Abstract
Research on metal salt-based deep eutectic solvent (DES) pretreatment is still in its infancy, and the effect of hydroxyl groups on Cl− in choline chloride (ChCl) is not resolved. In this study, a type IV DES composed of metal salt and glycerol (Gly) was prepared for pretreatment of moso bamboo to improve its enzymatic hydrolysis. The correlation between enzymatic hydrolysis and the contents of hemicelluloses and lignin was evaluated using the Box–Behnken design. The results showed that FeCl3-based DES was optimal among various DES. The solid recovery was reduced to 55.54% following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment, which was effective in the removal of hemicelluloses and lignin compared with ternary DES pretreatment (with ChCl) under mild conditions (100 °C, 3 h). With the increase of pretreatment temperature (120 °C, 2 h), a significant proportion of hemicelluloses (76.07%) and lignin (62.77%) was removed. The structure of FeCl3/Gly pretreatment residue was seriously damaged, and the glucose yield increased to 91.13% following enzymatic hydrolysis. This correlation indicated that the hemicelluloses’ content had a significant influence on enzymatic hydrolysis of the residue following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment. This study elucidates the pretreatment effect of metal salt-based DES, which will be helpful in the value-added conversion of moso bamboo under mild conditions.
1. Introduction
With the depletion of petrochemical resources and the deterioration of the environment, research on utilizing renewable and degradable resources as substitutes for fossil fuels has gained momentum. Lignocellulose, primarily composed of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin, is a clean and abundant renewable energy source that can be converted into high value-added products, such as materials and energy [1]. Cellulose is the backbone of the cell wall, and lignin and hemicelluloses are combined as ‘adhesives’ and ‘fillers’ through covalent bonds and physical effects [2]. The stubborn anti-degradation barrier of lignocellulose is formed by their chemical compositions and their structure, and thus, using these individual components effectively is challenging. Thus, lignocellulose must be pretreated to destroy its original dense structure.
Traditional pretreatment methods can be classified as physical, chemical, biological, or combined [3]. Generally, lignin suppresses the adsorption of cellulase onto cellulose through hydrophobic interactions, electrostatic interactions, and hydrogen bonding [4]. As a result, the pretreatment process should remove as much lignin as possible to reduce its impact on enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency [5]. With the growing concern about environmental protection, researchers are inclined to develop environmentally friendly green solvents. Recently, deep eutectic solvent (DES) has been employed to separate and modify lignocellulose. DES is a new green solvent whose properties are similar to those of ionic liquid (IL). However, DES is greener, less costly, and more accessible than IL [6]. Among them, type III DES is widely used to pretreat biomass because of its simple structure. However, the effect of neutral DES (such as Choline Chloride/glycerol, namely ChCl/Gly) on fractionation is limited [7]. The reason for the low efficiency of the ChCl/Gly system in separating hemicelluloses and lignin is that the Cl− of ChCl is surrounded by the hydroxyl groups of glycerol, forming weak hydrogen bonds, occupying the hydrogen bond acceptor (HBA) sites of Cl− thereby reducing the acidity of the solvent [8]. This is not sufficient to cleave the hydrogen and ether bonds in carbohydrates and lignin–carbohydrates complex (LCC). However, the acidity of neutral DES can be adjusted by replenishing acid with Lewis acid or Brønsted acid [9].
Metal chloride salts are cost-effective Lewis acids that exhibit excellent catalytic activity and low corrosivity. These advantageous features are conducive to the removal of lignin and hemicelluloses [10]. Therefore, metal chloride salts were added as Lewis acids into neutral DES to provide acidity and achieve a good separation effect, as reported in a previous paper [8]. It was found that metal chloride salts could act as a HBA in DES and form ternary DES with neutral binary DES. The addition of AlCl3∙6H2O in pretreatment solvent improved the acidity and the ability of the solvent to accept hydrogen bonds, and it broke down the hydrogen bond network in lignocellulose, thereby significantly improving the fractionation efficiency of the biomass. Anions in metal chloride salts exhibit a strong depolymerisation ability due to the disruption of the hydrogen bonding network of polysaccharides, followed by the formation of new hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl groups of polysaccharides [11]. Metal ions can complicate lignin functional groups, eliminate the inhibitory effects of lignin, and provide more active sites for cellulose [12]. A previous paper reported that the resulting degradation products can be dissolved in organic phases [13]. Thus, combining metal chloride salts with organic solvents is an ideal method for evaluating the influence of lignin and hemicelluloses on enzymatic hydrolysis.
In our present work, a type IV DES (without ChCl) composed of metal chloride salts and polyols was synthesised and used to pretreat moso bamboo under mild conditions to improve enzymatic hydrolysis, in which Gly acted as a hydrogen-bond donor (HBD) and directly cooperated with the metal cations. The surrounding effect of the polyol hydroxyl group on Cl− in ChCl-based DES can limit the cleavage of the existing hydrogen bonds in lignocellulose, which impedes the value-added conversion of lignocellulose under mild conditions. The metal chloride/Gly solvent system was proposed to avoid this problem. Moreover, the addition of metal chloride not only acted as an HBA in DES but also provided an acidic environment for pretreatment, which helped to improve the pretreatment effect. The changes in the residue following type Ⅳ DES (without ChCl) and the corresponding ternary DES (with ChCl) pretreatment were compared to examine its effect on the promotion of enzymatic hydrolysis. The effects of various type IV DES pretreatments with different metal cations (Fe3+, Al3+, and Zn2+) were also analysed to optimise the metal chloride salt-based DES for improving the enzymatic hydrolysis of bamboo. In addition, the correlation between the enzymatic saccharification efficiency and contents of hemicelluloses and lignin in pretreatment residues was analysed using the Box–Behnken design to identify the main factors that affect the enzymatic hydrolysis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) was received from Suichang, China, and was ground and sieved through a 60–80 mesh. The raw material was extracted using a 500 mL Soxhlet extractor with toluene/ethanol (2:1, v/v) until the siphon solution became colourless. The dewaxed moso bamboo containing 2.60% ash was air-dried to remove the toluene/ethanol solvent and then oven-dried at 60 °C to achieve a constant weight. Before pretreatment and component analysis, absolutely dry bamboo was obtained through oven-drying at 105 °C. The sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 98%, AR) was provided by Hangzhou Shuanglin Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China. The commercial cellulase (Cellic® CTec2, 100 FPU/mL) was kindly supplied by Novozymes, Beijing, China. The ChCl, Gly, anhydrous ferric chloride (FeCl3), anhydrous aluminium chloride (AlCl3), and anhydrous zinc chloride (ZnCl2,) were all purchased from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. All the chemicals were used without further purification.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of the DES
Type Ⅳ DES was prepared by mixing metal chloride salt (HBA) and Gly (HBD) in a molar ratio of 1:124. Specifically, the mixture was heated to 80 °C with magnetic stirring (600 rpm) until a clear homogeneous liquid was obtained. Based on the metal chloride salts, the resulting type Ⅳ DES solvents were denoted as FeCl3/Gly, AlCl3/Gly, and ZnCl2/Gly. For the control, a ternary DES with double HBAs was synthesised by ChCl, Gly and FeCl3 in a molar ratio of 62:124:1 and was named 3c-DES.
2.2.2. DES Pretreatment
A total of 50 g of the prepared DES and 5 g of the dewaxed moso bamboo (raw material) were added to a round-bottom flask and continuously magnetically stirred at 800 rpm at 80, 90, 100, 110, and 120 °C for 2, 3, and 4 h. At the end of the designated time, the reaction mixture was vacuum-filtered and sequentially washed with excess absolute ethanol and deionised water to obtain a neutral cellulose-rich residue. The residue was dried at 100 °C to achieve a constant weight for further analysis. All the experiments were performed in triplicate, and the average values are reported in this paper.
2.2.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Enzymatic hydrolysis was performed using Cellic® CTec2 at a loading of 15 FPU/g substrate. Briefly, 500 mg of cellulose-rich residue before and after the DES pretreatment was mixed with 25 mL of an acetate buffer (0.05 M, pH 4.8) and cellulase. The reaction mixture was incubated in an air bath shaker (DZH-2102, Jinghong, Shanghai, China) at 150 rpm and 50 °C for 48 h. The supernatant produced following enzymatic hydrolysis was diluted five times with deionised water and then filtered through a 0.22 µM water filter system for the enzymatic hydrolysis analysis. The corresponding glucose concentration was determined through high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Shimadzu LC-20AT, Shimadzu, Japan). Response surface methodology (RSM) was executed according to the Box–Behnken design assisting the Design Expert 13 statistical software to investigate the influence of hemicellulose and lignin contents on the glucose yield of pretreatment residue following enzymatic hydrolysis. The enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of residue was expressed by glucose yield, which was calculated using the following formula:
where 0.9 is the conversion factor of glucose to equivalent glucan; m is the weight of glucose following enzymatic hydrolysis (mg); and M is the weight of cellulose in the substrate for enzymatic hydrolysis (mg).
2.3. Characterisation of Moso Bamboo before and after the DES Pretreatment
2.3.1. Component Analysis
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory standard [14] was used to analyse the chemical composition of the moso bamboo before and after pretreatment. Glucan and xylan were quantified using the HPLC equipped with an Aminex HPX-87 H ion exclusion column and a refractive index detector. The retention ratio of glucan and the removal ratio of xylan and lignin were calculated using the following formulas:
where m1 and m2 represent the mass of the solid before and after pretreatment (g), respectively; cg and cx represent the concentration of glucose or xylose (mg/mL); V represents the volume of hydrolysis liquor, 86.73 mL; M0 represents the weight of sample for component analysis (mg). Ga, Xa, and La represent the mass of glucan, xylan, and lignin in the sample before pretreatment (mg), respectively. Gb, Xb and Lb represent the mass of glucan, xylan, and lignin in the sample following pretreatment (mg), respectively.
2.3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The microstructural changes and the surface characteristics of all the substrates were observed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Prior to the SEM image, all the samples were coated with gold. The images were collected using a ZEISS ULTRA 55 instrument (Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, Germany) at an accelerating voltage of 10 kV. The magnifications of the SEM images were ×100, ×500, and ×1000.
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction
The crystallinities of the untreated and pretreated raw material were determined via X-ray diffraction (XRD, ARL XTRA, Thermo ARL, Switzerland). The diffraction intensity of Cu Kα radiation was generated at 40 kV and 40 mA. The samples were scanned from 3° to 50° at a rate of 4°/min. The crystalline index (CrI) was calculated using the formula according to the Segal method [15].
where I002 iss the diffraction intensity at 2θ ≈ 22.5° (represented crystalline region) and Iam is the diffraction intensity at 2θ ≈ 16.5° (the represented amorphous region).
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy was used to analyse the change in chemical structures of the residue before and after the DES pretreatment. The samples were prepared through the potassium bromide tablet method and analyzed using a FT-IR spectrometer (Nicolet-5700, Thermo Nicolet Corporation, Madison, WI, USA). The scanning range was 500–4000 cm−1.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimisation of the DES Solvent System
3.1.1. Change in the Residual Component after Various DES Pretreatments
Different metal cation salt-based DESs were synthesised to pretreat moso bamboo at 100 °C for 3 h, and the fractionation effect was preliminarily analysed based on the changes in the residual components following pretreatment. As a control, 3c-DES pretreatment was performed under the same conditions to evaluate the effects of ChCl. The solid recovery and the component content of moso bamboo before and after DES pretreatment are shown in Table 1. The untreated raw material was mainly composed of cellulose (39.20%), hemicelluloses (16.30%), and lignin (27.60%), which were the same as in our previous work [16]. Following the 3c-DES pretreatment, the solid recovery increased by 83.98%, indicating a minor component change. The hemicelluloses and lignin removal ratios were 45.49% and 20.72%, respectively. Evidently, only the change in the proportion of hemicelluloses (reduced to 10.58% from 16.30% of raw material) was noticeable following 3c-DES pretreatment at 100 °C for 3 h. Wang et al. demonstrated that most of the hemicelluloses and lignin in the hybrid pennisetum can be removed following 3c-DES pretreatment at 120 °C for 6 h. Their results indicated that reinforcement pretreatment conditions had the ability to improve the fractionation of lignocellulose during 3c-DES pretreatment [17]. When compared with the 3c-DES pretreatment, the type Ⅳ DES (without ChCl) showed a better pretreatment effect under the mild condition (100 °C, 3 h). The solid recovery following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment reduced to 55.54%, indicating a dramatic fractionation. This pretreatment effect was verified by the removal ratios of hemicelluloses (65.89%) and lignin (56.33%). The consequence may be attributed to the formation of [MClx−1·Gly]+ between the metal chloride and Gly, which could weaken the surrounding effect of the hydroxyl group in Gly on Cl−. This weakened effect is conducive to the removal of hemicelluloses and lignin, thereby improving enzymatic hydrolysis.

Table 1.
Component analysis of the residues obtained from various solvents pretreatment.
The effects of different metal cation chlorides were investigated to assess the high efficiency of type Ⅳ DES pretreatment under mild conditions. Following ZnCl2/Gly pretreatment, the solid recovery was determined to be 86.35%, and only small amounts of hemicelluloses (11.98%) and lignin (9.08%) were removed, indicating a limitation of the ZnCl2-based type Ⅳ DES pretreatment under mild conditions (100 °C, 3 h). This result is in accordance with the performance of ZnCl2 in ternary DESs [17] and can be ascribed to ZnCl2, which is a weak HBA. Moreover, ZnCl2/Gly cannot easily break the existing hydrogen bonds between lignin and carbohydrates (LCCs) [18]. The pretreatment effect is considerably improved in the presence of strong HBAs (such as AlCl3 and FeCl3). The solid recoveries following AlCl3/Gly and FeCl3/Gly pretreatments were 63.82% and 55.54%, respectively, which were significantly lower than those obtained following ZnCl2/Gly pretreatment. The pretreatment effect of FeCl3/Gly was found to be stronger than that of AlCl3/Gly because of the high hemicelluloses (65.89%) and lignin (56.33%) removal ratios of FeCl3/Gly. These results collectively indicate that the best fractionation of moso bamboo was achieved via FeCl3/Gly solvent pretreatment.
3.1.2. Enzymatic Saccharification of Residue after Various DES Pretreatment
During enzymatic hydrolysis, the glucose yield of the residue obtained from pretreatment with various DES is shown in Figure 1. The glucose yield of the residue obtained from the 3c-DES pretreatment was 33.17%, which was higher than that (17.78%) of untreated moso bamboo after 48 h of enzymatic hydrolysis, as reported in our previous work [16]. This yield enhancement can be attributed to the destruction of the compact structure of the cell wall and the removal of only small amounts of the components by the 3c-DES pretreatment. Following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment, the enzymatic saccharification efficiency of the residue further improved to 67.87%, which was positively correlated with the removal of hemicelluloses and lignin. Similarly, the glucose yield of the AlCl3/Gly pretreatment residue was 59.78% following enzymatic hydrolysis, which was slightly lower than that of the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment residue. However, the glucose yield of the residue obtained from the ZnCl2/Gly pretreatment was only 24.75% due to its weak ability to remove of hemicelluloses and lignin. These results reveal that FeCl3/Gly pretreatment under mild conditions significantly promotes the enzymatic hydrolysis of the pretreatment residues.
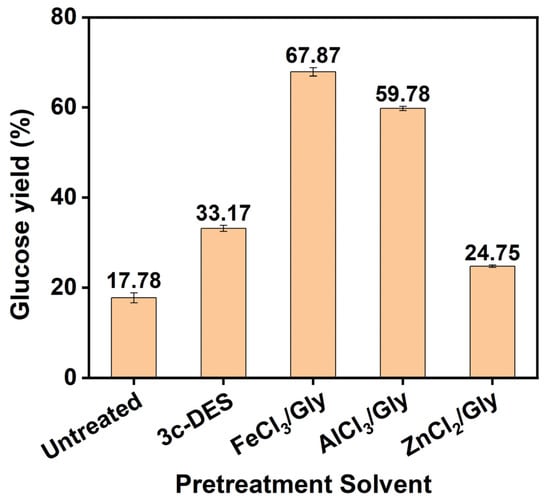
Figure 1.
Glucose yields following enzymatic hydrolysis of the residue before and after DES pretreatment. (Pretreated at 100 °C for 3 h).
3.2. Optimisation of the FeCl3/Gly Pretreatment Conditions
3.2.1. Effect of Temperature on the Residue’s Components
The solid recovery and component distribution of the residues following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment (for 3 h) at various temperatures are shown in Figure 2. With the increasing pretreatment temperature, solid recovery decreased from 88.06% (80 °C) to 48.96% (120 °C). Under mild conditions (from 80 °C to 100 °C), the downswing of the solid recovery (from 88.06% to 55.54%) was remarkable, and the proportions of hemicelluloses and lignin in the solid residue also gradually decreased, which was correlated with the increased removal ratios of hemicelluloses (from 2.05% to 65.89%) and lignin (from 19.12% to 56.33%), as shown in Figure 2b. This indicated that an increase in temperature during FeCl3/Gly pretreatment can improve the pretreatment effect. At a mild temperature (from 80 °C to 100 °C), the cellulose fraction was also influenced by the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment (i.e., the loss of cellulose <6% was observed). However, as the pretreatment temperature was further increased to 110 °C, solid recovery decreased to 53.84%, indicating that the negative correlation between temperature and solid recovery gradually weakened as the temperature was further increased to 110 °C. Relatively flat fluctuations were also shown in the proportions of the residue components and the removal ratio of hemicelluloses (slightly increased from 65.89% to 68.72%) and lignin (slightly increased from 56.33% to 59.82%). Notably, when the temperature was raised to 120 °C, the solid recovery broke through a moderate downward trend and declined continually to 48.96%. The removal ratios of hemicelluloses and lignin were relatively obvious, with cellulose loss as high as 12.51%. This indicated that the severe reaction conditions removed not only hemicelluloses and lignin but also some amorphous cellulose. The consequences were probably attributed to the decrease in viscosity and surface tension of the DES as well as the enhancement in the reactivity of the DES, which promoted the cleavage of the LCC bond and the increase in the removal ratio of lignin and hemicelluloses [19]. Thus, conditions other than temperature increment alone need to be investigated to optimise the effect of FeCl3/Gly pretreatment on the fractionation of bamboo.
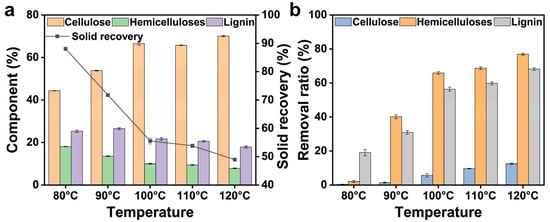
Figure 2.
Component changes (a) and removal ratios (b) of the residue following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at different temperatures for 3 h.
3.2.2. Effect of Time on the Residue Components
To explore and optimise the effect of pretreatment, the component changes in the residues obtained from the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 100–120 °C for different pretreatment durations were analysed. The corresponding results are presented in Figure 3. With prolonged pretreatment (from 2 h to 4 h), the percentage of cellulose slightly increased, whereas those of hemicelluloses and lignin slightly decreased. The increment of hemicelluloses and lignin removal ratio was less than 12.05% following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 100–120 °C for 2–4 h. Prolongation of the pretreatment time could promote contact between the substrate and the FeCl3/Gly solvent. Gly as an organic solvent had a certain dissolution effect, hence the lignin content decreased slightly [20]. For a short-duration pretreatment (2 h) at a higher temperature (120 °C), the cellulose loss was only 9.02%, which was less than that (12.51%) of those observed following 3-h-long FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 120 °C. This result suggested that long-duration pretreatment led to the removal of amorphous cellulose [21,22]. In addition, the influence of the pretreatment temperature on the fractionation of bamboo was stronger than that of the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment duration, which was consistent with the effect of ternary DES pretreatment at different temperatures and times [8,17]. Considering energy consumption and the fractionation effect, in this study, the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment conditions were optimised to 100 °C and 3 h as well as 120 °C and 2 h.
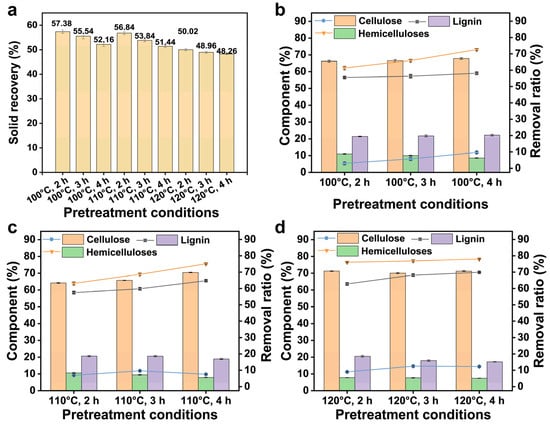
Figure 3.
Solid recovery (a), component changes and removal ratios of the residue following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment for different durations (at 100 °C (b), 110 °C (c), and 120 °C (d)).
3.3. Structural Analysis of the Residues after the DES Pretreatment
3.3.1. FT-IR Analysis
FT-IR spectroscopy results can explain the effect of DES pretreatment (with or without DES) on lignocellulose, particularly its structural destruction induced by the pretreatment. As shown in Figure 4, the broad absorption peak at approximately 3420 cm−1 originates from -OH in cellulose, indicating that the structure of cellulose did not significantly change during DES pretreatment. The FT-IR spectra of all the samples showed absorption peaks at 1160 and 898 cm−1, which could be attributed to the cellulose and the β-glycosidic bond between the glucose units in cellulose, respectively [23]. The 3c-DES pretreatment residue and untreated raw material exhibited similar spectra, which may be related to the changes in their components. The peak at 1030 cm−1 corresponded to C-O, C≡C, and C-C-O stretching between polysaccharides and lignin [24]. The absorption peak of the pretreatment residues following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at this point decreased or even faded away compared to that of the 3c-DES pretreatment residue, indicating the cleavage of LCC following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment. Meanwhile, during FeCl3/Gly pretreatment under mild conditions, the ether bonds in lignin can also be destructed, as indicated by the absorption peak at 1374 cm−1 [25]. The absorption peak of the lignin aliphatic group C=H at 833 cm−1 was weakened in the pretreatment substrate, indicating that lignin was removed. This was particularly evident in the FT-IR spectra of the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment residue. This change was in accordance with the component changes described in Section 3.1.1. The absorption peak at 1513 cm−1 represented the C=C bending vibration of the lignin aromatic ring, which still appeared in all the residue samples, indicating that some of the lignin was retained [26]. The absorption peak at 1737 cm−1 corresponded to the C-O and C=O bonds of the acetyl ester unit in hemicellulloses. The signal peak was significantly weakened in the spectra of the substrate following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment, indicating that the hemicelluloses were partially removed or degraded [23]. Among them, the spectra of the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment residues showed higher structural destruction than that of the 3c-DES pretreatment residue, and the structural disruption was aggravated under severe conditions during FeCl3/Gly pretreatment. This structural change has considerable potential for the improvement of enzymatic saccharification.
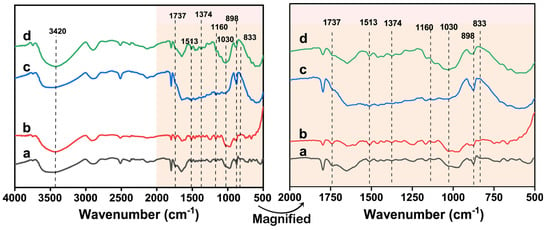
Figure 4.
FT-IR spectra of the untreated (a) and pretreated residues obtained from the 3c-DES pretreatment at 100 °C for 3 h (b), FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 100 °C for 3 h (c), and FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 120 °C for 2 h (d).
3.3.2. XRD Analysis
XRD patterns were used to evaluate the changes in the crystal structure of the bamboo before and after DES pretreatment. The XRD spectra of the raw material and the residues pretreated with 3c-DES and FeCl3/Gly are shown in Figure 5. The characteristic peaks of all the samples were located at 16.5° and 22.5°, corresponding to the 101 crystal and 002 crystal planes of cellulose I, respectively [12], which suggested that the crystalline variant did not happen during the 3c-DES and FeCl3/Gly pretreatments. The crystallinity index (CrI) of the raw material was 36.20%, as reported in our previous work [16]. Following 3c-DES pretreatment, CrI increased slightly to 39.13%, which might be related to changes in the residue components. Following FeCl3/Gly pretreatment under mild conditions (100 °C, 3 h), the CrI of the pretreatment residue increased tremendously to 75.70%, which was attributed mainly to the removal of the amorphous lignin and hemicelluloses [27]. This increases the surface accessibility of cellulases to cellulose, leading to an improvement in enzymatic saccharification [28]. When FeCl3/Gly pretreatment intensity was raised to 120 °C, 2 h, the CrI increased to 78.34%. The increase was less than 3% compared to that of the residue obtained from the mild pretreatment. This indicated that a further increase in the pretreatment intensity may destroy the crystalline structure of cellulose in the residue.
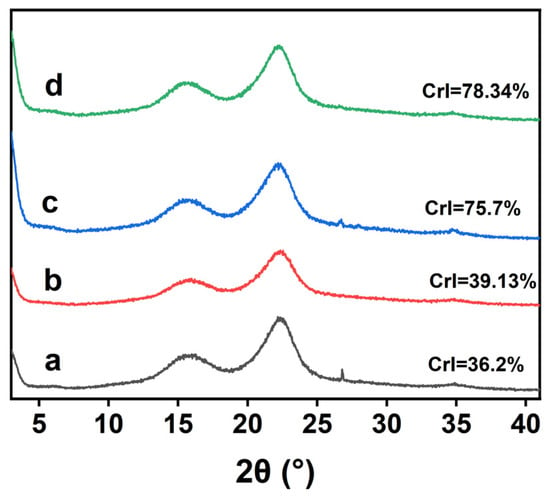
Figure 5.
XRD patterns of the untreated (a) and pretreated residues obtained from the 3c-DES pretreatment at 100 °C for 3 h (b), FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 100 °C for 3 h (c), and FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 120 °C for 2 h (d).
3.3.3. SEM Analysis
A qualitative study on the morphological changes of bamboo following DES pretreatment was conducted using SEM, which was important to explain the effect of DES pretreatment on enzymatic hydrolysis. As shown in Figure 6, the morphology of the untreated bamboo displayed an ordered arrangement of fibre and a relatively smooth and compact surface. This phenomenon undoubtedly constituted a disadvantage of enzymatic hydrolysis by suppressing the contact between cellulose and cellulase. Following DES pretreatment, the surfaces of pretreatment residues showed varying levels of destruction, and the fibres were disordered. Following 3c-DES pretreatment (100 °C, 3 h), the surface of the pretreatment residue ruptured, and rough cracks and some thick fibre bundle-like structures became visible, suggesting the partial removal of components. However, the dense structure was still present. These results are consistent with previous observations of the removal of small components. However, the surface of the residue obtained from FeCl3/Gly pretreatment under the same conditions was severely damaged and dissociated into fragments with a chip-like structure due to the removal of hemicelluloses and lignin, which promoted enzymatic saccharification. As the pretreatment temperature was increased to 120 °C for 2 h, the surface gullies on the sample deepened, and the surface became rough and exhibited tiny fragments. The originally dense structure of bamboo was destroyed, and the entire structure became loose, which significantly increased the accessibility of cellulase to cellulose and facilitated enzymatic hydrolysis.

Figure 6.
SEM images of the untreated (a1,a2,a3) and pretreated residues obtained through 3c-DES pretreatment at 100 °C for 3 h (b1,b2,b3), FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 100 °C for 3 h (c1,c2,c3), and FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 120 °C for 2 h (d1,d2,d3).
3.4. Effect of Hemicelluloses and Lignin on the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Residues
The enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency of cellulose plays an important role in sugar production and bioethanol production. Figure 7 shows the glucose yield following enzymatic hydrolysis of the residues obtained from different pretreatment conditions. As the reaction temperature and time gradually increased, the glucose yield of pretreatment residue showed an overall upward trend during enzymatic hydrolysis. This was due to the gradual increase in hemicelluloses and lignin removal during the pretreatment process, which exposed more cellulose and increased the contact between cellulose and cellulase. At mild pretreatment conditions (80–90°C, 2–4 h), the enzymatic hydrolysis of the residue was improved significantly, from 20.49% to 37.07%, by increasing the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment temperature and time (shown in Figure 7a). These results indicated that when the pretreatment conditions were not severe, both the pretreatment temperature and the time played a positive role in enzymatic hydrolysis. With the intensification of pretreatment conditions, the glucose yield following enzymatic hydrolysis of the residue obtained from 100 °C for 3 h and 110 °C for 2 h was 67.87% and 67.27%, respectively (Figure 7b). It was worth noting that in all the samples, the highest enzymatic saccharification efficiency (91.13%) was obtained through FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 120 °C for 2 h. However, the enzymatic saccharification efficiency of the pretreatment residue decreased to 83.62% with the reinforcement of the pretreatment conditions. This indicated that further removal of lignin did not lead to an increase in enzymatic hydrolysis, and that excessive removal of lignin led to the formation of tight structures between cellulose and inhibited the accessibility of enzymes to cellulose [17].
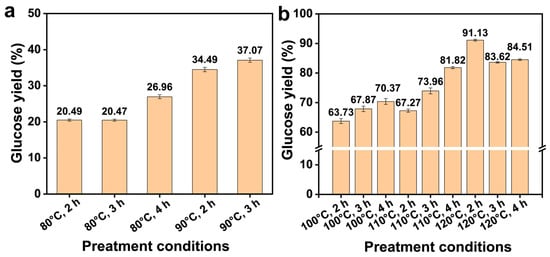
Figure 7.
The glucose yield following enzymatic hydrolysis of the pretreatment residues under 80–90 °C pretreatment (a), and (100–120 °C) pretreatment (b).
To determine whether hemicelluloses or lignin has a greater influence on the efficiency of enzymatic saccharification, the correlation between enzymatic hydrolysis and the contents of hemicelluloses and lignin was analysed through the Box–Behnken design, as shown in Figure 8. In this case, the p-value was less than 0.0001, confirming the significance of each coefficient. The model showed a good fit to the data, which was indicated by an R2 of 0.9632 as well as a signal-to-noise ratio of 27.7845 (greater than 4 is desirable) measured via Adeq precision. The proportion of hemicelluloses was a significant model term. The response surface plots showed that the proportion of hemicelluloses had a greater effect on the enzymatic hydrolysis than the proportion of lignin did. If the lignin content was constant (approximately 25%), decreasing the hemicellulose content can significantly improve the enzymatic saccharification efficiency. A similar result has been reported [29,30]. Recent studies have shown that when lignin removal reaches a certain level, enzymatic hydrolysis does not improve further [31]. Due to its high molecular weight, lignin is easily deposited on the surface of cellulose, forming steric hindrance and hindering the adsorption of cellulose onto cellulase [32].
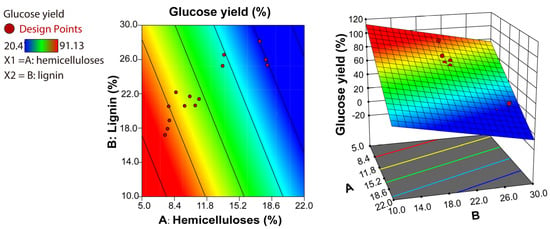
Figure 8.
Correlation between hemicelluloses and lignin contents in the substrate and glucose yield during enzymatic hydrolysis (left) and a three-dimensional model (right).
4. Conclusions
In this study, a type IV DES composed of a metal chloride and Gly was synthesised. Following the FeCl3/Gly pretreatment at 120 °C for 2 h, the removal ratios of hemicelluelluloses and lignin increased to 76.06% and 62.77%, respectively, and the glucose yield of the pretreatment residue was 91.13% following enzymatic hydrolysis. This detected yield was five times that of raw materials. Furthermore, because of the excessive removal of lignin, the substrate structure became more compact and the content of hemicelluloses influenced the enzymatic hydrolysis of the residue considerably. In summary, a type IV DES is an inexpensive and highly efficient green solvent with a low cost and high efficiency that facilitates the value-added conversion of biomass and promotes the industrialisation of products obtained from biomass.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, T.C. and G.G.; methodology, T.C. and G.G.; software, T.C. and G.G.; validation, T.C., G.G., D.S. and Y.T.; formal analysis, D.S.; investigation, G.G. and Y.T.; resources, T.C.; data curation, T.C. and G.G.; writing—original draft preparation, T.C. and G.G.; writing—review and editing, T.C.; supervision, T.C.; project administration, T.C.; funding acquisition, T.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 22208309; the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, grant number LQ21C160006; and the Science Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, grant number 20202290-Y.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All research data were presented in this contribution.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yogalakshmi, K.N.; Mohamed Usman, T.M.; Kavitha, S.; Saloni, S.; Shivani, T.; Kumar, S.A.; Banu, J.R. Lignocellulosic biorefinery technologies: A perception into recent advances in biomass fractionation, biorefineries, economic hurdles and market outlook. Fermentation 2023, 9, 238–262. [Google Scholar]
- Schmatz, A.A.; Masarin, F.; Brienzo, M. Lignin removal and cellulose digestibility improved by adding antioxidants and surfactants to organosolv pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse. BioEnergy Res. 2021, 15, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, M.C.; Bassin, I.D.; Cammarota, M.C. Microalgae and cyanobacteria biomass pretreatment methods: A comparative analysis of chemical and thermochemical pretreatment methods aimed at methane production. Fermentation 2022, 8, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Arantes, V.; Chandra, R.; Saddler, J. The lignin present in steam pretreated softwood binds enzymes and limits cellulose accessibility. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, R.; Tang, W.; Zheng, Y.; Meng, X. Improve Enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass by modifying lignin structure via sulfite pretreatment and using lignin blockers. Fermentation 2022, 8, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Xu, L.H.; Zhang, C.; Guo, K.N.; Yuan, T.Q.; Wen, J.L. A synergistic hydrothermal-deep eutectic solvent (DES) pretreatment for rapid fractionation and targeted valorization of hemicelluloses and cellulose from poplar wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Vasco, C.; Ma, R.S.; Quintero, M.; Guo, M.; Geleynse, S.; Ramasamy, K.K.; Wolcott, M.; Zhang, X. Unique low-molecular-weight lignin with high purity extracted from wood by deep eutectic solvents (DES): A source of lignin for valorization. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5133–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Meng, J.; Cheng, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, H. Multiple hydrogen bond coordination in three-constituent deep eutectic solvents enhances lignin fractionation from biomass. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 2711–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bai, X.; A, L.; Wan, C. High-solid lignocellulose processing enabled by natural deep eutectic solvent for lignin extraction and industrially relevant production of renewable chemicals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 12205–12216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Liu, Q.; Xin, H.; Jiang, E.; Ma, Q. Enhanced glucose production from cellulose and corn stover hydrolysis by molten salt hydrates pretreatment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 215, 106739–106744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, B.; Wei, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Clark, J.H.; Fan, J. An integrated process for the valorization of corn stover promoted by NaCl in a GVL/H2O system. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 1515–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.J.; Wang, B.; Huang, P.L.; Wen, J.L.; Sun, R.C. Effects of aluminum chloride-catalyzed hydrothermal pretreatment on the structural characteristics of lignin and enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 206, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S.; Wilson, D. Eutectic-based ionic liquids with metal-containing anions and cations. Chemistry 2007, 13, 6495–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sluiter, A.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2012.
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E.; Conrad, C.M. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the x-ray diffractometer. Tex. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, T.; Yao, S.; Tang, Y. Comparison of polyol-based deep eutectic solvents (DESs) on pretreatment of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) for enzymatic hydrolysis. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 189, 115767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.K.; Hong, S.; Wen, J.L.; Ma, C.Y.; Tang, L.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.J.; Li, S.; Shen, X.J.; Yuan, T.Q. Lewis acid-facilitated deep eutectic solvent (des) pretreatment for producing high-purity and antioxidative lignin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 8, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; De Oliveira Vigier, K.; Royer, S.; Jerome, F. Deep eutectic solvents: Syntheses, properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 7108–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, T.; Yao, J. Deep eutectic solvent with bifunctional Bronsted-Lewis acids for highly efficient lignocellulose fractionation. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 347, 126723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Improving the economy of lignocellulose-based biorefineries with organosolv pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299, 122695–122707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, X.; Fang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X. Integrated bioprocess for cellulosic ethanol production from wheat straw: New ternary deep-eutectic-solvent pretreatment, enzymatic saccharification, and fermentation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, L.; Xie, X.; Fan, D.; Ouyang, X.; Fan, W.; Qiu, X. Enhanced production and separation of short-chain glucan oligomers from corn stover in an unacidified LiBr molten salt hydrate via pre-extraction of hemicellulose. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 8812–8819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.F.; Yang, H.Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, Z.J. The effect of alkaline extraction of hemicellulose on cocksfoot grass enzymatic hydrolysis recalcitrance. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 178, 114654–114663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, R.; Jaiswal, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Jaiswal, A.K. Evaluation of ultrasound assisted potassium permanganate pre-treatment of spent coffee waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhao, Q.; Su, R.; Huang, R.; Qi, W. Enhanced enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulose by ethanolassisted FeCl3 pretreatment. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2017, 61, 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Loow, Y.L.; Wu, T.Y.; Lim, Y.S.; Tan, K.A.; Siow, L.F.; Jahim, J.M.; Mohammad, A.W. Improvement of xylose recovery from the stalks of oil palm fronds using inorganic salt and oxidative agent. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 138, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Gou, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Esterification of cellulose using carboxylic acid-based deep eutectic solvents to produce high-yield cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isci, A.; Erdem, G.M.; Bagder Elmaci, S.; Sakiyan, O.; Lamp, A.; Kaltschmitt, M. Effect of microwave-assisted deep eutectic solvent pretreatment on lignocellulosic structure and bioconversion of wheat straw. Cellulose 2020, 27, 8949–8962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Pan, X.J. Woody biomass pretreatment for cellulosic ethanol production: Technology and energy consumption evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4992–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, L.P.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Marabezi, K.; da Silva Curvelo, A.A. Delignification of sugarcane bagasse using glycerol-water mixtures to produce pulps for saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 10040–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.W.; Xia, S.Q.; Ma, P.S. Facile pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass using deep eutectic solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, M.; Pu, Y.Q.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Klett, A.S.; Thies, M.; Zheng, Y. Inhibitory effects of lignin on enzymatic hydrolysis: The role of lignin chemistry and molecular weight. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).