A Review of the Arrival, Effects, and Management of Bagrada hilaris in South America: The Case of Chile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Host Plant Range, Crop Damage, and Economic Impacts
| Plant Family | Scientific Name | Plant Type/Use | Reference | Surface Cultivated in Chile/ha | Regional Distribution in Chile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amaranthaceae | Beta vulgaris L. subsp. maritima | Weed | [33] | Atacama—Valparaíso | |
| Beta vulgaris L. | Crop | [4,34] | 1937 | Arica—La Araucanía | |
| Chenopodium álbum L. | Weed | [4,32] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Spinacia oleracea L. | Crop | [4] | 1161 | Atacama—Magallanes | |
| Amaryllidaceae | Allium cepa L. | Crop | [34] | 8607 | Arica—La Araucanía |
| Anacardiaceae | Mangifera indica L. | Crop | [4,34] | 10 | Arica |
| Apiaceae | Daucus carota H. | Crop | [4] | 3038 | Arica—Los Lagos |
| Asteraceae | Carduus pycnocephalus L. | Weed | [34] | Coquimbo—Los Lagos | |
| Carthamus oxyacantha M. | Weed | [4,34] | Coquimbo—Araucanía | ||
| Chrysanthemum sp. L. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Atacama—Los Lagos | ||
| Cynara scolynus L. | Crop | [4] | 1535 | Arica—La Araucanía | |
| Cynara cardunculus L. | Weed | [33] | Coquimbo—Biobio | ||
| Dahlia sp. L. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Atacama—Magallanes | ||
| Lactuca sativa L. | Crop | [4,34] | 8309 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Lactuca serriola L. | Weed | [33] | Antofagasta—La Araucanía | ||
| Schkuhria pinnata L. | Weed | [4] | Arica—Coquimbo | ||
| Sonchus arvensis L. | Weed | [4] | Magallanes | ||
| Sonchus asper L. | Weed | [33] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Sonchus oleraceus L. | Weed | [33] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Brassicaceae | Barbarea verna M. | Weed | [4] | Metropolitana—Los Lagos | |
| Brassica campestris L. | Weed | [4,32] | Valparaíso—Biobio | ||
| Brassica juncea L. | Crop | [4,34] | 0.02 | Metropolitana | |
| Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala | Crop | [4,34] | 27.2 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Brassica oleracea L. var. botrytis | Crop | [4,33] | 1803.4 | Arica—La Araucanía | |
| Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata | Crop | [4,33] | 2901.3 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Brassica oleracea L. var. gemmifera | Crop | [4] | 100 | Arica—La Araucanía | |
| Brassica oleracea L. var. itálica | Crop | [4,33,34] | 2289.1 | Arica—La Araucanía | |
| Brassica oleracea L. var. oleracea | Crop | [39] | 2640 | Arica—La Araucanía | |
| Brassica napus L. | Crop | [39] | 32,650 | Biobio—Los Lagos | |
| Brassica rapa L. subsp. chinensis | Crop | [39] | 20 | Metropolitana | |
| Brassica rapa L. subsp. japonica | Crop | [39] | 5 | Metropolitana | |
| Brassica rapa L. subsp. oleifera | Weed | [4,34] | Biobio—Los Lagos | ||
| Brassica rapa L. subsp. rapa | Pasture | [4,34] | Biobio—Los Lagos | ||
| Brassica rapa L. subsp. narinosa | Weed | [4] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Brassica rapa L. subsp. nipposinica | Weed | [4] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Capsella bursa-pastoris L. | Weed | [4,33,34] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Descurainia sophia L. | Weed | [4,34] | Metropolitana—Magallanes | ||
| Descurainia nuttallii C. | Weed | [33] | Antofagasta—Magallanes | ||
| Descurainia pimpinellifolia B. | Weed | [32] | Antofagasta—Maule | ||
| Eruca sativa L. | Crop | [4,33] | Coquimbo—La Araucanía | ||
| Hirschfeldia incana L. | Weed | [4,33,34] | Atacama—Araucanía | ||
| Lepidium latifolium L. | Weed | [4,34] | Antofagasta—Maule | ||
| Lepidium auriculatum R. and K. | Weed | [32] | Antofagasta—Magallanes | ||
| Lepidium pseudodidymum T. | Weed | [32] | Valparaíso—Magallanes | ||
| Lobularia marítima L. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Tarapacá—Los Lagos | ||
| Matthiola sp. A. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Antofagasta—Coquimbo | ||
| Raphanus sativus L. | Crop | [4,33,34] | Valparaíso—Maule | ||
| Raphanus raphanistrum L. | Weed | [4,33,34] | Antofagasta—Los Lagos | ||
| Sisymbrium irio L. | Weed | [4,34] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Cannabaceae | Cannabis sativa L. | Crop | [4,34] | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Capparaceae | Capparis spinosa L. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Arica—Valparaíso | |
| Convolvulaceae | Convolvulus arvensis L. | Weed | [4] | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Cuscuta reflexa R. | Weed | [34] | Arica—Los Lagos | ||
| Cucurbitaceae | Citrullus lanatus T. | Crop | [4] | 2842 | Atacama—Biobio |
| Cucumis melo L. | Crop | [4] | 2919 | Atacama—La Araucanía | |
| Momordica dioica R. | Crop | [4,34] | Coquimbo—La Araucanía | ||
| Euphorbiaceae | Ricinus communis L. | Weed | [4,34] | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Fabaceae | Arachis hypogaea | Crop | [34] | Valparaíso—Ñuble | |
| Indigofera sp. L. | Weed | [4,34] | Arica | ||
| Medicago sativa L. | Pasture | [4,34] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Medicago polymorpha L. | Pasture | [34] | Arica—Los Rios | ||
| Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Crop | [4,34] | 12,942 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Phaseolus lunatus L. | Crop | [4,34] | Arica—Los Lagos | ||
| Pisum sativum L. | Crop | [4,34] | 1800 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Robinia pseudoacacia L. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Valparaíso—Biobio | ||
| Trifolium alexandrinum L. | Pasture | [4,34] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Trifolium resupinatum L. | Pasture | [34] | Arica—Magallanes | ||
| Vicia sp. L. | Crop | [4,34] | 1790 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Vigna mungo L. | Crop | [4,34] | 550 | Coquimbo—Los Lagos | |
| Linaceae | Abelmochus sculentus L. | Crop | [4,34] | Experimental in Chile | |
| Alcea sp. L. | Ornamental | [4] | Antofagasta—Aysén | ||
| Gossypium sp. L | Ornamental | [4,34] | Experimental in Chile | ||
| Linum usitatissimum L. | Crop | [34] | 250 | Valparaíso—Ñuble | |
| Malva sylvestris L. | Weed | [39] | Antofagasta—Maule | ||
| Moraceae | Morus alba L. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Coquimbo—La Araucanía | |
| Plantaginaceae | Plantago major L. | Weed | [34] | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Poaceae | Avena sativa L. | Crop | [4] | 71,685 | Valparaíso—Magallanes |
| Cynodon dactylon L. | Weed | [4,34] | Arica—Biobio | ||
| Hordeum vulgare L. | Crop | [4] | 30,000 | Atacama—La Araucanía | |
| Oryza sativa L. | Crop | [4] | 20,700 | Metropolitana—Biobio | |
| Sorghum bicolor L. | Crop | [4,34] | Valparaíso—La Araucanía | ||
| Tritricum aestivum L. | Crop | [4,34] | 216,733 | Coquimbo—Los Lagos | |
| Zea mayz L. | Crop | [4,34] | 56,792 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Polygonaceae | Rumex dentatus L. | Weed | [34] | Atacama—Aysén | |
| Rutaceae | Citrus sp. L. | Crop | [4,34] | 24,000 | Arica—Biobio |
| Solanaceae | Physalis peruviana L. | Crop | [4,34] | 5.5 | Arica—Maule |
| Solanum lycopersicum L. | Crop | [4,32,34] | 9302 | Arica—Los Lagos | |
| Solanum tuberosum L. | Crop | [4,34] | 26,986 | Coquimbo—Magallanes | |
| Theaceae | Camellia sinensis L. | Ornamental | [4,34] | Atacama—Magallanes |
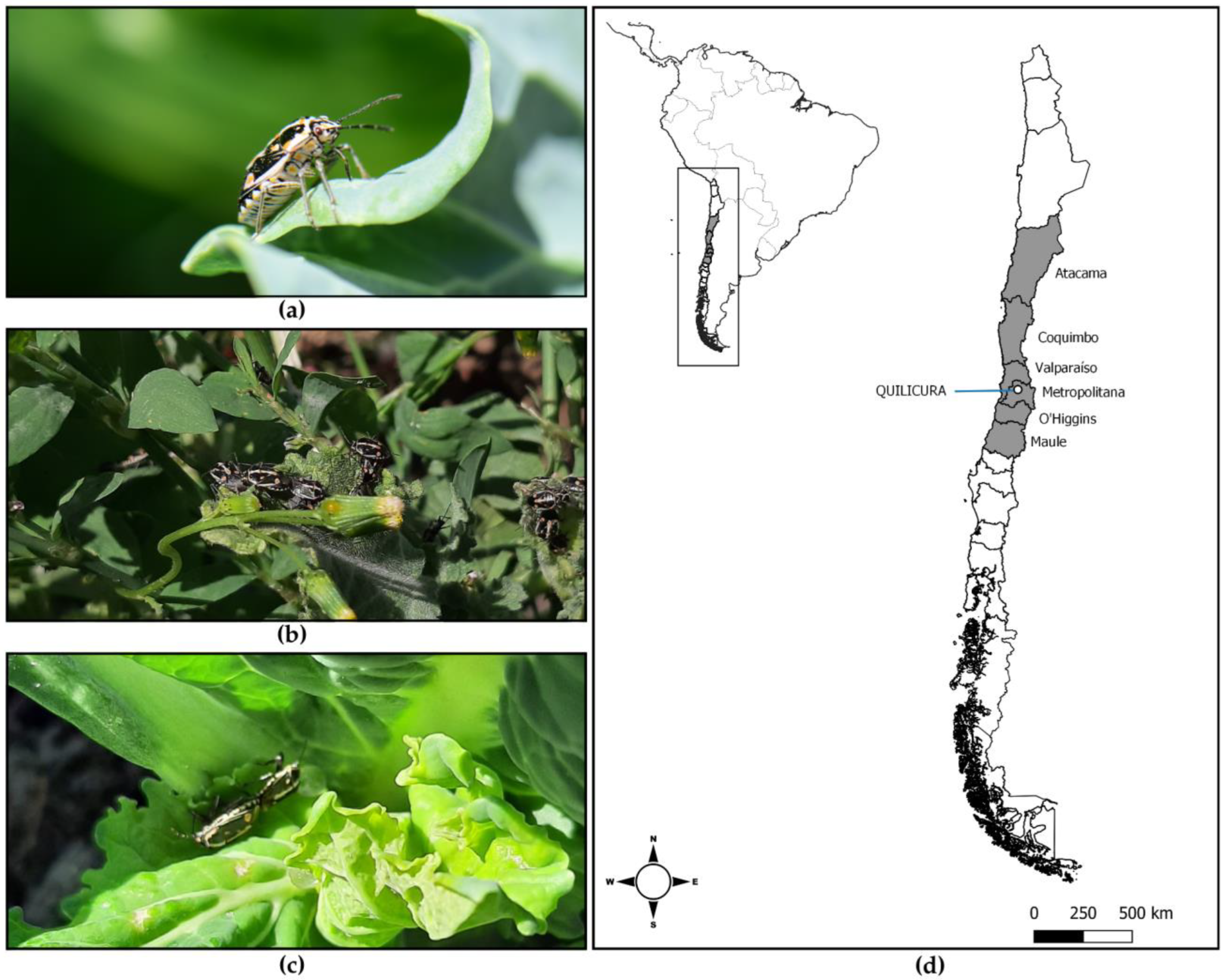
3. South America Invasion: The Case of Chile
4. Current Advances in Management Methods: Practical Implementations
4.1. Chemical Control
4.2. Biological Control
| Guild | Order | Family | Species | Recorded as Natural Enemies of B. hilaris | Recorded in Chile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasitoids | Diptera | Sarcophagidae | Sarcophaga kempi | [11,80] | No |
| Tachinidae | Alophora sp. * | [11,80] | Yes | ||
| Alophora indica | [80,81,82] | No | |||
| Alophora pusilla | [81] | No | |||
| Phasia sp. | [11] | Yes | |||
| Hymenoptera | Encyrtidae | Ooencyrtus californicus | [57] | No | |
| Ooencyrtus lucidus | [71] | No | |||
| Ooencyrtus sp. | [4] | No | |||
| Scelionidae | Gryon aetherium | [24,57,83] | Yes | ||
| Gryon myrmecophilum ** | [75] | ||||
| Gryon gonikopalense ** | [73] | ||||
| Gryon sp. | [80,82] | unknown | |||
| Idris elba | [84] | No | |||
| Psix sp. | [82] | No | |||
| Telenomus podisi | Walker unpublished cited by [4] | No | |||
| Telenomus samueli | [85] | No | |||
| Trissolcus basalis | [61,83,86,87] | No | |||
| Trissolcus erugatus | [57] | No | |||
| Trissolcus hullensis | [61,87] | No | |||
| Trissolcus hyalinipennis | [61,88] | Yes | |||
| Trissolcus sp. | [85] | Yes | |||
| Trissolcus utahensis | [61,87] | No | |||
| Typhodytes sp. | [80] | No | |||
| Trichogrammatidae | Trichogramma sp. | [78] | Yes | ||
| Predators | Acarina | Erythraeidae | Bochartia sp. | [89] | No |
| Araneae | Thomisidae | Misumenops temibilis | [78,79] | Yes | |
| Coleoptera | Carabidae | Cincindela sp. | [78,79] | Yes | |
| Coccinellidae | Adalia angulifera | [78,79] | Yes | ||
| Adalia bipunctata | [78,79] | Yes | |||
| Eriopis chilensis | [78,79] | Yes | |||
| Eriopis connexa chilensis | [78,79] | Yes | |||
| Eriopis eschscholtzi | [78,79] | Yes | |||
| Hippodamia convergens | [78,79] | Yes | |||
| Hippodamia variegata | [78,79] | Yes | |||
| Melyridae | Collops vittatus | [90] | No | ||
| Dermaptera | Forficulidae | Forficula auricularia | [4] | Yes | |
| Hemiptera | Nabidae | Nabis punctipennis | [78,79] | Yes | |
| Pentatomidae | Podisus maculiventris | [90] | No | ||
| Reduviidae | Rhynocoris segmentarius | [4] | No | ||
| Sinea diadema | [4] | No | |||
| Zelus renardii | [78,79] | Yes | |||
| Hymenoptera | Formicidae | Linepithema humile | [78,79,90] | Yes | |
| Monomorium ergatogyna | [91] | No | |||
| Solenopsis xyloni | [91] | No | |||
| Mantodea | Coptopterygidae | Coptopterix gayi | [78,79] | Yes | |
| Neuroptera | Chrysopidae | Crysoperla defreitasi | [78,79] | Yes |
4.3. Cultural Control Practices
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skendžić, S.; Zovko, M.; Živković, I.P.; Lešić, V.; Lemić, D. Effect of Climate Change on Introduced and Native Agricultural Invasive Insect Pests in Europe. Insects 2021, 12, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Huang, C.; Li, C.Y.; Zhou, H.X.; Ren, Y.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Xing, L.S.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, X.; Liu, B.; et al. Biology, Invasion and Management of the Agricultural Invader: Fall Armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 646–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagic, V.; Holding, M.; Venables, W.N.; Hulthen, A.D.; Schellhorn, N.A. Better Outcomes for Pest Pressure, Insecticide Use, and Yield in Less Intensive Agricultural Landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, C.S.; Perring, T.M.; Reed, D.A.; Palumbo, J.C.; Grasswitz, T.R.; Jones, W.A. Bagrada hilaris (Burmesiter). In Invasive Stink Bugs and Related Species (Pentatomoidea); McPherson, J.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boco Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 205–255. [Google Scholar]
- Alaniz, A.J.; Vergara, P.M.; Carvajal, M.A.; Fierro, A. Recent Rapid Colonization of the Invasive Species Bagrada hilaris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in the Collapsed Ecosystem Aculeo Lake, Chile. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2021, 69, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faúndez, E.I.; Larrea-Meza, S.; Carvajal, M.A. High, up and down: Updating the Distribution of the Painted Bug Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in Chile. Rev. Chil. Ent. 2018, 44, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Carvajal, M.A.; Alaniz, A.J.; Núñez-Hidalgo, I.; González-Césped, C. Spatial Global Assessment of the Pest Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae): Current and Future Scenarios. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.E.; Bundy, C.S.; Mcpherson, J.E. Unusual Ovipositional Behavior of the Stink Bug Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.E.; Bundy, C.S.; McPherson, J.E. Life History and Laboratory Rearing of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) with Descriptions of Immature Stages. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2015, 108, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, D.A.; Ganjisaffar, F.; Palumbo, J.C.; Perring, T.M. Effects of Temperatures on Immature Development and Survival of the Invasive Stink Bug Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 2497–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, J.C.; Perring, T.M.; Millar, J.G.; Reed, D.A. Biology, Ecology, and Management of an Invasive Stink Bug, Bagrada hilaris, in North America. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachan, G.C.; Purwar, J.P. Integrated Pest Management in Rapeseed and Mustard. In Entomology: Novel Approaches; Jain, P.C., Bhargava, M.C., Eds.; New India Publishing: New Delhi, India, 2007; pp. 399–423. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, D.A.; Palumbo, J.C.; Perring, T.M.; May, C. Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), An Invasive Stink Bug Attacking Cole Crops in the Southwestern United States. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2013, 4, C1–C7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.I.; Reed, D.A.; Perring, T.M.; Palumbo, J.C. Feeding Damage by Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) and Impact on Growth and Chlorophyll Content of Brassicaceous Plant Species. Arthropod Plant Interact. 2014, 8, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakelian, G. Bagrada hilaris . 2008. Available online: https://cisr.ucr.edu/invasive-species/bagrada-bug (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Bundy, C.S.; Grasswitz, T.R.; Sutherland, C. First Report of the Invasive Stink Bug Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) from New Mexico, with Notes on Its Biology. Southwest Entomol. 2012, 37, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faúndez, E.I.; Lüer, A.; Cuevas, Á.G.; Rider, D.A.; Valdebenito, P. First Record of the Painted Bug Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister, 1835) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in South America. Arq. Entomolóxicos 2016, 16, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Leiva Castro, V.P.; Smith Guerra, P.E. Evaluación del Establecimiento Potencial de las Plagas Bagrada hilaris y Halymorpha halys en las Principales Regiones Agrícolas de Chile. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.I.; Reed, D.A.; Perring, T.M.; Palumbo, J.C. Host Selection Behavior of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) on Commercial Cruciferous Host Plants. Crop. Prot. 2014, 59, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-I.; Reed, D.A.; Perring, T.M.; Palumbo, J.C. Diel Activity and Behavior of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) on Desert Cole Crops. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1726–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.V.; Grettenberger, I.; Godfrey, L. Insecticides Applied to Soil of Transplant Plugs for Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Management in Broccoli. Crop. Prot. 2016, 87, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrão, J.E.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Martínez, L.C.; Zanuncio, J.C. Side-Effects of Pesticides on Non-Target Insects in Agriculture: A Mini-Review. Sci. Nat. 2022, 109, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende-Teixeira, P.; Dusi, R.G.; Jimenez, P.C.; Espindola, L.S.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. What Can We Learn from Commercial Insecticides? Efficacy, Toxicity, Environmental Impacts, and Future Developments. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Gálvez, N.R.; Talamas, E.; Albornoz, M.V.; Flores, M.F.; Barros-Parada, W.; Bout, A. Gryon Aetherium Talamas (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae): Parasitoid of Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae) Adventive in Chile. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2021, 87, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, G.; Hogg, B.N.; Sforza, R.F.H. Anticipating the Arrival of a New Stinkbug Pest in Continental Europe: What Can We Learn from Preemptive Host Specificity Tests for Biocontrol? Entomol. Gen. 2024, 44, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, M.V.; Verdugo, J.A.; Flores, M.F.; Santander, C.C.; Bout, A. First Identification of Coccinellidae Species as Predators of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) in Chile: When Natives’ Species Perform Better than Exotic Ones. Ecol. Austral, 2024, submitted.
- Rojas-Gálvez, N.R. Evaluación Del Control Biológico de Bagrada hilaris con Entomófagos. Master’s Thesis, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso PUCV, Valparaiso, Chile, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, G.; Augé, M.; Talamas, E.; Roche, M.; Smith, L.; Sforza, R.F.H. First Laboratory Evaluation of Gryon Gonikopalense (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), as Potential Biological Control Agent of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Biol. Control 2019, 135, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, E.; Avila, G.; Barratt, B.; Cingolani, F.; Colazza, S.; Guarino, S.; Hoelmer, K.; Laumann, R.A.; Maistrello, L.; Martel, G.; et al. Biological Control of Invasive Stink Bugs: Review of Global State and Future Prospects. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2021, 169, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, C.; Mainardi, C.E.; Nieri, R.; Fouani, J.M.; Cemmi, A.; Cristofaro, M.; Anfora, G.; Mazzoni, V. The Effect of the Sterile Insect Technique on Vibrational Communication: The Case of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Insects 2023, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, G.G.; Storer, N.P. Life Systems of Polyphagous Arthropod Pests in Temporally Unstable Cropping Systems. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 467–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albornoz, M.V. Project: Diseño y Validación de Estrategias Para La Reducción Del Daño Económico Causado Por Bagrada hilaris En Brásicas, Mediante Unidades de Biodiversidad Funcional Tipo Push-Pull, Orientadas a La Pequeña Horticultura de La Región de Valparaíso; Centro Regional Ceres: Quillota, Chile, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Albornoz, M.V.; González-Santander, C.C.; González, E.; Cid, F.; Oyarce, C. Una Mirada Hacia el Manejo Sustentable de Plagas con Énfasis En Bagrada Hilaris En Cultivos de Brásicas; Centro Regional Ceres: Valparaíso, Chile, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vitta, P.N.; OIivares, O.N.; Bravo, A.J.; Canales, T.V.; Cuello, T.M. Antecedentes de Bagrada hilaris. In Alternativas Sustentables para el Manejo de Bagrada hilaris en Chile; Vitta, P.N., Ed.; INIA La Platina: Santiago, Chile, 2021; pp. 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo, J.C.; Natwick, E.T. The Bagrada Bug (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae): A New Invasive Pest of Cole Crops in Arizona and California. Plant Health Prog. 2010, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, S.; Arif, M.A.; Millar, J.G.; Colazza, S.; Peri, E. Volatile Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Emitted by Seedlings of Brassica Species Provide Host Location Cues to Bagrada hilaris. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriola, K.; Guarino, S.; Schlawis, C.; Arif, A.; Colazza, S.; Peri, E.; Schulz, S.; Millar, J.G. Identification of Brassicadiene, a Diterpene Hydrocarbon Attractive to the Invasive Stink Bug Bagrada hilaris, from Volatiles of Cauliflower Seedlings, Brassica Oleracea Var. Botrytis. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, L.B.; Leger, E.A.; Nowak, R.S. Invasion Triangle: An Organizational Framework for Species Invasion. Ecol. Evol. 2011, 1, 610–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAG Bagrada hilaris o Chinche Pintada. 2024. Available online: https://www.sag.gob.cl/ambitos-de-accion/bagrada-hilaris-o-chinche-pintada (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- EFSA Panel on Plant Health (PLH); Bragard, C.; Baptista, P.; Chatzivassiliou, E.; Di Serio, F.; Gonthier, P.; Jaques Miret, J.A.; Justesen, A.F.; Magnusson, C.S.; Milonas, P.; et al. Pest Categorisation of Bagrada hilaris. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faúndez, E.I.; Lüer, A.; Cuevas, Á.G. The Establishment of Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister, 1835) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in Chile, an Avoidable Situation? Arquivos Entomolóxicos 2017, 17, 239–241. [Google Scholar]
- ODEPA. Ficha de Costo Del Repollo. Oficina de Estudios y Políticas Agrarias. 2022. Available online: https://www.odepa.gob.cl/publicaciones/noticias/agro-en-la-prensa/ficha-de-costo-del-repollo (accessed on 29 September 2024).
- Palumbo, J.C. Impact of Bagrada Bug on Desert Cole Crops: A Survey of PCA/Growers in 2010 and 2011. Veg. IPM Update 2011, 3, 6. [Google Scholar]
- SAG Resolución N° 1.577/2017. Establece Control Obligatorio de La Plaga Chinche Pintada Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister, 1835) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). 2017. Available online: https://www.sag.gob.cl/content/establece-control-obligatorio-de-la-plaga-chinche-pintada-bagrada-hilaris-burmeister-1835-hemiptera-pentatomidae (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Carpintero, D.L.; Quiroga, V.N.; Celentano, E.; Holgado, M.G. Primer Registro de Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister, 1835) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Para La República Argentina. Hist. Nat. 2021, 11, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Faúndez, E.I. From Agricultural to Household Pest: The Case of the Painted Bug Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) in Chile. J. Med. Entomol. 2018, 55, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Peña, S.R. First Record in Mexico of the Invasive Stink Bug Bagrada hilaris, on Cultivated Crucifers in Saltillo. Southwest Entomol. 2014, 39, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitta, P.N.; Aguilar, G.V. Chinches de Importancia Hortofrutícola. Tierra Adentro 2021, 115, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lionello, P.; Abrantes, F.; Gacic, M.; Planton, S.; Trigo, R.; Ulbrich, U. The Climate of the Mediterranean Region: Research Progress and Climate Change Impacts. Regl. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 1679–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roco, L.; Poblete, D.; Meza, F.; Kerrigan, G. Farmers’ Options to Address Water Scarcity in a Changing Climate: Case Studies from Two Basins in Mediterranean Chile. Environ. Manag. 2016, 109, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrteimei, H.A.; Ash’aari, Z.H.; Muharram, F.M. Last Decade Assessment of the Impacts of Regional Climate Change on Crop Yield Variations in the Mediterranean Region. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higley, L.G.; Pedigo, L.P. Economic Injury Level Concepts and Their Use in Sustaining Environmental Quality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1993, 46, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, J.C.; Prabhaker, N.; Reed, D.A.; Perring, T.M.; Castle, S.J.; Huang, T.I. Susceptibility of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) to Insecticides in Laboratory and Greenhouse Bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.D.; Banks, J.E. Population-Level Effects of Pesticides and Other Toxicants on Arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofangsazi, N.; Hogg, B.N.; Hougardy, E.; Stokes, K.; Pratt, P.D. Host Searching Behavior of Gryon gonikopalense and Trissolcus hyalinipennis (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), Two Candidate Biological Control Agents for Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Biol. Control 2020, 151, 104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, B.; Kalyan, R.; Ahuja, U.; Singh, S.K.; Sundria, M.M.; Dhandapani, A. Integrated Management Strategy for Painted Bug, Bagrada hilaris (Burm.) Inflicting Injury at Seedling Stage of Mustard (Brassica juncea) in Arid Western Rajasthan. Pestic. Res. J. 2008, 20, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Hogg, B.N.; Grettenberger, I.M.; Borkent, C.J.; Stokes, K.; Zalom, F.G.; Pickett, C.H. Natural Biological Control of Bagrada hilaris by Egg Predators and Parasitoids in North-Central California. Biol. Control 2022, 171, 104942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The Sublethal Effects of Pesticides on Beneficial Arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainali, B.P.; Kim, S.; Lim, U.T. Effects of Combining Releases of Non-Viable Host Eggs with Insecticide Application on Riptortus Pedestris Population and Its Egg Parasitoids. J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2012, 15, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, U.T.; Mahmoud, A.M.A. Ecotoxicological Effect of Fenitrothion on Trissolcus nigripedius (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) an Egg Parasitoid of Dolycoris baccarum (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Asia Pac. Entomol. 2008, 11, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjisaffar, F.; Talamas, E.J.; Bon, M.C.; Gonzalez, L.; Brown, B.V.; Perring, T.M. Trissolcus hyalinipennis Rajmohana & Narendran (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae), a Parasitoid of Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae), Emerges in North America. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2018, 65, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, F.; Reitz, S.; Jalali, M.A.; Ziaaddini, M.; Izadi, H. Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Two Commercial Insecticides on Egg Parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) of Green Stink Bugs (Hem: Pentatomidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.B.; de Bueno, A.F. Conservation Biological Control Using Selective Insecticides—A Valuable Tool for IPM. Biol. Control 2018, 126, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.W.; Johnson, A.C.; Pandey, S.; Cullen, R.; González-Chang, M.; Wratten, S.D.; Gurr, G.M. History, Current Situation and Challenges for Conservation Biological Control. Biol. Control 2019, 131, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.M.; Carvalho, G.A.; Souza, W.R.; De Freitas Bueno, A. Toxicity of Insecticides to the Egg Parasitoids Telenomus podisi and Trissolcus teretis (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae). Rev. Bras Entomol. 2022, 66, e20220035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantedeschi, R.; Grützmacher, A.D.; de Pazini, J.B.; Bueno, F.A.; Machado, L.L. Selectivity of Pesticides Registered for Soybean Crop on Telenomus podisi and Trissolcus basalis. Pesqui Agropecu. Trop. 2018, 48, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira, R.; do Nascimento, D.V.; Barbosa, P.R.R.; Simmons, A.M.; Torres, J.B. Predation Performance and Survival of Susceptible and Pyrethroid-Resistant Eriopis connexa Germar (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to Insecticides Used in Brassica Crops. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, B.N.; Grettenberger, I.M.; Borkent, C.J.; Prager, S. Parasitism by Gryon aetherium (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae) on Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) Eggs in Northcentral California. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, M.; René, F.H.S. Development, Survivorship and Reproduction of Gryon aetherium Talamas (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), an Egg Parasitoid of Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae), under Eight Constant Temperatures. Biol. Control 2023, 180, 105185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, N.; Ganjisaffar, F.; Perring, T.M. Evaluation of the Physiological Host Range for the Parasitoid Ooencyrtus mirus, a Potential Biocontrol Agent of Bagrada hilaris. Insects 2020, 11, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjisaffar, F.; Perring, T.M. Life History Evaluation of Ooencyrtus lucidus, a Newly Described Egg Parasitoid of Bagrada hilaris. Insects 2020, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1994; ISBN 9780691000473. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, R.; Jones, W.A.; Bajwa, B.E.; Rashid, K. Egg Parasitoids from Pakistan as Possible Classical Biological Control Agents of the Invasive Pest Bagrada hilaris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae) 1. J. Entomol. Sci. 2015, 50, 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Hougardy, E.; Hogg, B.N. Host Patch Use and Potential Competitive Interactions Between Two Egg Parasitoids from the Family Scelionidae, Candidate Biological Control Agents of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe-Victoriano, M.; Talamas, E.J.; Sánchez-Peña, S.R. Scelionidae (Hymenoptera) Parasitizing Eggs of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae) in Mexico. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2019, 73, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hougardy, E.; Hogg, B.N. Factors Affecting Progeny Production and Sex Ratio of Gryon aetherium (Hymenoptera: Scelionidae), a Candidate Biological Control Agent for Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Insects 2022, 13, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, J.E.; Bundy, C.S.; Wheeler, A.G., Jr. Overview of the Superfamily Pentatomoidea. In Invasive Stink Bugs and Related Species (Pentatomoidea); McPherson, J.E., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cisternas, A.E.; Rodríguez, A.F.; Morales, R.A. Agentes de Control Natural de Bagrada hilaris En Chile. In Alternativas Sustentables para el Manejo de Bagrada hilaris en Chile; Vitta, P.N., Ed.; INIA La Platina: Santiago, Chile, 2021; pp. 45–66. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia, E.; Osman, A.; Olivares, P.N.; Cisternas, A.E.; Vitta, N. Protocolo de Manejo de Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister); Vitta, N., Ed.; Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias, Centro Regional de Investigación La Platina: Santiago, Chile, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Herting, B.; Simmonds, F.J. A Catalogue of Parasites and Predators of Terrestrial Arthropods. Section A. Host or Prey/Enemy; Commonwealth Agricultural: Slough, UK, 1971; Volume Section A, Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Crosskey, R.W. A Taxonomic Conspectus of the Tachinidae (Diptera) of the Oriental Region. Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) Entomol. 1976, 26, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, M.A.; Irshad, M.; Murtaza, M.; Ghani, M.A. Pentatomids Associated with Gramineae and Their Natural Enemies in Pakistan. Tech. Bull. Commonw. Inst. Biol. Control 1973, 16, 47–67. [Google Scholar]
- Talamas, E.J.; Bremer, J.S.; Moore, M.R.; Bon, M.C.; Lahey, Z.; Roberts, C.G.; Combee, L.A.; McGathey, N.; van Noort, S.; Timokhov, A.V.; et al. A Maximalist Approach to the Systematics of a Biological Control Agent: Gryon aetherium Talamas, Sp. Nov. (Hymenoptera, Scelionidae). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2021, 87, 323–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomeli-Flores, J.R.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, S.E.; Rodríguez-Levya, E.; González-Hernández, H.; Gariepy, T.D.; Talamas, E.J. Field Studies and Molecular Forensics Identify a New Association: Idris elba Talamas, Sp. Nov. Parasitizes the Eggs of Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister). J. Hymenopt. Res. 2019, 93, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajmohana, K. A Checklist of Scelioninae (Platygastridae: Hymenoptera) of India. Zoos Print J. 2006, 21, 2506–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, N.; Saidi, M.; Opiyo, A.; Kasina, M.; Guantai, M. Evaluation of Biological Control Option for Bagrada Bug (Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister)) in Kenya. Int. J. Hortic. Sci. 2024, 30, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjisaffar, F.; Talamas, E.J.; Bon, M.C.; Perring, T.M. First Report and Integrated Analysis of Two Native Trissolcus Species Utilizing Bagrada hilaris Eggs in California. J. Hymenopt. Res. 2020, 80, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fergusson, N.D.M. The Status of the Genus Allophanurus Kieffer (Hymenoptera: Proctotrupoidea, Scelionidae). Entomol. Mon. Mag. 1983, 119, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Thakar, A.V.; Misra, U.S.; Rawat, R.R.; Dhamdhere, S.V. A Record of Predatory Mite, Bochartia Sp., on Bagrada cruciferarum Kirkaldy. Indian J. Entomol. 1969, 31, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Grasswitz, T.R. Laboratory Evaluation of Predation Rates of Two Native Natural Enemies on the Exotic Pest Bagrada hilaris. J. Appl. Entomol. 2016, 140, 744–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, C.H.; Borkent, C.J.; Popescu, V.; Lightle, D.; Hogg, B.; Grettenberger, I. New Insights into Predation through Imaging. Biocontrol. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 196–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, J.E.; Wood, D.M.; González, C.R. Annotated Catalogue of the Tachinidae (Insecta, Diptera) of Chile. Zookeys 2021, 1064, 1–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, M.V.; González-Santander, C.C.; Alfaro-Tapia, A. Improved and Sustainable Management of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera, Pentatomidae) Mediated by Non-Host Plants in Cabbage Crops. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting, Entomology as Inspiration: Insects through Art, Science, and Culture, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 13–16 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rahat, S.; Gurr, G.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Mo, J.; Neeson, R. Effect of Plant Nectars on Adult Longevity of the Stinkbug Parasitoid, Trissolcus basalis. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2007, 51, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, H.R.; Skillman, V.P.; Galindo, G.; Lee, J.C. Floral Resources for Trissolcus japonicus, a Parasitoid of Halyomorpha halys. Insects 2020, 11, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolin, P.; Bresch, C.; Desneux, N.; Brun, R.; Bout, A.; Boll, R.; Poncet, C. Secondary Plants Used in Biological Control: A Review. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2012, 58, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.A.; Guarino, S.; Peri, E.; Colazza, S. Evaluation of Brassicaceae Seedlings as Trap Plants for Bagrada hilaris Burmeister in Caper Bush Cultivations. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badenes-Pérez, F.R. Trap Crops and Insectary Plants in the Order Brassicales. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2019, 112, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niassy, S.; Agbodzavu, M.K.; Mudereri, B.T.; Kamalongo, D.; Ligowe, I.; Hailu, G.; Kimathi, E.; Jere, Z.; Ochatum, N.; Pittchar, J.; et al. Performance of Push–Pull Technology in Low-Fertility Soils under Conventional and Conservation Agriculture Farming Systems in Malawi. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.F.; dos Santos, A.; Silveira, L.C.P.; Tomazella, V.B.; Ferraz, R.M. Push-Pull Cropping System Reduces Pests and Promotes the Abundance and Richness of Natural Enemies in Brassica Vegetable Crops. Biol. Control 2022, 166, 104832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, S.M.; Khan, Z.R.; Pickett, J.A. The Use of Push-Pull Strategies in Integrated Pest Management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 375–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albornoz, M.V.; González-Santander, C.C.; Oyarce, C. Push and Pull Method as an Ecological Alternative for the Sustainable Management of Bagrada hilaris. El MIsionero del Agro. 2021, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- González-Santander, C.C.; Barros-Parada, W. Evaluación de Plantas (Aromáticas y Ornamentales) y Aceites Esenciales con Potencial Acción Repelente Sobre Bagrada hilaris en Cultivo de Repollo. Master’s Thesis, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Valparaiso, Chile, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, E.; Allison, J.D.; Hurley, B.P.; Slippers, B.; Fourie, G. Life History Traits of the Pentatomidae (Hemiptera) for the Development of Pest Management Tools. Forests 2023, 14, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, E.; Vitta, N.; Altimira, F.; De La Barra, N. Hongos Entomopatógenos (HEP) Para Control de La Chinche Pintada (Bagrada hilaris); Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias, Centro Regional de Investigación La Platina: Santiago, Chile, 2019; Ficha técnica No. 20. [Google Scholar]
- Torres Acosta, R.I.; Humber, R.A.; Sánchez-Peña, S.R. Zoophthora Radicans (Entomophthorales), a Fungal Pathogen of Bagrada hilaris and Bactericera cockerelli (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae and Triozidae): Prevalence, Pathogenicity, and Interplay of Environmental Influence, Morphology, and Sequence Data on Fungal Identification. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 139, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, J.; Kushwaha, D.; Rai, A.B.; Singh, A.; Singh, B. Potential of Entomopathogens and Neem Oil against Two Emerging Insect Pests of Vegetables. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 87, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankin, G.; Santiagos, A.; Hermosilla, M.; Aballay, E.; San-Blas, E. A Novel Approach for the Biological Control of Invasive Bagrada Bugs with Entomopathogenic Nematodes. J. Pest Sci. 2022, 95, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakthatvatsalam, N.; Subharan, K.; Mani, M. Semiochemicals and Their Potential Use in Pest Management in Horticultural Crops. In Trends in Horticultural Entomology; Mani, M., Ed.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; pp. 283–312. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich, J.R. Sex Pheromones in Homoptera and Heteroptera. In Studies on Hemipteran Phylogeny; Schaefer, C.W., Ed.; Thomas Say Publications in Entomology: Lanham, MD, USA, 1996; pp. 199–233. [Google Scholar]
- Guarino, S.; de Pasquete, E.C.; Peri, E.; Alonzo, G.; Colazza, S. Role of Volatile and Contact Pheroniones in the Mating Behaviour of Bagrada hilaris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2008, 105, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.A.; Guarino, S.; Colazza, S.; Peri, E. The Role of (E)-2-Octenyl Acetate as a Pheromone of Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister): Laboratory and Field Evaluation. Insects 2020, 11, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scala, M.; Peccerillo, C.; Fouani, J.M.; Nieri, R.; Baser, N.; Verrastro, V.; Cristofaro, M.; Anfora, G.; Mazzoni, V. The Role of Substrate-Borne Vibrational Signals in the Sexual Communication of the Painted Bug, Bagrada hilaris. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2024, 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsignore, C.P.; Vacante, V. Pest Management in Organic Vegetable Greenhouses. In Handbook of Pest Management in Organic Farming; Vacante, V., Kreiter, S., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2018; pp. 374–413. [Google Scholar]
- Parsana, G.J.; Vyas, H.J.; Bharodia, R.K. Effect of Irrigation, Sowing Date and Nitrogen on the Incidence of Painted Bug, Bagrada hilaris Burm., in Mustard. J. Oilseeds Res. 2001, 18, 89–90. [Google Scholar]
- LeVeen, E.; Hodges, A.C. Bagrada Bug, Painted Bug, Bagrada hilaris (Burmeister) (Insecta: Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Department of Entomology and Nematology, UF/IFAS Extension 2014. Available online: http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Ivey, C.B.; Leppla, N.C.; Hodges, A.C.; Eger, J.E. Quality Control Applications for Recovering an Inbred Colony of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Insect Sci. 2023, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Chemical Group | Active Ingredient | Commercial Name | Toxicological Classification (*) | Visa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthranilic amides/Neonicotinoids | Chlorantraniliprole/Thiamethoxam | Voliam flexi 30+D24+BB2:E43 | IV (Green) (e) | No |
| Anthranilic amides/Pyrethroids | Chlorantraniliprole/λ-cyhalothrin | Ampligo 150 ZC | II (Yellow) (c) | No |
| Anthranilic diamides | Cyantraniliprole | Azyra | IV (Green) (e) | No |
| Benzoylphenyl ureas | Novaluron | Rimon 10 EC | IV (Green) (e) | No |
| Carbamates | Methomyl | Balazo 90 SP | Ib (Red) (b) | No |
| Greko 90 SP | Ib (Red) (a) | No | ||
| Kuik 90 SP | Ib (Red) (b) | No | ||
| Neonicotinoids | Acetamiprid | Mospilan | III (Blue) (d) | No |
| Quilate 700 WP | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Imidacloprid | Absoluto 20% SL | IV (Green) (e) | No | |
| Absoluto 70% WP | IV (Green) (e) | No | ||
| Confidor forte 200 SL | III (Blue) (d) | No | ||
| Imaxi 350 SC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Imidacloprid 200 SL Agrospec | IV (Green) (e) | No | ||
| Imidacloprid 70% WP Agrospec | III (Blue) (d) | No | ||
| Nuprid | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Thiamethoxam | Actara 25 WG | IV (Green) (e) | No | |
| Neonicotinoids/Benzoylphenyl ureas | Acetamiprid/Novaluron | Cormoran EC | II (Yellow) (c) | No |
| Neonicotinoids/Pyrethroids | Acetamiprid/λ-cyhalothrin | Gladiador 450 WP | II (Yellow) (c) | No |
| Imidacloprid/β-cyhalothrin | Connect 112.5 SC | III (Blue) (d) | No | |
| Imidacloprid/Deltamethrin | Muralla delta 190 OD | II (Yellow) (c) | No | |
| Thiamethoxam/λ-cyhalothrin | Engeo 247 ZC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | |
| Orbita SC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Organophosphates | Acephate | Orthene 75 SP | III (Blue) (d) | No |
| Chlorpyrifos | Chlorpirifos 48% EC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | |
| Chlorpirifos S 48O | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Chlorpyrifos 480 EC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Profenofos | Selecron 720 EC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | |
| Pyrethroids | α-cypermethrin | Mageos | III (Blue) (d) | No |
| Overkill | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| β-cyfluthrin | Bulldock 125 SC | III (Blue) (d) | No | |
| Predector 125 SC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Bifenthrin | Talstar 10 EC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | |
| Tripp | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| γ-cyhalothrin | Bull | IV (Green) (e) | No | |
| λ-cyhalothrin | Invicto 50 CS | II (Yellow) (c) | No | |
| Karate con tecnología zeon | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Knockout | III (Blue) (d) | No | ||
| Zero 5 EC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Permethrin | Permetrina 50 CE | II (Yellow) (c) | No | |
| Rayo 50 EC | II (Yellow) (c) | No | ||
| Tetranortriterpenoids | Azadirachtin | Neem-X | IV (Green) (e) | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albornoz, M.V.; Santander, C.C.; Alfaro-Tapia, A. A Review of the Arrival, Effects, and Management of Bagrada hilaris in South America: The Case of Chile. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101072
Albornoz MV, Santander CC, Alfaro-Tapia A. A Review of the Arrival, Effects, and Management of Bagrada hilaris in South America: The Case of Chile. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(10):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101072
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbornoz, Marta V., Camila C. Santander, and Armando Alfaro-Tapia. 2024. "A Review of the Arrival, Effects, and Management of Bagrada hilaris in South America: The Case of Chile" Horticulturae 10, no. 10: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101072
APA StyleAlbornoz, M. V., Santander, C. C., & Alfaro-Tapia, A. (2024). A Review of the Arrival, Effects, and Management of Bagrada hilaris in South America: The Case of Chile. Horticulturae, 10(10), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10101072






