Contrasting Responses of N2O Mitigation to Different Nitrification Inhibitors in Tea Plantation Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Soil Collection and Analysis
2.3. Experiment Design
2.4. Soil Gas Sampling and N2O Concentration Determination
2.5. Ammonia-Oxidizing Gene Abundance
2.6. Calculation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
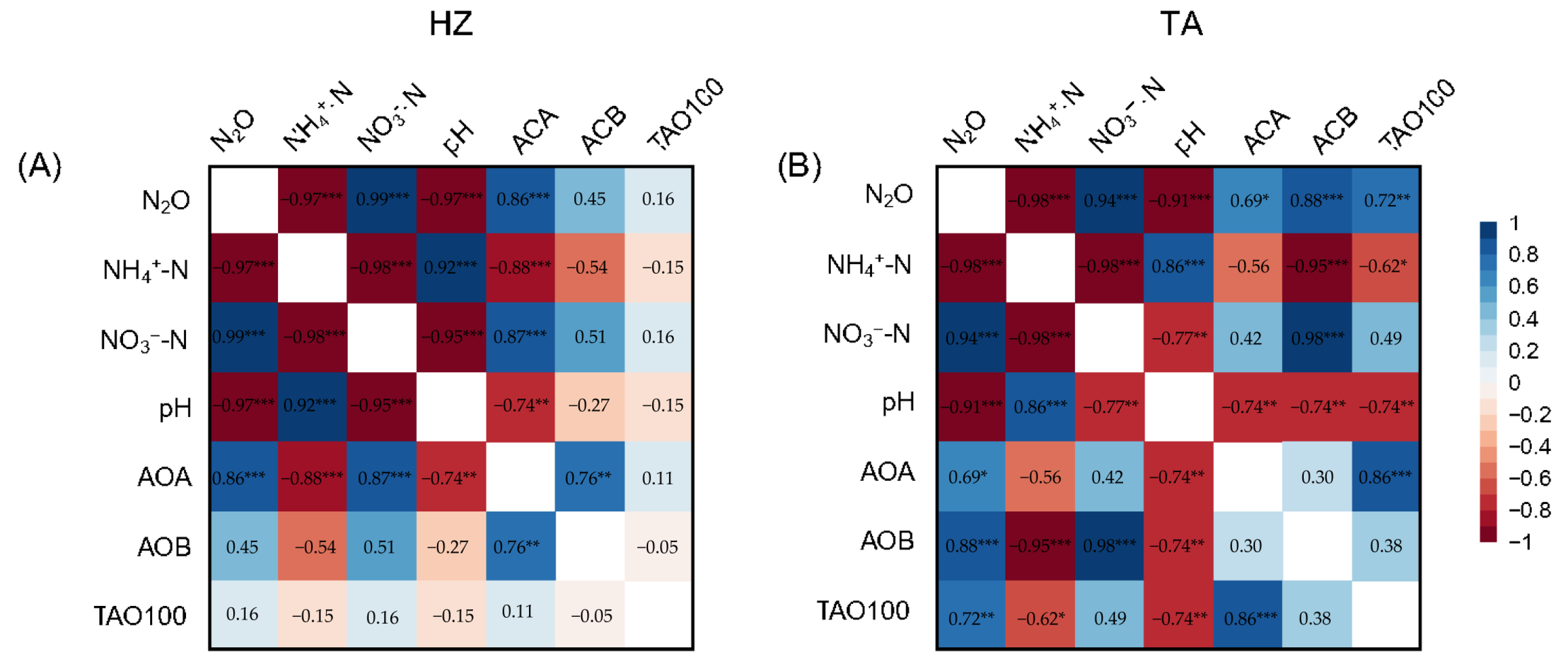
3.1. Soil NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and pH
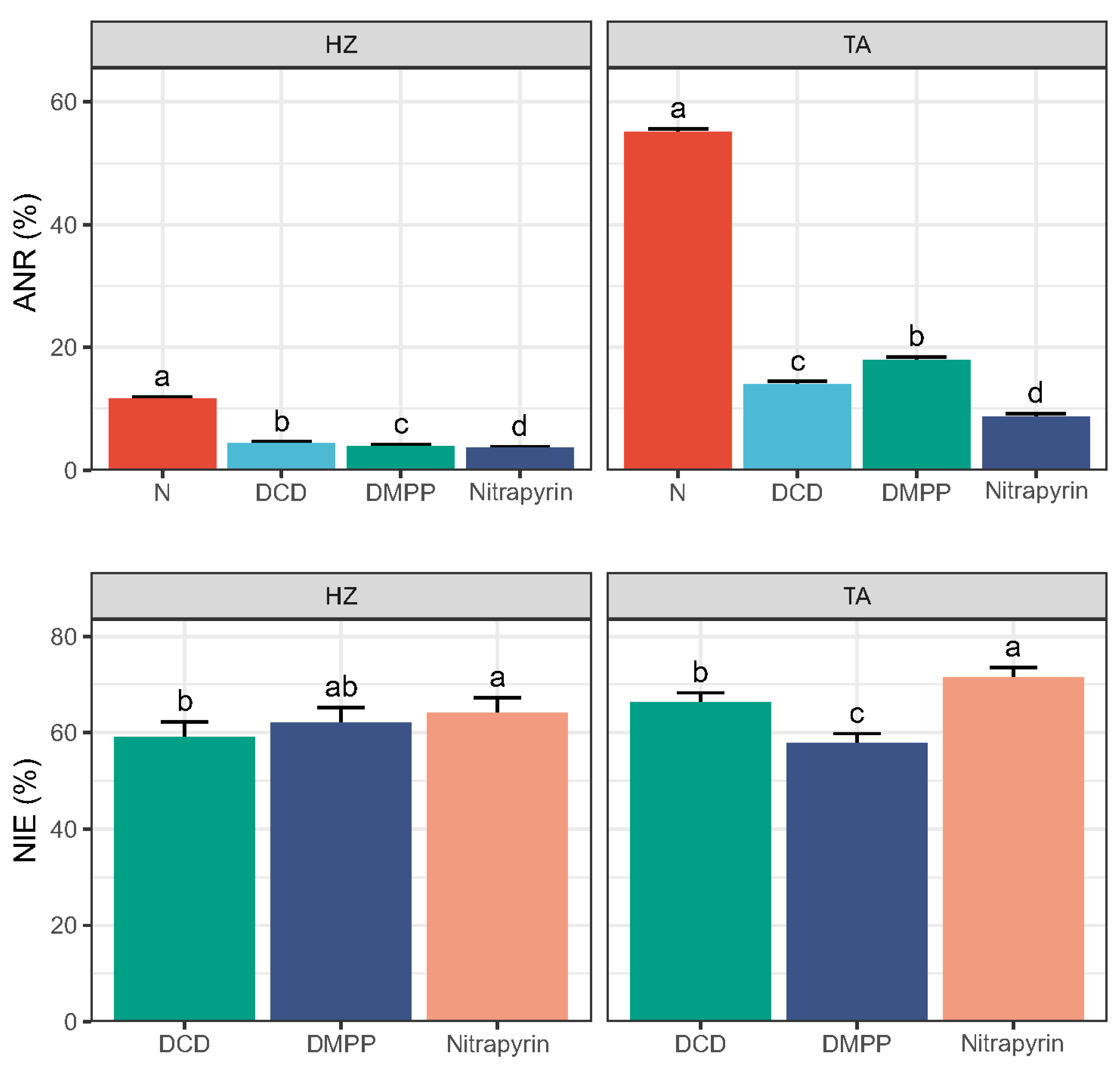
3.2. Apparent Nitrification Ratio and Nitrification Inhibition Efficiency
3.3. Soil N2O Emission
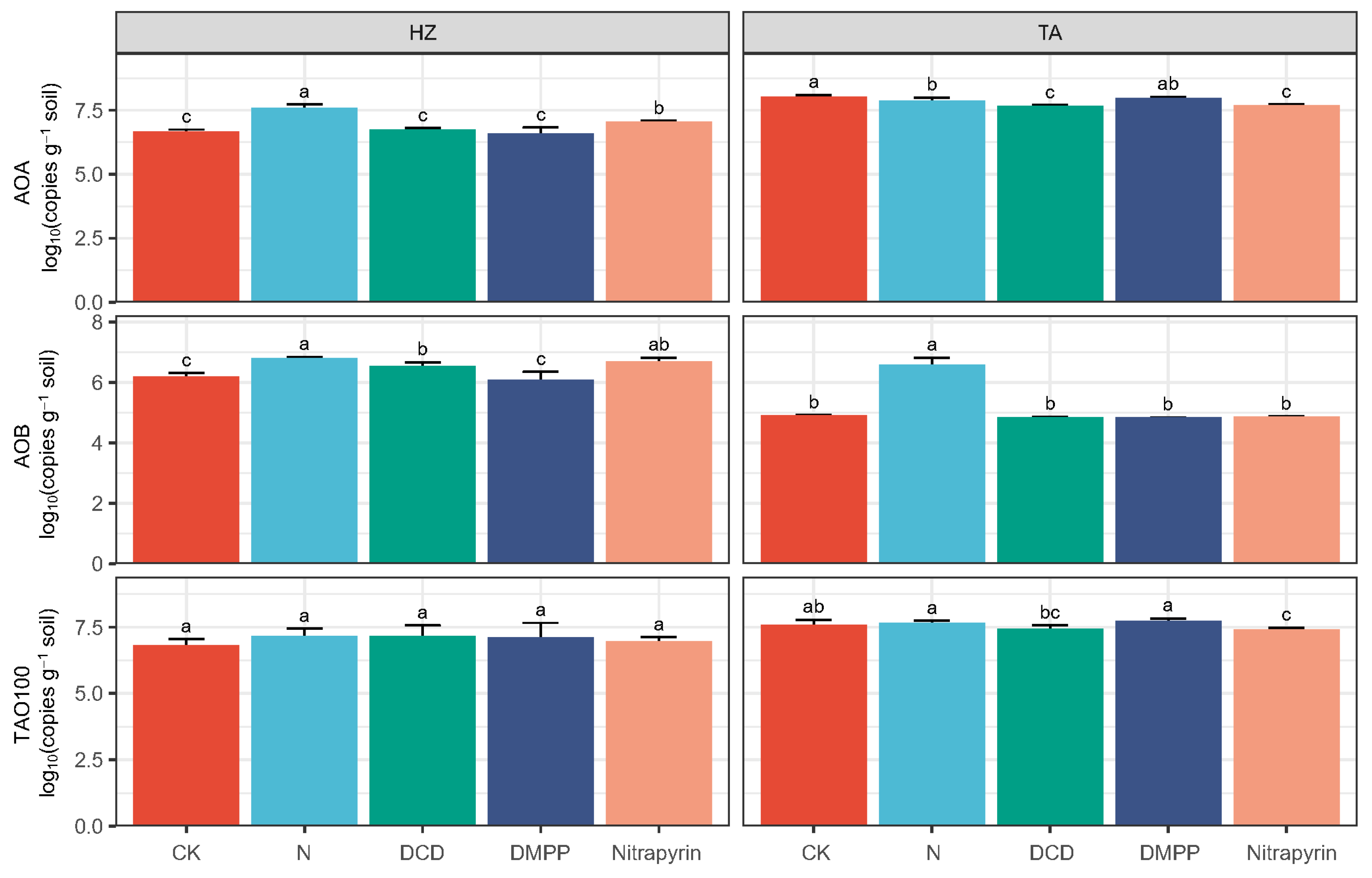
3.4. Abundances of amoA Genes
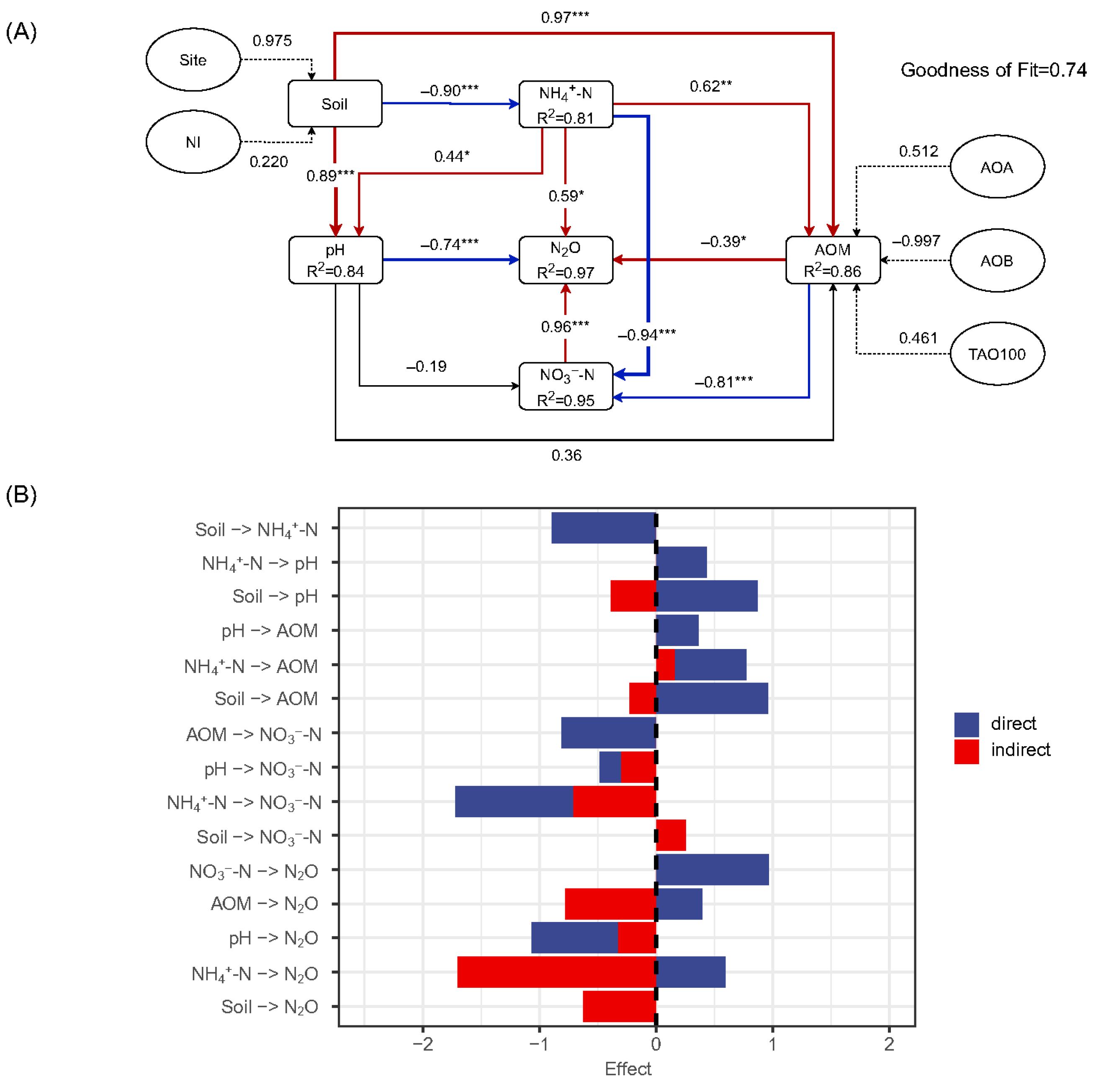
3.5. Structural Path Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Soil Properties on Nitrification Inhibition Efficiency
4.2. Efficiency of N2O Mitigation by NIs in Contrasting Soils
4.3. Ammonia-Oxidizing Microbes Driving N2O Emission
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Daniel, J.S.; Portmann, R.W. Nitrous Oxide (N2O): The Dominant Ozone-Depleting Substance Emitted in the 21st Century. Science 2009, 326, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Xu, R.; Canadell, J.G.; Thompson, R.L.; Winiwarter, W.; Suntharalingam, P.; Davidson, E.A.; Ciais, P.; Jackson, R.B.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; et al. A Comprehensive Quantification of Global Nitrous Oxide Sources and Sinks. Nature 2020, 586, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Bo, Y.; Adalibieke, W.; Winiwarter, W.; Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Sun, Z.; Tian, H.; Smith, P.; Zhou, F. The Global Potential for Mitigating Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Croplands. One Earth 2024, 7, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K. World Tea Production and Trade. Current and Future Development; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, K.; Liao, W.; Yi, X.; Niu, S.; Ma, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Ruan, J. Fertilization Status and Reduction Potential in Tea Gardens of China. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2019, 25, 421–432. [Google Scholar]
- Hirono, Y.; Sano, T.; Eguchi, S. Changes in the Nitrogen Footprint of Green Tea Consumption in Japan from 1965 to 2016. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44936–44948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Pan, Z.; Wang, R.; Yan, G.; Liu, C.; Su, Y.; Zheng, X.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Tea-Planted Soils as Global Hotspots for N2O Emissions from Croplands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 104018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, L.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J. Effects of Long-Term Nitrogen Application on Soil Acidification and Solution Chemistry of a Tea Plantation in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.; Wu, L.; Hu, R.; Younas, A.; Nunez-Delgado, A.; Xu, P.; Sun, Z.; Lin, S.; Xu, X.; et al. The Effects of pH Change through Liming on Soil N2O Emissions. Processes 2020, 8, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Sheng, X.; Bloszies, S.; et al. Intermediate Soil Acidification Induces Highest Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Yan, X.; Yagi, K. Evaluation of Effectiveness of Enhanced-Efficiency Fertilizers as Mitigation Options for N2O and NO Emissions from Agricultural Soils: Meta-Analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; He, W.; Smith, W.N.; Drury, C.F.; Jiang, R.; Grant, B.B.; Shi, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Global Evaluation of Inhibitor Impacts on Ammonia and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils: A Meta-Analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5121–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, J.R.; Souza, B.R.; Mazzetto, A.M.; Galdos, M.V.; Chadwick, D.R.; Campbell, E.E.; Jaiswal, D.; Oliveira, J.C.; Monteiro, L.A.; Vianna, M.S.; et al. Mitigation of Nitrous Oxide Emissions in Grazing Systems through Nitrification Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2023, 125, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, M.; Gao, X. Biological and Chemical Nitrification Inhibitors Exhibited Different Effects on Soil Gross N Nitrification Rate and N2O Production: A 15N Microcosm Study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 116162–116174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, J.; Fan, Q.; Yu, J.; Ma, Y.; Yin, J.; Liu, R. A Meta-Analysis to Examine Whether Nitrification Inhibitors Work through Selectively Inhibiting Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.L.; Carlos, F.S.; Barth, G.; Mühling, K.H. Do Tropical Climatic Conditions Reduce the Effectiveness of Nitrification Inhibitors? A Meta-Analysis of Studies Carried out in Brazil. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2023, 125, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Chen, H.; Duan, P.; Zhu, K.; Li, N.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, Q. Soil Microbial Communities as Potential Regulators of N2O Sources in Highly Acidic Soils. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2023, 5, 230178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, P.; Bo, X.; Wu, J.; Han, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, K.; Shen, M.; Wang, J.; Zou, J. Soil pH-Dependent Efficacy of DMPP in Mitigating Nitrous Oxide under Different Land Uses. Geoderma 2024, 449, 117018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Ji, L.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J. Heavy Nitrogen Application Increases Soil Nitrification through Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria Rather than Archaea in Acidic Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) Plantation Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pester, M.; Rattei, T.; Flechl, S.; Gröngröft, A.; Richter, A.; Overmann, J.; Reinhold-Hurek, B.; Loy, A.; Wagner, M. amoA-Based Consensus Phylogeny of Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea and Deep Sequencing of amoA Genes from Soils of Four Different Geographic Regions. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotthauwe, J.H.; Witzel, K.P.; Liesack, W. The Ammonia Monooxygenase Structural Gene amoA as a Functional Marker: Molecular Fine-Scale Analysis of Natural Ammonia-Oxidizing Populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 4704–4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatsu, M.; Tago, K.; Uchiyama, I.; Toyoda, A.; Wang, Y.; Shimomura, Y.; Okubo, T.; Kurisu, F.; Hirono, Y.; Nonaka, K.; et al. An Acid-Tolerant Ammonia-Oxidizing γ-Proteobacterium from Soil. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, H.; Hu, F.; Zhao, H. Effects of Rewetting on Soil Biota Structure and Nitrogen Mineralization, Nitrification in Air-Dried Red Soi. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2004, 41, 924–930. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, G.; Trinchera, L.; Russolillo, G.; Bertrand, F. Plspm: Partial Least Squares Path Modeling (PLS-PM). 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/plspm/index.html (accessed on 11 October 2025).
- Sahrawat, K.L. Factors Affecting Nitrification in Soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 39, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Ma, S.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, C. Effects of Commonly Used Nitrification Inhibitors—Dicyandiamide (DCD), 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate (DMPP), and Nitrapyrin—On Soil Nitrogen Dynamics and Nitrifiers in Three Typical Paddy Soils. Geoderma 2020, 380, 114637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Luo, J.; Lindsey, S.; Shi, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Effects of Soil Properties on Urea-N Transformation and Efficacy of Nitrification Inhibitor 3, 4-Dimethypyrazole Phosphate (DMPP). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.; Leung, P.M.; Daebeler, A.; Guo, J.; Hu, S.; Cook, P.; Nicol, G.W.; Daims, H.; Greening, C. Nitrification in Acidic and Alkaline Environments. Essays Biochem. 2023, 67, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hou, X.; Zhou, X.; Xin, X.; Wright, A.; Jia, Z. pH Regulates Key Players of Nitrification in Paddy Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 81, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.L.; Lehtovirta-Morley, L.E. Nitrification and beyond: Metabolic Versatility of Ammonia Oxidising Archaea. ISME J. 2023, 17, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Effect of Soil Organic Matter on Adsorption of Nitrification Inhibitor Nitrapyrin in Black Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.L.; Pitann, B.; Banedjschafie, S.; Mühling, K.H. Effectiveness of Three Nitrification Inhibitors on Mitigating Trace Gas Emissions from Different Soil Textures under Surface and Subsurface Drip Irrigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 359, 120969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggs, E.M.; Smales, C.L.; Bateman, E.J. Changing pH Shifts the Microbial Sourceas Well as the Magnitude of N2O Emission from Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 46, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuhel, J.; Šimek, M.; Laughlin, R.J.; Bru, D.; Chèneby, D.; Watson, C.J.; Philippot, L. Insights into the Effect of Soil pH on N2O and N2 Emissions and Denitrifier Community Size and Activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senbayram, M.; Chen, R.; Budai, A.; Bakken, L.; Dittert, K. N2O Emission and the N2O/(N2O + N2) Product Ratio of Denitrification as Controlled by Available Carbon Substrates and Nitrate Concentrations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 147, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C.; Wang, S. Mechanistic Insights into the Effects of N Fertilizer Application on N2O-Emission Pathways in Acidic Soil of a Tea Plantation. Plant Soil 2015, 389, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Yuan, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, W.; Fan, J.; Liu, D.; Ding, W. Organic Fertilizers Have Divergent Effects on Soil N2O Emissions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, B.; Ge, S.; Wang, Z.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Pathways and Organisms Involved in Ammonia Oxidation and Nitrous Oxide Emission. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 2213–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Gwak, J.; Rohe, L.; Giesemann, A.; Kim, J.; Well, R.; Madsen, E.; Herbold, C.; Wagner, M.; Rhee, S. Indications for Enzymatic Denitrification to N2O at Low pH in an Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaeon. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2633–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hirono, Y.; Yanai, Y.; Hattori, S.; Toyoda, S.; Yoshida, N. Isotopomer Analysis of Nitrous Oxide Accumulated in Soil Cultivated with Tea (Camellia sinensis) in Shizuoka, Central Japan. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 77, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Pinzon, P.A.; Prommer, J.; Sedlacek, C.J.; Sandén, T.; Spiegel, H.; Pjevac, P.; Fuchslueger, L.; Giguere, A.T. Inhibition Profile of Three Biological Nitrification Inhibitors and Their Response to Soil pH Modification in Two Contrasting Soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2024, 100, fiae072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiske, A.; Benckiser, G.; Herbert, T.; Ottow, J. Influence of the Nitrification Inhibitor 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate (DMPP) in Comparison to Dicyandiamide (DCD) on Nitrous Oxide Emissions, Carbon Dioxide Fluxes and Methane Oxidation during 3 Years of Repeated Application in Field Experiments. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibuike, G.; Palmada, T.; Saggar, S.; Giltrap, D.; Luo, J. A Comparison of the Threshold Concentrations of DCD, DMPP and Nitrapyrin to Reduce Urinary Nitrogen Nitrification Rates on Pasture Soils—A Laboratory Study. Soil Res. 2022, 61, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Hu, H.W.; Shen, J.P.; He, J.Z. Ammonia-Oxidizing Archaea Have More Important Role than Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria in Ammonia Oxidation of Strongly Acidic Soils. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatsu, M.; Katsuyama, C.; Tago, K. Overview of Recent Researches on Nitrifying Microorganisms in Soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 67, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mo, T.; Zhong, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; Li, Y. Synergistic Benefits of Lime and 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole Phosphate Application to Mitigate the Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Acidic Soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Properties | HZ | TA |
|---|---|---|
| Annual mean temperature (°C) | 17.0 | 12.0 |
| Annual total precipitation (mm) | 1533 | 840 |
| Soil taxonomy (USDA) | Ultisol | Luvisols |
| Soil texture (USDA) | Silty loam clay | Silt loam |
| Sand (%) | 23.8 | 30.8 |
| Silt (%) | 53.1 | 67.9 |
| Clay (%) | 23.1 | 1.3 |
| pH (%) | 3.51 | 5.62 |
| Total carbon (%) | 2.7 | 1.6 |
| Total nitrogen (%) | 0.27 | 0.12 |
| NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | 41.2 | 28.1 |
| NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | 19.3 | 9.4 |
| Available P (mg kg−1) | 358 | 112 |
| Available K (mg kg−1) | 213 | 106 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hua, W.; Niu, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Shi, Y.; Ni, K. Contrasting Responses of N2O Mitigation to Different Nitrification Inhibitors in Tea Plantation Soils. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121470
Hua W, Niu S, Zhao C, Wang J, Yang X, Shi Y, Ni K. Contrasting Responses of N2O Mitigation to Different Nitrification Inhibitors in Tea Plantation Soils. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(12):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121470
Chicago/Turabian StyleHua, Wei, Siyun Niu, Chenguang Zhao, Jie Wang, Xiangde Yang, Yuanzhi Shi, and Kang Ni. 2025. "Contrasting Responses of N2O Mitigation to Different Nitrification Inhibitors in Tea Plantation Soils" Horticulturae 11, no. 12: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121470
APA StyleHua, W., Niu, S., Zhao, C., Wang, J., Yang, X., Shi, Y., & Ni, K. (2025). Contrasting Responses of N2O Mitigation to Different Nitrification Inhibitors in Tea Plantation Soils. Horticulturae, 11(12), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11121470








