Synthetic Seed Production and Slow Growth Storage of In Vitro Cultured Plants of Iris pallida Lam.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
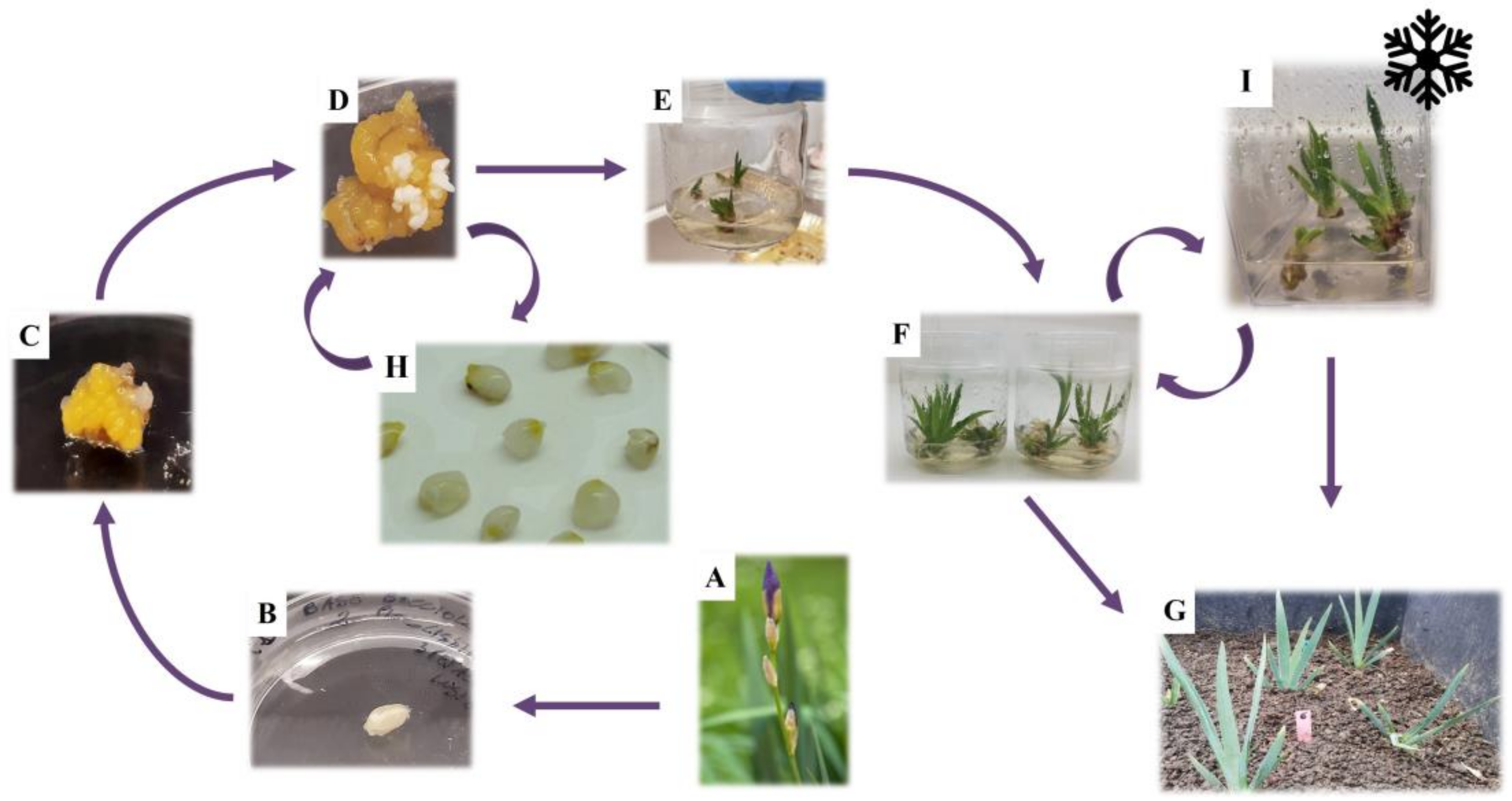
2.1. Induction of Somatic Embryos and Plantlet Regeneration
2.2. Slow Growth Storage (SGS)
Morphological and Biochemical Determinations
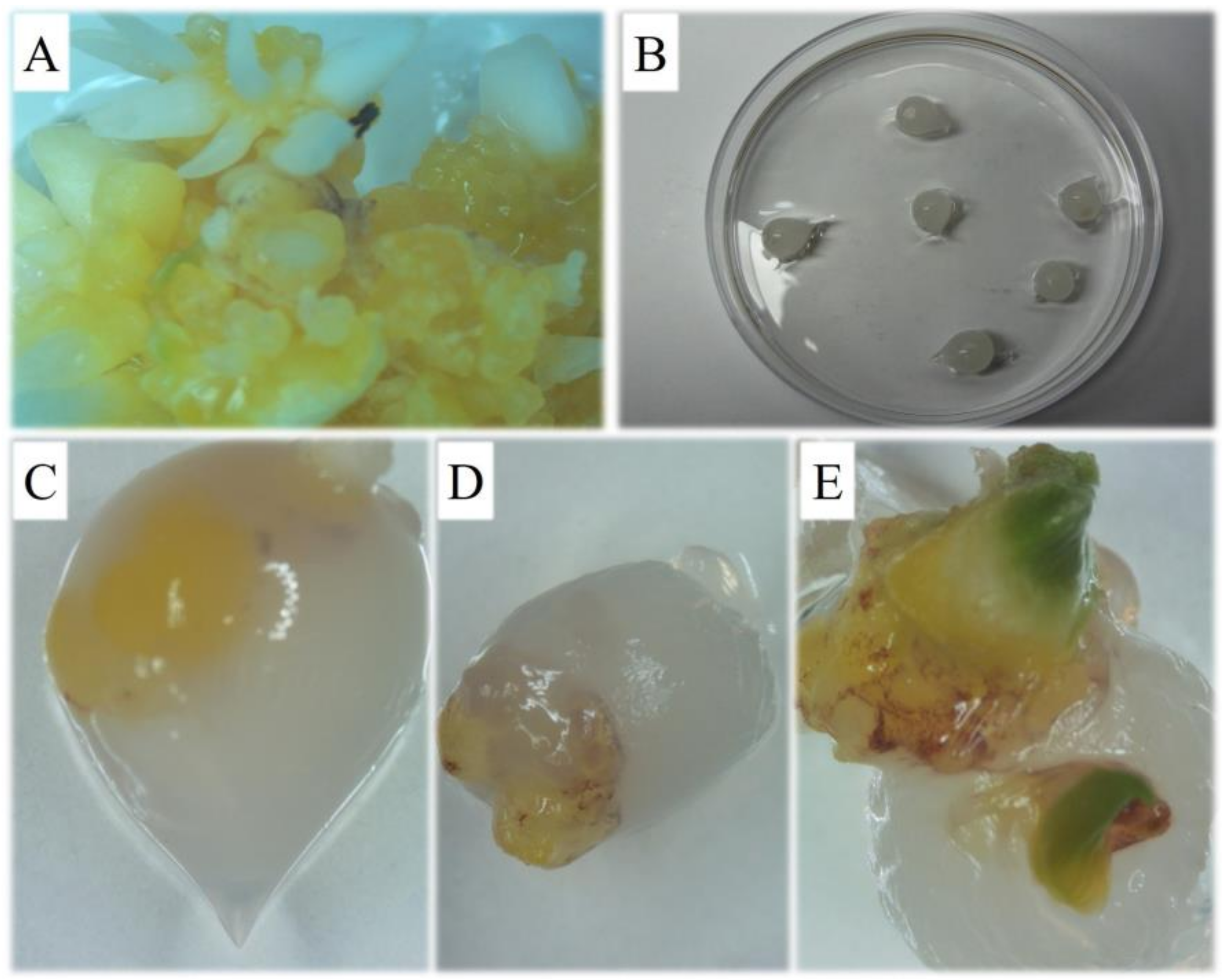
2.3. Synthetic Seeds Production and Storage
- (A)
- Fourteen days of storage at a cold temperature of 4 °C in a laboratory refrigerator;
- (B)
- Fourteen days of storage at a room temperature of 23 °C;
- (C)
- Twenty-eight days of storage at a cold temperature of 4 °C in a laboratory refrigerator;
- (D)
- Twenty-eight days of storage at a room temperature of 23 °C;
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
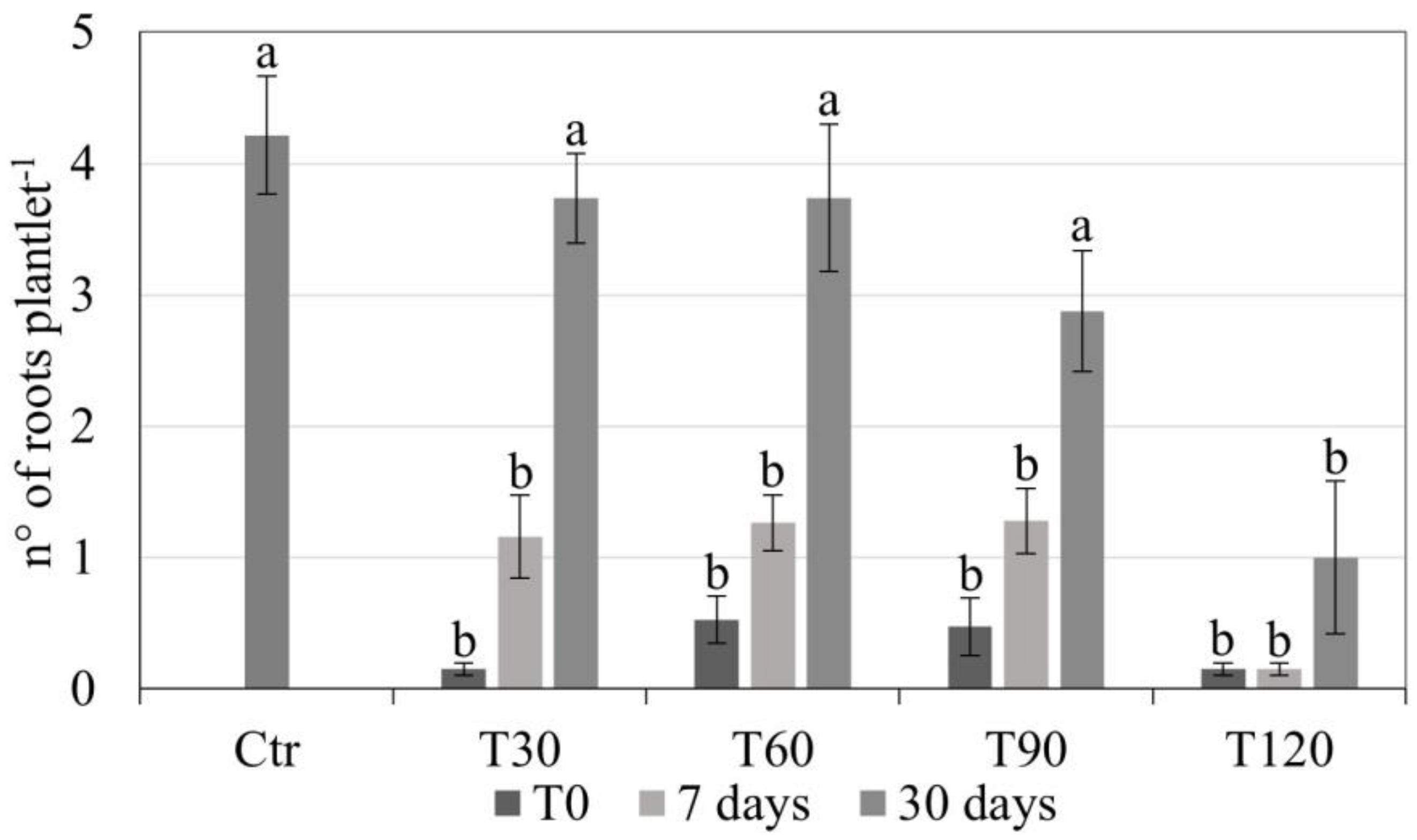
3.1. Slow Growth Storage (SGS)
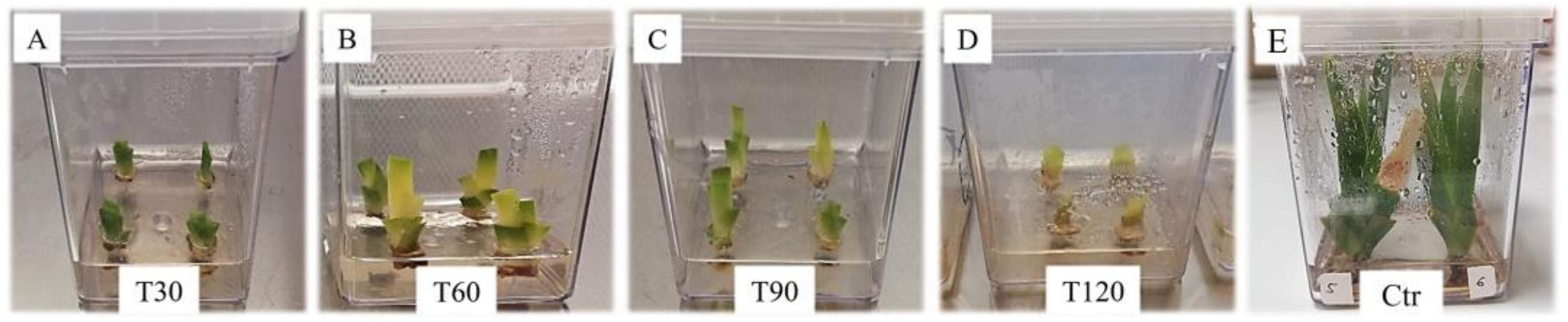
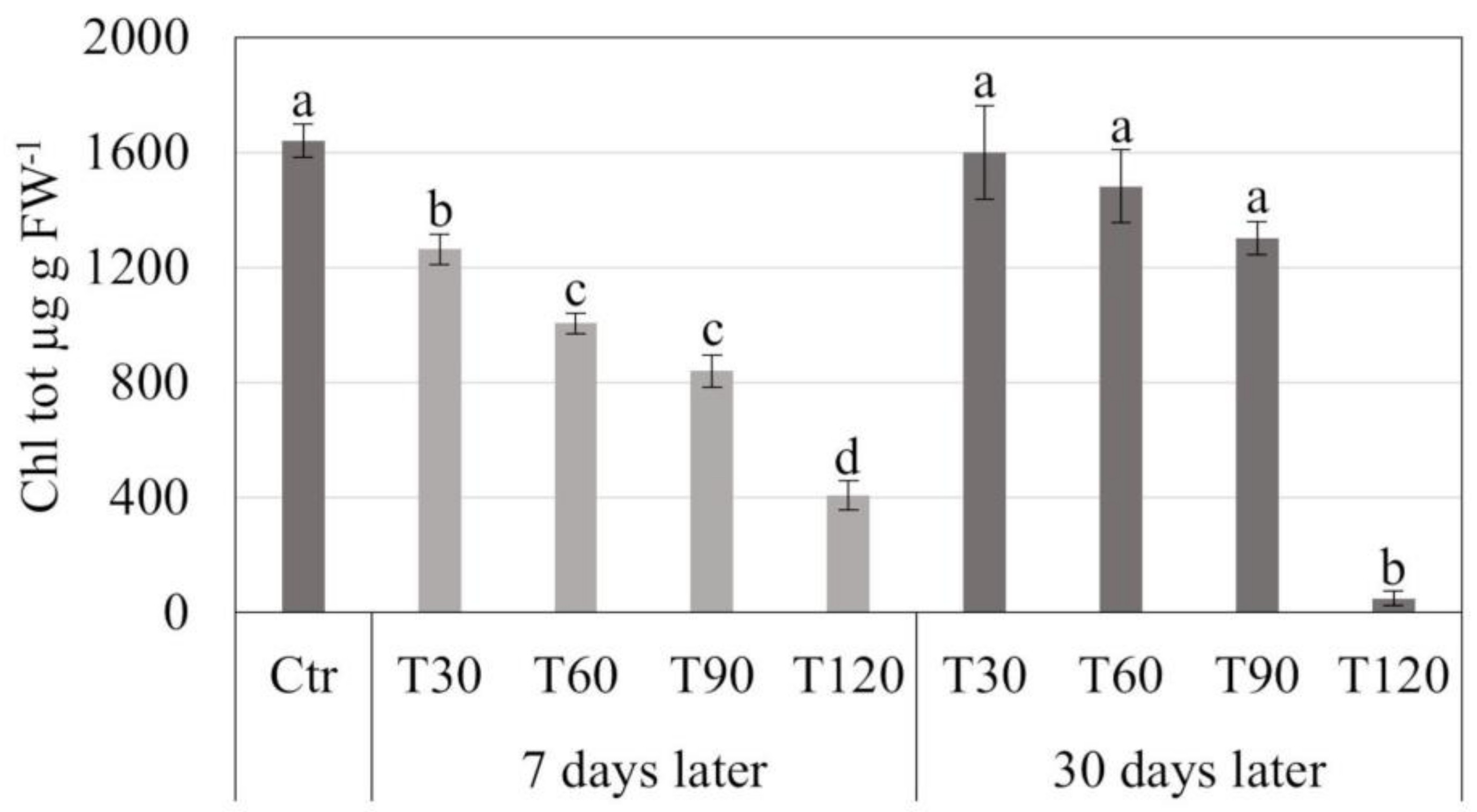
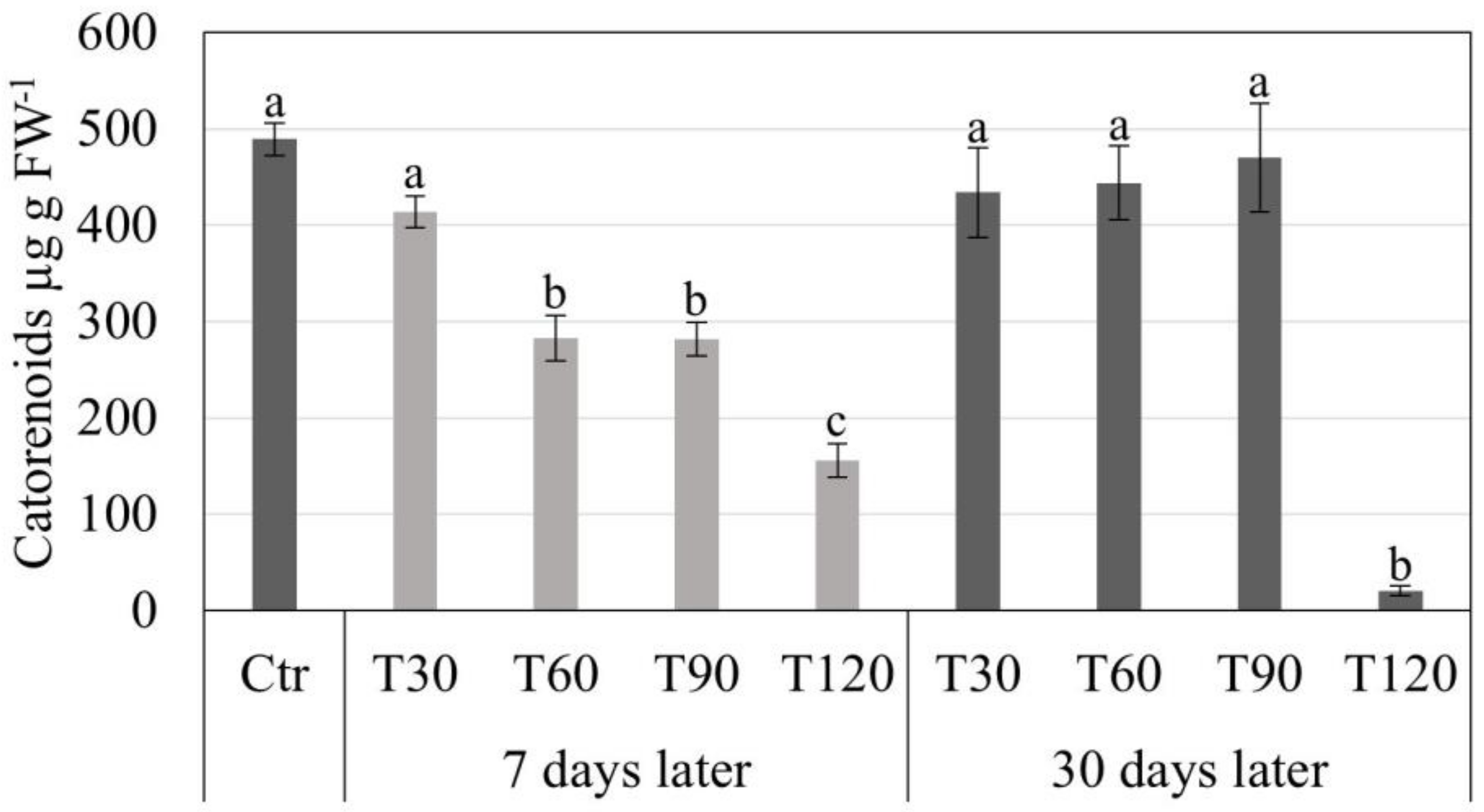
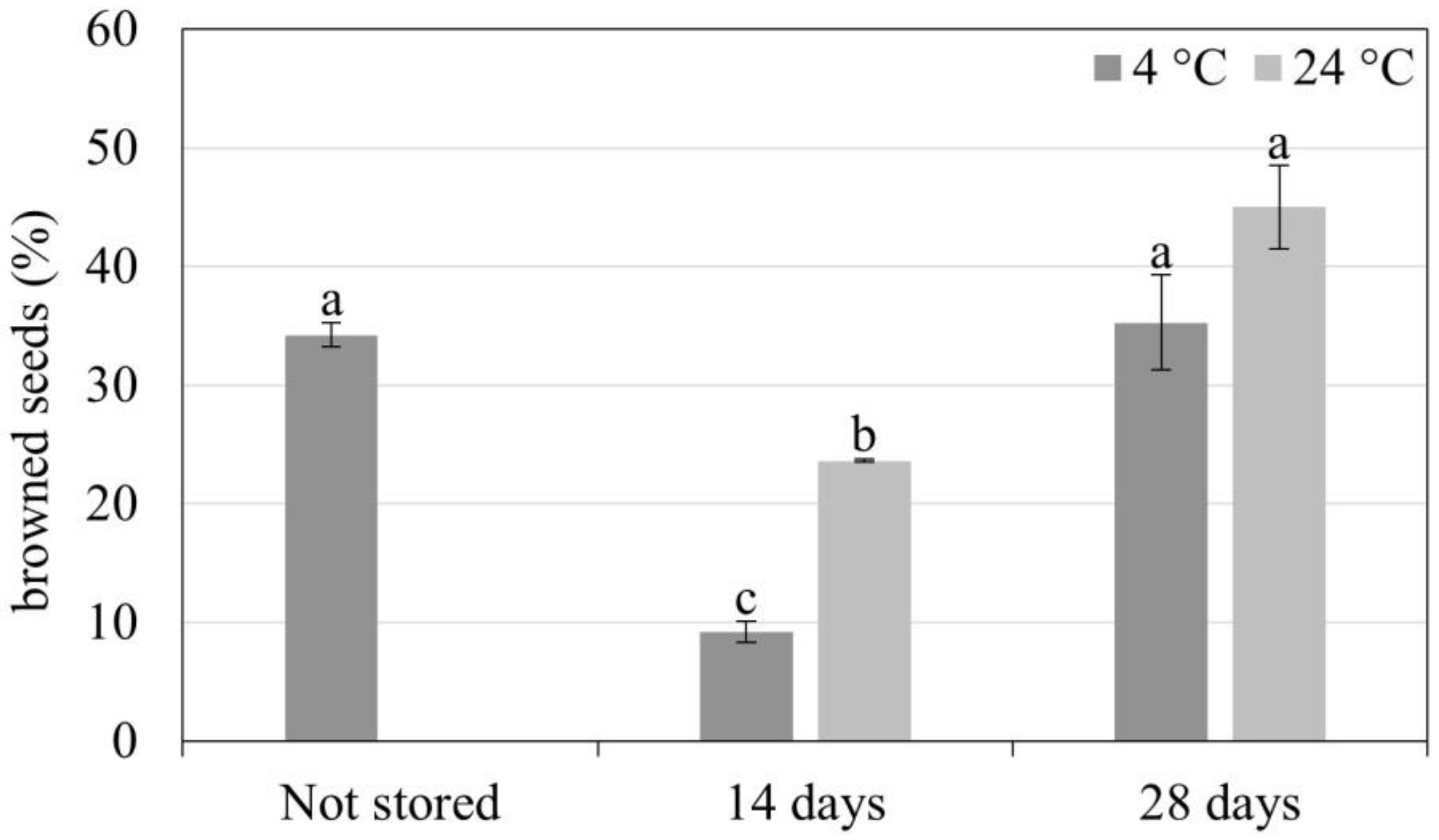
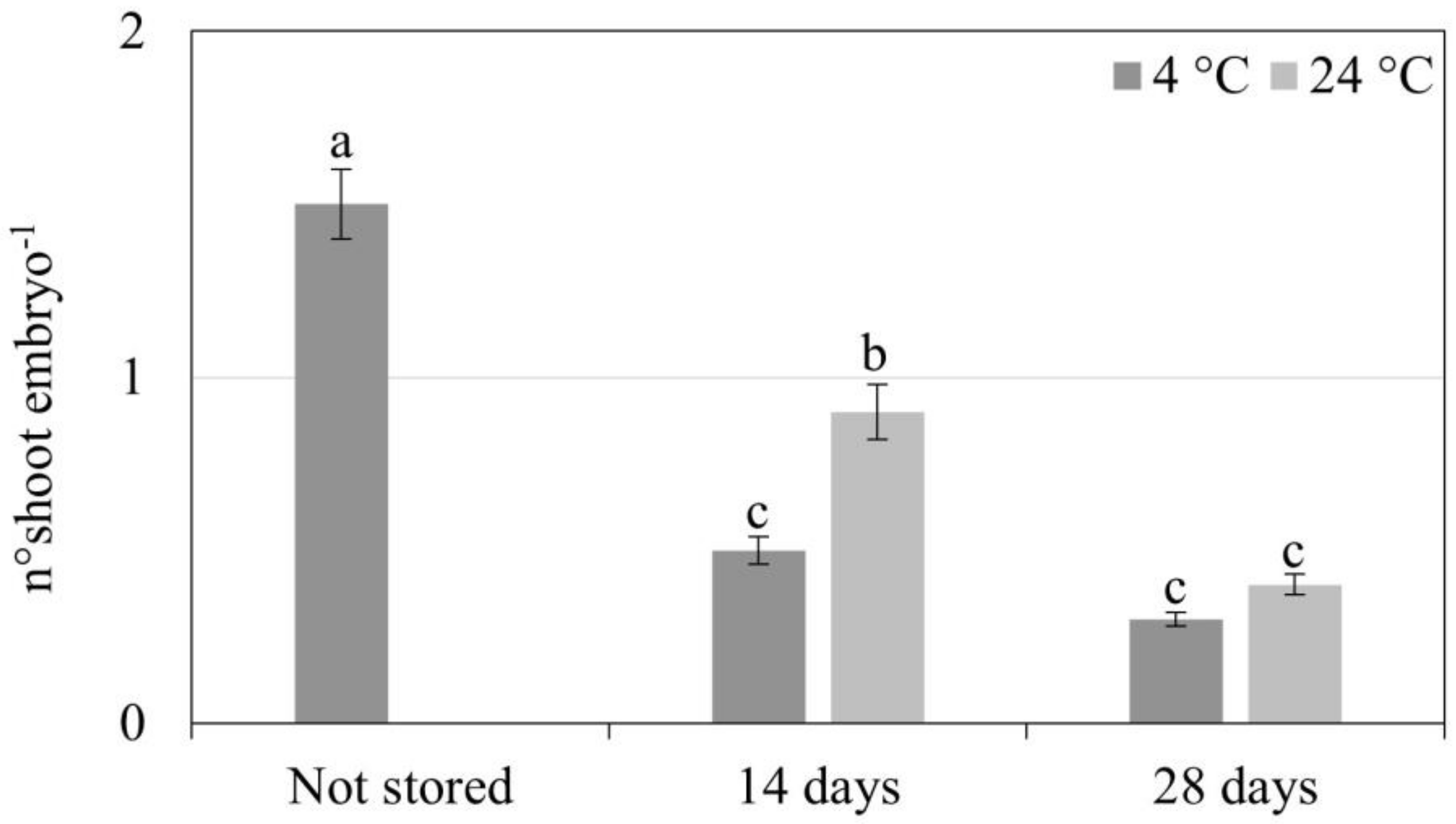
3.2. Synthetic Seed Production and Storage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Bonneval, E.; David, O.R.P.; Doré, J.; Hojlo, A.S.; Inrig, W.; Muller, C.; de Swardt, D. Iris: L’iris en Parfumerie; Coédition Nez éditions/Laboratoire Monique Rémy: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; p. 96. [Google Scholar]
- Khatib, S.; Faraloni, C.; Bouissane, L. Exploring the Use of Iris Species: Antioxidant Properties, Phytochemistry, Medicinal and Industrial Applications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaenicke, L.; Marner, F.J. The irones and their origin. Pure Appl. Chem. 1990, 62, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchi, C.; Rubiolo, P. Analysis of constituents of iris rhizomes. Part I: High performance liquid chromatographic-particle beam-mass spectral analysis of iridals from Iris pallida rhizomes. Phytochem. Anal. 1993, 4, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascough, G.D.; Erwin, J.E.; Van Staden, J. Micropropagation of Iridaceae—A review. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2009, 97, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchesini, M.; Bedini, L.; Florio, E.F.; Maggini, R.; Malorgio, F.; Pezzarossa, B.; Mensuali-Sodi, A. The improvement of Iris pallida propagation by somatic embryogenesis. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1155, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubi, H.; Yepes, L.M.; Fuchs, M. In vitro storage of micropropagated grapevine rootstocks at low temperature. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2019, 55, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzilazarou, S.; Kostas, S.; Joachim, M.; Economou, A. Regeneration of Viburnum dentatum L. from alginate-encapsulated shoot explants after short-term cold storage and assessment of genetic stability using ISSR analysis. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manokari, M.; Latha, R.; Privadharshini, S.; Jogam, P.; Shekhawat, M.S. Short-term cold storage of encapsulated somatic embryos and retrieval of plantlets in grey orchid (Vanda tessellata (Roxb.) Hook. ex G. Don). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2021, 144, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.T.; Arrillaga, I.; Sales, E.; Perez-Oliver, M.A.; Gonzalez-Mas, M.D.C.; Corredoira, E. Micropropagation, characterization, and conservation of Phytophthora cinnamomi-tolerant holm oak mature trees. Forests 2021, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahtan, A.A.; Abdel-Salam, E.M.; Alatar, A.A.; Wang, Q.C.; Faisal, M. An Introduction to Synthetic Seeds: Production, Techniques, and Applications. In Synthetic Seeds; Faisal, M., Alatar, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Maqsood, M.; Khusrau, M.; Mujib, A.; Kaloo, Z.A. Synthetic seed technology in some ornamental and medicinal plants: An overview. In Propagation and Genetic Manipulation of Plants; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, R.; Maheshwari, S. Synthetic seed technology, application and future trends. EPH-Int. J. Agric. Environ. Res. 2023, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamborg, O.L.; Miller, R.A.; Ojima, K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1968, 50, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Pigments of Photosynthetic Biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 148, 350–382. [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann, F. Use of biotechnologies for the conservation of plant biodiversity. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2011, 47, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, C.; Ozudogru, E.A.; Lambardi, M.; Dradi, G. In vitro conservation of ornamental plants by slow growth storage. In Proceedings of the VII International Symposium on In Vitro Culture and Horticultural Breeding, Ghent, Belgium, 18–22 September 2011; Volume 961, pp. 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzarossa, B.; Bretzel, F.; Malorgio, F.; Borghesi, E.; Maggini, R.; Scaramuzzi, S. La coltivazione del Giaggiolo in Toscana: Dalla marginalità alla valorizzazione. Colt. Protette 2016, 2016, 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Fürtauer, L.; Weiszmann, J.; Weckwerth, W.; Nägele, T. Dynamics of Plant Metabolism during Cold Acclimation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambardi, M.; Ozudogru, E.A.; Jain, S.M. (Eds.) Protocols for Micropropagation of Selected Economically-Important Horticultural Plants; Humana Press: Hertfordshire, UK, 2013; Volume 994, p. 490. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, E.E.; Harding, K.; Debouck, D.; Dumet, D.; Escobar, R.; Mafla, G.; Panis, B.; Panta, A.; Tay, D.; Houwe Van den, I.; et al. Refinement and Standardization of Storage Procedures for Clonal Crops. Global Public Goods Phase 2: Part 1. Project Landscape and General Status of Clonal Crop In Vitro Conservation Technologies; System-Wide Genetic Resources Programme (SGRP): Rome, Italy, 2011; p. 86. ISBN 978-92-9043-905-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ruta, C.; Lambardi, M.; Ozudogru, E.A. Biobanking of vegetable genetic resources by in vitro conservation and cryopreservation. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 3495–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha-um, S.; Kirdmanee, C. Minimal growth in vitro culture for preservation of plant species. Fruit Veg. Cereal Sci. Biotechnol. 2007, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesini, M.; Mensuali-Sodi, A.; Massai, R.; Gucci, R. Development of Autotrophy and Tolerance to Acclimatization of Myrtus Communis Transplants Cultured In Vitro under Different Aeration. Biol. Plant. 2001, 44, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchesini, M.; Pacifici, S.; Maggini, R.; Pardossi, A.; Mensuali, A. A novel microfloating culture system for the in vitro rooting of Echinacea angustifolia D.C.: Photosynthetic performance and production of caffeic acid derivatives. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2019, 136, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiferle, C.; Lucchesini, M.; Maggini, R.; Pardossi, A.; Mensuali-Sodi, A. In vitro culture of sweet basil: Gas exchanges, growth, and rosmarinic acid production. Biol. Plant. 2014, 58, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polivanova, O.B.; Bedarev, V.A. Hyperhydricity in Plant Tissue Culture. Plants 2022, 11, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, K.E.; Ford-Lloyd, B.V. Encapsulation of nodal cuttings and shoot tips for storage and exchange of cassava germplasm. Plant Cell Rep. 2003, 21, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.D.; Trueman, S.J. Encapsulation technology for short-term preservation and germplasm distribution of the African mahogany Khaya senegalensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2011, 107, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standardi, A.; Micheli, M. Encapsulation of in vitro-derived explants: An innovative tool for nurseries. In Protocols for Micropropagation of Selected Economically-Important Horticultural Plants; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 397–418. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, P.; Rathor, S.; Sharma, P.; Sen, J.; Kaur, H.; Singh, J. Development of novel gastroretentive salbutamol sulfate-loaded sodium alginate-pectin bubble beads prepared by co-axial needle air-injection method and in vivo clinical evaluation by ultrasound studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 122, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Majd, A.; Naseri, L.; Iranbakhsh, A.; Jafari, M. Optimization of somatic embryogenesis, synthetic seed production, and evaluation of genetic fidelity in Teucrium polium L. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2023, 59, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.R.; Anis, M.; Al-Etta, H.A. Encapsulation technology for short-term storage and germplasm exchange of Vitex trifolia L. Rendiconti Lincei 2015, 26, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, H.; Jaiswal, U.; Jaiswal, V.S. Synthetic seed: Prospects and limitations. Curr. Sci. 2000, 78, 1438–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Khilwani, B.; Kaur, A.; Ranjan, R.; Kumar, A. Direct somatic embryogenesis and encapsulation of somatic embryos for in vitro conservation of Bacopa monnieri (L.) Wettst. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. (PCTOC) 2016, 127, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilpha, J.; Pandian, S.; Largia, M.J.V.; Sohn, S.I.; Ramesh, M. Short-term storage of Solanum trilobatum L. synthetic seeds and evaluation of genetic homogeneity using SCoT markers. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 15, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqsood, M.; Mujib, A.; Khusrau, M. Preparation and low temperature short-term storage for synthetic seeds of Caladium bicolor. Not. Sci. Biol. 2015, 7, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhlaq, M.; Hafiz, I.A.; Micheli, M.; Ahmad, T.; Abbasi, N.A.; Standardi, A. In vitro storage of synthetic seeds: Effect of different storage conditions and intervals on their conversion ability. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 5712–5721. [Google Scholar]
- Micheli, M.; Hafiz, I.A.; Bazzurri, N.; Standardi, A. Methodological development for the synthetic seeds production of Moraiolo. Olive Bioteq. 2006, 1, 155–158. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meucci, A.; Ghelardi, C.; Chietera, G.; Mensuali, A. Synthetic Seed Production and Slow Growth Storage of In Vitro Cultured Plants of Iris pallida Lam. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10030272
Meucci A, Ghelardi C, Chietera G, Mensuali A. Synthetic Seed Production and Slow Growth Storage of In Vitro Cultured Plants of Iris pallida Lam. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(3):272. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10030272
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeucci, Annalisa, Cristina Ghelardi, Giorgiana Chietera, and Anna Mensuali. 2024. "Synthetic Seed Production and Slow Growth Storage of In Vitro Cultured Plants of Iris pallida Lam." Horticulturae 10, no. 3: 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10030272
APA StyleMeucci, A., Ghelardi, C., Chietera, G., & Mensuali, A. (2024). Synthetic Seed Production and Slow Growth Storage of In Vitro Cultured Plants of Iris pallida Lam. Horticulturae, 10(3), 272. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10030272





