Abstract
Aroma is an important factor in the measurement of the quality and market value of oolong tea. However, it is hard to develop an oolong tea with good aroma quality using unsuitable tea varieties. To explore the key factors of tea varieties in the formation of oolong tea aromas, the fresh leaves of the Chungui variety (CG, suitable for oolong tea, Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) and the Fuyun No. 6 variety (F6, unsuitable for oolong tea, Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) were harvested and treated by withering and mechanical stress in order. Then, aroma, transcriptome, and jasmonate (JA) contents, and weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), of samples were investigated. The contents of characteristic oolong tea aromas, including indole, (E)-β-ocimene, (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, and jasmine lactone, were all accumulated in much higher quantities in the CG variety after withering and mechanical stress. Accordingly, the coding genes of aroma formation synthases TSB2, OCS, NES, AFS, and LOX1, and related genes in MVA, MEP, and ALA pathways, were all much more highly activated. These differential reactions are mainly caused by the higher accumulation of jasmonates, especially methyl jasmonate, a type of important plant signal chemical, in CG after mechanical stress. WGCNA analysis indicated 34 different transcription factors from different families are predicted to be involved in this jasmonate-responsive reaction.
1. Introduction
Tea (Camellia sinensis) is the second most popular beverage in the world after water. Tea is rich in various secondary metabolites, such as aroma substances, catechins, theanine, and caffeine, which determine its unique flavor quality. Although the total aroma components only account for 0.03% of dry tea, they are one of the most important factors when measuring the quality and market value of made tea [1]. Oolong tea is a unique tea type originating in Fujian province, China, that possesses a natural flowery or fruity flavor and is deeply loved by consumers. Thus, the most important part in oolong tea sensory evaluation is aroma quality, which accounts for 30% of the total score under the current standard of China [2]. In addition, although there is a lack of direct evidence, the aroma of oolong tea may also be beneficial to human health because of its sedative effect on autonomic nerve activity, the ability to improve mood before mental stress load, etc. [3,4].
The mechanism of oolong tea aroma formation after harvest is complex and regulated by various factors such as plant hormones, transcript factors, and RNA or DNA methylation levels [5,6,7]. In recent years, studies have recognized that the most characteristic aromas of oolong tea are (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, (E)-β-ocimene, indole, and jasmine lactone [8,9]. These aromas are formed in large quantities under mechanical stress during the Zuoqing process of making oolong tea [5]. Therefore, large studies have focused on the mechanism of key aroma formation during oolong tea withering [10] or the Zuoqing [11,12] process.
Although appropriate processing procedures are important for the formation of the characteristic aroma of oolong tea, the suitability of the tea variety is also a vital and fundamental factor for the formation of the characteristic aroma of oolong tea. Long-term production experience of oolong tea recognized that, even under most delicate workmanship, it is hard to develop an oolong tea with good aroma quality using unsuitable tea varieties. Additionally, in our previous study, the relative contents of the key aromas of (E)-nerolidol and indole in oolong tea made using the Chungui (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze, CG) variety, an oolong tea variety suitable for producing a good aroma, accounted for 50.4% of the total aromas, but only 3.8% of the total aromas in an oolong tea made using the Fuyun No. 6 (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze, F6) variety, a tea variety unsuitable for oolong tea [13]. However, the differential aroma formation patterns of different tea varieties under the same oolong tea procedures are still unknown. Thus, to address this question, the aroma content, global gene expression patterns, and plant hormone contents of fresh leaves, withered leaves, and leaves treated by mechanical stress of the two tea varieties were analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
CG and F6 tea leaves were collected from tea plants with the same growth trend, one bud, and three leaves. The tea plants were cultivated on an organic ecological tea plantation in Fu’an, Fujian Province, China, under the same, natural conditions. Post-harvest samples (CGP and F6P) were withered indoors for 2 h (CGW and F6W), followed by a unique process called Yaoqing (also known as turnover, rotation, or tossing) for 10 min, and the leaves were then spread for 4 h (CGM and F6M).
Additionally, leaves from the oolong tea unsuitable varieties of Fudingdabaicha (FD, Camellia sinensis) and Fuxuan (FX, Camellia sinensis), and the oolong tea suitable varieties of Ruixiang (RX, Camellia sinensis) and Jinmudan (JMD, Camellia sinensis), were also collected and underwent a mechanical stress stage for further use in jasmonate (JA) content determination.
2.2. GC-MS Conditions and Qualitative Analysis of Aroma Metabolites
After sampling, the volatiles in the fiber coating were desorbed for 5 min at 250 °C in split-less mode in the injection part of the GC apparatus (Model 8890, Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA). The identification and quantification of volatile compounds were carried out using 8890 GC and a 7000D mass spectrometer (Agilent) that was equipped with a 30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm DB-5MS (5% phenyl-polymethylsiloxane) capillary column. Using helium as the carrier gas, the linear velocity was 1.2 mL·min−1. The temperature of the injector was 250 °C and the temperature of the detector was 280 °C. The oven temperature was set to 40 °C (3.5 min), with a temperature rise of 10 °C·min−1 to 100 °C, a temperature rises of 7 °C·min−1 to 180 °C, a temperature rises of 25 °C·min−1 to 280 °C, and an insulation time of 5 min. The mass spectrum was recorded in electron collision (EI) ionization mode at 70 eV. The quadrupole mass detector, ion source, and transmission line temperatures were set to 150, 230, and 280 °C, respectively. MS in ion monitoring (SIM) mode was selected for accurate scanning. The internal standard for calibration was [3,4,5,6-2H4]-Methyl 2-Hydroxybenzoate (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
Qualitative analysis was conducted using MassHunter software B.06 (Agilent Qualitative System). The deconvolution parameter peak width was set to 20, and the requirements for resolution, sensitivity, and chromatographic peak shape were set to medium. The minimum matching factor was set to 70. The substance identification was carried out based on the obtained mass spectrometry data and the mass spectra of the standard substances provided by the NIST (2020) library. Then, the retention index (RI) of each volatile substance was calculated using the formula (RI = 100Z + 100[TR(x) − TR(z)]/[TR(z + 1) − TR(z)]) [14], using a mixture of C7-C40 alkane solutions under the same GC-MS analysis conditions as the standard. TR(x), TR(z), and TR(z + 1) represent volatile substance and retention temperatures of alkanes with carbon numbers z and z + 1, respectively, and TR(z) < TR(x) < TR(z + 1). Then, further qualitative confirmation was conducted based on literature reports [15]. The RI screening standard was RIi ± 30, where RIi represents the reference value of the literature.
2.3. Transcriptome RNA-Sequencing and Differential Expression Gene (DEG) Analysis
The total RNA was extracted from leaves of CG and F6 using the RNAprep Pure Plant Kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China). The RNA quality and integrity of the extracted RNA were assessed using the Bio-analyzer 2100 system (Agilent) and the NanoDrop ND-2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo, Munich, Germany), respectively. Then, mRNA fragments were extracted from the total RNA as cDNA synthesis templates. Afterwards, the short fragment was connected to the adapter and selected for PCR amplification. Finally, sequencing was performed on the Illumina HiSeqTM 2500 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
Clean reads were handled by removing low-quality reads, adapters, and ploy-A reads. The clean reads were uniquely aligned to the Tieguanyin (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) genome [16] using HISAT2.2.4 [17] with the default parameters. The expression of transcripts was evaluated using Fragments per Kilobase of transcript per Million Fragments (FPKM). The biological variability of the samples was assessed using the Pearson correlation coefficient, where an r2 value close to 1 indicates repeated high correlation. Expressions obtained by adjusting the p-value using the Benjamini–Hochberg adjustment with fold change ≥2 and false discovery rate (FDR) were considered as differentially expressed genes (DEGs). DEGs were obtained through sample relationship analysis using KEGG enrichment analysis.
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Verification Analysis
To verify the reliability of the RNA-Seq data, key DEGs were selected for qRT-PCR analysis. The qRT-PCR detection system of the sample was performed as previously described [18]. The glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (GAPDH) was used as the reference gene [18]. Samples of three separate biological replicas were used for analysis. The relative expression of the studied genes was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method. Specific primers designed based on sequenced CDS sequences were used for RT-qPCR, as shown in Table S1.
2.5. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
The R-packages 4.1.3 WGCNA was used as previously described [19]. The default formula (connection strength = |(correlation + 1)/2|β) was used to standardize the matrix of all FPKM values for each DEG at each time point and convert it into an adjacency matrix. The β value represents the soft threshold of the correlation matrix, which gives the weight value with the strongest correlation.
The blockwiseModules command was used to construct gene networks and identify modules. The parameters were set as follows: mergeCutHeight = 0.5, minModuleSize = 30, and default values retained for other parameters. To identify the modules most associated with some representative volatile substances, we calculated the module intrinsic gene (ME) value for each module using the ME command, and then calculated the correlation between the representative volatile component and the corresponding module.
2.6. Plant Hormone Metabolite Profiling and Analysis
The extraction and quantification of plant hormone metabolites (including auxin, cytokinins, abscisic acid, jasmonates, salicylic acid, gibberellins, ethylene, strigolactones, and melatonine) were carried out using a UPLC-ESI-MS/MS system (Applied Biosystems 6500 Triple Quadrupole, ExionLCTM AD, UPLC, SCIEX, Framingham, MA, USA) according to standard procedures. The content of plant hormones is expressed in ng·g−1 fresh weight by an external standard method. The range of standard solution is 0.01 ng·mL−1 to 500 ng·mL−1, except for TRP and SAG (0.2–10,000 ng·mL−1). The surgery was performed according to the previous description [20].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) and construction of loading plots of volatiles’ data were performed using Simca 13.0 software. The column chart of volatiles’ relative content, of different tea samples, were analyzed using one-way or two-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni multiple comparisons test used to determine the significance of each sample, with GraphPad Prism 8.0.2 software.
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Key Aroma Components between CG and F6 before and after Mechanical Stress
Volatile metabolome analysis was conducted to validate the different aroma formation abilities of CG and F6 before and after mechanical stress. Volatiles were detected and main principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted. In the PCA plot, the first principal component (PC1) is 73.5% and second principal component (PC2) is 12.0%, accounting for 85.5% of total volatile information (Figure 1a). This indicates that PC1 and PC2 represent the majority of the aroma information of the samples. The CGP, CGW, F6P and F6W samples are located on the PC1 positive axis and are close to each other. However, after mechanical stress, the CGM and F6M are both located on the PC1 negative axis, away from fresh leaves and withered samples, while CGM is located on the positive axis of PC2 and F6M is located on the negative axis of PC2 (Figure 1a). In the loading plot of PCA, the characteristic aromas of oolong tea’s indole, (E)-β-ocimene, (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, and jasmine lactone are all located in the second quadrant of the loading plot, consistent with the CGM position (Figure 1b). In addition, indole is the compound farthest from the center point of the coordinate axis, and it is reported that indole plays an important role in the characteristic aroma quality of CG oolong tea [13]. On the other side, volatiles like (Z)-3-hexenyl acetate are in the third quadrant, consistent with F6M (Figure 1b).
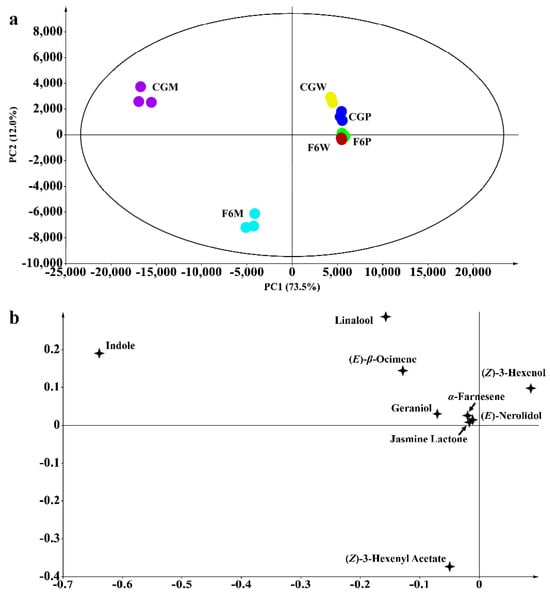
Figure 1.
Principal component analysis of aroma components of Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) and Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. (a) Principal component analysis plot and (b) the loading plot of samples’ key volatiles before and after mechanical stress. CGP = CG plucked leaves, F6P = F6 plucked leaves, CGW = CG withered leaves, F6W = F6 withered leaves, CGM = leaves of CG after mechanical stress, and F6M = leaves of F6 after mechanical stress.
Consistent with the results of PCA, the contents of indole, (E)-β-ocimene, (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, geraniol, linalool, and jasmine lactone are not significantly different in CG and F6 fresh leaves, but are significantly accumulated in CGM and significantly higher than those in F6M (Figure 2). This indicates that tea varieties suitable for oolong tea have a stronger ability to form the characteristic aroma of oolong tea under the same mechanical stress.
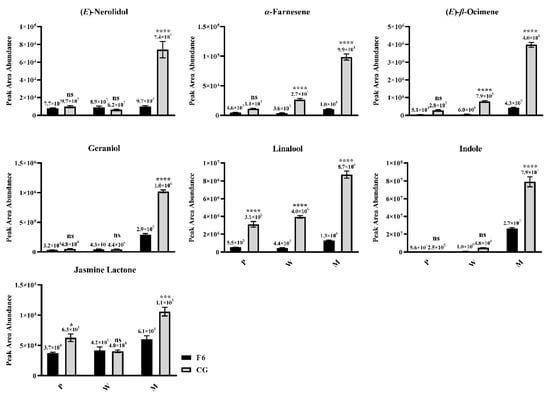
Figure 2.
Key aroma contents in Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) and Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. P = plucked leaves, W = withered leaves, M = after mechanical stress leaves. ‘ns’ represents non-significant association; ‘*’ represents p < 0.05; ‘***’ represents p < 0.001; ‘****’ represents p < 0.0001.
3.2. Differences in Key Aroma Synthetase Genes Expression in CG and F6 before and after Mechanical Stress
To better understand the molecular mechanism of the different responses of CG and F6 after mechanical stress related to key aroma formation, three independent replicates of the samples were subjected to RNA-Seq. The GC percentages of the samples ranged from 44.25% to 45.45% (Table S1), and the average coverage of transcriptome data relative to the reference genome was all higher than 89.85%, indicating high-quality reads worthy of further analysis.
Studies have proved that (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, β-ocimene, indole, and jasmine lactone formation are controlled by (E)-nerolidol synthase, α-farnesene synthase, β-ocimene synthase tryptophan synthase β-subunit, and 9-lipoxygenase 1 [21,22,23,24,25,26]. In this study, two (E)-nerolidol synthase genes (CsNES1, CsTGY08G0000361 and CsNES2, CsTGY08G0001705), two α-farnesene synthase genes (CsAFS1, CsTGY08G0000370 and CsAFS2, CsTGY08G0000372), two β-ocimene synthase genes (CsOCS1, CsTGY05G0001284 and CsOCS2, CsTGY05G0001285), two tryptophan synthase β-subunit 2 genes (CsTSB2a, CsTGY08G0000242 and CsTSB2b, CsTGY08G0000243), and one lipoxygenase gene 1 (CsLOX1: CsTGY03G0001273) were found to be differentially expressed between CGM and F6M. The expression levels of these genes and corresponding aromas were all continuous and significantly increased after withering and mechanical stress in CG cultivars (Figure 3). Although these genes were also more highly expressed in F6 after withering and mechanical stress, the increase was significantly lower than that in CG (Figure 3). However, the expression levels of CsNES1, CsNES2, CsTSB2a, and CsTSB2b in F6M were significantly lower than those in F6W. The expression trends of the partial key genes mentioned above were further verified by qRT-PCR analysis (Figure S3).
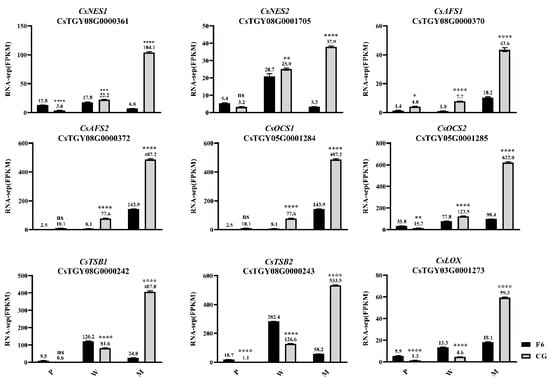
Figure 3.
Key aroma synthase genes’ expression levels in Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) and Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. P = plucked leaves, W = withered leaves, M = after mechanical stress leaves. ‘ns’ represents non-significant association; ‘*’ represents p < 0.05; ‘**’ represents p < 0.01; ‘***’ represents p < 0.001; ‘****’ represents p < 0.0001.
3.3. Differences in Key Aroma Upstream or Regulator Genes Expression in CG and F6 before and after Mechanical Stress
(E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, β-ocimene, linalool, and geraniol belong to sesquiterpenoids or monoterpenes volatiles, and form from mevalonate (MVA) or methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways. From the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of F6M and CGM, two acetyl-CoA C-acetyltransferase genes (CsACAT1, CsTGY04G0001833 and CsACAT2, CsTGY05G0000720), two hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA synthase genes (CsHMGS1, CsTGY12G0001868 and CsHMGS2, CsTGY14G0001311), one hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase gene (CsHMGR, CsTGY07G0000990) and one diphosphomevalonate decarboxylase gene (CsMVD, CsTGY01G0000237) were found to be significantly more highly expressed in CG (Figure 4).
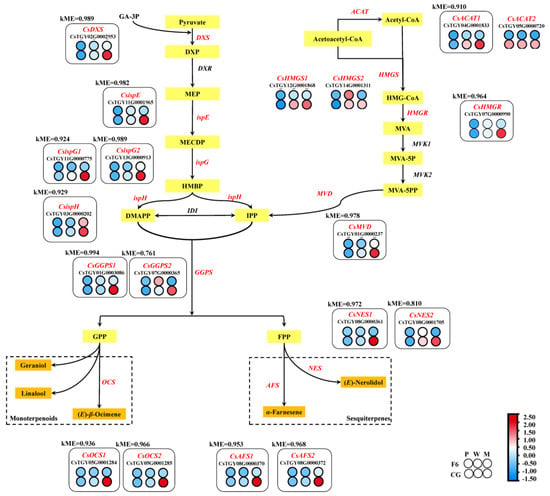
Figure 4.
Transcript profiling of key differential genes in the mevalonate (MVA) and methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways in Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) and Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. Heat map representation of the expression level of key genes is shown in the figure. Gene expression is displayed as a heat map depicting the log2 (FPKM) values. Red and blue dots and size indicate up- and downregulated genes, respectively.
In the MEP pathway, one 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase gene (CsDXS, CsTGY02G0002953), one (E)-4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase gene (CsispE, CsTGY11G0001965), two (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl-diphosphate synthase genes (CsispG1, CsTGY11G0000775 and CsispG2, CsTGY13G0000913), one (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl-diphosphate reductase gene (CsispH, CsTGY03G0000202), and two geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase genes (CsGGPS1, CsTGY01G0003086 and CsGGPS2, CsTGY07G0000365) were found to be differentially expressed in F6M and CGM. These DEGs’ expression levels were also found to be continuous and significantly upregulated after withering and mechanical stress in CG (Figure 4).
Recently, research has illustrated that excessive m6A sites in mRNAs of terpenoid biosynthesis-related genes, including CsDXS, result in destabilization of these mRNAs, which can be stabilized by an RNA m6A eraser during the oolong tea withering process [27]. In this study, an RNA m6A eraser gene CsALKBH10B (CsTGY11G0001763) was found to be significantly accumulated in CGW and CGM.
The jasmonate-responsive transcription factor CsMYC2a (CsTGY12G0001520) has been reported to be the major regulator of CsTSB2 by binding to its promoter, where the DNA methylation degree reduces and the DNA methyltransferase 3 (CsDMR3, CsTGY05G0002797) expression level decreases after mechanical stress [28,29]. In this study, CsMYC2a gene expression models in two different tea cultivars were highly similar between CsTSB2a and CsTSB2b before and after mechanical stress (Figure S5b). At the same time, CsDMR3 gene expression was continuous and significantly decreased after withering and mechanical stress in CG. However, mechanical stress had no significant effect on the expression level of the CsDMR3 gene in F6 (Figure S5c). These findings suggest that the CsMYC2a gene is activated and the CsDMR3 gene is inhibited after mechanical stress of CG, which together participate in the high expression of downstream genes such as CsTSB2a and CsTSB2b.
3.4. Differences in Jasmonate (JA) Content in CG and F6 before and after Mechanical Stress
The enrichment of F6M and CGM DEGs from the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) showed that the α-linolenic acid (ALA) metabolism pathway and plant hormone signal transduction play different roles in aroma accumulation regulation in different tea varieties (Figure S4). ALA, one type of important plant phytohormone, is the main synthetic pathway of JAs, and can regulate the biosynthesis of volatiles and act as an upstream signal in plants like tea [30].
The contents of more than fifty important plant hormones have been investigated, including those of JAs, ABAs (abscisic acids), auxins, CKs (cytokinins), ETHs (ethylenes), GAs (gibberellins), and SAs (salicylic acids) (Table S4). Only JAs were found to be much more highly accumulated in CG (Figure 5). The contents of JA precursors including (Z)-12-oxophytodienoic acid (OPDA), 3-oxo-2-(2-(Z)-Pentenyl) cyclopentane-1-butyric acid (OPC-4), and 3-oxo-2-(2-(Z)-pentenyl) cyclopentane-1-hexanoic acid (OPC-6) were significantly higher in CG than in F6 after mechanical stress (Figure 5a–c). However, jasmonoyl-L-isoleucine (JA-Ile) and dihydrojasmonic acid (H2JA) were not significantly different between F6M and CGM (Figure 5d–f), whereas the jasmonates methyl jasmonate (MeJA), N-[(-)-jasmonoyl]-(L)-phenalanine (JA-Phe), and N-[(-)-jasmonoyl]-(L)-valine (JA-Val) were all significantly higher in CG and F6 after mechanical stress (Figure 5g–i). Specifically, the content of MeJA in CGM was 110.80 ng·g−1 and reached 5.67 times higher than that in F6M (Figure 5h). In other tea varieties, the contents of JA, MeJA, JA-Phe, and JA-Val were also significantly higher in varieties suitable for oolong tea after mechanical stress (Figure S6d,g–i). Thus, JAs, particularly MeJA, play an important role in the differential accumulation of key oolong tea aromas in different tea varieties.
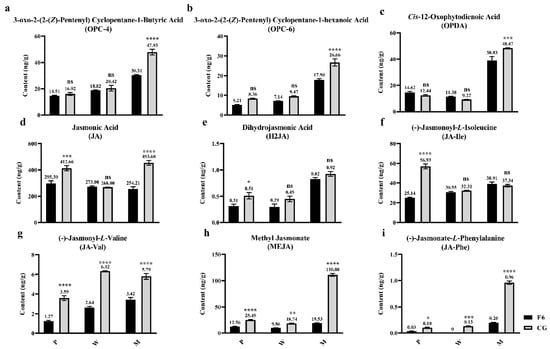
Figure 5.
Contents of (a) 3-oxo-2-(2-(Z)-Pentenyl) Cyclopentane-1-Butyric acid (OPC-4), (b) 3-oxo-2-(2-(Z)-Pentenyl) Cyclopentane-1-hexanoic acid (OPC-6), (c) Cis-12-Oxophytodienoic Acid (OPDA), (d) Jasmonic Acid, (e) Dihydrojasmonic acid (H2JA), (f) Jasmonoyl-L-Isoleucine (JA-Ile), (g) N-[(-)-jasmonoyl]-(L)-Valine (JA-Val), (h) Methyl Jasmonate (MeJA), (i) N-[(-)-Jasmonoyl]-(L)-Phenalanine (JA-Phe) in Fuyun No. 6 (F6, Camellia sinensis) and Chungui (CG, Camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. ‘ns’ represents non-significant association; ‘*’ represents p < 0.05; ‘**’ represents p < 0.01; ‘***’ represents p < 0.001; ‘****’ represents p < 0.0001.
In the upstream ALA pathway, six phospholipase A1 genes (CsDAD1a, CsTGY03G0002557; CsDAD1b, CsTGY04G0000465; CsDAD1c, CsTGY06G0002250; CsDAD1d, CsTGY14G0001487; CsDAD1e, CsTGY15G0000101; and CsLCAT3, CsTGY07G0001487), one 9-lipoxygenase gene (CsLOX1, CsTGY03G0001273), one 13-lipoxygenase gene (CsLOX2, CsTGY02G0002259), two hydroperoxide dehydratase genes (CsAOS1, CsTGY03G0000213 and CsAOS2, CsTGY09G0002564), three allene oxide cyclase genes (CsAOC1, CsTGY01G0003195; CsAOC2, CsTGY01G0003196; and CsAOC3, CsTGY02G0000431), one 12-oxophytodienoic acid reductase gene (CsOPR, CsTGY09G0001642), one OPC-8:0 CoA ligase gene (CsOPCL, CsTGY11G0000579), one acyl-CoA oxidase gene (CsACX, CsTGY04G0002746), two enoyl-CoA hydratase genes (CsMFP1, CsTGY14G0001893 and CsMFP2, CsTGY09G0000155), and one acetyl-CoA acyltransferase gene (CsACAA, CsTGY11G001487) were screened as being differentially expressed between F6M and CGM. All these upstream genes were highly expressed in CG after mechanical stress (Figure 6).
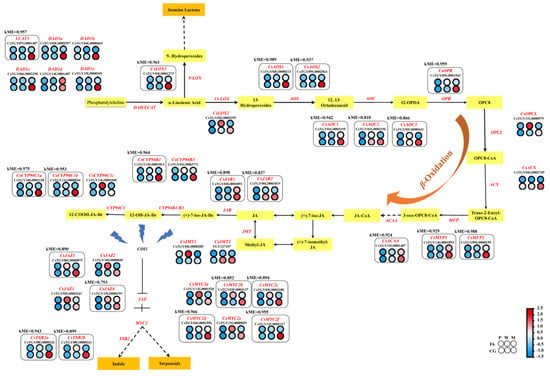
Figure 6.
Transcript profiling of key differential genes in the alpha-linolenic acid metabolism pathway in Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) and Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. Heat map representation of the expression level of key genes is shown in the figure. Gene expression is displayed as a heat map depicting the log2 (FPKM) values. Red and blue dot and size indicate up- and downregulated genes, respectively.
After β-oxidation of the ALA pathway, two jasmonate O-methyltransferase genes (CsJMT1, CsTGY04G0000285 and CsJMT2, TGY127107), four jasmonate ZIM domain-containing protein genes (CsJAZ1, CsTGY06G0000075; CsJAZ2, CsTGY10G0000049; CsJAZ3, CsTGY02G0003243; and CsJAZ4, CsTGY15G0000159), two jasmonic acid-amino synthetase genes (CsJAR1, CsTGY03G0003091 and CsJAR2, CsTGY06G0001819), five jasmonoyl-L-amino acid 12-hydroxylase genes (CsCYP94B1, CsTGY15G0001013; CsCYP94B3, CsTGY01G0003771; CsCYP94C1a, CsTGY10G0001128; CsCYP94C1b, CsTGY11G0000544; and CsCYP94C1c, CsTGY13G0001040), and six transcription factor MYC2 genes (CsMYC2a, CsTGY12G0001520; CsMYC2b, CsTGY03G0003137; CsMYC2c, CsTGY03G0003180; CsMYC2d, CsTGY04G0001556; CsMYC2e, CsTGY11G0000029; CsMYC2f, CsTGY12G0002117) were also screened as being differentially expressed between F6M and CGM. All these upstream genes were highly expressed in CG after mechanical stress (Figure 6).
3.5. WGCNA Analysis of CG and F6 before and after Mechanical Stress
To comprehensively investigate the differential gene regulatory network of aroma formation before and after wounding stress in the two varieties, a total of 22,058 DEGs was used to conduct a weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), generating ten modules. The correlation between the aroma components and each module was calculated using the peak area data of CG and F6 before and after mechanical stress. From the cluster dendrogram, the aromas including indole, (E)-β-ocimene, (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, geraniol, linalool, and jasmine lactone-related genes are all clustered in the lightcyan module (Figure 7a).
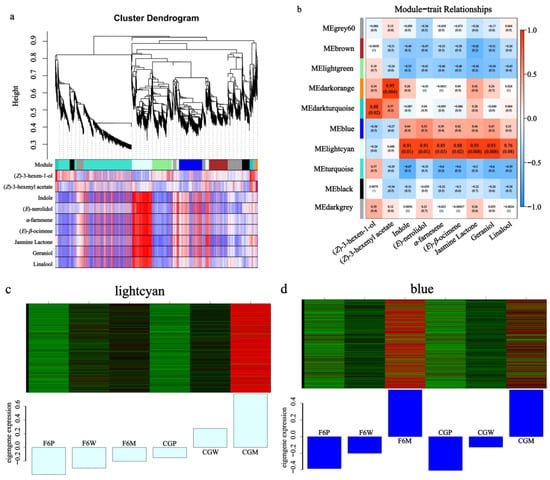
Figure 7.
The co-expression network of DEGs and key aromas in Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) and Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. (a) The hierarchical clustering tree of WGCNA. The colored boxes below represent genes with similar expression patterns. The red and blue boxes below represent the correlation between aroma and color modules. Red color indicates high correlations and blue indicates low correlations. (b) The heat map of nine aroma components with each module. Red color indicates high correlations and blue indicates low correlations. (c,d) The DEGs’ expression level in different samples of the lightcyan and blue modules.
The module trait relationship showed that indole, (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, (E)-β-ocimene, jasmine lactone, geraniol, and linalool were positively correlated with lightcyan and blue modules, while all these aromas were significantly correlated with the lightcyan module, with p-values reaching 0.01, 0.01, 0.03, 0.02, 0.008, 0.008, and 0.08, respectively (Figure 7b). The mRNA expression level heat map of the lightcyan module shows that the overall gene expression level showed a continuous and significant increase after mechanical stress and much higher accumulation in the CG than in the F6 variety, indicating that these module genes may play a vital role in aroma differential formation among different tea varieties (Figure 7c). By comparison, in the blue module, the gene expression level is also continuous and significantly increases after mechanical stress in both the CG and F6 varieties. The blue module explains why F6 also accumulates some characteristic aromas after withering and mechanical stress (Figure 7d).
In the lightcyan module, total 1117 DGEs were screened out and 397 genes were annotated by KEGG, which mainly comprised enrichment in plant hormone signal transduction (35), alpha-Linolenic acid metabolism (14), terpenoid backbone biosynthesis (10), and sesquiterpenoid or monoterpenoid biosynthesis (11). All key aroma synthesis genes CsNES1 (kME = 0.927), CsNES2 (kME = 0.810), CsAFS1 (kME = 0.953), CsAFS2 (kME = 0.968), CsOCS1 (kME = 0.936), CsOCS2 (kME = 0.966), CsTSB2a (kME = 0.943), CsTSB2b (kME = 0.899), CsLOX1 (kME = 0.961) were found in the lightcyan module of WGCNA. Upstream of isoprenoid biosynthesis, CsACAT1 (kME = 0.910), CsHMGR (kME = 0.964), CsMVD (kME = 0.978) in MVA, CsDXS (kME = 0.989), CsispE (kME = 0.982), CsispG1 (kME = 0.924), CsispG2 (kME = 0.989), CsispH (kME = 0.929), CsGGPS1 (kME = 0.994), and CsGGPS2 (kME = 0.761) were found in MEP. CsLCAT3 (kME = 0.957), CsLOX1 (kME = 0.961), CsAOS1 (kME = 0.989), CsAOS2 (kME = 0.937), CsAOC1 (kME = 0.942), CsAOC2 (kME = 0.818), CsAOC3 (kME = 0.866), CsMFP1 (kME = 0.930), CsMFP2 (kME = 0.989), CsACAA (kME = 0.924), CsJAR1 (kME = 0.898), CsJAR2 (kME = 0.837), CsCYP94B1 (kME = 0.964), and CsCYP94C1a (kME = 0.975) were also found in the lightcyan module of WGCNA and had a high-connection relation with it. The jasmonate-responsive genes CsJAZ1 (kME = 0.890) and CsJAZ2 (kME = 0.793), and transcription factors (TFs) CsMYC2b (kME = 0.852), CsMYC2c (kME = 0.894), CsMYC2d (kME = 0.966), and CsMYC2f (kME = 0.955), were also found in the WGCNA lightcyan module (Table S3).
The co-expression result of the lightcyan module showed that CsALKBH10B had a high correlation towards genes including CsDXS (whight = 0.523), CsispG1 (whight = 0.463), CsispG2 (whight = 0.574), CsispH (whight = 0.404), CsNES1 (whight = 0.510), CsNES2 (whight = 0.345), CsOCS2 (whight = 0.542), CsLOX1 (whight = 0.507), CsTSB1 (whight = 0.483), and CsTSB2 (whight = 0.429) (Tables S4 and S5).
Then, the relationships of those key aroma synthase genes with TF-encoding genes in the lightcyan module were screened, finding 34 different TFs from six TF families: WRKY, MYB, ERF, E2F, bZIP, and bHLH. The key aroma genes CsNES1, CsNES2, CsAFS1, CsAFS2, CsLOX1, CsOCS1, CsOCS2, CsTSB2a, and CsTSB2b are potentially regulated by 15, 26, 4, 27, 32, 4, 4, 18, and 17 TFs, respectively. Four TFs genes, namely CsbZIP4 (CsTGY10G0000858), CsMYC2d (CsTGY04G0001556), CsWRKY75 (CsTGY10G0000078), and CsWRKY31 (CsTGY08G0000177) are predicted to be involved in regulating all of the key aroma synthase genes mentioned above. This indicates the wide targeting and important regulation function of these TFs in the lightcyan module and the expression of the key aroma genes.
4. Discussion
Suitable tea varieties are a vital factor for the formation of the characteristic aromas of oolong tea. In this study, oolong tea’s characteristic aromas, including (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, β-ocimene, linalool, geraniol, indole, and jasmine lactone, were much more highly accumulated in the CG variety, which is suitable for oolong tea, after mechanical stress than in the F6 tea variety. These results are highly consistent with previous studies of oolong tea [13] and long-term production experience.
The characteristic aromas mentioned above are synthesized from MVA, MEP, and α-linolenic acid metabolism pathways by their synthetases. Studies have proved in vitro that recombinant enzymes of CsNES1, CsNES2, CsAFS1, CsAFS2, CsOCS1, CsOCS2, CsTSB2a, CsTSB2b, and CsLOX1 were able to act with their substrates to generate relevant aromas [21,22,23,24,25,26]. Correspondingly, in this study, oolong tea’s characteristic aroma synthetase genes from different pathways were all much more highly expressed in CG, especially after mechanical stress. Similarly, most of the expression levels of the upstream key enzyme genes of MVA, MEP, and ALA metabolism pathways were also observed to be much higher in CG. Thus, we suppose there must be a master regulator in oolong tea’s characteristic aroma formation.
KEGG enrichment showed that the DEGs of the two tea cultivars after mechanical stress were significantly related to the ALA metabolism pathway and plant hormone signal transduction. The jasmonates are mainly synthesized from the ALA metabolism pathway and control the expression of an estimated 67–85% of wound- and insect-regulated genes in Arabidopsis leaves [31]. Additionally, the jasmonate-responsive transcription factor gene CsMYC2a, which is able to activate the CsTSB2a, CsTSB2b, CsNES1, and CsNES2 genes’ expression, was also observed to be highly expressed in CG after mechanical stress [28,29]. Finally, JA, MeJA, JA-Phe, and JA-Val were screened out as being significantly more highly accumulated in CG and two other tea varieties suitable for oolong tea after mechanical stress. MeJAs in the CG variety after mechanical stress were about ten times higher than those in F6, and may be the key active ingredient. MeJAs are critical to plants under outer stress and affect secondary metabolic processes [32]. It is well known that MeJAs are important for the aroma formation of oolong tea. External application of MeJAs can affect volatile synthesis efficiency and is able to increase expression of genes in the α-linolenic acid degradation pathway, which produces massive amounts of JA and quickly activates the holistic JA-pathway inner tea leaves [33,34]. Thus, JAs, especially MeJAs, play an important role in the differential accumulation of key oolong tea aromas in different tea varieties.
In this study, the ALA pathway upstream and fatty acid β-oxidation key genes were found to be much more highly activated in CG after mechanical stress. CsLOX1, CsLOX2, CsAOS1, CsAOS2, CsAOC1, CsAOC2, and CsAOC3 may play an important role in the JA formation of CG. The LOX catalytic products 9(S) and 13(S) hydroperoxy fatty acids are substrates for at least six different families of enzymes, which are also the important substrates of JAs [35]. Interestingly, 13-LOX was considered the most relevant to JA formation but in our results, CsLOX1, a 9-LOX enzyme gene, was strongly related to aroma formation in CG. Additionally, in an antisense rice line, 9-LOX1 was shown to be able to increase JA levels and generate JA-mediated responses against external stress [36].
A key step in JA biosynthesis is its catalysis by AOS, using already-oxygenated fatty acid hydroperoxide substrates, to 12,13(S)-epoxy-octadecatrienoic acid [37]. Then, under AOC alone or with AOS, it generates (9S,13S)-oxo-phytodienoic acid (OPDA) or (7S, 11S)-dnOPDA. The β-oxidation core enzymes, including ACX and MFP, are both vital in JA formation under wounding. In Arabidopsis, ACX1 is responsible for about 80% of JA production after wounding, and a lack of MFP genes also reduces JA accumulation [38,39]. Thus, the overall higher activation of key enzyme genes in ALA metabolism in CG after mechanical stress leads to the accumulation of JAs, including MeJA.
WGCNA results showed that an RNA m6A eraser CsALKBH10B (CsTGY11G0001763) was found and showed a high correlation towards to aroma synthetase genes. This RNA m6A eraser was able to regulate the global m6A levels of tea leaves and may participate in the decrease in the CsDXS gene m6A level in the oolong tea manufacturing process [27]. Similarly, in this study, a strong connection was found between CsALKBH10B and JA biosynthesis upstream key enzyme genes CsLCAT3, CsLOX1, CsAOS1, CsAOC1, CsMFP1, and CsMFP2, and isoprenoid biosynthesis upstream key enzyme genes CsDXS, CsispG1, and CsispG2. However, the relationship between m6A levels and JA formation needs to be further investigated.
Thirty-four different TFs from six TF families, WRKY, MYB, ERF, E2F, bZIP, and bHLH, potentially participate in the regulation of key aroma synthesis genes in CG after mechanical stress. CsbZIP4, CsMYC2d, CsWRKY75, and CsWRKY31 showed the highest connection with all oolong tea key aromas in the lightcyan module in these TFs. The basic leucine zipper protein (bZIP) was reported to play multiple roles in abiotic stress responses in tea plants [40]. CsbZIP4 is overexpressed in Arabidopsis and upregulated by ABA [41]. The connection between CsbZIP4, and mechanical stress and JAs, is still unknown. MYC2, a basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) family transcription factor, is known to be a positive regulator of JA-dependent responses [42]. CsMYC2a has been proved to be able to promote the CsTSB2 expression level and increase indole content in oolong tea [28]. However, CsMYC2a did not appear in the lightcyan module. On the contrary, CsMYC2d, CsMYC2b, CsMYC2c, and CsMYC2f were screened out, which may indicate several MYC2s were involved. CsWRKY31 and CsWRKY75 belong to the WRKY family, which holds central positions, mediating fast and efficient activation of defense programs under abiotic stresses [43]. WRKY member genes can be much more highly induced by ABA or MeJA, rapidly, in tea plants [44]. Thus, in this study, TFs from WRKY, MYB, ERF, E2F, bZIP, and bHLH, which have been reported to be mostly activated by abiotic stresses, may participate in the aroma regulation of different tea varieties to varying degrees and their functions need to be further proved.
5. Conclusions
In this research, the contents of characteristic oolong tea aromas, including indole, (E)-β-ocimene, (E)-nerolidol, α-farnesene, and jasmine lactone, were all found to be much more highly accumulated in CG, a variety suitable for oolong tea. Accordingly, the coding genes of aroma formation synthases TSB2, OCS, NES, AFS, and LOX1, and related genes in the MVA, MEP, and ALA pathways, were all much more highly activated. These differential reactions are mainly caused by the higher accumulation of jasmonates, especially methyl jasmonate, a type of important plant signal chemical, in CG after mechanical stress. WGCNA analysis indicated 34 different transcription factors from different families are predicted to be involved in this jasmonate-responsive reaction.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10050520/s1, Figure S1. Principal component analysis loading plot of all volatiles of F6 and CG samples before and after mechanical stress; Figure S2. (Z)-3-hexen-1-ol and (Z)-3-hexenyl acetate in Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) and Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress; Figure S3. Measurement of expression of six key aroma synthesis genes by real-time fluorescence quantification PCR and verification by RNA-seq; Figure S4. Scatter map of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis results of F6M and CGM differentially expressed genes; Figure S5. Key potential aroma regulator gene expression level in Chungui (CG, camellia sinensis) and Fuyun No. 6 (F6, camellia sinensis) varieties before and after mechanical stress. Figure S6. Jasmonate precursor, jasmonate, and jasmonate derivative contents in six tea varieties after mechanical stress; Table S1 Results on quality evaluation of RNA-seq data before and after mechanical stress of CG and F6; Table S2. Fluorogenic quantitative PCR primers; Table S3. Volatile peak area of CG and F6 tea varieties before and after mechanical stress; Table S4. Plant hormone relative contents in six tea varieties after mechanical stress; Table S5. Module eigengene value of genes with the lightcyan module; Table S6. Module eigengene value from transcript factor or CsALKBH10B to key aroma synthase genes in the lightcyan module; Table S7. Module eigengene value from transcript factor or CsALKBH10B to key aroma synthase upstream genes in the lightcyan module.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.-L.L., Q.-S.Z. and H.-L.D.; methodology, X.-L.L., R.-Y.S. and C.-S.C.; software, Y.-C.Z.; validation, C.-S.C.; formal analysis, C.-S.C.; investigation, X.-L.L. and C.-S.C.; resources, X.-M.Y., Z.-H.L. and Z.-H.C.; data curation, X.-L.L. and Y.-C.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.-L.L.; writing—review and editing, X.-L.L., X.-R.K. and C.-S.C.; visualization, X.-L.L.; supervision, C.-S.C.; project administration, C.-S.C. and X.-R.K.; funding acquisition, X.-L.L. and C.-S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (Grant No.CARS-19); Agricultural High-quality Development Surpasses the “5511” Collaborative Innovation Project (Grant No.XTCXGC2021004); Scientific and Technological Innovation Team of Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Grant No.CXTD2021006-1); Fujian Natural Science Foundation Project (Grant No.2022J01476); Basic Scientific Research Projects of Fujian Provincial Public Welfare Research Institutes (Grant No.2022R1029004, Grant No.2022R1029003, Grant No.2021R1029007).
Data Availability Statement
The RNA-seq data of tea sample before and after mechanical stress can be found in the Genome Sequence Archive [45] in National Genomics Data Center [46], China National Center for Bioinformation/Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GSA: CRA011618) that are publicly accessible at https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa accessed on 26 June 2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, X.; Su, X.; Yang, Z. Chinese oolong tea: An aromatic beverage produced under multiple stresses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 23776-2018; Sensory Evaluation Methods for Tea. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Kuroda, K.; Inoue, N.; Ito, Y.; Kubota, K.; Sugimoto, A.; Kakuda, T.; Fushiki, T. Sedative effects of the jasmine tea odor and (R)-(−)-linalool, one of its major odor components, on autonomic nerve activity and mood states. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 95, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoto, A.; Fukui, N.; Kaneda, C.; Shoko, T.; Keiichi, G.; Fumio, N.; Hidehiko, Y. Black tea aroma inhibited increase of salivary chromogranin-A after arithmetic tasks. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2018, 37, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, P.; Deng, H.; Ye, N.; Sun, Y. Architecture and Dynamics of the Wounding-Induced Gene Regulatory Network During the Oolong Tea Manufacturing Process (Camellia sinensis). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 788469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tian, C.; Zhu, C.; Lai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Guo, Y. Hidden players in the regulation of secondary metabolism in tea plant: Focus on non-coding RNAs. Beverage Plant Res. 2022, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gu, D.; Wu, S.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Liao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Yang, Z. Feasible strategies for studying the involvement of DNA methylation and histone acetylation in the stress-induced formation of quality-related metabolites in tea (Camellia sinensis). Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Baldermann, S.; Watanabe, N. Recent studies of the volatile compounds in tea. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldermann, S.; Yang, Z.; Katsuno, T.; Tu, V.A.; Mase, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Watanabe, N. Discrimination of Green, Oolong, and Black Teas by GC-MS Analysis of Characteristic Volatile Flavor Compounds. Sci. Rep. 2014, 5, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, Y.; Mei, X.; Katsuno, T.; Kobayashi, E.; Dong, F.; Watanabe, N.; Yang, Z. Regulation of formation of volatile compounds of tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves by single light wavelength. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Gu, D.; Liao, Y.; Xu, X.; Jia, Y.; Deng, R.; Song, C.; Yang, Z. Elucidation of (Z)-3-Hexenyl-β-glucopyranoside Enhancement Mechanism under Stresses from the Oolong Tea Manufacturing Process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6541–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Z.-W.; Wu, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.-X.; Teng, R.-M.; Zhuang, J. Differentially expressed protein and gene analysis revealed the effects of temperature on changes in ascorbic acid metabolism in harvested tea leaves. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Deng, H.L.; Zhong, Q.S.; You, X.M.; Ruan, Q.C.; Shan, R.Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Chen, C.S. Aromatic differentiations of oolong teas. Acta Tea Sin. 2021, 62, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Van, H.; Kratz, P.D. A generalization of the retention index system including linear temperature programmed gas-liquid par-tition chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Cao, G.; Hou, X.; Huang, M.; Du, P.; Tan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Development of a widely targeted volatilomics method for profiling volatilomes in plants. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Shi, L.; Gong, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, D.; Vasseur, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. Haplotype-resolved genome assembly provides insights into evolutionary history of the tea plant Camellia sinensis. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Reyes, A.; Huber, W. Detecting differential usage of exons from RNA-seq data. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-W.; Deng, H.-L.; Wu, Q.-Y.; Liu, B.-B.; Yue, C.; Deng, T.-T.; Lai, Z.-X.; Sun, Y. Validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in post-harvest leaves of tea plant (Camellia sinensis). PeerJ 2018, 7, e6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zeng, L.; Xu, X.; Jia, Y.; Dong, F.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, Z. Functional Characterization of An Allene Oxide Synthase Involved in Biosynthesis of Jasmonic Acid and Its Influence on Metabolite Profiles and Ethylene Formation in Tea (Camellia sinensis) Flowers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Z.; Cai, J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.; Li, Y.X.; Chen, Y.; Yun, J.Y.; Xu, T.; Kang, H.S. N6-Methyladenosine mRNA methylation is important for salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2021, 106, 1759–1775. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Liu, X.; Gui, J.; Mei, X.; Fu, X.; Dong, F.; Tang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z. Formation of (E)-nerolidol in tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves exposed to multiple stresses during tea manufacturing. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, L.; Liao, Y.; Li, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, Z. Formation of α-Farnesene in Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves Induced by Herbivore-Derived Wounding and Its Effect on Neighboring Tea Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xie, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Han, W.; Wu, R.; Li, X.; Guan, Y.; et al. New Insights into Stress-Induced β-Ocimene Biosynthesis in Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves during Oolong Tea Processing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 11656–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Gui, J.; Fu, X.; Mei, X.; Zhen, Y.; Ye, T.; Du, B.; Dong, F.; Watanabe, N.; et al. Formation of Volatile Tea Constituent Indole During the Oolong Tea Manufacturing Process. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5011–5019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, X.; Liao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Jia, Y.; Dong, F.; Yang, Z. Biosynthesis of Jasmine Lactone in Tea (Camellia sinensis) Leaves and Its Formation in Response to Multiple Stresses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3899–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, C.; Tian, C.; Shi, B.; Xu, K.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lai, Z.; et al. RNA Methylome Reveals the m6A-Mediated Regulation of Flavor Metabolites in Tea Leaves under Solar-Withering. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2023, 21, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Hou, X.; Liao, Y.; Yang, Z. Low temperature synergistically promotes wounding-induced indole accumulation by INDUCER OF CBF EXPRESSION-mediated alterations of jasmonic acid signaling in Camellia sinensis. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2172–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, S.; Gu, D.; Zeng, L.; Yang, Z. Involvement of DNA methylation in regulating the accumulation of the aroma compound indole in tea (Camellia sinensis) leaves during postharvest processing. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudareva, N.; Klempien, A.; Muhlemann, J.K.; Kaplan, I. Biosynthesis, function and metabolic engineering of plant volatile organic compounds. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, I.F.; Farmer, E.E. Jasmonates. In Arabidopsis Book; Somerville, C., Meyerowit, E., Eds.; The American Society of Plant Biologists: Rockville, MD, USA, 2010; p. e0129. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Y.; Zheng, W.; He, Y.; Hong, S.-B.; Zhu, Z. Global analysis of transcriptional response of Chinese cabbage to methyl jasmonate reveals JA signaling on enhancement of secondary metabolism pathways. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 189, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Xie, D.; Qi, D.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Schreiner, M.; Lin, Z.; Baldermann, S. Methyl Jasmonate-Induced Changes of Flavor Profiles During the Processing of Green, Oolong, and Black Tea. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ma, C.; Qi, D.; Lv, H.; Yang, T.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Z. Transcriptional responses and flavor volatiles biosynthesis in methyl jasmonate-treated tea leaves. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosblech, A.; Feussner, I.; Heilmann, I. Oxylipins: Structurally diverse metabolites from fatty acid oxidation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Ren, N.; Qi, J.; Lu, J.; Xiang, C.; Ju, H.; Cheng, J.; Lou, Y. The 9-lipoxygenase Osr9-LOX1 interacts with the 13-lipoxygenase-mediated pathway to regulate resistance to chewing and piercing-sucking herbivores in rice. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, A.; Stintzi, A. Enzymes in jasmonate biosynthesis-Structure, function, regulation. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilmiller, A.L.; Koo, A.J.; Howe, G.A. Functional Diversification of Acyl-Coenzyme A Oxidases in Jasmonic Acid Biosynthesis and Action. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 812–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delker, C.; Zolman, B.K.; Miersch, O.; Wasternack, C. Jasmonate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana requires peroxisomal β-oxidation enzymes—Additional proof by properties of pex6 and aim1. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Wang, L.; Yue, C.; Hao, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y. Isolation and expression analysis of 18 CsbZIP genes implicated in abiotic stress responses in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 97, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.-L.; Wang, L.; Qian, W.-J.; Hao, X.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; Wang, X.-C. Positive Regulation of CsbZIP4 Transcription Factor on Salt Stress Response in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Acta Agron. Sin. 2017, 43, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, O.; Chico, J.M.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J.; Solano, R. JASMONATE-INSENSITIVE1 encodes a MYC transcription factor essential to discriminate between different jasmonate-regulated defense responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1938–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulgem, T.; Somssich, I. E Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zheng, C.; Yao, M.; Chen, L. The tea plant CsWRKY26 promotes drought tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Beverage Plant Res. 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, A.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Sun, Y.; et al. The Genome Sequence Archive Family: Toward Explosive Data Growth and Diverse Data Types. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CNCB-NGDC Members and Partners. Database Resources of the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D27–D38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).