Abstract
Momordica charantia is a climbing plant often used in traditional medicine to treat a large number of diseases, including diabetes. Salinity is one of the main stressors faced by plants, affecting almost half of irrigated agricultural land and constantly increasing. The aim of this study was to determine the resistance of some bitter cucumber genotypes to salt stress by means of dry matter analysis, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, malondialdehyde content, chlorophyll fluorescence, and potassium (K)/silicon (Si) and calcium (Ca)/silicon (Si) atomic ratios. Two varieties of bitter cucumber and three experimental lines were used for the experiment. Treatments with different saline solutions (100 mM of NaCl and 200 mM of NaCl) were applied and compared with an untreated control (0 mM of NaCl). The analyses revealed an increase in the dry matter content of the varieties subjected to salt stress. The Line 4 genotype showed an increase of up to 37.2% compared to the control when treated with 200 mM of NaCl. Following the analysis of the chlorophyll a content, a 38% decrease in its amount compared to the control was observed when treated with 100 mM of saline and 58.6% when treated with 200 mM of NaCl in genotype Line 4. Line 3 showed an increase in the chlorophyll a content compared to the control by 53% in the case of saline treatment with 200 mM. After the analysis of the chlorophyll b content, a 44% decrease was revealed in the case of Line 4 in the variant treated with 100 mM compared to the control and a 61% decrease in the 200 mM NaCl treatment. The highest increase in the concentration of malondialdehyde was recorded in the case of Line 4 in the variant treated with 200 mM of NaCl by 41% compared to the control. The maximum quantum yield of PS II decreased in the treated variants compared to the control plants. The most pronounced difference compared to the control was registered in the case of Line 4, where the treatment with 100 mM of NaCl caused a decrease of 16%, and the treatment with 200 mM caused a decrease of 25%. In the case of the atomic ratio, significant decreases in K and Ca were observed in the NaCl-treated variants. The observed differences between the values obtained for each studied genotype highlight the different degrees of their resistance to salinity.
1. Introduction
Momordica charantia is a tropical climbing plant that belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family. Popularly known as bitter cucumber, karela, bitter gourd, or balsam pear, this plant is widely cultivated across South America, Asia, and East Africa [1]. Bitter cucumber is a multifunctional species with a remarkably long history in traditional medicine. Momordica charantia contains a wide range of biologically active chemicals, including proteins, alkaloids, acids, saponins, flavonoids, steroids, triterpenes, and acids, due to which the plant possesses antiviral, antifungal, antibacterial, antiparasitic, antitumor, and hypoglycemic properties, being considered green insulin [2,3]. Bitter cucumber is valued in food for its high content of minerals, such as copper (Cu), calcium (Ca), iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), and zinc (Zn).
The fruit is rich in several nutrients, such as vitamins A and C, tocopherols, thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folic acid [4,5].
Salt stress impacts nearly every aspect of plant physiology and biochemistry, leading to significantly reduced crop yields. Salinity is an important abiotic stress factor that affects almost 50% of irrigated agricultural lands [6]. Irrigated agriculture is expected to increase by 20% in the coming years, which will likely expand the arable areas affected by salinity, posing a serious challenge to food security [7]. Salinity causes two different types of stress. The first stress observed is the osmotic stress that results from an imbalance in the availability of water around plant roots caused by high concentrations of solutes that significantly limit the growth and normal development of plants and the amount of biomass [8]. The installation of osmotic stress causes low water absorption and reduced plant growth. Plants can withstand the first phase of salt stress through a reduction in cell expansion and stomatal closure [9].
In the second phase of salt stress, ions accumulated in plants reach toxic concentrations. Both sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl–) can have detrimental effects on plant metabolism, causing poor nutrient uptake and deficient biomass accumulation [10,11].
The most important process that is affected in plants subjected to salt stress is photosynthesis. Maintaining photosynthesis at an optimal level depends on the protection of pigments, which are defended from the slightest signs of the installation of abiotic stress and, in general, considered an index of the plant’s level of adaptation to unfavorable environmental conditions [12,13]. The increased salt content in photosynthetic tissues causes a contraction of the thylakoid membrane. In chloroplasts, K+ is replaced by Na+, resulting in damage to photosynthetic system II (PS II) [14,15,16]. This system is a protein–pigment complex embedded in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts, having a role in capturing sunlight and splitting the water molecule (H2O) into oxygen (O2), protons (H+), and electrons (e−) [17]. Light energy captured by chlorophyll is used in photochemical reactions to carry out the process of photosynthesis or, if in excess, is dissipated by non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) with heat release or emitted as chlorophyll fluorescence. Chlorophyll fluorescence is a very sensitive indicator of changes in photosynthesis, which can be recorded with great precision [18,19]. Photosystem II is a useful parameter to examine the effects of adverse environmental conditions on crop photosynthetic performance. In conditions of salt stress, the repair of photosystem II is affected, resulting in photoinhibition showing higher values and photosynthetic efficiency showing lower values [20,21,22,23]. Another effect of salt stress is the appearance of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Since the O2 concentrations are high during photosynthesis, ROS are especially formed in the chloroplasts [24]. These oxygen species can severely disrupt plant metabolism through oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids [25].
Lipid peroxidation causes the destruction of the integrity of cell membranes, which affects their selective permeability, disrupting essential cellular processes. The destruction of cell membranes leads to a process of protein lysis in the membrane system, thus affecting vital functions such as signaling and the structural stability of the cell [26,27]. malondialdehyde (MDA) is one of the most important products of the peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in biomembranes, which highlights the level of damage to the membrane system under the action of salt stress [28]. MDA is considered a marker of oxidative stress at the cellular level, with high levels indicating an intense lipid-peroxidation process and, therefore, poor resistance. The presence of MDA triggers enzymatic defense mechanisms [29,30]. Maintaining cell membrane stability is an indicator for identifying tolerant and stress-sensitive varieties in many crops [29,30,31,32].
Maintaining an optimal supply of K and Ca, as well as reducing Na absorption, are essential features of a high tolerance to salt stress. A high cytosolic K/Na ratio is specific to tolerant cultivars and is used as a parameter to identify salt-tolerant cultivars. Varieties with higher salt tolerance have lower K efflux. Salt stress causes an increase in the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration, leading to various downstream reactions. Ca is essential for maintaining selective K uptake by the plant at high Na concentrations [33,34,35].
Salinity causes a negative economic impact, both due to the reduction in agricultural production and the need to manage saline soils. Due to the nutritional and medicinal importance of bitter cucumber, the interest in this plant is constantly growing. Its culture has become more and more important with its spread in different areas. In the specialized literature, there are numerous scientific works that deal with the problem of the resistance of bitter cucumber to salt stress, and, in particular, the aim is to increase the potential for adaptation to salinity by applying treatments such as methionine, jasminic acid, proline, and ascorbic acid [12,36,37].
The aim of this work was to identify the behavior of some genotypes of Momordica charantia under salt stress. The aim was to determine the adaptation capacity of some genotypes (Brâncusi, Rodeo, Line 1, Line 3, and Line 4) in order to identify the tolerant ones with the aim of obtaining favorable crop yields on saline soils. In order to determine the level of tolerance, some parameters specific to salt stress (physical, biochemical, and physiological) were monitored, such as chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, malondialdehyde, Fv/Fm, F0, Fm, dry matter, and K/Si ratios, respectively, Ca/Si.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Procedure for Obtaining Plant Material
The plant material used in this analysis consisted of leaves from various bitter cucumber genotypes. The purpose of using these genotypes is the possibility of their cultivation in the field under the conditions of the temperate continental climate specific to Romania. The difference between the genotypes lies in the appearance and size of the fruits (Figure 1).

Figure 1.
The appearance of fruits of different sizes for the Momordica charantia genotypes studied: (a) Brâncusi variety fruits; (b) Fruit Line 3; (c) Fruit Line 4; (d) Fruits of the Rodeo variety; (e) Fruit Line 1. A description of each genotype has been added to the Supplementary Information section, Table S1.
To obtain them, seeds of equal size of bitter cucumbers belonging to two varieties (Brâncusi and Rodeo varieties) and three experimental lines (Line 1, Line 3, and Line 4) were sown in cells in the greenhouse of the Research Institute for Agriculture and Environment (ICAM) belonging to “Ion Ionescu de la Brad” University of Life Sciences, Iași, Romania. For seed germination, a temperature of 28 °C was fixed in the greenhouse. After the germination of the seeds, when the plants were in phenophase 102 of the BBCH scale (corresponding to the presence of the first two true leaves on the main stem), they were moved to vegetation pots with a volume of 12 L. The substrate used both for germination and in the vegetation pots was the same. Information about the properties of the substrate used can be found in Supplementary Information Table S2. For each genotype, 9 plants were used and were divided as follows: 3 control plants, 3 plants treated with 100 mM saline (V1), and 3 plants treated with 200 mM saline (V2). The experiment was moved to the Solarium of the University, where the humidity was about 60% and the and the temperature was identical to that outside. Thus, the temperature during the day was between 26 and 28 °C, and during the night, it was between 20 and 22 °C. To determine the effect of salinity on the 5 genotypes, the plants were treated with saline solutions at concentrations of 0 mM of NaCl—control (M), 100 mM of NaCl—V1, and 200 mM of NaCl—V2. In total, three treatments were applied in three different developmental phenophases approximately 10 days apart. The first treatment was applied in phenophase 201 BBCH (representing the formation of the first lateral shoot), the second treatment was applied in phenophase 501 BBCH (representing the formation of the first flower on the plant), and the last treatment was applied in phenophase 701 BBCH (being equivalent to the emergence of the first fruit). The plants were treated with an amount of 300 mL of saline solution per treatment. The plant growth procedure was similar to that presented in our previous work on bitter cucumber [38,39]. The leaves used for dry matter analysis, XRF analysis, malondialdehyde, and chlorophyll pigments were harvested 7 days after the application of the last treatment. Fluorescence analysis was performed in the field on day 7 after the last treatment. Analyzes were performed using fully mature leaves located on the mid-section of the main shoot.
2.2. Procedure for Determination of Dry Matter
A known amount of fresh leaves was oven-dried for 5 h at 105 °C. The weights were considered constant when they remained unchanged between two weighings, indicating that the leaves were perfectly dry. Once identical values were obtained at two weighings, the percentage of dry matter was calculated. Three repetitions of this analysis were performed and averaged.
2.3. Procedure for Determining the Height and Number of Fruits
The average height of the plants was obtained by measuring the plants with the help of a tape measure and making the averages for each variant of the 5 genotypes. For the average number of fruits per plant, fruit counts were made on the plants of each variant, and the averages were then made. Biometric analyses were carried out 7 days after the application of the last treatment and were carried out on each plant from the analyzed variants (M, V1, and V2) of each genotype.
2.4. Procedure for the Determination of Photosynthetic Pigments
A sample of 0.5 g was used for the analysis of photosynthetic pigments. A mixed sample was prepared by shredding and homogenizing nine leaves (three each from three plants of the same variant) in 80% acetone—Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). The average sample was made to avoid high consumption of chemicals; thus, only 1 replication was made for each variant (M, V1, and V2) of the 5 genotypes. The extraction was carried out using a Gooch filter. The resulting extract was brought to a final volume of 50 mL with acetone. Readings for the determination of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b were taken at 663 and 645 nm. Quantification of absorbances was carried out using specific calculation formulas:
where A663 and A645 represent the absorbances measured at 645 nm and 663 nm [40,41].
Chlorophyll a (mg/g) = 12.25·A663 − 2.79·A645
Chlorophyll b (mg/g) = 21.5·A645 − 5.1·A663
2.5. Procedure for Determination of Lipid Peroxidation
The level of lipid peroxidation was studied by measuring the amount of malondialdehyde resulting from the reaction with thiobarbituric acid (TBA)—Merck—according to the method proposed by Heath and Packer in 1968. A 0.5 g mixed sample (prepared as described for chlorophyll analysis) was used for each measurement. The plant material was homogenized with 10 mL of trichloroacetic acid (TCA)—Merck—at 5% concentration, and the homogenate was centrifuged for 10 min at 15,000 revolutions per minute. A total of 1 mL of the supernatant was pipetted, then 2 mL of 0.5% TBA and 2 mL of 20% TCA were added. The obtained mixture was heated at 95 °C for 30 min; then, to stop the reaction, it was rapidly cooled in an ice bath. The product was centrifuged for 10 min at 10,000 revolutions per minute. The absorbance of the obtained supernatant was read at 532 nm. The amount of MDA was estimated using the molar extinction coefficient, 115 mM−1cm−1. This coefficient was reported in the specialized literature. Using the coefficient resulted in the formula C(mM) = A/115 [42]. As in the case of chlorophyll, the aim was to reduce the excessive consumption of chemicals, which is why only one replication was carried out.
2.6. The Procedure for Determining the Parameters F0 and Fm and the Ratio of Fv/Fm
The maximum quantum yield of PS II represents its maximum efficiency and is calculated based on the following formula: Fv/Fm. This ratio is given by the device but can also be calculated using the following formula: (Fm − F0)/Fm. The fluorometer is equipped with a light source that is applied to the plant material and determines the excitation of the chlorophyll in the sample, thus determining the fluorescence. The minimum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light (F0) and the maximum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light (Fm) are values determined by the apparatus together with the Fv/Fm ratio. Six reads were taken for each variant of the five genotypes (M, V1, and V2). Data used are the mean of six replicates. The analyses performed in this paper were chosen to cover as many aspects of salt stress as possible. Thus, determinations were pursued for oxidative stress, ionic stress, and osmotic stress.
2.7. Characterization Methods
UV-Vis spectra were recorded on a Specord 210 Plus—Analitik Jena (Jena, Germany) spectrophotometer in 1 cm diameter cuvettes. Fluorescence was quantified using the Chlorophyll Fluorometer OS30p+—Opti-Sciences, Inc. (Huston, TX, USA). The device offers direct reading and graphical display of Fv/Fm and Fv/F0 measurements. It features a red Strasser OJIP light source with self-calibration at 3500 μmole. The fluorimeter displays an automatic 8-point, 25 ms rolling average to determine the maximum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light (Fm) [43]. The presence and ratio of K to Ca were determined using an EX-2600 X-Calibur SDD energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence (EDXRF) system—Xenemetrix Ltd. (Migdal HaEmek, Israel). Apart from the qualitative assessment, we performed a quantitative evaluation of the K content, considering that Si is constant. Measurements were performed under identical conditions for all samples (40 μA, 15 kV, 10 s, in air). The Kα1 peaks for Ca and K were identified, and their intensity (in Counts) was used to calculate the K/Si and Ca/Si ratios using the following formulas: K/Si = (IK/39.1)/(ISi/28) and Ca/Si = (ICa/40)/(ISi/28). The analysis was performed directly on the biological material; being a mass analysis, a single replication was performed.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Two-Way Anova, Student’s t-test, Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient, and principal component analysis (PCA) statistical tests were used in this paper. The Two-Way Anova test was carried out using Microsoft Excel 2016 in order to evaluate the influence of two factors on one variable. In this study, the influence of saline treatments and studied genotypes were analyzed [44,45]. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to determine the normal distribution of the data in order to perform the Two-Way Anova Test.
Student’s t-test was performed using Microsoft Excel to test the differences between the means of two independent groups of data. In the case of the present study, group I was represented by the values obtained in the control of each of the three analyses on which it was performed, group II was represented by the values for the treatment with 100 mM of NaCl, and group III was represented by the values obtained when treated with 200 mM of NaCl [46].
The PCA analysis was performed for a better visualization of the obtained data. This was done with Origin 2021 9.8.0.200.
3. Results
3.1. Chlorophyll a and Chlorophyll b
The amounts of chlorophyll a varied according to the concentration of the applied saline treatment (Figure 2A). For the control, the values fluctuated between 8.45 mg/mL in the case of Line 3 and 13.67 mg/mL for Line 4. The variants treated with 100 mM of NaCl presented chlorophyll values between 8.34 mg/mL in Line 4 and 11.57 mg/mL in the case of the Rodeo variety. In the variants treated with 200 mM of NaCl, the chlorophyll a values were between 5.65 mg/mL in the case of Line 4 and 12.99 mg/mL in Line 3.
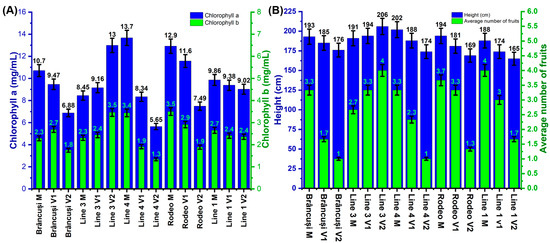
Figure 2.
(A) Effect of salt stress on the concentration of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in the leaves of bitter cucumber genotypes expressed in mg/mL. Two-Way Anova test showed a highly significant statistical influence of treatments on chlorophyll a and b content (p < 0.001). (B) The effect of salt stress on plant height measured in cm and the number of fruits per plant. Error bars represent standard error (0.05).
In the case of the control plants, the chlorophyll b (Figure 2A) values fluctuated between 2.31 mg/mL in the case of Line 3 and 3.5 mg/mL in the Rodeo variety. In the plants from the variants treated with 100 mM of NaCl, the lowest value was observed in the case of Line 4 (1.91 mg/mL) and the highest value in the case of the Brâncusi variety (2.69 mg/mL). Regarding plants treated with the 200 mM saline solution, the lowest value was recorded in Line 4 (1.34 mg/mL), and the highest value of chlorophyll b was noted in Line 3 (3.44 mg/mL). Figure S2 shows the appearance of plants subjected to saline stress compared to untreated plants in terms of the amount of chlorophyll. The plants in border A were subjected to salt stress, and those in border B were control plants.
3.2. Height and Average Number of Fruits
In the case of control variants, the highest average plant height was noted in Line 4 (202 cm), and the lowest average height was observed in Line 1 (188 cm) (Figure 2B). In the case of the variants subjected to the saline treatment with 100 mM, the average height values fluctuated between 174 cm in Line 1 and 194 cm in Line 3. In the variants that were subjected to the treatment with 200 mM of NaCl, the highest value was recorded in Line 3 (206 cm), and the smallest was recorded in Line 1 (165 cm). In the case of the average number of fruits per plant in the control variants, the highest value was recorded in Line 1 (4), and the lowest value was recorded in Line 3 (2.67) (Figure 2B). In the variety treated with 100 mM saline solution, the most fruits were found in the Rodeo and Linia 3 varieties (3.33), and the fewest fruits were found in the Brâncusi variety (1.67). The variant treated with 200 mM of NaCl presented a maximum number of fruits per plant of four in Line 3 and a minimum number of one in the Brâncusi variety and Line 4.
3.3. Dry Matter
After analyzing the data in Figure 3a, a fluctuation of the percentage values of the amount of dry matter was observed in the control plants between 16.29% in Line 4 and 20.15% in the Rodeo and Line 1 genotypes. In the case of treatment with 100 mM saline, the values fluctuated between 20.55% in Line 1 and 22.98% in the Brâncusi variety. Treatment with 200 mM of NaCl determined a minimum value of dry matter in genotype Line 3 (21.85%) and a maximum value in genotype Line 1 (22.56%).
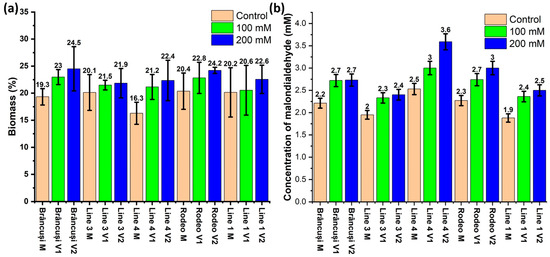
Figure 3.
(a) Effect of salt stress on dry matter percentage in bitter cucumber leaves for each studied genotype. Error bars represent the standard deviation (n = 3). (b) The effect of salt stress on the concentration of malondialdehyde in the leaves of the bitter gourd varieties and lines studied after the application of the third treatment. Values are expressed in mM. Error bars represent the standard error (0.05). The Two-Way Anova test showed a highly significant statistical influence of treatments and genotypes on malondialdehyde concentration (p < 0.001).
3.4. Malondialdehyde (MDA)
Malondialdehyde (Figure 3b) showed control plant values between 1.88 mM in the case of Line 3 and 2.53 mM in Line 4. In the case of the variants treated with a saline solution of 100 mM of NaCl, the highest value of malondialdehyde was recorded in Line 1 (2.33 mM), and the highest value was recorded in the Rodeo variety (2.74 mM). Plants treated with a 200 mM NaCl saline solution showed malondialdehyde values between 2.40 mM in Line 1 and 3.59 mM in Line 4.
3.5. Maximum Quantum Yield of PS II (Fv/Fm)
In Figure 4a, a fluctuation of the values was observed in the control variants; the values fluctuated between 0.75 in the Brâncusi variety and 0.8 in Line 4. In the variant treated with 100 mM of NaCl, the highest value was recorded in Line 3 (0.74), and the lowest was recorded for the Rodeo variety (0.67). In the case of the variant treated with the most concentrated saline solution, the maximum value of the Fv/Fm ratio was recorded in Line 3 (0.71), and the minimum value was recorded in the case of the Rodeo variety (0.61).
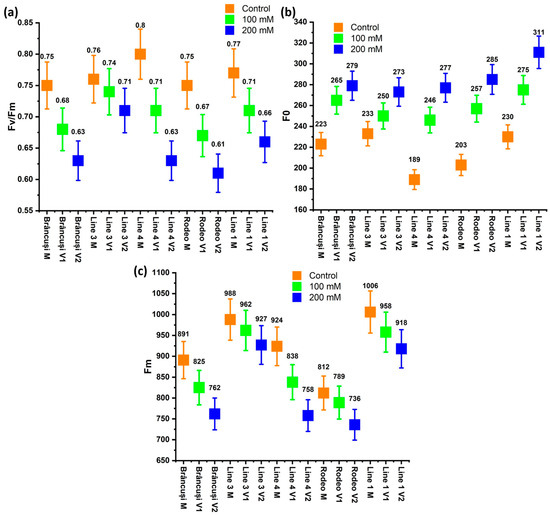
Figure 4.
The effect of saline stress on some fluorescence parameters: (a) the maximum quantum yield of PS II; (b) minimum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light; (c) maximum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light. The Two-Way Anova test showed a highly significant statistical influence of the genotypes (p < 0.005) and a distinctly significant influence (p < 0.005) of the treatments on the maximum quantum yield of PS II (p < 0.001). Bars represent standard error (0.05).
3.6. Minimum Fluorescence Yield in the Absence of Photosynthetic Light (F0)
Following the analysis of the values of the minimum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light (F0), values were recorded in the case of untreated controls between 198 in Line 4 and 230 in Line 1 (Figure 4b). When applying the 100 mM saline treatment, the lowest value for F0 was recorded in Line 4 (246) and the highest in Line 1 (275). In the case of the 200 mM saline treatment, the highest value was recorded in Line 1 (311), and the lowest was recorded in Line 3 (273).
3.7. Maximum Fluorescence Yield in the Absence of Photosynthetic Light (Fm)
The maximum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light (Fm) showed, in the case of the untreated control, the lowest value in the Brâncusi variety (891) and the highest value in Line 1 (1006) (Figure 4c). In the variant treated with a saline solution of 100 mM of NaCl, the maximum value of Fm was recorded in Line 3 (962), and the minimum value was observed in the Rodeo variety (789). In the case of treatment with 200 mM of NaCl, the maximum value was observed in the case of Line 3 (927), and the minimum value was observed in the case of Line 4 (758).
3.8. X-ray Fluorescence (XRF)
In the case of this XRF analysis, Si was used as a reference, yielding quantitative K/Si and Ca/Si ratios. The reports are presented in Table 1 and in Figure S1. A strong positive linear correlation was registered between the two reports (r = 0.8), which implies a similar behavior of calcium and potassium in the studied genotypes. In the case of the control variant, the highest value of the two ratios was observed in Brâncuși, and the lowest value was noted in Line 1. With the 100 mM NaCl treatment, the highest values of the ratios were noted in the Brâncusi variety, and the lowest values were noted in Line 4. In the version treated with 200 mM saline solution, the lowest values of the ratios were noted in Line 3, and the lowest values were in the Rodeo variety.

Table 1.
Analysis of elements K, Ca, and Si performed via XRF analysis.
The Kolmogorov–Smirnov statistical test confirmed the normal distribution of the data used to perform the Two-Way Anova tests. According to the Two-Way Anova test (Table S3), the amounts of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b showed statistically highly significant differences (p < 0.001) in the case of the variable a Treatment and statistically insignificant (p > 0.1) in the case of the variable b Genotype. The Two-Way Anova test highlighted that the differences recorded between the chlorophyll values in the studied variants were due to the applied NaCl treatments and not to genotypes.
The Two-Way Anova test (Table S3) revealed highly significant differences (p < 0.001) in the case of malondialdehyde, both in the case of the variable a treatment and in the case of the variable b genotype. According to the results of the Anova test, it could be concluded that the values of malondialdehyde are influenced both by the saline treatments applied and by the studied bitter cucumber genotypes. It can be admitted that the null hypothesis (H0) was rejected, and the alternative hypothesis (H1) was accepted.
The Two-Way Anova test (Table S3) revealed statistically significant (p < 0.001) differences in the values of the maximum quantum yield of PS II in the case of the variable Genotype and distinctly significant differences (p < 0.005) in the case of Treatment. Following these observations, it was concluded that H0 was rejected and H1 was accepted in both cases.
Following the analysis of the results obtained after applying the Student t-test on chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b (Table 2), a significant difference (p one-tail < 0.05) was observed between the control (I) and the variant treated with 100 mM of NaCl (II) and a weak statistical difference (p one-tail < 0.1) in the case of the control (I) and the variant treated with 200 mM of NaCl (III). There were no statistically significant differences between the two treatments (II and III) (p one-tail > 0.1). The weak statistical differences or their absence were due to the different behavior of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in the case of Line 3, where their values increased in the treated plants compared to the other studied genotypes.

Table 2.
Statistical differences between Momordica charantia genotypes between the control variant and the variants treated with saline solutions in terms of chlorophyll, malondialdehyde, and the maximum quantum yield of PS II.
The Student’s t-test (Table 2) revealed highly significant differences (p one-tail < 0.001) from a statistical point of view between the control (I) and the variant treated with 100 mM of NaCl (II). In the case of the control (I) and the variant treated with 200 mM of NaCl, distinctly significant statistical differences were observed (p one-tail < 0.005), and weakly significant statistical differences were recorded between the two treatments with saline solutions (II and III) (p one-tail < 0.1). Based on the observations made (Table 2), it could be concluded that the null hypothesis (H0) was rejected, and the alternative hypothesis (H1) was accepted.
The Student’s t-test (Table 2) revealed distinctly statistically significant differences (p ≤ 0.01) in the fluorescence values in the case of comparisons between the untreated control (I) and the treatment with 100 mM of NaCl (II), as well as with the treatment with 200 mM of NaCl. In the case of the two treatments (II and III), the differences in the chlorophyll fluorescence values were statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05). Following the observations made on the basis of the Student’s t-test, it could be concluded that H0 was rejected and H1 was accepted.
Due to the large amount of analyzed data, it was decided to use principal component analysis for a more efficient compression (Figure 5). The results of the PCA analysis indicated that the first two components had an eigenvalue > 1. According to the biplots, the genotypes were spread across three-quarters of the biplot, indicating a significant level of genetic variation among the tested genotypes. Biplot analysis was performed with two main factors (F1 and F2) for both the control and the two saline treatments (100 mM of NaCl and 200 mM of NaCl). The control biplot (Figure 5A) explained 90.27% of the total variability, and it can be seen that all variables contribute almost equally to the variance explained by PC1 and PC2. The PCA biplot for 100 mM of NaCl (Figure 5B) explained 75.84% of the total variability, showing that BM%, CI b, Fm, and Fv/Fm were the most discrepant parameters. In the case of this biplot, the most sensitive genotype to salt stress can be observed: Line 4, which is very weakly correlated with malondialdehyde, because it increases in sensitive genotypes. The PCA biplot for the 200 mM NaCl treatment (Figure 5C) showed 81.78% of the total variability, reflecting that F0, K/Si, Cl a, and Cl b are the most discriminated traits. In the case of this representation, a much better correlation of the sensitive genotype was observed with malondialdehyde, but also with biomass because the percent dry matter tends to increase in genotypes affected by stress. The cluster formed by Linia 4, Rodeo, and Brâncuși also highlights the poor resistance of the varieties to salinity. The most resistant genotype, Line 3, is strongly correlated with the parameters K/Si, Fv/Fm, Cl a, Cl b, and Ca/Si, which represent the main parameters of salinity resistance. Similar results have been reported in the specialized literature [47,48,49].
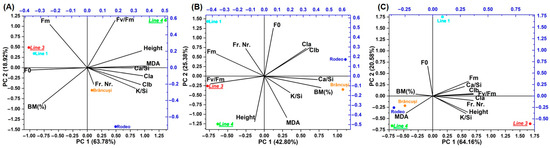
Figure 5.
Principal component analysis for control (A), 100 mM of NaCl (B), and 200 mM of NaCl (C). BM%—biomass represented by dry matter determined as a percentage; Cl a—chlorophyll a; Cl b—chlorophyll b; MDA—malondialdehyde; F0—minimum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light; Fm—maximum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light; Fv/Fm—the maximum quantum yield of PS II; K/Si—potassium—silicon ratio; Ca/Si—calcium—silicon ratio; height; Fr. Nr.—fruit number.
4. Discussion
4.1. Dry Matter
The accumulation of osmolytes in plant cells is indispensable for achieving osmotic balance under saline conditions. Organic substances with the role of osmolytes, such as sugars and amino acids, determine a high concentration of the vacuolar juice necessary to absorb water from saline soils [50]. This effect was highlighted by the study of the five genotypes of Momordica charantia. Following the analysis of the data in Figure 3a, a general tendency to increase the percentage amount of dry matter was observed in the variants subjected to saline stress compared to the control values. The biggest difference compared to the control variant was noted in the Line 4 genotype, where the treatment with 100 mM of NaCl caused a 29% increase in the amount of dry matter compared to the untreated control, and the treatment with 200 mM of NaCl caused a 37.2% increase. These pronounced increases highlight a poor adaptation to salt stress. This result is consistent with our previous study on metabolites accumulated in bitter cucumber genotypes, where the highest amounts of proline and aromatic amino acids were recorded in Brâncusi and Linia 4 [39]. Line 3 showed the lowest increase in percent dry matter compared to the untreated control. Treatment with 100 mM of NaCl caused a 6% increase in dry matter and 200 mM of NaCl 8%. A high amount of osmolytes, although it does not disrupt the vital activity of the plant, implies a directed energy consumption in this sense and energy used under normal conditions in growth and development processes, so through the analysis, we can deduce a lower total amount of biomass in plants that present high amounts of osmolytes.
4.2. Plant Height and Number of Fruits
Through osmotic stress and induced ion imbalance, salt stress affects plant growth and development [51]. The general tendency in the studied genotypes was to reduce the plant height and the number of fruits. The strongest decrease in height was achieved in Line 4, where the variant treated with 100 mM of NaCl presented a 7% decrease compared to the untreated control, and in the 200 mM NaCl variant, 14% (Figure 2B). Similar results were reported by Sunjeet Kumar et al. in their study on stress resistance of some genotypes of Oenanthe javanica. The authors state that the strongest decreases were recorded in tolerant genotypes [52]. Genotype Line 3 showed a slight increase in the height of stressed plants typical of resistant genotypes. In plants treated with 100 mM of NaCl, the increase was 1.5% compared to the control, and in plants treated with 200 mM of NaCl, the average height increased by 6% compared to the control. This behavior can be explained by the installation of the first stress phase according to the bifactorial model proposed by Munns, unlike the other studied genotypes that passed into the ionic stress phase. Between the analysis of the height and the average number of fruits, a strong positive linear correlation r=0.73 was recorded, which implies that with the decrease in the height of the plants, the number of fruits also decreased.
4.3. Chlorophyll a and Chlorophyll b
According to the review by Shanhu Hao et al. (2021), the amount of chlorophyll decreases in sensitive plants when subjected to salt stress [53]. Following the analysis of the chlorophyll a values, a general tendency to decrease its amount was observed in the variants treated with saline solutions, except for Line 3, where a directly proportional increase in chlorophyll a was noted with the concentration of the applied saline solution (Figure 2A). In this genotype, compared to the untreated control, the amount of chlorophyll a in the treatment with 100 mM of NaCl increased by 8.4%, and in the case of the variant treated with 200 mM of NaCl, a value of chlorophyll a 53% higher than the control was observed. This increase in the amount of chlorophyll highlights not only the increased resistance of the genotype to salt stress conditions but also the fact that the plants fit into the biphasic model proposed by Munns in 1993 [50]. It can thus be deduced that Line 3 is in the osmotic stress phase, which explains the increases observed compared to the other Momordica charantia genotypes that are in the toxic stress phase. Keeping plants from Line 3 for a longer period of time in the osmotic stress phase, correlated with an increase in the amount of chlorophyll, can be considered a mechanism of their resistance to saline stress compared to the other studied genotypes. The strongest decrease in the amount of chlorophyll was noted in Line 4. In this genotype, the amount of chlorophyll decreased by 38% in the variant treated with 100 mM saline solution and by 58.6% compared to the untreated control in the variant treated with 200 mM of saline. The reduced amount of chlorophyll in the case of the Line 4 genotype can be seen in Figure S2A compared to control plants in Figure S2B. A study by Khalid A. Al-Gaadi et al. on tomato genotypes treated with salt water revealed a pronounced decrease in the amount of chlorophyll, showing similarities with the results obtained in the present study [54].
The correlation between chlorophyll b and chlorophyll a was r = 0.98 (Table S4). Due to this aspect, the behavior of chlorophyll b was almost identical to that of chlorophyll a. A general trend of decreasing chlorophyll b can be observed in all studied genotypes except for Line 3, where the values in the case of the treated variants increase by 5.6% in the treated variant with 100 mM of NaCl and by 49% in the version treated with 200 mM of NaCl (Figure 3). According to specialized literature, in the case of salinity-resistant plants, chlorophyll increases to maintain the normal physiological state even under unfavorable conditions [55]. Among the genotypes studied, the most pronounced decrease was recorded in Line 4, where the treatment with 100 mM of saline caused a decrease in the amount of chlorophyll b by 44% compared to the untreated control. The treatment with 200 mM of saline resulted in a 61% decrease in chlorophyll b compared to the control.
4.4. Malondialdehyde
After analyzing Figure 3b a trend of increasing malondialdehyde (MDA) values was observed. A study by Jin Cheng Xing et al. (2019) on the effect of salinity on the growth of Portulaca oleracea revealed the same general reaction of increasing MDA content in plants treated with NaCl [56]. The strongest increase in the amount of malondialdehyde was recorded in Line 4, where treatment with 100 mM of saline produced a 17% increase compared to the untreated control, and treatment with 200 mM of saline caused a 41% increase in MDA compared to the witness. These differences between the untreated control and the variants exposed to salt stress highlight an accentuated peroxidation of lipids by ROS, thus allowing us to conclude that Line 4 is the most sensitive genotype studied regarding salt stress. In a study by Dajiang Wang et al. (2022) on salt stress in three Malus species, the authors showed percentage values of MDA increase similar to the present study [28]. Compared to Line 4, the smallest differences between the control and saline-treated variants were recorded in Line 3. In this genotype, salinity caused an 18% percent increase in MDA for 100 mM NaCl treatment and a 23% increase for treatment with 200 mM of NaCl. The reduced amounts of MDA in plants subjected to salt stress highlight their good resistance to adverse factors [57,58].
4.5. Maximum Quantum Efficiency of PSII
Among the fluorescence parameters, the most important is the maximum quantum efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm). A significant decrease in this ratio highlights the fact that the plants are subjected to stress that causes a reduction in photosynthesis [18,59,60]. The general trend observed in the saline-treated variants was a decrease in the Fv/Fm ratio. Decreases in this parameter have been reported in the specialized literature at similar saline concentrations [61]. Among the genotypes studied, the most pronounced decreases were recorded in the case of Line 4, followed by the Brâncusi variety. In Line 4, in the case of the variant treated with 100 mM of NaCl, the maximum quantum efficiency of PS II decreased by 16%, and in the case of treatment with 200 mM of NaCl, the value decreased, compared to the untreated control, by 25%. The decrease in Fv/Fm implies that there is a significant destruction of photosystem II, which causes a decrease in chlorophyll content and a low photosynthetic rate that can reduce plant growth and yield [62].
4.6. Minimum Fluorescence Yield in the Absence of Photosynthetic Light
The increase in the minimum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light (F0) value can be explained by the activation of the processes of dissipation of excessive light energy in the form of heat or fluorescence to protect the plants against damage caused by salt stress (Figure 5B). The most pronounced difference between the control and treated variants was recorded in Line 4. In the case of this line, the plants treated with 100 mM saline solution showed an increase in F0 by 30%, and in the case of treatment with 200 mM saline solution, the value of F0 increased by 46%. In their study on the correlation between chloroplast ultrastructure and fluorescence parameters in rice, Koji Yamane et al. (2008) reported increases in F0 with applied saline treatments [63]. The maintenance of very small differences in the case of F0 highlights that Line 3 was affected by salt stress at a very low level, indicating good salinity resistance. In the V1 variant, Line 3 showed an increase of 7% and in the case of the V2 variant, a 17% increase compared to the control was noted.
4.7. Maximum Fluorescence Yield in the Absence of Photosynthetic Light
Maximum fluorescence yield in the absence of photosynthetic light (Fm) showed a tendency toward decreasing values in the case of variants treated with saline solutions (Figure 5C). The decrease in Fm values in plants subjected to salt stress may indicate a reduction in the plant’s ability to efficiently use solar energy, which may be the result of a photosystem II deterioration process [18]. The strongest decrease compared to the control was recorded in the case of Line 4, where the variants treated with 100 mM saline solution recorded values 9.3% lower than in the case of control plants, and the variants treated with 200 mM showed a decrease in values by 18% compared to the untreated witness. The smallest differences between control and treated plants were recorded in line 3. In this genotype, the variant treated with 100 mM of NaCl showed a decrease of 2.63%, and the variant treated with 200 mM of NaCl showed a decrease compared to the control of 6.47%. Yu-Chang Tsai et al. (2019), in their paper on the efficiency of photosynthesis in the context of salt stress in Oryza sativa, obtained lower Fm values in plants subjected to salt stress; thus, the authors positively correlated salinity with the Fm values obtained [18].
4.8. X-ray Fluorescence
The use of silicon as a reference element in the XRF analysis was made due to the low amount found in the plant and due to its inertness toward the biological environment [64,65]. The analysis tracked the ratios of silicon to K and Ca, two essential elements in plants, antagonistic to Na [66]. By the inertia of Si, we consider that the fluctuations of the two ratios are given by the fluctuations of the amounts of K and Ca in control plants and those subjected to saline stress. Following the analysis of the spectra in Table 1 and Figure S1, a general downward trend of the two ratios can be observed. Considering the ratios determined and the fact that in plants treated with NaCl, there were decreases in the amounts of Ca and K due to the supply of Na, it can be assumed that there is an ionic imbalance. Similar effects of decreasing the amounts of calcium and potassium, under saline stress conditions, have been reported in other scientific works using atomic absorption spectrometry as an analytical technique [33,34]. The reduced amount of K in plant cells subjected to salt stress is determined by the excessive influx of Na into the cytoplasm, which causes the depolarization of the membrane potential [67]. Thus, using well-known information about the K/Na ratio, we tried to indirectly determine the amount of Na in the studied genotypes. The data provided by the XRF analysis reveal the greatest decreases in both K/Si and Ca/Si at Line 4, where decreases in calcium amounts were observed at 53.3% in the V1 variant and 61.79% compared to the control in the V2 variant. Compared to these very significant decreases, the smallest differences were observed in Line 3 (Table 1), where calcium ratios decreased by a maximum of 3.18% in plants treated with 100 mM of NaCl and by 10.21% in plants treated with 200 mM of NaCl in comparison with the untreated control. This insignificant decrease in values highlights the ability of plants to selectively absorb the necessary elements. This property can be considered a component of the resistance mechanism of the genotype to salt stress. Both calcium and potassium are considered essential elements in plants, with a role in growth and development [68,69], so the analysis of these elements can be correlated with the plant’s ability to produce biomass. Considering the above, in the present paper, a single resistance mechanism identified in the Line 3 genotype is supported with experimental evidence.
For a better understanding of the adaptation mechanism observed at Line 3, a scheme was made with the variations of each studied parameter (Figure 6).
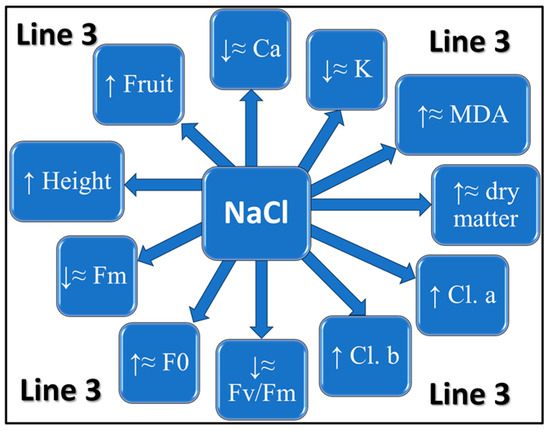
Figure 6.
General scheme of the adaptation mechanism observed in Line 3. The scheme represents the variations of each studied perimeter in the variants subjected to stress (V1, V2) compared to the untreated control (M); ↑—increase, ↓—decrease, ≈ approximately equal.
5. Conclusions
The genotypes of Momordica charantia used in the present study showed significant variation in various parameters under normal and salt-stress conditions. The monitored parameters can be used to identify bitter cucumber genotypes resistant to salt stress. These results were confirmed by PCA analysis.
Due to a large amount of chlorophyll, a maximum quantum yield of the high photosynthetic system II and optimal amounts of Ca and K, Line 3 stood out as the most resistant genotype, which was confirmed by the physiognomic appearance of the stressed plants. For this reason, the genotype could be used for crops on saline soils. The presented results make it possible to open new research directions with the perspective of identifying other possible resistance mechanisms. In future research, we aim to analyze the effect of salt stress on the bioactive substances that make the species used in traditional medicine.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10090893/s1, Table S1: A brief description of the Momordica charantia genotypes studied. Table S2: The culture substrate, proportions, and features. Table S3: Ananalysis of variance of Momordica charantia genotypes subjected to salt stress in terms of chlorophyll, malondialdehyde, and PS II maximum quantum yield. Table S4: Pearson’s test for the degree of correlation between chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Figure S1: XRF spectra: (a) Brâncusi control; (b) Brâncuși V1; (c) Brâncuși V2; (d) Line 3 control; (e) Line 3 V1; (f) Line 3 V2; (g) Line 4 control; (h) Line 4 V1; (i) Line 4 V2; (j) Rodeo control; (k) Rodeo V1; (l) Rodeo V2; (m) Line 1 control; (n) Line 1 V1; (o) Line 1 V2. Figure S2: An image captured during the experiment, 7 days after the application of the last treatment. The image highlights the visible differences between Line 4 genotype plants subjected to salt stress (panel A) and control plants (panel B).
Author Contributions
Ș.O.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Visualization, Formal Analysis, and Writing—Original Draft; C.S.: Conceptualization and Validation; A.E.M.: Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, and Writing—Review and Editing; C.D.J.: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review and Editing, and Supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Joseph, B.; Jini, D. Antidiabetic effects of Momordica charantia (bitter melon) and its medicinal potency. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2013, 3, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, R.; Samadder, A.; Banerjee, J. Anti-diabetic Activity of Momordica Charantia or Bitter Melon: A Review. Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 3, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Abascal, K.; Yarnell, E. Using bitter melon to treat diabetes. Altern. Altern. Ther. 2005, 11, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwai, K.E.; Rao, K.S.; Kaluwin, C.; Jones, G.P.; Rivett, D.E. Chemical Composition of Momordica charantia L. Fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 1762–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, D.; Sangha, M.K.; Singh, M.; Pathak, M.; Bala, M. Variation of Mineral Composition in Different Fruit Parts of Bitter Gourd (Momordica charantia L.). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2023, 201, 4961–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Physiological processes limiting plant growth in saline soils: Some dogmas and hypotheses. Plant Cell Environ. 1993, 16, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrasek, G.; Rathod, S.; Manohara, K.K.; Gireesh, C.; Anantha, M.S.; Sakhare, A.S.; Parmar, B.; Yadav, B.K.; Bandumula, N.; Raihan, F.; et al. Salt Stress in Plants and Mitigation Approaches. Plants 2022, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slabu, C.; Zörb, C.; Steffens, D.; Schubert, S. Is salt stress of faba bean (Vicia faba) caused by Na+ or Cl− toxicity? J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, S.; Premkumar, A. Ion Changes and Signaling under Salt Stress in Wheat and Other Important Crops. Plants 2024, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, S. Salt Resistance of Crop Plants: Physiological Characterization of a Multigenic Trait. In The Molecular and Physiological Basis of Nutrient Use Efficiency in Crops; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 443–455. [Google Scholar]
- Munns, R. Plant Adaptations to Salt and Water Stress: Differences and Commonalities, 1st ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Alisofi, S.; Einali, A.; Sangtarash, M.H. Jasmonic acid-induced metabolic responses in bitter melon (Momordica charantia) seedlings under salt stress. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivellini, A.; Carmassi, G.; Scatena, G.; Vernieri, P.; Ferrante, A. Molecular and physiological responses to salt stress in salinity-sensitive and tolerant Hibiscus rosa-sinensis cultivars. Mol. Hortic. 2023, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, U.K.; Gökçe, Z.N.O.; Gökçe, A.F. Salt Stress and Plant Molecular Responses. Intech 2016, 11, 13. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/books/advanced-biometric-technologies/liveness-detection-in-biometrics (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Murata, N.; Takahashi, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Allakhverdiev, S.I. Photoinhibition of photosystem II under environmental stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Bioenerg. 2007, 1767, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.; Gulzar, S.; Aziz, I.; Hussain, T.; Gul, B.; Khan, M.A. Effects of salinity and ascorbic acid on growth, water status and antioxidant system in a perennial halophyte. AoB Plants 2015, 7, plv004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.; Jiao, Q.; Jia, T.; Hu, X. The photosystem-II repair cycle: Updates and open questions. Planta 2024, 259, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Chen, K.C.; Cheng, T.S.; Lee, C.; Lin, S.H.; Tung, C.W. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis in diverse rice varieties reveals the positive correlation between the seedlings salt tolerance and photosynthetic efficiency. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peršić, V.; Ament, A.; Antunović Dunić, J.; Drezner, G.; Cesar, V. PEG-induced physiological drought for screening winter wheat genotypes sensitivity—Integrated biochemical and chlorophyll a fluorescence analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 987702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi-Golezani, K.; Hosseinzadeh-Mahootchi, A.; Farhangi-Abriz, S. Chlorophyll a fluorescence of safflower affected by salt stress and hormonal treatments. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Carrow, R.N.; Duncan, R.R. Photosynthetic responses to salinity stress of halophytic seashore paspalum ecotypes. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Kreslavsky, V.; Bharti, S.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Jajoo, A. Analysis of salt stress induced changes in Photosystem II heterogeneity by prompt fluorescence and delayed fluorescence in wheat (Triticum aestivum) leaves. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2011, 104, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, U.K.; Gökçe, Z.N.Ö.; Gökçe, A.F. Drought and salt stress effects on biochemical changes and gene expression of photosystem II and catalase genes in selected onion cultivars. Biologia 2021, 76, 3107–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, W. The effect of hydrogen peroxide on CO2 fixation of isolated intact chloroplasts. BBA-Bioenerg. 1976, 440, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, K. Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Yang, M.M.; Kong, D.S.; Zhang, Y.J. Effect of Drought Stress on Lipid Peroxidation, Osmotic Adjustment and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity of Leaves and Roots of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. Seedling. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 65, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, H.; Sivakumar, P.; Chakrabarty, R.; Thomas, G. Scavenging of reactive oxygen species in NaCl-stressed rice (Oryza sativa L.)—Differential response in salt-tolerant and sensitive varieties. Plant Sci. 2003, 165, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavi Kishor, P.B.; Suravajhala, P.; Rathnagiri, P.; Sreenivasulu, N. Intriguing Role of Proline in Redox Potential Conferring High Temperature Stress Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 867531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, T.; Lin, Z.; Bao, L.; Hui, T.; Cui, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Su, C.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, M.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of tolerant and sensitive varieties reveals that phenylpropanoid biosynthesis contributes to salt tolerance in mulberry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasar, F.; Ellialtioglu, S.; Yildiz, K. Effect of salt stress on antioxidant defense systems, lipid peroxidation, and chlorophyll content in green bean. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2008, 55, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, C.; Lakshmi, A.; Giridarakumar, S. Changes in the antioxidant enzyme efficacy in two high yielding genotypes of mulberry (Morus alba L.) under NaCl salinity. Plant Sci. 2001, 161, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Harish; Singh, R.K.; Verma, K.K.; Sharma, L.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Meena, M.; Gour, V.S.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; et al. Recent developments in enzymatic antioxidant defence mechanism in plants with special reference to abiotic stress. Biology 2021, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Q.; Mei, X.R.; Fujiyama, H. Adequate internal water status of NaCl-salinized rice shoots enhanced selective calcium and potassium absorption. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2006, 52, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eker, S.; Cömertpay, G.; Konuşkan, Ö.; Ülger, A.C.; Öztürk, L.; Çakmak, I. Effect of salinity stress on dry matter production and ion accumulation in hybrid maize varieties. Turkish J. Agric. For. 2006, 30, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Li, Q.H.; Yu, Y.N.; Qiao, Y.M.; Haq, S.U.; Gong, Z.H. The CBL–CIPK pathway in plant response to stress signals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhalipour, M.; Gohari, G.; Esmaielpour, B.; Behnamian, M.; Giglou, M.T.; Milani, M.H.; Bahrami, M.K.; Kulak, M.; Ioannou, A.; Fotopoulos, V.; et al. Effect of melatonin foliar sprays on morphophysiological attributes, fruit yield and quality of Momordica charantia L. under salinity stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 205, 108194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Azooz, M.M.; Prasad, M.N.V. Ecophysiology and Responses of Plants under Salt Stress; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ostaci, Ștefănica; Covașă, M.; Slabu, C.; Marta, A.E.; Jităreanu, C.D. Ostaci Ștefănica; Covașă, M.; Slabu, C.; Marta, A.E.; Jităreanu, C.D. Estimation of Chlorophyll Content and Determination of Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Bitter Cucumber (Momordica charantia L.) Leaves under Saline Stress Conditions. Sci. Pap. Ser. B Hortic. 2023, LXVII, 663–668. [Google Scholar]
- Ostaci, Ș.; Slabu, C.; Marta, A.E.; Covașă, M.; Miniață, I.; Jităreanu, C.D. Spectral Study of Some Metabolites Involved in the Adaptation Reaction of Bitter Cucumber (Momordica charantia) to Saline Stress. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocariu, M.; Marta, A.E.; Jităreanu, C.D.; Chelariu, E.-L.; Căpşună, S.; Cara, I.G.; Amișculesei, P.; Istrate, A.-M.; Chiruță, C. A Study on the Development of Two Ornamental Varieties of Ipomoea batatas Cultivated in Vertical Systems in the Northeastern Region of Europe. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, E.; Arzani, K.; Moallemi, N.; Barzegar, M. Evaluation of Chlorophyll Content and Chlorophyll Fluorescence Parameters and Relationships between Chlorophyll a, b and Chlorophyll Content Index under Water Stress in Olea europaea cv. Dezful. Int. Sch. Sci. Res. Innov. 2012, 6, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Aldesuquy, H.S.; Baka, Z.A.; Al-Shahaby, O.A.; Ghanem, H.E. Growth, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities as a selection criterion for the salt tolerance of wheat cultivars irrigated by Seawater. Phyt.-Ann. Rei Bot. 2013, 53, 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- OS30p+. Available online: https://www.optisci.com/os30p.html (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Bevans, R. Two-Way ANOVA|Examples & When To Use It., Scribbr. Available online: https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/two-way-anova/ (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- Kenton, W. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Explanation, Formula, and Applications. Available online: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/anova.asp (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Goulden, C.H. Methods of Statistical Analysis, 2nd ed. Available online: https://www.statisticshowto.com/probability-and-statistics/t-test/ (accessed on 2 May 2024).
- Aslam, M.; Maqbool, M.A.; Zaman, Q.U.; Shahid, M.; Akhtar, M.A.; Rana, A.S. Comparison of different tolerance indices and PCA biplot analysis for assessment of salinity tolerance in lentil (Lens culinaris) genotypes. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2017, 19, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, J.; Prashanth, J.E.P.; Rajesh, N.; Reddy, S.M.; Pinjari, O.B. Principal component analysis approach for comprehensive screening of salt stress-tolerant tomato germplasm at the seedling stage. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubushar, M.; El-Hendawy, S.; Tahir, M.U.; Alotaibi, M.; Mohammed, N.; Refay, Y.; Tola, E. Assessing the Suitability of Multivariate Analysis for Stress Tolerance Indices, Biomass, and Grain Yield for Detecting Salt Tolerance in Advanced Spring Wheat Lines Irrigated with Saline Water under Field Conditions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Passioura, J.B.; Colmer, T.D.; Byrt, C.S. Osmotic adjustment and energy limitations to plant growth in saline soil. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, L. Effects of salt stress on ion content, antioxidant enzymes and protein profile in different tissues of Broussonetia papyrifera. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 85, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Ji, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ke, W.; Hou, H. Effect of Salt Stress on Growth, Physiological Parameters, and Ionic Concentration of Water Dropwort (Oenanthe javanica) Cultivars. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 660409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A review on plant responses to salt stress and their mechanisms of salt resistance. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaadi, K.A.; Tola, E.; Madugundu, R.; Zeyada, A.M.; Alameen, A.A.; Edrris, M.K.; Edrees, H.F.; Mahjoop, O. Response of leaf photosynthesis, chlorophyll content and yield of hydroponic tomatoes to different water salinity levels. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0293098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Motos, J.R.; Ortuño, M.F.; Bernal-Vicente, A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Sanchez-Blanco, M.J.; Hernandez, J.A. Plant responses to salt stress: Adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy 2017, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.-C.; Dong, J.; Wang, M.-W.; Liu, C.; Zhao, B.-Q.; Wen, Z.-G.; Zhu, X.; Ding, H.; Zhao, X.-H.; Hong, L.-Z. Effects of NaCl stress on growth of Portulaca oleracea and underlying mechanisms. Rev. Bras. Bot. 2019, 42, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhuang, J.; Fan, Y.; Shen, B. Mapping of QTLs for Leaf Malondialdehyde Content Associated with Stress Tolerance in Rice. Rice Sci. 2009, 16, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; Sun, S.; Lu, X.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, K.; Liu, J. Effects of Salt Stress on the Antioxidant Activity and Malondialdehyde, Solution Protein, Proline, and Chlorophyll Contents of Three Malus Species. Life 2022, 12, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murchie, E.H.; Lawson, T. Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis: A guide to good practice and understanding some new applications. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3983–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidi, L.; Lo Piccolo, E.; Landi, M. Chlorophyll fluorescence, photoinhibition and abiotic stress: Does it make any difference the fact to be a C3 or C4 species? Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahanger, M.A.; Aziz, U.; Alsahli, A.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Influence of exogenous salicylic acid and nitric oxide on growth, photosynthesis, and ascorbate- glutathione cycle in salt stressed Vigna angularis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracheboud, Y.; Leipner, J. The Application of Chlorophyll Fluorescence to Study Light, Temperature, and Drought Stress. In Practical Applications of Chlorophyll Fluorescence in Plant Biology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, K.; Kawasaki, M.; Taniguchi, M.; Miyake, H. Correlation between chloroplast ultrastructure and chlorophyll fluorescence characteristics in the leaves of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown under salinity. Plant Prod. Sci. 2008, 11, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, D.; Deshmukh, R.; Sonah, H.; Menzies, J.G.; Reynolds, O.; Ma, J.F.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Bélanger, R.R. The controversies of silicon’s role in plant biology. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, E. Chapter 1 Silicon in plants: Facts vs. concepts. Stud. Plant Sci. 2001, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Wakeel, A. Potassium-sodium interactions in soil and plant under saline-sodic conditions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2013, 176, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaha, D.V.M.; Ueda, A.; Saneoka, H.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Yaish, M.W. The role of Na+ and K+ transporters in salt stress adaptation in glycophytes. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Rong, K.; Zhao, W.; Khan, S.A. Impact of saline stress on the uptake of various macro and micronutrients and their associations with plant biomass and root traits in wheat. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Day, D.A.; Fricke, W.; Watt, M.; Arsova, B.; Barkla, B.J.; Bose, J.; Byrt, C.S.; Chen, Z.; Foster, K.J.; et al. Energy costs of salt tolerance in crop plants. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1072–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).