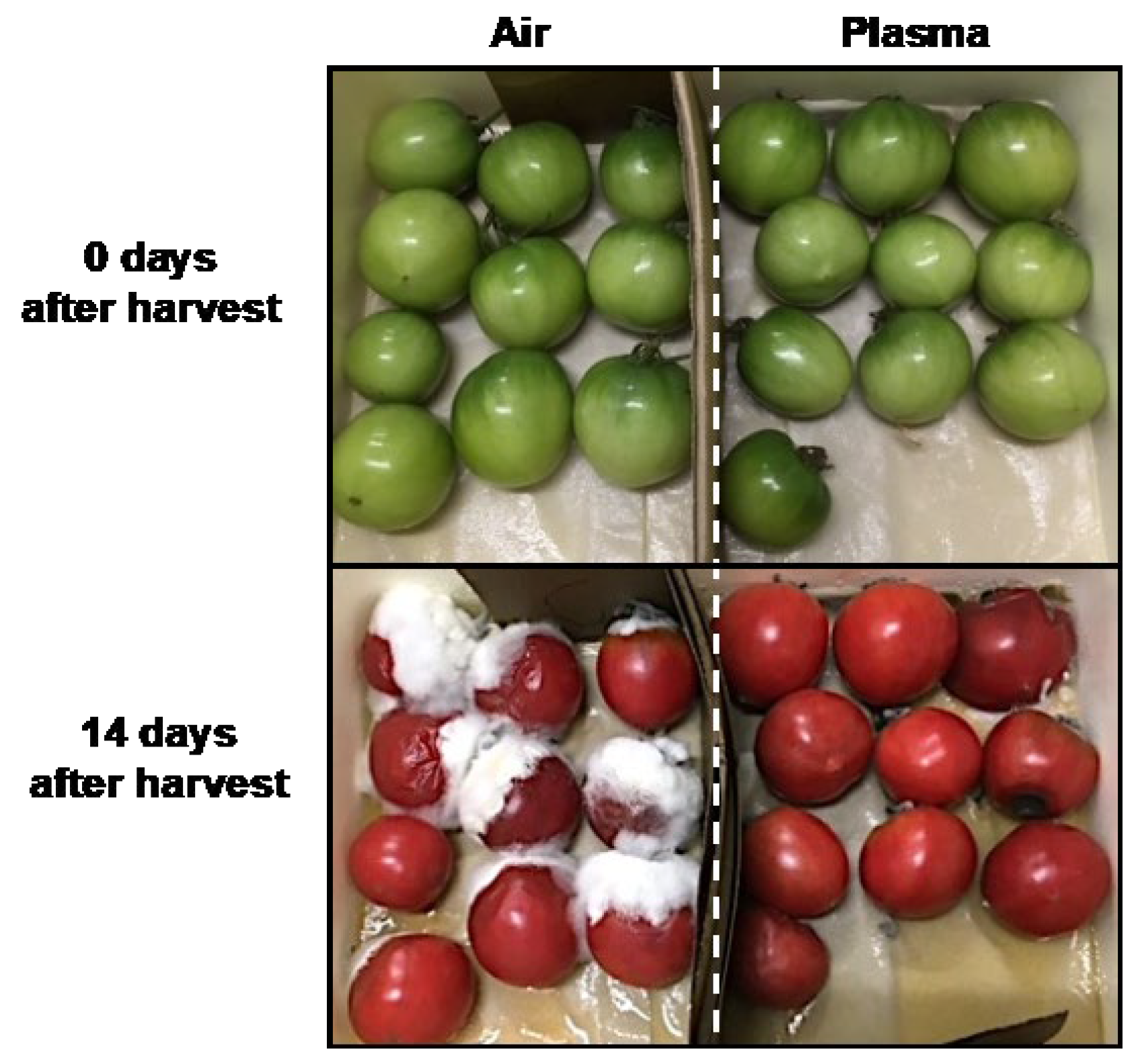
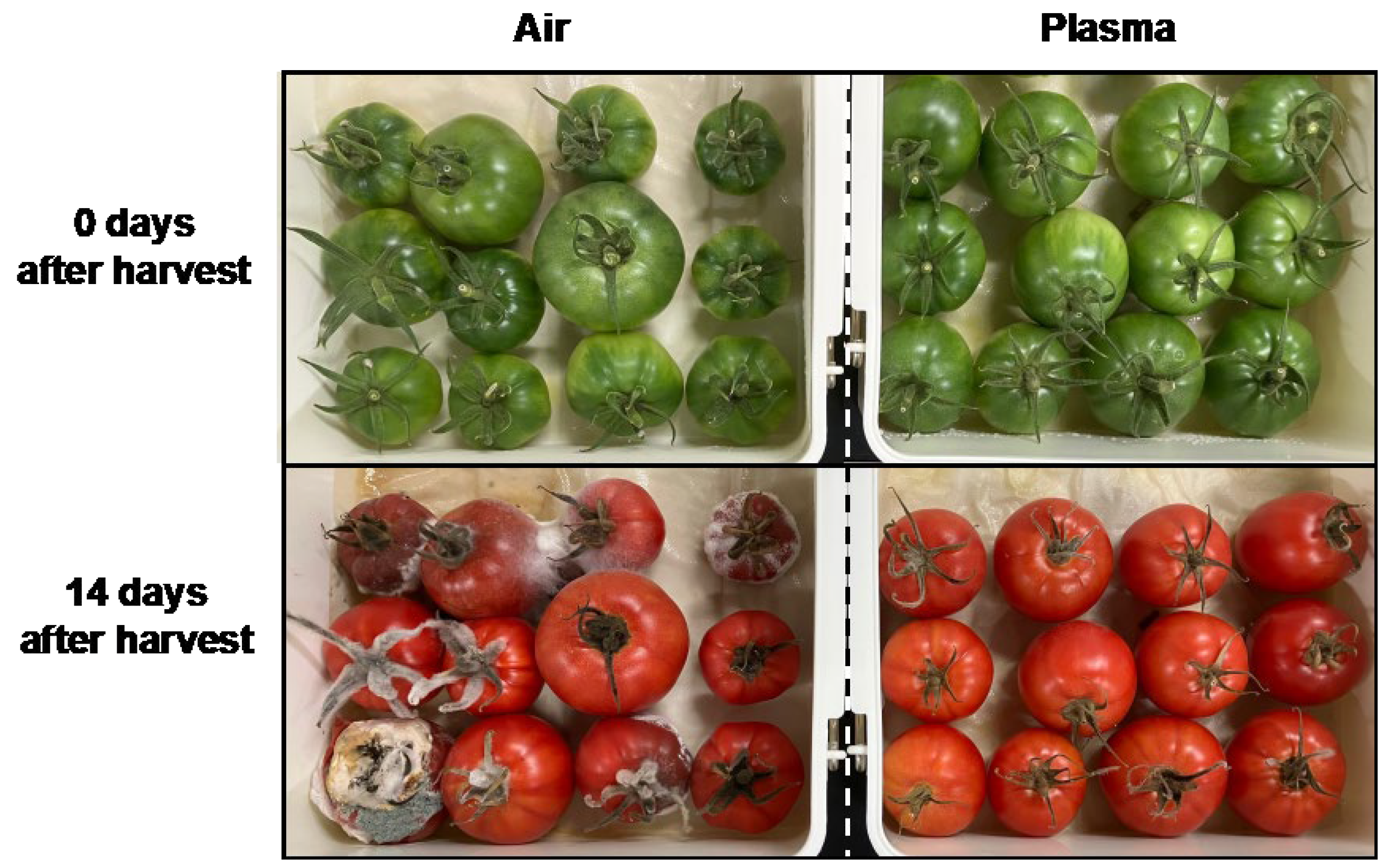
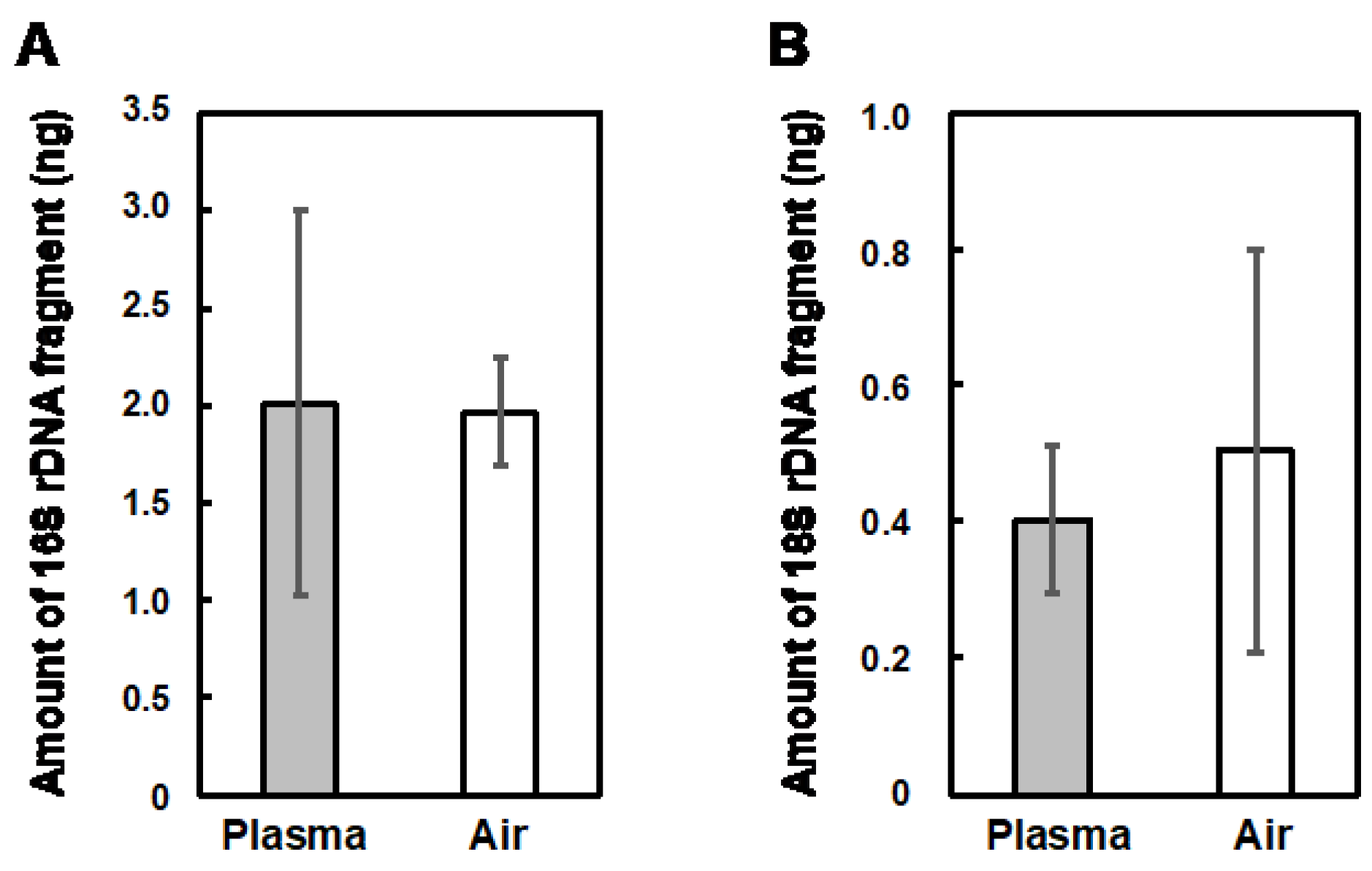
3.4. Influence of the Plasma Treatment on the Preservation Status of Tomato Fruits and on the Microbiome on the Surface of Tomato Fruits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Primer Name (1) | Nucleotide Sequence (2) |
|---|---|
| 515F | ACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGTGCCAGCMGCCGCGGTAA |
| 806R | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTGGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT |
| ITS1F_KYO1 | ACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTCTHGGTCATTTAGAGGAASTAA |
| ITS2_KYO2 | GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTTTYRCTRCGTTCTTCATC |
| 2ndF | AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACAC-Index2-ACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGC |
| 2ndR | CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGAT-Index1-GTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTG |
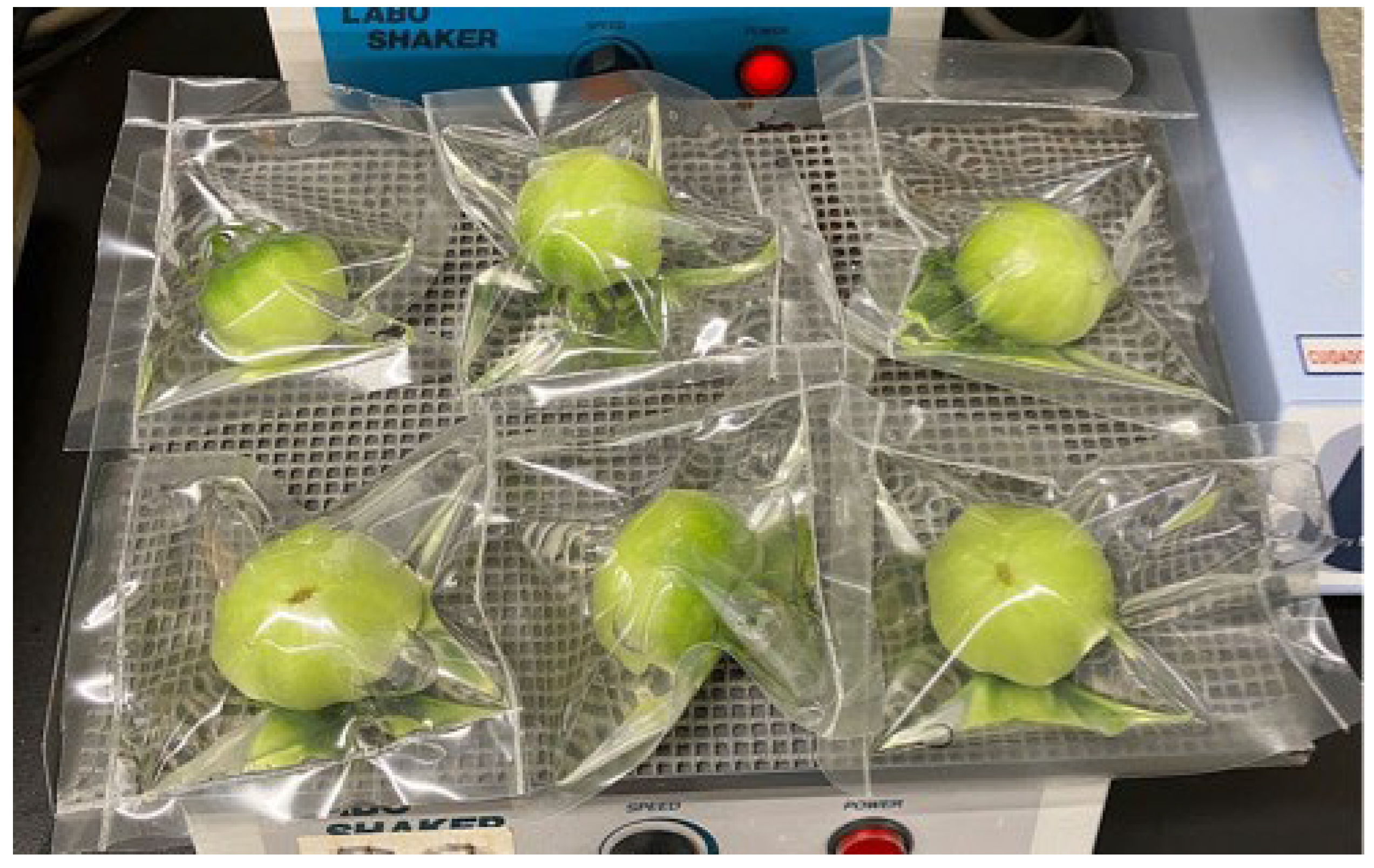


Appendix B
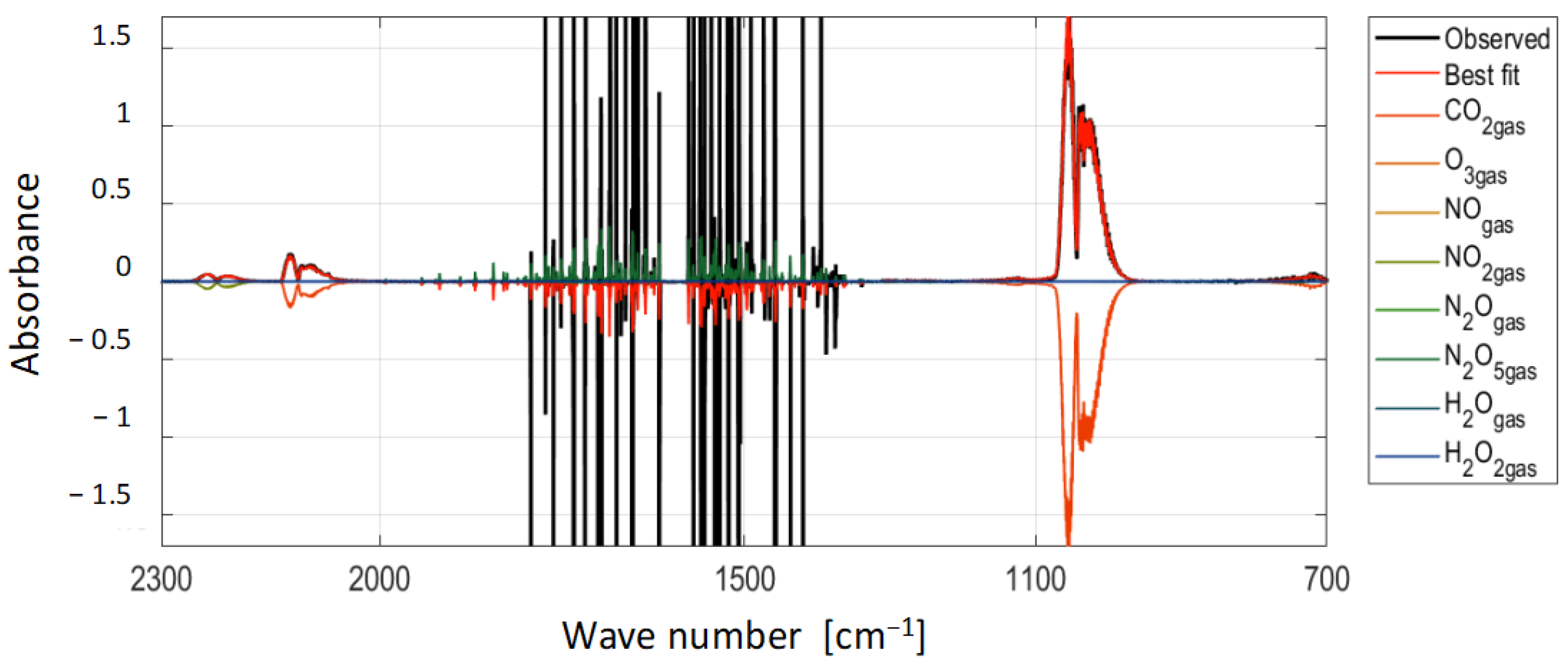
| Species | Densities [cm−3] | LOD [cm−3] |
|---|---|---|
| O3 | 1.9 × 1016 | 1 × 1014 |
| NO | <LOD | 4 × 1014 |
| NO2 | <LOD | 4 × 1013 |
| N2O | 1.6 × 1014 | 4 × 1013 |
| N2O5 | <LOD | 2 × 1013 |
| HNO3 | <LOD | 4 × 1013 |
| H2O2 | <LOD | 2 × 1014 |




References
- Min, S.C.; Roh, S.H.; Niemira, B.A.; Boyd, G.; Sites, J.E.; Fan, X.; Sokorai, K.; Jin, T.Z. In-package atmospheric cold plasma treatment of bulk grape tomatoes for microbiological safety and preservation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Park, G. The effects of plasma on plant growth, development, and sustainability. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskow, A.; Howling, A.; Furno, I. Mechanisms of plasma-seed treatments as a potential seed processing technology. Front. Phys. 2021, 9, 617345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, N.; Ji, H.; Zhang, X.; Dong, C.; Yu, J.; Yan, S.; Chen, C.; Liang, L. Effects of atmospheric cold plasma treatment on the storage quality and chlorophyll metabolism of postharvest tomato. Foods 2022, 11, 4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, M.; Attolico, G.; Capozzi, V.; Cozzolino, R.; Corvino, A.; de Chiara, M.L.V.; Pace, B.; Pelosi, S.; Ricci, I.; Romaniello, R.; et al. Emerging postharvest technologies to enhance the shelf-life of fruit and vegetables: An overview. Foods 2022, 11, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, T.; Takashima, K.; Sasaki, S. Integrated transport model for controlled delivery of short-lived reactive species via plasma-activated liquid with practical applications in plant disease control. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process 2024, 44, 1165–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrin, D.; Magureanu, M.; Mandache, N.B.; Ionita, M. The effect of non-thermal plasma treatment on wheat germination and early growth. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 29, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivachandiran, L.; Khacef, A. Enhanced seed germination and plant growth by atmospheric pressure cold air plasma: Combined effect of seed and water treatment. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, R.; Yan, J. Study on activation and improvement of crop seeds by the application of plasma treating seeds equipment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 655, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Honnorat, B.; Yang, H.; Arancibia, J.; Rajjou, L.; Rousseau, A. Non-thermal DBD plasma array on seed germination of different plant species. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 025401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Ghimire, B.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Cold atmospheric plasma-activated water irrigation induces defense hormone and gene expression in tomato seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Koga, K.; Okumura, T.; Shiratani, M. Impact of atmospheric pressure plasma treated seeds on germination, morphology, gene expression and biochemical responses. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 60, 040502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.P.; Davis, K.; Gilani, S.; Alonzo, C.-A.; Dobrynin, D.; Friedman, G.; Fridman, A.; Rabinovich, A.; Fridman, G. Reactive nitrogen species produced in water by non-equilibrium plasma increase plant growth rate and nutritional yield. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2013, 13, S19–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, A.; Byrns, B.; King, W.; Andhvarapou, A.; Fields, J.; Knappe, D.; Fonteno, W.; Shannon, S. Fertilization of radishes, tomatoes, and marigolds using a large-volume atmospheric glow discharge. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process 2014, 34, 1271–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichiansan, V.; Chatmaniwat, K.; Sungkorn, M.; Leksakul, K.; Chaopaisarn, P.; Boonyawan, D. Effect of plasma-activated water generated using plasma jet on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L. var. cerasiforme) seedling growth. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Wang, G.; Tian, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Fang, J. Non-thermal plasma-activated water inactivation of food-borne pathogen on fresh produce. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisani, M.; Berardinelli, A.; Cevoli, C.; Cecchini, M.; Ragni, L.; Pasquali, F. Effects of sanitizing treatments with atmospheric cold plasma, SDS and lactic acid on verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes in red chicory (radicchio). Food Cont. 2017, 78, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaraj, C.; Jaiganesh, V.; Akshay Kumar, H.M.; Biswas, M.K. Harnessing cold plasma: An innovative strategy for managing postharvest fungal infections in plants. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 2024, 24, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, A.; Konishi, H.; Ando, S.; Sato, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Tsushima, S.; Yoshida, S.; Morikawa, T.; Kaneko, T.; Takahashi, H. Management of bakanae and bacterial seedling blight diseases in nurseries by irradiating rice seeds with atmospheric plasma. Plant Pathol. 2017, 66, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Yagyu, Y.; Yonesu, A.; Shiratani, M. Sterilization characteristics of the surfaces of agricultural products using active oxygen species generated by atmospheric plasma and UV light. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 605FR03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, N.; Patil, S.; Moiseev, T.; Bourke, P.; Mosnier, J.; Keener, K.; Cullen, P. In-package atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment of strawberries. J. Food Eng. 2015, 161, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazzina, I.; Tappi, S.; Rocculi, P.; Sacchetti, G.; Berardinelli, A.; Marseglia, A.; Rizzi, F. Effect of cold plasma treatment on the functional properties of fresh-cut apples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8010–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Cui, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z. Potential use of atmospheric cold plasma for postharvest preservation of blueberries. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 179, 111564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limnaios, A.; Pathak, N.; Bovi, G.G.; Fröhling, A.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Taoukis, P.S.; Schlüter, O. Effect of cold atmospheric pressure plasma processing on quality and shelf life of red currants. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, T.; Cong, K.; Suo, A.; Wu, C. Influence of cold plasma on quality attributes and aroma compounds in fresh-cut cantaloupe during low temperature storage. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 154, 112893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinxin, L.; Can, Z.; Menglu, H.; Cui, S.; Jinping, C.; Jingyu, W.; Huang, L. Effect of cold atmospheric plasma on the gray mold rot of postharvest mulberry fruit. Food Cont. 2022, 137, 108906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ran, C.; Geng, W.; Han, L.; Ostrikov, K.K. Temporal evolution characteristics of the excited species in a pulsed needle-water discharge: Effect of voltage and frequency. Plasma Process. Polym. 2023, 20, e2200134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, K.; Hu, Y.; Goto, T.; Sasaki, S.; Kaneko, T. Liquid spray transport of air–plasma-generated reactive species toward plant disease management. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 354004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Takashima, K.; Kimura, Y.; Nihei, K.; Konishi, H.; Kaneko, T. Humidification effect of air plasma effluent gas on suppressing conidium germination of a plant pathogenic fungus in the liquid phase. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 1900004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, K.; bin Ahmad Nor, A.S.; Ando, S.; Takahashi, H.; Kaneko, T. Evaluation of plant stress due to plasma-generated reactive oxygen and nitrogen species using electrolyte leakage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 60, 010504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. S1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toju, H.; Tanabe, A.S.; Yamamoto, S.; Sato, H. High-coverage ITS primers for the DNA-based identification of Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes in environmental samples. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugan, M.; Asnicar, F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable, and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Măgureanu, M.; Sîrbu, R.; Dobrin, D.; Gîdea, M. Stimulation of the germination and early growth of tomato seeds by non-thermal plasma. Plasma Chem. Plasma Proc. 2018, 38, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, J.; Dong, Y. Effect of cold plasma treatment on seedling growth and nutrient absorption of tomato. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 044007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappi, S.; Gozzi, G.; Vannini, L.; Berardinelli, A.; Romani, S.; Ragni, L.; Rocculi, P. Cold plasma treatment for fresh-cut melon stabilization. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Ponce, L.; Reyes, J.; Troncoso-Contreras, G.; Valenzuela-Tapia, G. Effect of low-pressure cold plasma (LPCP) on the wettability and the inactivation of Escherichia coli and Listeria innocua on fresh-cut apple (Granny Smith) skin. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Min, S.C. Moisture vaporization-combined helium dielectric barrier discharge-cold plasma treatment for microbial decontamination of onion flakes. Food Cont. 2018, 84, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srey, S.; Park, S.Y.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.-D. Reduction effect of the selected chemical and physical treatments to reduce L. monocytogenes biofilms formed on lettuce and cabbage. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, A.; Niemira, B.A.; Gurtler, J.B.; Fan, X.; Sites, X.J.; Boyd, G.; Chen, H. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of aerobic microorganisms on blueberries and effects on quality attributes. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, I.H.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, H.S.; Min, S.C. Microbial decontamination system combining antimicrobial solution washing and atmospheric dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma treatment for preservation of mandarins. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2020, 162, 111102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, A.; Ziuzina, D.; Boehm, D.; Bourke, P. Effects of cold plasma on wheat grain microbiome and antimicrobial efficacy against challenge pathogens and their resistance. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 335, e108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravlje, J.; Regvar, M.; Starič, P.; Mozetič, M.; Vogel-Mikuš, K. Cold plasma affects germination and fungal community structure of buckwheat seeds. Plants 2021, 10, e851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Duan, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, X.; Li, B.; Zhuang, J.; Feng, J.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z. Microbiota characterization of atmospheric cold plasma treated blueberries. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 180, 114720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Tong, M.; Yuan, S.; Liu, H. Responses of the microbial community structure in Fe(II)-bearing sediments to oxygenation: The role of reactive oxygen species. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2019, 3, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrios, L.; Rentsch, J.D. Linking reactive oxygen species (ROS) to abiotic and biotic feedbacks in plant microbiomes: The dose makes the poison. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, H.; Takashima, K.; Miyashita, S.; Sasaki, S.; Derib, A.A.; Kato, K.; Kanayama, Y.; Kaneko, T. Managing the Microbiome on the Surface of Tomato Fruit by Treatment of Tomato Plants with Non-Thermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma During Cultivation. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11030276
Takahashi H, Takashima K, Miyashita S, Sasaki S, Derib AA, Kato K, Kanayama Y, Kaneko T. Managing the Microbiome on the Surface of Tomato Fruit by Treatment of Tomato Plants with Non-Thermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma During Cultivation. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(3):276. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11030276
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Hideki, Keisuke Takashima, Shuhei Miyashita, Shota Sasaki, Abebe Alemu Derib, Kazuhisa Kato, Yoshinori Kanayama, and Toshiro Kaneko. 2025. "Managing the Microbiome on the Surface of Tomato Fruit by Treatment of Tomato Plants with Non-Thermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma During Cultivation" Horticulturae 11, no. 3: 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11030276
APA StyleTakahashi, H., Takashima, K., Miyashita, S., Sasaki, S., Derib, A. A., Kato, K., Kanayama, Y., & Kaneko, T. (2025). Managing the Microbiome on the Surface of Tomato Fruit by Treatment of Tomato Plants with Non-Thermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma During Cultivation. Horticulturae, 11(3), 276. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11030276






