Crop Nutrition and Soil Fertility Management in Organic Potato Production Systems
Abstract
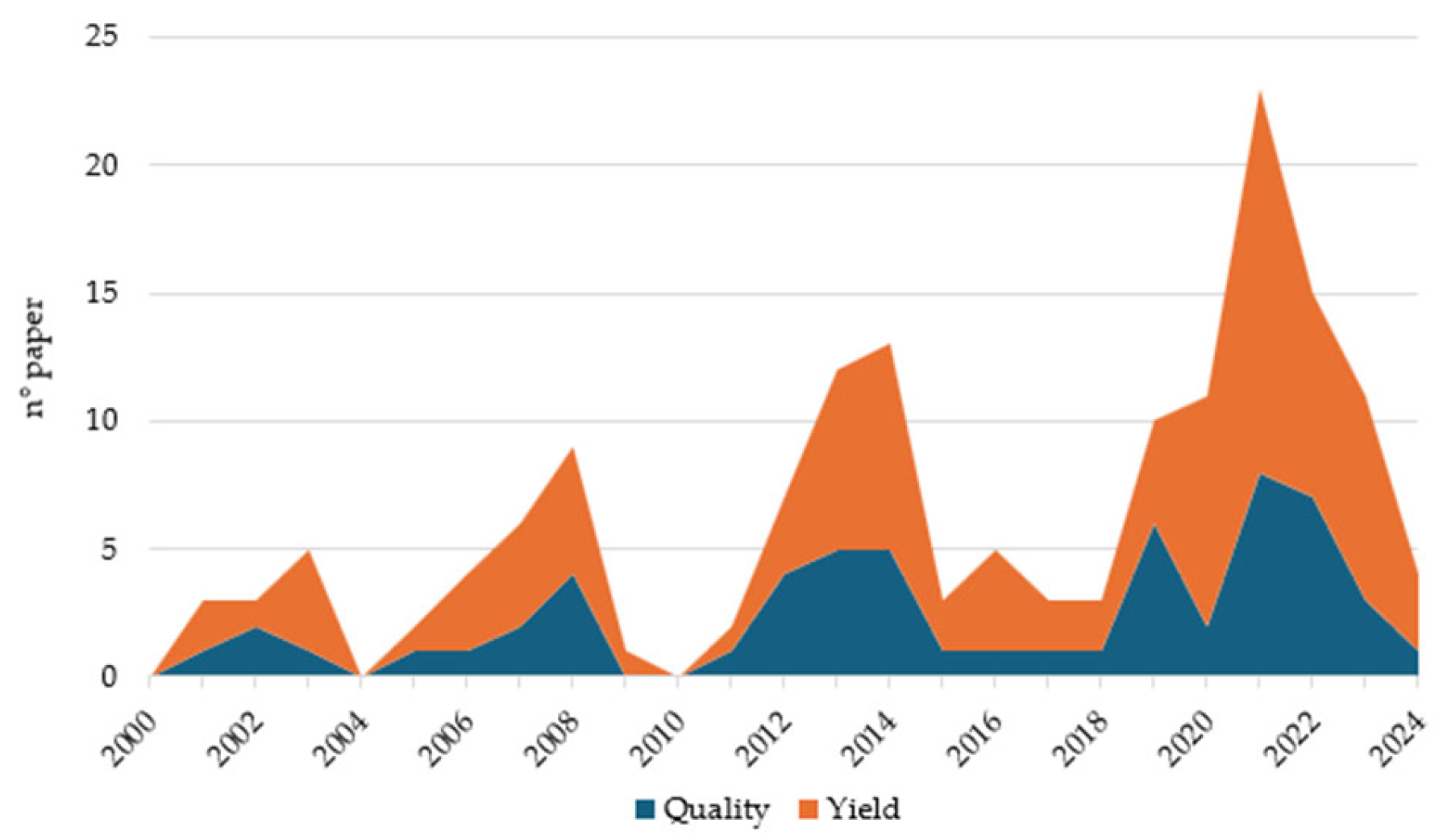
1. Introduction
2. Crop Nutrition and Soil Fertility Management in Organic Potato
- Crop rotation;
- Cultivation of nitrogen-fixing plants and other green manure crops to restore the soil fertility;
- Choosing resistant varieties and breeds and techniques that encourage natural pest control.
3. Animal Manure in Organic Potato Cultivation
4. Green Manure in Organic Potato Cultivation
5. Organic Amendments in Organic Potato Cultivation
5.1. Compost
5.2. Vermicompost
5.3. Biochar
6. Biostimulants in Organic Potato Cultivation
6.1. Humic Substances
6.2. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
6.3. Biofertilizers
7. Conclusions
8. Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willer, H.; Meier, C.; Schlatter, B.; Dietemann, L.; Kemper, L.; Trávníček, J. (Eds.) The World of Organic Agriculture. Statistics and Emerging Trends 2022; Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL, Frick, and IFOAM–Organics International: Bonn, Germany, 2022; pp. 20–31. [Google Scholar]
- FAO 2021. FAOSTAT Online Database. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/#home (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Tamm, L.; Smit, A.B.; Hospers, M.; Janssens, S.R.M.; Buurma, J.S.; Molgaard, J.-P.; Lærke, P.E.; Hansen, H.H.; Hermans, A.; Bødker, L.; et al. Assessment of the Socio-Economic Impact of Late Blight and State-of-the-Art Management in European Organic Potato Production Systems; FiBL: Frick, Switzerland, 2004; Available online: http://orgprints.org/2936 (accessed on 15 May 2024).
- Eurostat. Agriculture, Forestry and Fishery Statistics, 2020 ed.; Eurostat: Luxembourg, 2020; Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/3217494/12069644/KS-FK-20-001-EN-N.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Djaman, K.; Sanogo, S.; Koudahe, K.; Allen, S.; Saibou, A.; Essah, S. Characteristics of organically grown compared to conventionally grown potato and the processed products: A review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzyńska, K.; Trawczyński, C.; Pietraszko, M. Environmental and agronomical factors limiting differences in potato yielding between organic and conventional production system. Agriculture 2023, 13, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponisio, L.C.; M’Gonigle, L.K.; Mace, K.C.; Palomino, J.; De Valpine, P.; Kremen, C. Diversification practices reduce organic to conventional yield gap. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20141396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finckh, M.R.; Schulte-Geldermann, E.; Bruns, C. Challenges to organic potato farming: Disease and nutrient management. Potato Res. 2006, 49, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempelos, L.; Barański, M.; Sufar, E.K.; Gilroy, J.; Shotton, P.; Leifert, H.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Hasanaliyeva, G.; Rosa, E.A.S.; Hajslova, J.; et al. Effect of climatic conditions, and agronomic practices used in organic and conventional crop production on yield and nutritional composition parameters in potato, cabbage, lettuce and onion; results from the long-term NFSC-trials. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehesranta, S.J.; Koistinen, K.M.; Massat, N.; Davies, H.V.; Shepherd, L.V.; McNicol, J.W.; Cakmak, I.; Cooper, J.; Lück, L.; Kärenlampi, S.O.; et al. Effects of agricultural production systems and their components on protein profiles of potato tubers. Proteomics 2007, 7, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Habermeyer, J.; Zinkernagel, V.; Reents, H.J. Impact and interaction of nitrogen and Phytophthora infestans as yield-limiting and yield-reducing factors in organic potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) crops. Potato Res. 2006, 49, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.W.; Cooper, J.; Tétard-Jones, C.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Barański, M.; Eyre, M.; Shotton, P.N.; Volakakis, N.; Cakmak, I.; Ozturk, L.; et al. The influence of organic and conventional fertilisation and crop protection practices, preceding crop, harvest year and weather conditions on yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum) in a long-term management trial. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 49, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierna, A.; Mauromicale, G. Potato growth, yield and water productivity response to different irrigation and fertilization regimes. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierna, A.; Mauromicale, G. Sustainable and profitable nitrogen fertilization management of potato. Agronomy 2019, 9, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, S.; Mauromicale, G.; Ierna, A. Response of seed-grown globe artichoke to different levels of nitrogen fertilization and water supplies. Acta Hortic. 2005, 681, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierna, A.; Lombardo, G.M.; Mauromicale, G. Yield, nitrogen use efficiency and grain quality in durum wheat as affected by nitrogen fertilization under a Mediterranean environment. Exp. Agric. 2016, 52, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembiałkowska, E. Quality of plant products from organic agriculture. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, V.; Bárta, J.; Švajner, J.; Diviš, J. Soil nitrogen variability in relation to seasonal nitrogen cycling and accumulation of nitrogenous components in starch processing potatoes. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B-Soil Plant Sci. 2012, 62, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2018/848 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 on organic production and labelling of organic products and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 834/2007. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=OJ:L:2018:150:TOC (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Lynch, D.H.; Zheng, Z.; Zebarth, B.J.; Martin, R.C. Organic amendment effects on tuber yield, plant N uptake and soil mineral N under organic potato production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2008, 23, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaye, Y. Effect of combined application of organic manure and nitrogen fertilizer rates on yield and yield components of potato: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2217603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, M.E.; Leblanc, H.A.; Kameko, C. Potencial de mineralización de nitrógeno de Bokashi, compost y lombricompost producidos en la Universidad Earth. Tierra Trop. 2007, 3, 183–197. [Google Scholar]
- Harraq, A.; Sadiki, K.; Bourioug, M.; Bouabid, R. Organic fertilizers mineralization and their effect on the potato “Solanum tuberosum” performance in organic farming. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2022, 21, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofo, A.; Zanella, A.; Ponge, J.F. Soil quality and fertility in sustainable agriculture, with a contribution to the biological classification of agricultural soils. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 1085–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, P.; Pagar, V. Organic Nutrient, Resources and Its Fortification. In Advances in Agricultural and Horticultural Sciences; Department of Agricultural Entomology, Shri Vaishnav Institute of Agriculture: Indore, India, 2022; pp. 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, T.C.; Zotti, M.; Fang, Y.; Giannino, F.; Mazzoleni, S.; Bonanomi, G.; Cai, Y.; Chang, S.X. Soil aggregation in relation to organic amendment: A synthesis. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 2481–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäder, P.; Fliessbach, A.; Dubois, D.; Gunst, L.; Fried, P.; Niggli, U. Soil fertility and biodiversity in organic farming. Science 2002, 296, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlisnikovský, L.; Menšík, L.; Kunzová, E. The effect of soil-climate conditions, farmyard manure and mineral fertilizers on potato yield and soil chemical parameters. Plants 2021, 10, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tein, B.; Kauer, K.; Eremeev, V.; Luik, A.; Selge, A.; Loit, E. Farming systems affect potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tuber and soil quality. Field Crops Res. 2014, 156, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempelos, L.; Cooper, J.; Wilcockson, S.; Eyre, M.; Shotton, P.; Volakakis, N.; Orr, C.H.; Leifert, C.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Tétard-Jones, C. Quantitative proteomics to study the response of potato to contrasting fertilisation regimes. Mol. Breed. 2013, 31, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajšlová, J.; Schulzova, V.; Slanina, P.; Janne, K.; Hellenäs, K.E.; Andersson, C.H. Quality of organically and conventionally grown potatoes: Four-year study of micronutrients, metals, secondary metabolites, enzymic browning and organoleptic properties. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 514–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herencia, J.F.; García-Galavís, P.A.; Dorado, J.A.R.; Maqueda, C. Comparison of nutritional quality of the crops grown in an organic and conventional fertilized soil. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warman, P.R.; Havard, K.A. Yield, vitamin and mineral contents of organically and conventionally grown potatoes and sweet corn. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 68, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makaraviciute, A. Effect of organic and mineral fertilizers on the yield and quality of different potato varieties. Agric. Food Sci. 2003, 1, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Wszelaki, A.L.; Delwiche, J.F.; Walker, S.D.; Liggett, R.E.; Scheerens, J.C.; Kleinhenz, M.D. Sensory quality and mineral and glycoalkaloid concentrations in organically and conventionally grown redskin potatoes (Solanum tuberosum). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bártová, V.; Diviš, J.; Bárta, J.; Brabcová, A.; Švajnerová, M. Variation of nitrogenous components in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tubers produced under organic and conventional crop management. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 49, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffrath, A.; Milz, E. Effect of presprouting, organic nitrogen-fertilization and copper-treatment on yield and quality of potato in organic farming. Gesunde Pflanz. 2008, 60, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, A.; Carillo, P.; Bulmetti, G.S.; Fuggi, A.; Barbieri, G.; De Pascale, S. Potato yield and metabolic profiling under conventional and organic farming. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 28, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Monaco, A.L.; Pandino, G.; Parisi, B.; Mauromicale, G. The phenology, yield and tuber composition of ‘early’ crop potatoes: A comparison between organic and conventional cultivation systems. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2013, 28, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Pandino, G.; Mauromicale, G. Nutritional and sensory characteristics of “early” potato cultivars under organic and conventional cultivation systems. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Pandino, G.; Mauromicale, G. The mineral profile in organically and conventionally grown “early” crop potato tubers. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 167, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierna, A.; Parisi, B. Crop growth and tuber yield of “early” potato crop under organic and conventional farming. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 165, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudzińska, M.; Czerko, Z.; Zarzyńska, K.; Borowska-Komenda, M. Bioactive compounds in potato tubers: Effects of farming system, cooking method, and flesh color. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierczak, R.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Hallmann, E.; Kopczyńska, K.; Zarzyńska, K. The impact of organic vs. conventional agricultural practices on selected quality features of eight potato cultivars. Agronomy 2019, 9, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keutgen, A.J.; Wszelaczyńska, E.; Pobereżny, J.; Przewodowska, A.; Przewodowski, W.; Milczarek, D.; Tatarowska, B.; Flis, B.; Keutgen, N. Antioxidant properties of potato tubers (Solanum tuberosum L.) as a consequence of genetic potential and growing conditions. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafeeva, E.; Komissarov, A.; Ishbulatov, M.; Safin, K.; Davletshin, F. Cattle Manure Disposal on Potato Growing Fields in Conditions of the Southern Forest-Steppe of the Bashkortostan Republic. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4195–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, T.; Schüler, C.; Haase, N.U.; Heß, J. Suitability of organic potatoes for industrial processing: Effect of agronomical measures on selected quality parameters at harvest and after storage. Potato Res. 2007, 50, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierna, A.; Parisi, B.; Melilli, M.G. Overall quality of “early” potato tubers as affected by organic cultivation. Agronomy 2022, 12, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierna, A.; Melilli, M.G.; Parisi, B. Effects of organic versus conventional cultivation system on nutritional quality of early potato tubers. In Proceedings of the III International Organic Fruit Symposium and I International Organic Vegetable Symposium, Catania, Italy, 14–17 December 2021; Volume 1354, pp. 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ierna, A.; Melilli, M.G.; Parisi, B. Sensory characteristics of raw and cooked early potato tubers as affected by organic cultivation. In Proceedings of the III International Organic Fruit Symposium and I International Organic Vegetable Symposium, Catania, Italy, 14–17 December 2021; Volume 1354, pp. 375–382. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, C.E.; Amin, M.; Hernández, E.; González, C.J. Effect of compost, farmyard manure and/or chemical fertilizers on potato yield and tuber nutrient content. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2006, 23, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñaloza Monroy, J.; Reyes Ramírez, A.K.; González Huerta, A.; Pérez López, D.D.J.; Sangerman-Jarquín, D.M. Fertilización orgánica con tres niveles de gallinaza en cuatro cultivares de papa. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agrícolas 2019, 10, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Baniuniene, A.; Zekaite, V. The effect of mineral and organic fertilizers on potato tuber yield and quality. Agron. Vēstis Latv. J. Agron. 2008, 11, 202–206. [Google Scholar]
- Caliskan, M.E.; Kilic, S.; Gunel, E.; Mert, M. Effect of farmyard manure and mineral fertilization on growth and yield of early potato (Solanum tuberosum) under the Mediterranean conditions in Turkey. Indian J. Agron. 2004, 49, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Akhter, S.; Majid, N.M.; Ferdous, J.; Alam, M.S. Integrated nutrient management for potato (‘Solanum tuberosum’) in grey terrace soil (Aric Albaquipt). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Asghari, M.T.; Mir, R.; Fard, A. The effect of farmyard manure and nitrogen fertilizer on some characteristics of potato (Solanum tuberosum var. Agria). Biharean Biol. 2015, 9, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, U.; Qureshi, F. Effect of nitrogen and farmyard manure on yield, nutrient content and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Biolife 2014, 2, 786–791. [Google Scholar]
- Asfaw, F. Effect of integrated soil amendment practices on growth and seed tuber yield of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) at Jimma Arjo, Western Ethiopia. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2016, 6, 38–63. [Google Scholar]
- Mama, A.; Jeylan, J.; Aseffa, A.W. Effects of different rates of organic and inorganic fertilizer on growth and yield components of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in Jimma Are, southwest Ethiopia. Int. J. Res. 2016, 4, 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Alemayehu, M.; Jemberie, M.; Yeshiwas, T.; Aklile, M. Integrated application of compound NPS fertilizer and farmyard manure for economical production of irrigated potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in highlands of Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1724385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanaw, T. Israel Zewide. Fertility Management on Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Crop. Res. Rev. J. Crop Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gitari, H.I.; Gachene, C.K.; Karanja, N.N.; Kamau, S.; Nyawade, S.; Schulte-Geldermann, E. Potato-legume intercropping on a sloping terrain and its effects on soil physico-chemical properties. Plant Soil 2019, 438, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedunchezhiyan, M.; Suja, G.; Ravi, V. tropical root-and tuber crops-based cropping systems—A review. Curr. Hortic. 2022, 10, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.C.; Watkins, K.B.; Teasdale, J.R.; Abdul-Baki, A.A. Cover crops in sustainable food production. Food Rev. Int. 2000, 16, 121–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reents, H.J.; Möller, K. Effect of different green manure catch crops grown after peas on nitrate dynamics in soils and on yield and quality of subsequent potatoes and wheat. In Proceedings of the 13th International IFOAM Scientific Conference, Basel, Switzerland, 28–31 August 2000; Alföldi, T., Lockeretz, W., Niggli, U., Eds.; IFOAM: Zürich, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 73–75. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, R.P.; Griffin, T.S. Control of soilborne potato diseases using Brassica green manures. Crop Prot. 2007, 26, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégo, G.; Martinez, M.; Antigüedad, I.; Launay, M.; Sanchez-Pérez, J.M.; Justes, E. Evaluation of the impact of various agricultural practices on nitrate leaching under the root zone of potato and sugar beet using the STICS soil–crop model. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canali, S.; Ciaccia, C.; Tittarelli, F. Soil fertility management in organic potato: The role of green manure and amendment applications. In Sustainable Potato Production: Global Case Studies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 453–469. [Google Scholar]
- Ledgard, S.F. Nitrogen cycling in low input legume-based agriculture, with emphasis on legume/grass pastures. Plant Soil 2001, 228, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Båth, B.; Ekbladh, G.; Ascard, J.; Olsson, K.; Andersson, B. Yield and nitrogen uptake in organic potato production with green manures as pre-crop and the effect of supplementary fertilization with fermented slurry. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2006, 24, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sincik, M.; Turan, Z.M.; Göksoy, A.T. Responses of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to green manure cover crops and nitrogen fertilization rates. Am. J. Potato Res. 2008, 85, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchino, H.; Iwama, K.; Jitsuyama, Y.; Ichiyama, K.; Sugiura, E.R.I.; Yudate, T.; Nakamura, S.; Gopal, J. Effect of interseeding cover crops and fertilization on weed suppression under an organic and rotational cropping system: 1. Stability of weed suppression over years and main crops of potato, maize and soybean. Field Crops Res. 2012, 127, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campiglia, E.; Paolini, R.; Colla, G.; Mancinelli, R. The effects of cover cropping on yield and weed control of potato in a transitional system. Field Crops Res. 2009, 112, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, R.P.; Halloran, J.M. Management effects of disease-suppressive rotation crops on potato yield and soilborne disease and their economic implications in potato production. Am. J. Potato Res. 2014, 91, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamdavaa, T.; Friedel, J.K. Effect of pre-crops, cover crops and manure application on organic potato production in a field experiment in eastern Austria. Acta Fytotech. Zootech. 2016, 18, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibabaw, A.; Alemayehu, G.; Adgo, E.; Asch, F.; Freyer, B. Effects of organic manure and crop rotation system on potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tuber yield in the highlands of Awi Zone. Ethiop. J. Sci. Technol. 2018, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremeev, V.; Talgre, L.; Kuht, J.; Mäeorg, E.; Esmaeilzadeh-Salestani, K.; Alaru, M.; Loit, E.; Runno-Paurson, E.; Luik, A. The soil microbial hydrolytic activity, content of nitrogen and organic carbon were enhanced by organic farming management using cover crops and composts in potato cultivation. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2020, 70, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyiraneza, J.; Chen, D.; Fraser, T.; Comeau, L.P. Improving soil quality and potato productivity with manure and high-residue cover crops in Eastern Canada. Plants 2021, 10, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittl, T.F.; Grønmyr, F.; Bakken, I.; Løes, A.K. Effects of organic amendments and cover crops on soil characteristics and potato yields. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2023, 73, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margus, K.; Eremeev, V.; Loit, E.; Runno-Paurson, E.; Mäeorg, E.; Luik, A.; Talgre, L. Impact of farming system on potato yield and tuber quality in Northern Baltic Sea climate conditions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamiev, D.; Abaev, A.; Tedeeva, A.; Khokhoeva, N.; Tedeeva, V. Use of green manure in organic farming. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 403, p. 012137. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, R.; Brito, L.M.; Coutinho, J. Organic production of horticultural crops with green manure, composted farmyard manure and organic fertiliser. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2017, 33, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakopoulos, D.; Scholberg, J.M.; Lantinga, E.A.; Tittonell, P.A. Influence of reduced tillage and fertilization regime on crop performance and nitrogen utilization of organic potato. Org. Agric. 2016, 6, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Drakopoulos, D.; Scholberg, J.M.; Lantinga, E.A. Influence of reduced tillage and fertilisation regime on soil quality indicators in an organic potato production system. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2018, 34, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Culp, D.A.; Peterson, S.; Nicholson, K.; Geisseler, D. Cover crops prove effective at increasing soil nitrogen for organic potato production. Calif. Agric. 2019, 73, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandy, A.S.; Porter, G.A.; Erich, M.S. Organic amendment and rotation crop effects on the recovery of soil organic matter and aggregation in potato cropping systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passoni, M.; Borin, M. Effects of different composts on soil nitrogen balance and dynamics in a biennial crop succession. Compos. Sci. Util. 2009, 17, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.R.; Sanderson, J.B.; MacLeod, J.A. Influence of compost on the physical properties and organic matter fractions of a fine sandy loam throughout the cycle of a potato rotation. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 84, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, S.F.; Hassan, H.A.; El-Mogy, M.M. Impact of bio-and organic fertilizers on potato yield, quality and tuber weight loss after harvest. Potato Res. 2015, 58, 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, S.H.; Sharifi, M.; Hann, S.W.; Chow, T.L. Crop productivity and nutrient bioavailability in a potato-based three-year rotation as affected by composted pulp fiber residue application and supplemental irrigation. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 744–756. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C.; Zebarth, B.J.; Burton, D.L.; Goyer, C.; Moreau, G.; Dixon, T. Effect of diverse compost products on potato yield and nutrient availability. Am. J. Potato Res. 2019, 96, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitkevičienė, N.; Kulaitienė, J.; Jarienė, E.; Levickienė, D.; Danillčenko, H.; Średnicka-Tober, D.; Rembiałkowska, E.; Hallmann, E. Characterization of bioactive compounds in colored potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivars grown with conventional, organic, and biodynamic methods. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illera-Vives, M.; Seoane Labandeira, S.; Iglesias Loureiro, L.; López-Mosquera, M.E. Agronomic assessment of a compost consisting of seaweed and fish waste as an organic fertilizer for organic potato crops. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1663–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.Z.; Lynch, D.H.; Sharifi, M.; Burton, D.L.; Hammermeister, A.M. The effect of green manure and organic amendments on potato yield, nitrogen uptake and soil mineral nitrogen. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2016, 32, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo-Monge, M.A.; Aparicio, S.; Escobedo-Monge, M.F.; Marugán-Miguelsanz, J.M. Long-term effects of the application of urban waste compost and other organic amendments on Solanum tuberosum L. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willekens, K.; De Vliegher, A.; Vandecasteele, B.; Carlier, L. Effect of compost versus animal manure fertilization on crop development, yield and nitrogen residue in the organic cultivation of potatoes. In Proceedings of the Second Scientific Conference of the International Society of Organic Agriculture Research (ISOFAR), Modena, Italy, 18–20 June 2008; pp. 576–579. [Google Scholar]
- El-Tantawy, I.M.; El-Ghamry, A.M.; Habib, A.H. Impact of farmyard manure and manure compost tea on potato yield and soil fertility. J. Soil Sci. Agric. Eng. 2009, 34, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, E.; Larkin, R.P.; Tavantzis, S.; Erich, M.S.; Alyokhin, A.; Gross, S.D. Rapeseed rotation, compost and biocontrol amendments reduce soilborne diseases and increase tuber yield in organic and conventional potato production systems. Plant Soil 2014, 374, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.E.S.; Al-Easily, I.A.S.; AS Nawar, D. Impact of biochar addition on productivity and tubers quality of some potato cultivars under sandy soil conditions. Egypt. J. Hortic. 2017, 44, 199–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, K.P.; Dhami, N.B.; Sharma, P.N.; Neupane, J.D.; Shrestha, J. Growth and yield responses of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to biochar. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 2, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Mawof, A.; Prasher, S.; Bayen, S.; Nzediegwu, C. Effects of biochar and biochar-compost mix as soil amendments on soil quality and yield of potatoes irrigated with wastewater. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 2600–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooque, A.A.; Zaman, Q.; Abbas, F.; Hammad, H.M.; Acharya, B.; Easu, T. How can potatoes be smartly cultivated with biochar as a soil nutrient amendment technique in Atlantic Canada? Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Xing, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, H. Increase in potato yield by the combined application of biochar and organic fertilizer: Key role of rhizosphere microbial diversity. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1389864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollick, M.O.A.; Paul, A.K.; Alam, I.; Sumon, M.M. Effect of biochar on yield and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum) tuber. Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2020, 11, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Siddique, A. Impact of biochar base organic amendment on morphological changes and yield of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Spec. Ugdym. 2022, 2, 865–871. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, B.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; Lv, C.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L. Pilot-scale composting of typical multiple agricultural wastes: Parameter optimization and mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 287, 121482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.; Lynch, D.H.; Zebarth, B.J.; Zheng, Z.; Martin, R.C. Evaluation of nitrogen supply rate measured by in situ placement of Plant Root Simulator™ probes as a predictor of nitrogen supply from soil and organic amendments in potato crop. Am. J. Potato Res. 2009, 86, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amlinger, F.; Götz, B.; Dreher, P.; Geszti, J.; Weissteiner, C. Nitrogen in biowaste and yard waste compost: Dynamics of mobilisation and availability—A review. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2003, 39, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Heaney, D.; Henriquez, B.; Solberg, E.; Bittner, E. A four-year study on influence of biosolids/MSW cocompost application in less productive soils in Alberta: Nutrient dynamics. Compos. Sci. Util. 2006, 14, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmore, A.P. Determination of the mineralization of nitrogen from composted chicken manure as affected by temperature. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2007, 77, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyiraneza, J.; Snapp, S. Integrated management of inorganic and organic nitrogen and efficiency in potato systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Singer, J.W. Soil nitrogen response to coupling cover crops with manure injection. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2010, 87, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.L.; Wu, T.Y.; Lim, P.N.; Shak, K.P.Y. The use of vermicompost in organic farming: Overview, effects on soil and economics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edussuriya, R.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Jayasinghe, C.; Pathirana, C.; Vithanage, M. Influence of biochar on growth performances, yield of root and tuber crops and controlling plant-parasitic nematodes. Biochar 2023, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Tan, X.; Huang, X.; Zeng, G.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, B. Biochar to improve soil fertility. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Viaene, N.; Vandecasteele, B.; D’Hose, T.; Debode, J.; Cremelie, P.; De Tender, C.; Moens, M. Traditional and new soil amendments reduce survival and reproduction of potato cyst nematodes, except for biochar. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, P.; Siddique, A. Biochar-based organic amendments on soil health, nutrient status and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum). Plant Sci. Today 2024, 11, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibowo, C.; Wijaya, K.; Biyantara, A.L. Effect of organic fertilizer and application of charcoal on quality of potato tuber variety Atlantic. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 653, p. 012125. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 Laying down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of EU Fertilising Products and Amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003. 2019. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A32019R1009 (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Toward a sustainable agriculture through plant biostimulants: From experimental data to practical applications. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijwel, A.K.; Al-redha, A.A.; Bresim, T.H. Response of some traits of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to the addition of the ground palm remnants compost and foliar with humic acid. Plant Arch. 2019, 19, 94–97. [Google Scholar]
- Rizk, F.A.; Shaheen, A.M.; Singer, S.M.; Sawan, O.A. The productivity of potato plants affected by urea fertilizer as foliar spraying and humic acid added with irrigation water. Middle East J. Agric. Res. 2013, 2, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sarhan, T.Z. Effect of humic acid and seaweed extracts on growth and yield of potato plant (Solanum tuberosum L) Desiree cv. Mesop. J. Agric. 2011, 39, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Man-Hong, Y.; Lei, Z.; Sheng-Tao, X.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Jing-Hui, L. Effect of water soluble humic acid applied to potato foliage on plant growth, photosynthesis characteristics and fresh tuber yield under different water deficits. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.Y.; Yoo, K.S.; Suh, S.G. Tuber growth and quality of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) as affected by foliar or soil application of fulvic and humic acids. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 55, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekin, Z. Integrated use of humic acid and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria to ensure higher potato productivity in sustainable agriculture. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadas, W.; Dziugieł, T. Quality of new potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) in response to plant biostimulants application. Agriculture 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, P.; Hodge, A.; Goodlass, G.; Bending, G.D. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and organic farming. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 113, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrier, L.A.; Watson, C.A. The potential role of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi in the bioprotection of plants against soil-borne pathogens in organic and/or other sustainable farming systems. Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2004, 60, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavo, A.; Abbate, C.; Mauromicale, G. Plant allelochemicals: Agronomic, nutritional and ecological relevance in the soil system. Plant Soil 2019, 442, 23–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäder, P.; Edenhofer, S.; Boller, T.; Wiemken, A.; Niggli, U. Arbuscular mycorrhizae in a long-term field trial comparing low-input (organic, biological) and high-input (conventional) farming systems in a crop rotation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, X.; An, L.; Feng, H. Prospect of beneficial microorganisms applied in potato cultivation for sustainable agriculture. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 2150–2158. [Google Scholar]
- Duffy, E.M.; Cassells, A.C. The effect of inoculation of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) microplants with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on tuber yield and tuber distribution. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douds, D.D., Jr.; Nagahashi, G.; Reider, C.; Hepperly, P.R. Inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increases the yield of potatoes in a high P soil. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2007, 25, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijri, M. Analysis of a large dataset of mycorrhiza inoculation field trials on potato shows highly significant increases in yield. Mycorrhiza 2016, 26, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravifar, S.; Farahvash, F.; Aliasgharzad, N.; Yarnia, M.; Khoei, F.R. Effects of different irrigation regimes and two arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on some physiological characteristics and yield of potato under field conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chifetete, V.W.; Dames, J.F. Mycorrhizal interventions for sustainable potato production in Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 593053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Abbate, C.; Pandino, G.; Parisi, B.; Scavo, A.; Mauromicale, G. Productive and physiological response of organic potato grown under highly calcareous soils to fertilization and mycorrhization management. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.; Scavo, A.; Abbate, C.; Pandino, G.; Parisi, B.; Mauromicale, G. Mycorrhizal inoculation improves mineral content of organic potatoes grown under calcareous soil. Agriculture 2021, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkadhum, M.H.; Manea, A.I.; Mahmoud, S.S. Effect of Mycorrhizal Addition and Organic Fertilization on the Growth and Yield of Potato in Autumn Season. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2023; Volume 1262, p. 042004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloo, B.; Makumb, B.; Mbega, E. Plant growth promoting rhizobacterial biofertilizers for sustainable crop production: The past, present, and future. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1002448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Hussein, S.D.; El-Oksh, I.; El-Shorbagy, T.; El-Bahiry, U.A. Effect of chicken manure, compost and biofertilizers on vegetative growth, tuber characteristics and yield of potato crop. Egypt. J. Hortic. 2002, 29, 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, F.; Hassien, A.; Muhamed, M.; Ahimed, A. Growth, yield and nutrient concentration of potato plants. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Minin, V.B.; Popov, V.D.; Maksimov, D.A.; Ustroev, A.A.; Melnikov, S.P.; Papushin, E. Developing of modern cultivation technology of organic potatoes. Agron. Res. 2020, 18, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Al Hadidi, N.; Hasan, H.; Pap, Z.; Tóth, F.; Papp, O.; Drexler, D.; Ganszky, D.; Kappel, N. Beneficial Effects of Microbial Inoculation to Improve Organic Potato Production under Irrigated and Non-Irrigated Conditions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2024, 31, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Larkin, R.P. Relative effects of biological amendments and crop rotations on soil microbial communities and soilborne diseases of potato. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, C.; Huenchuleo, M.J.; Michaud, A.; Solano, J. Micorrización en un cultivo de papa adicionado del biofertilizante Twin-N establecido en un Andisol de la Región de La Araucanía. Idesia 2016, 34, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Organic Products | Nutrient Content (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| N | P2O5 | K2O | |
| Farmyard manure | 0.5–1.5 | 0.2–0.4 | 0.5–1.0 |
| Crop residues | 0.34–0.63 | - | 1–6 |
| Organic waste | 3.03 | 2.63 | 1.4 |
| Green manure | 40–60 | 2.5–6.55 | 0.0327 |
| Vermicompost | 2–3 | 1.55–2.25 | 1.85–2.25 |
| Compost | 2 | 0.5–1 | 2 |
| Biogas slurry | 1.4–1.8 | 1.1–1.7 | 0.8–1.3 |
| Amendments | Impact on Tuber Yield | Impact on Tuber Quality | Location | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swine manure-sawdust compost | decrease | Canada | Lynch et al. [20] | |
| Worm-compost | increase | Morocco | Harraq et al. [23] | |
| Compost + green manure | increase | Italy | Canali et al. [68] | |
| Biochar + liquid digestate | - | Norway | Rittl et al. [79] | |
| Food residues + MSWC | increase | Italy | Passoni & Borin [87] | |
| Compost | increase | - | Canada | Carter et al. [88] |
| Compost | increase | Egypt | El-Sayed et al. [89] | |
| Pulp-fiber compost | increase | Canada | Fahmy et al. [90] | |
| Different types of compost | no effect | Canada | Wilson et al. [91] | |
| Compost | increase phenolics, flavonoids, anthocyanins | Lithuania | Vaitkevičienė et al. [92] | |
| On-farm compost (fish waste, seaweed, pine bark) | increase | increase reducing sugars | Spain | Illera-Vives et al. [93] |
| MSWC 1 and paper mill biosolid compost | decrease | Canada | Alam et al. [94] | |
| MSWC | increase | increase micronutrients | Spain | Escobedo-Monge et al. [95] |
| On-farm prepared compost | increase | Belgium | Willekens et al. [96] | |
| Farmyard compost, compost tea | increase | increase dry matter, specific gravity | Egypt | El-Tantawy et al. [97] |
| Conifer-based compost + green manure+ biofertilizer | increase | United States | Bernard et al. [98] | |
| Biochar | increase | Egypt | Youssef et al. [99] | |
| Biochar | increase | Nepal | Upadaya et al. [100] | |
| Biochar, biochar + compost | increase | Canada | Mawof et al. [101] | |
| Biochar + recommended NPK | increase | Canada | Farooque et al. [102] | |
| Biochar + organic fertilizer | increase | China | Hou et al. [103] | |
| Biochar + recommended NPK | increase | increase dry matter, specific gravity | Bangladesh | Mollick et al. [104] |
| Biochar + vermicompost + bonemeal, others | increase | India | Singh & Siddique [105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ierna, A.; Distefano, M. Crop Nutrition and Soil Fertility Management in Organic Potato Production Systems. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080886
Ierna A, Distefano M. Crop Nutrition and Soil Fertility Management in Organic Potato Production Systems. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(8):886. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080886
Chicago/Turabian StyleIerna, Anita, and Miriam Distefano. 2024. "Crop Nutrition and Soil Fertility Management in Organic Potato Production Systems" Horticulturae 10, no. 8: 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080886
APA StyleIerna, A., & Distefano, M. (2024). Crop Nutrition and Soil Fertility Management in Organic Potato Production Systems. Horticulturae, 10(8), 886. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080886









