Abstract
Postharvest shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edodes) often undergo browning under low-temperature, high-humidity storage conditions, which significantly reduces their commercial value and constrains industry development. However, the molecular mechanisms regulating this process remain unclear. In this study, we used ‘Nongxiang No. 1’ as the experimental material and observed that during storage, the L* value of caps and stipes decreased continuously, shifting from light brown to dark brown-black. Concurrently, the relative electrical conductivity increased by approximately 3.07-fold, and the membrane lipid peroxidation product malondialdehyde (MDA) content increased by approximately 7.9-fold. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity initially increased then declined, indicating that elevated membrane permeability accelerates senescence. Peroxidase (POD) activity exhibited a significant upward then downward trend and improved 75.83% at day 22 of postharvest storage, with LEHP1, LEHP2, and LEHP3 gene expression patterns closely aligning with these changes. Specifically, LEHP2 and LEHP3 expression was upregulated by 23.8-fold and 2.35-fold on day 22 than day 0. Cis-element analysis identified MYB binding sites in all three LEHP genes. Genome-wide screening combined with qRT-PCR revealed two MYB transcription factors, LeMYB2 and LeMYB5, whose expression synchronized with LEHP genes. Transient expression assays in tobacco leaves confirmed their nuclear localization, consistent with transcription factor characteristics. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) and Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay (DLR) experiments further demonstrated that LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 directly activate LEHP2 and LEHP3 promoters, highlighting their key regulatory roles in postharvest browning of shiitake mushrooms.
1. Introduction
Lentinula edodes, also known as shiitake mushroom, is a basidiomycete fungus belonging to the family Tricholomataceae within the order Agaricales of the class Basidiomycetes. As a medicinal and edible mushroom, it is rich in nutrients and bioactive compounds [1,2]. In recent years, the global demand for fresh shiitake mushrooms has surged, positioning China as the world’s leading producer and exporter. In 2023, China’s shiitake mushroom production reached approximately 13.04 million tons, maintaining its status as the top cultivated edible fungus [3]. The increasing yield has led to widespread acceptance of shiitake mushroom prices, making it a key component in the recommended dietary pattern by FAO [4]. Fresh shiitake mushrooms contain over 90% water; during postharvest storage and transportation, they maintain high respiration rates and metabolic activity. The endogenous nutrients are rapidly depleted, and due to the absence of protective periderm or wax layers on the surface, they are highly susceptible to mechanical damage [5,6]. Consequently, during storage and shelf life, quality deterioration phenomena such as water loss, cap opening, epidermal damage, browning of the mushroom flesh, decay, and off-odor are common, leading to loss of commercial value and economic losses [7]. Notably, browning significantly impacts the marketability of shiitake mushrooms [8].
Although browning of postharvest shiitake mushrooms has become one of the critical industry issues requiring urgent resolution, research on the regulatory mechanisms underlying browning remains significantly lagging behind that of other horticultural products. Browning in postharvest shiitake mushrooms primarily involves enzymatic browning and non-enzymatic browning. Enzymatic browning is a damaging process characterized by cellular damage: during senescence of mushroom, the intercellular membranes are disrupted, allowing phenolic substrates to interact extensively with browning-related enzymes such as peroxidase (POD) and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) [8,9,10]. Concurrently, the depletion of soluble proteins, carbohydrates, and other nutrients further accelerates cellular disintegration, thereby promoting enzymatic browning [8]. Current research on the browning of fresh shiitake mushrooms predominantly focuses on analyzing enzyme activities, such as those of PPO, and elucidating their mechanisms [11,12,13,14]. However, despite mentions of peroxidase in the context of fungal browning, there is a paucity of in-depth studies on the screening and mechanistic analysis of key regulatory genes involved in peroxidase activity [8]. Peroxidase is an enzyme capable of catalyzing the oxidation of hydrogen peroxide, phenolic compounds, and hydrocarbon oxidation products [15], playing a vital role in the browning process of horticultural products [7,16,17]. PODs can be categorized into three types—Type I, II, and III—based on their sequence and origin. Type I includes non-secretory proteins, Type II consists of secretory proteins mainly found within fungal genomes, and Type III comprises plant-specific secretory peroxidases [18]. Heme peroxidases (HPs), which belong to Type I peroxidases, are known for their strong antioxidant activity. They use hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as an electron acceptor to catalyze redox reactions involving phenolics, ascorbic acid, indole compounds, and inorganic ions [19]. These enzymatic activities are closely linked to postharvest problems in plants, such as browning, texture deterioration, and nutrient loss [20]. Although large fungi possess extensive peroxidase systems, the specific role of heme peroxidases in the postharvest storage of shiitake mushrooms remains unclear.
Transcription factors (TFs) are proteins present in eukaryotic organisms that regulate gene transcription by binding to cis-acting elements of target genes, thereby activating or repressing their expression [21]. This mechanism constitutes a primary pathway for the regulation of gene expression at the transcriptional level. Transcription factors encompass families such as MYB, bHLH, bZIP, AP2/ERF/GCC box, WRKY (characterized by WRKYGQK motif and zinc finger domains) [21]. MYB TFs are ubiquitously distributed in eukaryotes and play crucial roles in plant physiological processes, including primary and secondary metabolism, developmental regulation, and responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Notably, MYB proteins serve as key regulators in phenolic compound metabolism, with well-studied roles in the biosynthesis of proanthocyanidins, anthocyanins, flavonoids, and lignin [22]. Furthermore, research indicates MYB transcription factors also presented in fungi; however, studies on MYB TFs are more prevalent in small-sized fungi, with comparatively limited research in larger fungi, and even fewer investigations in shiitake mushrooms [23,24,25]. Moreover, the specific functions of MYB transcription factors in browning processes remain unclear.
This study characterizes the browning process of shiitake mushrooms during postharvest storage by measuring L values. To further elucidate the underlying mechanisms of browning, genes closely associated with this process were then identified. Subsequent gene characterization and validation were conducted, and a comprehensive investigation into the transcriptional regulation mechanism of the LeMYB transcription factor on the LEHPs gene during postharvest browning was performed using molecular biology techniques. Despite extensive research on postharvest browning in mushrooms, the specific regulatory interactions between LeMYB transcription factors and key enzymes like LEHPs remain poorly understood. This study fills this critical gap by systematically unraveling the transcriptional network linking LeMYB to POD activity, which has not been previously reported in shiitake mushrooms. The findings provide valuable insights into the molecular basis of browning in shiitake mushrooms, offering a significant reference for future research into its underlying mechanisms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials of Shiitake Mushrooms
The tested shiitake mushroom variety is Nongxiang No. 1, harvested from Shanxi Guangling Beiye Edible Mushroom Development Co., Ltd. (Datong, China). Fresh Shiitake mushrooms with optimal growth conditions, uniform cap development, consistent developmental stages, free from mechanical damage, and unopened caps were selected as samples. Immediately after harvesting, the mushrooms were transported to the laboratory and stored in a cold storage for preservation, in which the temperature was 3 °C, and RH was 85~90%.
2.2. Assessment of Browning Degree and Measurement of Skin Color
The L* value s was assessed referring the method of Deng et al. [26] with certain modifications. Shiitake mushroom fruiting bodies from the same batch at different storage time points were dissected to observe internal mycelial color changes. Colorimetric analysis was performed using the UltraScanPRO colorimeter (Beijing Xinaoyike Optoelectronic Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) to determine the surface whiteness value of the Shiitake mushrooms, expressed as L*. The experiment was carried out using three biological replicates. A higher L* value indicated a lighter degree of browning [13].
2.3. Sampling and Processing of Shiitake Mushroom Fruiting Body
Fresh shiitake mushrooms were stored at 3 °C, with cap samples collected at days 0, 3, 7, 12, 22, 27, and 34 of storage (the sampling method is shown in Figure S1). Hemispherical slices were cut along the center axis of the mushroom samples, and then the samples were chopped and mixed, rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen, and subsequently stored in aliquots at −80 °C for future analysis.
2.4. Measurement of Browning Related Indices
2.4.1. POD Activity Assay
A hemispherical section of the shiitake mushroom was excised along the central axis, minced, and homogenized. Precisely 2 g of the homogenate was measured and transferred into a mortar, to which 8 mL of isotonic saline solution was added. The mixture was ground into a slurry on ice, and the entire homogenate was subsequently transferred into a 10 mL centrifuge tube. Following centrifugation at 4000 rpm for 10 min, the supernatant was collected for enzymatic activity analysis. POD activity was quantified using a commercial assay kit (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China), the experiment was conducted with three independent biological replicates.
2.4.2. SOD Activity Assay
Sample collection and processing followed the same procedure as Section 2.4.1 SOD activity was measured using a specific SOD activity assay kit (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The experiment was performed with three independent biological replicates.
2.4.3. MDA Content Determination
MDA levels were quantified using a commercial MDA assay kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China). Sample preparation was consistent with the above method, and MDA content was measured according to the kit instructions. Three biological replicates were performed, and the average value was reported.
2.4.4. Relative Electrical Conductivity Measurement
This section is referenced from the method of Guo et al. [13] with some modifications. The cap tissue of L. edodes was sectioned into small fragments using a sterile scalpel. A total of 2 g aliquot was transferred into a 50 mL centrifuge tube containing 30 mL of ultrapure water. The initial electrical conductance was measured as (P0). The sample was then incubated at 25 °C for 1 h, and the electrical conductance was recorded as (P1). Subsequently, the sample was subjected to thermal denaturation by boiling in water for 30 min, cooled to ambient temperature (25 °C), and the final conductance was measured as (P2). The experiment was performed with three independent biological replicates. The relative electrical conductivity was calculated using the formula:
Relative conductivity (%) = [(P1 − P0)/(P2 − P0)] × 100%.
2.5. Relative Expression Measurements of Selected Genes
2.5.1. Extraction of Total RNA from Shiitake Mushrooms
The mushroom tissues were pulverized into fine powder in liquid nitrogen utilizing a mortar and pestle. A 1 g aliquot of the powder was subjected to total RNA isolation according to the manufacturer’s protocol of the Polysaccharides & Polyphenolics-rich Plant Total RNA Kit (Hangzhou Simgen Biological Reagents Development Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China). The yield and purity of the isolated RNA were quantified using a high-precision UV spectrophotometer, and RNA integrity was evaluated through agarose gel electrophoresis. RNA samples exhibiting optimal concentration, purity, and integrity were stored at −80 °C. The experiment was performed with three independent biological replicates.
2.5.2. Reverse Transcription of RNA
Total RNA was subjected to reverse transcription to synthesize complementary DNA (cDNA) utilizing the PrimeScriptTM RT reagent Kit (Beijing Quanshijin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) with gDNA Eraser, in accordance with the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.5.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Primer sequences for upstream and downstream amplification were designed using Primer 5.0 software and synthesized by Beijing Tsingke Biotech Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) (Table S1). The fluorescent dye SYBR Green used in the reaction was obtained from BIO-RAD. The β-Actin gene served as the internal reference; the relative gene expression levels were quantified using the 2−ΔΔCt method [27]. The experiment was performed with three independent biological replicates.
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis and Subcellular Localization of the LeMYB2/5
2.6.1. Bioinformatics Analysis of the LeMYB2/5 Gene Family
The gene structures of selected MYB transcription factors were analyzed and visualized using Tbtools 2.341 software [28]. Nucleic acid properties were examined with the online Sequence Manipulation Suite (https://annotathon.org/sms2/, accessed on 15 July 2025). Protein molecular formulas, amino acid residue counts, relative molecular weights, isoelectric points, instability indices, aliphatic indices, and total average hydropathicity were analyzed using the online ProtParam tool (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 15 July 2025). Conserved motifs within the proteins were identified and illustrated via MEME Suite (https://meme-suite.org/meme/, accessed on 15 July 2025), while secondary structural distributions were analyzed and mapped using the online PRABI platform.
2.6.2. Subcellular Localization of LeMYB2/5 Transcription Factors in Tobacco
The experimental method was referred from Yuan et al. and Deng et al. [25,27] with some modifications. Fusion constructs of pEAQ-GFP-MYB2 and pEAQ-GFP-MYB5 driven by the CaMV 35S promoter were generated (the primers used to construct the MYB-2/5-GFP vector are shown in Table S2). The pEAQ-GFP vector served as a control. These constructs were transiently expressed in five-week-old Nicotiana tabacum via agroinfiltration. Fluorescent signals were observed using fluorescence inverted microscopy.
2.7. EMSA
The method from Yuan et al. [25] was carried out with slight modifications. The coding sequences of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 were cloned into the pCold GST expression vector (using KpnI and PstI sites) and transformed into Escherichia coli Transetta cells (the primers used to construct the MYB-2/5-pCold GST vector are shown in Table S3). Bacterial cultures were induced with 0.1 mM IPTG at 15 °C for 24 h. Cells were harvested and lysed via sonication. The fusion proteins were purified using buffers containing varying imidazole concentrations. Protein purity was assessed by SDS-PAGE. Biotin-labeled probes were synthesized by labeling the core sequence of the target gene promoter (CAGTTG) with a 3’ biotin labeling kit (the Promoter Probe Primer is shown in Table S4). EMSA was performed using the Chemiluminescent EMSA Kit from Beyotime Biotechnology (Shanghai, China).
2.8. DLR
The experimental method from Yuan et al. [25] was carried out with slight modifications. The transcriptional regulation of the target gene (POD) by MYB transcription factors was evaluated using a dual-luciferase transient expression system. Full-length MYB sequences were cloned into the pEAQ vector as effectors (the primers sequences of dual-luciferase reporter gene experimental vector are shown in Table S5), while the promoter region of the target gene was inserted into the pGREENII0800-LUC vector as the reporter. These constructs were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain EHA105, cultured, and adjusted to an OD600 of 0.5 with infiltration buffer. The effector and reporter constructs were mixed at a 9:1 ratio and infiltrated into tobacco leaves. After 60 h of incubation in a controlled environment chamber, samples were collected for luciferase (LUC) and Renilla (REN) enzyme activity assays, performed by Yeasen Biotechnology (Shanghai, China).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
All data were statistically analyzed using SPSS 27.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and are presented as mean ± SD of three independent replicates. Differences with a p-value less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism 9.5.0.
3. Results
3.1. The Browning Degree of Shiitake Mushroom—The Color of the Cap and the Flesh
As shown in Figure 1A,B, during storage, the whiteness (L*) values of both the cap and the flesh of the shiitake mushrooms exhibited a decreasing trend, with the highest values at day 0 and the lowest at day 34. Figure 1C illustrated that, in terms of visual appearance, the cap’s brown coloration gradually intensifies, turning to a dark brown-black by day 34. The browning process is notably pronounced, and the commercial value diminishes progressively during storage. The browning of the cap can serve as a primary physiological phenotype for studying shiitake mushroom browning.
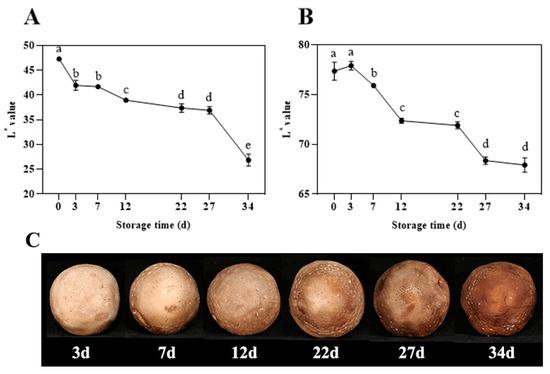
Figure 1.
Changes in L* value of cap (A) and fruitbody (B), and appearance (C) of shiitake mushrooms during storage. Variations in lowercase letters signify a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) at different times.
3.2. Browning Related Indices During the Storage of Shiitake Mushrooms
3.2.1. Results of SOD Enzyme Activity, MDA Levels, and Electrical Conductivity Changes During the Storage of Shiitake Mushrooms
As shown in Figure 2A, during the entire storage, SOD activity exhibited an initial increase followed by a decline. From days 0 to 7 of storage, the SOD activity within the fruiting bodies gradually rises, reaching a peak of 1538.73 U g−1 on the 7th day. From days 7 to 27, SOD enzyme activity showed a decreasing trend. The MDA content, as depicted in Figure 2B, generally increased throughout the storage, rising from an initial 9.9 nmol mg−1 to 78.20 nmol mg−1, with a brief decrease in the early stage, possibly due to reduced accumulation of harmful substances within cells under low-temperature storage. As storage time extends, the MDA levels in the mushrooms gradually increase. According to Figure 2C, with prolonged storage, the relative electrical conductivity showed an overall upward trend, indicated a gradual increase in cell membrane permeability. During the first 3 days of storage, the membrane permeability slightly increases. After day 3, the permeability of the mushroom cell membrane rapidly rises, reaching a relative electrical conductivity of 48.86% after 22 days. Throughout the storage period, by day 34, the membrane permeability of the mushrooms increases to 57.96%.
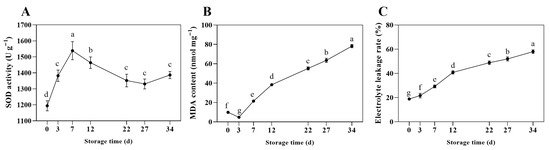
Figure 2.
Changes in SOD enzyme activity (A), MDA levels (B), and electrical conductivity (C) of shiitake mushrooms during storage. Variations in lowercase letters signify a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) at different times.
3.2.2. Results of POD Enzyme Activity and LEHPs Gene Relative Expression Changes During the Storage of Shiitake Mushrooms
As illustrated in Figure 3A, the POD enzymatic activity within the fungal fruiting body during postharvest storage demonstrated an initial upregulation followed by a rapid decline. Specifically, from day 0 to day 22, enzymatic activity increased from 150.33 U·g−1 to 264.33 U·g−1, reaching a maximum at day 22 before decreasing subsequently. Concurrently, the transcriptional levels of the LEHP gene family during storage were quantified (Figure 3B–D). The data revealed that the expression profiles of LEHP1, LEHP2, and LEHP3 predominantly exhibited an initial induction followed by repression throughout the storage period, with all expression levels significantly exceeding those observed at baseline. The peak relative expression levels occurred at days 27, 22, and 22, with values of 22.44, 23.82, and 2.36, respectively. The overall gene expression trajectories aligned with the observed fluctuations in POD enzymatic activity.
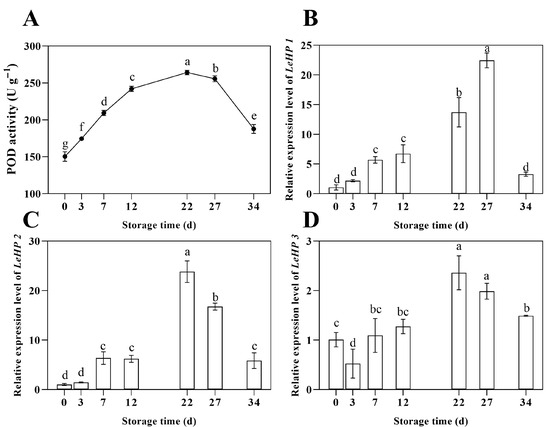
Figure 3.
Changes in POD enzyme activity (A), relative expression level of LEHP1 (B), LEHP2 (C), and LEHP3 (D) of shiitake mushrooms during storage. Variations in lowercase letters signify a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) at different times.
3.3. Analysis of Cis-Acting Progenitors of the LEHP 1, 2, 3 Gene
As illustrated in Figure 4, the Shiitake mushroom LEHPs gene contains multiple cis-acting elements associated with hormone responsive, stress response, and light responsive, as well as binding sites for transcription factors. This finding suggested that the Shiitake mushroom LEHPs gene may be regulated by MYB transcription factors to exert its functional role.
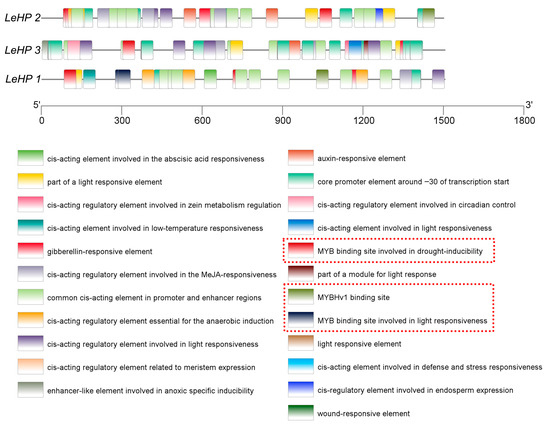
Figure 4.
Promoter cis-regulatory element analysis for the LEHPs genes (Different colored cartons show various cis-regulatory elements), the regions highlighted by the red boxes in the figure correspond to the cis-regulatory elements of MYB transcription factors.
3.4. LeMYB Gene Relative Expression Changes During the Storage of Shiitake Mushrooms
As illustrated in Figure 5, during the postharvest storage of shiitake mushrooms, the expression levels of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 genes exhibited a notable peak prior to day 12, specifically on days 3 and 7, respectively. Subsequently, both MYB transcription factors demonstrated a gradual increase in expression after day 12. The relative expression levels of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 reached their maximum at day 27 of storage, with values of 190.03 and 464.70, respectively. The overall expression patterns of these transcription factors were consistent with the trend observed for the LEHP gene.
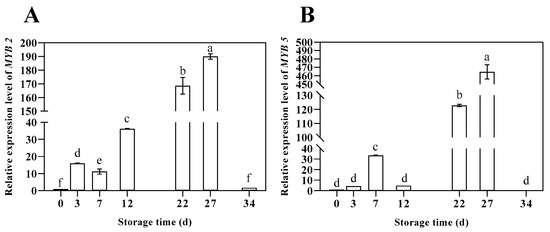
Figure 5.
Changes in relative expression level of MYB2 (A) and MYB5 (B) of shiitake mushrooms during storage. Variations in lowercase letters signify a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) at different times.
3.5. Bioinformatics Analysis and Subcellular Localization of LeMYB2/5
3.5.1. Bioinformatics Analysis of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5
Gene structure prediction results indicated that the DNA sequences of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 contain eight and five exons, respectively (Figure S2). Protein basic property predictions, summarized in Table S6, revealed that LeMYB2 has a relatively lower molecular weight (20,155.10 Da), whereas LeMYB5 exhibited a higher molecular weight (46,710.56 Da). Composition analysis showed that leucine and serine were the most abundant amino acids in both LeMYB transcription factors. The theoretical isoelectric point ranged from 65.38 to 85.93, with an average hydrophobicity index between −0.88 and −0.65, and an instability index from 49.08 to 59.87. Eukaryotic cell half-life predictions suggested a stability exceeding 20 h for both proteins, indicated that these LeMYB proteins were hydrophilic and stable. MEME motif analysis identified ten conserved motifs, each distributed across both LeMYB proteins (Figure S3). Secondary structure predictions showed that the structural compositions of the two LeMYB transcription factors are similar, predominantly consisting of unordered coils (Cc) and alpha-helices (Hh) (Table S7). Distribution analysis revealed that these structural elements are evenly dispersed throughout the entire amino acid sequences (Figure S4).
3.5.2. Subcellular Localization of LeMYB2/5 Transcription Factors
As shown in the figure, the positive control exhibited prominent green fluorescence labeling around the cells. The fusion proteins of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 emitted fluorescent signals localized within the nucleus (Figure 6), indicated that both LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 were nuclear proteins.
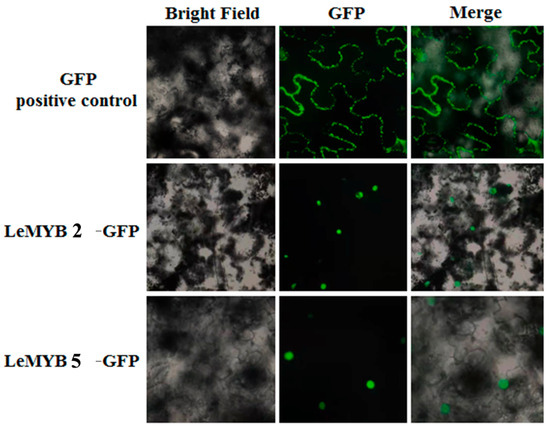
Figure 6.
Subcellular localization of LeMYB2/5.
3.6. Browning Regulation Mechanisms Mediated by LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 in Postharvest Shiitake Mushrooms
3.6.1. Analys of EMSA
As shown in Figure 7A,B, the purified LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 proteins exhibited bands consistent with the predicted molecular weights of the fusion proteins, indicated high purity and concentration of a single band, suitable for EMSA analysis. Figure 7C–F demonstrated that when only labeled probes were added, a single probe band is observed. Upon addition of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 proteins along with the labeled probes, a shifted band corresponding to protein–probe complexes appeared in the upper region. When an excess of unlabeled probe was introduced prior to the labeled probe, the intensity of the protein–probe complex diminished, indicated competitive binding. Conversely, the addition of mutated probes at equivalent molar ratios does not affect the formation of the protein–probe complexes. These results collectively confirmed that LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 specifically bind to the promoter elements of LEHP2 and LEHP3.
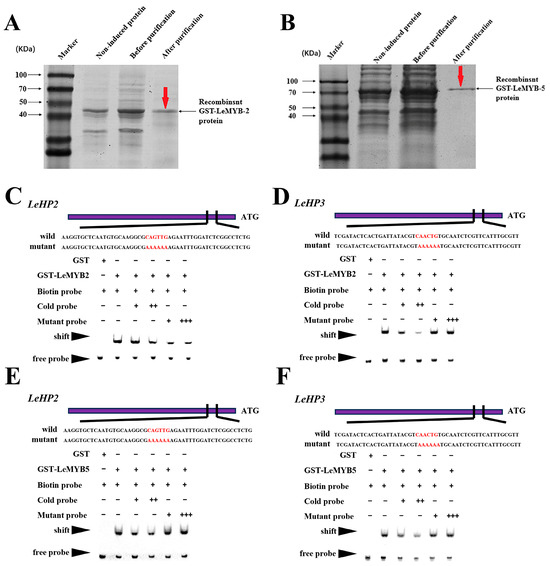
Figure 7.
SDS-SPAG gel detection of purified LeMYB2 (A) and LeMYB5 (B) proteins, EMSA validation of LeMYB2 bind promoters’ elements in the promoters of LEHP2 (C), LeMYB2 bind promoters’ elements in the promoters of LEHP3 (D), LeMYB5 bind promoters’ elements in the promoters of LEHP2 (E), LeMYB5 bind promoters’ elements in the promoters of LEHP3 (F). The promoter elements are indicated in red font; “Mutant” denoted probes derived from promoter mutations; “Biotin Probe” referred to biotin-labeled probes; “Cold Probe” indicated unlabeled probes without biotin modification.
3.6.2. Analys of DLR
The proteins of transcription factors LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 specifically bind to the promoters of LEHP2 and LEHP3 (Figure 8A). When the LUC/REN values of the negative control were set as 1, co-introduction of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 with LEHP2 and LEHP3 into tobacco results in significantly elevated LUC/REN ratios compared to the negative control, indicating that LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 can activate the promoter activity of LEHP2 and LEHP3 (Figure 8C,D).
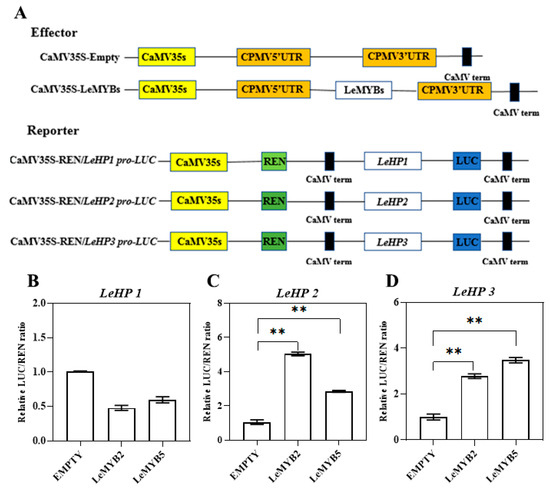
Figure 8.
The in vivo activation of LeMYB2/5 on the promoters of LEHP2 and LEHP3: Schematic diagram of reporter and effector constructs (A); LUC/REN ratio of the LEHP1 promoter (B); LUC/REN ratio of the LEHP2 promoter (C); LUC/REN ratio of the LEHP3 promoter (D). Variations in ** signify a statistically significant difference (p < 0.01) at different times.
4. Discussion
This study focuses on the fruiting body of Shiitake mushroom ‘Nongxiang No. 1’, systematically analyzed the physiological phenotypic characteristics associated with postharvest browning. It revealed that the transcription factors LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 participated in the browning process by directly activating the expression of LEHP2 and LEHP3 genes. These findings provide new theoretical insights into the regulatory network governing postharvest browning in Shiitake mushrooms and offer methodological references for analyzing the relationship between transcription factors and enzyme activity in postharvest physiology of edible fungi.
L* values serve as a primary quality indicator for evaluating browning in edible fungi [13]. Over storage duration, the L* values of the cap and flesh continuously decline, indicated a color change from light brown to dark brownish black (Figure 1). Cellular damage in fresh mushrooms, closely associated with membrane lipid peroxidation induced by reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation, contributes to this process. MDA, a byproduct of lipid peroxidation, functions as an effective marker for membrane damage. Although cell membranes typically exhibit selective permeability, environmental stressors cause electrolyte leakage due to alterations in lipid composition and membrane structure, resulting in increased conductivity. The attack of reactive oxygen species accelerates lipid oxidation of the mushroom cell membrane, enhancing membrane permeability and damage, which triggers programmed cell death and subsequently induces browning [12,13]. The findings of this study demonstrated that with prolonged storage, relative electrical conductivity and MDA content significantly increase (Figure 2B,C), indicated heightened membrane permeability and an accelerated browning process in shiitake mushrooms; this process appears to involve participation of related enzymatic activities. POD, SOD, and other enzymes are critical indicators for assessing the stress resistance of edible fungi [13]. Normal physiological metabolism in plants produces ROS; to mitigate ROS accumulation, the organism activates specific defense regulatory systems. Enzymes such as SOD and POD play prominent roles in scavenging ROS within the organism. SOD catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide anion radicals generated during metabolism into less toxic H2O2. POD effectively decomposes H2O2, converting it into harmless water and oxygen. In the presence of H2O2, POD also facilitates the breakdown of lethal and pathogenic oxidative phenolic compounds, thereby enhancing the organism’s self-defense mechanisms [13,29,30], but also exacerbate the browning process [31]. In this study, SOD and POD activities initially increased and subsequently decreased over the storage period (Figure 2A and Figure 3A). Similar trends have been reported by Guo et al. and Liu et al. [12,13], indicated a consistent pattern of enzymatic activity throughout storage. Further specific analysis of shiitake mushrooms confirmed this general trend, demonstrating a strong correlation between these enzymatic activities and browning progression, Related studies have also reported that POD is one of the enzymes responsible for the browning of litchi [32]. HPs constitute a class of peroxidases, with identified members spanning from green algae to angiosperms [20]. In this study, 3 LEHP genes were also identified from the mushroom genome, and their expression levels were analyzed across different storage stages. The results showed that LEHP1, LEHP2, and LEHP3 exhibited a pattern of initial upregulation followed by downregulation, consistent with the trend observed in POD activity (Figure 3B–D). The up-regulation of LEHPs expression may promoted polyphenol oxidation reaction and accelerated the browning process in conjunction with the elevated POD activity. This synergy suggested that the LEHPs gene may serve as a key molecular basis for the regulation of POD activity. Further cis-acting element analysis indicated that the L. edodes HPs genes contain cis-acting elements and MYB binding sites associated with plant hormones, stress responses, and light signaling (Figure 4), suggested that their regulatory function may be mediated through MYB transcription factors.
Transcription factors are extensively involved in fungal development and stress responses [24]. Structural analysis indicates that transcription factors typically comprise four domains: a DNA-binding domain, a transcriptional regulatory domain, a nuclear localization signal, and oligomerization sites [21,22]. Among the most studied transcription factors, the MYB gene family represents the largest class, widely distributed across eukaryotes [24]. This study, based on genomic analysis and relative expression pattern in Shiitake mushroom, identified 2 MYB transcription factors whose expression patterns are consistent with the LEHP gene (Figure 5). Subcellular localization assays revealed that both LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 are nuclear proteins (Figure 6). The presence of MYB binding sites within the LEHP promoter region further supported that LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 exhibited fundamental characteristics of transcription factors. MYB transcription factors extensively involved in diverse biological processes including developmental regulation, secondary metabolite biosynthesis, hormone signal transduction, and responses to biotic stresses (such as pathogens) as well as abiotic stresses (such as drought, low temperature, and salinity) [22,24,25]. Recent advances in functional studies of the MYB family have elucidated their specific regulatory mechanisms across various plant species. Notably, in the context of secondary metabolite biosynthesis, MYB transcription factors exhibit prominent roles. For instance, systematic phylogenetic analyses, co-expression network assessments, and functional validations have demonstrated that jsMYB141 and jsMYB170 modulate key genes in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway (PAL, 4CL, CHI, FLS), thereby influencing the accumulation of phenolic compounds such as quercetin, kaempferol, and rutin [33]. Similar breakthroughs have been achieved in Camellia sinensis, where integrated transcriptomic, metabolomic, and biochemical-genetic data reveal that the tea MYB transcription factor family (including MYB8, MYB99, MYB85, MYB86) plays critical roles in the development of apical meristems (involving stem, epidermal cells, stomata) and in the biosynthesis of flavonoids (e.g., catechins, anthocyanins), caffeine, and theanine. These studies further delineate the molecular mechanisms underlying the regulation of phenolic compounds such as catechins and flavonols [34]. Additionally, the regulation of postharvest physiological processes by MYB transcription factors is increasingly recognized. In studies of tuber browning post-cutting in potato, Meng et al. [35] identified that the R2R3-MYB transcription factor StODO1 directly binds to and activates the promoters of StuPPO1-3 genes. Overexpression of StODO1 in potato tubers markedly enhances browning, correlating with increased polyphenol oxidase (PPO) activity, total phenolic content, and decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. In this study, EMSA and DLR assays confirmed that LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 directly activate the promoters of LEHP2 and LEHP3 genes in L. edodes (Figure 7 and Figure 8), with subcellular localization and DNA-binding assays indicating their capacity to regulate LEHP gene transcription. By modulating heme oxygenase activity, these MYB factors influence postharvest browning in edible fungi, highlighting their critical roles in fungal physiology after harvest. However, it was also important to note that browning became severe on day 34, whereas the activities of POD and the expression levels of LEHPs and LeMYB2/5 showed a tendency to decline after 22–27 days. This observation aligns with reports by Liu et al. [12], which indicated that with extended storage duration, the browning degree of Agaricus bisporus deepens, accompanied by a gradual increase in MDA content and relative electrical conductivity; conversely, the activities of POD and SOD enzymes exhibit a pattern of initial elevation followed by reduction. Additionally, during apple browning, Zhao et al. [36] observed that the browning of fresh-cut apples intensified over time, with SOD, POD, and PPO enzyme activities displaying a similar rise-then-fall trend. The occurrence of this phenomenon may be attributed to several factors: (1) accumulation and ongoing reactions of browning products—although the activity of the MYB-LEHP module declines after 22–27 days, phenolic substrates and ROS accumulated and activated early on may persist. When POD activity peaks early, substantial quinone intermediates are generated, which can subsequently undergo non-enzymatic spontaneous polymerization, leading to the formation of stable melanin pigments. Research indicates that phenolic compounds can undergo autoxidation and produce browning products even in the absence of enzymes [37]. This process results in pronounced browning observed at day 34, representing a delayed effect where browning becomes visually apparent only after gene expression has decreased. (2) The browning process is regulated by multiple factors; browning is not solely controlled by the MYB-LEHP module. In the later stages of storage, other factors may predominate, such as physical damage, which can cause gradual disintegration of cell wall and membrane structures, releasing more phenolic compounds and enzymes, thereby exacerbating browning [12]. Additionally, there may be other unidentified regulatory factors, such as transcription factors or signaling pathways that become dominant in the later stages. Therefore, while the MYB-LEHP module plays a critical role in initiating browning, the subsequent browning process is driven by a complex interplay of early accumulated products, physical damage, and other unknown factors. This underscores that browning is a multi-stage, multi-factorially regulated dynamic process, and the activity of a single module cannot fully predict the final browning outcome.
This discovery broadens the understanding of MYB functions within edible mushroom biology. In summary, MYB transcription factors are not only central to traditional roles in plant growth and development, but also exhibit functional versatility in secondary metabolite accumulation, stress responses, and postharvest physiological regulation. These findings underscore the importance of MYB transcription factors not only in traditional plant growth and development but also in advancing sustainable agricultural practices through their multifaceted regulatory roles.
5. Conclusions
The study identified a significant correlation between POD activity and postharvest browning phenotypes, with POD activity dynamics closely mirroring browning progression. Expression analysis of LEHP genes demonstrated congruent expression patterns with POD activity fluctuations. Promoter analysis revealed MYB binding sites within LEHP regulatory regions. Two MYB transcription factors, LeMYB2 and LeMYB5, were co-expressed with LEHP during postharvest storage, and subcellular localization confirmed their nuclear localization. EMSA and DLR assays verified that LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 directly bind to and activate LEHP2 and LEHP3 promoters, elucidating their regulatory functions in browning. Collectively, these findings indicated that LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 participated in the regulation of postharvest pileus browning in L. edodes through direct transcriptional activation of LEHP2 and LEHP3 genes. This research provided a theoretical foundation for understanding transcriptional regulatory mechanisms during physiological development in other edible fungi. The elucidation of browning regulation mechanisms offers strategies to reduce postharvest losses and optimize resource efficiency in edible mushroom production. By advancing the understanding of gene networks underlying postharvest quality maintenance, this work underscores the role of molecular research in achieving sustainable agricultural practices that address global challenges in food preservation and environmental adaptation. Given the complexity of the browning mechanism, future studies should validate the interaction networks of homologous LeMYB transcription factors and other transcription factor families involved in browning, as well as explore the potential target genes of LeMYB2 and LeMYB5 to further elucidate their regulatory networks.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae11101176/s1; Figure S1: Schematic diagram of sampling for shiitake mushroom samples collected at different storage periods; Figure S2: Schematic representation of the LeMYB2/5 gene structures; Figure S3: Conserved motif analysis of LeMYB2/5; Figure S4: LeMYB2/5 secondary structure distribution projections; Table S1: The primers used for gene cloning and qRT-PCR analysis; Table S2: Primers used to construct the MYB-2/5-GFP vector; Table S3: Primers used to construct MYB-2/5-pCold GST vector; Table S4: Promoter Probe Primer; Table S5: Construction of primer sequences of dual-luciferase reporter gene experimental vector; Table S6: Property analysis of translated amino acid sequences of LeMYB2/5 genes; Table S7: LeMYB2/5 secondary structure projections.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.D.; methodology, B.D. and X.Y.; software, H.Z.; validation, Y.L.; formal analysis, B.D.; investigation, J.L.; Resources, H.Z.; data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, B.D. and X.Y.; writing—review and editing, H.Z.; visualization, C.C.; supervision, Y.L.; project administration, B.D.; funding acquisition B.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 32102053); the Major Special Science and Technology Projects of Shanxi Province (202301140601015); the Young Science & Technology Leadership Program of Shanxi Agricultural University (2022YQPYGC08); and the Key Scientific and Technological Innovation Team of Edible Fungi of Shanxi Province (201805D131009).
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study can be made available by the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EMSA | Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay |
| DLR | Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| POD | Peroxidase |
| PPO | Polyphenol oxidase |
| HPs | Heme peroxidases |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| TFs | Transcription factors |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative Real-Time PCR |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
References
- Kupcova, K.; Stefanova, I.; Plavcova, Z.; Hosek, J.; Hrouzek, P.; Kubec, R. Antimicrobial, cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant activity of culinary processed shiitake medicinal mushroom (Lentinus edodes, Agaricomycetes) and its major sulfur sensory-active compound-lenthionine. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2018, 20, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, U.; Eo, H.J. Influence of storage temperature on levels of bioactive compounds in shiitake mushrooms (Lentinula edodes). Mycobiology 2023, 51, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analysis of the Results of the National Edible Fungi Statistical Survey in 2023; Tridge. 2024. Available online: https://www.tridge.com/news/analysis-of-the-results-of-the-national-edib-fxovru (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Liang, G.; Gong, W.; Li, B.; Zuo, J.; Pan, L.; Liu, X. Analysis of heavy metals in foodstuffs and an assessment of the health risks to the general public via consumption in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Chen, W.; Jia, Z. Effect of simulated transport vibration on the quality of shiitake mushroom (Lentinus edodes) during storage. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Yashima, T. Water concentration and rate of decrease in shiitake cultivation log during fruiting body development, as measured by MRI. Fungal Biol. 2023, 127, 1362–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cui, X.; Song, Z.; Kong, W.; Kang, Y.; Kong, W.; Ng, T.B. Coating shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edodes) with a polysaccharide from Oudemansiella radicata improves product quality and flavor during postharvest storage. Food Chem. 2021, 352, 129357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Ren, R.; Yao, L.; Tong, L.; Li, J.; Wang, D.; Gu, S. Effect of hyperbranched poly-L-lysine and chitosan treatment on quality of shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edodes) during cold storage. Food Meas. 2024, 18, 9560–9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Sun, D.-W. Research advances in browning of button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus): Affecting factors and controlling methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 90, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Meng, L.; Zhang, G.; Yang, X.; Pang, B.; Cheng, J.; He, B.; Sun, F. Unraveling crop enzymatic browning through integrated omics. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1342639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, N.; Yan, R.; Guan, W.; Brennan, C.S.; Gao, H.; Peng, B. Effects of UV-C treatment on browning and the expression of polyphenol oxidase (PPO) genes in different tissues of Agaricus bisporus during cold storage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 139, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Liu, P.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y. The mechanism of preharvest treatment of polysaccharide from Lentinus edodes residue on inhibiting browning of postharvest Agaricus bisporus. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 227, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, X.; Gong, P.; Guo, J.; Deng, D.; He, G.; Ji, C.; Wang, R.; Long, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Effect of shiitake mushrooms polysaccharide and chitosan coating on softening and browning of shiitake mushrooms (Lentinus edodes) during postharvest storage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilley, A.; McHenry, M.P.; McHenry, J.A.; Solah, V.; Bayliss, K. Enzymatic browning: The role of substrates in polyphenol oxidase mediated browning. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.-J.; Wang, H.-X.; Zhang, J.-X. A Novel peroxidase from fresh fruiting bodies of the mushroom Pleurotus pulmonarius. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chang, M.; Meng, J.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Feng, C. Effect of ozone treatment on the quality and enzyme activity of Lentinus edodes during cold storage. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, B.; Zhong, R.; Chen, Y.; Fang, F.; Huang, X.; Pang, X.; Zhang, Z. Characterization of a longan pericarp browning related peroxidase with a focus on its role in proanthocyanidin and lignin polymerization. Food Chem. 2024, 461, 140937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passardi, F.; Bakalovic, N.; Teixeira, F.K.; Margis-Pinheiro, M.; Penel, C.; Dunand, C. Prokaryotic origins of the non-animal peroxidase superfamily and organelle-mediated transmission to eukaryotes. Genomics 2007, 89, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liers, C.; Bobeth, C.; Pecyna, M.; Ullrich, R.; Hofrichter, M. DyP-like peroxidases of the jelly fungus Auricularia auricula-judae oxidize nonphenolic lignin model compounds and high-redox potential dyes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, C.D.T.; Costa, J.H.; Germano, T.A.; Rocha, R.D.O.; Ramos, M.V.; Bezerra, L.P. Class III plant peroxidases: From classification to physiological functions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L. A generalist regulator: MYB transcription factors regulate the biosynthesis of active compounds in medicinal plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 4729–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, Y.; Zheng, Y. Multiple functions of MYB transcription factors in abiotic stress responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, M.; Huang, H.; Liu, X.; Meng, D. Methyl jasmonate-induced postharvest disease resistance in Agaricus bisporus is synergistically regulated by AbbZIP2 and AbMYB11 to facilitate ROS balance. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 228, 113667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gao, W.; Wu, X.; Zhao, M.; Qu, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J. Genome-wide characterization and expression analyses of pleurotus ostreatus MYB transcription factors during developmental stages and under heat stress based on de novo sequenced genome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, Z.; Jiao, L.; Meng, D. A 3R-MYB transcription factor is involved in Methyl Jasmonate-Induced disease resistance in Agaricus bisporus and has implications for disease resistance in Arabidopsis. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 73, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Jia, C.; Jia, W.; Li, Y.; Chang, M.; Zhang, H. Mechanism of high-voltage electrostatic field treatment in maintaining the postharvest quality of Agaricus bisporus. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wang, W.; Ruan, C.; Deng, L.; Yao, S.; Zeng, K. Involvement of CsWRKY70 in salicylic acid-induced citrus fruit resistance against Penicillium digitatum. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Kitazawa, H.; Guo, Y. Improving the property of a reproducible bioplastic film of glutenin and its application in retarding senescence of postharvest Agaricus bisporus. Food Biosci. 2022, 48, 101796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricia Twala, P.; Mitema, A.; Baburam, C.; Aliye Feto, N. Breakthroughs in the discovery and use of different peroxidase isoforms of microbial origin. AIMS Microbiol. 2020, 6, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Feng, D.; Li, K.; Han, S.; Lv, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zeng, G.; Qin, X.; Shen, X.; Liu, S. Integrated transcriptome and DNA methylome analysis reveal the browning mechanism in Agaricus bisporus. Gene 2025, 955, 149437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, J.-H. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma on the activity, structure and conformation of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and on the activity of litchi peroxidase (POD). LWT 2021, 141, 111078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, D.; Wei, R.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Pan, X. Genome-wide characterization, identification, and function analysis of candidate JsMYB genes involved in regulating flavonol biosynthesis in Juglans sigillata Dode. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 317, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Xia, E.; Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Tong, W.; Tang, Q.; Tadege, M.; Fernie, A.R.; Zhao, J. Diverse roles of MYB transcription factors in regulating secondary metabolite biosynthesis, shoot development, and stress responses in tea plants (Camellia sinensis). Plant J. 2022, 110, 1144–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q. The R2R3-MYB transcription factor StODO1 functions as a positive regulator of polyphenol oxidase and enzymatic browning in Solanum tuberosum L. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 227, 113575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zou, Q.; Bao, T.; Kong, M.; Gu, T.; Jiang, L.; Wang, T.; Xu, T.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Transcription factor MdbZIP44 targets the promoter of MdPPO2 to regulate browning in Malus domestica Borkh. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 214, 108934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Iqbal, A.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Murtaza, A.; Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Hu, W. Changes in browning degree and reducibility of polyphenols during autoxidation and enzymatic oxidation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).