Genome-Wide Identification of the bHLH Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Anthocyanin Synthesis in Lagerstroemia indica Leaves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification of bHLH Gene Family in L. indica
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of LibHLH Proteins in L. indica
2.3. Analysis of Conserved Motifs and Cis-Acting Elements of Promoters
2.4. Chromosomal Mapping and Collinearity Analysis of LibHLHs in L. indica
2.5. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Prediction
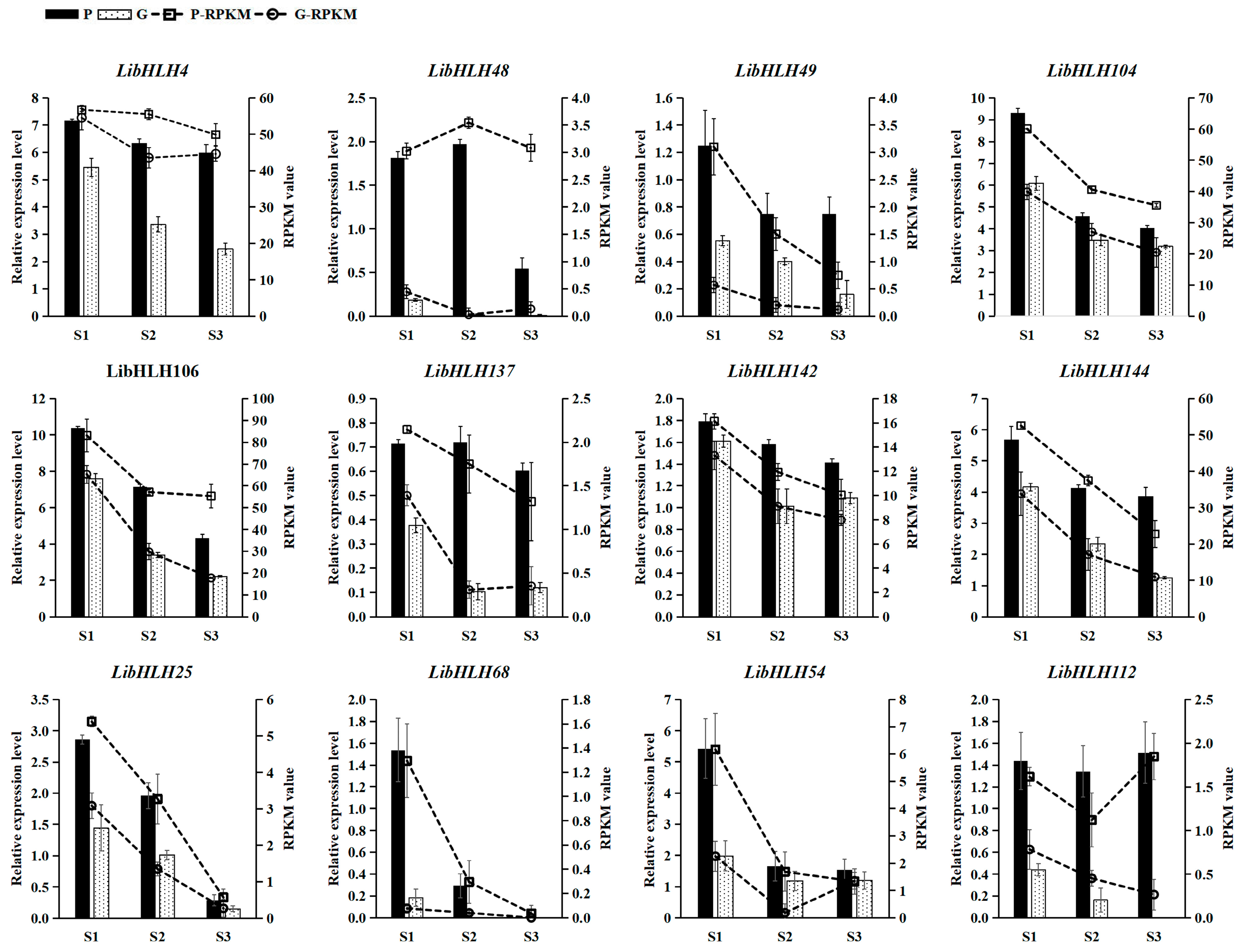
2.6. Gene Expression Analysis of LibHLHs
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Protein Characteristics Analysis of the bHLH Gene Family in L. indica
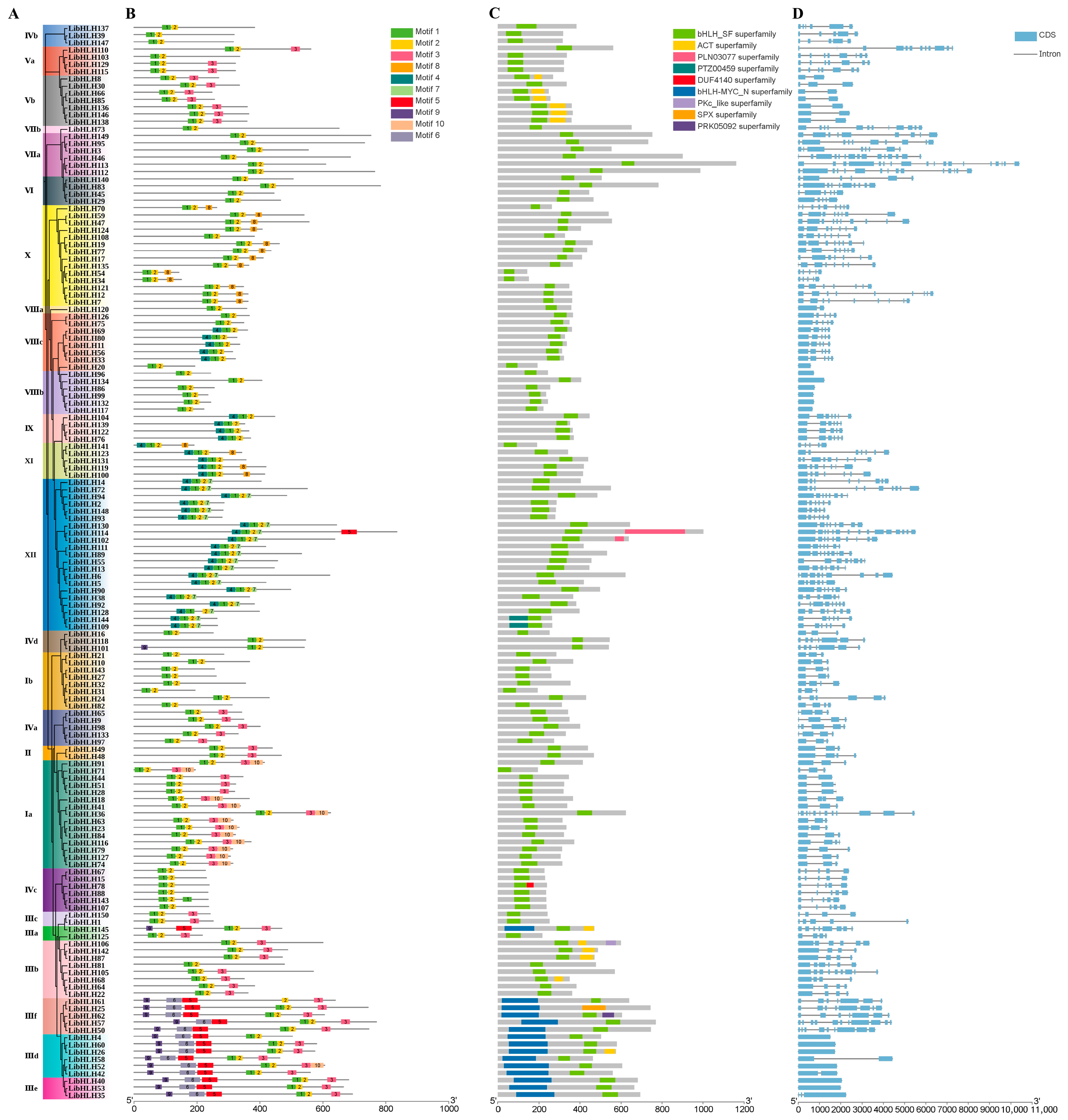
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the bHLH Gene Family in L. indica
3.3. Gene Structure and Cis-Acting Elements of the bHLH Gene Family in L. indica
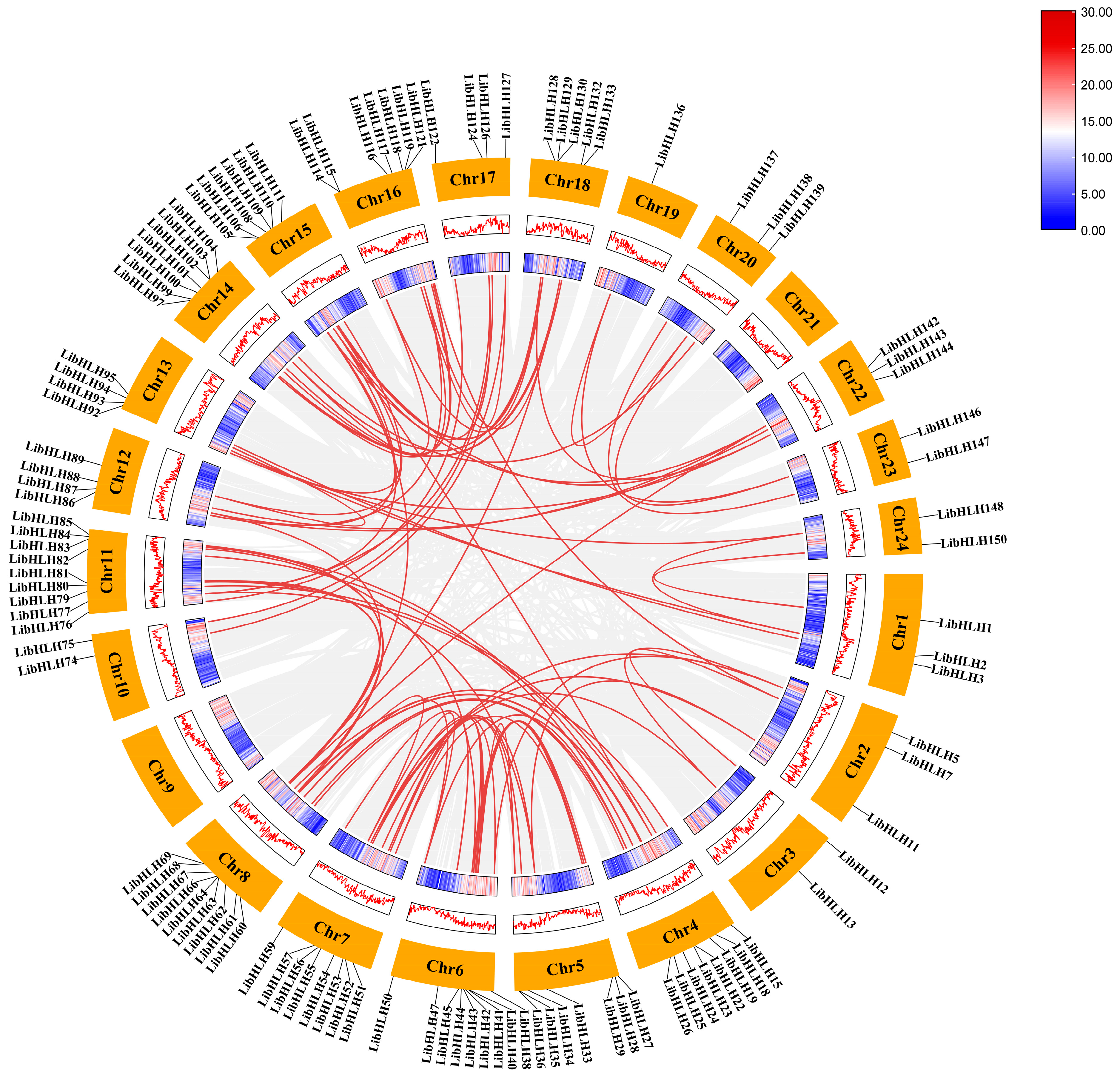
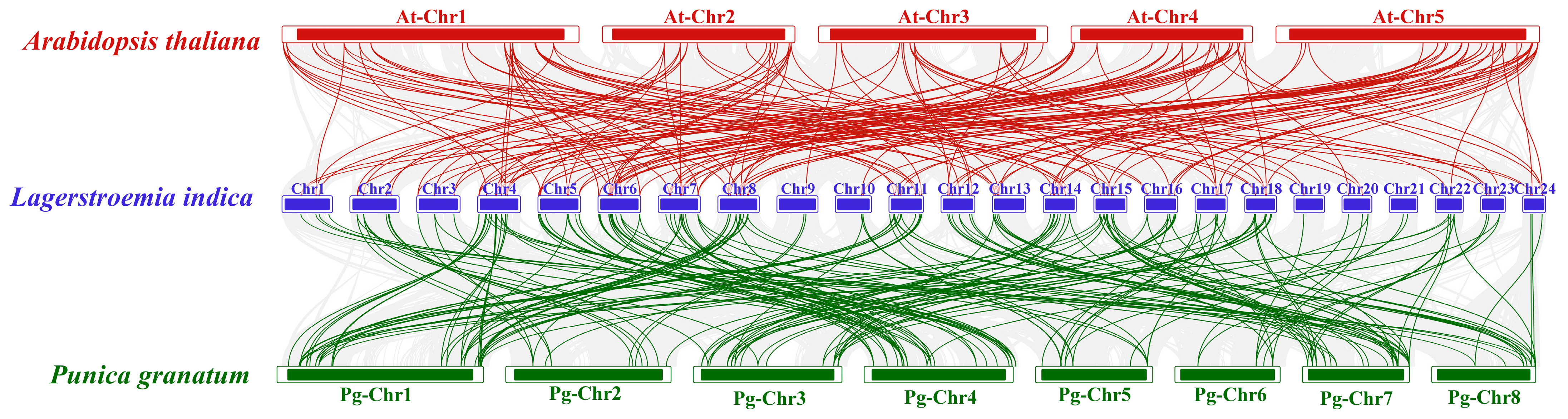
3.4. Chromosomal Distribution and Collinearity Analysis of LibHLH Genes
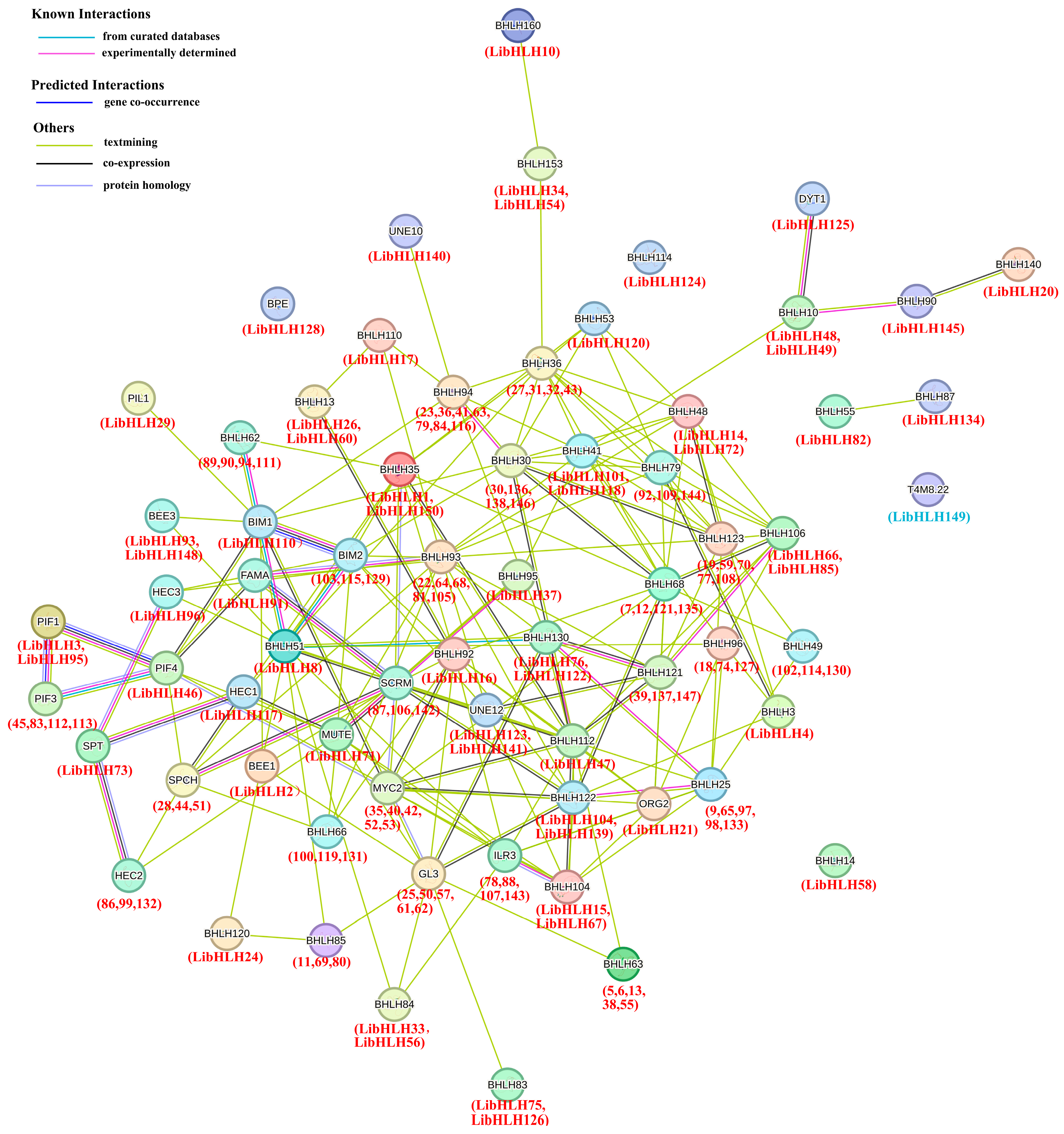
3.5. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis of LibHLH Genes
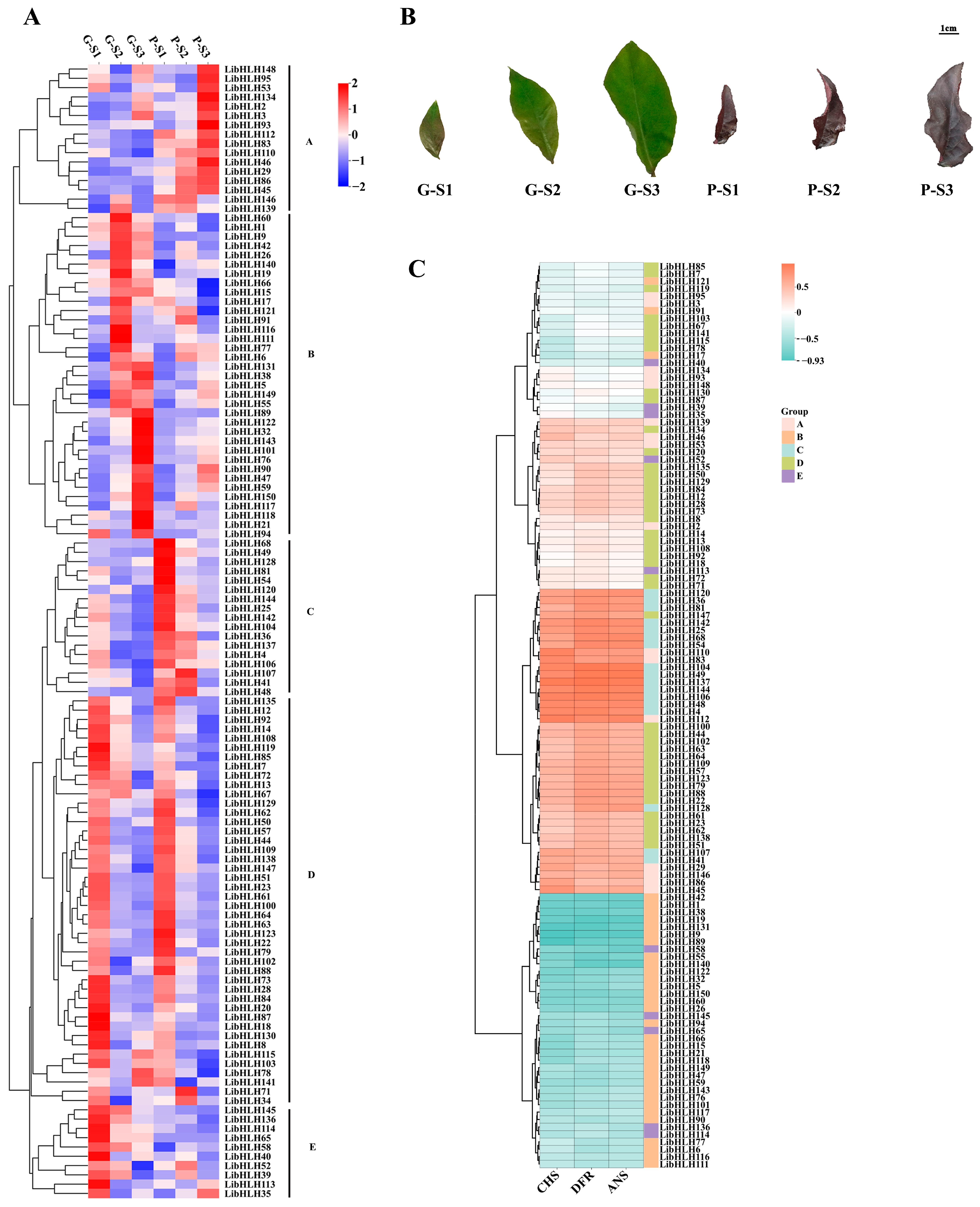
3.6. Expression Patterns of LibHLHs in L. indica with Different Leaf Colors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heim, M.A.; Jakoby, M.; Werber, M.; Martin, C.; Weisshaar, B.; Bailey, P.C. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor family in plants: A genome-wide study of protein structure and functional diversity. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. Origin and Diversification of Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix Proteins in Plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledent, V.; Vervoort, M. The Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein Family: Comparative Genomics and Phylogenetic Analysis. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 754–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, A.; Machemer, K.; Braun, E.L.; Grotewold, E. Evolutionary and comparative analysis of MYB and bHLH plant transcription factors. Plant J. 2011, 66, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Huq, E.; Quail, P.H. The Arabidopsis Basic/Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1749–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Duan, X.; Jiang, H.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Basic/Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor Family in Rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yao, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Fang, J.; Deng, H.; Yao, Q.; Kang, T.; Guo, X. Basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) gene family in rye (Secale cereale L.): Genome-wide identification, phylogeny, evolutionary expansion and expression analyses. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Liao, Y.; Kim, S.-U.; Chen, Z.; Nie, G.; Cheng, S.; Ye, J.; Xu, F. Genome-wide identification and characterization of bHLH family genes from Ginkgo biloba. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wen, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Dong, S. Genome-wide identification, expression analysis, and potential roles under low-temperature stress of bHLH gene family in Prunus sibirica. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1267107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Li, M.-Y.; Wu, X.-J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, J.; Xiong, A.-S. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix family transcription factors and their role in responses to abiotic stress in carrot. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Feng, R.; Ma, R.; Shen, Z.; Cai, Z.; Song, Z.; Peng, B.; Yu, M. Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix superfamily members in peach. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelain, M.; Le Hir, R.; Bellini, C. The non-DNA-binding bHLH transcription factor PRE3/bHLH135/ATBS1/TMO7 is involved in the regulation of light signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Physiol. Plant. 2012, 145, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Urao, T.; Ito, T.; Seki, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Arabidopsis AtMYC2 (bHLH) and AtMYB2 (MYB) function as transcriptional activators in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichsen, D.M.; Nemhauser, J.; Muramitsu, T.; Maloof, J.N.; Alonso, J.; Ecker, J.R.; Furuya, M.; Chory, J. Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth. Genetics 2002, 162, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.-F.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kang, H.-G. Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factors: Regulators for Plant Growth Development and Abiotic Stress Responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Z.; Cui, X.Y.; Li, X.F.; Zhao, P.S. Genome-wide identification of bHLH transcription factors related to plant development and abiotic stress response in sand rice (Agriophyllum squarrosum (L.) Moq.)). Genetica 2025, 153, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, N.; Basu, R.; Ojha, M.; Chattopadhyay, S. MYC2-mediated Regulation of FLC Controls Photomorphogenic Growth and Flowering Time. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 43, 1352–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, V.; North, H.; Frey, A.; Sotta, B.; Seo, M.; Okamoto, M.; Nambara, E.; Marion-Poll, A. Functional analysis of Arabidopsis NCED6 and NCED9 genes indicates that ABA synthesized in the endosperm is involved in the induction of seed dormancy. Plant J. 2006, 45, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L.; Soppe, W.J.J.; Xiang, Y. REVERSAL OF RDO5 1, a Homolog of Rice Seed Dormancy4, Interacts with bHLH57 and Controls ABA Biosynthesis and Seed Dormancy in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 1933–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.; Zhu, J.Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Interaction between BZR1 and PIF4 integrates brassinosteroid and environmental responses. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 802–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.A.; Ye, R.G.; Liu, X.; He, Q.Q.; Qiao, J.Y.; Charrier, L.; Geisler, M.; Gao, Z.Y.; Qian, Q.; Qi, Y.H. The OsbHLH166-OsABCB4 module regulates grain length and weight via altering auxin efflux. Sci. Bull. 2025, 70, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.M.; Feng, B.J.; Wen, M.R.; Du, C.; Zhong, X.Q.; Lu, Q.C.; Gong, G.P.; Mo, J.H.; Huang, H.Z.; Zhang, S.C.; et al. The transcription factors PIF4 and PIF5 interact with WRINKLED1 to modulate fatty acid biosynthesis during seed maturation. Plant Physiol. 2025, 197, kiaf141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.Z.; Sun, Y.B.; Gao, Z.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Guo, Q.; Sun, S.K.; Zhang, M.H.; Han, Y.T.; Irfan, M.; Chen, L.J.; et al. LvbHLH13 Regulates Anthocyanin Biosynthesis by Activating the LvMYB5 Promoter in Lily (Lilium ‘Viviana’). Horticulturae 2024, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, P.B.; Chen, G.Q.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.C.; Lian, H.L. FvhHLH9 Functions as a Positive Regulator of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis by Forming a HY5-bHLH9 Transcription Complex in Strawberry Fruits. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.R.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Chang, P.; Li, L.L.; Zhang, L.Y. Identification and Characterization of MYB-bHLH-WD40 Regulatory Complex Members Controlling Anthocyanidin Biosynthesis in Blueberry Fruits Development. Genes 2019, 1010, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yao, Y.; An, L.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yao, X.; Wu, K. Isolation and expression analysis of the HvnAnt2 gene in qingke barley (Hordeum vulgare L. var. nudum Hook. f.) varieties with different grain colours. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2024, 60, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Chen, B.B.; Zhang, G.Y.; Chen, L.X.; Dong, Q.; Wen, J.Q.; Mysore, K.S.; Zhao, J. Regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis by Medicago truncatula bHLH transcription factor MtTT8. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 905–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaart, J.G.; Dubos, C.; De La Fuente, I.R.; van Houwelingen, A.; de Vos, R.C.H.; Jonker, H.H.; Xu, W.J.; Routaboul, J.M.; Lepiniec, L.; Bovy, A.G. Identification and characterization of MYB-bHLH-WD40 regulatory complexes controlling proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa) fruits. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesi, N.; Debeaujon, I.; Jond, C.; Pelletier, G.; Caboche, M.; Lepiniec, L. The TT8 gene encodes a basic helix-loop-helix domain protein required for expression of DFR and BAN genes in Arabidopsis siliques. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1863–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Ha, S.H. A Radish Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factor, RsTT8 Acts a Positive Regulator for Anthocyanin Biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Song, X.X.; Yang, N.; Chen, L.Q.; Xiang, L.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, K.G. Expression of the subgroup IIIf bHLH transcription factor CpbHLH1 from Chimonanthus praecox (L.) in transgenic model plants inhibits anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Cell Rep. 2020, 39, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Z.; Liu, S.; Zeng, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Cai, N. Exploring the Molecular Mechanism underlying the Stable Purple-Red Leaf Phenotype in Lagerstroemia indica cv. Ebony Embers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Shen, P.; Chi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, M.; Pan, H. The anthocyanin formation of purple leaf is associated with the activation of LfiHY5 and LfiMYB75 in crape myrtle. Hortic. Plant J. 2024, 10, 1230–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liang, X.H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.R.; Cai, M.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.R.; Zhang, Q.X.; Pan, H.T. Functional analysis of Aux/IAAs and SAURs on shoot growth of Lagerstroemia indica through virus-Induced gene silencing (VIGS). Forests 2020, 11, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.C.; Chen, Z.L.; Ju, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Cai, M.; Pan, H.T.; Zhang, Q.X. Reference gene selection for qRT-PCR analysis of flower development in Lagerstroemia indica and L. speciosa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.; Dolan, L. The arabidopsis bHLH transcription factor family. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Ji, X.Y.; Nie, X.G.; Qu, M.; Zheng, L.; Tan, Z.L.; Zhao, H.M.; Huo, L.; Liu, S.N.; Zhang, B.; et al. Arabidopsis AtbHLH112 regulates the expression of genes involved in abiotic stress tolerance by binding to their E-box and GCG-box motifs. New Phytol. 2015, 207, 692–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, Y.; Gou, L.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Pi, E. Regulatory Mechanisms of bHLH Transcription Factors in Plant Adaptive Responses to Various Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 677611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.C.; Martin, C.; Toledo-Ortiz, G.; Quail, P.H.; Huq, E.; Heim, M.A.; Jakoby, M.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. Update on the basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2497–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Chen, H. Comparative functional genomics analysis of bHLH gene family in rice, maize and wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Jakada, B.H.; Fakher, B.; Greaves, J.G.; Niu, X.; Su, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, S.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y. Genome-wide study of pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) bHLH transcription factors indicates that cryptochrome-interacting bHLH2 (AcCIB2) participates in flowering time regulation and abiotic stress response. BMC Genomics 2020, 21, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.; Tao, W.; Li, T.; Pan, W.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Nie, X.; Cui, L. Genome-wide Identification, Evolution and Expression Analysis of Basic Helix-loop-helix (bHLH) Gene Family in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Curr. Genomics 2020, 21, 624–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Bai, M.; Chen, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yang, L.; Gu, C. Identification of bHLH transcription factors and screening of anthocyanin-related genes in Lagerstroemia indica. Genetica 2024, 152, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhao, T.; Du, D.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Sun, Y.; Pan, Y. Genome- and Transcriptome-Wide Characterization and Expression Analyses of bHLH Transcription Factor Family Reveal Their Relevance to Salt Stress Response in Tomato. Plants 2025, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lv, W.; Zhang, H.; Ma, L.; Li, P.; Ge, L.; Li, G. Genome-wide analysis of the basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor family in maize. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Ai, W.; Lu, X. Genome-Wide Identification of the bHLH Gene Family in Magnolia sieboldii and Response of MsPIFs to Different Light Qualities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Lin, X.; Wei, M.; Feng, G.; Liu, H.; Shao, J.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Z. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) Transcription Factor Family in Gastrodia elata. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 43, 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Guo, C.; Shan, H.; Kong, H. Divergence of duplicate genes in exon–intron structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.Q.; Ding, A.Q.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.R.; Bao, F.; Zhang, Q.X. Genome-Wide Identification and Low-Temperature Expression Analysis of bHLH Genes in Prunus mume. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 762135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Geng, L.; Jiang, L.; Sui, Y.; Luo, L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C. Genome-wide identification of the bHLH transcription factor family in Rosa persica and response to low-temperature stress. PeerJ 2024, 11, e16568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liang, Y.X.; Yan, T.T.; Wang, X.C.; Zhou, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, B.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Liao, J.C.; et al. The photomorphogenic repressors BBX28 and BBX29 integrate light and brassinosteroid signaling to inhibit seedling development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 2266–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.E.; Moreno-Piovano, G.; Chan, R.L. The antagonistic basic helix-loop-helix partners BEE and IBH1 contribute to control plant tolerance to abiotic stress. Plant Sci. 2018, 271, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAlister, C.A.; Ohashi-Ito, K.; Bergmann, D.C. Transcription factor control of asymmetric cell divisions that establish the stomatal lineage. Nature 2007, 445, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, M.; Sato, A.; Renhu, N.; Yamamoto, T.; Oka, N.; Zhu, J.K.; Tada, Y.; Suzaki, T.; Miura, K. MYC-type transcription factors, MYC67 and MYC70, interact with ICE1 and negatively regulate cold tolerance in Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakov, V.P.; Fialko, A.; Yugay, Y.A. Involvement of epigenetic factors in flavonoid accumulation during plant cold adaptation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 216, 109096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Yu, W.; Gao, Y.; Ni, J.; Yin, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Bai, S.; Teng, Y. Light-Induced Basic/Helix-Loop-Helix64 Enhances Anthocyanin Biosynthesis and Undergoes CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC1-Mediated Degradation in Pear. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 1684–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Zhao, C.Z.; Wang, S.W.; Gao, N.; Wang, X.X.; Na, X.F.; Wang, X.M.; Bi, Y.R. PIF4-PAP1 interaction affects MYB-bHLH-WD40 complex formation and anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 268, 153558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Park, E.; Choi, G. PIF3 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in an HY5-dependent manner with both factors directly binding anthocyanin biosynthetic gene promoters in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 49, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, L.; Guo, Y.; Han, X.; Ding, A.; Shu, J. Genome-Wide Identification of the bHLH Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Anthocyanin Synthesis in Lagerstroemia indica Leaves. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101219
Feng L, Guo Y, Han X, Ding A, Shu J. Genome-Wide Identification of the bHLH Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Anthocyanin Synthesis in Lagerstroemia indica Leaves. Horticulturae. 2025; 11(10):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101219
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Lu, Yanhong Guo, Xu Han, Aiqin Ding, and Jing Shu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of the bHLH Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Anthocyanin Synthesis in Lagerstroemia indica Leaves" Horticulturae 11, no. 10: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101219
APA StyleFeng, L., Guo, Y., Han, X., Ding, A., & Shu, J. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of the bHLH Gene Family and Expression Analysis in Anthocyanin Synthesis in Lagerstroemia indica Leaves. Horticulturae, 11(10), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11101219





