Abstract
Sweet pepper is a crop that benefits from phytosanitary treatments with low environmental impact, especially the successful control of pests through the introduction of biological control agents in greenhouses. However, predators that naturally occur in these surroundings often enter greenhouses. The precise roles of these natural predators and their interactions with the introduced predatory insects and mites are often unknown. This study investigated the relationships between Nesidiocoris tenuis, which is naturally present, and Amblyseius swirskii and Orius laevigatus, which are two species of generalist predators released for the control of multiple pests. This study was conducted for two years on 13 commercial sweet pepper crops in various types of greenhouses (tunnels and traditional greenhouses) in Sicily. The environmental complexity value (ECV) for each site was estimated based on 18 points detected around the site according to the different habitats that occurred at each coordinate. The results showed that the occurrence of N. tenuis in greenhouses, independently of their typology (tunnel or traditional greenhouse), was mainly promoted by the greater diversification of habitats immediately surrounding the pepper crops (in a circular area with a diameter of 500 mt), with an increase in its density during the crop season. Moreover, N. tenuis–O. laevigatus’s co-occurrence in flowers suggested that they were not impacted by each other’s presence and that their co-occurrence had a significant effect on pest reduction, although their co-occurrence was density-dependent. As an intraguild predator, N. tenuis competed with O. laevigatus for Frankliniella occidentalis when many predators were present. In addition, N. tenuis also competed with A. swirskii when they both occurred in flowers at a higher density. This study highlights the importance of pepper plant flowers in promoting a higher occurrence of juvenile forms of N. tenuis within flowers. Amblyseius swirskii colonized the plants in 3 weeks, distributing itself almost uniformly over the leaves with a clear control action against not only Bemisia tabaci but also F. occidentalis when present on the flowers. Thus, this concurrent analysis of several commercial pepper sites within the same production area suggests that, even with similar pest control plans, the diverse variability in the presence of natural enemies must be considered when selecting control strategies for pepper crop pests and that N. tenuis, favored by complex surrounding habitats, contributes actively to pest reduction.
1. Introduction
Sustainable production is a significant goal in agriculture sectors at both local and global levels [1,2,3,4,5]. Current control strategies are mainly oriented toward reducing inputs, such as fertilizers and pesticides, for healthier crop production with a lower environmental impact. The environmentally friendly control of insects and mites harmful to crops is a priority across all crops, and in protected environments, such as greenhouses, it has had some success. The key pests of sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) are the western flower thrip (WFT) Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) and the silverleaf whitefly Bemisia tabaci Gennadius (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) [6]. In addition, mites, such as Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae) and Polyphagotarsonemus latus Banks (Acari: Tarsonemidae), and aphids are secondary pests, which can all cause direct injury as a result of sap removal and honeydew build-up, resulting in sooty mold, physiological disorders, and the transmission of plant viruses [7,8].
The management of the WFT and silverleaf whitefly in greenhouse-grown pepper crops by the inoculative release of predatory insects and mites has been successful in many countries [9]. Biotic control strategies are based on the release of generalist biocontrol agents, such as the predatory mite Amblyseius swirskii Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and the minute pirate bug Orius laevigatus Fieber (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae) [9,10,11]. The use of other predatory species varies, such as Phytoseiulus persimilis Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and Neoseiulus californicus McGregor, 1954, for the control of T. urticae, as does the use of traditional approaches through phytosanitary interventions with active ingredients that safeguard useful species [12]. Particularly widespread in recent years is the use of A. swirskii as an efficient biological control agent for whiteflies and, secondarily, thrips and spider mites, which are economically damaging pests of ornamental plants and vegetable crops grown in greenhouses and fields worldwide. Amblyseius swirskii has become one of the most successful external biocontrol agents in protected agriculture since its introduction into the market in 2005 [11,13,14].
Mirid bugs (Hemiptera: Miridae) are generalist predators widely known for their predatory actions, with different successes against various pests, especially in horticultural and vegetable crops [15,16,17,18,19]. Several studies, under both laboratory and field conditions [15], have shown that allotropy (variation in the trophic regime) is common in different species of mirids and involves a change from a phytophagous diet to a zoophagous diet or vice versa [20]. Under particular plant host and temperature conditions [21], these characteristics result in different mirids becoming pests, with phytophagy increasing, especially at low prey densities [22,23]. Such phytophagy raises many concerns in areas of recent spread, as seen, for example, for the species Nesidiocoris tenuis Reuter [24], which is considered a biocontrol agent in Italy. In contrast, it is considered a major phytophagous pest in areas like the South of France [25]. This species is being studied through the aid of traps with the aim of introducing monitoring as an indication of population levels [26] or to identify alternative plant hosts to crops capable of reducing or diluting the damage caused by their phytophagy [27]. In Mediterranean environments, N. tenuis has wide potential for use in the biological control of Aleyrodidae in various crops [28]. This species is widespread in southern Italy and is among the most frequent in vegetable production environments. They are abundant in habitats surrounding greenhouses and are known to enter them naturally, for example, those containing sweet pepper crops. It often predominates among mirids and is reported as a biotic agent in protected growing environments for tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, and beans, among others [21,29,30,31,32]. Although N. tenuis in the Mediterranean is considered to be a generalist predator [17,33], it does not always exert the desired control action against herbivores. This is related to uncertainties associated with its variability in geographical occurrence and abundance, even following its augmentative release [15]. The impacts of habitat-level environmental complexity on N. tenuis remain largely understudied, and there is a significant gap in our understanding of the potential seasonal incursions of the species into greenhouses or other protected environments. Therefore, further research is warranted to explore these aspects comprehensively. The data obtained would also be able to provide direct indications for the possible conservation of habitats or the need to increase complexity around protected environments, such as greenhouses or tunnels, especially in conditions in which many producers suspect that the mirid N. tenuis can also be considered a pest for pepper crops (personal communication, September–December 2020).
In operational practice, even less is known about the competitive action of this species with other species used in biological control, such as O. laevigatus and A. swirskii. In the current study area, pepper plants have a brief period of cultivation, and the short-term effects of shared predation, such as apparent mutualism [34,35], can determine the dynamics of the pests and predators involved. Therefore, in terms of effective biological control, it is important to assess whether the effects of shared predation on pest levels are positive or negative.
Here, our primary questions were as follows: How does the complexity of the habitat surrounding greenhouses impact the distribution of N. tenuis and its effects on the predatory insects (O. laevigatus) and mites (A. swirskii) introduced into greenhouses? And how does the naturally co-occurring predator interact with the predatory species O. laevigatus and A. swirskii, especially in floral structures? We explored these questions in a pepper crop area where N. tenuis is widespread and is among the most frequent species in greenhouses and other vegetable production environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Systems
This study was conducted on 13 sweet pepper crops (hereafter, sites) in Sicily, southern Italy, in 2020 and 2021 (Figure 1) (latitude 38°4′, longitude 15°41′). The coastal area of this study borders the Mediterranean Sea (Agrigento district), at altitudes between 10 and 50 m a.s.l. next to SiteCode: ITA040010-Natura 2000. The investigated area is of a meso- and thermo-Mediterranean xerophile type, being mainly open, short-grass annual grasslands rich in therophytes growing on oligotrophic soils on base-rich, often calcareous substrates. The average temperature in the study area (1971–2000) is ~17.4 °C, with an average rainfall of 500 mm per year (concentrated in the autumn) and a dry summer period of ~5 months [36]. This habitat consists of Mediterranean grasslands characterized by a perennial vegetation community known as Thero-Brachypodietea and Thero-Brachypodietalia: Thero-Brachypodion. Poetea bulbosae is a plant community consisting of two main associations: Astragalo-Poion bulbosae (basiphile) and Trifolio periballion (silicolous) (see details in Supplementary Data). Grasslands that have been degraded or abandoned because of fire, grazing, and agricultural activities are relatively widespread. Several study sites were located near other horticultural areas, with protected cultivation, seedlings, olive groves, and vineyards (winemaking and table grapes). In contrast, others were located in the vicinity of private buildings with gardens, and some were located close to the sea (Figure 1). Crop sites were selected to promote the independence of observations. The average distance between sites was ~1 km; thus, it was assumed that the predator presence at each site was independent of other sites.
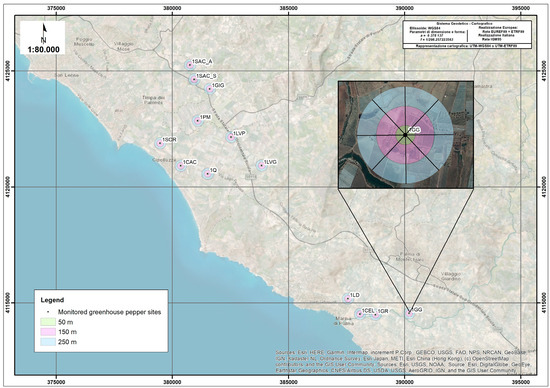
Figure 1.
Map showing the study sites and how the area surrounding each pepper crop was monitored at 50, 150, and 250 m from the crop to estimate the environmental complexity value (ECV).
2.2. Sites of Study and Pest Control Plans
The 13 monitored sites were of different sizes and types (Table 1). In this study, pepper crops comprised tunnels (ten sites), big tunnels (one site), and greenhouses (two sites), all formed of iron frames and plastic covers. Tunnels (Ts) or high tunnels (HTs) are a type of hemicylindrical-protected environment similar to plastic houses, from 2 m to 2.5 m in height and 3 to 5 m wide. At all sites, pepper cultivation followed melon cultivation (Cucumis melo) and was repeated in each site for more than 3 years during the summer–winter period. The plants (Altea F1, Seoul, and Ciccior F1 cultivated varieties) were transplanted above all in August and irrigated once or twice a week. Phytosanitary control was followed as a precaution for all phytophagous and fungi species generally present before natural enemies were introduced, and, for specific cases, particular phytosanitary treatments limited to a single group of plants or tunnels were carried out among the pepper sites monitored. For example, the control of broad mites Polyphagotarsonemus latus Banks (Acari: Tarsonemidae) was conducted through powdered or wettable sulfur distributed on infested and neighboring plants. Pyrimor® (Pirimicarb) was used for aphid attacks detected in the tunnels. Overall, the pesticide treatment plans and strategies were also determined through discussion with specialists in Koppert products, including those reduced side effects toward the natural enemies introduced: www.Koppert.en (accessed on 1 September 2020). In three monitored pepper sites, pheromone traps were inserted to detect the presence of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisduval, 1833) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), the flights of which were also monitored through the detection of larval attack. For the latter pest, treatments were carried out with different formulations of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner, 1915, Kurstaki (B.t.). Generally, insecticide soil drenches using Minecto alpha® [9.14% (100 g/L) (Cyantraniliprole + Acibenzolar-S-methyl)] were installed 8–10 days after planting and then activated 7 days later. Before the release of natural enemies and in consideration of the harmful effects on introduced species, pesticides with abamectin (A.I.) and spinosad (A.I.) were applied fifteen and seven days before, respectively.

Table 1.
Thirteen sweet pepper sites were surveyed (2020 and 2021), including the typology of the greenhouse environment (T = tunnel, HT = high tunnel, G = greenhouse), size (number of plants), and geographical position.
2.3. Introduction of Natural Enemies for the Control of Pepper Pests
The plant starts as a single stem, trained into two or more stems as soon as the first vigorous lateral stems appear. The release of predators took place at the first bifurcation of the three-branched plants. The predatory mites and insects used were A. swirskii (Swirski Ulti-Mite) and O. laevigatus (Thripor-L©) and were obtained from Koppert Biological Systems (Berkel en Rodenrijs, The Netherlands), with a density per square meter according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The mite predator A. swirskii was inserted with the help of bags distributed on all the rows of peppers. Each bag of Swirski Ulti-Mite (approximately 250 mites per bag) was hung on every 5 or 6 pepper plants, while O. laevigatus was distributed at a dose of one individual per square meter. No pollen or additional food sources were provided. The possible presence of natural enemies was unknown for each site before starting the trials.
2.4. Data Collection
2.4.1. In Situ Monitoring of Species
Weekly monitoring occurred from a week before the introduction of beneficial insects (approximately the first weeks of September) to December. All counts to estimate pest and predator density for each site were performed in situ on the same day, 2 or 3 days a week. The succession of monitored sites was random. The sampling included each pepper site (Table 1). Pepper plants bloom constantly, and one flower for every 1000 pepper plants was randomly sampled in both tunnel and greenhouse settings, counting, in addition, WFTs (neanids and adults), O. laevigatus (neanids and adults), N. tenuis (neanids and adults), and A. swirskii. The presence or absence of aphids or other species in the flowers was recorded. Counting B. tabaci involved determining the number of adults on a single leaf collected randomly at three-quarters of the height of the plants per 1000 plants. Finally, to assess the presence of N. tenuis and predatory mites, pepper leaves at three-quarters of the height of the plants were collected, and the presence or absence of N. tenuis and A. swirskii was evaluated. In total, 4700 and 4347 flowers and leaves were sampled for 2020 and 2021, respectively. Each flower and leaf were examined by a hand-held magnification lens (20×; Eschenbach®, Nürnberg, Germany).
2.4.2. Determining the Environment Surrounding Each Study Site
To quantify the landscape-level environmental complexity at each study site, the surroundings of each site were monitored in terms of the presence of natural enemies. A 0.5 km buffer was marked around each study site. Then, six coordinates were established, three each at 50, 150, and 250 m from the center of the buffer zone, with a weight attributed to each (pi = 1.5, 1.0, and 0.5 for 50, 150, and 50 m, respectively). The different habitats that occurred at each coordinate were recorded as (a) a greenhouse or tunnel, (b) arable land, (c) uncultivated, (d) private gardens, (d) orchards, (e) olive groves, or (f) river courses or drainage valleys. For each habitat detected, its complexity was determined in terms of the number of herbaceous, shrub, and tree species, the presence of walls and uncultivated areas, windbreaks, and so on; a value from 1 to 7 was then assigned, with 1 being the least complex (a) and 7 (f) being the most complex. This resulted in a complexity value (CV) for each point. The environmental CV (ECV) for each site was estimated based on the weighted average of the 18 points detected by the site (Figure S1). The average obtained was used to calculate the ECV per site using Equation (1):
2.5. Data Analysis
To analyze the presence or absence of N. tenuis and co-occurrence with O laevigatus in each flower, we used generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs) with a log link function [37]. To analyze N. tenuis presence, the random factor was the site surveyed, and the independent variables included in the model were the ECV, number of WFTs, number of O. laevigatus, size (number of pepper plants in the site), and the week of monitoring, the latter being a discrete variable. For the co-occurrence of O. laevigatus–N. tenuis data (presence or absence of both species in the same flower), the random factor was the sites surveyed, and the predictor variables included in the model were the number of WFTs, O. laevigatus, N. tenuis, size (number of pepper plants in the site), the week of monitoring, and the presence or absence of A. swirskii in each flower. To highlight if the WFT populations in flowers differ in the presence or absence of N. tenuis, A. swirskii, and O. laevigatus, Welch’s unequal variances t-test was performed each year. To evaluate the relationship for all pairs of variables in each site, a scatter plot matrix and Pearson correlation matrix for monitored sites were drawn to visualize the bivariate relationships between combinations of variables. In addition, the association between B. tabaci and A. swirskii on leaves was tested using a Spearman rank correlation test. The association between N. tenuis on each flower and the presence or absence of N. tenuis on leaves for each site and week was tested using a Spearman rank correlation test. All data are expressed as untransformed values (±SE). SPSS v.23 [38] was used for all data analyses, and SigmaPlot 13.0 [39] was used to produce all graphs.
3. Results
The linear model highlighted that ECV and WFTs had a major effect on predicting the presence of N. tenuis in each year surveyed (Table 2a, F values). The site’s size and the monitoring week also affected the presence of N. tenuis. According to the fixed coefficients, an increasing ECV value was more likely to predict the presence of N. tenuis (2020: coefficient value = 1.77 ± 0.139; T-value = 12.74; p < 0.001; 2021: coefficient value = 0.767; T-value = 10.96; p < 0.001) and a slightly negative relationship with WFT and O. laevigatus in 2020 (Table 2b). This study’s minimum estimated ECV value was 1.44, whereas the maximum was 3.

Table 2.
The results of the generalized linear mixed model used to predict Nesidiocoris tenuis presence with a log link function (a,b).
The predictive model used to verify the N. tenuis–O. laevigatus association in flowers highlights that the simultaneous presence of the two predators in one flower was mainly connected to the density of these predators and is not influenced by the presence of mites and aphids across different years, except for the size of pepper sites in 2021 (Table 3a). The N. tenuis–O. laevigatus association was determined by the variation in the density of each species (coefficient value for N. tenuis = 1.12 and 1.49, p < 0.001; O. laevigatus = 0.99 and 1.50, p < 0.001, respectively, for 2020 and 2021) (Table 3b).

Table 3.
The generalized linear mixed model results were used to predict the presence of Nesidiocoris tenuis–Orius laevigatus association in flowers with a log link function (a,b).
The abundance of N. tenuis in flowers was 0.12 ± 0.06; N = 4782 and 0.17 ± 0.079; N = 4348 in each year, mainly being juveniles rather than adults (2020: mean = 0.11 ± 0.005 versus 0.02 ± 0.002, 2021: mean = 0.15 ± 0.008 versus 0.02 ± 0.002, respectively). The maximum number of individuals found per flower was six. Each year, of the 13 sites monitored over the growing season, N. tenuis was found at almost all sites, with clear differences between sites (Table S1). The seasonal abundance of N. tenuis changed weekly and showed a clear increase with predator O. laevigatus abundance during the pepper season (Figure 2). In both 2020 and 2021, there were significantly less WFTs in flowers with N. tenuis than in flowers where this predator was absent (Figure 3). The correlation with WFT points to an inverse relationship with N. tenuis in pepper flowers confirmed by correlation (2020: r = −0.107, p < 0.001; N = 4782; 2021: r = −0.087, p < 0.001; N = 4341) (Table S2). The relationship between the mean number of N. tenuis on the leaves and flowers was positively related to the N. tenuis population on pepper plants (2020: r = 0.326, p < 0.001, N = 168; 2021: r = 0.785, p < 0.001, N = 172, Figure S2).
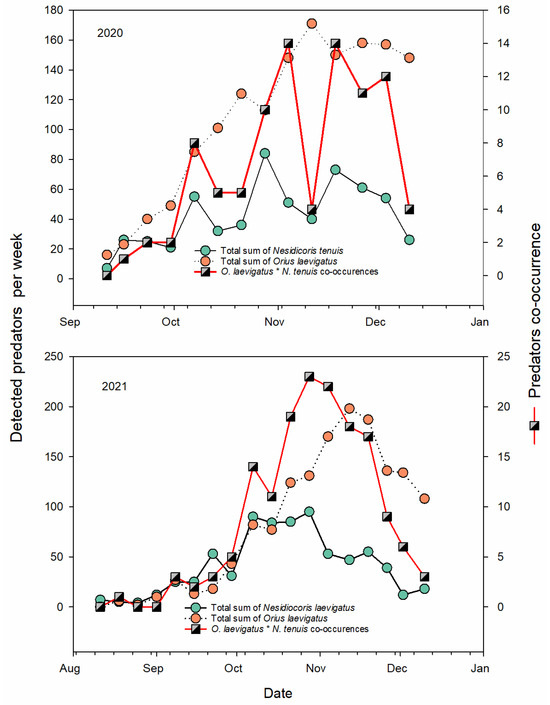
Figure 2.
Weekly variation in the abundance of predatory bugs (adults and nymphs) and their co-occurrence on flowers for all monitored pepper sites.
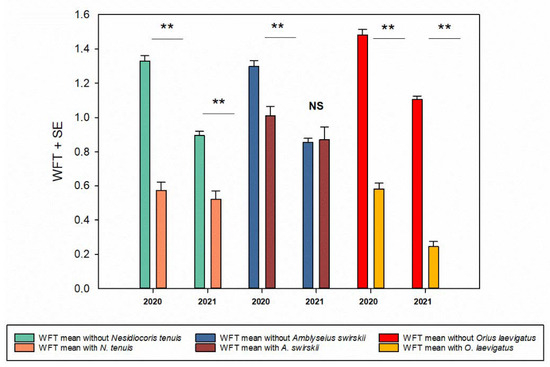
Figure 3.
Western flower thrip (WFT) mean abundance in pepper flowers with or without presence of its natural enemies (2020, 2021). T statistic value (Nesidiocoris tenuis): 13.16, df = 1, 925; p < 0.001) (2020) and 47.42, df = 1, 700; p < 0.001 (2021). Amblyseius swirskii: 4.49, df = 1, 1321; p =< 0.001) (2020) and −0.206, df = 1, 720; p = 0.84 (2021). Orius laevigatus: 18.35, df = 1, 3695; p < 0.001) (2020) and 24.79, df = 1, 4334; p < 0.001 (2021). Asterisks show significant differences at p < 0.001 and NS = Not significant.
The abundance of O. laevigatus per flower for all sites was 0.31 ± 0.009 and 0.338 ± 0.088 (average ± SE for each year), with more juveniles than adult forms (2020: 0.234 ± 0.076 versus 0.08 ± 0.04, 2021: mean = 0.24 ± 0.008 versus 0.10 ± 0.005, respectively) (Table S1). In the pepper flowers, there was a negative relationship between WFTs and O. laevigatus (r = −0.185, N = 4781; p < 0.001 and r = −0.251, N = 4336; p < 0.001 for 2020 and 2021, respectively) (Figure 4). There was a slight negative relationship between O. laevigatus and N. tenuis for all sites only for 2021 (2020: r = −0.027, p = 0.066, N = 4782; 2021: r = −0.036, p = 0.018, N = 4329), but this competition had no negative effect on pest regulation (see Table S1, Figure 4). In both years, there were significantly less WFTs in flowers with O. laevigatus than in flowers where this predator was absent (Figure 3).
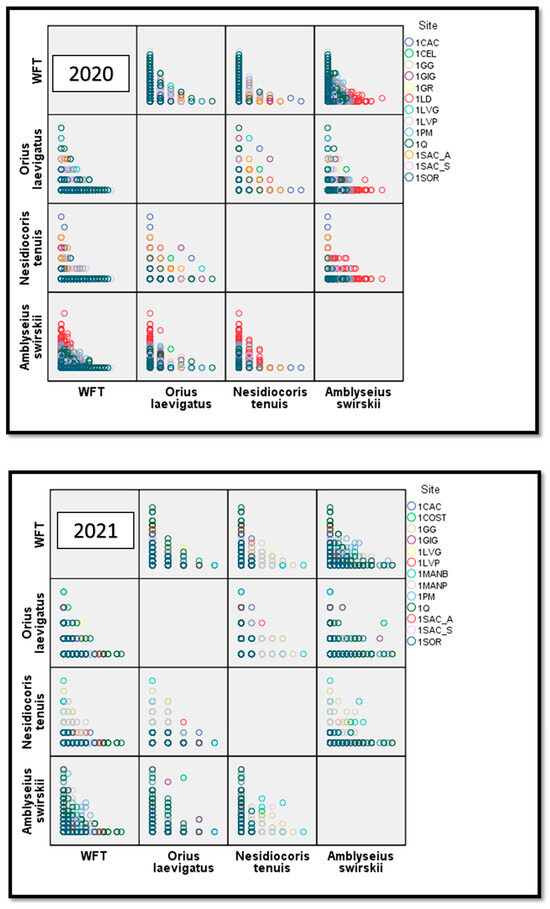
Figure 4.
Scatter plot matrix indicating the correlation between white flower thrips (WFTs) and the predators Orius laevigatus, Nesidiocoris tenuis, and Amblyseius swirskii (2020 above, 2021 below). The figures represent the number of juveniles and predators in each flower for each species.
The presence of A. swirskii in flowers varied between sites, with this species detected in 16% of the sampled flowers, with an overall mean of 0.93 ± 0.041 (N = 4782) in 2020 and 8.4% and 0.33 ± 0.021 (N = 4348) in 2021. The mean per flower was highly variable between sites (Table S1). The number of A. swirskii in the pepper flowers also varied, from a minimum of 1 to a maximum of 35. There was a negative relationship in 2020 among A. swirskii, WFTs, and O. laevigatus in the flowers (r = −0.074, N = 4782; p < 0.001 for WFT and r = −0.086, N = 4782; p < 0.001 for O. laevigatus). The same negative relationship was confirmed in 2021 (Table S2, Figure 3). Aphids occurred in only 2.52% and 2% of flowers (2020: N = 4783, 2021: N = 4346). However, in 2020, there were significantly less WFTs in flowers with A. swirskii than in flowers where this predator was absent (Figure 3).
In some sites and each year, species of springtails were found in the pepper flowers (see Supplementary Data, Figure S3).
In the leaves, A. swirskii was nearly uniformly distributed from the fifth week of sampling in all sites for each year and from the third week of sampling in a few sites; the percentage of leaves sampled on which A. swirskii was found exceeded 50%. The presence of the predatory mite remained constant (>85% of leaves) until the end of the sampling period (Figure 5). The relationship with the number of adults of B. tabaci on the leaves showed that the presence of this predator limits the development of the whitefly population (2020: rs = −0.074, p < 0.001, N = 4783; 2021: rs = −0.049, p =0.001, N = 4341). The seasonal abundance of B. tabaci changed weekly and showed a clear decrement during the season (Figure 6).
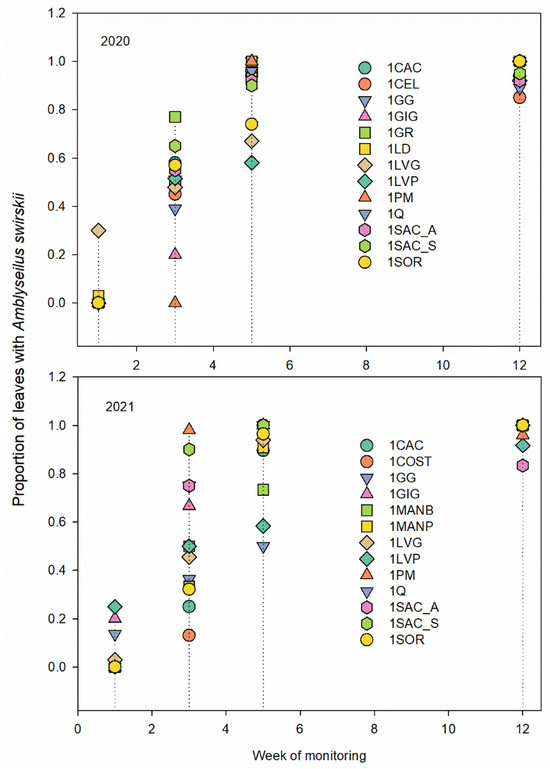
Figure 5.
Amblyseius swirskii’s presence on pepper leaves variation during different monitoring weeks (weeks 1, 3, 5, and 12) at different pepper sites.
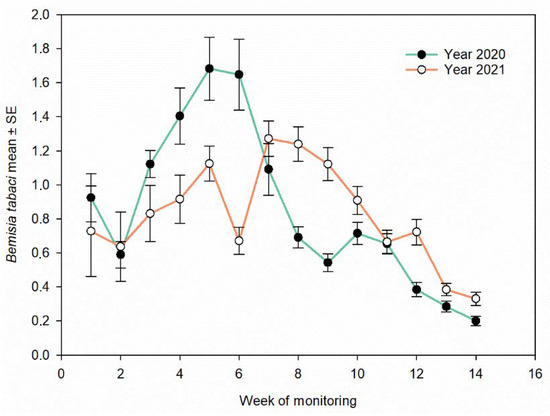
Figure 6.
Weekly variation in the abundance of Bemisia tabaci on pepper leaves at all sites.
4. Discussion
Pepper plants in the study area are cultivated in autumn–winter, and the short-term effects of shared predation, such as apparent mutualism, could determine the pest–predator dynamics, especially in sites where natural predators occur, such as N. tenuis. Therefore, for biological control programs, it is important to assess whether the effects of shared predation on pest levels are positive or negative.
This study provides evidence that the dispersal of N. tenuis is not uniform in the same climatic area, as it is more likely to occur in a pepper crop located close to biodiversity-rich habitats compared with more uniform and biodiversity-poor sites. Parolin et al. [40] identify a fundamental role of secondary plants in improving pest management in crops, and the results of the current study confirm the importance of the interaction between the crop area and its immediate surrounding environment. The different types of uncultivated habitats and protected environments near greenhouses and tunnels may support distinct communities of plants, herbivores, and natural enemies. Therefore, diversified landscapes may represent the greatest potential for conserving biodiversity and maintaining pest control services.
Several studies confirm the important role of secondary plants in surrounding and nearby crops and greenhouses’ habitats [41,42,43,44,45]. Generally, mirid bugs in the Mediterranean area move in greenhouses commonly at the end of the spring cycle [46,47], whereas little information is available for the autumn–winter season, particularly where this study was performed. Saulich and Musolin [48] highlighted that N. tenuis has homodynamic seasonal development and that its autumn and winter generations are related to food availability and temperature [49,50,51]. The presence of, and increase in, natural mirid predators within the crop increases the probability of the co-occurrence of O. laevigatus with N. tenuis, explaining, in part, their competitive relationship with pepper flowers. Although associations among different species are also known among mirids, it is essential to understand how such interactions affect the distribution preference of individual predatory species within the plant [52,53]. The co-occurrence of several predators on the plant, especially in the flower, is positive overall, but the introduction of more predators for the control of WFTs and B. tabaci would not necessarily result in the same effect for the different predators’ distribution patterns on the plants [54]; however, previous research highlighted the efficiency of predatory mirids against WFT on different hosts and under controlled climatic conditions [52]. Pepper flowers were attractive for juveniles of N. tenuis feeding, and their preponderant presence highlighted how the flower of pepper plants could favor the establishment of crop species. Pepper plant injury in this study was not investigated, but it is not an issue in these pepper crops for which no damage has been detected.
The constant and uniform occurrence of A. swirskii on pepper plants in this study also highlighted their predatory action on WFTs when they co-occur in flowers, although the high density of O. laevigatus significantly reduced the abundance of the predatory mite. Bouagga et al. [55] reported the competitive action of O. laevigatus against A. swirskii [54]; however, the established presence of A. swirskii on flowers for the growing season in one site (1PM-2020) meant that WFTs could not increase above a certain threshold even in the absence or reduced presence of O. laevigatus.
Future investigations are needed to understand other factors that can play a role in the relationships between the abundance of N. tenuis and introduced natural enemies in protected pepper crops and sites. It might be that, in some sites, the abundance of N. tenuis could also be influenced by the production of pollen by host plants or by the effects of fires on the immediate surrounding areas, which negatively impacted the flora that hosts this species. Another unresolved issue to investigate is the understanding of the mechanisms by which landscape composition drives natural enemy–herbivore interactions or explore alternative specific host plants in the crop area such as the widespread Dittrichia viscosa L. Future efforts are necessary to develop tools that inform farmers when habitat conservation would be beneficial in terms of providing an increased understanding of how landscape effects are modulated by local farm management and the biology of pests and their enemies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10060614/s1, Figure S1. For example, calculate the environmental complexity values (ECVs) in the various coordinates analyzed for each site. The ECV values ranged from a minimum of 0.5 to a maximum of 10.5. Figure S2. Weekly mean of Nesidiocoris tenuis on leaf and flower (2020 left, 2021 right). Figures represent juveniles and adults in leaves or flowers. Figure S3. (a) Entomobrya sp (Fam. Entomobryidae: Entomobryinae); (b) springtails Entomobrya sp. on pepper flower; (c) Seira sp. (Fam. Entomobryidae: Seirinae); (d) lateral view of Seira sp. Table S1. The mean and standard deviation at different sites. At different sites, Orius laevigatus, Nesidiocoris tenuis, Amblyseius swirskii, and WFTs are the total of juveniles and adults for each flower. Table S2. Pearson correlation matrix of juveniles and adults of western fly thrips (WFTs), Orius laevigatus, Amblyseius swirskii, and Nesidiocoris tenuis on pepper flowers from each study site.
Author Contributions
C.P.B.: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, and funding acquisition. J.v.B.: writing—original draft preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partly supported by the Internal Grant Agency (FFABBR, funding basic research activities 2017) assigned to C.P. Bonsignore. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, publication decision, or manuscript preparation.
Data Availability Statement
The data sets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank “Cooperativa Agricola Palumbo Più” for providing the facilities for experiments. Francesco Manti is thanked for providing geographical information and Domenico Folino for helping create the graphical abstract. All photos in the figures are by the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Ehrlich, P.R.; Ehrlich, A.; Daily, G. Food Security, Population and Environment. Popul. Dev. Rev. 1993, 19, 1–32. Available online: www.jstor.org/stable/2938383 (accessed on 19 March 2021). [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Sustainable Horticulture and Resource Management. In XXVII IHC-S11 Sustainability through Integrated and Organic Horticulture; Prange, R.K., Bishop, S.D., Eds.; ISHS: Leuven, Belgium, 2008; Volume 767, pp. 19–44. [Google Scholar]
- Pretty, J. Agricultural sustainability: Concepts, principles and evidence. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, P.; Upadhyay, S.; Raghubanshi, A.S. Human Overpopulation and Food Security: Challenges for the Agriculture Sustainability. In Environmental Issues Surrounding Human Overpopulation; Singh, R.P., Singh, A., Srivastava, V., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 12–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Measuring the Environmental Performance of Agriculture across OECD Countries; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tommasini, M.G.; Maini, S. Frankliniella occidentalis and other thrips harmful to vegetable and ornamental crops in Europe. In Wageningen Agricultural University Papers; Wageningen Agricultural University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 95, pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- De Barro, P.J.; Liu, S.S.; Boykin, L.M.; Dinsdale, A.B. Bemisia tabaci: A statement of species status. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortes, I.M.; Moriones, E.; Navas-Castillo, J. Tomato chlorosis virus in pepper: Prevalence in commercial crops in southeastern Spain and symptomatology under experimental conditions. Plant. Pathol. 2012, 61, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lenteren, J.C. The state of commercial augmentative biological control: Plenty of natural enemies but a frustrating lack of uptake. BioControl 2012, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, F.J.; Bolckmans, K.; Belda, J.E. Control of Bemisia tabaci and Frankliniella occidentalis in cucumber by Amblyseius swirskii. BioControl 2011, 56, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, F.J.; Knapp, M.; van Houten, Y.M.; Hoogerbrugge, H.; Belda, J.E. Amblyseius swirskii: What made this predatory mite such a successful biocontrol agent? Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 65, 419433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonsignore, C.P.; Vacante, V. Influences of botanical pesticides and biological agents on Orius laevigatus—Frankliniella occidentalis dynamics under greenhouse conditions. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2012, 52, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, Z.; Fathipour, Y.; Farazmand, A. Age-stage predation capacity of Phytoseiulus persimilis and Amblyseius swirskii (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on susceptible and resistant rose cultivars. Int. J. Acarol. 2016, 4, 224228. [Google Scholar]
- Buitenhuis, R.; Shipp, L.; Scott-Dupree, C. Dispersal of Amblyseius swirskii Athias-Henriot (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on potted greenhouse chrysanthemum. Biol. Control 2010, 52, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A.; La-Spina, M.; Lacasa, A. Numerical response of Nesidiocoris tenuis (Hemiptera: Miridae) preying on Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in tomato crops. Eur. J. Entomol. 2014, 111, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Pérez-Hedo, M.; Colazza, S.; Urbaneja, A. The predatory mirid Dicyphus maroccanus as a new potential biological control agent in tomato crops. BioControl 2014, 59, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Hedo, M.; Urbaneja, A. Prospects for predatory mirid bugs as biocontrol agents of aphids in sweet peppers. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouagga, S.; Urbaneja, A.; Rambla, J.L.; Flors, V.; Granell, A.; Jaques, J.A.; Pérez-Hedo, M. Zoophytophagous mirids provide pest control by inducing direct defences, antixenosis and attraction to parasitoids in sweet pepper plants. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1286–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leman, A.; Ingegno, B.L.; Tavella, L.; Janssen, A.; Messelink, G.J. The omnivorous predator Macrolophus pygmaeus, a good candidate for the control of both greenhouse whitefly and poinsettia thrips on gerbera plants. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, G. Introduzione Allo Studio Dell’entomologia; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 1951; Volume I, p. 950. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Siscaro, G.; Lo Pumo, C.; Tropea Garzia, G.; Tortorici, S.; Gugliuzzo, A.; Ricupero, M.; Biondi, A. Temperature and tomato variety influence the development and the plant damage induced by the zoophytophagous mirid bug Nesidiocoris tenuis. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbaneja, A.; Tapia, G.; Stansly, P. Influence of host plant and prey availability on developmental time and survivorship of Nesidiocoris tenuis (Het.: Miridae). Biocontr. Sci. Technol. 2005, 15, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.A. Factors influencing zoophytophagy in the plantbug Nesidiocoris tenuis (Heteroptera: Miridae). Agric. For. Entomol. 2008, 10, 7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Diaz, G.; Marconi, T.; Avila, C.A.; Villanueva, R. Persistence of the Exotic Mirid Nesidiocoris tenuis (Hemiptera: Miridae) in South Texas. Insects 2021, 12, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnó, J.; Castañé, C.; Riudavets, J.; Gabarra, R. Risk of damage to tomato crops by the generalist zoophytophagous predator Nesidiocoris tenuis (Reuter) (Hemiptera: Miridae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2010, 100, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.R.; Harte, S.J.; Bray, D.P.; Farman, D.I.; James, R.; Silva, C.X.; Fountain, M.T. Hero turned villain: Identification of components of the sex pheromone of the tomato bug, Nesidiocoris tenuis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2021, 47, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konan, K.A.J.; Monticelli, L.S.; Ouali-N’goran, S.-W.M.; Ramirez-Romero, R.; Martin, T.; Desneux, N. Combination of generalist predators, Nesidiocoris tenuis and Macrolophus pygmaeus, with a companion plant, Sesamum indicum: What benefit for biological control of Tuta absoluta? PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, A.; Zappalà, L.; Di Mauro, A.; Tropea Garzia, G.; Russo, A.; Desneux, N.; Siscaro, G. Can alternative host plant and prey affect phytophagy and biological control by the zoophytophagous mirid Nesidiocoris tenuis? Biocontrology 2016, 61, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacante, V.; Tropea Garzia, G. Nesidiocoris tenuis: Antagonista naturale di aleurodidi. Inf. Fitopatol. 1994, 4, 23–28. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Castañé, C.; Alomar, O.; Goula, M.; Gabarra, R. Colonization of tomato greenhouses by the predatory mirid bugs Macrolophus caliginosus and Dicyphus tamaninii. Biol. Control 2004, 30, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, H.; Uefune, M.; Ozawa, R.; Takabayashi, J. Olfactory response of the omnivorous mirid bug Nesidiocoris tenuis to eggplants infested by prey: Specificity in prey developmental stages and prey species. Biol. Control 2015, 91, 4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeily, S.; Amin Samih, M.; Izadi, H. Induced eggplant resistance against Trialeurodes vaporariorum triggered by jasmonic acid, abscisic acid, and Nesidiocoris tenuis feeding. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2020, 110, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, K.B.; Visser, S.; Dalíková, M.; Provazníková, I.; Urbaneja, A.; Pérez-Hedo, M.; Marec, F.; Werren, J.H.; Zwaan, B.J.; Pannebakker, B.A.; et al. Jekyll or Hyde? The genome (and more) of Nesidiocoris tenuis, a zoophytophagous predatory bug that is both a biological control agent and a pest. Insect Mol. Biol. 2021, 30, 188209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abrams, P.A.; Holt, R.D.; Roth, J.D. Apparent competition or apparent mutualism? Shared predation when populations cycle. Ecology 1998, 79, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.C.; Gamelin, E.F.; Johnson, E.G.; Hines, A.H. Density-dependent indirect effects: Apparent mutualism and apparent competition coexist in a two-prey system. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2012, 456, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climate-Data.org©/AM OP/OpenStreetMap Contributors USt-IdNR: DE279133320. 2021. Available online: https://it.climate-data.org/search/?q=palma+di+montechiaro (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- McCullagh, P.; Nelder, J. Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. Released: IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; Version 23.0; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2015; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Sigmaplot 13.0. Systat Copyright © Systat Software; Systat Software Inc.: San Jose, CA, USA, 2018.
- Parolin, P.; Bresch, C.; Poncet, C.; Desneux, N. Functional characteristics of secondary plants for increased pest management. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2012, 58, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomar, Ò.; Goula, M.; Albajes, R. Colonisation of tomato fields by predatory mirid bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) in northern Spain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 89, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingegno, B.L.; Pansa, M.G.; Tavella, L. Plant preference in the zoophytophagous generalist predator Macrolophus pygmaeus (Heteroptera: Miridae). Biol. Control 2011, 58, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Guo, X.; Tan, X.; Desneux, N.; Zappala, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S. Using Calendula officinalis as a floral resource to enhance aphid and thrips suppression by the fower bug Orius sauteri (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae). Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karp, D.S.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Meehan, T.D.; Martin, E.A.; DeClerck, F.; Grab, H.; Gratton, C.; Hunt, L.; Larsen, A.E.; Martínez-Salinas, A.; et al. Crop pests and predators exhibit inconsistent responses to surrounding landscape composition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7863–E7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardanuy, A.; Figueras, M.; Matas, M.; Arnó, J.; Agustí, N.; Alomar, Ò.; Albajes, R. Banker plants and landscape composition influence colonisation precocity of tomato greenhouses by mirid predators. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 95, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnero, A.; Dıaz, S.; Amador, S.; Hernández, M.; Hernández, E. Impact of Nesidiocoris tenuis Reuter (Hemiptera: Miridae) on whitefly population in protected tomato crops. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 2000, 23, 259. [Google Scholar]
- Malausa, J.C.; Drescher, J.; Franco, E. Prospectives for the use of the predacious bug Macrolophus caliginosus Wagner, (Heteroptera: Miridae) on glasshouse crops. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 1987, 10, 106107. [Google Scholar]
- Saulich, A.K.; Musolin, D.L. Seasonal development of plant bugs (Heteroptera, Miridae): Subfamily Bryocorinae. Entomol. Rev. 2019, 99, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, G.E.; Bale, J.S.; Sterk, G. Thermal biology and establishment potential in temperate climates of the predatory mirid Nesidiocoris tenuis. BioControl 2009, 54, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavkare, O.; Sharma, P.L.; Chandel, R.S.; Verma, S.C.; Fand, B.B. Temperature impact on the phenology of Nesidiocoris tenuis feeding on Tetranychus urticae: Simulation through life cycle modelling. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 2319–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingegno, B.L.; Messelink, G.J.; Leman, A.; Sacco, D.; Tavella, L. Development and thermal activity thresholds of European mirid predatory bugs. Biol. Control 2021, 152, 104423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messelink, G.J.; Janssen, A. Increased control of thrips and aphids in greenhouses with two species of generalist predatory bugs involved in intraguild predation. Biol. Control 2014, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdikis, D.; Lucas, E.; Garantonakis, N.; Giatropoulos, A.; Kitsis, P.; Maselou, D.; Panagakis, S.; Lampropoulos, P.; Paraskevopoulos, A.; Lykouressis, D.; et al. Intraguild predation and sublethal interactions between two zoophytophagous mirids, Macrolophus pygmaeus and Nesidiocoris tenuis. Biol. Control 2014, 70, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaeser, P.; Sengonca, C.; Zegula, T. The potential use of different predatory bug species in the biological control of Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Pest Sci. 2004, 77, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouagga, S.; Urbaneja, A.; Pérez-Hedo, M. Combined use of predatory mirids with Amblyseius swirskii (Acari: Phytoseiidae) to enhance pest management in sweet pepper. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).