Visual Analyses of Hot Spots and Frontiers in Zanthoxylum planispinum Research Based on CiteSpace
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources and Research Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Research Method
3. Analysis of Z. planispinum’s Research Status
3.1. Publication Volume Analysis
3.2. Published Paper Author Analysis
3.3. Visual Analysis of Research Institutions
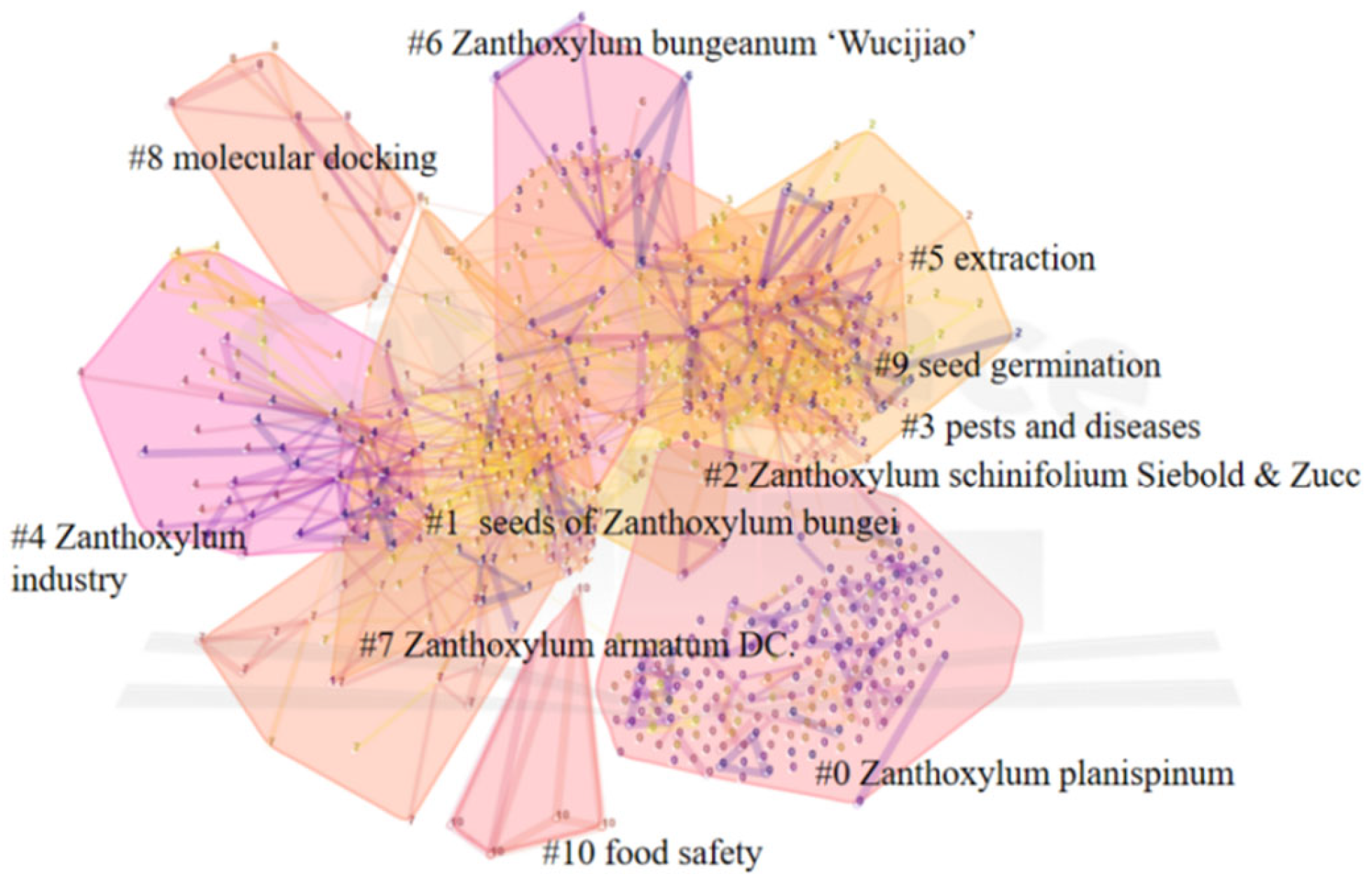
4. Research Hotspot and Frontier Analyses of Z. planispinum
4.1. Research Hotspot Analysis
4.1.1. Germplasm Resource Management
4.1.2. Zanthoxylum Planispinum Cultivation and Management Techniques
4.1.3. Zanthoxylum planispinum Seed Oil Extraction
4.1.4. Flavonoid Extraction Technique Optimization and a Z. planispinum Antioxidant Activity Correlation Analysis
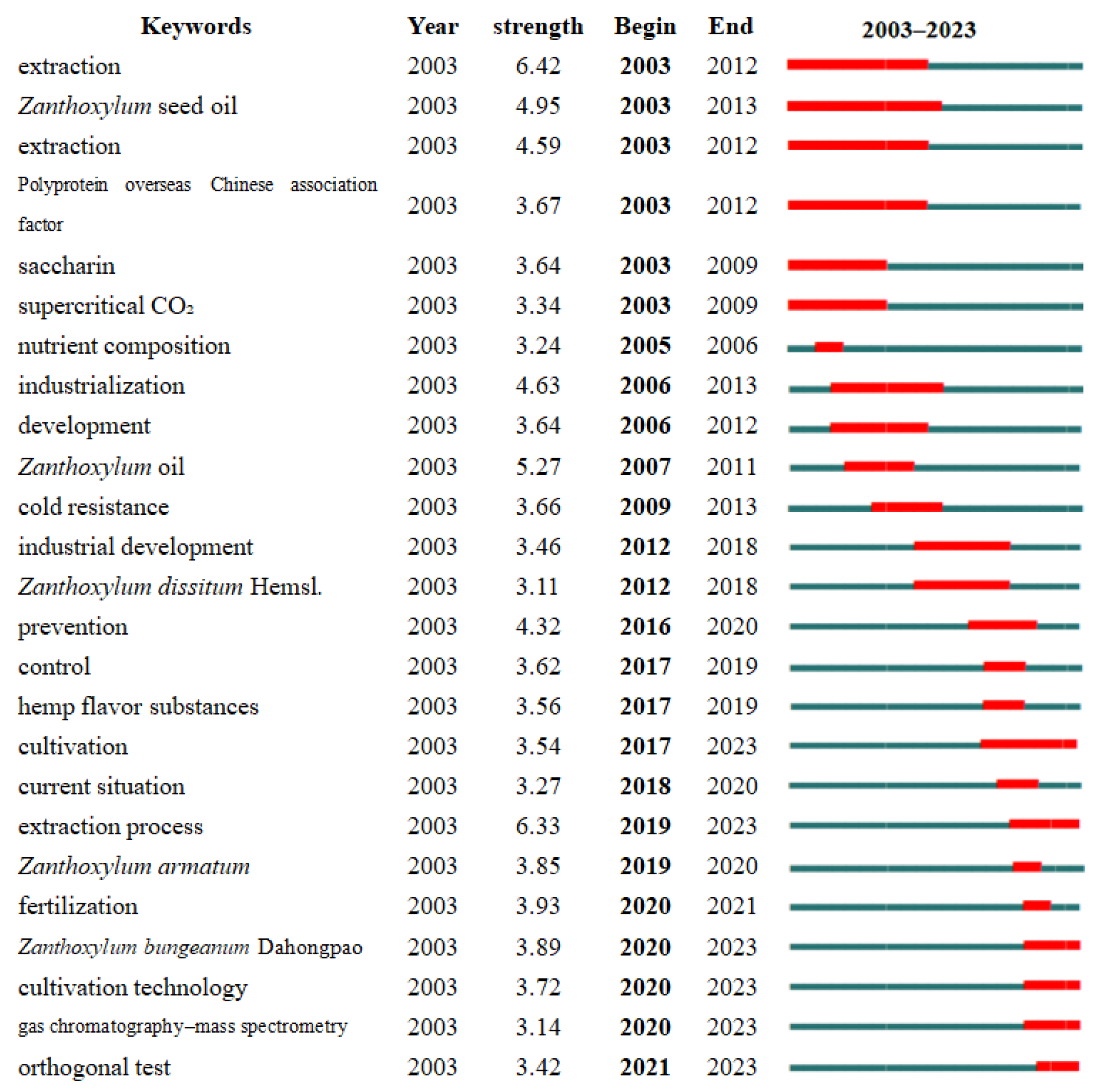
4.2. Research Frontier Analysis
4.2.1. Study of Unified and Standardized Nomenclature, and Adaptative Mechanisms, of Zanthoxylum Germplasm Resources
4.2.2. Study of the Directional Cultivation of Z. planispinum
4.2.3. Study of the Extraction and Processing of the Functional Components of Z. planispinum
4.2.4. Research on the Construction of a Z. planispinum Industrial Chain
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lan, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Q. Comparative study on transdermal penetration promotion between volatile oil of Zanthoxylum and its main components. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B 2014, 15, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Lei, H.X.; Xiang, Z.B.; Duan, Y.Q.; Xin, H.L.; Han, T.; Su, J. Phytochemistry and health functions of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim and Zanthoxylum schinifolium Sieb. et Zucc as pharma-foods: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Wang, J.L.; Zhu, L.; Li, T.; Jiang, W.D.; Zhou, J.; Peng, W.; Wu, C.J. Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. (Rutaceae): A Systematic Review of Its Traditional Uses, Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, and Toxicology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, G.Z.; Zhang, L.H. Research progress on drought resistance of prickly ash. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2023, 41, 302–310. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, L.Z.; Hao, J.B.; Hu, Y.L.; Du, C.H.; Lu, B.; Chen, Y.D.; Dong, J.H. Etiological analysis of yellow flower disease of Zanthoxylum planispinum in Yunnan province. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2024, 36, 2410–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.Y.; Tian, C.R. Present situation and prospect analysis of development and utilization of Zanthoxylum planispinum. Food Res. Dev. 2008, 8, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Z.H.; Xu, D.P.; Pu, B.; Wang, R.L.; Ye, M. Predicting distribution of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. in China. BMC Ecol. 2020, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.L.; Wen, C.H.; Ma, L.T.; Ho, C.L.; Tung, G.S.; Tien, C.C.; Chu, F.H. Monoterpene synthases contribute to the volatile production in tana (Zanthoxylum ailanthoides) through indigenous cultivation practices. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 202, 107969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Han, F.T.; Chen, C.N.; Zhao, A.G.; Wang, D.M. Time-series based metabolomics reveals the characteristics of the color-related metabolites during the different coloration stages of Zanthoxylum bungeanum peel. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.N.; Wang, Y.; Kan, H.; Hao, J.B.; Hu, Q.; Lu, B.; Liu, Y. Comparison of different drying techniques for Zanthoxylum bungeanum leaves: Changes in color, microstructure, antioxidant capacities, and volatile components. LWT 2023, 188, 115469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Tariq, A.; Pan, K.; Graciano, C.; Sun, F.; Song, D.; Abiodun Olatunji, O. Role of Glycine max in improving drought tolerance in Zanthoxylum bungeanum. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.Q.; Liang, C.Q.; Jiao, J.H.; Ruan, Z.; Sun, M.J.; Fu, X.; Zhao, J.C.; Wang, T.; Zhong, S.Y. Exogenous priming of chitosan induces resistance in Chinese prickly ash against stem canker caused by Fusarium zanthoxyli. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.C.; Yang, L.; Fu, Q.W.; Fu, Y.; Tian, Q.Q.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.W. The current situation of Zanthoxylum bungeanum industry and the research and application prospect. A review. Fitoterapia 2023, 164, 105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Kang, M.; Liang, X.F. Optimization of Supercritical CO2 Extraction Process of Volatile Oil from Zanthoxylum armatum DC. Food Res. Dev. 2023, 44, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.Y.; Ding, C.F.; Guo, R.R.; Zhao, J.Z.; Ma, D.W.; Fan, K.; Zhang, L.C.; Zhang, R.P.; Hu, W.Y.; Yu, H.F. Chemical constituents from the pericarps of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. and their chemotaxonomic significance. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2023, 109, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaomei, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.S. Research Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Digital Archives in China from 1999 to 2020. Lantai World 2021, 579, 63–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.P.; Ku, Y.; Li, H.Y. Current Status and Traditional Chinese Medicine Translation Research Based on Citespace Analysis. J. Basic Chin. Med. 2024, 30, 356–361. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.R.; Du, Y.; Jin, Y.T.; Liu, F.Y.; He, S.S.; Guo, Y.H. Articles on hemorrhagic shock published between 2000 and 2021: A CiteSpace-Based bibliometric analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhou, Y.F.; Chen, Y.X.; Hu, T.F.; Liu, Z.H.; Huang, J.A.; Li, Q. Visual analysis of Oolong tea aroma research based on CiteSpace. Food Ferment. Ind. 2023, 49, 344–351. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.H.; Qian, H.N. Knowledge Map Analysis of Chinese Medicine Treatment of Diabetes Foot based on Literature Visualization Software. World China Medicne 2020, 15, 2648–2652+2655. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.J.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.G.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Xie, Y.G. Analysis on the variety of the phenotypic character of green pepper germplasm resources in southwest China. South China Agr. 2021, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Xue, H.D.; Wang, D.W.; Sun, Y. RAPD Analysis of the Germplasm Resources of Zanthoxylum bungeanum. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2011, 26, 96–100. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.W. Technology of labor-saving cultivation and management in Zanthoxylum province. Northwest Hort. 2023, 6, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, Y.; Yuan, S.J.; Shi, Y.J. Simplified Management Technology of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. Shaanxi Forest Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 110–113. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.H.; Zeng, P.; Chen, Z.; Gong, X.; Tang, W. Research Progress on Grass Cultivation Under Chinese Prickly Ash Forest. Mod. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 5, 65–66+68. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.G.; Luo, S.H.; Liu, S.; Wan, S.J.; Li, J.Q.; Chen, J.Y.; Zuo, H.J.; Pei, X.F. Zanthoxylum bungeanum seed oil inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing ERK/c-JUN/NFATc1 pathway and regulating cell cycle arrest in RAW264.7 cells. J. Ethnoharmacol. 2022, 289, 11509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.J.; Lu, B.J.; Qin, Z.; Sui, B.; Pang, H.L.; Qin, G.Y. Analysis of pepper seed oil and amino acid of defatted meal. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 44, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, A.; Misic, D.; Zizovic, I.; Dicastillo, C.L.; Velásquez, E.; Rajewska, A.; Rozas, B.; Catalán, L.; Vidal, C.P.; Guarda, A.; et al. Supercritical fluid and cocrystallization technologies for designing antimicrobial food packaging PLA nanocomposite foams loaded with eugenol cocrystals with prolonged release. CEJ Adv. 2024, 481, 148407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.F.; Ge, B.G.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, F.T. Optimization Extraction Process of Pepper Seed Oil. China Fruit Veg. 2017, 37, 8–11+15. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, J.W.; Song, J.; Guo, X.L.; Xu, C.M.; Zou, Q. Study on Optimization of Supercritical Extraction Technology of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Seed Oil and α-linolenic Acid by Response Surface Method. China Condiment 2021, 46, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, S.P.; Zhang, L.W. Study on scavenging free radical of total flavones of Mulberry. J. Shanxi Normal Univ. 2009, 23, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, L.X.; Zhang, S.M.; Qiu, H.X.; Yao, Y.Q.; Liu, S.T.; Qian, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhao, Q.D.; Li, Y.B. Rapid classification and identification of chemical components in three different Zanthoxylum species by ultra-high-performance-liquid chromatography quadrupole-orbitrap-mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2024, 47, e2300670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.T.; Liu, L.L. Optimization of Extraction Process and Antioxidant Activity of Flavonoids from Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. Shandong Agr. Sci. 2022, 54, 118–124. [Google Scholar]
- Calis, Z.; Mogulkoc, R.; Baltaci, A.K. The Roles of Flavonols/Flavonoids in Neurodegeneration and Neuroinflammation. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukhrambam, P.D.; Devi, K.K.; Maibam, C.; Mutum, R.D.; Devi, M.L.; Das, S. Phenolics and flavonoids from Polygonum posumbu and comparision of flavonoid compounds content in different tissues (leaves, stems and roots). Fitoterapia 2024, 174, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.W.; Huang, Y.L.; Zhang, H.Y. Bioactive compounds ectracted with different solvents from Zanthoxylum Bungeanum Maxim. seeds and comparison of their antioxidant activities. Packag. Food Mach. 2021, 39, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.M.; Guo, X.L.; Li, Q.X.; Li, J.F.; Tang, R.Y.; Zou, Q.; Du, X.G. The Study of Anti-oxidative and Anti-proliferative Activities of Total Flavonoids Extract from Hanyuan Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2020, 41, 296–301+314. [Google Scholar]
- Okagu, I.U.; Ndefo, J.C.; Aham, E.C.; Udenigwe, C.C. Zanthoxylum Species: A Comprehensive Review of Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacological and Nutraceutical Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Jiang, T.T.; Huang, Z.L.; Wang, M.X. Knowledge domain and trend of disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis: A study based on CiteSpace. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, C.; Andrade, S.; Ferreira, H.; Matos, C.; Martins, S.; Moutinho-Pereira, J. The Synergetic Effect of Light Spectra and Selenium Supplementation on Eruca sativa Mill. Growth and Physiological and Metabolic Responses. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Q.; Zhuo, Z.; Peng, Y.; Xu, D. Chemical Composition Variation in Essential Oil and Their Correlation with Climate Factors in Chinese Prickly Ash Peels (Zanthoxylum armatum DC.) from Different Habitats. Molecules 2024, 29, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Q.Q.; Liang, S.D.; Jiang, H.Q. Application of Zanthoxylum plant extract in the protection of cultural relics painting and calligraphy. Technol. Wind 2024, 1, 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, V.V.; da Hora Borges, M.A.; Jatobá da Silva, K.C.; dos Santos Costa, R.; Santo, R.F.d.E.; Velozo, E.d.S.; Villarreal, C.F.; Azeredo, F.J. Preclinical Pharmacokinetic Study and Lung Penetration of a Coumarin Extracted from Zanthoxylum tingoassuiba. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Serial Number | Issuing Office | Quantity | Serial Number | Issuing Office | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Northwest A&F University | 162 | 16 | Yunnan Agricultural University | 43 |
| 2 | Southwest University | 130 | 17 | Qin’an County Forestry Bureau of Gansu Province | 36 |
| 3 | Sichuan Agricultural University | 116 | 18 | Sichuan Academy of Forestry Sciences | 36 |
| 4 | Guizhou Normal University | 94 | 19 | Hebei Academy of Forestry and Grassland Science | 32 |
| 5 | Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine | 76 | 20 | Guizhou Academy of Forestry | 32 |
| 6 | Guizhou University | 74 | 21 | Shaanxi University of Science & Technology | 27 |
| 7 | Gansu Agricultural University | 68 | 22 | Chengdu University | 26 |
| 8 | Sichuan Tourism University | 65 | 23 | Henan Institute of Science and Technology | 25 |
| 9 | Guangxi Medical University | 63 | 24 | Xihua University | 24 |
| 10 | Nanjing Institute for Comprehensive Utilization of Wild Plants | 59 | 25 | Gansu University of Chinese Medicine | 24 |
| 11 | Yangling Vocational & Technical College | 53 | 26 | Shaanxi Hancheng Sichuan Pepper Research Institute | 23 |
| 12 | Sichuan University | 50 | 27 | Sichuan Higher Institute of Cuisine | 21 |
| 13 | Central South University of Forestry and Technology | 48 | 28 | Shandong Agricultural University | 21 |
| 14 | Longnan City Economic Forestry Research Institute | 47 | 29 | Shaanxi Normal University | 21 |
| 15 | Sichuan Academy of Botanical Engineering | 44 | 30 | Beijing University of Chinese Medicine | 20 |
| Serial Number | Keywords | Count | Centrality | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zanthoxylumschinifolium Siebold & Zucc. | 167 | 0.15 | 2004 |
| 2 | Essential oil | 66 | 0.02 | 2004 |
| 3 | Technique of cultivation | 59 | 0.01 | 2010 |
| 4 | Z. planispinum industry | 56 | 0.02 | 2006 |
| 5 | Z. bungeanum ‘Wucijiao’ | 54 | 0.04 | 2003 |
| 6 | plant diseases and insect pests | 49 | 0.01 | 2015 |
| 7 | Z. planispinum Sieb. et Zucc. | 48 | 0.04 | 2013 |
| 8 | production | 42 | 0.01 | 2004 |
| 9 | Z. planispinum seed | 40 | 0.06 | 2006 |
| 10 | Zanthoxylum armatum cv. jiuyeqing | 37 | 0.01 | 2008 |
| 11 | Z. oil | 36 | 0.05 | 2007 |
| 12 | Chinese Z. planispinum oil | 33 | 0.04 | 2011 |
| 13 | quality | 30 | 0.02 | 2004 |
| 14 | Chemical composition | 29 | 0.01 | 2004 |
| 15 | Z. planispinum var. Dintanensis | 28 | 0.04 | 2007 |
| 16 | Z. bungeanum seed oil | 25 | 0.02 | 2003 |
| 17 | Leaf of Bunge Z. planispinum | 24 | 0.01 | 2012 |
| 18 | Extraction craft | 21 | 0.01 | 2017 |
| 19 | Gas chromatography—mass spectrometry | 19 | 0.04 | 2004 |
| 20 | Antioxidant activity | 18 | 0.01 | 2012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Guo, Y.; Yang, G.; Yu, Y. Visual Analyses of Hot Spots and Frontiers in Zanthoxylum planispinum Research Based on CiteSpace. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070714
Yang S, Guo Y, Yang G, Yu Y. Visual Analyses of Hot Spots and Frontiers in Zanthoxylum planispinum Research Based on CiteSpace. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(7):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070714
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shunsong, Youyan Guo, Guangguang Yang, and Yanghua Yu. 2024. "Visual Analyses of Hot Spots and Frontiers in Zanthoxylum planispinum Research Based on CiteSpace" Horticulturae 10, no. 7: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070714
APA StyleYang, S., Guo, Y., Yang, G., & Yu, Y. (2024). Visual Analyses of Hot Spots and Frontiers in Zanthoxylum planispinum Research Based on CiteSpace. Horticulturae, 10(7), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10070714






