The Effect and Potential Mechanism of Fulvic Acid on Flavonoids in Lemon Leaves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Plant Treatment and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation and HPLC-DAD/MS Analysis Condition
2.4. Preparation of Standard Solutions and Establishment of the Standard Curve
2.5. Methodological Evaluation
2.6. ELISA Assay
2.7. q-PCR Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
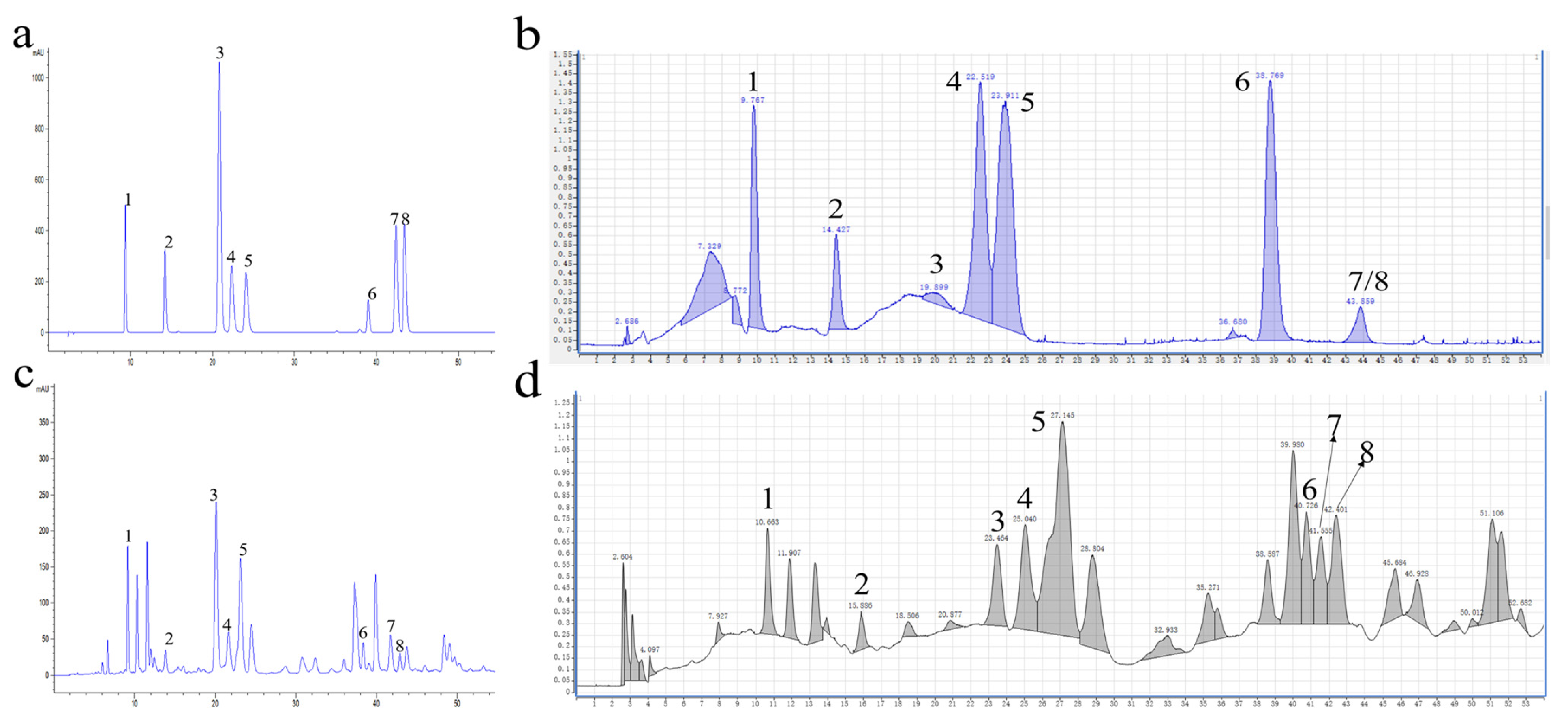
3.1. Identification of Flavonoids in Extract from Lemon Leaves
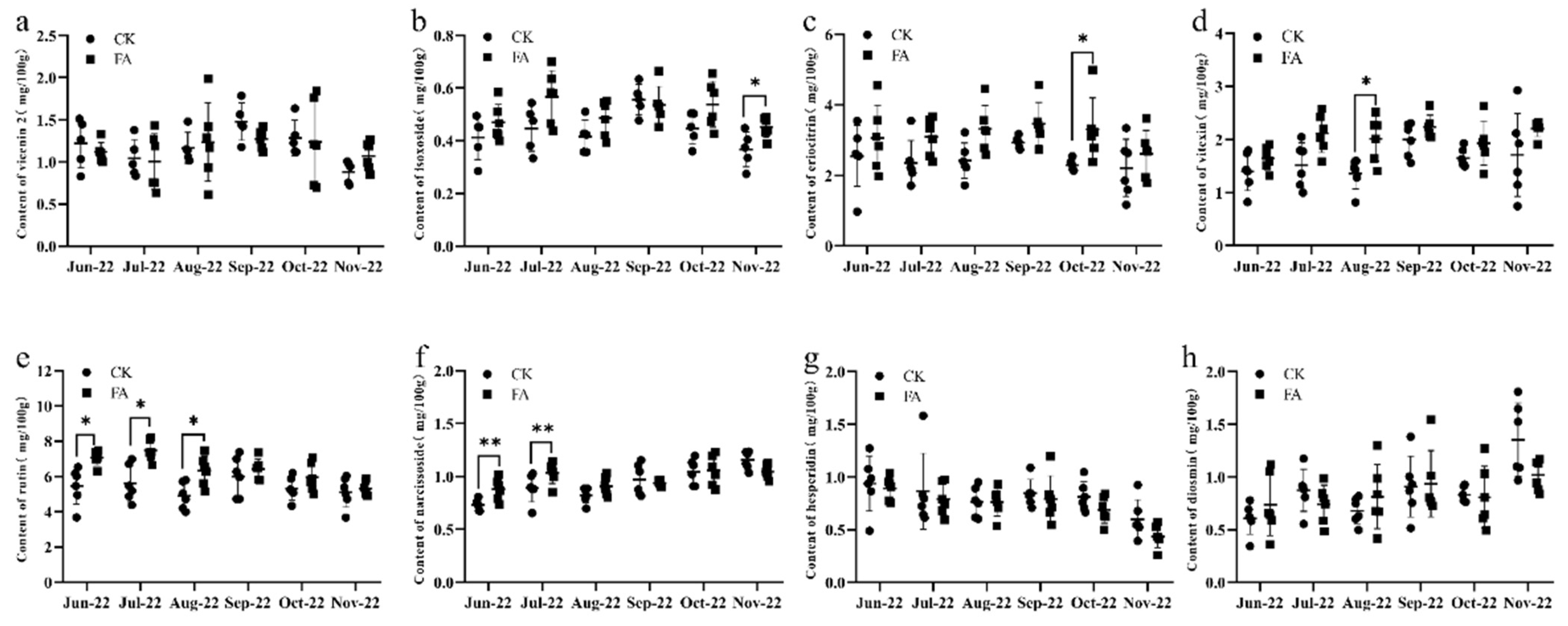
3.2. Contents of Eight Flavonoids in Extract from Lemon Leaves Treated/Untreated with FA over Six Consecutive Collection Periods
3.3. Methodological Evaluation
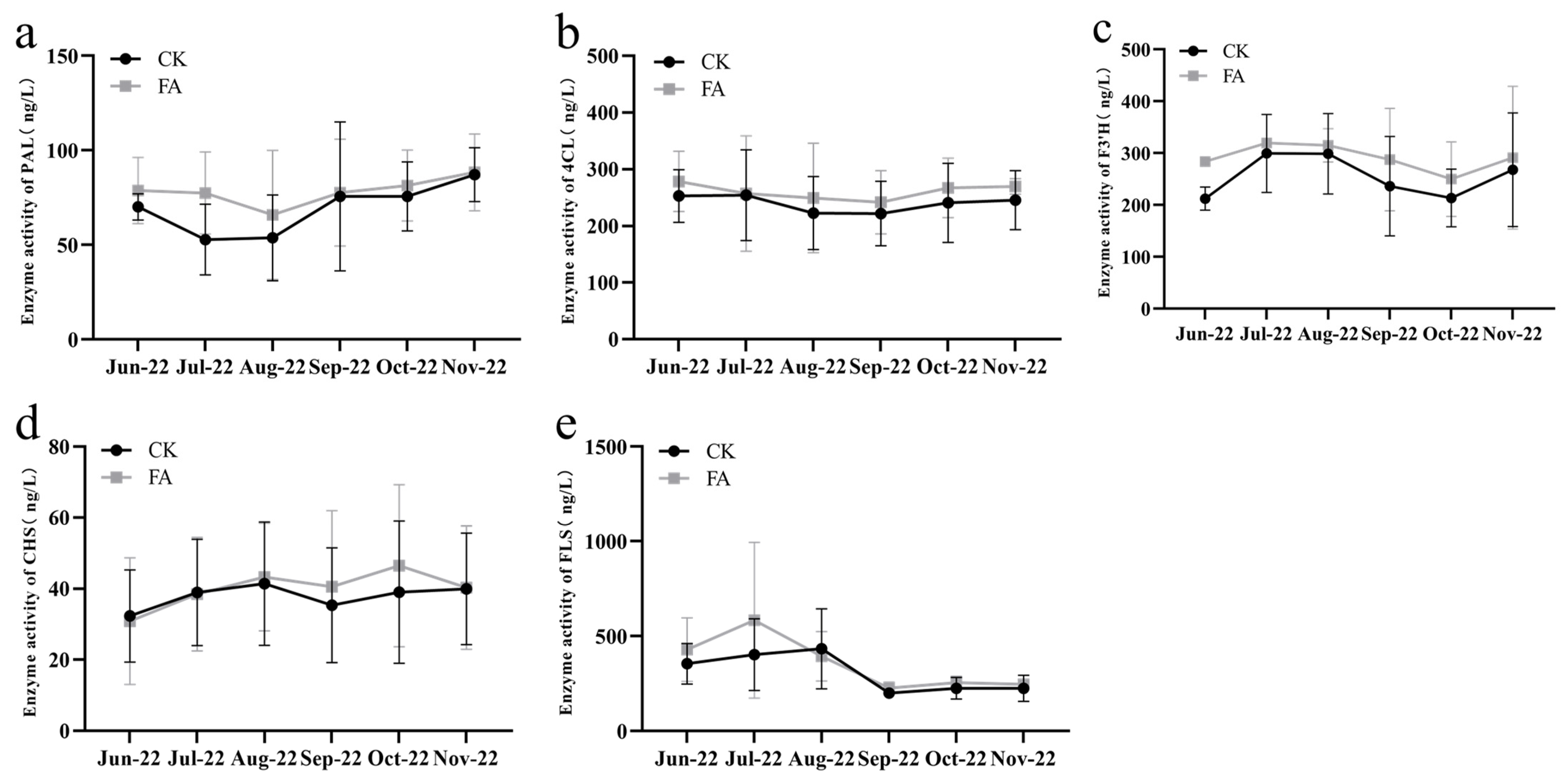
3.4. The Activity of the Flavone Biosynthetic Enzyme Determined by ELISA
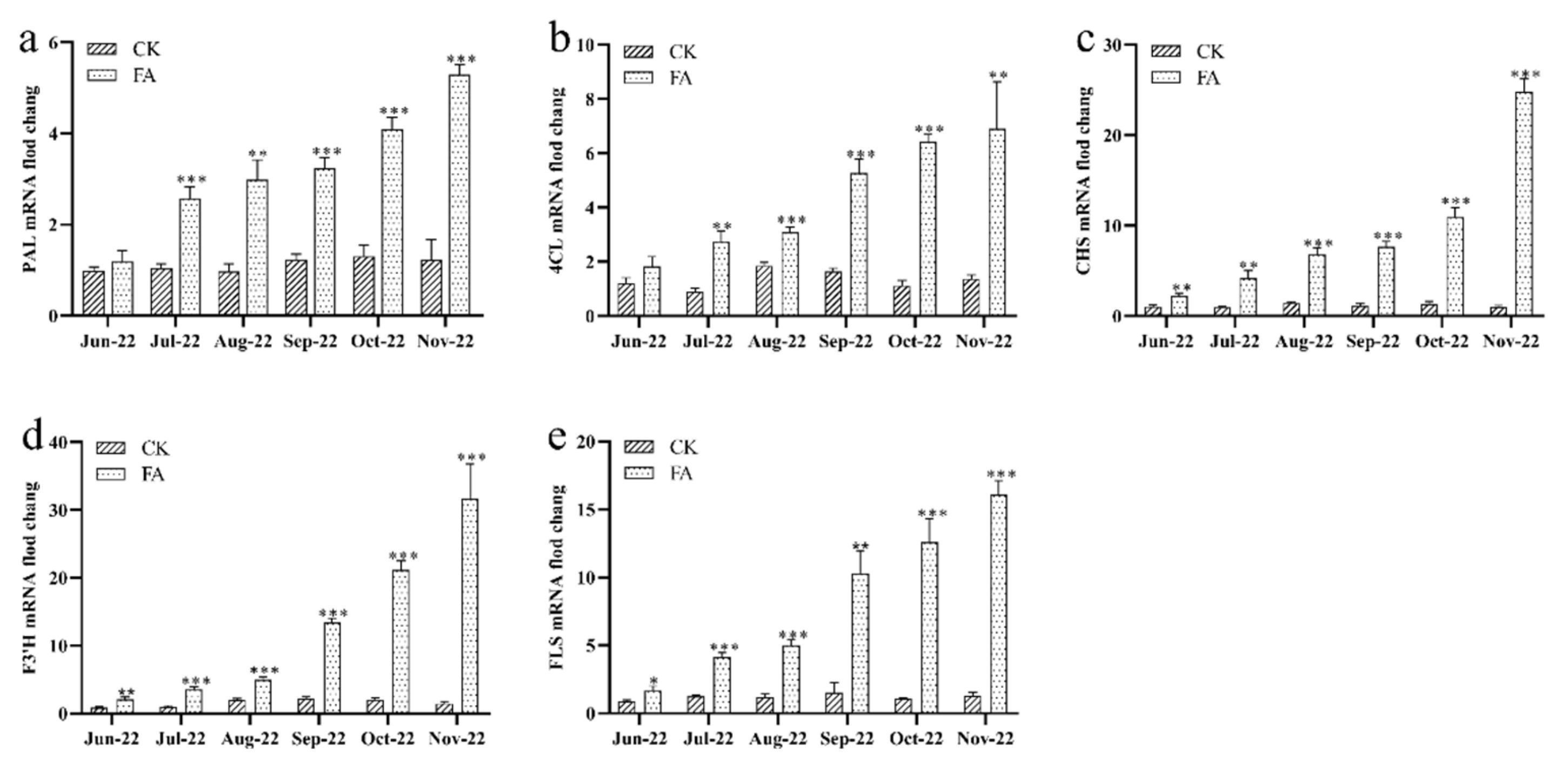
3.5. The Gene Expression of Flavone Biosynthetic Enzyme Determined by q-PCR
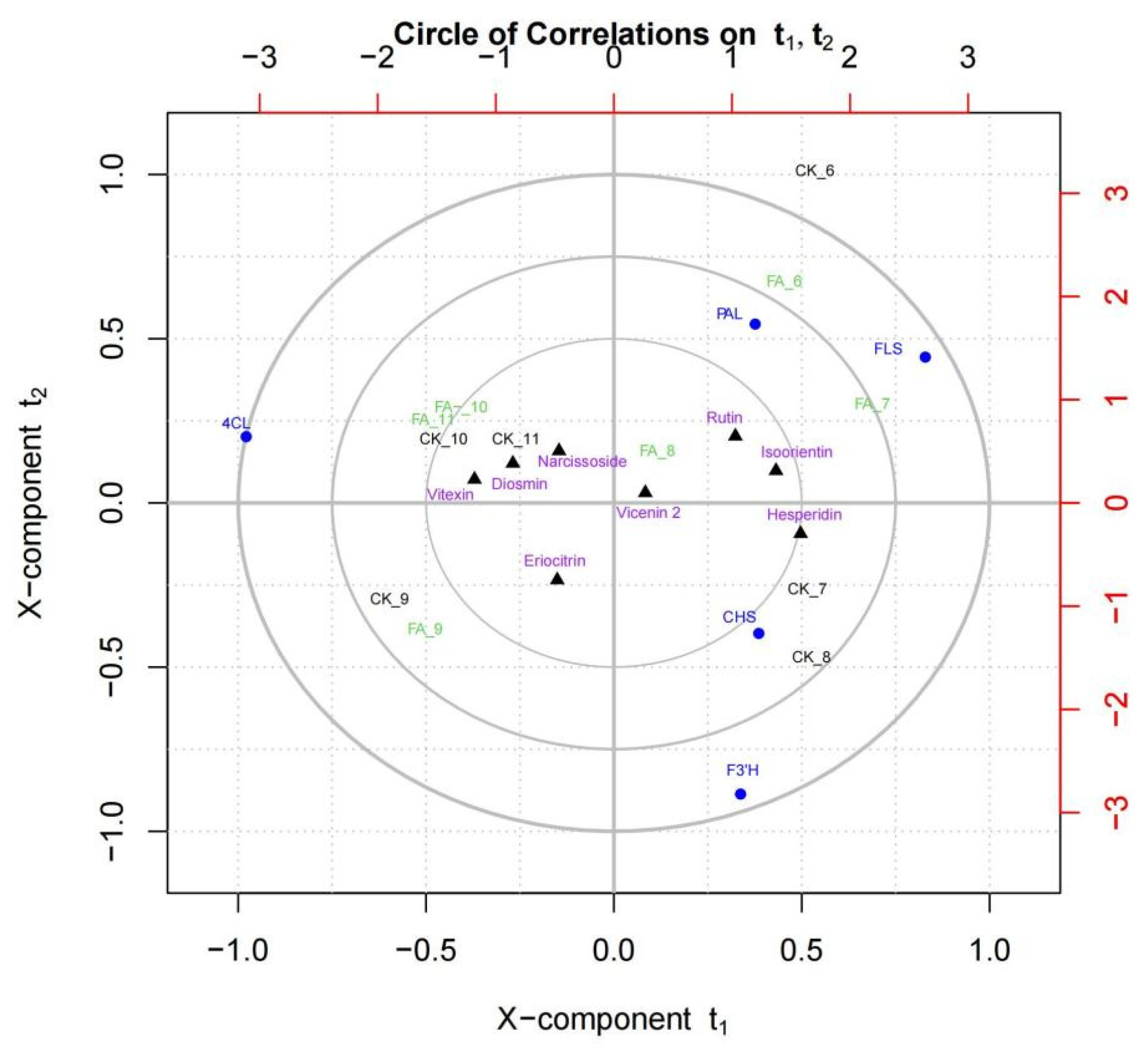
3.6. Correlation between Flavonoid Contents and Flavone Biosynthetic Enzyme Activities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Li, S.; Ho, C.T. Dietary bioactives and essential oils of lemon and lime fruits. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptaa, G.; Agarwalb, U.; Kaura, H.; Kumara, N.R.; Guptab, P. Aphicidal effects of terpenoids present in Citrus limon on Macrosiphum roseiformis and two generalist insect predators. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathesius, U. Flavonoid functions in plants and their interactions with other organisms. Plants 2018, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, F.M.M.; Ribeiro, C.B.; Cesar, T.B.; Milenkovic, D.; Cabral, L.; Noronha, M.F.; Sivieri, K. Lemon flavonoids nutraceutical (Eriomin®) attenuates prediabetes intestinal dysbiosis: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 7283–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilbao, M.L.M.; Andrés-Lacueva, C.; Jáuregui, O.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Determination of flavonoids in a Citrus fruit extract by LC–DAD and LC–MS. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1742–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, A.W.L.A.; Machado, K.D.C.; Machado, K.D.C.; Figueiredo, D.D.R.; David, J.M.; Islam, M.T.; Uddin, S.J.; Shilpi, J.A.; Costa, J.P. In vitro antioxidant properties of the biflavonoid agathisflavone. Chem. Cent. J. 2018, 12, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Chen, J.B.; Cao, J.P.; Li, X.; Sun, C.D. Citrus flavonoids and their antioxidant evaluation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 3833–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninfali, P.; Antonelli, A.; Magnani, M.; Scarpa, E.S. Antiviral properties of flavonoids and delivery strategies. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Sehrawat, N.; Sharma, A.; Yadav, M.; Verma, P.; Sharma, A.P. Multifaceted antiviral therapeutic potential of dietary flavonoids: Emerging trends and future perspectives. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 2028–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, N.; Gahlawat, S.K.; Lather, V. Flavonoids: A nutraceutical and its role as anti-inflammatory and anticancer agent. In Plant Biotechnology: Recent Advancements and Developments; Gahlawat, S., Salar, R., Siwach, P., Duhan, J., Kumar, S., Kaur, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 255–270. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.D.; Tu, Y.L.; Lao, S.H.; Wu, M.T.; Yin, H.T.; Wang, L.Q.; Liao, W.Z. The role and mechanism of citrus flavonoids in cardiovascular diseases prevention and treatment. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7591–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.X.; Xu, H.H.; Yang, K.; Shi, M.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; He, M.M. The application of fulvic acid in fruit tree production. Mod. Hortic. 2021, 22, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Savarese, C.; Cozzolino, V.; Verrillo, M.; Vinci, G.; Martino, A.D.; Scopa, A.; Piccolo, A. Combination of humic biostimulants with a microbial inoculum improves lettuce productivity; nutrient uptake; and primary and secondary metabolism. Plant Soil 2022, 481, 285–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Qiu, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Fan, K.; Gai, Z.; Dong, G.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; et al. Fulvic acid ameliorates drought stress-induced damage in tea plants by regulating the ascorbate metabolism and flavonoids biosynthesis. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, J.X.; Yang, F.; Dai, W.F.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, M. The positive effects of humic/fulvic acid fertilizers on the quality of Lemon fruits. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q. Study on the Effect of Humic Acid on Volatile Oil and Flavonoids in Lemon Leaves and Its Mechanism. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Preliminary Study on the Mechanism of High Temperature Inhibiting the Symptoms of Tartrazine Pulse disease. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University, El Paso, TX, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Dai, W.F.; Li, B.C.; Li, J.X.; Zhang, M. Effect of continuous irrigation with humic acids on total flavonoids content in leaves of Citrus limon ‘Yunning 1’. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2021, 30, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Wang, C.; Kuang, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Advance in flavonoids biosynthetic pathway and synthetic biology. China J. Chin. Mater. 2016, 22, 4124–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Doseff, A.; Grotewold, E. Flavones: From biosynthesis to health benefits. Plants 2016, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, C.; An, W.; Zhou, J.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Integrated metabolome and transcriptome during fruit development reveal metabolic differences and molecular basis between Lycium barbarum and Lycium ruthenicum. Metabolites 2023, 13, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Li, W.W.; Jia, K.; Liao, K.; Liu, L.Q.; Fan, G.Q.; Zhang, S.K.; Wang, Y.T. Metabolomic and transcriptomice analyses of flavonoid biosynthesis in apricot fruits. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1210309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Patra, B.; Singh, S.K.; Paul, P.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pattanaik, P.; Yuan, L. Terpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus: Effects and prospects of environmental factors in metabolic engineering. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 2085–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, M.; Kuiry, R.; Pal, P.K. Understanding the consequence of environmental stress for accumulation of secondary metabolites in medicinal and aromatic plants. J. Appl. Res. Med. Arom. Plants 2020, 18, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | Primer Sequences |
|---|---|
| CHS | F: 5′-GCTTTGTTCGGTGATGGTG-3′ R: 5′-GCTTTGTTCGGTGATGGTG-3′ |
| PAL | F: 5′-GGAACAAGGCATTACACGG-3′ R: 5′-AGATTTGAAGGCAACCCATT-3′ |
| 4CL | F: 5′-TCAATCGCAACATTACTCCA-3′ R: 5′-CAGCATTCAACGACTCCC-3′ |
| F3′H | F: 5′-GTGTCGGTGCCTGCTGTG-3′ R: 5′-GCATACGGACTTGCTGGGT-3′ |
| FLS | F: 5′-TAGGGTTAGGTGTTGAAGGGC-3′ R: 5′-CGTGGGCAAGGTGGGTAG-3′ |
| Actin | F: 5′-CATCCCTCAGCACCTTCC-3′ R: 5′-CCAACCTTAGCACTTCTCC-3′ |
| Peak No. | Standard | Sample | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tR (min) | Compound Name | Molecular Formula | UV λmax (nm) | [M-H]− | tR (min) | UV λmax (nm) | [M-H]− | |||||
| Theoretical Exact Mass (Da) | Mean Measured Mass (Da) | Mass Accuracy (ppm) | Theoretical Exact Mass (Da) | Mean Measured Mass (Da) | Mass Accuracy (ppm) | |||||||
| 1 | 9.739 | Vicenin 2 | C27H30O15 | 334 | 593.1506 | 593.1525 | 3.20 | 9.295 | 334 | 593.1506 | 593.1516 | 1.69 |
| 2 | 14.215 | Isoorientin | C21H20O11 | 350 | 447.0927 | 447.0940 | 2.91 | 14.063 | 345 | 447.0927 | 447.0936 | 2.01 |
| 3 | 20.843 | Eriocitrin | C27H32O15 | 283 | 595.1663 | 595.1675 | 2.02 | 20.604 | 283 | 595.1663 | 595.1674 | 1.85 |
| 4 | 22.392 | Vitexin | C21H20O10 | 340 | 431.0978 | 431.0985 | 1.62 | 22.173 | 340 | 431.0978 | 431.0987 | 2.09 |
| 5 | 24.094 | Rutin | C27H30O16 | 355 | 609.1456 | 609.1471 | 2.46 | 23.731 | 355 | 609.1456 | 609.1470 | 2.30 |
| 6 | 38.988 | Narcissoside | C28H32O16 | 254 | 623.1612 | 623.1627 | 2.41 | 38.558 | 254 | 623.1612 | 623.1620 | 1.28 |
| 7 | 42.379 | Hesperidin | C28H34O15 | 283 | 609.1819 | 609.1827 | 1.31 | 41.870 | 283 | 609.1819 | 609.1828 | 1.48 |
| 8 | 43.409 | Diosmin | C28H32O15 | 350 | 607.1663 | 607.1663 | 0 | 42.867 | 350 | 607.1663 | 607.1673 | 1.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Y.; Yang, F.; Dai, W.; Yuan, C.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. The Effect and Potential Mechanism of Fulvic Acid on Flavonoids in Lemon Leaves. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10020144
Ren Y, Yang F, Dai W, Yuan C, Qin Y, Li J, Zhang M. The Effect and Potential Mechanism of Fulvic Acid on Flavonoids in Lemon Leaves. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10020144
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Youdi, Fan Yang, Weifeng Dai, Cheng Yuan, Yi Qin, Jinxue Li, and Mi Zhang. 2024. "The Effect and Potential Mechanism of Fulvic Acid on Flavonoids in Lemon Leaves" Horticulturae 10, no. 2: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10020144
APA StyleRen, Y., Yang, F., Dai, W., Yuan, C., Qin, Y., Li, J., & Zhang, M. (2024). The Effect and Potential Mechanism of Fulvic Acid on Flavonoids in Lemon Leaves. Horticulturae, 10(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10020144





