EDI-YOLO: An Instance Segmentation Network for Tomato Main Stems and Lateral Branches in Greenhouse Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We substituted the original backbone with EfficientNetV1 [10], achieving a balance between feature representation and computational efficiency while improving segmentation of morphologically complex tomato stems.
- We developed the C2f-DWR module [11], which incorporates multi-scale dilated convolution to strengthen feature perception across spatial scales, directly addressing the challenge of similar elongated structures.
- We incorporated the iRMB into the neck network [12] to enhance spatial-structure perception of tomato stems, specifically targeting dense occlusion in greenhouse environments.
- We constructed a specialized tomato stem segmentation dataset collected in greenhouses and applied five data-augmentation strategies to improve generalization across diverse lighting and occlusion scenarios.
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
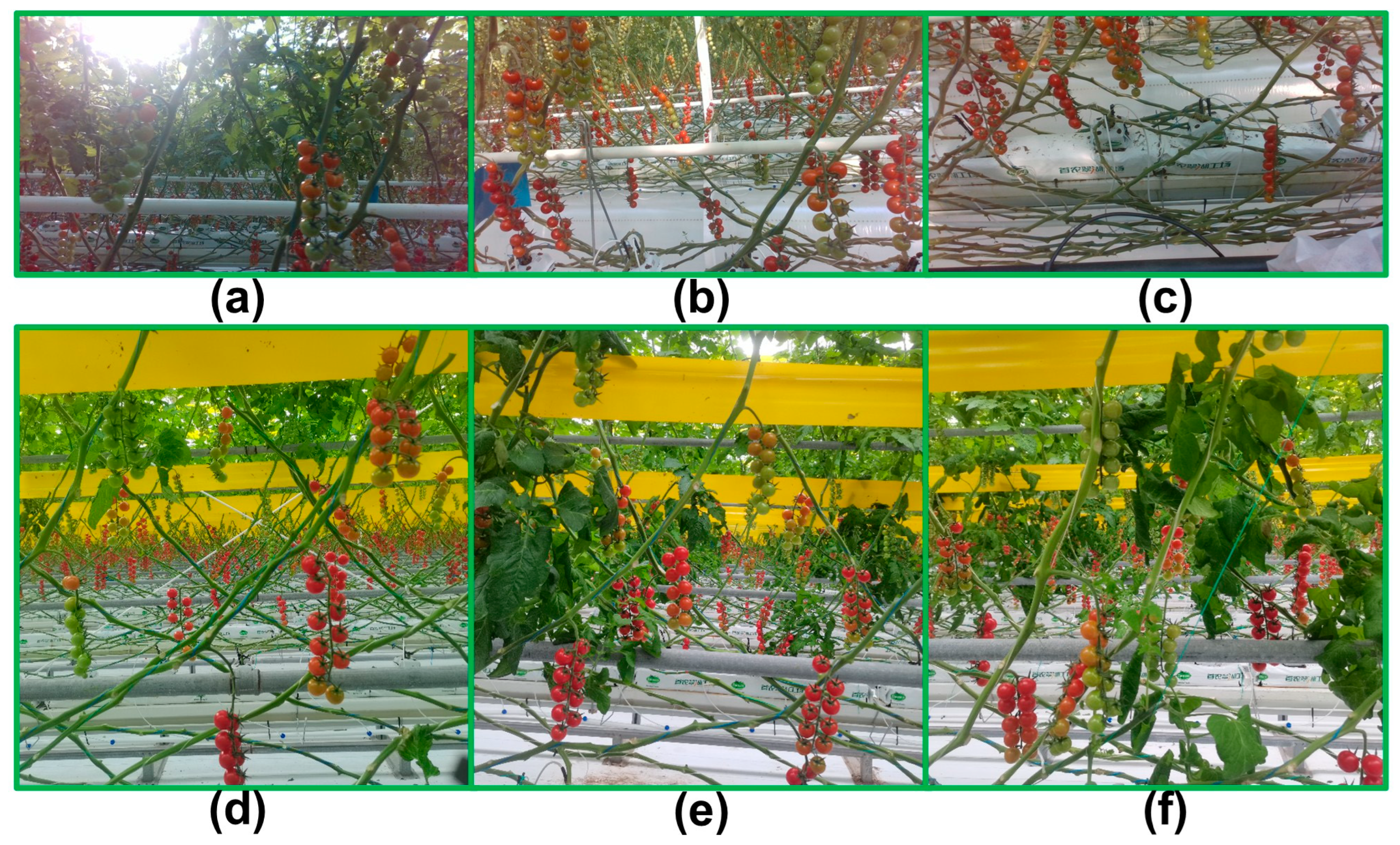
3.1.1. Data Acquisition
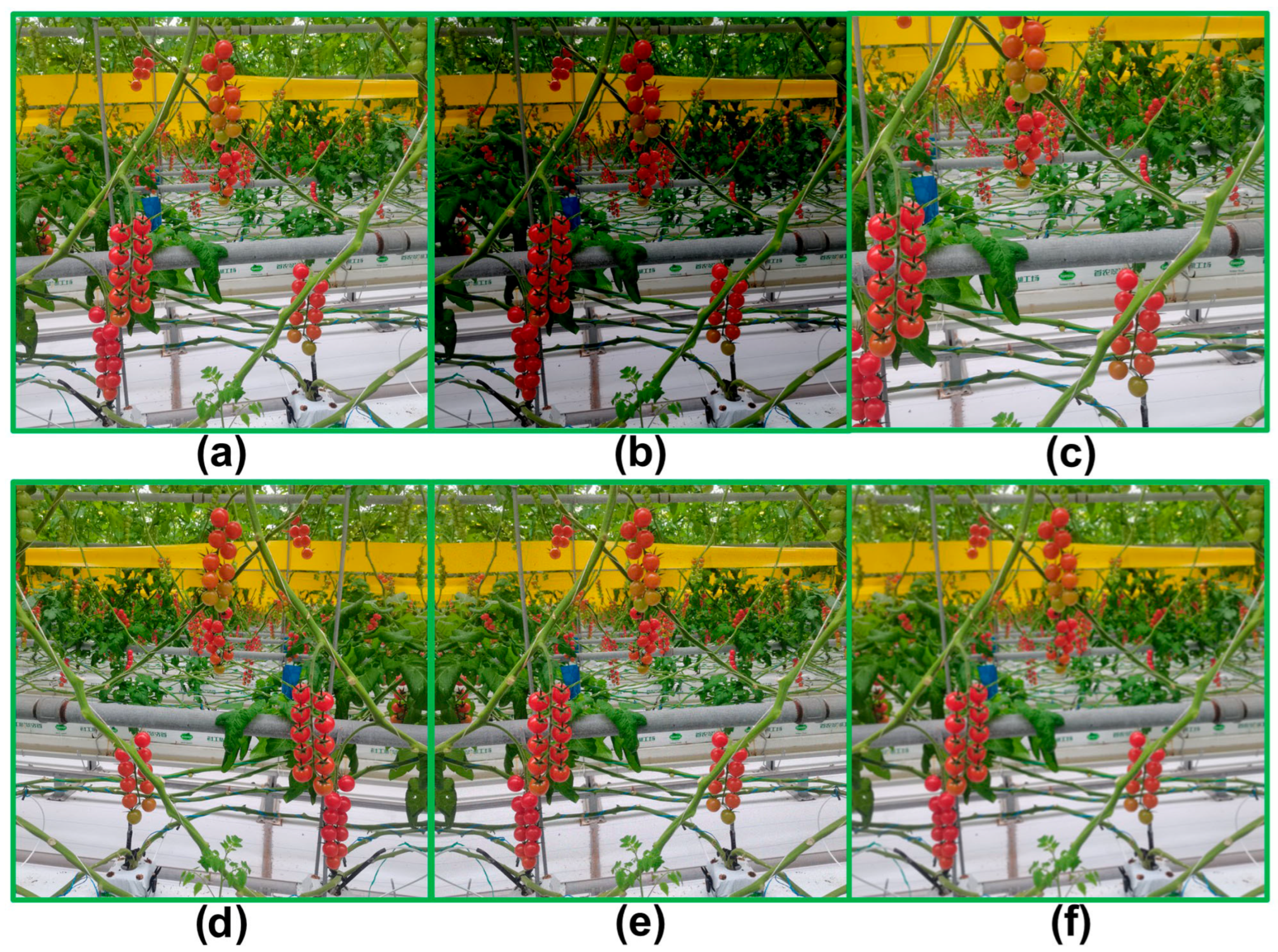
3.1.2. Data Augmentation
3.2. The Structure of EDI-YOLO
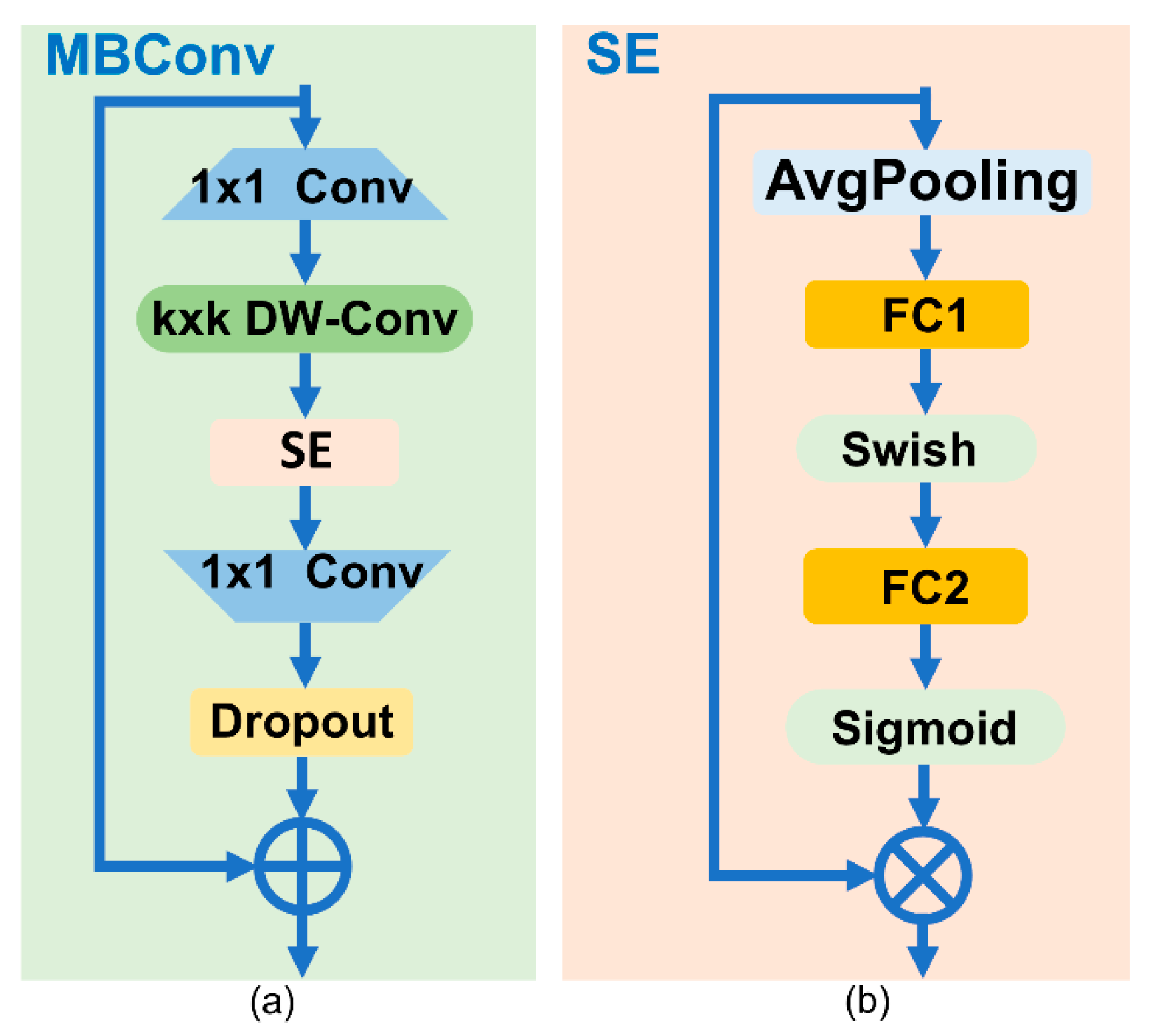
3.3. EfficientNetV1
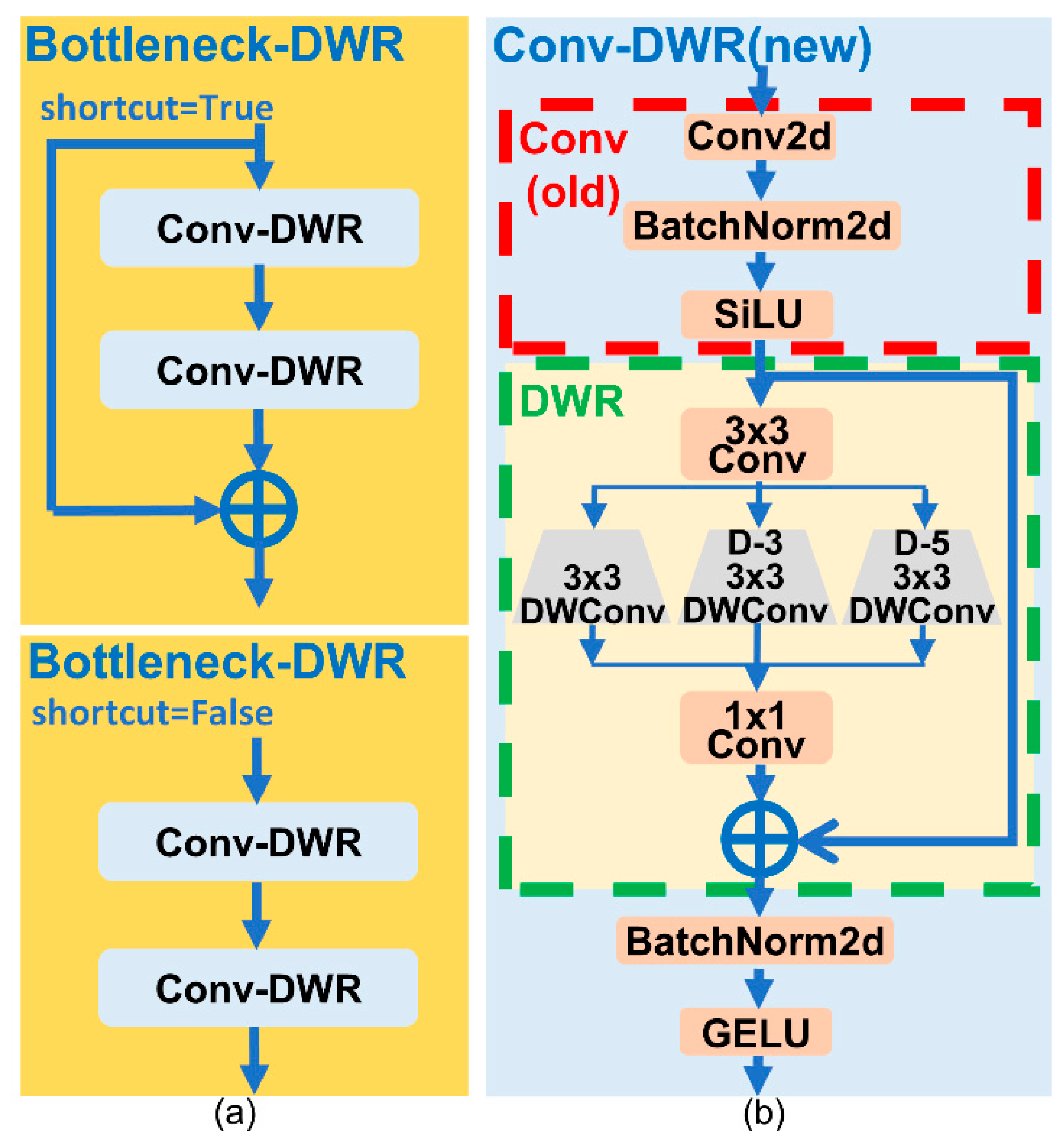
3.4. C2f-DWR
3.5. iRMB
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.1. Experiment Environment
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Analysis
4.3.1. Data Augmentation Comparative Experiment
4.3.2. Backbone Network Comparison Experiment
4.3.3. Comparative Experiment of Feature Extraction Module
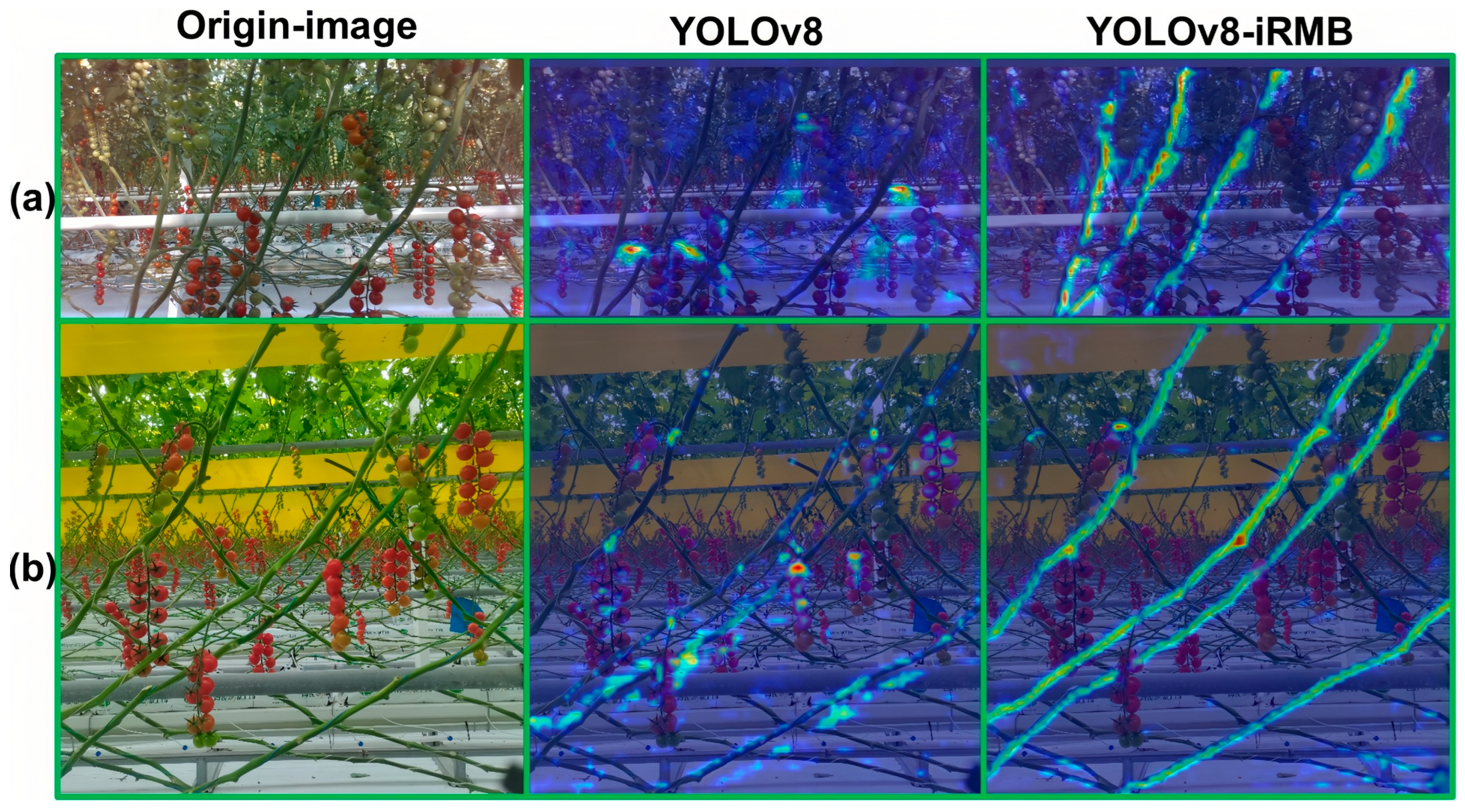
4.3.4. Comparative Experiment on Attention Mechanisms
4.3.5. Ablation Experiments of Different Improved Modules
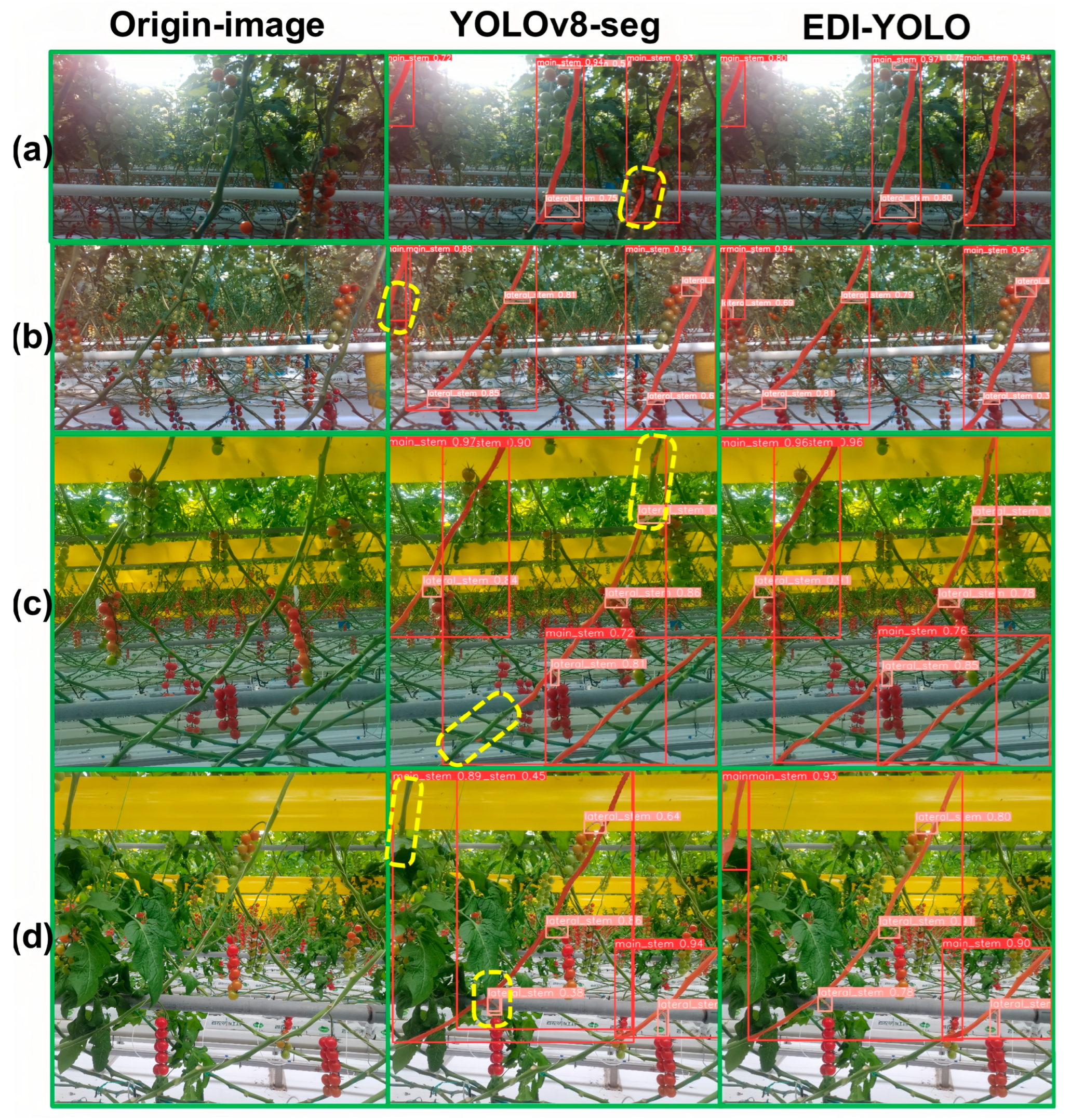
4.3.6. Comparative Experiment Between EDI-YOLO and YOLOv8n-seg
4.3.7. Comparative Experiments of Different Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wikipedia. List of Countries by Tomato Production. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_countries_by_tomato_production (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Kim, J.Y.; Pyo, H.R.; Jang, I.; Kang, J.; Ju, B.K.; Ko, K.E. Tomato harvesting robotic system based on Deep-ToMaToS: Deep learning network using transformation loss for 6D pose estimation of maturity classified tomatoes with side-stem. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 201, 107300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, L. The development and prospect of agricultural robots in China. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2015, 27, 865–871. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, V.; Debnath, B.; Mghames, S.; Mandil, W.; Parsa, S.; Parsons, S.; Ghalamzan-E., A. Towards autonomous selective harvesting: A review of robot perception, robot design, motion planning and control. J. Field Robot. 2023, 41, 2247–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Su, J.; Huang, R.; Quan, W.; Song, Y.; Fang, Y.; Su, B. Fusing attention mechanism with Mask R-CNN for instance segmentation of grape cluster in the field. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 934450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H. Conditional Convolutions for Instance Segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2020, Proceedings of the 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12346, pp. 282–298. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.; Qi, K.; Na, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C. Improved YOLOv8-seg network for instance segmentation of healthy and diseased tomato plants in the growth stage. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultralytics. Explore Ultralytics YOLOv8. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov8/ (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, S.; Dai, Z.; Dai, Y.; Xu, X. DWRSeg: Rethinking efficient acquisition of multi-scale contextual information for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.01173. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Rethinking Mobile Block for Efficient Attention-Based Models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1389–1400. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C. Robust tomato recognition for robotic harvesting using feature images fusion. Sensors 2016, 16, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.H.; Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Shabbir, S.; Saeed, A.S.M. Mature tomato fruit detection algorithm based on improved HSV and watershed algorithm. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Evans, A.; Zhang, L. Segmentation of tomato leaf images based on adaptive clustering number of k-means algorithm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 165, 104962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, G. Grasping point detection of randomly placed fruit cluster using adaptive morphology segmentation and principal component classification of multiple features. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 158035–158050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Sun, H.; Xia, Y.; Kang, J. Real-time cucumber target recognition in greenhouse environments using color segmentation and shape matching. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Ren, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, F. A method for tomato plant stem and leaf segmentation and phenotypic extraction based on skeleton extraction and supervoxel clustering. Agronomy 2024, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jiang, Q.; Guan, H.; Wang, L.; Wu, X. Calculation method of phenotypic traits for tomato canopy in greenhouse based on the extraction of branch skeleton. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Wang, S.; Shuai, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Feng, Y. Recognition and detection of greenhouse tomatoes in complex environment. Trait. Signal. 2022, 39, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appe, S.N.; Arulselvi, G.; Balaji, G.N. CAM-YOLO: Tomato detection and classification based on improved YOLOv5 using combining attention mechanism. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solimani, F.; Cardellicchio, A.; Dimauro, G.; Petrozza, A.; Summerer, S.; Cellini, F.; Renò, V. Optimizing tomato plant phenotyping detection: Boosting YOLOv8 architecture to tackle data complexity. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yang, B.; Yu, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; et al. Tomato stem and leaf segmentation and phenotype parameter extraction based on improved red billed blue magpie optimization algorithm. Agriculture 2025, 15, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J. Recognition for stems of tomato plants at night based on a hybrid joint neural network. Agriculture 2022, 12, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B. Visual Tracking Method of Tomato Plant Main-Stems for Robotic Harvesting. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 11th Annual International Conference on CYBER Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelligent Systems (CYBER), Jiaxing, China, 27–31 July 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 886–890. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Fang, J.; Zhao, Y. A multi-target identification and positioning system method for tomato plants based on VGG16-UNet model. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yu, W.; Qin, L.; Wang, J.; Jia, P.; Liu, Q.; Lei, X.; Yang, M. Stem and leaf segmentation and phenotypic parameter extraction of tomato seedlings based on 3D point cloud. Agronomy 2025, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, Q.; Liu, C.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xie, F.; Li, T.; Zhao, C. MTA-YOLACT: Multitask-aware network on fruit bunch identification for cherry tomato robotic harvesting. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 146, 126812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, A.; Zou, X.; Wang, H. YOLOv8n-DDA-SAM: Accurate cutting-point estimation for robotic cherry-tomato harvesting. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, Y.; Jeong, H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, K.-B.; Lee, J.Y. Deep learning-based object detection in augmented reality: A systematic review. Comput. Ind. 2022, 139, 103661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liang, F.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.; Mou, X. An Efficient and Accurate Surface Defect Detection Method for Wood Based on Improved YOLOv8. Forests 2024, 15, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; Gan, C.; Han, S. EfficientViT: Lightweight Multi-Scale Attention for High-Resolution Dense Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 17256–17267. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Song, T.; Yang, D.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, L. LDConv: Linear deformable convolution for improving convolutional neural networks. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 149, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Chen, J.; Mian, A. DualConv: Dual convolutional kernels for lightweight deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 34, 9528–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, D.; Nalamada, T.; Arasanipalai, A.U.; Hou, Q. Rotate to Attend: Convolutional triplet attention module. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3138–3147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Kan, M.; Shan, S.; Chen, X. Self-Supervised Equivariant Attention Mechanism for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 12275–12284. [Google Scholar]
- Ultralytics. Ultralytics YOLOv5. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolov5/ (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv9: Learning What You Want to Learn Using Programmable Gradient Information. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2024, Proceedings of the 18th European Conference, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ultralytics. Ultralytics YOLO11. Available online: https://docs.ultralytics.com/models/yolo11/ (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. YOLOv12: Attention-centric real-time object detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]



| Parameter Category | Parameter Setting |
|---|---|
| Initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| Optimizer weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| IoU | 0.7 |
| Training cycle | 200 |
| Image size | 640 × 640 |
| Batch | 16 |
| Workers | 8 |
| Data | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin data | 77.9 | 68.4 | 70.3 | 26.3 |
| Enhanced data | 79.7 | 73.3 | 75.1 | 31.4 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Origin-Backbone | 79.7 | 73.3 | 75.1 | 31.4 | 12.0 |
| ResNet50 | 79 | 68.1 | 70.5 | 26.7 | 10.3 |
| EfficientViT2 | 76.3 | 66.6 | 68.7 | 26.4 | 13.3 |
| EfficientNetV1 | 82.9 | 74 | 77.4 | 33.8 | 9.4 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2f | 79.7 | 73.3 | 75.1 | 31.4 | 12.0 |
| C2f-AKConv | 79.8 | 72.1 | 73.9 | 30.3 | 11.8 |
| C2f-DualConv | 81.5 | 70.2 | 74.4 | 30.8 | 11.3 |
| C2f-DWR | 79.6 | 73.8 | 76.5 | 30.9 | 12.3 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 79.7 | 73.3 | 75.1 | 31.4 | 12 |
| TripletAtt | 80.6 | 71.7 | 75.6 | 31.5 | 12 |
| MultiSEAM | 81.3 | 71.3 | 74.4 | 31.1 | 12.4 |
| iRMB | 80.9 | 73.9 | 76.6 | 31.4 | 12.7 |
| Model | EfficientNetV1 | C2f-DWR | iRMB | P (%) | R (%) | F1 (%) | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n-seg | 79.7 | 73.3 | 76.4 | 75.1 | 31.4 | |||
| E-YOLO | √ | 82.9 | 74.0 | 78.2 | 77.4 | 33.8 | ||
| C-YOLO | √ | 79.6 | 73.8 | 76.6 | 76.5 | 30.9 | ||
| I-YOLO | √ | 80.9 | 73.9 | 77.2 | 76.6 | 31.4 | ||
| ED-YOLO | √ | √ | 83.1 | 74.6 | 78.4 | 78.3 | 33.4 | |
| EI-YOLO | √ | √ | 81.5 | 75.4 | 78.2 | 78.6 | 34.5 | |
| DI-YOLO | √ | √ | 82.9 | 72.6 | 77.2 | 76.7 | 31.4 | |
| EDI-YOLO | √ | √ | √ | 83.5 | 76.0 | 79.4 | 79.3 | 33.9 |
| Model | Class | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n-seg | main_stem | 89.8 | 42.6 |
| lateral_branch | 60.4 | 20.2 | |
| EDI-YOLO | main_stem | 93.4 | 46.6 |
| lateral_branch | 65.2 | 21.1 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP50 (%) | F1 (%) | GFLOPs | Parameter (M) | FPS (f/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask-RCNN | 47.4 | 58.8 | 48.2 | 52.4 | 18.6 | 44.0 | 33.2 |
| CondInst | 72.1 | 67 | 63.4 | 69.4 | 20.9 | 34.0 | 67.3 |
| YOLOv5s-seg | 72.7 | 67 | 66.7 | 69.7 | 25.7 | 7.4 | 291.9 |
| YOLOv7tiny-seg | 80 | 75.5 | 75.4 | 77.7 | 47.7 | 7.0 | 240.2 |
| YOLOv8n-seg | 79.7 | 73.3 | 75.1 | 76.4 | 12.0 | 3.3 | 288.4 |
| YOLOv9c | 82.7 | 76.8 | 79.4 | 79.6 | 157.6 | 27.6 | 81.5 |
| YOLOv11s-seg | 79.4 | 74.4 | 76.1 | 79.8 | 35.3 | 10.1 | 201.4 |
| YOLOv12s-seg | 81.9 | 72 | 75.4 | 76.6 | 35.2 | 9.9 | 142.4 |
| EDI-YOLO | 83.5 | 76 | 79.3 | 79.4 | 10.4 | 8.0 | 86.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, P.; Yang, N.; Lin, S.; Xiong, Y. EDI-YOLO: An Instance Segmentation Network for Tomato Main Stems and Lateral Branches in Greenhouse Environments. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101260
Ji P, Yang N, Lin S, Xiong Y. EDI-YOLO: An Instance Segmentation Network for Tomato Main Stems and Lateral Branches in Greenhouse Environments. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(10):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101260
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Peng, Nengwei Yang, Sen Lin, and Ya Xiong. 2025. "EDI-YOLO: An Instance Segmentation Network for Tomato Main Stems and Lateral Branches in Greenhouse Environments" Horticulturae 11, no. 10: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101260
APA StyleJi, P., Yang, N., Lin, S., & Xiong, Y. (2025). EDI-YOLO: An Instance Segmentation Network for Tomato Main Stems and Lateral Branches in Greenhouse Environments. Horticulturae, 11(10), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101260




