Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) YTH Domain-Containing RNA-Binding Protein (YTP) Family Members Participate in Low-Temperature Treatment and Waterlogging Stress Responses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Analysis of the SlYTP Gene Family
2.2. Plant Growth and Treatments
2.3. Gene Clone and qRT-PCR
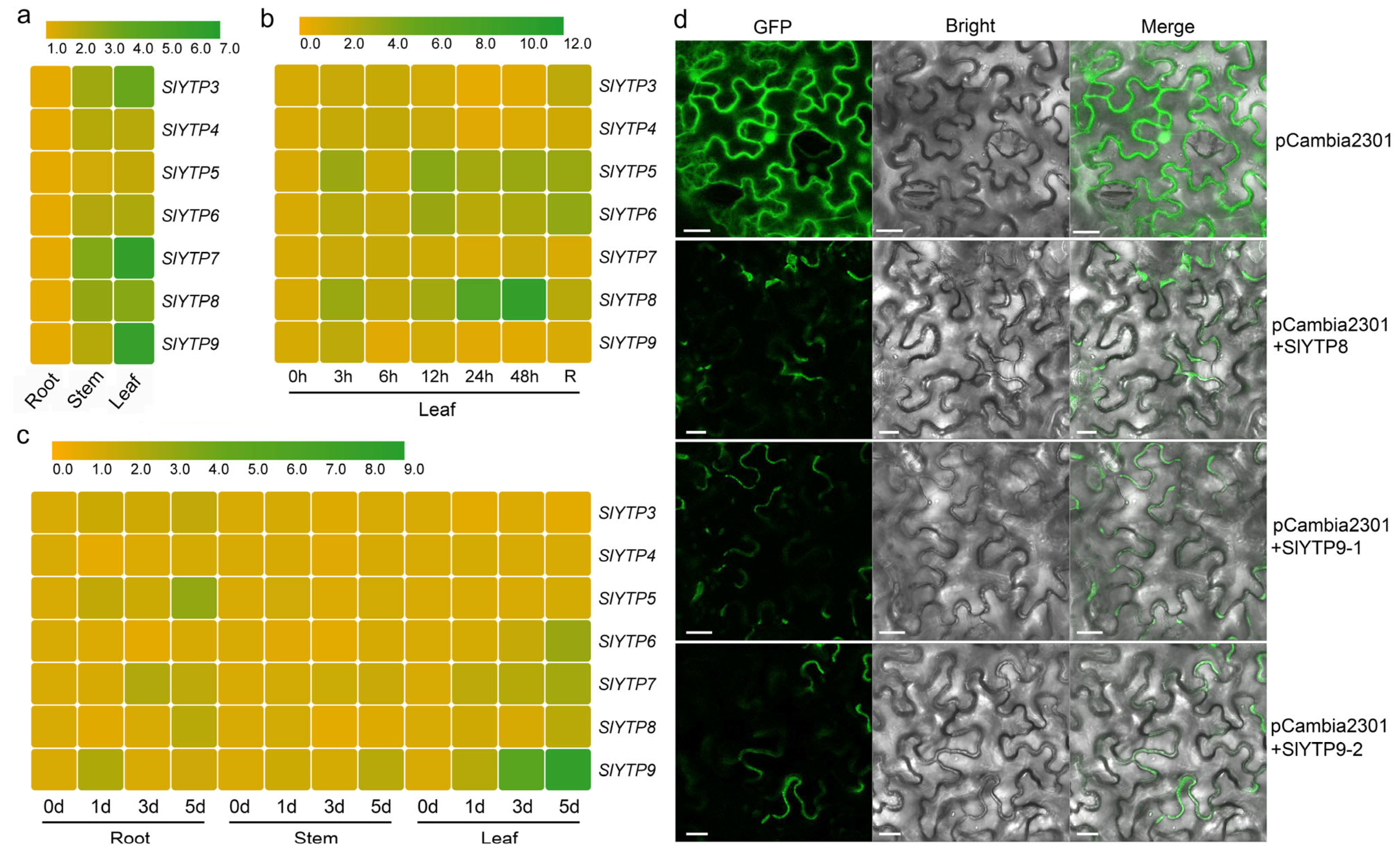
2.4. Subcellular Localization
2.5. Tomato Transformation
2.6. Measurement of Stress-Related Physiological Indexes
2.7. Prediction Transcription Factors and Interacting Proteins
3. Results
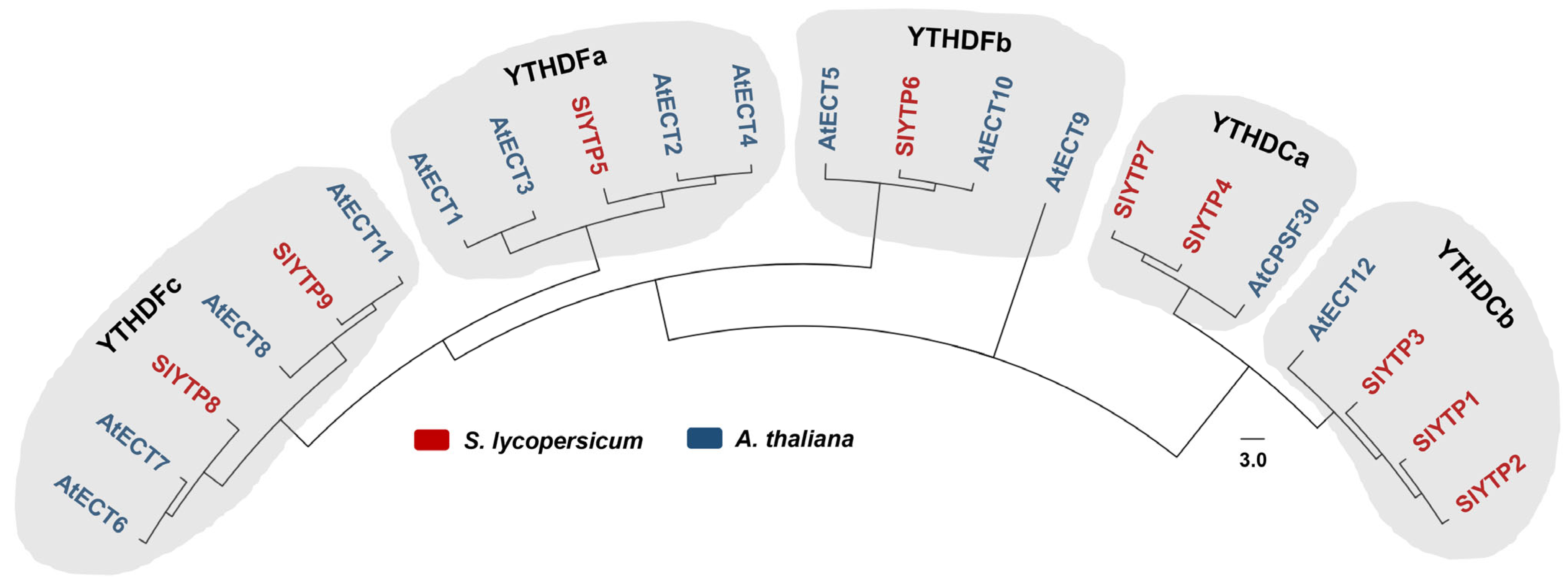
3.1. SlYTP Family Member Identification and Analysis
3.2. Expression Levels of SlYTPs in Different Tomato Tissues and under Various Stresses
3.3. Overexpression of SlYTP8 Changes the Chilling Resistance of Tomato
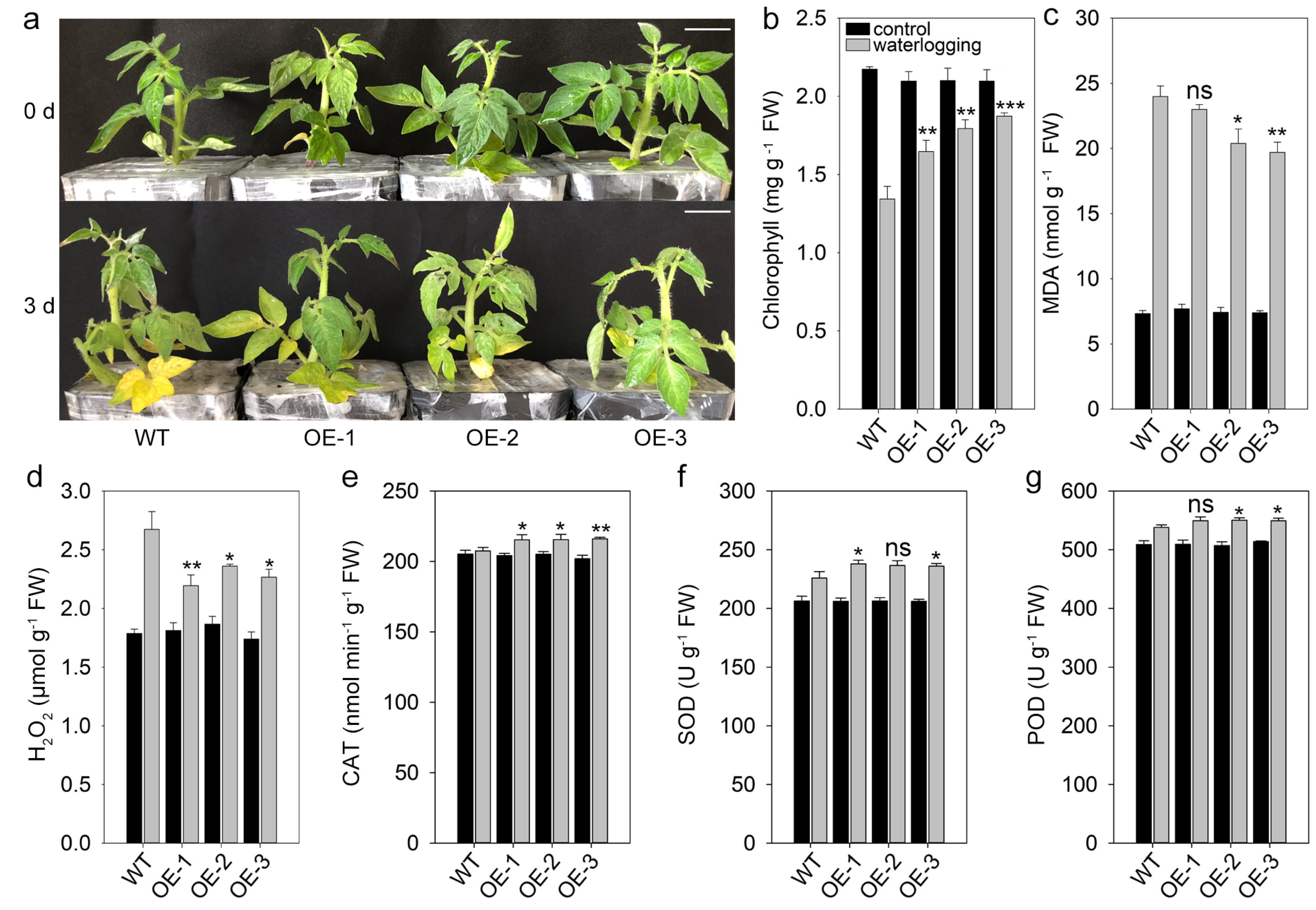
3.4. Overexpression of SlYTP9-2 Increases Waterlogging Resistance of Tomatoes
3.5. Prediction of Transcription Factors Binding with SlYTP8 or SlYTP9 Promoter and Interaction Proteins of SlYTP8 and SlYTP9
4. Discussion
4.1. SlYTP Family Member Identification and Analysis
4.2. Expression Patterns of SlYTP8 and Its Function in Tomato Low-Temperature Stress Resistance
4.3. Expression Patterns of SlYTP9-2 and Its Function in Tomato Waterlogging Stress Resistance
4.4. Prediction of Transcription Factors Binding with SlYTP8 or SlYTP9 Promoter and Interaction Proteins of SlYTP8 and SlYTP9
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Wiener, D.; Schwartz, S. The epitranscriptome beyond m6A. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, M.; Rajan, K.S.; Mullasseri, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Zhou, M.; Sharma, A.; Ramasamy, S.; Wei, Q. Exploring N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in tree species: Opportunities and challenges. Hortic. Res. 2023, 11, uhad284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Cai, Z.; Jia, G. Principles, functions, and biological implications of m6A in plants. RNA 2024, 30, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, M.; Harada, B.T.; Behm, M.; He, C. RNA modifications modulate gene expression during development. Science 2018, 361, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Tayier, S.; Cai, Z.; Jia, G. RNA methylation in mammalian development and cancer. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2021, 37, 811–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2014, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.; Han, D.; Ma, H.; Weng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.; He, C. N6-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Adhikari, S.; Dahal, U.; Chen, Y.S.; Hao, Y.J.; Sun, B.F.; Sun, H.Y.; Li, A.; Ping, X.L.; Lai, W.Y.; et al. Nuclear m6A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, H.; Hsu, P.J.; Liu, C.; He, C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtas, M.N.; Pandey, R.R.; Mendel, M.; Homolka, D.; Sachidanandam, R.; Pillai, R.S. Regulation of m6A Transcripts by the 3′→5′ RNA Helicase YTHDC2 Is Essential for a Successful Meiotic Program in the Mammalian Germline. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Sun, H.; Xu, C. YTH Domain: A Family of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Readers. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.D.; Jaffrey, S.R. Rethinking m6A Readers, Writers, and Erasers. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 33, 319–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arribas-Hernández, L.; Bressendorff, S.; Hansen, M.H.; Poulsen, C.; Erdmann, S.; Brodersen, P. An m6A-YTH Module Controls Developmental Timing and Morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 952–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Hong, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Song, F. Genome-wide identification, biochemical characterization, and expression analyses of the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1169–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Luo, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wu, T.; Chen, G. Genome-Wide Identification, Classification and Expression Analysis of m6A Gene Family in Solanum lycopersicum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bie, X.M.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.S.; Gao, X.Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in common wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.H.; Song, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Duan, H.C.; Jia, G. The m6A Reader ECT2 Controls Trichome Morphology by Affecting mRNA Stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas-Hernández, L.; Rennie, S.; Schon, M.; Porcelli, C.; Enugutti, B.; Andersson, R.; Nodine, M.D.; Brodersen, P. The YTHDF proteins ECT2 and ECT3 bind largely overlapping target sets and influence target mRNA abundance, not alternative polyadenylation. eLife 2021, 10, e72377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wei, L.; Chen, Z.; Cai, Z.; Lu, Q.; Wang, C.; Tian, E.; Jia, G. m6A readers ECT2/ECT3/ECT4 enhance mRNA stability through direct recruitment of the poly(A) binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Liu, K.; Kim, E.Y.; Medina-Puche, L.; Dong, H.; Di, M.; Singh, R.M.; Li, M.; Qi, S.; Meng, Z.; et al. The m6A reader ECT1 drives mRNA sequestration to dampen salicylic acid-dependent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 746–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Liu, C.; Meng, F.; Hu, L.; Fu, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, N.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, F. The m6A reader MhYTP2 regulates MdMLO19 mRNA stability and antioxidant genes translation efficiency conferring powdery mildew resistance in apple. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Ao, Q.; Qiu, T.; Tan, C.; Tu, Y.; Kuang, T.; Yang, Y. Tomato SlYTH1 encoding a putative RNA m6A reader affects plant growth and fruit shape. Plant Sci. 2022, 323, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, Q.; Qiu, T.; Liao, F.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Y. Knockout of SlYTH2, encoding a YTH domain-containing protein, caused plant dwarfing, delayed fruit internal ripening, and increased seed abortion rate in tomato. Plant Sci. 2023, 335, 111807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D200–D203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Hennig, L.; Gruissem, W. Gene-expression analysis and network discovery using Genevestigator. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waese, J.; Provart, N.J. The Bio-Analytic Resource for Plant Biology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1533, 119–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Guo, T.; Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Shao, Y.; Liang, B.; Jia, X.; Gong, X.; Ma, F. Functional analysis of apple MhYTP1 and MhYTP2 genes in leaf senescence and fruit ripening. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 221, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, N.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, J.; Ma, F.; Liu, C. Overexpression of MdARD4 Accelerates Fruit Ripening and Increases Cold Hardiness in Tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Guan, Q.; van Nocker, S.; Liu, C.; Ma, F. Overexpression of the RNA binding protein MhYTP1 in transgenic apple enhances drought tolerance and WUE by improving ABA level under drought condition. Plant Sci. 2019, 280, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yin, L.; Liang, D.; Li, C.; Ma, F.; Yue, Z. Delayed senescence of apple leaves by exogenous melatonin treatment: Toward regulating the ascorbate-glutathione cycle. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Yang, D.C.; Meng, Y.Q.; Jin, J.; Gao, G. PlantRegMap: Charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1104–D1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Ao, Q.; Tan, C.; Yang, Y. Genome-wide identification and characterization of YTH domain-containing genes, encoding the m6A readers, and their expression in tomato. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Yue, Z.; Liang, D.; Ma, F. Genome-wide identification of members in the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in apple and expression analysis of their responsiveness to senescence and abiotic stresses. Gene 2014, 538, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, Y. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of m6A readers-YTH domain-containing genes in alfalfa. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutenaire, J.; Deragon, J.-M.; Jean, V.; Benhamed, M.; Raynaud, C.; Favory, J.-J.; Merret, R.; Bousquet-Antonelli, C. The YTH domain protein ECT2 is an m6A reader required for normal trichome branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 986–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.Z.; Zhao, X.F.; Liu, C.Z.; Ma, F.F.; Wang, F.; Gao, X.-Q.; Zhang, X.S. Interaction between RNA helicase ROOT INITIATION DEFECTIVE 1 and GAMETOPHYTIC FACTOR 1 is involved in female gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5757–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, A.; Tanikawa, K.; Tsunetomi, M.; Takai, K.; Ikeda, H.; Konno, J.; Torigoe, T.; Maeda, H.; Kutomi, G.; Okita, K.; et al. RNA helicase YTHDC2 promotes cancer metastasis via the enhancement of the efficiency by which HIF-1α mRNA is translated. Cancer Lett. 2016, 376, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, Q.; Shi, L.; Tayier, S.; Jia, G. Arabidopsis N6-methyladenosine reader CPSF30-L recognizes FUE signals to control polyadenylation site choice in liquid-like nuclear bodies. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Z.; Duan, H.; Mi, L.; Hu, W.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, B. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the YTH domain-containing RNA binding protein family in Citrus sinensis. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2019, 144, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.P.; Pickering, B.F.; Jaffrey, S.R. Reading m6A in the Transcriptome: m6A-Binding Proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arribas-Hernández, L.; Simonini, S.; Hansen, M.H.; Paredes, E.B.; Bressendorff, S.; Dong, Y.; Østergaard, L.; Brodersen, P. Recurrent requirement for the m6A-ECT2/ECT3/ECT4 axis in the control of cell proliferation during plant organogenesis. Development 2020, 147, dev189134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente, A.M.; Manavski, N.; Rohn, P.T.; Schmid, L.M.; Garcia-Molina, A.; Leister, D.; Seydel, C.; Bellin, L.; Möhlmann, T.; Ammann, G.; et al. The plant cytosolic m6A RNA methylome stabilizes photosynthesis in the cold. Plant Commun. 2023, 4, 100634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Y.; Xie, H.; Wang, S.; Hua, J.; Wu, Y. m6A mRNA modification promotes chilling tolerance and modulates gene translation efficiency in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 1466–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Guo, T.; Sun, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, P.; Shao, Y.; Liang, B.; Gong, X.; Ma, F. Functions of two Malus hupehensis (Pamp.) Rehd. YTPs (MhYTP1 and MhYTP2) in biotic- and abiotic-stress responses. Plant Sci. 2017, 261, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L. Functional interdependence of N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase complex subunits in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarowar, S.; Oh, H.W.; Cho, H.S.; Baek, K.H.; Seong, E.S.; Joung, Y.H.; Choi, G.J.; Lee, S.; Choi, D. Capsicum annuum CCR4-associated factor CaCAF1 is necessary for plant development and defence response. Plant J. 2007, 51, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Li, C.; Liu, F.; Jiang, H.; Li, S.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Li, C. The Arabidopsis homologs of CCR4-associated factor 1 show mRNA deadenylation activity and play a role in plant defence responses. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.R.; Lin, R.N.; Huang, H.W.; Li, L.; Cai, T.; Zhu, J.K.; Chen, S.; He, X.J. The CCR4-NOT complex component NOT1 regulates RNA-directed DNA methylation and transcriptional silencing by facilitating Pol IV-dependent siRNA production. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, P.A.; Boavida, L.C.; Santos, M.R.; Becker, J.D. AtNOT1 is required for gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1289–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motomura, K.; Arae, T.; Araki-Uramoto, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ichihashi, Y.; Shibata, A.; Shirasu, K.; Takeda, A.; et al. AtNOT1 Is a Novel Regulator of Gene Expression during Pollen Development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, N. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) YTH Domain-Containing RNA-Binding Protein (YTP) Family Members Participate in Low-Temperature Treatment and Waterlogging Stress Responses. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050522
Zhang Y, Guo T, Li J, Jiang L, Wang N. Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) YTH Domain-Containing RNA-Binding Protein (YTP) Family Members Participate in Low-Temperature Treatment and Waterlogging Stress Responses. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(5):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050522
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yidan, Tianli Guo, Jingyuan Li, Libo Jiang, and Na Wang. 2024. "Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) YTH Domain-Containing RNA-Binding Protein (YTP) Family Members Participate in Low-Temperature Treatment and Waterlogging Stress Responses" Horticulturae 10, no. 5: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050522
APA StyleZhang, Y., Guo, T., Li, J., Jiang, L., & Wang, N. (2024). Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) YTH Domain-Containing RNA-Binding Protein (YTP) Family Members Participate in Low-Temperature Treatment and Waterlogging Stress Responses. Horticulturae, 10(5), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050522





