Fish Emulsions, Cyano-Fertilizer, and Seaweed Extracts Affect Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Plant Architecture, Yield, and Fruit Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
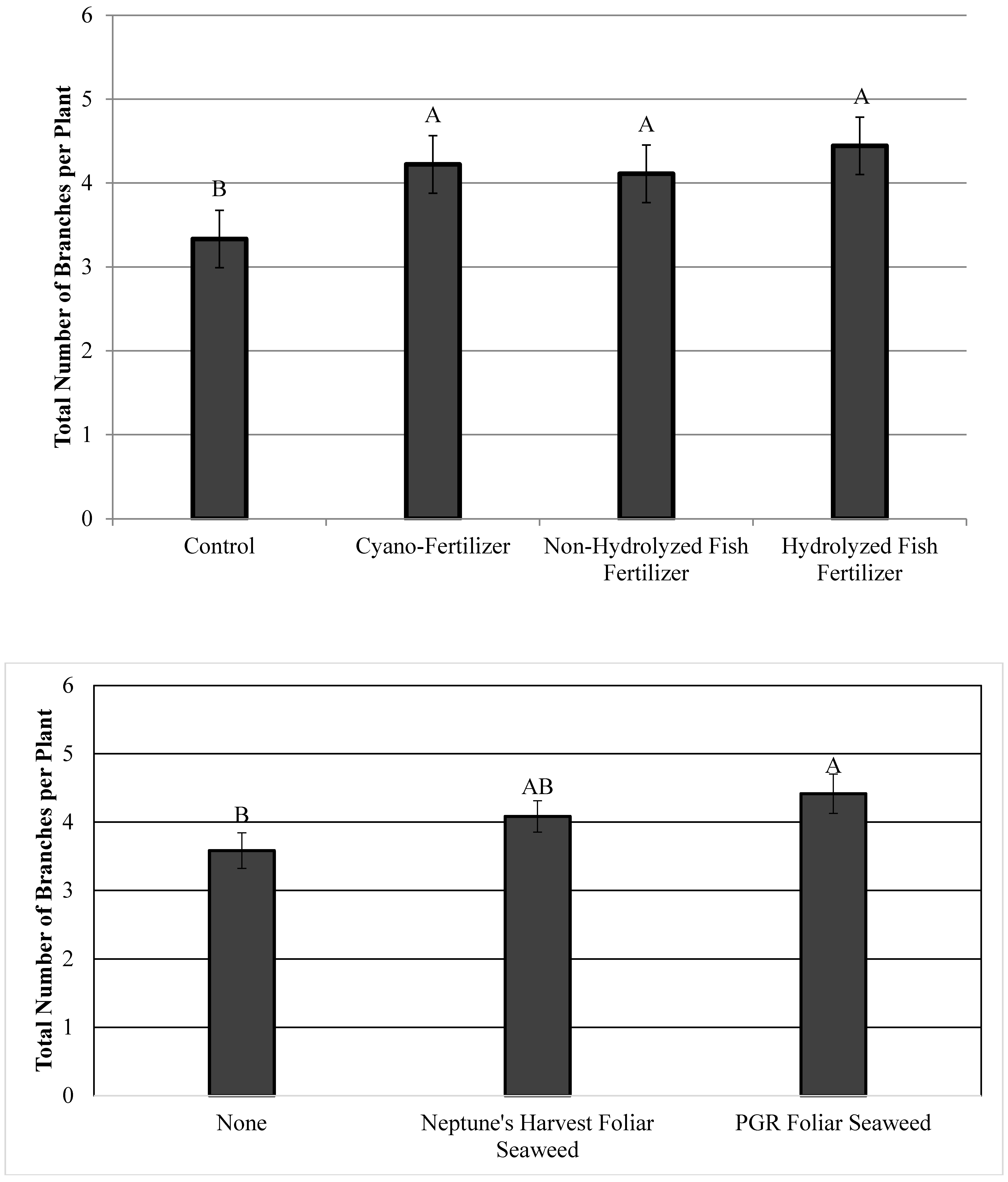
3.1. Plant Architecture
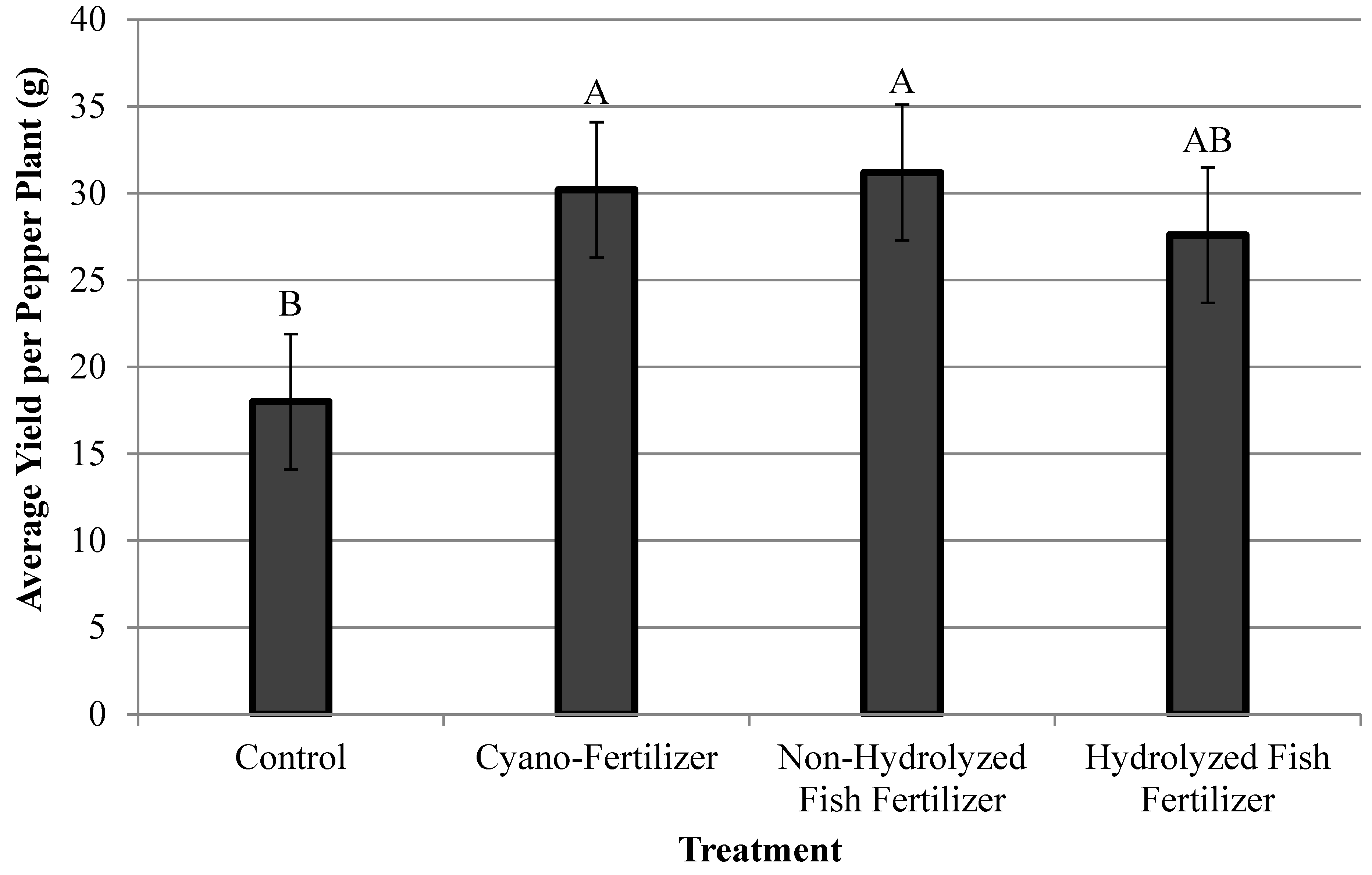
3.2. Pepper Yield
3.3. Fruit Quality
3.4. Foliar Phytohormone Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Department of Agriculture. Natural Resource Conservation Service, Plants, Capsicum annuum L. Available online: https://plants.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CAAN4 (accessed on 23 June 2016).
- United States Department of Agriculture. Agricultural Marketing Service, Market News. Available online: https://www.marketnews.usda.gov (accessed on 23 June 2016).
- Hallmann, E.; Rembialkowska, E. Characterization of antioxidant compounds in sweet bell pepper (Capsicum annuum) under organic and conventional growing systems. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2012, 92, 2409–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Sheu, M.; Hsish, Y.; Wang, R.; Chiang, Y.; Hung, C. Β-carotene reverses multidrug resistance cancer cells by selectively modulating human P-glycoprotein function. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiragun, M.; Hiragun, T.; Oseto, I.; Ochida, K.; Yanase, Y.; Tanaka, A.; Okame, T.; Ishikawa, S.; Mihara, S.; Hide, M. Oral administration of β-carotene or lycopene prevents atopic dermatitis-like dermatitis in HR-1 mice. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, D.N.; Lachman, W.H.; Check, R.M.; Vernell, H.F. The influence of nitrogen levels on flowering and fruit set of peppers. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1969, 81, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yan, H.; Qin, L.; Niu, X.; Zhao, L.; Cai, Y. Optimizing water and nitrogen management for green pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) under drip irrigation in sub-tropical monsoon climate regions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminifard, M.H.; Aroiee, H.; Ameri, A.; Fatemi, H. Effect of plant density and nitrogen fertilizer on growth, yield and fruit quality of sweet pepper (Capsicum annum L.). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 7, 859–866. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Tal, A.; Aloni, B.; Karni, L.; Rosenberg, R. Nitrogen nutrition of greenhouse pepper. ii. Effects of nitrogen concentration and NO3:NH4 ratio on growth, transpiration, and nutrient uptake. HortScience 2001, 36, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrea-Lopez, R.; Diaz de la Garza, R.I.; Valiente-Banuet, I.I. Effects of substrate salinity and nutrient levels on physiological response, yield, and fruit quality of Habanero pepper. HortScience 2014, 49, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoder, N.; Davis, J.G. Organic fertilizer comparison on growth and nutrient content of three kale cultivars. HortTechnology 2020, 30, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, D. Bulletin: Response of Vegetables to Cytex, a Cytokinin Preparation; Oregon State University Dept. of Horticulture: Corvallis, OR, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, B.; Suggars, A. Biostimulants: Myths and realities. Turfgrass Trends 2001, 10, 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyu, O.M.; Adeigbe, O.O.; Awopetu, J.A. Foliar application of the exogenous plant hormones at pre-blooming stage improves flowering and fruiting in cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.). J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 14, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, C.; Trumbare, S.E.; Davidson, E.A.; Vicca, S.; Janssens, I. Sensitivity of decomposition rates of soil organic matter with respect to simultaneous changes in temperature and moisture. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2015, 7, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barminski, R.; Storteboom, H.N.; Davis, J.G. Development and evaluation of an organically-certifiable growth medium for cultivation of cyanobacteria. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2623–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolde, G.; Asmamaw, M.; Sido, M.Y.; Yigrem, S.; Wolde-meskel, E.; Chala, A.; Storteboom, H.; Davis, J.G. Optimizing a cyanobacterial biofertilizer manufacturing system for village-level production in Ethiopia. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 3983–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmamaw, M.; Wolde, G.; Yohannes, M.; Yigrem, S.; Woldemeskel, E.; Chala, A.; Davis, J.G. Comparison of cyanobacterial bio-fertilizer with urea on three crops and two soils of Ethiopia. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 14, 588–596. [Google Scholar]
- Sterle, D.G.; Stonaker, F.; Ela, S.; Davis, J.G. Cyanobacterial biofertilizer as a supplemental fertilizer for peaches: Yield, trunk growth, leaf nutrients and chlorosis. J. Am. Pomol. Soc. 2021, 75, 165–175. Available online: http://www.pubhort.org/aps/75/v75_n3_a5.htm (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Sukor, A.; Amer, F.S.M.; Vanamala, J.; Davis, J.G. Phytohormones in organic fertilizers influence β-carotene concentration and marketable yield of lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Acta Hortic. 2022, 1348, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukor, A.; Qian, Y.; Davis, J.G. Organic nitrogen fertilizer selection influences water use efficiency in drip-irrigated sweet corn. Agriculture 2023, 13, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, A.; Davis, J.G. Optimizing organic carrot (Daucus carota var. sativus) yield and quality using fish emulsions, cyanobacterial fertilizer, and seaweed extracts. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Sinha, R.P.; Yyagi, M.B.; Kumar, A. Cyanobacterial secondary metabolites. Int. J. Pharma Biosci. 2011, 2, 144–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wenz, J.; Davis, J.G.; Storteboom, H. Influence of light on endogenous phytohormone concentrations of a nitrogen-fixing Anabaena sp. cyanobacterium culture in open raceways for use as fertilizer for horticultural crops. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 3371–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Salicylic acid signaling in disease resistance. Plant Sci. 2014, 228, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Roldan, V.; Fermas, S.; Brewer, P.B.; Puech-Pagès, V.; Dun, E.A.; Pillot, J.P.; Letisse, F.; Matusova, R.; Danoun, S.; Portais, J.C.; et al. Strigolactone inhibition of shoot branching. Nature 2008, 455, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Offringa, R.; Heuvelink, E. Auxin-induced fruit set in Capsicum annuum L. requires downstream gibberellin biosynthesis. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 31, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, J.S. Jasmonate-inducible plant defenses cause increase parasitism of herbivores. Nature 1999, 399, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.; Wright, L.P.; Gershenzon, J.; Wasternack, C.; Hause, B.; Schaller, A.; Stintizi, A. Jasmonic acid and its precursor 12-oxophtodienoic acid control different aspects of constitutive and induced herbivore defenses in tomato. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, N.; Sasaki-Sekimoto, Y.; Obayashi, T.; Kikuta, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Ainai, T.; Yagi, K.; Sakura, N.; Suzuki, H.; Masuda, T.; et al. 12-Oxo-Phytodienoic acid triggers expression of a distinct set of genes and plays a role in wound-induced gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 1268–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, M.S.; Davis, J.G. Beyond soil inoculation: Cyanobacteria as a fertilizer replacement. Nitrogen 2023, 4, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlund, A.; Eklof, S.; Sundberg, B.; Moritz, T.; Sandberg, G. A microscale technique for gas chromatography-mass spectrometry measurements of pictogram amounts of indole-3 acetic acid in plant tissues. Plant Physiol. 1995, 108, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhan, Y.; Feng, X.; Huang, Z.-A.; Sun, C. Identification and expression profiling of the auxin response factors in Capsicum annuum L. under abiotic stress and hormone treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, H.L.; Aguiar, L.; Leitão, A.; Lourdes Taborda, M. Effects of growth regulators for fruit setting on pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) production. Acta Hortic. 1986, 191, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Chen, J.; He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Sun, L. DNA Methylation is involved in the regulation of pepper fruit ripening and interacts with phytohormones. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 1928–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzistathis, T.; Tsaniklidis, G.; Papaioannou, A.; Giannakoula, A.; Koukounaras, A. Comparative approach on the effects of soil amendments and controlled-release fertilizer application on the growth, nutrient uptake, physiological performance and fruit quality of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Sun, T.; Huang, W.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X. Preharvest reduction in nutrient solution supply of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) contributes to improve fruit quality and fertilizer efficiency while stabilizing yields. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwan, M.W.M.; El-Hamahwy, M.A.M. Improved productivity and quality associated with salicylic acid application in greenhouse pepper. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanopoulos, C.; Bouranis, D.; Passam, H.C. Comparative development, maturation, and ripening of seedless and seed-containing bell pepper fruits. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 164, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
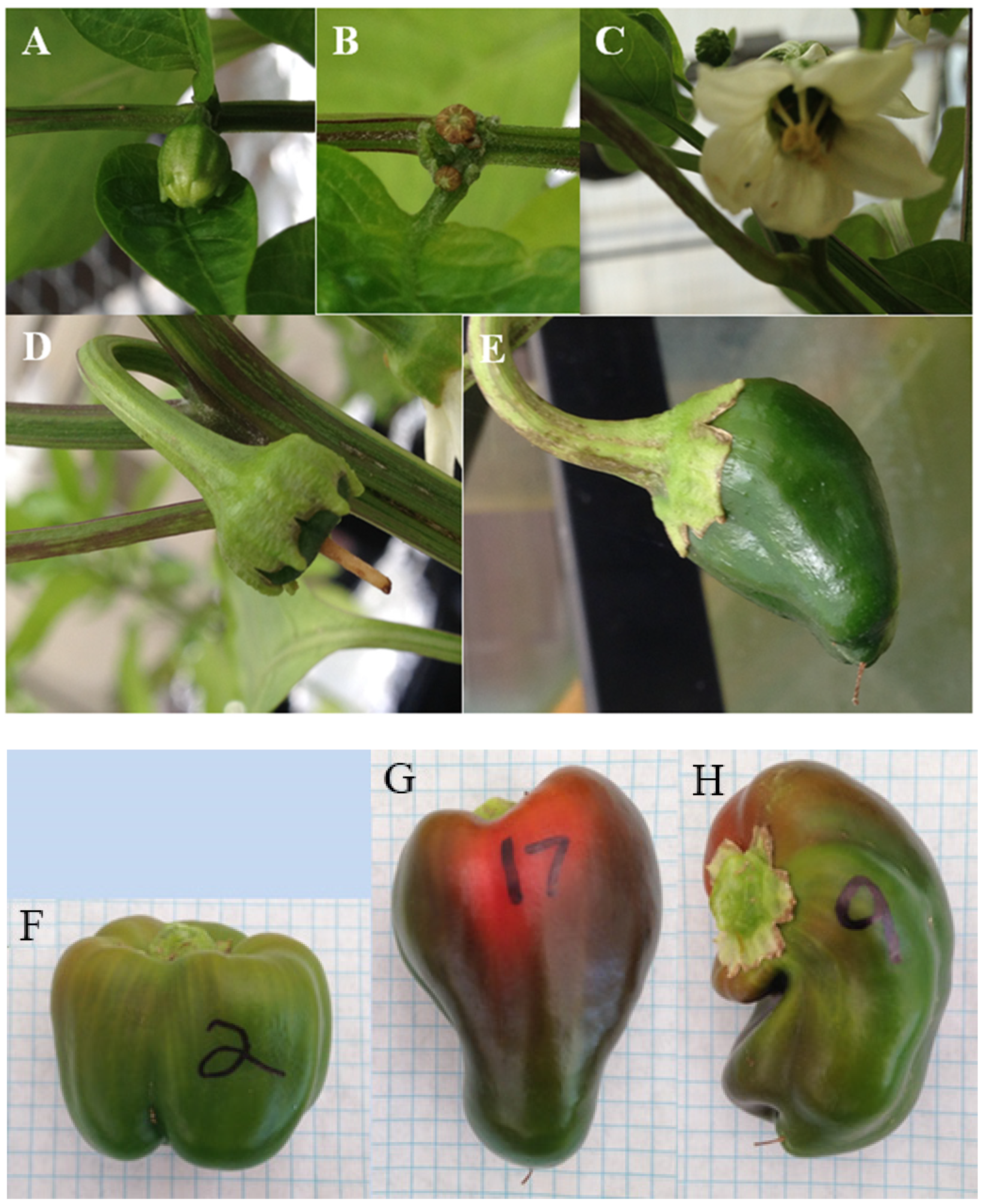

| Date | Soil N Fertilizer Applied | Volume of Fertilizer Mix |
|---|---|---|
| kg N ha−1 | L pot−1 | |
| 28 February 2015 | 0.9 | 0.10 |
| 13 March 2015 | 1.7 | 0.10 |
| 23 March 2015 | 0.4 | 0.20 |
| 30 March 2015 | 3.7 | 0.20 |
| 8 April 2015 | 3.3 | 0.20 |
| 17 April 2015 | 4.0 | 0.30 |
| 28 April 2015 | 4.1 | 0.30 |
| 7 May 2015 | 1.2 | 0.30 |
| 14 May 2015 | 2.3 | 0.40 |
| 19 May 2015 | 1.6 | 0.40 |
| 26 May 2015 | 2.8 | 0.40 |
| 5 June 2015 | 1.6 | 0.40 |
| 12 June 2015 | 2.1 | 0.40 |
| 19 June 2015 | 2.1 | 0.15 |
| Total | 31.8 | 3.85 |
| Date | Volume of Seaweed Solution Applied |
|---|---|
| mL | |
| 3 March 2015 | 5 |
| 20 March 2015 | 10 |
| 16 April 2015 | 20 |
| 7 May 2015 | 20 |
| 28 May 2015 | 25 |
| 19 June 2015 | 25 |
| Total | 105 |
| Treatment | Auxin | Salicylic Acid | Auxin | Salicylic Acid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg kg−1 | kg ha−1 | |||
| Fertilizers | ||||
| Cyano-fertilizer | 6.50 × 10−5 | 5.92 × 10−3 | 9.73 × 10−5 | 0.01 |
| Hydrolyzed fish fertilizer | 3.97 × 10−4 | 0.018 | 6.30 × 10−7 | 1.22 × 10−4 |
| Non-hydrolyzed fish fertilizer | 1.436 | 0.077 | 9.26 × 10−4 | 1.16 × 10−5 |
| Foliar Seaweeds | ||||
| Seacom PGR seaweed | 0.802 | 48.17 | 4.52 × 10−7 | 2.72 × 10−5 |
| Neptune’s Harvest seaweed | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Treatment | Flowers Alive or Dead | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Day 109 | Harvest (Day 135) | ||
| Alive | Dead | % Abscissions | |
| Control | 2.3 AB | 3.0 B | 65.4 A |
| Cyano-fertilizer | 2.2 AB | 4.4 A | 54.8 AB |
| Hydrolyzed fish fertilizer | 3.7 A | 2.6 B | 51.8 B |
| Non-hydrolyzed fish fertilizer | 1.8 B | 5.0 A | 55.6 AB |
| Phytohormone | N Fertilizer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Cyano-Fertilizer | Hydrolyzed Fish Fertilizer | Non-Hydrolyzed Fish Fertilizer | |
| Abscisic acid (pg/mg) | 21.48 B | 41.04 AB | 76.27 AB | 131.8 A |
| Jasmonic acid (pg/mg) | 271.3 | 266.7 | 418.0 | 302.4 |
| 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid (relative abundance) | 294.6 AB | 189.2 B | 299.9 AB | 350.0 A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wickham, A.; Davis, J.G. Fish Emulsions, Cyano-Fertilizer, and Seaweed Extracts Affect Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Plant Architecture, Yield, and Fruit Quality. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050491
Wickham A, Davis JG. Fish Emulsions, Cyano-Fertilizer, and Seaweed Extracts Affect Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Plant Architecture, Yield, and Fruit Quality. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(5):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050491
Chicago/Turabian StyleWickham, Allison, and Jessica G. Davis. 2024. "Fish Emulsions, Cyano-Fertilizer, and Seaweed Extracts Affect Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Plant Architecture, Yield, and Fruit Quality" Horticulturae 10, no. 5: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050491
APA StyleWickham, A., & Davis, J. G. (2024). Fish Emulsions, Cyano-Fertilizer, and Seaweed Extracts Affect Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Plant Architecture, Yield, and Fruit Quality. Horticulturae, 10(5), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10050491






