Abstract
Antibiotics have been detected in tiny environmental matrices all over the world, which caused a lot of concern. To solve this problem, biological treatment can be a low-cost and high-efficiency way. The use of biochar adsorbents made from the residual sludge of sewage for wastewater treatment can achieve pollutant removal while realizing pollutant reduction and reuse, which is of great significance for green development. In this study, a prepared biochar-based adsorbent (PBA) was modified and used for norfloxacin (NOR) removal. The composition of the adsorbent was characterized, and the influence of application factors on adsorption performance was investigated. After being modified and optimized, an overall removal efficiency of 84% was achieved for NOR in 4 h. The adsorption behavior was spontaneous and consistent with the Lagergren pseudo-second kinetic model and Langmuir model. The adsorption capacity of PBA reached 8.69 mg·L−1 for NOR. A total removal efficiency of 62% was obtained for five mixed quinolone antibiotics by PBA. The PBA could be well regenerated and reused five times. This study explored a new method of the bio-waste utilization of sewage sludge for antibiotic removal from wastewater.
1. Introduction
The disposal of sewage sludge with moisture content over 80% is a problem of growing importance in municipal wastewater treatment plants (MWTPs) [1]. To reduce the associated health problem and hindrances, the sludge must be thickened and undergo further treatment. The current feasible methods for further treatment are agriculture applications, anaerobic digestion, thermal treatments, etc. [2,3]. Compared with other methods, hydrothermal treatment represents a promising way to disintegrate the bio flocs in the sludge, improve the dehydration ability [4], and gain valuable biochar products, which can be utilized as adsorbents, catalysts, and fuels [5,6]. Recent studies focused on this biochar-based adsorbent have shown its potential to remove pollutants from wastewater due to its porous structure with abundant active sites contributed by biological flocs, and the relatively low cost compared with commercial adsorbents [7,8,9]. It is worth noting that the thermal-hydrolyzed sewage sludge biochar (TSSB) without further modification shows relatively poor adsorption capacities under the high concentration of the pollutants [10]. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the adsorption performance by modifying the TSSB. As a result, research into the improving methods of this TSSB adsorbent for different specific applications has become a hotspot in this research field.
Antibiotics, a class of emerging organic micro-pollutants, have become a subject of scientific and public concern because of their potential bioactive properties and adverse effects on the aquatic environment [11]. Among them, quinolone antibiotics were one of the most recently utilized in clinical practice [12]. MWTPs are among the main sources of antibiotics’ release into various compartments of the environment worldwide [13]. Conventional activated sludge processes are generally ineffective in removing antibiotics [14]; therefore, an additional treatment process is needed to enhance antibiotic removal from MWTP effluent. Compared with membrane processes and advanced oxidation processes [15,16] that suffer the limitation of high cost and unintended by-products, adsorption processes are considered to be one of the most feasible techniques for antibiotic removal, which has advantages in performance efficiency and cost effectiveness [17]. A wide source of raw materials can be adapted to prepare adsorbents for antibiotic contamination control. Hence, it explores a new way for the utilization of sewage sludge. Combined with the TSSB adsorbents mentioned above, a method of sludge reuse to remove antibiotics from MWTP effluent is proposed.
In the present study, a novel method of preparing a biochar-based adsorbent from TSSB with nitric acid modification was proposed. To evaluate the performance of the prepared adsorbent, a typical quinolone antibiotic of norfloxacin (NOR) was chosen as the target pollutant in the synthetic wastewater. Adsorption experiments and model analyses were performed to evaluate the feasibility of applying TSSB to NOR removal from wastewater, and the results of the adsorption capacity and reuse ability of the prepared biochar-based adsorbent (PBA) indicated its practicability in quinolone antibiotic contamination control. The present study provides a practical method of antibiotic removal for MWTPs that takes sewage sludge reduction, reuse, and recycling into account simultaneously.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Water Samples
All chemicals were purchased commercially and used without further purification. Reagent solutions for the experiments were prepared with analytical reagent-grade chemicals and Milli-Q water (18.2 MΩ, Milli-Q Biocel, Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). pH was adjusted by 0.1 M HCl and 0.1 M NaOH. Synthetic wastewater 1 (SW1) was prepared by the Milli-Q water spiked with NOR without pH adjustment. Synthetic wastewater 2 (SW2) was prepared by the actual effluent (AE) spiked with NOR without pH adjustment. The effluent collected from a local MWTP over three consecutive days was mixed, filtered through 0.22 μm membrane filters, and then stored at 4 °C before use. The water qualities of the effluent are listed in Table S1.
2.2. PBA Preparation and Its Reusability
The TSSB was collected from the thermal hydrolysis process (Figure S1) in the same MWTP as the AE. The TSSB was firstly ground and passed through 2 mm sieves to gain the raw biochar adsorbent (RBA), then soaked (1:50, w/v) in 0.1 M HNO3 and stirred under 30 °C for 240 min, and then filtered and rinsed repeatedly with Milli-Q water until the filtrate to neutral pH. The PBA was finally obtained by the dried filter residue after grinding and passing through 2 mm sieves. A chemical regeneration procedure was conducted to evaluate the reusability of PBA. The used PBA was collected by centrifugation and eluted with 0.1 M NaOH, then separated and washed with Milli-Q water to remove the residual NaOH until the pH of the eluent was stable. The eluted precipitate was dried at 60 °C for 12 h to obtain regenerated PBA (rPBA) for the reuse experiments.
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
Adsorption experiments were investigated by means of batch tests with efficient mixing (agitated on a mechanical PBAker with 170 r·min−1), and 3 independent tests were conducted to study NOR removal for each condition, with solution samples taken in triplicate. For adsorption kinetics tests, 100 mL SW1 with 10 mg·L−1 NOR was placed into a conical flask and then adjusted pH to neutral. After the addition of 100 mg of PBA, the conical flask was agitated under a constant temperature (30–50 °C), and aliquots were withdrawn at the predetermined time. For adsorption equilibrium tests, 50 mL SW1 with a specified concentration (5.0–18 mg·L−1) of NOR was placed into a conical flask, then added a specified amount (2.5–500 mg) of PBA and adjusted pH to 7, next agitated under a constant temperature (30–50 °C) for 240 min. Control tests that did not add PBA (i.e., blanks) were also conducted to confirm that changes in the blank NOR concentration during the long-term mixing were negligible. For the other concern of influential parameter initial pH and ionic strength, experiments with the same procedure, adding 50 mg PBA into 50 mL SW1 with 10 mg·L−1 NOR and then agitating at 30 °C for 240 min, were conducted. The specific experimental conditions were (1) adjusting the initial pH to 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, and 13, respectively, and (2) adding NaCl and CaCl2 to make the ionic strength 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 M, respectively.
2.4. Quantification and Adsorbent Characterization
To quantify the NOR concentration in the aqueous phase, 2.0 mL aliquots were withdrawn and filtered immediately through 0.22 μm membrane filters, then determined by UV-Vis spectrophotometry (Hach DR-6000, HACH, Loveland, CO, USA) at 272 nm. Ciprofloxacin-d8 HCl was adopted as an internal standard to qualify data accuracy. The NOR concentrations in the solid phase were calculated from the mass balance. The ash content was determined by the Thermal Gravimetric Analyzer (TGA-50, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface areas of the adsorbents were obtained by the nitrogen gas adsorption–desorption method (ASAP 2020 HD88, Maclin Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA). The SEMs of PBA and rPBA were obtained by field-emission scanning electron microscope (Carl Zeiss, ZEISS SUPRA® 55, Oberkochen, Germany). The elementary composition was tested by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (Thermo Fisher, ESCALAB 250Xi, Waltham, MA, USA). The zero-charge point pH (pHpzc) of the sorbent was determined by the pH drift method (Mettler, IE438, Zurich, Switzerland).
2.5. Analytical Modeling
Adsorption kinetics were calculated by Lagergren pseudo-first-order [18] and pseudo-second-order [19] dynamics equations:
Integrating both sides:
where qm was the theoretical equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg·g−1), qt was the adsorption capacity at time t (mg·g−1), t was the adsorption time (min), and K1 was the pseudo-first-level kinetic rate constant (min−1).
where qm was the theoretical equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg·g−1), qt was the adsorption capacity at time t (mg·g−1), t was the adsorption time (min), and K2 was the pseudo-second-level kinetic rate constant (g·(mg·min)−1).
The intra-particle diffusion of NOR was depicted by Weber–Morris model [20]:
where kdif was the constant of diffusion rate within the adsorbent particles (mg·(g·min1/2)−1) and I was a constant (mg·g−1).
Langmuir adsorption isotherm model equation:
where qe was the mass of unit adsorbent at adsorption equilibrium (mg·g−1), qm was the theoretical saturation adsorption capacity of unit adsorbent (mg·g−1), Ce was the equilibrium concentration (mg·L−1), and KL was Langmuir adsorption constant (L·mg −1).
Thermodynamics-related formulae were calculated by Van’t Hoofman model:
where ΔGθ was the change in Gibbs free energy (kJ·mol−1), ΔHθ was the enthalpy change (KJ·mol−1), ΔSθ was the entropy change (J·(mol·K)−1), T was the temperature (K), R was a thermodynamic constant (8.314 J·(mol·K)−1), and Kd was the distribution coefficient of adsorbent in solid-liquid phase (mL·g−1).
Ash content was
where m2 was mass of cauterized residue at constant weight (g) and m1 was weight of sample (g).
The adsorption capacity of sludge hydrochar adsorbents for NOR were calculated as
The removal efficiency of NOR was determined as
Langmuir-model-derived separation factor or equilibrium parameter RL was
where RL was the constant separation factor of solid-liquid adsorption system, dimensionless.
Lagergren pseudo-first-order dynamics equation was
Integrating both sides:
where qm was the theoretical equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg·g−1), qt was the adsorption capacity at time t (mg·g−1), t was the adsorption time (min), and K1 was the pseudo–first level kinetic rate constant (min−1).
Freundlich adsorption isothermal model equation:
where KF was Freundlich adsorption constant (), which reflects the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent; 1⁄n was empirical constant, dimensionless.
3. Results
3.1. The Superiority of PBA over RBA for Adsorptive NOR Removal
The removal efficiency of NOR by RBA was only 21.4%, which was not applicable in practical application. The NOR adsorption performances of different modified RBA were tested (Text S1), and the PBA with the best performance of NOR removal was adopted. The removal efficiency of NOR by PBA reached 3.95 times as high as that of RBA (Figure S2a), and the changes in the main inorganic components and crystal structures were negligible (Figure S2b). The characteristics of the RBA and PBA are listed in Table 1. On the one hand, the increment in ash content and the decrement in carbon composition indicated that organic matters in the RBA were partially oxidized or dissolved by nitric acid, which may result in adverse effects on NOR adsorption. On the other hand, favorable changes in NOR removal were also induced: (1) the BET surface area of PBA increased significantly by 21% as compared with that of RBA, with more oxygen-containing functional groups for NOR bonding simultaneously, and (2) the hydrophilicity and polarity of PBA were improved inferring from the increment of the O/C and (O + N)/C composition, respectively. The superiority of PBA over RBA for adsorptive NOR removal was mainly based on the combination of the mentioned above changes. A PBA with a larger specific area and well-developed pore structure is expected to adsorb the antibiotic molecules through a pore-filling mechanism [21].

Table 1.
The characteristics of the RBA and PBA.
3.2. NOR Adsorption Kinetics for PBA
The effects of PBA dosage and initial NOR concentration on NOR removal were conducted, and the adsorption kinetic experiments were conducted based on their results. Figure 1a shows the NOR removal efficiency at different PBA dosages. The removal efficiency increased from 24.5% to 84.1%, with a higher PBA dosage (1 g·L−1), due to more adsorption sites provided by the adsorbents. The removal efficiency increased to 90.8% when the PBA concentration was 10 g·L−1. The slowdown in the adsorption rate was due to the fact that (1) a limited amount of adsorbed mass led to a tendency to decrease the adsorption capacity per unit mass of PBA and (2) a higher dosage of adsorbent might also have caused particle aggregation, which reduced the total specific surface area. Therefore, a high dose of adsorbent dosage would not only increase the cost, but it would also lead to underutilization of the sites on adsorbent; 1 g·L−1 was suitable for subsequent tests. Figure 1b demonstrates the effect of the initial concentrations of NOR on the adsorption capacity of PBA and the removal efficiency of NOR. As the NOR concentration increased, the adsorption capacity of PBA for NOR increased linearly, and the removal rate showed a trend of increase and then gradually decreased. More NOR molecules were driven to move toward the adsorption sites by a higher-pressure gradient, making the adsorption capacity of the PBA increase with the increase in NOR concentration. Hence, the adsorbent could be applied to wastewater containing higher concentrations of antibiotics, such as for treating effluents from pharmaceutical industries and hospitals. Figure 1c shows the time-course changes in NOR concentrations in the adsorption experiments, and the corresponding solid phase concentrations (i.e., the amount of NOR adsorbent on the PBA) calculated by mass balance are shown in Figure 1d. Compared with the pseudo-first-order model, the Lagergren pseudo-second-order model was better for investigating the adsorption process (dashed line). The parameters obtained from the fitting are listed in Table 2. The saturated solid phase concentration calculated by the Lagergren pseudo-second-order model (8.732 mg·g−1) was similar to the experimentally obtained results (8.686 mg·g−1). And the lower temperature was more favorable for NOR adsorption by PBA, which was likely to be a result of the lower desorption rate of NOR from PBA. The results suggested that the adsorption capacity was proportional to the number of active sites, and the NOR was probably adsorbed via physical interactions [22].
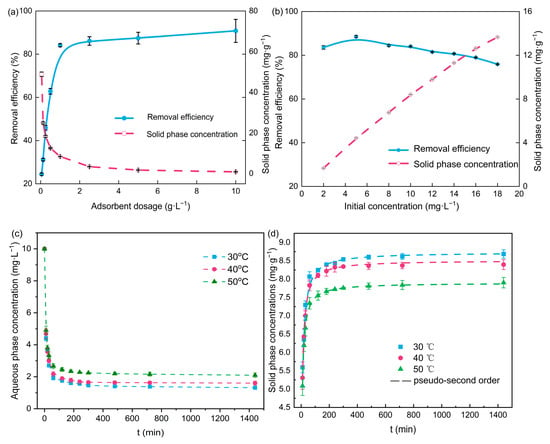
Figure 1.
NOR removal efficiency under different (a) adsorbent dosages and (b) initial NOR concentrations. (c) NOR removal and (d) simulation of the adsorption kinetics of NOR on PBA.

Table 2.
Kinetic parameters of NOR adsorption on PBA at different temperatures.
The intra-particle diffusion depicted by the Weber–Morris model to analyze the rate-limited step in the adsorption process is shown in Figure 2 and Table 3. The adsorption process was divided into three stages: membrane diffusion, intra-particle diffusion, and adsorption equilibrium at 0–60 min, 120–240 min, and 300–1400 min, respectively. In the first stage, the NOR quickly diffused to the outer surface of the PBA, which was not yet occupied. In the second stage, most of the active sites on the surface of the PBA had been occupied, and the adsorbed NOR began to diffuse into the pores of the PBA. The diffusion resistance resulted in a lower adsorption rate. In the third stage, the adsorption basically reached the equilibrium state, and the kdif value decreased to less than 1% of the first stage. The lower concentration of NOR residue and fewer active sites of PBA might lead to weaker force to drive the mass transfer of NOR from bulk solution to the PBA surface. In the present study, the extensions of the three linear segments did not cross the origin, indicating that the intra-particle diffusion was not the predominant rate control step, and the whole adsorption process was the result of a combination of multiple dynamics. The same results can also be obtained from previous studies [23].
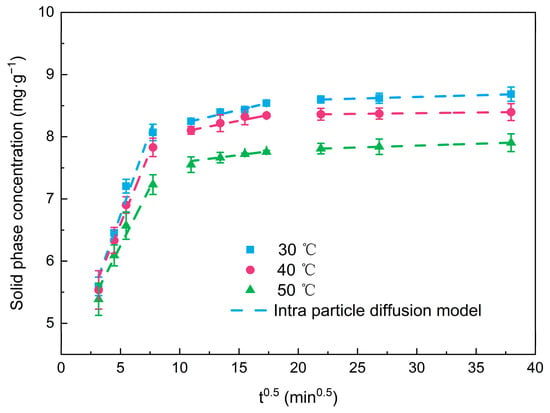
Figure 2.
Intra-particle diffusion models of NOR on PBA.

Table 3.
Parameters of NOR adsorption on PBA calculated using the Weber–Morris (intra-particle diffusion) model.
3.3. NOR Adsorption Isotherms of PBA
Adsorption isotherms at different temperatures are shown in Figure 3a, and relevant parameters obtained by fitting are listed in Table 4. Solid phase NOR concentration obtained by the experiments under low temperatures was higher than that obtained under higher temperatures, which indicated the exothermic nature of the adsorption process. The experiment data fitted well with the Langmuir and Freundlich models. A single-layer chemical adsorption process can be described by the Langmuir isotherm, while the Freundlich isotherm indicates a multilayer and heterogeneous adsorption. The correlation coefficient (R2) for the Langmuir model was greater than 0.99 under all conditions, which suggested that the adsorption of NOR on PBA was monolayer molecule adsorption. The value of adsorption capacity (qm) was gradually decreased as the temperature increased. Additionally, the maximum adsorption capacity of PBA was calculated to be 29.08 mg·g−1, which provided a broad potential for NOR removal from wastewater. The separation factor RL variation is shown in Figure 3b. The value of RL being between 0 to 1 also suggested that the monolayer molecule adsorption was predominant in NOR adsorption by PBA.
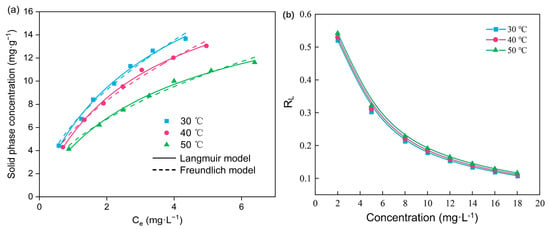
Figure 3.
(a) Adsorption isotherms of NOR on PBA. (b) RL changes in NOR adsorption on PBA.

Table 4.
Parameters of Langmuir and Freundlich models for adsorptive NOR removal by PBA.
3.4. NOR Adsorption Thermodynamics of PBA
The performance of NOR adsorption by PBA was determined by the thermodynamic parameters. Free energy (ΔGθ), enthalpy (ΔHθ), and entropy (ΔSθ) tabulated in Table 5 were obtained from Van’t Hoofman plots. The negative value of ΔGθ at lower temperatures indicated that the adsorption of NOR onto PBA was spontaneous. But the values of ΔGθ became less negative with increasing temperature, especially at a higher temperature of 50 °C, indicating that a lower temperature was suitable for the NOR adsorption process. The magnitude of ΔHθ can give an idea about the type of adsorption process. The negative value of calculated ΔHθ indicated the exothermic nature of the adsorption process. Therefore, the NOR adsorption decreased, and the process was inhibited at higher temperatures, which was consistent with the results discussed in Results 3.2 and 3.3. The absolute value of ΔHθ was lower than 40, suggesting that the adsorption processes of NOR onto PBA could be attributed to a combined physiochemical reaction rather than a purely physical or chemical adsorption process. The negative value of ΔSθ suggested that the random movement of NOR at the solid/liquid interface decreased, and the adsorption might decrease steric hindrance.

Table 5.
Thermodynamic parameters of NOR adsorption by PBA.
3.5. Effect of pH and Ion Strength on NOR Removal
NOR adsorption is significantly influenced by pH conditions due to the differences in NOR species and the charge properties of a PBA surface under different pH values. The pHpzc which indicated the degree of functionalization of PBA was obtained by Figure 4a, and the electrical neutrality at the PBA surface was at pH = 4.14. The NOR removal efficiency under the pH value between 1.0 and 13.0 are shown in Figure 4b. The higher removal efficiencies were achieved at a pH value between 6.09 to 8.74, under which the main species of NOR were amphiphilic and neutral molecules [24]. Under the other pH conditions, the H+ (or OH−) adsorbed on PBA reduced the NOR-adsorbed concentration by hindering NOR+ (or NOR−) from contacting the PBA surface through electrostatic repulsion and/or competing for adsorption sites, which resulted in lower NOR removal efficiency.
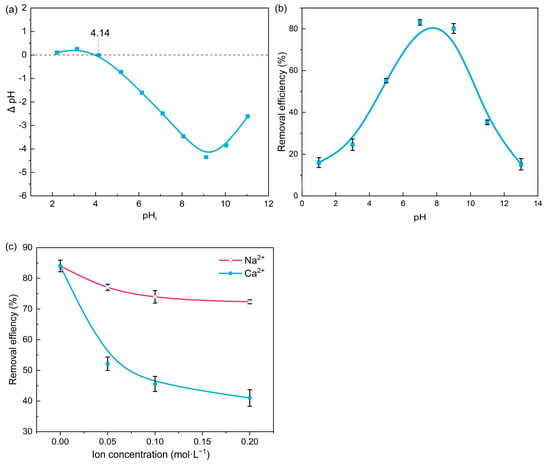
Figure 4.
(a) pHpzc of PBA and removal efficiency of NOR under different (b) pH and (c) ionic conditions.
The real wastewater contains a certain level of salt ions, which would affect the PBA adsorption capacity. The effects of ionic strength on adsorptive NOR removal by PBA are shown in Figure 4c. The presence of Na+/Ca2+ inhibited the NOR removal, and the effect of Ca2+ was more significant than Na+ was. This may be attributed to site competition, chelation, reduction of hydrophobic forces, and electrostatic attraction, which had already been reported in previous studies [25,26].
3.6. Potential of PBA for Practical Applications
A large amount of organic and inorganic pollutants is frequently detected in real wastewater, which has an adverse impact on NOR adsorption. To evaluate the potential of PBA for practical applications, adsorption experiments of adding 50 mg PBA into 50 mL SW1 or SW2 with 10 mg·L−1 NOR and then agitating at 30 °C for 240 min were conducted. The NOR removal efficiency in SW1 achieved 84 ± 1.5%, while, in contrast, it was reduced to 77 ± 0.6% in SW2. The decrement indicated that the substances in actual effluent inhibited the adsorption process. The TOC removal in SW1 was 5.06 ± 0.07 mg·L−1, while, in contrast, it was 20.18 ± 0.12 mg·L−1 in SW2. The increment in TOC removal was greater than the TOC induced by spiking NOR (around 6.02 mg·L−1), which indicated that the decrease in NOR removal was probably attributed to the dissolved organic matter in actual effluent. This result is consistent with previous research [27]. To further test its performance in complex situations, experiments on the adsorptive removal of mixed antibiotics by PBA were conducted. Five antibiotics, including NOR, ciprofloxacin (CIP), lomefloxacin (LOM), enrofloxacin (ENR), and ofloxacin (OFL), were mixed and added into SW1 or SW2 as the target contaminants in practical application. The total concentration of mixed antibiotics was 10 mg·L−1, where each antibiotic was 2 mg·L−1. The removal efficiency is shown in Figure 5a. The overall removal efficiency of mixed antibiotics reached 78% and 62% in SW1 and SW2, respectively, which showed the good performance of PBA for NOR adsorption in complex circumstances.
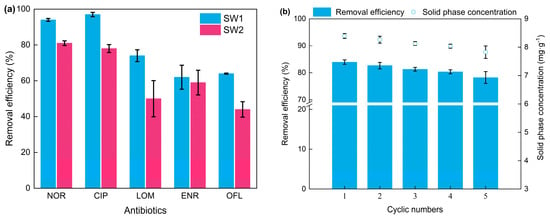
Figure 5.
(a) Comparison between adsorption effect of mixed antibiotics in SW1 and SW2 tested after 4 h. (b) Removal efficiency of NOR by rPBA.
The reusability of adsorbent is crucially important to minimize the cost. Figure 5b shows the results of NOR removal efficiency and solid phase NOR concentration of the adsorption experiments using the repeatedly regenerated PBA (rPBA). When compared with the first cycle, the NOR removal efficiency and solid phase NOR concentration only reduced by 6.8% in the fifth cycle. No obvious difference in the rough surface and the pore structure was observed in the adsorbent morphology between PBA and rPBA after reusing for five cycles (Figure 6). The results indicated the used PBA could be efficiently regenerated by a simple and economical procedure using a low concentration of alkali solution, thus providing a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way of reducing, reusing, and recycling biological products in activated sludge WWTPs.
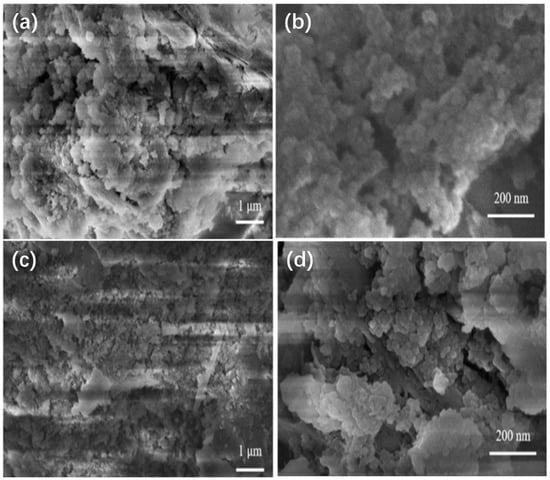
Figure 6.
SEM of PBA after five cycles of adsorption. (a,b) are the surface structures of PBA at 1 μm and 200 nm scales. (c,d) are the surface structures of PBA at 1 μm and 200 nm scales after five adsorption tests.
4. Discussion
Generally, raw biochar adsorbents initially prepared by sewage sludge are not suitable for the removal of high-concentration pollutants due to their limited adsorption capacities. Therefore, modification is an essential step to improve adsorption performance. The modification with HNO3 made the adsorbents have more oxygen-containing functional groups and porous structure, which accelerated the diffusion of antibiotic molecules to the outer surface and combined with active sites of PBA [28]. Considering the electrostatic attraction between NOR and PBA, pH was an important factor that affected the removal efficiency. At pH 3, quinolone antibiotics presented as predominantly cationic due to their −NH or −N groups being bound to H+. As the pH increased, the −COOH of the antibiotics became −COO− by losing H+, and the portion of quinolone antibiotics came to amphoteric or anionic [29]. According to pHpzc values, PBA can be used for NOR removal within the PH range from 6 to 10, with a NOR removal efficiency of around 60%.
The adsorption kinetics of PBA can be better described by the Lagergren pseudo-second-order model. Simulation results indicated the adsorption process was controlled by external boundary layer diffusion and intra-particle diffusion, which was similar to the results of a previous study [30]. However, the adsorption process cannot be recognized as a strict chemical adsorption process because the physical adsorption of large molecules also could be described by the Lagergren pseudo-second-order model. Further, according to thermodynamics data, the absolute value of ΔHθ was less than 40, which indicated that the adsorption process was more likely to be a physical process.
The RL of PBA was lower at 30 °C than at 50 °C, suggesting that it was more suitable to be used under room temperatures. Combined with its good performance of mixed antibiotic removal and recyclability, PBA could be considered as a potential candidate for treating antibiotics in aquaculture, medical and pharmaceutical wastewater, etc. To deeply understand the adsorption mechanism such as hydrogen bond, electrostatic attraction, and π–π interaction formed by the interaction between functional groups and antibiotics, DFT calculations can be expected in future studies. And the opex and capex costs are to be analyzed for practical application.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, a novel sludge hydrolyzed adsorbent modified with HNO3 was used for quinolone antibiotic removal from synthetic wastewater. This easily synthesized PBA exhibited high NOR-removal efficiency due to its oxygen-containing functional groups and porous structure. The adsorption behavior of NOR onto PBA could be well described by the pseudo-second-order model, and the tested adsorption capacity was close to the calculated value. The adsorption process was physiochemically related to the number of adsorption sites, and one molecule occupied only one adsorption site during the process, which was spontaneous and more favorable at room temperatures. Additionally, the overall removal efficiency reached higher than 60% for mixed antibiotics by PBA from complex wastewater, and the recycled rPBA remained over 90% of its initial adsorption capacity for NOR after 5 cycles. Cost analyses are to be carried out to evaluate the values of rPBA for antibiotic removal from real wastewater in future studies. Considering the efficiency of antibiotic adsorption by PBA and the reusability of rPBA prepared from waste and into an eco-friendly adsorbent, this study proposed a potentially sustainable way of antibiotic removal from wastewater by the biochar-based adsorbent in wide application.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation9080752/s1. Table S1: The main components in the secondary treatment wastewater used in this study; Figure S1: The flow chart of thermal hydrolysis of excess sludge from an MWTP; Figure S2: The (a) antibiotic removal efficiency and (b) XRD of RBA with different modification methods.
Author Contributions
Methodology and software, Y.G.; formal analysis, X.L. and M.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; review and editing, G.S. and L.D.; funding acquisition, L.D. and Y.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Top Talent of SZTU (grant no. GDRC202115) and the Science, Technology and Innovation Commission of Shenzhen Municipality (grant no. GXWD20201231165807007-20200810165349001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Lin, J.; Chi, Q.; Wang, Y. Migration and risk assessment of heavy metals in sewage sludge during hydrothermal treatment combined with pyrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.X.; Zhang, B.; Saad, E.M.; Ingall, E.D.; Tang, Y.Z. Speciation evolution of zinc and copper during pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization treatments of sewage sludges. Water Res. 2018, 132, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, A.; Zhang, R.; Ngo, H.H.; He, X.; Ma, J.; Nan, J.; Li, G. Life cycle assessment of sewage sludge treatment and disposal based on nutrient and energy recovery: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Yu, G.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y. Hydrothermal and alkaline hydrothermal pretreatments plus anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge for dewatering and biogas production: Bench-scale research and pilot-scale verification. Water Res. 2017, 117, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhan, L.; Ok, Y.S.; Gao, B. Minireview of potential applications of hydrochar derived from hydrothermal carbonization of biomass. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 57, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Kumar, M.; Mohapatra, S.; Singh, S.K. Nutrient rich rich biomass and effluent sludge wastes co-utilization for production of biochar fertilizer through different thermal treatments. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguyal, F.; Sarmah, A.K.; Gao, W. Synthesis of magnetic biochar from pine sawdust via oxidative hydrolysis of FeCl2 for the removal sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 321, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, M.I.; Gao, B.; Yao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zimmerman, A.; Mosa, A.; Pullammanappallil, P.; Ok, Y.S.; Cao, X. A review of biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 46, 406–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.; Wang, B.; Wu, P.; Lee, X.Q.; Xing, Y.; Chen, M.; Gao, B. Adsorption of emerging contaminants from water and wastewater by modified biochar: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainab, S.M.; Junaid, M.; Xu, N.; Malik, R.N. Antibiotics and antibiotic resistant genes (ARGs) in groundwater: A global review on dissemination, sources, interactions, environmental and human health risks. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, I.T.; Santos, L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: A review of the European scenario. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 736–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, I.; Rizzo, L.; McArdell, C.S.; Manaia, C.M.; Merlin, C.; Schwartz, T.; Dagot, C.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: A review. Water Res. 2013, 47, 957–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Yan, M.; Lin, J.; Xu, L.; Gong, H.; Gong, H. A Review of Processes for Removing Antibiotics from Breeding Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Vatanpour, V.; Khataee, A. Removal of antibiotics from wastewaters by membrane technology: Limitations, successes, and future improvements. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, R.K.; Ishaque, F.; Ahn, Y.H. Fate of antibiotic resistant genes in wastewater environments and treatment strategies-A review. Chemosphere 2022, 298, 134671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoon, B.L.; Ong, C.C.; Saheed, M.S.M.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C.; Lam, S.S.; Juan, J.C. Conventional and emerging technologies for removal of antibiotics from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 122961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonin, J.P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Chen, L.; Xia, S.Q.; Zhao, J.F.; Chovelon, J.M.; Renault, N.J. Biosorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by dried activated sludge. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, S.X.; Chen, J.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Chen, Y.P. Adsorption of Pb(II) on mesoporous activated carbons fabricated from water hyacinth using H3PO4 activation: Adsorption capacity, kinetic and isotherm studies. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 293, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Tomul, F.; Ha, N.T.H.; Nguyen, D.T.; Lima, E.C.; Le, G.T.; Chang, C.T.; Masindi, V.; Woo, S.H. Innovative spherical biochar for pharmaceutical removal from water: Insight into adsorption mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 394, 122255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, É.C.; Adebayo, M.A.; Machado, F.M. Kinetic and equilibrium models of adsorption. In Carbon Nanomaterials as Adsorbents for Environmental and Biological Applications; Bergmann, C.P., Machado, F.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 33–69. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Li, H.; Li, G.C.; Gao, B.Y.; Yue, Q.Y.; Li, X.B. Characterization and ciprofloxacin adsorption properties of activated carbons prepared from biomass wastes by H3PO4 activation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 217, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, P.; Yang, L.; Wu, L.; He, L.; Gao, F.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Z. Iron/zinc and phosphoric acid modified sludge biochar as an efficient adsorbent for fluoroquinolones antibiotics removal. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.F.; Xiao, W.L.; Niu, B.H.; Duan, W.Z.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, Y. Highly efficient adsorption of fluoroquinolone antibiotics using chitosan derived granular hydrogel with 3D structure. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 281, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Lu, H.J.; Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Jing, L.Y.; He, X.H. Fabrication of magnetic alginate beads with uniform dispersion of CoFe2O4 by the polydopamine surface functionalization for organic pollutants removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.S.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Chen, H.; Gao, B. Ball milled biochar effectively removes sulfamethoxazole and sulfapyridine antibiotics from water and wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.W.; Meng, Z.F.; Song, E.; Sun, X.X.; Hu, X.L.; Li, W.B.; Liu, Z.; Gao, S.; Song, B. Co-adsorption capabilities and mechanisms of bentonite enhanced sludge biochar for de-risking norfloxacin and Cu2+ contaminated water. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.Q.; Yang, W.Y.; Wang, Z.; Hao, X.D. Role of extracellular polymeric substance in adsorption of quinolone antibiotics by microbial cells in excess sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 370, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, G.; Pan, L.; Li, C.; You, F.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Shang, X. Study of ciprofloxacin removal by biochar obtained from used tea leaves. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).