Abstract
Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) is a globally significant vegetable and relies on cytoplasmic male sterile (CMS) lines for hybrid seed production. The NWB CMS type is favored over Ogura CMS for its ease in maintainer screening. Despite its varied mitochondrial configurations and unvalidated sterile gene, we re-sequenced the mitochondrial genome of NWB CMS Tibet A and verified the function of the sterility gene via genetic transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. The mitochondrial genomes of Tibet A could be assembled into circular DNA molecules, with a mitochondrial genome size of 239,184 bp. Our analysis indicated that the specific orf463a was the CMS-associated gene in Tibet A, sharing sequence consistency with the CMS gene in DCGMS and NWB CMS YB-A. Collinearity analysis showed that the mitochondrial genomes of NWB CMS Tibet A, DCGMS, and NWB CMS YB-A share the same mitotype, with structural variations due to recombination via a 9731 bp long repeat sequence and a 508 bp short repeat sequence. Driven by the Ap3 promoter, transgenic Arabidopsis with orf463a exhibited male sterility, confirming the gene’s potential role in CMS. In this study, we assembled a new isomeric form of NWB CMS mitochondrial genome and proved the function of the candidate sterile gene.
1. Introduction
Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) is a phenomenon in which the pistils function normally, but the stamens fail to produce viable pollen. This condition has been identified in over 150 plant species [1]. In 1976, groundbreaking research by American scholars established the link between mitochondrial DNA variation and the occurrence of CMS through a comparative analysis of mitochondrial genome enzyme fragments of maize T CMS and normal [2]. Numerous studies have demonstrated that CMS is caused by specific open reading frames (ORFs) formed by the homologous recombination of repeat sequences within the mitochondrial genome [3,4]. Sterility can be reversed by nuclear restorer genes (RR) or maintained by the recessive genotype (rr). Breeders have extensively utilized CMS in the selective breeding of hybrid crops, significantly contributing to increases in crop yield, quality, and resistance [5,6,7,8,9].
The identification of the CMS genes is crucial for understanding the molecular basis of CMS and for its application in breeding. However, because of its maternal inheritance, it cannot be verified using classical genetic mapping as with nuclear genes. Instead, traditional methods involve comparing the transcript or protein levels of sterile lines with maintainer lines, restorer lines, or hybrids between sterile lines and restorer lines. For instance, the identification of the maize T CMS sterility gene URF-13 was accomplished by analyzing and comparing proteome differences in the sterile line and the F1 generation of the hybrid [10]. Similarly, sterility genes in wheat AP CMS (orf256) and sugar beet I-12 CMS (orf129) were confirmed using analogous methods [11,12]. The sterility genes in rice HL CMS (orfH79), rice RT98A CMS (orf113), and rapeseed Pol CMS (orf224) were identified by comparing the differences in mitochondrial transcripts between the sterile lines and their corresponding maintainer lines [13,14,15]. Recently, the advent of cost-effective, high-throughput sequencing technology has revolutionized the validating of sterility genes. By comparing mitochondrial genome sequences between sterile lines and maintainer lines through sequencing, researchers can swiftly identify sterile line-specific ORFs and validate candidate sterility genes. This approach has successfully been used in the detecting of sterility genes in various crops, such as orf352 in rice RT120 CMS [16], the orf507 in pepper Peterson CMS [17], the orf346 in rapeseed Nsa CMS [18], the orf725 in onion T CMS [19], and the orf88 in mandarin [20], among others.
Mitochondrial transgenesis and gene editing techniques are the most direct means to validate the functionality of sterility genes. Most of the successful cases of mitochondrial gene genetic transformation have been achieved by fusing a mitochondrial targeting signal (Mitochondrial Targeting Sequence, MTS) to the front end of a sterility gene, combined with the use of an another specific expression genes’ promoter (such as AP3, TA29, Lat52). For example, the Lat52 promoter was combined with the atp9 mitochondrial targeting signal to genetically transform tobacco with the maize T CMS sterile gene URF-13, resulting in a sterile phenotype [21]. The MTS of coxIV was fused to the 5’ end of the sterility gene orf147 of pigeonpea A4 CMS, which was driven by the AP3 gene promoter, resulting in sterile phenotypes in transgenic Arabidopsis and tobacco plants [22]. Similarly, infertility transgenic Arabidopsis plants were successfully obtained by integrating the rapeseed hau CMS sterility gene orf288 with the MTS of Rfp under the control of the 35S promoter [23]. With the advancement of gene editing technologies, recent applications involving mitochondria-targeted transcription activator-like effector nucleases (mito-TALENs) have enabled targeted knockout of orf79 in rice (BTA CMS) and orf125 in rapeseed (Kosena CMS), resulting in plants with restored fertility, which offers a novel method for exploring the functions of mitochondrial sterility genes [24]. However, the construction process of mito-TALENs vectors is complex, making it difficult for general laboratories to master this technology. Meanwhile, the simpler and more efficient CRISPR-Cas9 technology has not yet achieved a breakthrough in plant mitochondrial gene editing [25,26]. Therefore, traditional transgenic technology remains the main method for verifying mitochondrial gene functions.
Radish (Raphanus sativus L.) is an essential crop of the Brassicaceae family, which can be used as a vegetable, oil crop, and cover plant [27]. As a typical cross-pollinated plant, it demonstrates significant heterosis. Utilizing cytoplasmic male sterility to produce commercial F1 hybrids is the main approach for hybrid variety breeding [27]. In 1968, Japanese researchers first discovered Ogura CMS in radish [28]. Subsequently, this cytoplasm type was transferred into other Brassicaceous crops through crossing or cell fusion, becoming the most extensively studied and widely applied CMS in Brassicaceous crops [29]. By comparing the differences in mitochondrial transcripts between the sterile line and fertility-reverted somatic hybrids of Ogura CMS in Brassica napus, the sterile gene orf138 was identified [30,31]. The ORF138 protein has a transmembrane domain that acts on the inner membrane of mitochondria, which exerts cytotoxicity, leading to energy deficiency in pollen development and causing sterility [32,33]. Mitochondrial genome sequencing later revealed extensive recombination in Ogura CMS, with orf138 at the edge of the largest unique sequences [34]. In 2005, Nahm et al. discovered NWB CMS, which completely differs from Ogura CMS, with some visible non-functional pollen. Although 58 breeding lines from various countries were crossed with the NWB CMS, no restorer line was detected [35]. More recently, another new radish CMS designated as Dongbu cytoplasmic and for genic male sterility (DCGMS) introduced from Uzbekistan was found. The DCGMS showed a phenotype similar to that of NWB CMS. NWB CMS-specific molecular marker bands can be amplified in almost all radish germplasms, including DCGMS, speculating that NWB CMS and DCGMS might be the same type [36]. The DCGMS mitochondrial genome sequencing uncovered a chimeric gene, orf463, which may be a candidate gene for its sterility. This gene has significant characteristics of CMS genes, located in a unique sequence region, comprising a chimera of 128 bp partial sequences of the coxI gene and 1261 bp of unknown sequences, encoding 12 transmembrane structural proteins [37]. Yamagishi et al. found that the orf463 is present in black radishes, and identified that the DCGMS mitotype coexists with the black radish mitotype in a sub-stoichiometric ratio [38]. Subsequently, researchers discovered that the mitochondrial genome structure of NWB CMS in YB-A is completely consistent with the Japanese black radish, and DCGMS is a repeat sequence-mediated allelic isomer. Another coexisting isomeric form was confirmed in YB-A, but it failed to assemble this mitochondrial genome structure successfully [39]. The expression level of the NWB CMS sterility gene orf463a in sterile buds is significantly higher, and sterile plants can be obtained using fertile strains containing the orf463a as the female parent crossed with normal cytoplasm, indirectly proving that orf463a is the candidate gene for sterility in NWB CMS [38,39,40]. However, there is still no direct evidence that the gene causes male infertility.
To analyze the differences in the mitochondrial genome configurations of radish NWB CMS under various nuclear genotypes, this study re-sequenced the radish NWB CMS mitochondrial genome. This was achieved by combining Illumina and PacBio sequencing technologies, successfully assembling the presumed isomeric form previously identified by Wang et al. [39]. Furthermore, by employing genetic transformation techniques to introduce the sterility gene orf463a into Arabidopsis, plants exhibiting the sterility phenotype were successfully produced, providing direct evidence that orf463a is capable of inducing cytoplasmic male sterility. These studies will lay the groundwork for further analysis of the cytoplasmic male sterility mechanism and the nucleo-cytoplasmic interaction relationship in radish NWB CMS.
2. Results
2.1. Mitochondrial Genomes Composition of Tibet A and Tibet B
Utilizing Illumina HiSeq and PacBio sequencing technologies, both the mitochondrial genomes of NWB CMS sterile line Tibet A and the maintainer line Tibet B were successfully assembled into circular sequences with sizes of 239,184 bp (NCBI No.OM867576) and 258,440 bp (NCBI No.OM867577), respectively. The GC contents of Tibet A and Tibet B genomes were 45.14% and 45.20%, respectively, aligning closely with other Brassicaceae crops. The Tibet A mitochondrial genome is 19,256 bp smaller than Tibet B, with the primary differences attributed to variations in intergenic regions and repeat sequences (Table 1).

Table 1.
Mitochondrial genome composition of Tibet A and Tibet B.
Both Tibet A and B mitochondrial genomes contain 33 protein-coding genes, 3 rRNA genes, and 16 types of tRNA genes (Figure 1, Table S1). Among the 33 conserved protein-coding genes, 18 are associated with the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis, comprising nine Complex I genes (nad1, nad2, nad3, nad4, nad4L, nad5, nad6, nad7, and nad9), one Complex III gene (cob), three Complex IV genes (cox1, cox2, and cox3), and five Complex V genes (atp1, atp4, atp6, atp8, and atp9). Additionally, five genes are related to the biogenesis of cytochrome C (ccmFC, ccmFN1, ccmFN2, ccmB, and ccmC), eight genes encode ribosomal protein (rpl2, rpl5, rpl16, rps3, rps4, rps7, rps12, and rps14), and the remaining two encode maturase (matR) and orfX (tatc). Both mitochondrial genomes of Tibet A and Tibet B have two copies of atp9, and compared to Tibet A, there is variation causing non-synonymous mutation (from valine to isoleucine) at the 22nd amino acid position between two atp9 genes, which is consistent with the difference within the DCGMS mitotype and NWB CMS YB-A mitotype [37,39], while the sequences of two atp9 genes in Tibet B mitotype are entirely identical.
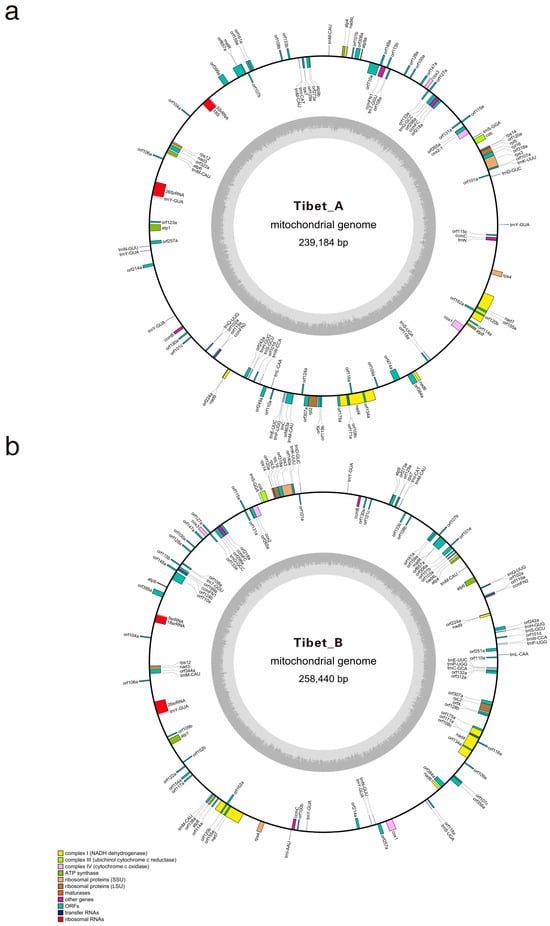
Figure 1.
Organization of the mitochondrial genomes of NWB CMS sterile-line Tibet A (a) and maintainer line Tibet B (b). Genes on the forward and reverse stands are depicted on the circle’s outside and inside, respectively. The two gray layers represent the GC content in the mitochondrial genome.
2.2. Screening for Genes Responsible for Male Sterility in Tibet A Mitogenome
To identify genes associated with CMS, the mitochondrial genomes of Tibet A and Tibet B were compared to detect mutations in 33 protein-coding genes, and the specific ORFs were also analyzed. We detected nine SNPs in eight protein-coding genes between the mitochondrial genomes of Tibet A and Tibet B, which led to amino acid changes at all eight sites, and one gene showed an indel mutation (Table 2). These variation sites are confirmed to be generally present in the mitochondrial genomes of radishes and are unrelated to male sterility [34,37,39,41].

Table 2.
Sequence variations between Tibet A and Tibet B mitochondrial genes encoding known proteins.
Additionally, we used the ORF Finder software to scan for orfs (≥300 bp) within the mitochondrial genomes of the NWB CMS sterile line Tibet A and the maintainer line Tibet B. A total of 62 and 73 orfs of unknown function were detected in Tibet A and Tibet B, respectively, with 11 being specific to Tibet A (Table 3). Further sequence feature analysis on the particular orfs in the Tibet A mitogenome identified six orfs (orf119C, orf123a, orf261a, orf322a, orf381a, orf463a) that could encode transmembrane proteins. Among them, orf463a, which encodes 12 transmembrane domains, is located in a unique region of the Tibet A mitochondrial genome and shares a 128 bp homologous sequence with coxI. orf463a possesses the typical characteristics of a sterility gene, making it a candidate sterility gene for Tibet A (Figure S1). The sequence comparison indicated that the orf463a is identical to the previously reported DCGMS sterility gene orf463, as well as the sterility gene orf463a associated with NWB-CMS YB-A.

Table 3.
Features of unique orf genes in Tibet A.
Analyzing the specific ORFs of the maintainer line Tibet B, we found that its orf138a is homologous to orf138 in Ogura CMS. It differs by five SNPs from the Type A orf138 sequence in the mitochondrial genome AB694744.1 [34], with non-synonymous mutations occurring at positions 391 and 392 (from arginine to glutamic) and position 394 (from leucine to valine) (Figure S2). The results showed that orf138a differed from the reported nine types (Type A→I) of orf138 sequences [42], hence it was named Type J. The maintainer line Tibet B is fertile. When used as the female parent in crosses with Ogura CMS maintainer lines, it yielded a fully fertile F2 generation, indicating that it contains multiple pairs of homozygous restorer genes, or that the variant of orf138 does not cause cytoplasmic male sterility.
2.3. Explores the Relationship among the Three Mitogenomes of Tibet A, NWB YB-A, and DCGMS
Previous research discovered that the mitochondrial genome of NWB CMS YB-A (GenBank No.MN056360) was an isomeric form of DCGMS mitogenome (GenBank No.KC193578), and coexisted with another mitochondrial genome structure in YB-A mtDNA [39]. To further clarify the relationship among the three mitogenomes of Tibet A, YB-A, and DCGMS, we analyzed the similarities in syntenic sequences, using the Tibet A sequences as a reference. The comparative analysis found that the three mitochondrial sequences are almost the same, containing a small number of SNPs and indels that may be caused by sequencing bias. However, the organization of the three mitochondrial genomes is different: the mitogenome of Tibet A only has one inverted region of 93,573 bp compared to YB-A, and it exhibits one inversion and one translocation + inversion compared to KC193578 (Figure 2).
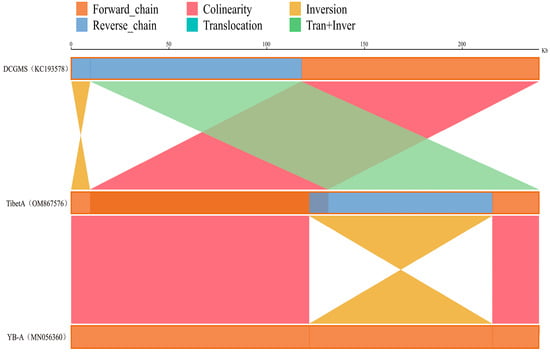
Figure 2.
Analysis of syntenic sequences among the DCGMS (KC193578), NWB CMS YB-A (MN056360), and Tibet A lines. The three parallel bars represent the mitochondrial genomes. Dark-orange and blue regions in each bar represent the forward and reverse directions of the aligned genome, respectively. Lines between the two bars indicate the synteny types and locations as follows: deep-pink, dark-yellow, and light-green represent collinearity, inversion, and translocation + inversion, respectively.
Further analysis revealed that ‘active’ recombination events mediated by a 508 bp short repeat sequence and a 9731 bp long repeat sequence led to multipartite configurations (Figure 3a). The NWB CMS YB-A mitochondrial genome exhibited a tricircular organization, comprising a master circle (MC1) and two subgenomic circles, SC1 and SC2. These subgenomic circles are derived from recombination events involving a 508 bp short repeat sequence. Through inverse recombination at this short repeat sequence, SC1 and SC2 could merge to create another master circle (MC2) sequenced in this study. Similarly, MC2 has the potential to spawn subgenomes S3 and S4 by undergoing recombination at a 9731 bp long repeat sequence. Finally, S3 and S4 could engage in recombination, forming another master circle, MC3 (reportedly the form in the DCGMS mitochondrial genome). To verify all of the genomic organizations, we completed PCR amplifications with primers binding to the recombination breakpoints designed by Wang et al. [39]. The PCR data confirmed that three master circles and four subgenomic circles exist within Tibet A mtDNA (Figure 3b). Furthermore, to overcome the limitations of PCR-based detection of recombination events, we propose the ratio of recombinants using some specific long reads obtained through PacBio sequencing (Figure 3c). Our result indicated that three isoforms of the mitogenome coexist in Tibet A mtDNA. However, only MC2 could be assembled into a circle form.
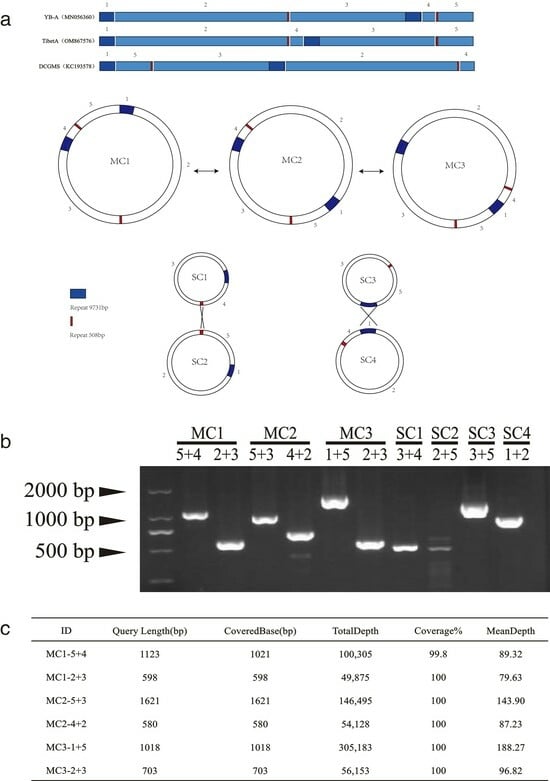
Figure 3.
(a) Schematic diagram presenting the five syntenic blocks among the DCGMS, NWB CMS YB-A, and TibetA mitochondrial genomes, the three convertible master circles (MC), and the combinable subgenomic circles (SC). Cross lines between SC1 and SC2 and between SC3 and SC4 indicate the recombination locations. The filled boxes represent repeat sequences. (b) PCR-amplified products with primers annealing to sequence blocks around the junctions. (c) The PacBio sequencing data for the sequence of MC1(5 + 4)/MC1(2 + 3)/MC2(5 +3)/MC2(4 + 2)/MC3(1 + 5)/MC3(2 + 3) amplification.
2.4. Expression of orf463a in Arabidopsis Severely Affects the Development of Floral Organs
To verify whether the candidate gene orf463a can cause male abortion, we designed four over expression vectors for the genetic transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana (Figure 4a). The V35S and VAP3-1 constructs contained the 35S and AP3 promoters, respectively, carrying orf463a fused with the mitochondrial targeting sequence of the yeast nuclear coxIV gene. To assess whether orf463a retains functionality without a mitochondrial targeting peptide, a VAP3-2 vector was constructed without the coxIV pre-sequences, in which the orf463a was driven by the AP3 promoter. The VAP3-CK vector, with the β-glucuronidase (GUS) gene driven by the AP3 promoter, was transformed into the plants as a control.
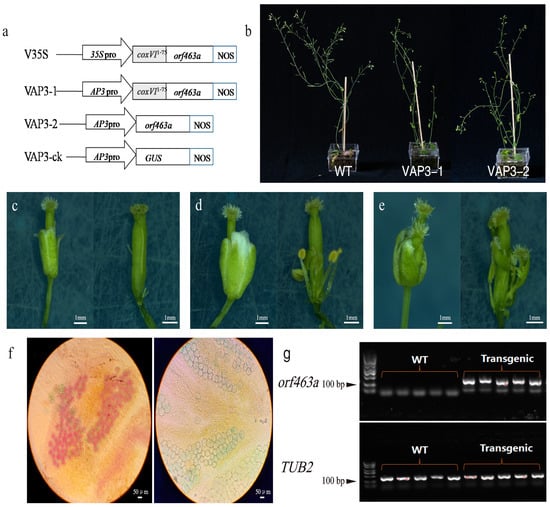
Figure 4.
(a) Vectors for genetic transformation of Arabidopsis. (b–e) Sterile phenotypic characteristics resulting from the genetic transformation of Arabidopsis via vectors VAP3-1 or VAP3-2. (f) Alexander staining of wild-type Arabidopsis anthers (left) and petal-deficient abortion anthers (right). (g) Expression analysis of orf463a in transgenic Arabidopsis plants.
A total of 85 T1 generation positive plants were obtained from the genetic transformation of the four vectors (Table S2 and Figure S3). Only plants transformed with vectors VAP3-1 and VAP3-2 could induce the male abortion phenotype (Figure 4b). Further observation of the male sterile flowers in Arabidopsis revealed differences in phenotypes compared to radish NWB CMS and DCGMS [35,36]. The characteristics of sterile floral organs in Arabidopsis could be classified into three types: First, petal-less abortion, where the petals completely degenerated, leaving one–two very thin filaments visible after the sepals were pulled apart and no stamens (Figure 4c). Second, petal-deficient abortion, where the petals vary in length and number from normal flowers, with stamen filaments shortened, a reduced number of stamens, and some anthers degenerated, while non-degenerated anthers carried pollen (Figure 4d). Third, petal-like stamen abortion, where the morphology of the stamen turned petal-like, and the tips contained papillae similar to that found on the stigma (Figure 4e). Notably, these three types of flowering abnormalities can be observed in VAP3-1 or VAP3-2 transgenic progeny, and often, all three phenotypes are present in the same plant. Alexander’s staining was used to stain the anthers of wild-type Arabidopsis and the petal-deficient abortion. The pollen in the chambers of the wild-type anthers could be stained red, while the pollen within the incomplete petal stamens could not be stained red, indicating that the pollen was not viable (Figure 4f). Subsequently, the pollen from the petal-deficient anthers were used to pollinate transgenic sterile plants, which did not produce seeds, proving that the pollen is abortive. Meanwhile, two sterile T1 plants transformed with the VAP3-1 and VAP3-2 vectors were randomly selected and crossbred with wild-type pollen. All T2 progeny exhibited a male sterile phenotype, indicating that the male sterility phenotype was inheritable. RT-PCR analysis was performed to examine the expression of the chimeric gene in the transgenic plants. The results showed that orf463a is ectopically expressed in transgenic sterile plants (Figure 4g). All results demonstrated that orf463a can cause sterility in transgenic Arabidopsis plants driven by the AP3 promoter, and the mitochondrial targeting signal is not necessary. The N-terminal sequence of ORF463a was predicted by iPSORT to contain a mitochondrial targeting peptide “https://ipsort.hgc.jp/ (accessed on 26 January 2024)”, while SingnalP3.0 analysis suggested that the N-terminal sequence of ORF463a might be a signal anchor peptide (signal anchor probability: 0.937). Therefore, orf463a itself may possess a mitochondrial targeting function, which could satisfactorily account for its ability to affect the development of floral organs in trans-genic Arabidopsis thaliana, even without a mitochondrial targeting sequence.
3. Discussion
3.1. The Mitochondrial Genomes of Tibet A and NWB CMS YB-A and DCGMS Are Coexisting Isoforms of the Same Mitotype
Plant mitochondrial genomes commonly contain a large number of repeat sequences, ranging in size from 20 bp to 140 kbp. These repeat sequences play a vital role in the recombination process of mitochondrial genomes [43]. Repeat sequences can mediate homologous recombination or rearrangement, leading to the formation of subgenomic structures or isomers. This can result in heterogeneity of the mitochondrial genome, allowing different substoichiometric mitochondrial genomes to coexist, which is related to the evolution of the mitochondrial genome [44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. Multipartite structures of mtDNA have been commonly observed in many plant species. For example, the tobacco mitochondrial genome demonstrates a complex arrangement, characterized by two isomeric master circles along with six subgenomic circles [51]. In radish, the mitochondrial genome also exhibits the coexistence of multiple types. Park et al. confirmed another configuration of Ogura CMS, which compared with the Ogura CMS mitochondrial genome reported by Tanaka et al., had an 80 kb sequence inverted. This recombination, mediated by a 311 bp short repeat sequence, resulted in the creation of two subgenomes. The merging of these two subgenomes with two possible orientations produced these two isomeric master circles. PCR results confirmed that all multipartite structures coexist within the same mtDNA [37]. In this study, we discovered that Tibet B is a new type of Ogura CMS, designated as Type J, based on the differences in the orf138 sequences [42]. We analyzed the similarities in syntenic sequences with the Ogura CMS Type A mitochondrial genome (Genbank: NO.AB694744.1) and the Type F Ogura CMS sequenced by Japanese researchers (Genbank: NO.AP018472.1). A high degree of collinearity was observed between the Type J mitogenome and Type A mitogenome, reaching 100%, whereas an approximate 88kb inversion was detected between Type J and Type F (Figure S4). The inversion was mediated by a 443 bp repeat sequence, and it remains uncertain whether these two mitochondrial genomes coexist within Tibet B mtDNA. Similarly, Wang et al. previously confirmed the existence of three master circular mitogenomes in NWB CMS YB-A mtDNA: the YB-A mitogenome, the DCGMS mitogenome, and another new mitochondrial haplotype. Nevertheless, attempts to assemble this novel mitochondrial haplotype were unsuccessful [39]. In our study, we successfully sequenced and assembled the mitochondrial genome of Tibet A, identifying it as the previously uncharacterized mitotype within the NWB CMS YB-A mtDNA, as anticipated by Wang et al. [39]. The mitochondrial genome sequences of Tibet A showed great similarity to those of the NWB CMS YB-A and DCGMS lines, with only minor variations such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions or deletions (indels), likely resulting from sequencing artifacts. Notably, the Tibet A mitochondrial genome undergoes recombination through a 508 bp short repeat sequence, thereby establishing the NWB CMS YB-A mitochondrial configuration. Moreover, it possesses the potential to evolve into the DCGMS mitochondrial configuration via a 9731 bp long repeat sequence. Subsequent verification using both PCR and PacBio sequencing data confirmed the coexistence of these three mitochondrial genomes within the Tibet A mtDNA.
3.2. Genetic Transformation Confirms That orf463a Is the Functional Gene Controlling Pollen Abortion in NWB CMS
Genetic transformation is one of the most direct ways to verify gene function [52]. Most successful cases of genetic transformation of CMS sterility genes are achieved by fusing an MTS at the front of the candidate gene driven by the promoter of an anther-specific expression gene (such as AP3, TA29, Lat52). Among them, the promoter of AP3 is commonly used and has been successful in the transgenic verification of sterility genes in multiple crops, such as the beet I-12 CMS sterility gene orf129 in tobacco, the rapeseed hau CMS sterility gene orf288 in Arabidopsis, and the pigeonpea A4 CMS sterility gene orf147 in both Arabidopsis and tobacco, all resulting in sterile phenotypes [12,22,23]. In this study, genetic transformation vectors were constructed using the 35S and AP3 promoters. It was found that positive Arabidopsis plants transformed with orf463a using the AP3 promoter with or without the MTS of coxIV could obtain male sterile phenotypes. Using iPSORT and Sing-nalP3.0 software, it was found that the N-terminal sequence of ORF463a may be a mitochondrial targeting signal peptide, which indicated that the anther-specific promoter was necessary for the expression of orf463a. The sterile phenotypes of transgenic Arabidopsis plants were different from those of radishes [35,36], with three different characteristics: petal-less, petal-deficient, and stamen–carpel conversion. The sterility gene may not only affect the development of stamens but also significantly influence petal development. A similar phenomenon was observed in the transformation of the rapeseed hau CMS sterility gene orf288 into Arabidopsis, but the specific reasons still require further study [53].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
We collected a local variety called “Tibet Radish” from the Tibet region in China, which has a purplish–red skin, white flesh, and an inverted long conical shape. The hybrid radish variety “CR301” was purchased from the Beijing Shinong Seed Co. (Beijing, China) (i.e., subsidiary of NongWoo Bio Co., Suwon-si, Republic of Korea) and confirmed to be NWB CMS through the NWB-specific molecular marker designed by Nahm et al. in 2005 [35]. Using “Tibet Radish” as the male parent and “CR301” as the female parent, we have developed, through six generations of backcrossing and self-fertilization, the corresponding NWB CMS sterile line (named Tibet A) and the maintainer line (named Tibet B), for the purpose of mitochondrial genome sequencing (Figure S5).
4.2. Mitochondrial DNA Extraction, Sequence, and Genome Assembly
Mitochondrial DNA was isolated from approximately 5 g etiolated seedlings, according to the instructions of the plant mitochondrial DNA extraction kit (GMS20023.7, GENMED SCIENTIFICS INC, Shanghai, China). Mitochondrial DNA quality was assessed using Qubit 3.0 and NanoDrop2000. A combination of short-read (Illumina HiSeq 4000, San Diego, CA, USA) and long-read sequencing (PacBio Sequel II) technologies was employed to acquire the full-length mitochondrial genome sequence. Initially, around 1 μg of homozygous and fragmented mitochondrial DNA underwent short insert library construction following the NEBNext® Ultra™ DNALibrary Prep Kit for Illumina®instructions (New England Biolabs, MA, USA). The library underwent sequencing using an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 with a 150 bp paired-end read length (BIOZERON Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). Then, following the instructions of the PacBio Express Template Prep Kit 2.0 (PacBio, Menlo Park, CA, USA), approximately 5 μg of high-quality mitochondrial DNA was prepared using BluePippin size selection from Sage Science and sequenced on the Sequel II system. Furthermore, data processing involved the removal of Illumina raw reads containing adapters, possessing a quality score below 20 (Q < 20), or containing ≥10% undetermined bases and duplicate reads. The short fragments were reassembled utilizing GetOrganelle v1.6.4 and compared with mitochondrial protein-coding genes in the plant mitochondrial genome database “https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/release/mitochondrion/ (accessed on 23 August 2023)”. Subsequently, Pacbio long reads were mapped to the potential mitochondrial contigs using BLASR v5.1 [54]. Lastly, putative long mitochondrial reads were assembled using Canu v2.1.1 [55].
4.3. Gene Annotation
Mitochondrial genes were annotated based on the sequence homology alignment. The encoded proteins were annotated utilizing the online prediction tool GeSeq [56]. Additionally, tRNA and rRNA in the genome were predicted using tRNAscan-SE and rRNAmmer [57,58]. Scanning for whole-genome ORFs in plant mitochondria was accomplished through the ORFFinder “http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html (accessed on 25 August 2023)”. OrganellarGenomeDRAW software (version 1.2) was used to draw the mitochondrial genome maps [59].
4.4. Prediction of Transmembrane Domains and Comparative Analysis of Radish Mitochondrial Genomes
The transmembrane domain-encoding sequences in the orf gene were predicted using the TMHMM server version 2.0 [60]. Repeat sequence analysis was conducted using REPuter software “http://bibiserv.techfak.uni-bielefeld.de/reputer/ (accessed on 26 August 2023)”. MUMmer (version 3.23) and LASTZ (version 1.03.54) analyzed the collinearity between radish mitochondrial genomes. Additionally, SNPs were identified with MUMmer and BLAT (version 35), whereas indels were detected using LASTZ (version 1.03.54), BWA, and SAMtools. To identify the fragments originating from the chloroplast sequence in the mitochondrial genome, BLASTN was used to align the radish mitochondrial genome to the radish chloroplast genome (NCBI No.NC_024469.1), with parameters set as the e-value of 1 × 10−5, and length of ≥100 bp.
4.5. Detection of Mitochondrial Genome Isoforms
PCR was employed to identify mitochondrial genome isoforms within Tibet A mi-tochondrial DNA (mtDNA) using 10 pairs of primers designed by Wang et al. [36]. Radish leaf DNA extraction was carried out according to the instructions of the plant genomic DNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The PCR reaction consisted of 25 μL, comprising 40 ng DNA, 2.5 μL of 10× Taq Plus Buffer (containing Mg2+), 2 μL of 2.5 mM Super pure dNTPs, 0.5 μL of each of 10 μM forward and re-verse primers, 0.5 μL of 2.5 U/μL Taq Plus, with ddH2O added of up to 25 μL. The PCR program was as follows: 94 °C for 5 min; 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 56 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 1 min; 72 °C for 10 min. The amplified PCR products were examined with electrophoresis on a 1.5% agarose gel. The correct product was sequenced by Tsingke-BioTec, Beijing, China.
4.6. Vector Construction and Genetic Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana
The vectors employed in this study encompass PMD18-T and pCAMBIA2300. PMD18-T serves as a TA cloning vector, facilitating the integration and subsequent sequencing of exogenous DNA fragments, while pCAMBIA2300 is utilized for the insertion of target fragments, enabling genetic transformation in Arabidopsis. The experimental strains included the Escherichia coli host strain DH5α, the yeast strain Y187, and the Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101. Specifically, E. coli DH5α was leveraged for plasmid amplification, the yeast strain Y187 for the amplification of mitochondrial targeting signal sequences, and the A. tumefaciens strain GV3101 for conducting genetic transformation experiments in Arabidopsis.
The construction of genetic transformation vectors followed the methodology described by Jing et al. [53], which involves constructing vectors harboring the Arabidopsis thaliana another specific gene APETAL3 (AP3) promoter (ranging from −1 to −867 bp) and the Cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter [50]. Mitochondrial localization sequences (1 to 75 bp), derived from coxIV (the mitochondrial transit peptide of cytochrome oxidase subunit IV from yeast), along with the coding frame of orf463a, were amplified using primers coxVIF, T-463aF, and 463aL. These components were subsequently fused via overlapping extension PCR. Vectors lacking the mitochondrial targeting sequence were also constructed for comparative purposes. All PCR products were cloned into the pCAMBIA2300 vector, with the employed primers detailed in Supplementary Table S3.
Arabidopsis thaliana Columbia ecotype served as the biological material for this study. Genetic transformation was executed using an optimized floral dip method, as previously enhanced by Clough and Bent [61]. Post-transformation, Arabidopsis seeds were sown on medium supplemented with Basta, aiding the selection of transformants. Positive T1 plants were verified through PCR analysis utilizing specific primers, the sequences of which are enumerated in Supplementary Table S3.
4.7. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from flower buds of Arabidopsis thaliana transgenic positive plants. The extraction process was performed according to the protocol provided by the RNAprep Pure Plant Total RNA Extraction Kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The concentration and quality of the total RNA were assessed using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer and 1% non-denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis, respectively. Following this, cDNA was synthesized from 2 μg of total RNA using the FastKing RT Kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). To detect the expression of orf463a in transgenic Arabidopsis sterile strains, RT-PCR was conducted with the TUB2 gene serving as an internal control. The primers used for RT-PCR are listed in Table S3. The amplification conditions were as follows: an initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min; followed by 30 cycles of 98 °C for 10 s, 55 °C for 15 s, and 72 °C for 2 min; with a final extension step at 72 °C for 10 min.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a novel isomeric form of NWB CMS line in radish was unveiled through re-sequencing its mitochondrial genome. We confirmed that orf463a serves as the candidate sterility gene for NWB CMS. The mitochondrial genomes of Tibet A, NWB CMS YB-A, and DCGMS were identified as co-existing isomers, all belonging to the same mitotype. It was established that orf463a can cause male sterility in transgenic Arabidopsis driven by the AP3 promoter without a mitochondrial targeting signal (MTS).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/horticulturae10040395/s1. Figure S1: The feature ofsterility candidate gene orf463a. (a) Transmembrane domains. (b) Alignment with coxI gene. Figure S2: Alignment of the base (a) and amino acid sequence (b) between 0gura CMS Type A-orf138 and Tibet B-orf138 (Type J). Figure S3: PCR amplification of transgenic Arabidopsis positive plants. Figure S4: (a) Analysis of syntenic sequences among the 0gura CMS(AB694744.1), Kosena (AP018472.1), and Tibet B lines. (b) Schematic diagram presenting the five syntenic blocks among Ogura CMS (AB694744.1), Kosena (AP018472.1), and Tibet B lines. The two convertible master circles (MC), and the combinable subgenomic circles (SC). Figure S5: The breeding process of NWB CMS sterile line Tibet A and maintainer line Tibet B. Table S1: Types and number of tRNA. Table S2: Number of transgenic plants obtained with each constructs. Table S3: PCR and qRT-PCR primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L. and X.L.; methodology, X.L.; software, X.L. and L.L.; validation, J.R. and F.Y.; formal analysis, C.K.; investigation, X.L. and J.R.; resources, X.L. and X.Y.; data curation, X.L. and L.L.; writing, X.L.; supervision, H.L. and Y.T.; project administration, F.Y. and M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Key Project supported by the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U22A20494), the 1+9 Open Competition Project of Sichuan Academy of Agricultural Sciences (1+9KJGG002), the Natural Science Foundation of Sichuan province (2023NSFSC1241), the Independent Innovation of Sichuan province (2022CCZX067) and the 14th Five-Year Plan Vegetable Breeding Project of Sichuan province (2021YFYZ0022).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article and Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Laser, K.D.; Lersten, N.R. Anatomy and cytology of microsporogenesis in cytoplasmic male sterile angiosperms. Bot. Rev. 1972, 38, 425–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levings, C.S.; Pring, D.R. Restriction endonuclease analysis of mitochondrial DNA from normal and Texas cytoplasmic male-sterile maize. Science 1976, 193, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, M.R.; Bentolila, S. Interactions of mitochondrial and nuclear genes that affect male gametophyte development. Plant Cell 2004, 16, S154–S169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, R.; Gupta, K.J.; Colombo, N. Mitochondrion role in molecular basis of cytoplasmic male sterility. Mitochondrion 2014, 19, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohra, A.; Jha, U.C.; Adhimoolam, P.; Bisht, P.; Singh, N.P. Cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) in hybrid breeding in field crops. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 967–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.W.; Xie, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Chen, L.T. Advances in understanding the molecular mechanisms of cytoplasmic male sterility and restoration in rice. Plant Reprod. 2017, 30, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D.B. Molecular control of male fertility for hybrid breeding. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Dey, S.S.; Bhatia, R.; Kumar, R.; Behera, T.K. Current understanding of male sterility systems in vegetable Brassicas and their exploitation in hybrid breeding. Plant Reprod. 2019, 32, 231–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.Y.; Yang, X.D.; Zhao, N.; Hu, Z.Y.; Mackenzie, S.A.; Zhang, M.Y.; Yang, J.H. Exploiting sterility and fertility variation in cytoplasmic male sterile vegetable crops. Hortic. Res. 2022, 9, uhab039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, R.E.; Timothy, D.H.; Levings, C.S. A mitochondrial protein associated with cytoplasmic male sterility in the T cytoplasm of maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 5374–5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Hedgcoth, C. A chimeric gene (orf256) is expressed as protein only in cytoplasmic male-sterile lines of wheat. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 26, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.P.; Shinada, H.; Onodera, Y.; Komaki, C.; Mikami, T.; Kubo, T. A male sterility-associated mitochondrial protein in wild beets causes pollen disruption in transgenic plants. Plant J. 2008, 54, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, P.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, Y.G. Discovery of mitochondrial chimeric-gene associated with cytoplasmic male sterility of HL-rice. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2002, 47, 744–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, K.; Kazama, T.; Motomura, K.; Toriyama, K. Whole genomic sequencing of RT98 mitochondria derived from Oryza rufipogon and northern blot analysis to uncover a cytoplasmic male sterility-associated gene. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Brown, G.G. Suppression of cytoplasmic male sterility by nuclear genes alters expression of a novel mitochondrial gene region. Plant Cell 1991, 3, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, M.; Kazama, T.; Murata, H.; Motomura, K.; Toriyama, K. Whole mitochondrial genome sequencing and transcriptional analysis to uncover an RT102-type cytoplasmic male sterility-associated candidate gene derived from Oryza rufipogon. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, Y.D.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, B.D.; Kang, B.C. Extensive structural variations between mitochondrial genomes of CMS and normal peppers (Capsicum annuum L.) revealed by complete nucleotide sequencing. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, S.F.; Mei, D.S.; Liu, J.; Zaman, Q.U.; Zhang, H.Y.; Hao, M.Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, H.; Cheng, H.T.; Hu, Q. Organelle genome composition and candidate gene identification for Nsa cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica napus. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.; Yang, T.J.; Kim, S. Identification of a gene responsible for cytoplasmic male-sterility in onions (Allium cepa L.) using comparative analysis of mitochondrial genome sequences of two recently diverged cytoplasms. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019; 132, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yin, Z.P.; Wu, X.M.; Li, C.C.; Xie, K.D.; Deng, X.X.; Grosser, J.W.; Guo, W.W. Assembly of Satsuma mandarin mitochondrial genome and identification of cytoplasmic male sterility-specific ORFs in a somatic cybrid of pummelo. Tree Genet. Genomes 2020, 16, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, V.; Kuriakose, B.; Sridhar, V.V.; Thomas, G. Transformation and analysis of tobacco plant var Petit havana with T-urf13 gene under anther-specific TA29 promoter. Biotech 2011, 1, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar-Mathur, P.; Gupta, R.; Reddy, P.S.; Reddy, B.P.; Reddy, D.S.; Sameerkumar, C.V.; Saxena, R.K.; Sharma, K.K. A novel mitochondrial orf147 causes cytoplasmic male sterility in pigeonpea by modulating aberrant anther dehiscence. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 97, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, S.; Gao, J.; Wei, C.; Chen, F.; Li, X.; Wen, J.; Yi, B.; Ma, C.; Tu, J.; Fu, T.; et al. Transcript levels of orf288 are associated with the hau cytoplasmic male sterility system and altered nuclear gene expression in Brassica juncea. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazama, T.; Okuno, M.; Watari, Y.; Yanase, S.; Koizuka, C.; Tsuruta, Y.; Sugaya, H.; Toyoda, A.; Itoh, T.; Tsutsumi, N.; et al. Curing cytoplasmic male sterility via TALEN-mediated mitochondrial genome editing. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Su, T.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, M. The development of mitochondrial gene editing tools and their possible roles in crop improvement for future agriculture. Adv. Genet. 2021, 3, 2100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, S.I.; Nakazato, I. Genome editing of plant mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 19, pcad162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, S.W.; Hatakeyama, K.; Takahata, Y. The use of genome information for intergeneric hybridization breeding. In The Radish Genome; Nishi, T., Kitashiba, H., Eds.; Springer Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 189–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ogura, H. Studies on the new male sterility in Japanese radish, with special reference to the utilization of this sterility towards the practical raising of hybrid seeds. Mem. Fac. Agric. Kagoshima Univ. 1968, 6, 39–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.G. Male sterility and fertility restoration in crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 579–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonhomme, S.; Budar, F.; Férault, M.; Pelletier, G. A 2.5 kb NcoI fragment of Ogura radish mitochondrial DNA is correlated with cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica cybrids. Curr. Genet. 1991, 19, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonhomme, S.; Budar, F.; Lancelin, D.; Small, I.; Defrance, M.C.; Pelletier, G. Sequence and transcript analysis of the Nco2.5 Ogura-specific fragment correlated with cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica cybrids. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1992; 235, 340–348. [Google Scholar]
- Grelon, M.; Budar, F.; Bonhomme, S.; Pelletier, G. Ogura cytoplasmic male-sterility (CMS)-associated orf138 is translated into a mitochondrial membrane polypeptide in male-sterile Brassica cybrids. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1994, 243, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duroc, Y.; Gaillard, C.; Hiard, S.; Defrance, M.C.; Pelletier, G.; Budar, F. Biochemical and functional characterization of ORF138, a mitochondrial protein responsible for Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassiceae. Biochimie 2005, 87, 1089–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Yasumoto, K.; Yamagishi, H.; Terachi, T. A complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Ogura-type male-sterile cytoplasm and its comparative analysis with that of normal cytoplasm in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahm, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, S.W.; Joo, G.Y.; Harn, C.H.; Yang, S.G.; Min, B.W. Development of a molecular marker specific to a novel CMS line in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005; 111, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.P.; Park, S.; Lim, C.; Kim, H.; Lim, H.; Ahn, Y.; Sung, S.K.; Yoon, M.K.; Kim, S. Discovery of a novel cytoplasmic male-sterility and its restorer lines in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008; 117, 905–913. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.Y.; Lee, Y.P.; Lee, J.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, S.; Yang, T.J. Complete mitochondrial genome sequence and identification of a candidate gene responsible for cytoplasmic male sterility in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) containing DCGMS cytoplasm. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013; 126, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Shiiba, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Fukunaga, A. Mitochondrial orf463 causing male sterility in radish is possessed by cultivars belonging to the ‘Niger’ group. Euphytica 2019, 215, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Hao, W.; Li, J.; Qi, M.; Zhang, L. Mitochondrial genome sequencing reveals orf463a may induce male sterility in NWB cytoplasm of radish. Genes 2020, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Fukunaga, A.; Terachi, T. Appearance of male sterile and black radishes in the progeny of cross between Raphanus raphanistrum and Raphanus sativus. Breed Sci. 2020, 70, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, H.; Terachi, T. Cytoplasmic male sterility and mitochondrial genome variations in radish. In The Radish Genome; Nishi, T., Kitashiba, H., Eds.; Springer Press: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 151–163. [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi, H.; Terachi, T. Intra- and inter-specific variations in the mitochondrial gene orf138 of Ogura-type male-sterile cytoplasm from Raphanus sativus and Raphaus raphanistrum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoop, V. Seed Plant Mitochondrial Genomes. In Complexity Evolving in Genomics of Chloroplasts and Mitochondria; Bock, R., Knoop, V., Eds.; Springer Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 175–200. [Google Scholar]
- Bellaoui, M.; Martin-Canadell, A.; Pelletier, G.; Budar, F. Low-copy-number molecules are produced by recombination, actively maintained and can be amplified in the mitochondrial genome of Brassicaceae: Relationship to reversion of the male sterile phenotype in some cybrids. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1998, 257, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta-Montiel, M.; Lyznik, A.; Woloszynska, M.; Janska, H.; Tohme, J.; Mackenzie, S. Tracing evolutionary and developmental implications of mitochondrial stoichiometric shifting in the common bean. Genetics 2001, 158, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualberto, J.M.; Newton, K.J. Plant Mitochondrial Genomes: Dynamics and mechanisms of mutation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2017, 68, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentolila, S.; Stefanov, S. A reevaluation of rice mitochondrial evolution based on the complete sequence of male-fertile and male-sterile mitochondrial genomes. Plant Physiol. 2012, 158, 996–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, N.; Kitagawa, K.; Takumi, S.; Nakamura, C. Mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in wheat, Aegilops and their nucleus-cytoplasm hybrids. Genetics 2002, 160, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guan, R.; Chang, S.; Du, T.; Zhang, H.; Xing, H. Substoichiometrically different mitotypes coexist in mitochondrial genomes of Brassica napus L. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Tsuda, M.; Yasumoto, K.; Terachi, T.; Yamagishi, H. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Brassica oleracea and analysis of coexisting mitotypes. Curr. Genet. 2014, 60, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, Y.; Watase, Y.; Nagase, M.; Makita, N.; Yagura, S.; Hirai, A.; Sugiura, M. The complete nucleotide sequence and multipartite organization of the tobacco mitochondrial genome: Comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in higher plants. Mol. Gen. Genome 2005, 272, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larosa, V.; Remacle, C. Transformation of the mitochondrial genome. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2013, 57, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, B.; Heng, S.P.; Tong, D.; Wan, Z.J.; Fu, T.D.; Tu, J.X.; Ma, C.Z.; Yi, B.; Wen, J.; Shen, J.X. A male sterility-associated cytotoxic protein ORF288 in Brassica juncea causes aborted pollen development. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antipov, D.; Korobeynikov, A.; McLean, J.S.; Pevzner, P.A. hybridSPAdes: An algorithm for hybrid assembly of short and long reads. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq-versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscanSE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Staerfeldt, H.H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohse, M.; Drechsel, O.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW): A tool for the easy generation of high-quality custom graphical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes. Curr. Genet. 2007, 52, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).