Abstract
Citrus depressa Hayata is a citrus cultivar grown in Japan and Taiwan. To assess the differences in genetic characteristics and volatile organic components (VOCs) in the leaves and edible parts of the fruits of 23 C. depressa accessions from different geographic origins, the tissues were analyzed using cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence markers and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. A phylogenetic cluster analysis demonstrated that Kagoshima accessions had a close genetic relationship with one another, with Okinawan “Izumi kugani-like” being the most distinct accession. The predominant volatiles in the leaves were γ-terpinene, p-cymene, limonene, and linalool. Multivariate analysis and volcano plots revealed distinct volatiles in the leaves of each cultivation region: piperitone and citronellal (Kagoshima); 5,9,9-trimethyl-spiro[3.5]non-5-en-1-one (Okinawa); and hexanal (Taiwan). Furthermore, the edible parts of Taiwanese fruits contained abundant amounts of monoterpenes, including linalool and 1,8-cineole. In contrast, Kagoshima and Okinawa accessions were rich in aldehydes and esters, respectively. In conclusion, the genetic and volatile profiles of 23 C. depressa accessions of different origins could be distinguished, and multivariate analysis suggested that C. depressa contains diverse VOCs depending on where it is cultivated. These findings demonstrate the exclusivity of C. depressa resources in each region, which could assist farmers and agro-industries in promoting food products derived from C. depressa fruits.
1. Introduction
Citrus depressa Hayata is a small citrus fruit that is widely distributed in the Nansei Islands, a southernmost archipelago of Japan that stretches from the Amami Islands of Kagoshima Prefecture to Okinawa Prefecture, with Taiwan as its southern neighbor (Figure 1a). The fruit of this citrus cultivar has a yellowish-green appearance with a strong sourness and unique odor [1,2]. It is generally used to prepare juice, jam, and sweets in processed foods and beverages, or its fruits are used as a seasoning, whether squeezed or its peel shaved off over food. The volatile organic components (VOCs) of the C. depressa fruit, which are mainly composed of monoterpene hydrocarbons, especially limonene, γ-terpinene, and p-cymene, are present in a distinct ratio compared with other common citrus cultivars in the regions [2,3,4]. In addition, C. depressa fruit contains various bioactive substances, such as flavonoids, phenols, carotenoids, and limonoids [5,6]. These substances are known to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and neuroprotective effects, which are beneficial to human health [6].
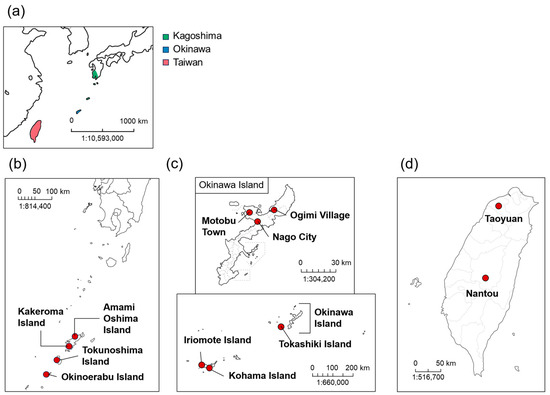
Figure 1.
(a) Map of cultivation areas of C. depressa in Japan and Taiwan; maps of initial collection sites of C. depressa at (b) Kagoshima Prefecture, (c) Okinawa Prefecture, and (d) Taiwan.
Phenotypic variations in citrus plants, including VOC production that contributes to fruit quality, could be caused by various factors, such as genetics, environment, and different cultivation practices [7]. However, the key differentiation factors may be primarily based on genetic variation, as C. depressa has a variety of accessions across its cultivation regions [8,9,10,11]. The cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) has been reported to be useful for accession identification and for revealing the diversity of citrus genetic resources [10,12]. It is a convenient method for DNA analysis that requires small amounts of sample and can be performed using simple equipment. Shimada et al. identified 708 CAPS markers in citrus variety identification [12]. CAPS markers utilize amplified DNA digested with a restriction endonuclease, and genetic polymorphisms are revealed by the presence or absence of specific restriction site polymorphisms [10,12]. Generally, leaves are used in the analysis because they are unaffected by the harvest season and may thus provide a sufficient quantity of materials for examination [11].
The fruits and leaves of citrus plants emit various VOCs, including monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, esters, aldehydes, and alcohols [2,3,4]. The predominant compounds of these tissues, such as limonene, γ-terpinene, and linalool, are expected to exhibit antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-stress effects [6,13,14]. In contrast, the flavor quality of citrus fruits is determined by various components, in which VOCs play an important role in producing aroma traits [15]. Moreover, the edible parts of citrus fruits are known to have distinct aroma characteristics and thus influence the development of fruits suitable for processed foods and beverages, as well as consumer preferences [15]. Studies on the differences in composition and content among citrus accessions are important for quality assessment in the food processing industry. Multivariate statistical analyses of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) data can be used to visualize the differentiation and production areas of citrus fruits [2,4,16,17]. Information on the distinctiveness of individual citrus accessions is critical for assisting local customers and producers in selecting unique fruits and derived food products based on their regional advantages. Moreover, farmers can benefit from these findings by understanding that their fruits have distinct aromas.
To the best of our knowledge, no study has yet reported the characterization of the genetics and VOCs in the leaves of C. depressa of Japanese (Kagoshima and Okinawa Prefectures) and Taiwanese origins. Moreover, the comparison of VOCs in the edible parts of this small citrus fruit remains limited. Thus, this study aimed to characterize the genetic differences between 23 accessions of C. depressa from different geographic origins in Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan and to evaluate the VOC profiles of their leaves and edible fruit parts. Genetic differentiation of these accessions was determined by CAPS analysis, whereas VOCs in the leaves and fruit edible parts were analyzed by solid-phase microextraction (SPME)-GC-MS analysis followed by multivariate profiling.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of C. depressa Leaves and Fruits
The leaves and fruits of 23 C. depressa accessions were collected from Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan during the mature fruit harvest season (Figure 1b–d). Five accessions of Kagoshima (KGS) origin, i.e., “Amami Oshima”, “Kakeroma”, “Okinoerabu”, “Tokunoshima 1”, and “Tokunoshima 2”, were collected from Toso Orchard, Faculty of Agriculture, Kagoshima University in December 2020. Sixteen Okinawan (OKN) accessions (“Hijakunibu”, “Iriomote”, “Ishikunibu”, “Izumi kugani”, “Izumi kugani-like”, “Kaachi”, “Kabuchi-hybrid”, “Katsuyama kugani”, “Kohama”, “Motobu”, “Nakamoto seedless”, “Ogimi 1”, “Ogimi 2”, “Ogimi kugani”, “Sokihidai”, and “Tokashiki”) were obtained from the Okinawa Prefectural Agricultural Research Center Nago Branch in December 2020. Two Taiwanese (TWN) C. depressa accessions (“Nantou” and “Taoyuan” lines) were collected from Nantou and Taoyuan regions, respectively, in November 2021. The environmental conditions for the cultivation of C. depressa in Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan, including latitude, longitude, and climate, are presented in Supplementary Table S1. Upon arrival at the laboratory, the leaves were immediately frozen using liquid nitrogen and stored at −25 °C prior to analysis. Fruits from the three biological replicates were peeled, and the edible parts of the fruits were hand-squeezed using a stainless-steel juicer (Minex Metal, Niigata, Japan). The total soluble solids and total acidity of the juices were measured using a PAL-BX ACID F5 (Atago, Tokyo, Japan). The juice of the fruit edible parts was then stored at −25 °C prior to analysis. The samples were stored for less than six months before the measurements.
2.2. CAPS Assay
Total DNA was extracted from the leaves using Isoplant II (Nippon Gene, Tokyo, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The following restriction enzymes were used: HindIII, PvuII, HhaI, HinfI, DraI, RsaI, HaeIII, HincII and EcoRV (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan). Citrus-specific genetic markers (19 types, Table 1) constructed by Shimada et al. [12] were used for CAPS analysis. The PCR reaction mixture was prepared to 12.5 µL and was composed of 10 ng template DNA, 10 pmol primer, 1× volume reaction buffer, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM dNTPs, and 0.5-unit Prime Taq DNA polymerase (GeNet Bio, Daejeon, Republic of Korea). PCR reactions were performed in an Applied Biosystems Veriti 200 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) thermal cycler with initial heating at 94 °C for 3 min and held for 30 s, followed by a four-step heating process at 62, 60, 58, and 56 °C (30 s each). Afterwards, the thermal process was held at 72 °C for 1 min (2 cycles), followed by repeated heating at 94 °C for 30 s, 54 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 2 min for 35 cycles. The heating was then extended at 72 °C for 7 min. The PCR products were digested with restriction enzymes as follows: PCR products (4 µL) were mixed with reaction buffer (1 µL) and 2–3 units of restriction enzyme, and then diluted to a final volume of 10 µL with sterilized water. After digestion at 37 °C for 4 h, the digested genetic mixture was separated by gel electrophoresis on a 1.5% agarose (Takara Bio) and stained with GelRed® (Biotium, Hayward, CA, USA). The resulting bands were then detected under UV light, and the band patterns were labeled as “aa”, “bb” and “ab” according to their fragment size [10,12]. The genetic polymorphism distance was calculated, and the genetic distance between C. depressa accessions was presented in a phylogenetic cluster tree using the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) (MEGA Version 4.1, Tempe, AZ, USA).

Table 1.
CAPS markers and genotype combinations of C. depressa leaves of Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan origins.
2.3. VOC Analysis Using SPME-GC-MS
C. depressa leaves were crushed using a multi-beads shocker at 2000 rpm for 15 s (Yasui Kikai, Osaka, Japan). The crushed mixture of leaves (50 mg fresh weight) was then transferred into a 20 mL vial, followed by the addition of an internal standard of cyclohexanol (20 µL, 0.01% w/v, Fujifilm Wako Pure Chemical, Osaka, Japan)) and EDTA solution (1 mL, 150 mM, pH 7.5, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). As for the fruit edible part, squashed juice (2 mL), 1-hexanol (10 µL, 0.05% w/v, Tokyo Chemical Industry, Tokyo, Japan) as internal standard, and EDTA solution were placed into 20 mL vial. The mixture was then subjected to SPME (40 °C, equilibrium 5 min, adsorption 10 min) on a CombiPAL autosampler (CTC Analytics, Zwingen, Switzerland) and GC-MS analysis [17]. The SPME fiber was DVB/CAR/PDMS (1 cm), with a film thickness of 50/30 µm (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA). GC-MS analysis was performed using a 7890B-5977A MSD (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA); the column was DB-5MS (30 m × 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 µm film thickness, Agilent Technologies). The temperature of the injector was set to 250 °C, set to a split mode with a split ratio of 10:1. The column temperature was raised from 55 °C to a final temperature of 200 °C at a rate of 3 °C/min and maintained at the final temperature for 1.67 min. The carrier gas was helium applied at a flow rate of 1 mL/min, and the mass detector was set to an ionization voltage of 70 eV (EI) with a scan range of m/z 35–350. Both the ion source and the interface temperatures were set at 230 °C. Non-processed chromatographic peak data (MS abundance) were converted to NetCDF format, and the data were aligned and annotated using MS-DIAL Version 4.8 (RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science, Kanagawa, Japan). The compounds were identified based on MS library (NIST 14) and Retention Index (RI) comparisons. The chromatographic peaks were normalized to internal standard peak.
2.4. Multivariate Analysis of VOC Profile of C. depressa Leaves and Fruit Edible Parts
Chromatographic peak data (MS abundance) were normalized to internal standard, log10-transformed, and unit variance scaled prior to use as a dataset for multivariate statistical analysis. Principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) were performed using SIMCA Version 17 (Sartorius AG, Göttingen, Germany). To determine significant VOCs, volcano plots were visualized, composed of the variable influence in the projection (VIP) from OPLS-DA, log2-fold change (FC) values, and p-values, which were adjusted by false discovery rate (FDR) correction for multiple testing using the R package LIMMA (https://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/limma.html) accessed on 1 May 2022 [17].
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Characteristics of C. depressa of Different Origins
The 23 accessions of C. depressa were classified according to 12 combinations of CAPS markers/restriction enzymes (AI0224/HindIII, AI032/HindIII, Bf0158-2/PvuII, Bf0158-3/PvuII, Cp0419/(no cut), Cp1308/HindIII, Mf0097/DraI, Tf0154/HaeIII, Tf0300/DraI, Tf0318/HincII, Tf0396/EcoRV, and Tf0419/PvuII) (Table 1). The band patterns earned from the electrophoresis (labeled “aa”, “ab”, or “bb” according to its fragment size) were used to evaluate the genetic parental relationships among the C. depressa accessions. The phylogenetic cluster plot, which was visualized as a dendrogram constructed from the CAPS data, classified C. depressa into four major groups: A, B, C, and D, as indicated by the first and second branches of the dendrogram (Figure 2). Group A included half of the Okinawan accessions and all Kagoshima accessions. Specifically, “Kaachi” and “Iriomote” were close to “Tokunoshima 1”, followed by “Hijakunibu”, “Nakamoto seedless”, “Ishikunibu”, “Izumi Kugani”, and “Kohama”. The “Tokunoshima 1” line was different from the other four Kagoshima accessions for having band patterns of Bf0158-2/PvuII and Bf0158-3/PvuII (found to be both “bb“), which was discovered to be genetically closer to Okinawan “Kaachi”. Meanwhile, the Okinawan accession closest to other Kagoshima accessions was “Sokihidai”. Then again, the Kagoshima accessions are genetically close to one another, especially “Amami Oshima”, “Kakeroma”, “Tokunoshima 2”, and “Okinoerabu”. Next, the dendrogram branch of Group B solely consisted of “Izumi kugani-like” of Okinawan origin. On the other hand, Group C was composed of Okinawan accessions, such as “Katsuyama kugani”, “Ogimi kugani”, and “Ogimi 1”, indicating a close genetic linkage among these common Okinawan lines. Group D was composed of “Kabuchi-hybrid”, “Motobu”, “Tokashiki”, and “Ogimi 2” of Okinawan origin and the two Taiwanese accessions. These two accessions were found to be not so genetically distant from each other, yet “Nantou” was the closest to Okinawa “Motobu” line, while “Taoyuan” was closer to the Okinawa “Ogimi 2” and “Tokashiki” lines.
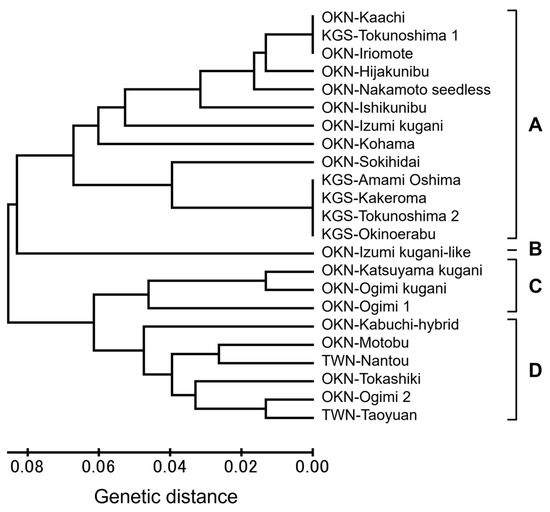
Figure 2.
Dendrogram of C. depressa accessions generated by the UPGMA cluster analysis of CAPS markers. The accessions were categorized into four groups at the first and second branches as Groups A–D.
3.2. VOC Profile of C. depressa Leaves of Different Origins
In total, 63 VOCs were identified from the 100 chromatographic peaks detected in the leaves of the 23 accessions of C. depressa (Supplementary Table S2). The average of the relative percentage of the identified VOCs in all accessions was 98.7% of total normalized intensity. The average of log10 normalized intensity for the Kagoshima accessions was 1.80, with a maximum value of 1.91 in “Kakeroma” and a minimum value of 1.67 in “Okinoerabu” (Figure 3a). On the other hand, the average for the Okinawan accessions was 1.63, with a maximum value of 1.91 in “Ogimi 1” and a minimum value of 1.29 in “Kabuchi-hybrid”. The average value for Taiwanese accessions in “Taoyuan” was 1.65, with a maximum value of 1.69 in “Nantou” and a minimum value of 1.61 in “Taoyuan”.
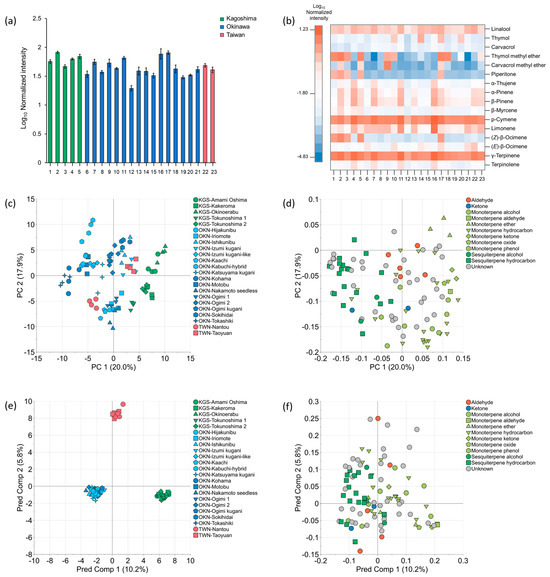
Figure 3.
Normalized intensities and multivariate statistical plots of VOCs in C. depressa leaves: (a) normalized intensities of total compounds; (b) heat map of normalized intensities of major compounds; (c) PCA score plot; (d) PCA loading plot; (e) OPLS-DA score plot; (f) OPLS-DA loading plot. Accession numbers in (a,b) are as follows: (1) KGS-Amami Oshima, (2) KGS-Kakeroma, (3) KGS-Okinoerabu, (4) KGS-Tokunoshima 1, (5) KGS-Tokunoshima 2, (6) OKN-Hijakunibu, (7) OKN-Iriomote, (8) OKN-Ishikunibu, (9) OKN-Izumi kugani, (10) OKN-Izumi kugani-like, (11) OKN-Kaachi, (12) OKN-Kabuchi-hybrid, (13) OKN-Katsuyama kugani, (14) OKN-Kohama, (15) OKN-Motobu, (16) OKN-Nakamoto seedless, (17) OKN-Ogimi 1, (18) OKN-Ogimi 2, (19) OKN-Ogimi kugani, (20) OKN-Sokihidai, (21) OKN-Tokashiki, (22) TWN-Nantou, and (23) TWN-Taoyuan.
The predominant VOCs in the leaves were monoterpenes, and the heat map visualized the normalized intensity of 16 VOCs derived from the top 10 predominant compounds in each accession (Figure 3b). p-Cymene, γ-terpinene, limonene, and linalool were the main components of 23 accessions of C. depressa leaves, while the VOCs in moderate amounts depending on the accessions were the following five compounds: thymol, thymol methyl ether, carvacrol methyl ether, piperitone, and (Z)-β-ocimene. Kagoshima accessions except “Tokunoshima 1” were rich in thymol methyl ether, piperitone, and (Z)-β-ocimene. On the other hand, Okinawan “Izumi kugani-like”, “Kohama”, “Ogimi 1”, and “Sokihidai”, had higher amounts of thymol. Furthermore, Okinawan “Ogimi 1” contained the five moderate VOCs in much higher quantities, and Okinawan “Izumi Kugani” had a characteristic of containing greater amounts of carvacrol methyl ether.
The PCA plot, which was created to represent the distinction between C. depressa accessions based on chromatographic peaks, roughly elicited several groups of accessions distinguished from one another (Figure 3c,d). Five accessions from Kagoshima were plotted in a diagonal linear cluster, from the PC1-positive/PC2-negative quadrant to the PC1-positive/PC2-positive quadrant. Two Okinawan accessions, “Tokashiki” and “Kohama”, were assembled distinctively from the others as they were plotted around the PC1 axis on its negative end (zero and near to ordinates on PC2). Moreover, Okinawan “Kabuchi-hybrid” was solely plotted on the farthest position of the PC1-negative/PC2-positive quadrant. Other Okinawan accessions and Taiwanese “Nantou” and “Taoyuan” were intertwined with each other and have not separated themselves as a distinctive group. The positive direction of PC1 in the loading plot was dominated by monoterpenes, while the negative direction was occupied by sesquiterpenes (Figure 3d); it can be inferred that the monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes can be associated with the Kagoshima accessions and the group of “Kohama” and “Tokashiki”, respectively. Aldehydes such as hexanal, (E)-2-hexenal, octanal, and nonanal were located near the center and were considered characteristic of the two Taiwanese accessions and several Okinawan accessions.
Differences in the VOC composition of C. depressa according to the cultivation regions were further visualized using OPLS-DA plots (Figure 3e,f). The score plots of the VOC data effectively distinguished all the accessions based on their origins. The plot associated Kagoshima accessions with monoterpenes (piperitone, (Z)-ocimene, citronellal, and α-phellandrene); Okinawa accessions with sesquiterpenes (α-caryophyllene, β-elemene, and bicyclogermacrene), decanal, and 5,9,9,-trimethyl-spiro[3.5]non-5-en-1-one; and Taiwanese accessions with hexanal (Figure 3f). The most distinctive VOCs were all from 100 detected chromatographic peaks and were calculated and represented in a volcano plot (Figure 4) based on the selection criteria of VIP > 1.0, FDR < 0.05, and log2FC > 1.0. As for the distinguishable VOCs between Okinawan and Kagoshima accessions, leaves of Okinawan accessions were significantly higher in terpenes, such as α-cubebene, carvacrol, and β-elemene, and a ketone, namely 5,9,9,-trimethyl-spiro[3.5]non-5-en-1-one (log2FC = 1.10, 1.07, 1.03, and 1.02, respectively). Conversely, Kagoshima accessions were significantly higher in 10 monoterpenes which include piperitone, thymol methyl ether, citronellal, (Z)-β-ocimene, and 1,8-cineole (log2FC = 7.48, 7.01, 6.57, 4.30, and 3.31, respectively) (Figure 4a, Supplementary Table S3). Moreover, between Okinawan and Taiwanese accessions, three VOCs including decanal, α-caryophyllene, and 5,9,9,-trimethyl-spiro[3.5]non-5-en-1-one (log2FC = 3.87, 3.27, and 1.48, respectively) were significantly higher in Okinawan accessions rather than the ones of Taiwan, with four compounds including hexanal, camphene, terpinene-4-ol, and α-terpineol (log2FC = 2.27, 1.09, 1.06, and 1.03, respectively.) which were significantly higher in Taiwan than in Okinawa (Figure 4b, Supplementary Table S3). Furthermore, between Kagoshima and Taiwan accessions, those of Kagoshima were found to be greater in monoterpenes and aldehydes such as piperitone, citronellal, (Z)-β-ocimene, decanal, and 1,8-cineole (log2FC = 6.38, 5.17, 4.08, 3.56, and 3.28, respectively), while Taiwanese accessions were significantly higher in aldehydes and sesquiterpenes as follows: hexanal, α-cadinene, selina-3,7(11)-diene, β-selinenol, α-maaliene (log2FC = 2.19, 1.25, 1.08, 1.08, and 1.06, respectively) (Figure 4c, Supplementary Table S3). Of these three regional comparisons, Kagoshima accessions had significantly greater intensities of piperitone and citronellal, as indicated by their large log2FC values compared to Okinawan and Taiwanese accessions.
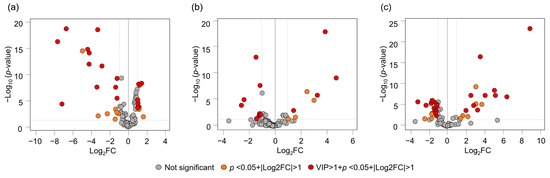
Figure 4.
Volcano plots of VOCs of C. depressa leaves: (a) comparison between Okinawa and Kagoshima accessions; (b) comparison between Okinawa and Taiwan accessions; (c) comparison between Kagoshima and Taiwan accessions.
3.3. VOC Profile of C. depressa Fruit Edible Parts of Different Origins
A total of 59 VOCs were identified from the 102 chromatographic peaks detected in the edible parts of the 23 accessions of C. depressa (Supplementary Table S2). The average of the relative percentage of the identified VOCs in all accessions was 84.1% of total normalized intensity. The relative normalized intensities of the total volatiles were higher in Taiwanese fruits compared to Okinawa and Kagoshima, with averages of 2.03, 1.17, and 0.81, respectively (Figure 5a). Among the 23 accessions, “Nantou” (2.24) and “Taoyuan” (1.83) from Taiwan and “Kabuchi-hybrid” (1.70), “Ishikunibu” (1.63), and “Motobu” (1.61) from Okinawa were expected to have a strong volatile intensity, while “Kakeroma” (0.54) from Kagoshima was suggested to be low.
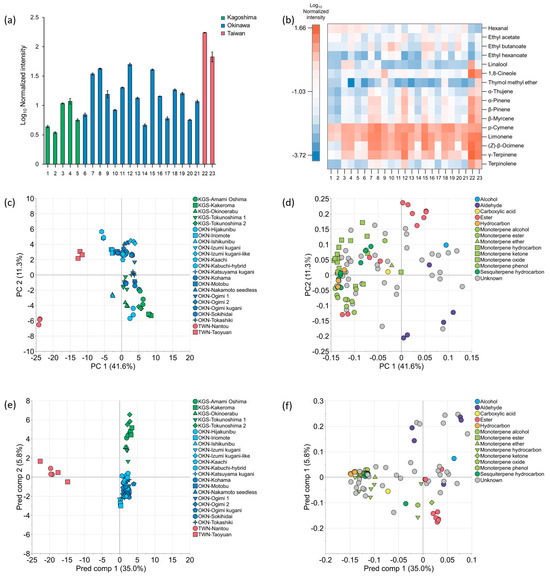
Figure 5.
Normalized intensities and multivariate statistical plots of VOCs in C. depressa fruit edible parts: (a) normalized intensities of total compounds; (b) heat map of normalized intensities of major compounds; (c) PCA score plot; (d) PCA loading plot; (e) OPLS-DA score plot; (f) OPLS-DA loading plot. Accession numbers in (a,b) are as follows: (1) KGS-Amami Oshima, (2) KGS-Kakeroma, (3) KGS-Okinoerabu, (4) KGS-Tokunoshima 1, (5) KGS-Tokunoshima 2, (6) OKN-Hijakunibu, (7) OKN-Iriomote, (8) OKN-Ishikunibu, (9) OKN-Izumi kugani, (10)OKN-Izumi kugani-like, (11) OKN-Kaachi, (12) OKN-Kabuchi-hybrid, (13) OKN-Katsuyama kugani, (14) OKN-Kohama, (15) OKN-Motobu, (16) OKN-Nakamoto seedless, (17) OKN-Ogimi 1, (18) OKN-Ogimi 2, (19) OKN-Ogimi kugani, (20) OKN-Sokihidai, (21) OKN-Tokashiki, (22) TWN-Nantou, and (23) TWN-Taoyuan.
The heat map revealed the normalized intensity of the top 10 VOCs of each of 23 accessions, and especially p-cymene, limonene, (Z)-β-ocimene, and γ-terpinene were highly present in C. depressa fruit edible parts (Figure 5b). The other 12 components, including aldehydes, esters, and monoterpenes, showed differences in content among accessions. Kagoshima accessions contained a greater amount of hexanal, while esters (ethyl butanoate, ethyl hexanoate, and ethyl acetate) were characteristic in several Okinawan fruits, such as the “Kaachi”, “Motobu”, “Nakamoto seedless”, “Ogimi 2”, and “Sokihidai” lines. Additionally, Taiwanese “Nantou” and Kagoshima “Okinoerabu” and “Tokunoshima 1” were rich in linalool; both Taiwanese accessions and the Okinawan “Izumi kugani” were rich in 1,8-cineole; and “Taoyuan” was rich in thymol methyl ether. Other monoterpene hydrocarbons were similar to the total volatile intensity results (Figure 5a); thus, the higher the amount of VOCs, the more abundant the monoterpene hydrocarbons tended to be in Taiwanese and Okinawan accessions.
The PCA plot revealed the singularly divided accessions of the two Taiwanese accessions and Okinawan “Kabuchi-hybrid”, and other accessions from Okinawa and Kagoshima origins which were not distinctively separated (Figure 5c). Specifically, Taiwanese “Nantou” was located in the farthest position in the quadrant of PC1-negative and PC2-negative. On the other hand, Taiwanese “Taoyuan” and Okinawan “Kabuchi-hybrid” were plotted in the quadrant of PC1-negative and PC2-positive. Moreover, there was a tendency in the PC2 axis, in which the accessions queued from positive and negative in the order of Okinawa to Kagoshima origin. Most VOCs were outlined in the negative direction of PC1 in the loading plot, indicating that Taiwanese fruits contained greater amounts of these compounds (Figure 5d). In contrast, the esters (methyl butanoate, methyl hexanoate, methyl octanoate, ethyl acetate, ethyl butanoate, ethyl hexanoate, and ethyl octanoate) were located in the PC1-positive/PC2-positive quadrant near the PC2 axis, whereas the aldehydes (hexanal, heptanal, octanal, and nonanal) were located in the PC1-positive/PC2-negative quadrant.
OPLS-DA was subsequently performed on the VOCs in the edible parts of fruits of different origins (Figure 5e,f). The plot illustrates the contributions of aldehyde compounds (hexanal and heptanal) to Kagoshima accessions, ester compounds (methyl butanoate, methyl hexanoate, and ethyl hexanoate) to Okinawa accessions, and monoterpene and sesquiterpene compounds to Taiwanese accessions (Figure 5f). In addition, the volcano plots allowed for the distinction of VOCs in the fruits of Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan origins (Figure 6). As for the VOCs found to be distinguishable between Okinawan and Kagoshima origins, Okinawan accessions were found to be significantly higher in 13 VOCs, which included esters and monoterpene hydrocarbons such as (Z)-β-ocimene, methyl octanoate, methyl hexanoate, α-pinene, and β-pinene (log2FC = 3.08, 2.30, 2.24, 2.15, and 2.14, respectively), while Kagoshima fruits were found to be significantly higher in aldehydes such as hexanal, octanal, heptanal, and nonanal (log2FC = 1.61, 1.48, 1.38, and 1.03, respectively) (Figure 6a, Supplementary Table S4). On the other hand, regarding Okinawan and Taiwanese accessions, esters and aldehydes of methyl butanoate, hexanal, methyl hexanoate, methyl octanoate, and ethyl butanoate (log2FC = 4.37, 3.62, 3.57, 3.21, and 2.92, respectively) were found to be significantly higher in Okinawan accessions, while Taiwanese fruits were characterized with monoterpenes such as alloocimene, terpinolene, fenchol, α-terpinene, and γ-terpinene (log2FC = 5.83, 5.79, 5.68, 5.30, and 5.09, respectively) (Figure 6b, Supplementary Table S4). In addition, for the VOCs distinguishable between Kagoshima and Taiwanese accessions, five VOCs (hexanal, heptanal, methyl butanoate, ethyl butanoate, and octanal: log2FC = 5.23, 4.12, 2.48, 2.06, and 1.66, respectively) were richer in Kagoshima fruits, while monoterpene hydrocarbons (terpinolene, γ-terpinolene, β-myrcene, β-pinene, and (Z)-β-ocimene: log2FC = 7.37, 7.02, 6.94, 6.81, and 6.72 respectively) were more abundant in Taiwanese accessions (Figure 6c, Supplementary Table S4).
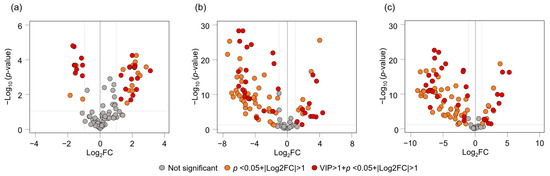
Figure 6.
Volcano plots of VOCs of C. depressa fruit edible parts: (a) comparison between Okinawa and Kagoshima accessions; (b) comparison between Okinawa and Taiwan accessions; (c) comparison between Kagoshima and Taiwan accessions.
4. Discussion
The 19 CAPS genotype mixtures used were able to classify 23 C. depressa accessions from three regions (Okinawa, Kagoshima, and Taiwan) and revealed their intraspecific variation/uniformity (Table 1 and Figure 2). Accessions from Kagoshima, except “Tokunoshima 1”, were elicited to be genetically close to each other. Moreover, the accessions were divided into Okinawan and Kagoshima lines, and the outcome agreed with the results of a previous study [9]. The C. depressa cultivar is considered to have Asian Mandarin origins with Okinawan indigenous C. ryukyuensis as parents [18]. Accordingly, “Tokunoshima 1” of Kagoshima may have been brought in from the same parents as the Okinawan lines, which were originally cultivated in the main island of Okinawa. Moreover, the Taiwanese accessions “Nantou” and “Taoyuan” were found to be genetically close to Okinawan accessions. Okinawa and Taiwan are the original distribution sites of C. depressa, suggesting that the parents may be closely related [18]. “Izumi kugani-like” was found to have many homozygous genetic patterns among the 23 C. depressa accessions. This fact suggests the possibility of “Izumi kugani-like” being the pure variation and has different genetic properties from other accessions [10]. In the current study, 12 combinations of CAPS markers/restriction enzymes were found to be effective in differentiating C. depressa cultivars, which is valuable when considering the genetic properties of C. depressa. This result also demonstrates that these CAPS marker/restriction enzyme compositions are useful for identifying variations in C. depressa accessions from larger collection sites and other similar small-type citrus cultivars or their hybrid varieties, as they are known to have more intraspecific variety than other citrus fruits in the region [8,9]. Taken together, C. depressa contains abundant genetic resources based on regional differences, despite the commonality of the accessions. These outcomes provide basic information on the genetic association between the major C. depressa accessions of the cultivar from different cultivation regions (Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan), which could explain the variations in their phenotypes, including yield, disease resistance, and flavor traits. The identification of C. depressa accessions could also lead to the development of new varieties and an increase in their commercial value.
The total content of VOCs in the leaves showed small differences among the different cultivation regions and accessions; however, their VOC profiles varied (Figure 3a,b). As for accessions of Kagoshima, except “Tokunoshima 1”, the four accessions were commonly rich in thymol methyl ether, piperitone, and (Z)-β-ocimene and were closely plotted to each other on PCA (Figure 3b–d). This outcome agrees with their genetic characteristics (Figure 2), which suggests the possibility of the existence of genetic information that manifests in the production of certain VOCs in leaves and, hence, contributes to their unique odor quality. Meanwhile, on the PCA plot, the Okinawan and Taiwanese accessions differed from Kagoshima accessions (except “Tokunoshima 1”) as they were plotted around the origin and further to the negative direction of the PC1 axis. The two accessions of Okinawa (“Kohama” and “Tokashiki”) which were located on the PC1 negative direction were revealed to have abundant sesquiterpenes (bicyclogermacrene, α-copaene, α-cubebene, β-elemene, and δ-cadinene), indicating their potential distinct aroma traits which can emit greater green and herbal odor [19]. Among Okinawan accessions, “Kabuchi-hybrid” was uniquely abundant in γ-muurolene, suggesting that it can generate a more citrusy-oily odor [20]. Taiwanese “Taoyuan” and Okinawan accessions which were plotted along the PC1 axis on the PC2 positive direction were rich in hexanal, indicating that its specific green aroma may enrich odor properties of the leaves [21]. On the other hand, Kagoshima “Tokunoshima 1”, Taiwanese “Nantou”, and Okinawan accessions which were located on the PC2 negative direction were abundant in monoterpenes (limonene, p-cymene, γ-terpinene, and linalool) and sesquiterpenes (β-caryophyllene, germacrene B, and elemol). These volatile constituents are known to have typical citrus and woody-spicy odors, respectively [19,20]. These leaves can be used to enhance the aroma of steamed food or brewed tea because they are rich in monoterpenes, which are abundant in C. depressa fruits. The genetic and VOC data of the leaves were partially associated with the Kagoshima accessions; however, the outcome did not fully agree with the differentiation of Okinawan and Taiwanese accessions (Figure 2). Nevertheless, the metabolic and physicochemical traits of citrus differ despite the commonality of accessions and cultivation environments [11,17]. Although C. depressa usually inherits the parents’ genetic information as a polyembryonic plant, there are occasions where mutations occur in nuclear embryos [9,10,18,22]. Therefore, genetic and VOC differences in C. depressa accessions may be caused by genetic changes and environmental factors [9,10].
The OPLS-DA visualization plot allowed the grouping of the three regions based on their VOCs, and further indicated that monoterpenes were useful for the identification of leaves of Kagoshima origin, sesquiterpenes from Okinawa, and hexanal from Taiwan (Figure 3e,f). Moreover, volcano plots allowed for further distinct volatile components when the two cultivation regions were compared (Figure 4, Supplementary Table S3). In detail, the VOC markers which can identify C. depressa accessions according to their cultivated regions are as follows: 5,9,9-trimethyl-spiro[3.5]non-5-en-1-one for Okinawa; piperitone, citronellal, (Z)-β-ocimene, 1,8-cineole, α-phellandrene, and nerol for Kagoshima; and hexanal for Taiwan. Compared to Okinawan accessions, leaves of Kagoshima origin have a citrus-minty odor, while Taiwanese leaves have a green-floral aroma [19,21]. Piperitone and citronellal were particularly promising as volatile markers that can distinguish between cultivation origins, given the large range in absolute values of log2FC in Kagoshima compared to the other two regions (6.38–7.48 and 5.17–6.57, respectively). In Southeast Asia, the leaves of citrus fruits are often used for seasoning purposes that contribute to the flavor quality of cooking; thus, C. depressa leaves are potential sources for such food applications [23]. The leaves from accessions such as “Tokunoshima 1” (Kagoshima) and “Nantou” (Taiwan), as well as Okinawan “Iriomote”, “Kaachi”, “Nakamoto seedless”, and “Ogimi 1”, have typical aroma qualities from monoterpenes similar to its fruit, therefore they can be useful for flavoring dishes. Because leaves contain more biomass than fruits, they can be acquired any time of the year, and citrus leaves can be a great source of VOCs with antioxidant and potent antibacterial activities [24,25]. Taken together, the VOC profile data for each accession of C. depressa could be used more easily than those for fruits to classify the distinctiveness of each cultivation region, and the leaves are potential aroma resources for cooking and other food applications.
The edible fruit parts of Taiwanese accessions containing more VOCs than those from Okinawa and Kagoshima were elicited using heat maps and PCA plots (Figure 5a,b). Taiwanese “Nantou” could be characterized by its high monoterpene levels; this line was found to have the genetic ability to produce greater amounts of terpenes such as α-terpinol and linalool [11]. Okinawan accessions were plotted along the PC2 axis distributing from the PC2 positive to negative direction, as Kagoshima fruits shared the positions on the PC2 negative direction, indicating that some of Okinawan accessions such as “Hijakunibu”, “Ishikunibu”, “Katsuyama kugani”, “Kohama”, and “Ogimi kugani” might have a similar composition of volatiles to fruits of Kagoshima origins (Figure 5c,d). Through the loading plot, relationships were found between esters and aldehydes in the Okinawan and Kagoshima fruits, respectively. Kagoshima accessions and Okinawan “Kabuchi-hybrid” could be identified from the other accessions on PCA analysis, and the result agrees with the results from the PCA analysis of the leaves (Figure 3). Conversely, although the Taiwanese accessions had high levels of VOCs in their fruits, there was no correlation with the leaf VOC profiles, which indicated that the two plant sections had distinct metabolic pathways for producing secondary metabolites, such as volatile constituents [24,25]. The VOC markers of C. depressa fruits that identified each cultivation region were discovered through the OPLS-DA plot as follows: aldehydes for Kagoshima, esters for Okinawa, and monoterpenes for Taiwan (Figure 5e,f). Furthermore, the volcano plots identified significant region-specific VOCs: Kagoshima was rich in aldehydes such as hexanal, heptanal, octanal, and nonanal; Okinawa in methyl butanoate, methyl hexanoate, methyl octanoate, and ethyl hexanoate; and Taiwan in terpinolene, γ-terpinene, β-myrcene, alloocimene, and β-pinene (Figure 6, Supplementary Table S4). These compounds and physicochemical traits of C. depressa fruits might influence their sensory properties. For instance, juices made from the fruit edible parts of Taiwanese accessions with high VOCs concentration could contribute to their overall citrusy aromas, followed by green and herbal scents, whereas juices made from fruits of Okinawa and Kagoshima accessions would be associated with a fruity aroma (Supplementary Figure S1). In addition, Okinawa and Kagoshima accessions were discovered to contain more sugar than Taiwanese fruits, with greater soluble solid/titratable acidity ratios being observed; hence, Taiwanese fruits could be distinguished by their strong sourness, whereas Okinawa and Kagoshima fruits would be regarded as sweeter [2,17]. In contrast, the Taiwanese accessions contained more amino acids [17]. The overall flavor of fruits can vary considerably owing to variations in the characteristics of volatile compounds and metabolites, as well as variations in accessions and cultivation environments. The results of VOC profiles of C. depressa fruits provide valuable information that can be applied to the manufacture of beverages and processed foods with distinct flavor properties. For instance, Kagoshima and Okinawan fruits are best used for fresh consumption or are processed into juices, whereas the rich aroma of Taiwanese fruits can be used as a base ingredient for producing various processed foods and beverages. Furthermore, combining fruits of different origins can result in a new type of C. depressa product that is more akin to the preferences of both producers and consumers. The current study mainly explored the genetic characteristics and VOC profiles of the major accessions of Japanese and Taiwanese C. depressa; however, other minor accessions of the cultivar in these regions require further investigated. Future studies should investigate the flavor characteristics and sensory properties of processed food products manufactured from C. depressa fruits, such as beverages.
5. Conclusions
Twelve CAPS markers showed effective genetic polymorphisms for differentiating the 23 accessions of C. depressa from Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan. The genetic distance and VOC profiles of the leaves of Kagoshima origin were similar; however, the volatile compositions varied in the Okinawan and Taiwanese accessions. Multivariate analysis revealed distinct volatile constituents in the leaves, with the Kagoshima accession contained significantly greater amounts of piperitone and citronellal. The OPLS-DA plots showed variations in the volatile constituents of fruit edible parts across three cultivation regions, indicating the diversity in their potent aroma characteristics. The edible fruit parts of the Kagoshima accessions were distinguished by higher quantities of aldehydes, whereas Okinawan and Taiwanese fruits contained greater amounts of esters and monoterpenes. These results provide important information on the genetic characteristics and VOC profiles of C. depressa leaves and edible parts of various accessions from Japan and Taiwan. The genetic alignment of 23 major accessions of C. depressa could benefit farmers for molecular breeding and agrobiotechnology industries in these regions. These findings could also facilitate the development of distinct flavors by food and beverage processing industries.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10090939/s1, Table S1: Climatic and environmental conditions in the cultivation areas of C. depressa; Table S2: Composition of volatile organic compounds in C. depressa leaves and fruit edible parts; Table S3: Log2-fold changes, false discovery rates, and variable influence in the projection values of significant VOCs in C. depressa leaves; Table S4: Log2-fold changes, false discovery rates, and variable influence in the projection values of significant VOCs in C. depressa fruit edible parts; Figure S1: PCA biplots of predominant VOCs, physicochemical traits, and sensory properties of C. depressa fruit edible parts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.A., M.Y., F.M., S.-Y.L. and K.W.; methodology, Y.A., M.Y., S.-Y.L. and K.W.; software, M.O., Y.A. and M.Y.; validation, M.O., Y.A., M.Y., K.T. and K.W.; formal analysis, M.O., Y.A., M.K. and. M.Y.; investigation, M.O., Y.A., M.K. and. M.Y.; resources, Y.A., M.Y., F.M., S.-Y.L. and K.W.; data curation, M.O., Y.A.,and. M.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, M.O. and Y.A.; writing—review and editing, M.O., Y.A., M.Y. and K.W.; visualization, M.O.; supervision, Y.A., M.Y., K.T. and K.W.; project administration, Y.A. and K.W.; funding acquisition, Y.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Lotte Research Promotion Grant from the Lotte Foundation of Japan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
This work is part of the dissertation submitted by the first author in partial fulfillment of a PhD degree. All the authors provided informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article and Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kazuki Shimoda and Eriko Arakaki (University of the Ryukyus) for technical assistance in the VOC analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hirose, N. Characteristics of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) and development of its new applications. Nippon. Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi. 2012, 59, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikin, Y.; Fukunaga, H.; Yamano, Y.; Hou, D.X.; Maeda, G.; Wada, K. Effect of cultivation line and peeling on food composition, taste characteristic, aroma profile, and antioxidant activity of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) juice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 2384–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.Y.; Roan, S.F.; Lee, C.L.; Chen, I.Z. Volatile organic components of fresh leaves as indicators of indigenous and cultivated citrus species in Taiwan. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Musou-Yahada, A.; Yoshimoto, A.; Sakamoto, K.; Hirose, N.; Ohta, H. Multivariate analysis and characterization of flavonoids and volatile components of citrus fruits produced in Okinawa. Nippon. Shokuhin Kagaku Kogaku Kaishi. 2021, 68, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikin, Y.; Taira, I.; Inafuku-Teramoto, S.; Sumi, H.; Ohta, H.; Takara, K.; Wada, K. The composition of volatile aroma components, flavanones, and polymethoxylated flavones in Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) peels of different cultivation lines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7973–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Zhao, S.; Ning, Z.; Zeng, H.; Shu, Y.; Tao, O.; Xiao, C.; Liu, Y. Citrus fruits as a treasure trove of active natural metabolites that potentially provide benefits for human health. Chem. Cent. J. 2015, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederbacher, B.; Winkler, J.B.; Schnitzler, J.P. Volatile organic compounds as non-invasive markers for plant phenotyping. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5403–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, R.; Badenoch, N.; Miyagi, K.; Medoruma, K.; Osada, T.; Onishi, M. Multi-lineages of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) evaluated by using whole chloroplast genome sequences and its bio-diversity in Okinawa, Japan. Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takakura, A.; Tanabe, A.; Teramoto, S.; Kita, M. Diversity of Citrus depressa Hayata (Shiikuwasha) revealed by DNA analysis. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2017, 64, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Tani, K.; Kozai, N. The Morphological and genetic characteristics of local citrus grown on the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Trop. Agric. Dev. 2021, 65, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Liao, Y.Y.; Chen, P.A. Leaf volatiles and relevant gene expression as the specific characteristics in Citrus depressa accession discrimination. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Fujii, H.; Endo, T.; Ueda, T.; Sugiyama, A.; Nakano, M.; Kita, M.; Yoshika, T.; Shimizu, T.; Nesumi, H.; et al. Construction of a citrus framework genetic map anchored by 708 gene-based markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2014, 10, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikin, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Iwasaki, H.; Oku, H.; Wada, K. Stress amelioration and anti-inflammatory potential of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) essential oil, limonene, and γ-terpinene. J. Food Drug Anal. 2022, 30, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.X.; Wang, H.C.; Chu, Y.L.; Wu, Y.Z.; Liao, J.A.; Su, Z.Y. Essential oil from Citrus depressa peel exhibits antimicrobial, antioxidant and cancer chemopreventive effects. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 3982–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.J.P.; Costa, A.I.A.; Fliedel, G.; Cissé, M.; Bechoff, A.; Pallet, D.; Tomlins, K.; Pintado, M.M.E. Chemical-sensory properties and consumer preference of hibiscus beverages produced by improved industrial processes. Food Chem. 2017, 225, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Xu, C.; Chen, K. Citrus leaf volatiles as affected by developmental stage and genetic type. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17744–17766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asikin, Y.; Tamura, Y.; Aono, Y.; Kusano, M.; Shiba, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Mitsube, F.; Lin, S.Y.; Takara, K.; Wada, K. Multivariate profiling of metabolites and volatile organic compounds in Citrus depressa Hayata fruits from Kagoshima, Okinawa, and Taiwan. Foods 2023, 12, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.A.; Sugimoto, C.; Kinjo, H.; Azama, C.; Mitsube, F.; Talon, M.; Gmitter, F.G., Jr.; Rokhsar, D.S. Diversification of mandarin citrus by hybrid speciation and apomixis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Ye, X. The flavor characterization of ‘Huyou’ (Citrus changshanensis) essential oils extracted by conventional and novel methods. Agriculture 2024, 14, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asikin, Y.; Kawahira, S.; Goki, M.; Hirose, N.; Kyoda, S.; Wada, K. Extended aroma extract dilution analysis profile of Shiikuwasha (Citrus depressa Hayata) pulp essential oil. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dein, M.; Munafo, J.P., Jr. Characterization of odorants in southern mountain mint, Pycnanthemum pycnanthemoides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9722–9729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel-Roy, P.; Goldschmidt, E.E. The Biology of Citrus; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; p. 230. [Google Scholar]
- Nurdin, S.U.; Sabarina, D.; Astuti, S. Antidiabetic and antioxidant activities of bay, pandan, citrus leaves and their combination in vitro. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2019, 12, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, D.P.; Chaudhary, P.; Upadhyaya, S.R.; Ranjitkar, R.; Satyal, R.; Adhikari, A.; Satyal, P.; Parajuli, N. Chemical variability, antioxidant and larvicidal efficacy of EOs from Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck peel, leaf, and flower. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdarzadeh, F.; Hojjati, M. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of leaf, ripe and unripe peel of bitter orange (Citrus aurantium) essential oils. Nutr. Food Sci. Res. 2016, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).