Abstract
The BTB/POZ (broad-complex, tramtrack, and bric-a-brac) family of proteins is widespread in plants and animals and plays important roles in growth, development, metabolism, and environmental responses. There are few reports on BTB family genes in potato. In this study, 34 sequences containing conserved BTB domains were obtained from the potato gene database, and the phylogenetic, physical, and chemical properties, gene structure, conserved motif, domain, and chromosomal localization of the potato BTB protein family were analyzed via bioinformatics methods. In addition, we used qRT-PCR to detect 12 selected StBTB genes. The results confirmed that these genes are involved in cold, ABA, salt, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), drought, and low-nitrogen stress, which is highly important for elucidating BTB family members and studying stress response and tolerance mechanisms. This study provides a theoretical basis for the study of the function and expression of potato BTB and lays a solid foundation for further understanding the molecular mechanism of the potato BTB gene under various environmental stresses.
1. Introduction
There are many transcription factor families in plant genomes that generally activate or inhibit the expression of target genes by binding to their promoters and subsequently regulate plant growth and development. The BTB (broad-complex, tramtrack, and brick-a-brac) domain was originally thought to be a conserved motif found in Drosophila melanogaster; it is an evolutionarily conserved protein–protein interaction motif consisting of approximately 120 amino acid residues and has a wide range of functions in development and homeostasis, as well as in a wide range of interactions [1,2]. Members of the BTB family are also a class of transcription factors. This domain is composed of five α-helixes and three β-sheets, and each family member of the BTB protein family has one or more BTB structures [3]. The BTB protein family contains not only the BTB protein domain but also several other protein domains. These proteins include TRAF homology (MATH), ankyrin repeats (ANK), armadillo (ARM), zinc finger protein (TAZ), nonphototropic hypocotyl 3 (NPH3), BTB and C-terminus Kelch (BACK), tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR), proteins containing only the BTB domain, and other proteins, thus forming different subfamilies of BTB proteins and playing different roles [4,5,6,7].
The BTB protein has not only been extensively studied in animals but also plays an important role in many fields such as plant growth and development, stress resistance, protein ubiquitination and degradation, cell structure, ion channel, and cell cycle regulation [8,9]. Members of the BT subfamily negatively regulate nitrate absorption genes and NUE in plants, providing a basis for the improvement of NUE. This subfamily also responds to nutrition, stress, and hormones, and BTs’ proteins can interact with the E3 ligase CULLIN3. The nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related (NPR) subfamily is also a disease resistance protein that plays an important role in regulating broad-spectrum resistance and is a key gene for disease resistance [10,11,12,13,14]. In plants, many members of the BTB protein family are involved in mediating plant-related signal regulation, such as salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), abscisic acid (ABA), and gibberellin (GA3) [15].
Potato (Solanum tuberosum) is an annual herb of the Solanaceae genus Solanum and is the most important tuber crop and the fourth largest crop in the world [16,17]. In recent years, members of the BTB family have been identified in many plant species such as Arabidopsis thaliana [18], rice [19], and tomato [20]. However, there are few studies on the potato BTB family. In this paper, the BTB family of potato was excavated, and the bioinformatics analysis of the potato genome was carried out. On this basis, qRT-PCR verification was performed. The results showed that the BTB members in potato have high homology with the BTB members in A. thaliana and may have similar functions under different stresses. However, under different abiotic stresses, the gene expression is also different, indicating that the StBTB gene plays an important role in response to abiotic stresses. In summary, the results of this study preliminarily explored the function of potato StBTB gene, which laid a foundation for further study of its role and molecular mechanism in potato, and provided new ideas for the screening and breeding of highly tolerant potato plants.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials
The potato tissue culture-generated plants (Chuanyu No. 10 varieties) used in this study were preserved and provided by the Potato Research Center of Sichuan Agricultural University. High-quality potatoes were selected for tissue culture and stress treatment on ordinary MS medium. The potato culture condition was 28 °C, and the photoperiod was 16/8 h. Three potato seedlings at 8–9 leaf stage were selected for each treatment.
2.2. Search and Identification of Potato BTB Family Member Genes
The reference genome data of potato were derived from the Potato Genomics Resource (http://spuddb.uga.edu/, accessed on 15 December 2023), and the BTB/POZ (PF00651) from the Pfam database (https://pfam.xfam.org/, accessed on 15 December 2023) was used as the HMM file. The whole potato protein database was retrieved using Hmmer3.0 software. Then, incomplete and erroneous sequences were removed through the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) online website Conserved Domains Database.
2.3. Analysis of Basic Physical and Chemical Properties of Potato BTB Family Proteins
The online software EXPASy ProtParam 3.0 (https://web.ExPASy.org/protparam/, accessed on 15 December 2023) was used to analyze the basic physical and chemical properties of potato BTB gene family members, and the subcellular localization of the gene was predicted with ProtComp 9.0 (http://linux1.softberry.com, accessed on 15 December 2023).
2.4. Homology Analysis of BTB Family Proteins
MEGA7.0 software [21] was used to analyze 34 StBTB genes, and a phylogenetic tree was successfully constructed via the neighbor-joining method with 1000 replicates. Bootstrap value and position in the phylogenetic tree was used to assign 34 StBTB genes to appropriate clusters. Next, the constructed phylogenetic tree was beautified using the ChiPlot (https://www.chiplot.online/, accessed on 15 December 2023) [22].
2.5. Analysis of BTB Motifs, Gene Structures, and Domain in Potato
The structural information of the required StBTB gene was screened by TBtools (v1.120) software [23], and the motif of the gene was predicted using the MEME [24] (http://meme.sdsc.edu/meme/memeintro.html, accessed on 15 December 2023) online website. Finally, TBtools (v1.120) was used to visualize the genes. The parameter settings were as follows: motif maximum, 10; motif length range, 6~100. The conserved domains of potato BTB family were analyzed and visualized by NCBI conserved domain search, InterproScan and Pfam domain prediction tools.
2.6. Analysis of Chromosomal Location, Gene Duplication
The chromosome location information of each StBTB gene was obtained from the Spud DB database (http://spuddb.uga.edu/, accessed on 15 December 2023), and the gene location was visualized by TBtools (v1.120). At the same time, the collinear relationship of BTB family in potato was visualized.
2.7. Collinearity Analysis of the BTB Family
TBtools (v1.120) software was used for data preparation, and MCScanX was used to visualize the collinearity between potato and A. thaliana.
2.8. Gene Expression Analysis of Potato BTB Family Members
The potato transcriptome data were downloaded from the Solanaceae Genomics Resource database [25], the FPKM values of the corresponding transcripts of the BTB family members were retrieved in turn, and the clustering heatmap was drawn using TBtools (v1.120) software.
2.9. Expression Verification of Screened Genes
Through the expression of potato BTB family members under different abiotic stresses via a cluster heatmap, 12 genes whose expression increased in response to stress were identified. A control group and six groups receiving stress treatment were established. The control group had no stress, and the treatment groups included low temperature (4 °C), ABA (1 μmol/L), drought (5% PEG-6000), high salt (200 mmol/L), low nitrogen (0.75 mmol/L), and H2O2 (10 mmol/L). After 0 h and 6 h of treatment, the plants were quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until further use. Total RNA was extracted using Trizol® reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the RNAiso plus (TaKaRa, Osaka, Japan, Code No. 9108/9109) method, and the total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA using PrimeScript™ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (TaKaRa, Osaka, Japan, Code No. 6110A). SYBR® Premix Ex Taq II (Dalian, China, Code No. RR820A/B) was used for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. The fluorescence quantitative 10 microbiome system consisted of 5 μL fluorescence quantitative enzyme, 0.5 μL upper primer, 0.5 μL lower primer, 2.5 μL ddH2O, and 1.5 μL cDNA, and the program was set according to the instructions; three technical repetitions were used. Then, we used the 2−ΔΔCT method to calculate the relative expression of the genes [26]. The sequences of primers used in the experiment are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties and Subcellular Localization of Potato BTB Family
Finally, 34 StBTB genes of potato BTB protein family were screened out, numbered StBPM1~StPHL2, and their physical and chemical properties (isoelectric point, relative analysis quality, hydrophobicity, etc.) were analyzed for prediction. The number of amino acids (aa) encoded by 34 proteins ranged from 201 to 947, of which StEOL1 contained the greatest number of amino acids (947) and StBBK1 contained the least (only 201). The molecular weights ranged from 22.7 (StBBK1) to 107.6 (StEOL1) kDa. Except for a few proteins with molecular weights that were too large or too small, most of the protein molecular weights ranged from 50 to 80 kDa. The isoelectric points of 34 proteins ranged from 4.84 (StBBK2) to 9.18 (StBT1). Except for StBTB1/2/3, StNPL1/7/8/10, and StBTB1, the isoelectric points of the other genes ranged between 4.84 and 7.17, indicating that most of the amino acids encoded by the potato BTB family were acidic amino acids. The hydrophilicity was between −0.473 (StBT2) and −0.027 (StBTB2), and all proteins were hydrophilic and unstable. The results of subcellular localization prediction showed that most of the potato BTB family proteins were located in the nucleus (14); the remaining 10 were located in the cytoplasm and nucleus, 7 in the cytoplasm and 3 in the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus (Table 1).

Table 1.
Basic physical and chemical properties of the potato BTB family.
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of Potato BTB Protein
To elucidate the phylogenetic relationship of potato BTB proteins, multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis were performed on 34 potato BTB proteins (StBTBs) and 80 A. thaliana BTB proteins (AtBTBs) (Figure 1). The potato BTB proteins were mainly divided into nine subfamilies. The MATH group contained five StBTB members (StBPM1, StBPM2, StBPM3, StBPM4, and StBPM5). The TAZ group consisted of three StBTB members, StBTB1/2/3. Group NPH3 had more BTB members, namely, StNPL1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/9/10/11. The ANK group was mainly composed of StNPR1-1/2/3/4/5. The ARM group contained StARM1 and StARM2. Group BACK contained StBBK1, StBBK2, and StBBK3. The TPR group had only StEOL1. The BTB-ONLY group contained StBTB1 and StBTB2. The OTHER group contained StPHL1 and StPHL2. Within the subfamily, there was a significant difference in the BTB protein content between potato and A. thaliana. Among these different subfamilies, potato and A. thaliana have similar structural types. The NPH3 subfamily had the largest number of members among all the subfamilies, covering 11 potato BTB family genes and 30 A. thaliana BTB family genes. Among all TPR subfamilies, the number was the lowest, containing only one potato BTB family gene and three A. thaliana BTB family genes.
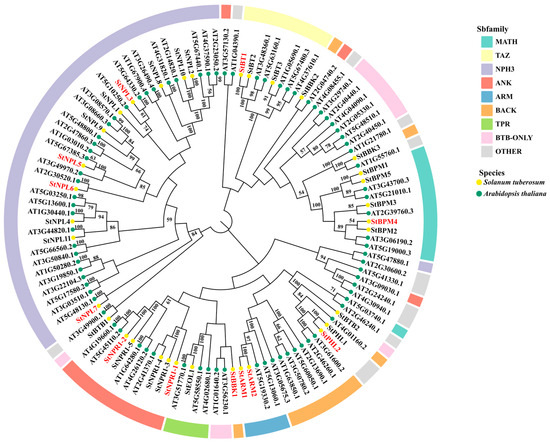
Figure 1.
Genetic evolution analysis of potato BTB family proteins. Note: Genes in red were used in subsequent experiments.
3.3. Analysis of the Conserved Motif, Gene Architecture, and Domains in Potato BTB Family Proteins
The conserved motif composition among members was not the same, but the motif composition, location, and number among subtribes exhibited collinearity. Among them, the conserved motif 1 is shared by all members; motif 9 is present in most StBTB protein sequences. At the same time, we analyzed the structure of the BTB family genes based on the annotation files. Most StBTB genes have 2–6 exons (StARM1 and StARM2 have 19 exons). In addition to StBTB2, StBBK2, StBT3, StNPL11, and StBPM3, most StBTB genes (29 out of 34 genes) have untranslated regions (Figure 2).
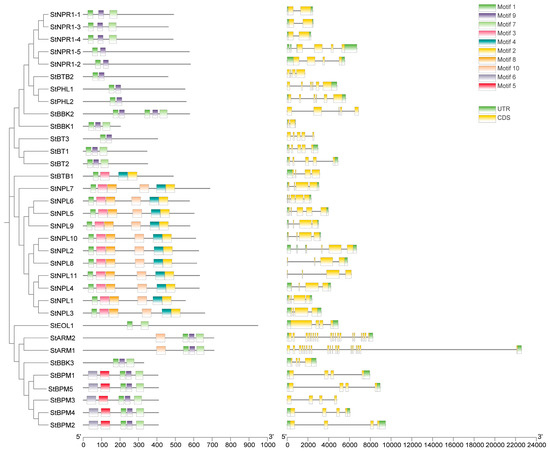
Figure 2.
Conserved motifs and structural analysis of potato BTB family proteins.
The BTB protein domains in the subfamily were similar in arrangement and contained similar functional domains, and there were significant differences in different domains between each subfamily (Figure 3).
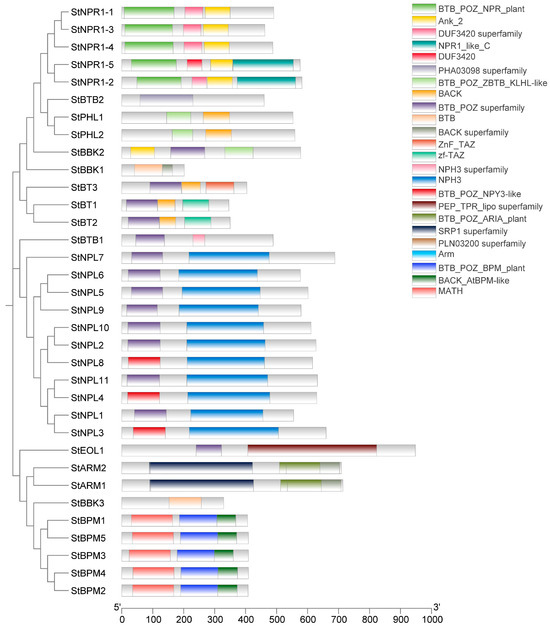
Figure 3.
Domain analysis of potato BTB family proteins. Domain accession numbers: BTB_POZ_NPR_plant(cd18310); Ank_2(PF12796); DUF3420 superfamily(cl13357); NPR1_like_C(PF11900); DUF3420(PF11900); PHA03098 superfamily(PF11900); BTB_POZ_ZBTB_KLHL-like(cd18186); BACK(cl28903); BTB_POZ superfamily(cl38908); BTB(PF00651); BACK superfamily(cl28903); ZnF_TAZ(cl02660); zf-TAZ(PF02135); NPH3 superfamily(cl03827); NPH3(PF03000); BTB_POZ_NPY3-like(cd18312); PEP_TPR_lipo superfamily(cl37187); BTB_POZ_ARIA_plant(cd18352); SRP1 superfamily(cl34886); PLN03200 superfamily(cl33659); Arm(PF00514); BTB_POZ_BPM_plant(cd18280); BACK_AtBPM-like(cd14736); MATH(cd00121).
3.4. Chromosome Localization and Collinearity Analysis of Potato BTB Gene
The BTB gene family members are unevenly distributed on the 11 chromosomes of ch01–ch11. Six genes, StBPM1, StBPM2, StPHL1, StNPL1, StNPL3, and StNPL2, were collected from the potato ch01 chromosome. There were five StBTB genes on ch07 (StNPL6, StNPR1-5, StNPL7, StBBK2, and StBBK3) and ch10 (StPHL2, StNPL10, StEOL1, StNPR1-4, and StNPR1-1) and four StBTB genes on ch02 (StNPL4, StNPL5, StNPR1-2). There were three genes in ch06 (StBBK1, StBT2, and StARM1), ch08 (StNPL8, StBT3, and StBTB2), and ch09 (StNPL9, StARM2, and StBPM4), and two StBTB genes, StNPL11 and StBPM5, were found on ch11. In addition, there was only one gene on each of the other three chromosomes (Figure 4).
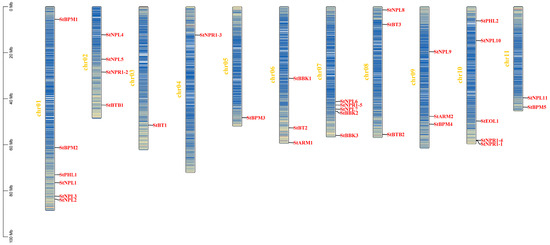
Figure 4.
Chromosomal localization of potato BTB family proteins.
Collinearity analysis within the potato BTB family is helpful for understanding its evolution and predicting repetitive events. As shown in Figure 5, a total of 11 pairs of fragment repeats were identified, including StBBK3/StBPM3, StARM1/StARM2, StBTB2/StNPL1, StBTB2/StPHL2, StPHL2/StNPL1, StBTB2/StNPL1, StNPL10/StNPL2, StNPR1-4/StNPR1-1, StBPM5/StBPM1, StBTB1/StNPL2, and StBTB1/StNPR1-2, and no tandem repeats.
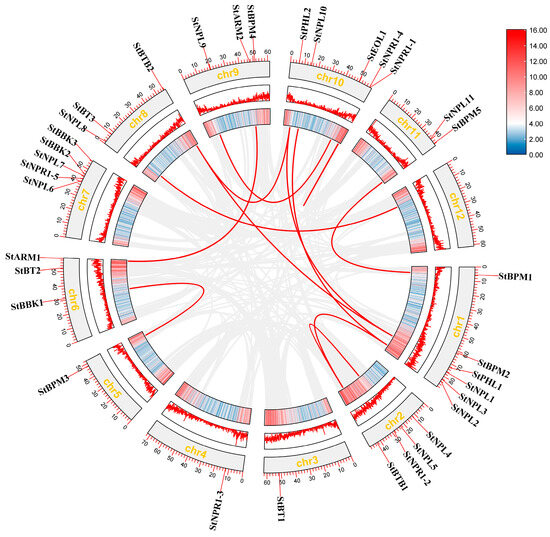
Figure 5.
Collinearity analysis of the BTB family in potato species.
3.5. Collinearity Analysis of BTB Family Genes between Potato and A. thaliana
The genes of the gene family are relatively conserved among species, and genomic collinearity analysis between species can confirm the degree of homology of the gene family between species. Therefore, we analyzed the collinearity between the members of the BTB family of potato and A. thaliana and found that the BTB family between the two species exhibited 34 pairs of collinearity (Figure 6).
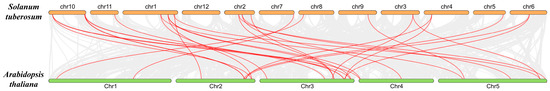
Figure 6.
Collinearity analysis of the BTB family genes in A. thaliana and potato.
3.6. Expression Profile Analysis of Potato BTB Family Genes
To analyze the specificity and function of potato BTB gene family expression, a clustering heatmap was drawn based on transcriptome data (Figure 7). The results showed that potato StBTB genes exhibited tissue-specific expression, mainly in roots. Some genes were mainly found in buds, calluses, stamens, sepals, petioles, carpels, and petals, suggesting that they play important roles in root growth and development and regulation. In addition, the expression of the StBTB gene was significantly upregulated under abiotic stress, especially under GA3 and salt stress, and the expression of some genes significantly increased under mannitol, ABA, and drought treatment. There is a certain linear relationship between the expression changes in some genes under these abiotic stresses. There may be interactions between different StBTBs, which play different physiological roles in different environmental response processes in potato.
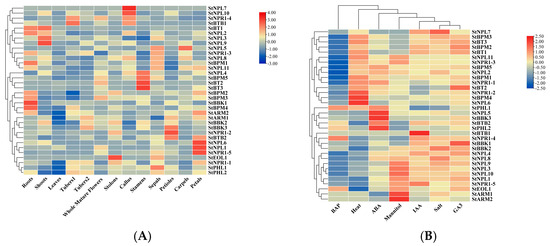
Figure 7.
Expression profile of BTB genes in potato: (A) expression profile in different tissues; (B) expression profile under different abiotic stresses.
3.7. Validation of Potato BTB Family Gene Expression under Abiotic Stress
To verify the response of the 12 genes of the BTB family under abiotic stress, the relative expression of genes under the six stress treatments was analyzed by qRT–PCR. Figure 8 clearly shows that under cold treatment, the expression of the StPHL2 gene did not significantly change, that of the StBT1, StNPL3, StNPR1-1, and StARM1 genes significantly decreased, and that of the other members significantly increased. Under ABA treatment, the StBPM4, StNPL7, StNPR1-1, StNPR1-2, and StARM2 genes were significantly upregulated and the other genes were significantly downregulated. Under salt stress, the expression of the StBPM4 and StPHL2 genes did not significantly change, the expression of the StNPL6, StNPR1-2, StARM2, and StBBK3 genes significantly increased, and that of the other genes significantly decreased. Under H2O2 treatment, the expression of the StBPM4, StNPL5, StARM1, and StBBK3 genes did not significantly change, the expression of the StNPL3, StNPR1-2, and StARM2 genes significantly decreased, and that of the remaining genes significantly increased. Under drought stress, the StBT1, StNPL3, and StNPL6 genes were significantly downregulated and the other genes were significantly upregulated. Under low-nitrogen stress, the expression of the StNPL6 and StNPR1-1 genes did not significantly change, that of the StNPL5 and StBBK3 genes significantly increased, and that of the other genes significantly decreased.
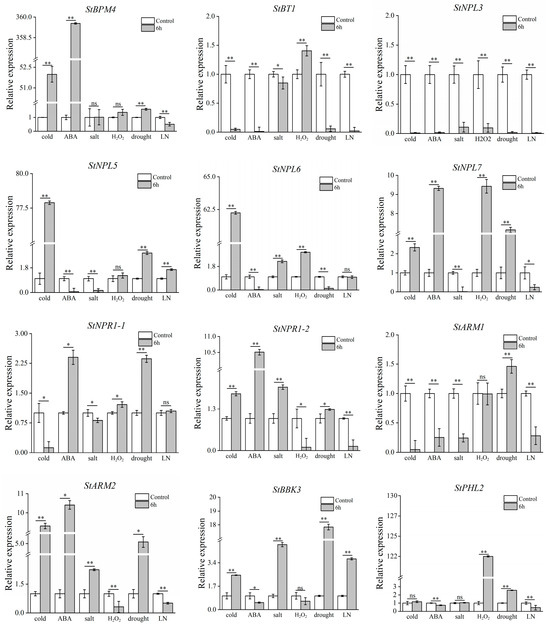
Figure 8.
Expression analysis of 12 StBTB genes selected under abiotic stress. * signifies the differences in gene expression as determined by the t-test (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ns: not significant). LN is low-nitrogen stress.
4. Discussion
The BTB/POZ protein-encoding gene family is characterized by its BTB domain, which mediates protein–protein interactions [27]. Although the BTB domain proteins are widely distributed in animals, plants, and microorganisms, they are highly conserved throughout evolution [28]. At present, research on the BTB/POZ protein has focused mainly on humans and animals (fruit flies [29] and mice [30]), while research on plants is relatively lacking, and there are few reports on plant abiotic stress, which has great potential.
The 34 potato BTB proteins identified in this study all contain this functional domain in the amino acid sequence. Therefore, it can be inferred that these plants belong to the typical plant BTB family. At the same time, most of the identified BTB protein genes also covered other types of functional domains. Based on the presence of other domains, we classified the identified potato BTB protein genes into nine subfamilies, namely, the Ankyrin, Armadillo, MATH, NPH3, BACK, TAZ, TPR, BTB-only, and other subfamilies. Different subfamilies of BTB protein genes may have different functions [31].
However, as a Solanaceae plant, there are few reports on the BTB family in potato. During the process of evolution, gene replication is accompanied by a certain loss, which leads to a certain difference in the number of gene families between species. According to previous studies, A. thaliana and rice contain 80 and 149 BTB proteins, respectively [32,33], only a few of which have been studied in detail. A total of 34 BTB family genes were identified from the potato genome database, which was significantly less than the number of BTB family genes in A. thaliana and rice, indicating that there was a large difference in the number of BTB proteins among different species.
According to the phylogenetic analysis of the BTB protein in potato and A. thaliana, 34 StBTB genes were divided into nine subfamilies (Figure 1). It was also found that most BTB protein genes had high homology with those of these two species. It is speculated that there may be similar functions between the two species, so the function of BTB genes in potato can be speculated according to the clustering relationship between the two species. According to the conservation of the BTB family and the distribution of genes with similar functions or the same functions in the same subfamily, the BTB protein not only has high conservation in different species but also has evolutionary conservation. The structure is associated with gene expression, and the domain is associated with the exercise of protein function. Next, we analyzed 10 conserved motifs and found that these StBTB motifs had different distributions within subfamilies but similar distributions within subfamilies. Most BTB proteins have motif 1, and different motifs determine the structure and function of genes [34]. Moreover, the structure of the BTB protein was analyzed. The structure of introns and exons affects the structure and function of proteins, thus affecting the growth and development of plants, and plays an important role in gene expression and regulation [35,36]. Most of the BTB protein genes have untranslated regions, and there are 2–6 exons. There was a certain correlation between the structure of the BTB gene and the arrangement of conserved motifs, which verified the classification within the BTB subfamily (Figure 2). We analyzed the domains contained in each gene, which may imply that different domains and combinations of domains have different functions (Figure 3).
As shown in Figure 3, except for ch12, 34 StBTB genes were unevenly distributed on 11 chromosomes, suggesting that the family members may be widely involved in physiological activities to maintain the life activities of potato. Gene replication is important for providing the original genetic material for biological evolution [37]. Gene families are usually extended through fragment replication and tandem replication, which is also the main mode of plant evolution [38]. In Figure 4, collinear relationships between gene pairs are shown. The genes of the same subfamily are basically similar in structure, and it is speculated that they may have similar functions in various processes of plant growth and development. At the same time, we analyzed and identified 11 pairs of fragment repeats and no tandem repeats. The results showed that 11 pairs of genes were formed by genome-wide replication, which may be the reason why potatoes have fewer BTB genes than other species. Figure 5 shows 34 collinearity pairs between A. thaliana and potato. It is suggested that the BTB family genes were strongly correlated between the two species during evolution, and it is speculated that there may be some similarity in gene structure and function.
The expression of genes in tissues is closely related to their functions [39,40]. According to the cluster heatmap in Figure 6, the expression of 10 StBTB genes was the highest in the roots and the remaining genes were mainly distributed in the buds, callus, stamens, sepals, petioles, carpels, and petals. It is speculated that the tissue expression specificity of the StBTB gene in potato may play different roles in regulating its growth and development.
Losses caused by abiotic stress conditions can lead to significant reductions in crop yields [41]. Previous studies have shown that BTBs are essential for plant growth and development and are involved in abiotic stress responses [42,43,44,45]. With climate and environmental changes, cultivating potato varieties resistant to abiotic stress is beneficial for improving yields and quality. Abscisic acid (ABA) plays a mediating role in the signaling pathway involved in the plant response to stress by initiating adaptive responses that help reduce crop yield losses [46]. Plant growth and development require appropriate temperatures, and plant cell structure and osmotic balance are disrupted by low-temperature stress, resulting in cell metabolism disorders [47]. Salt is an important environmental factor affecting plant growth and yield; high salt levels can cause plant yield reduction or death, and salt stress can damage the cell membrane and destroy plant ion homeostasis [47]. One of the main factors of plant damage under drought stress is the overproduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in organelles, which leads to the degradation of lipid catalase proteins and nucleic acids in cell membranes [48]. H2O2 is a component of intracellular ROS and is also an important signaling molecule involved in various physiological metabolic processes in plants. Excessive H2O2 can destroy biological macromolecules and poison cells [49]. Currently, in response to low-nitrogen conditions, nitrogen affects development, physiology, and metabolism, so it is important to study low-nitrogen stress [50]. Consequently, examining how plants withstand abiotic stress is essential.
Each impact is accompanied by the expression of the genes under it. Under low-temperature stress, the expression of the StBPM4, StNPL5, StNPL6, StNPL7, StNPR1-2, StARM2, and StBBK3 genes significantly increased. The expression of the StBPM4, StNPL7, StNPR1-1, StNPR1-2, and StARM2 genes was significantly upregulated under ABA stress. The expression of the StNPL6, StNPR1-2, StARM2, and StBBK3 genes significantly increased under salt stress. The expression of the StBT1, StNPL6, StNPL7, StNPR1-1, and StPHL2 genes was significantly upregulated under H2O2 stress. The expression levels of the StBPM4, StNPL5, StNPL7, StNPR1-1, StNPR1-2, StARM1, StARM2, StBBK3, and StPHL2 genes were significantly upregulated under drought stress. The expression of the StNPL5 and StBBK3 genes significantly increased under low-nitrogen stress. Similarly, the expression levels of StNPL7, StNPR1-1, StNPR1-2, and StARM2 significantly increased under ABA, salt, and drought stress. In summary, we further confirmed that StBTB family genes play important roles in the potato abiotic stress response.
5. Conclusions
In this study, 34 BTB genes were identified in potato, and these genes were analyzed in depth, including phylogeny, gene structure, conserved motifs and domains, chromosome location, gene collinearity, and expression pattern analysis. Its tissue expression and expression under stress indicate that it plays an important role in growth, development, and stress resistance. The 12 selected genes had different expression levels under different stress treatments, indicating that these genes were involved in the regulation of abiotic stress, and the expression levels of StNPL7, StNPR1-1, StNPR1-2, and StARM2 were significantly increased under ABA, salt, and drought stress. These genes may be important candidate genes for potato stress resistance. In general, this study laid a foundation for the study of function and expression in potato biotic stress response and provided a basis for genetic engineering and genetic improvement of potato plants.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10060543/s1: Table S1: StBTB gene primer selection.
Author Contributions
L.L. (Liqin Li) and H.F. designed the experiments and wrote the first draft of the manuscript; Y.L. (Yifei Lu) and B.R. performed the experiments; Y.L. (Yongjian Liu) and L.L. (Liming Lu) analyzed the data; and S.Y. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by State Key Laboratory of Crop Gene Exploration and Utilization in Southwest China (SKLZY202217) and the Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (Program No. 2022NSFSC0178).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bardwell, V.J.; Treisman, R. The POZ domain: A conserved protein-protein interaction motif. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1664–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wei, Y.; Reboul, J.; Vaglio, P.; Shin, T.-H.; Vidal, M.; Elledge, S.J.; Harper, J.W. BTB proteins are substrate-specific adaptors in an SCF-like modular ubiquitin ligase containing CUL-3. Nature 2003, 425, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaharbakhshi, E.; Jemc, J.C. Broad-complex, tramtrack, and bric-à-brac (BTB) proteins: Critical regulators of development. Genesis 2016, 54, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Torrado, R.; Yamada, D.; Defossez, P.A. Born to bind: The BTB protein-protein interaction domain. BioEssays 2006, 28, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Ohama, N.; Kidokoro, S.; Mizoi, J.; Takahashi, F.; Todaka, D.; Mogami, J.; Sato, H.; Qin, F.; Kim, J.S.; et al. BPM-CUL3 E3 ligase modulates thermotolerance by facilitating negative regulatory domain-mediated degradation of DREB2A in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8528–E8536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonchuk, A.; Balagurov, K.; Georgiev, P. BTB domains: A structural view of evolution, multimerization, and protein-protein interactions. Bioessays 2023, 45, e2200179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, T.; Stone, J.R.; Williams, A.J. All in the Family: The BTB/POZ, KRAB, and SCAN Domains. Mol. Cel. Biol. 2023, 21, 3609–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Tsai, S.-F.; Choo, K.-B. TDPOZ, a family of bipartite animal and plant proteins that contain the TRAF (TD) and POZ/BTB domains. Gene 2004, 324, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellmeier, W.; Taniuchi, I. The Role of BTB-Zinc Finger Transcription Factors During T Cell Development and in the Regulation of T Cell-mediated Immunity. Curr. Top. Microbiol. 2014, 381, 21–49. [Google Scholar]
- Boyle, P.; Le Su, E.; Rochon, A.; Shearer, H.L.; Murmu, J.; Chu, J.Y.; Fobert, P.R.; Després, C. The BTB/POZ Domain of the Disease Resistance Protein NPR1 Interacts with the Repression Domain of TGA2 to Negate Its Function. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3700–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandadi, K.K.; Misra, A.; Ren, S.X.; McKnight, T.D. BT2, a BTB Protein, Mediates Multiple Responses to Nutrients, Stresses, and Hormones in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, H.; Bernhardt, A.; Dieterle, M.; Hano, P.; Mutlu, A.l.; Estelle, M.; Genschik, P.; Hellmann, H. Arabidopsis AtCUL3a and AtCUL3b Form Complexes with Members of the BTB/POZ-MATH Protein Family. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araus, V.; Vidal, E.A.; Puelma, T.; Alamos, S.; Mieulet, D.; Guiderdoni, E.; Gutiérrez, R.A. Members of BTB gene family regulate negatively nitrate uptake and nitrogen use efficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Kong, D.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Li, F. Genome-Wide Identification of the NPR1-like Gene Family in Solanum tuberosum and Functional Characterization of StNPR1 in Resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum. Genes 2023, 14, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodger, F.J.; Jacobsen, J.V.; Gubler, F. GMPOZ, a BTB/POZ Domain Nuclear Protein, is a Regulator of Hormone Responsive Gene Expression in Barley Aleurone. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spooner, D.M. The potato: Evolution, biodiversity and genetic resources. J.G. Hawkes. Am. Potato J. 1990, 67, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierer, W.; Rüscher, D.; Sonnewald, U.; Sonnewald, S. Tuber and Tuberous Root Development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 551–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Poovaiah, B.W. A Novel Family of Ca2+/Calmodulin-Binding Proteins Involved in Transcriptional Regulation: Interaction with fsh/Ring3 Class Transcription Activators. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 54, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalmani, A.; Huang, Y.B.; Chen, Y.B.; Muhammad, I.; Li, B.B.; Ullah, U.; Jing, X.Q.; Bhanbhro, N.; Liu, W.T.; Li, W.Q.; et al. The highly interactive BTB domain targeting other functional domains to diversify the function of BTB proteins in rice growth and development. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 1311–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Su, X.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Yang, W.; Pan, Y.; Su, C.G.; Zhang, X.G. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the BTB domain-containing protein gene family in tomato. Genes Genom. 2018, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.M.; Chen, Y.R.; Cai, G.J.; Cai, R.L.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization by One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Chen, G.; Gu, Y.Q. OrthoVenn: A web server for genome wide comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W78–W84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Potato Genome Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leprince, O.A.P.D.C.D.G.L.D. The BTB/POZ domain: A new protein-protein interaction motif common to DNA- and actin-binding proteins. Cell Growth Differ. 1995, 6, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, K.F.; Engel, C.K.; Privé, G.G. Crystal structure of the BTB domain from PLZF. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12123–12128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zollman, S.; Godt, D.; Privé, G.G.; Couderc, J.L.; Laski, F.A. The BTB domain, found primarily in zinc finger proteins, defines an evolutionarily conserved family that includes several developmentally regulated genes in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10717–10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.Y.; Evans, S.E.; Fairall, L.; Schwabe, J.W.R.; Wagner, S.D.; Muskett, F.W. Backbone resonance assignment of the BCL6-BTB/POZ domain. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2018, 12, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, H.S.; Quint, A.; Brand, D.; Vivian-Smith, A.; Offringa, R. BTB and TAZ domain scaffold proteins perform a crucial function in Arabidopsis development. Plant J. 2009, 58, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stogios, P.J.; Downs, G.S.; Jauhal, J.J.S.; Nandra, S.K.; Privé, G.G. Sequence and structural analysis of BTB domain proteins. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingerich, D.J.; Hanada, K.; Shiu, S.H.; Vierstra, R.D. Large-scale, lineage-specific expansion of a bric-a-brac/tramtrack/broad complex ubiquitin-ligase gene family in rice. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 2329–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, H.X.; Li, J.B.; Huang, J.; Lu, M.Z.; Hu, J.J. The heat shock factor gene family in: A genome-wide survey and expression profiling during development and abiotic stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yang, S.-L.; Xie, L.-F.; Puah, C.S.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Yang, W.-C.; Sundaresan, V.; Ye, D. VANGUARD1 Encodes a Pectin Methylesterase That Enhances Pollen Tube Growth in the Arabidopsis Style and Transmitting Tract. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasca, D.; Yun, H.Y.; Giotopoulos, G.; Szybinski, J.; Evan, T.; Wilson, N.K.; Gerstung, M.; Gallipoli, P.; Green, A.R.; Hills, R.; et al. Cohesin-dependent regulation of gene expression during differentiation is lost in cohesin-mutated myeloid malignancies. Blood 2019, 134, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankoff, D. Gene and genome duplication. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, J.E.; Chapman, B.A.; Rong, J.; Paterson, A.H. Unravelling angiosperm genome evolution by phylogenetic analysis of chromosomal duplication events. Nature 2003, 422, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, D.; Basset, M.; Lepetit, M.; Conejero, G.; Gaymard, F.; Astruc, S.; Grignon, C. Tissue-specific expression of Arabidopsis AKT1 gene is consistent with a role in K+ nutrition. Plant J. 2002, 9, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govers, F.; Harmsen, H.; Heidstra, R.; Michielsen, P.; Prins, M.; van Kammen, A.; Bisseling, T. Characterization of the pea ENOD12B gene and expression analyses of the two ENOD12 genes in nodule, stem and flower tissue. Mol. Gener. Genet. MGG 1991, 228, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Nahar, K.; Alam, M.M.; Roychowdhury, R.; Fujita, M. Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 9643–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juranić, M.; Srilunchang, K.-o.; Krohn, N.G.; Leljak-Levanić, D.; Sprunck, S.; Dresselhaus, T. Germline-Specific MATH-BTB Substrate Adaptor MAB1 Regulates Spindle Length and Nuclei Identity in Maize. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 4974–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Park, S.J.; Van Eck, J.; Lippman, Z.B. Control of inflorescence architecture in tomato by BTB/POZ transcriptional regulators. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2048–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ren, Y.-R.; Wang, Q.-J.; Wang, X.-F.; You, C.-X.; Hao, Y.-J. Ubiquitination-Related MdBT Scaffold Proteins Target a bHLH Transcription Factor for Iron Homeostasis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 172, 1973–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Peng, L.; Xiong, J.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Y. AtSIBP1, a Novel BTB Domain-Containing Protein, Positively Regulates Salt Signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plants 2019, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasulu, N.; Harshavardhan, V.T.; Govind, G.; Seiler, C.; Kohli, A. Contrapuntal role of ABA: Does it mediate stress tolerance or plant growth retardation under long-term drought stress? Gene 2012, 506, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibberd, J.M.; Weber, A.P.M. Plant metabolism and physiology. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, H.; Liu, F.; Cai, J.; Dai, T.; Cao, W.; Jiang, D. Induction of chilling tolerance in wheat during germination by pre-soaking seed with nitric oxide and gibberellin. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 71, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Feng, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, K.; Xu, H. Overexpression of tomato SlTpx improves salt stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants by scavenging H2O2. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 2022, 151, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, B.; Rao, I.S.; Surekha, K.; Subrahmanyam, D.; Voleti, S.R.; Neeraja, C.N. Enhanced expression of OsSPL14 gene and its association with yield components in rice (Oryza sativa) under low nitrogen conditions. Gene 2016, 576, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).