Abstract
To meet the growing global demand for gluconic acid as a cement and concrete retarder, inexpensive and abundant lignocellulosic materials are regarded as the most suitable alternatives to starchy materials. However, their enzymatic hydrolysate contains not only glucose but also xylose, which negatively affects the performance of gluconic acid as a retarder. Notably, glucose is preferentially bio-oxidized into gluconic acid by Gluconobacter oxydans, but gluconic acid cannot be metabolized by Candida tropicalis. Given this, an artificially designed biological cascade process, respectively employing Gluconobacter oxydans and Candida tropicalis, was established to successfully carry out glucose conversion into gluconic acid, and xylose into a single-cell protein, using the enzymatic hydrolysate of corncobs as a feedstock. This sequential fermentation process produced 95.8 g/L gluconic acid and 9.0 g/L single-cell protein from one liter of the enzymatic hydrolysate that initially contained 98.1 g/L of glucose and 25.4 g/L of xylose. The mass-balance calculation showed that approximately 280 grams of gluconic acid and 27 grams of the single-cell protein could be harvested from 1000 grams of the corncob feedstock. The results suggest that the above-mentioned two-step bioconversion method is efficient in utilizing glucose and xylose from lignocellulosic hydrolysates.
1. Introduction
With the growing economy, worsening environmental pollution, and the scarcity of fossil resources, scientists are in search of green alternative energy sources worldwide [1]. Lignocellulosic biomass, a plentiful and potentially renewable biological resource, can be harvested from various sources, such as agricultural and forest residues [2]. Lignocellulose is composed mainly of lignin and two polysaccharides: cellulose and hemicellulose. It can be hydrolyzed into sugars and transformed into several value-added fuels and chemicals, such as biofuels and organic acids, by fermentation [3,4,5]. Before fermentation, lignocellulosic biomass requires pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis [6]. The high cost of pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis during lignocellulose degradation is still a problem that needs to be solved. Enzymatic hydrolysate mainly consists of glucose and xylose that are derived from hemicellulose and cellulose. Some cellulolytic bacteria have been identified and used to break down lignocellulosic biomass. However, the mechanisms involved in, and the processes used for, large-scale production are yet to be explored [7,8]. Thus, the environmentally friendly utilization and conversion of cellulose and hemicellulose polysaccharide components from lignocellulosic biomass is an economically feasible biorefinery process [9].
Studies have reported that lignocellulosic glucose can be used to produce a range of products, such as bioethanol [10], lactic acid [11], citric acid [12], and gluconic acid (GA) [13]. Among them, GA is preferable due to the advantages of its high yield, high availability, and extensive utilization in the chemical, food, and pharmaceutical industries [14]. Luo et al. reported that sodium gluconate as a concrete or cement retarder can increase setting times and fluidity, and also enhances mechanical performance and durability by improving pore structure and heterogeneity [15]. In addition, the high purity of GA or its derivatives (such as sodium/calcium gluconate) is nonessential as a cement or concrete additive [16,17]. Therefore, GA produced from enzymatic hydrolysate can be directly used as a cement or concrete additive without any purification, which potentially reduces the production cost. The current production process of GA is relatively mature, and the commonly used bacteria is Aspergillus niger. However, in the presence of inhibitors, the conversion ability of Aspergillus niger will be inhibited and the fermentation time will be extended [18]. Gluconobacter oxydans (G. oxydans), an aerobic Gram-negative bacterium belonging to the Acetobacter species, can rapidly perform incomplete oxidation of a range of sugars and polyols into corresponding acids or ketones using membrane-bound dehydrogenases. In addition, given its remarkable tolerance against lignocellulosic inhibitors, G. oxydans is regarded as the most preferable microorganism for the industrial production of GA from cellulosic glucose [19]. Zhang et al. reported that G. oxydans can be used for glucose conversion into GA from corn stover hydrolysate, meanwhile, G. oxydans showed good tolerance against various inhibitors generated from the degradation of lignocellulose [20].
In addition to glucose, the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass simultaneously releases about 25% xylose, which is the second largest sugar after glucose [21]. Xylose can be microbially transformed into various products, including ethanol [22], butanol [23], xylitol [24], and xylonic acid (XA) [25]. However, G. oxydans cannot simultaneously convert glucose and xylose into GA and XA, respectively. The remaining xylose in hydrolysate can cause excessive retardation of cement/concrete and therefore must be removed [26]. Compared with other xylose fermentation products, single-cell protein (SCP) is a good choice because it can be easily separated from the fermentation broth and can be used as a high-grade protein supplement in human food and animal feed [27]. Various SCP-producing microorganisms, including yeast, fungi, bacteria, and algae, have been reported. Yeast is the most widely used microorganism for its ability to grow on a variety of substrates, low risk of contamination, high protein content, and high B-complex vitamin content. Candida tropicalis (C. tropicalis), belonging to the genus Candida, can utilize xylose and has a high tolerance against inhibitors, such as furfural and phenols, produced during the degradation of lignocellulosic biomass [28,29,30]. C. tropicalis may also convert xylose to ethanol, which can affect the purity of gluconic acid in the fermentation broth; therefore, C. tropicalis is introduced to simultaneously remove xylose and obtain SCP as value-added product by controlling the conditions.
The goal of this study was to maximize the economic benefits of enzymatic hydrolysate from the abundant and inexpensive lignocellulosic biomass. We used two strains to convert fermentable sugars (glucose and xylose) from lignocellulosic hydrolysate into chemicals. Accordingly, GA and SCP were produced continuously in a two-step process using corncobs as raw material. First, G. oxydans was employed for the bio-oxidation of glucose into GA and then the remaining xylose was metabolized into SCP by C. tropicalis. This study provides a reference for the integrated use of glucose and xylose from a lignocellulosic hydrolysate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Maintenance
A G. oxydans strain from Nanjing Forestry University, China was genetically modified in the strain ATCC 621, and was stored at 4 °C on the sorbitol-agar medium containing 50 g/L sorbitol, 5 g/L yeast extract, and 15 g/L agar [31].
C. tropicalis was also from Nanjing Forestry University, China, and stored on the glucose–agar medium containing 10 g/L glucose, 5 g/L peptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, and 15 g/L agar at 4 °C.
2.2. Preparation of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pretreated Corncob Solids
The corncobs used as lignocellulosic feedstocks in this study contained 34.2% cellulose, 32.8% hemicellulose, and 19.2% lignin. Corncobs were pretreated in 1% H2SO4 at 150 °C for 30 min, with a solid/liquid ratio of 1:10. A 10 L reaction volume was autoclaved, and the mixture was centrifuged to separate the solid residue before enzymatic hydrolysis. The pretreated corncob solids were washed in water to obtain a neutral substrate pH and then air-dried for 24 h for enzymatic hydrolysis. The fed-batch operation, with solid loadings of 15, 20, and 25%, respectively, was employed for enzymatic hydrolysis in a 3 L bioreactor with a 1 L working volume for 96 h at 50 °C and 170 rpm metal-axis stirring. The pH was maintained at 4.8 using a citrate buffer and the amount of the used enzyme was 20 FPIU/g-glucan cellulase for enzymatic hydrolysis (CellicCTec2, Sigma Co., Shanghai, China).
2.3. Inoculum Preparation and Fermentations
G. oxydans fermentation: G. oxydans NL71 was first pre-activated in 50 mL medium (50 g/L sorbitol and 5 g/L yeast extract) in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer shaker flask and the culture was performed at 30 °C and 220 rpm for 24 h. Then, the strain was moved to 500 mL medium (100 g/L sorbitol and 10 g/L yeast extract) in a 2 L Erlenmeyer shaker flask and cultivated at 30 °C and 220 rpm for 24 h. The 50 mL fermentation medium consisted of a carbon source (100 g/L glucose and 25 g/L xylose, or enzymatic hydrolysates from corncobs), 5 g/L yeast extract, 0.5 g/L MgSO4, 1 g/L K2HPO4, 2 g/L KH2PO4 and 5 g/L (NH4)2SO4 in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer shaker flask. The medium pH was maintained with 20 g/L calcium carbonate. The initial inoculum of G. oxydans was 2 OD600 units and the fermentation was performed at 30 °C and 220 rpm for 24 h.
C. tropicalis fermentation: C. tropicalis was grown in 50 mL medium (20 g/L glucose, 20 g/L peptone, and 10 g/L yeast extract) in a 250 mL Erlenmeyer shaker flask and cultivated at 30 °C and 220 rpm for 24 h. The 50 mL fermentation medium consisted of 98.7 g/L GA, 25 g/L xylose, 5 g/L yeast extract, 0.5 g/L MgSO4, 1 g/L K2HPO4, 2 g/L KH2PO4 and 5 g/L (NH4)2SO4 in 250 mL Erlenmeyer shaker flasks, and the pH was adjusted to neutral with NaOH. The initial inoculum of C. tropicalis was 2 OD600 units, and the fermentation was performed at 30 °C and 220 rpm.
Co-fermentation by G. oxydans and C. tropicalis: The co-fermentation medium and condition were the same as of G. oxydans fermentation. The medium pH was maintained with 20 g/L calcium carbonate and the initial inoculum of G. oxydans and C. tropicalis were both 2 OD600 units, each.
Sequential fermentation: The sequential fermentation medium contained 50 mL medium containing enzymatic hydrolysate, 5 g/L yeast extract, 0.5 g/L MgSO4, 1 g/L K2HPO4, 2 g/L KH2PO4, and 5 g/L (NH4)2SO4; the medium pH for the first and second steps was adjusted by CaCO3 and NaOH, respectively. First, GA fermentation was performed at 30 °C and 220 rpm with an initial inoculum of 2 OD600 units G. oxydans; when glucose was utilized, the G. oxydans cells were removed by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 5 min. Second, SCP was produced at 30 °C and 220 rpm with an initial inoculum of 2 OD600 units C. tropicalis. Both reaction steps were carried out in 250 mL Erlenmeyer shaker flasks.
2.4. Analytical Methods
Optical density (OD) was measured by Amersham Biosciences UV/Visible spectrophotometer (Spectrumlab 752 s) at 600 nm. In the process of bacterial dry weight measurement, 6 equal volume bacterial culture mediums were first taken, of which 3 samples were measured for turbidity by ultraviolet spectrophotometer at the wavelength of 600 nm, and the other 3 were measured for bacterial dry weight using an infrared moisture analyzer, and the average value was taken, respectively. Then, linear fitting was performed according to the turbidities and dry weights, and the standard curve was drawn. One OD unit corresponded to 0.68 g/L dry weight of G. oxydans cells and 0.96 g/L dry weight of C. tropicalis cells, respectively.
The concentration of ethanol was analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (Agilent 1260) equipped with an Aminex Bio-Rad HPX-87H column. The mobile phase was 5 mmol/L H2SO4 and the flow rate was 0.6 mL/min. The concentrations of glucose, xylose, GA, 2-ketogluconic acid (2-KGA), and XA were analyzed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography (Dionex ICS-3000) linked to a CarboPacTM PA 10 column. The mobile phases were 100 mmol/L NaOH and 500 mmol/L sodium acetate, and the flow rate was 0.3 mL/min. At each interval, 1 mL of the fermentation broth samples were taken for the detection of fermentation products. All fermentation broth samples were centrifuged (10,000 rpm for 5 min) and the supernatant was diluted and used for analysis by HPLC and Dionex ICS-3000.
The yields of GA, 2-KGA, XA, and ethanol were calculated as follows:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Pretreated Corncob Solids
It is well known that lignocellulosic materials can be enzymatically hydrolyzed into fermentable sugar after effective pretreatment [32]. Moreover, a relatively higher content of fermentable sugars in enzymatic hydrolysate is preferable to make full use of the equipment and reduce production costs. For instance, in bioethanol production, the total fermentable sugar concentration must be over 80 g/L for economic considerations so that the final bioethanol concentration can theoretically reach 4% (w/v); therefore, a solid loading of over 15% is essential for enzymatic hydrolysis [33]. Corncobs are abundant and cheap lignocellulosic materials that can be pretreated and enzymatically hydrolyzed to obtain hydrolysate rich in fermentable sugars, which can then be biorefined into various high-value products [34,35].
In this study, the acid-pretreated corncob solids, containing 51.9% glucan, were enzymatically hydrolyzed with cellulases (20 FPIU/g glucan). From the industrial application, it is important to obtain high-concentration products from the fermentation of high-concentration glucose medium to decrease energy consumption and increase product quality. The batch mode with a high solid loading is the most effective way to increase the content of reducing sugars in enzymatic hydrolysate, but the method has the disadvantages of high viscosity, uneven mixing, poor heat transfer, and, in turn, the inhibition of product formation [36]. We found that the fed-batch operation can overcome these disadvantages and performed fed-batch enzymatic hydrolysis (5% solid loading every 12 h) to obtain a relatively high concentration of fermentable sugars. In addition, to evaluate the effect of total solid loading, we separately performed enzymatic hydrolysis with 15, 20, and 25% solid loadings in round-bottom flasks at 50 °C for 96 h.
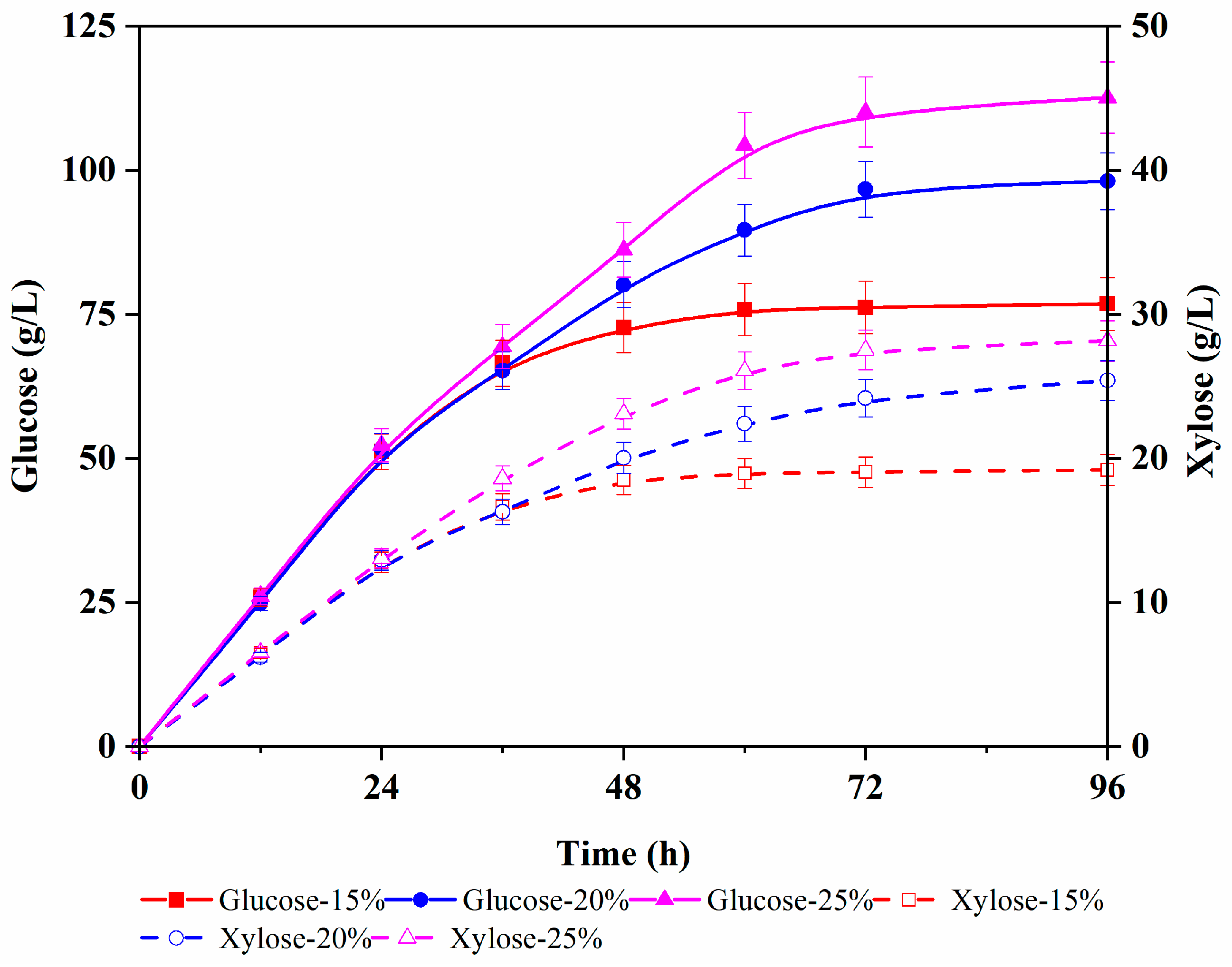
The time course analysis of enzymatic hydrolysis is shown in Figure 1, indicating that glucose content increased to almost maximum within 48 h in all three solid loadings. Also, the final glucose content linearly ascended with the increase in the total solid loading. Finally, 76.8, 98.1, and 112.6 g/L glucose content with yields of 88.8, 85.1, and 78.1% were achieved for 15, 20, and 25% solid loading, respectively. Notably, the solid loading of over 20% decreased the enzymatic hydrolysis yield to lower than 80%. The high solid loading (25%) resulted in the high viscosity of the slurry, which decreased enzyme diffusion into the interiors of the substrate, in turn lowering the enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency [37].
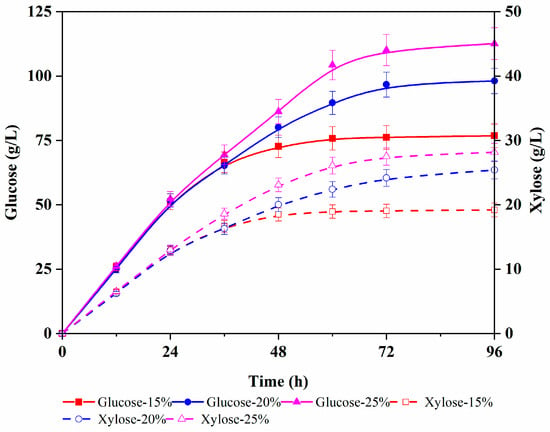
Figure 1.
Accumulation of glucose and xylose during the enzymatic hydrolysis of corn cob hydrolysate under different enzyme dosages with fed-batch operation (5% solids loading every 12 h).
Although a higher enzymatic hydrolysis yield could be achieved with 15% solid loading, the final total glucose content was lower than that of the 20% solid loading [36]. Therefore, 20% solid loading was found most suitable for the enzymatic hydrolysis of corncobs after dilute acid pretreatment. In addition, during the enzymatic hydrolysis, a certain amount of xylose was simultaneously released into the enzymatic solution [38]. Since corncob naturally contains glucan and xylan, and commercial cellulase normally contains hemicellulose, in the case of a 20% solid loading, 98.1 g/L glucose and 25.4 g/L xylose were co-produced after enzymatic hydrolysis for 96 h. In lignocellulosic hydrolysates, xylose is the second most abundant sugar and therefore should be efficiently utilized for cost-effectiveness. Accordingly, here, the potential utilization of mixed sugar (glucose and xylose) was investigated for preparing value-added products.
3.2. The Kinetics of G. oxydans for the Mixture Medium of Glucose and Xylose
Based on the above-mentioned results, the enzymatic hydrolysate from corncobs pretreated with a 20% solid loading, which contained 98.1 g/L glucose and 25.4 g/L xylose, was used in the subsequent experiments. To understand the metabolic kinetics of G. oxydans, we first used the simulation medium containing 100 g/L glucose and 25 g/L xylose, and the results are shown in Figure 2a.
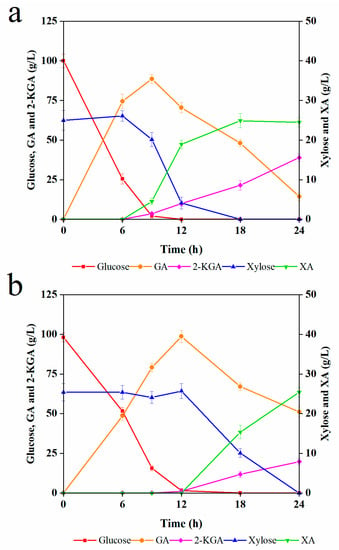
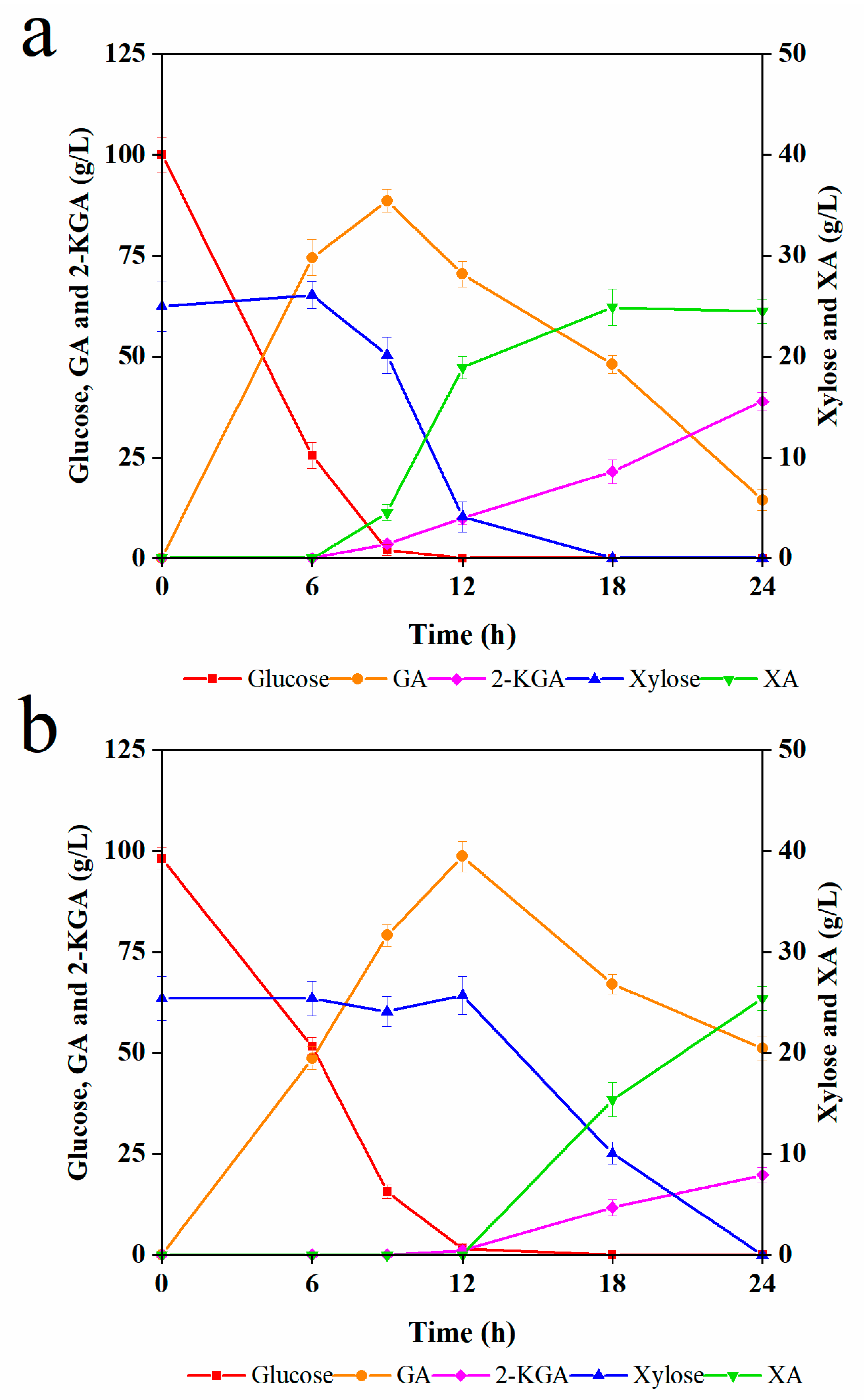
Figure 2.
Simultaneous fermentation of glucose and xylose by G. oxydans of: (a) simulation solution; and (b) enzymatic hydrolysate.
The results of the simulation solution showed that G. oxydans effectively converted glucose into GA within 9 h, producing 88.6 g/L GA with a yield of 81.4%. Importantly, though xylose can be utilized by G. oxydans, xylose utilization was repressed until the glucose was used up. Eventually, 25 g/L xylose was converted to 24.9 g/L XA, and a portion of GA was simultaneously converted to 2-KGA. As shown in Figure 2a, xylose was completely consumed at 18 h. Meanwhile, partial GA continued to be oxidized, requiring a longer fermentation time, producing 38.9 g/L 2-KGA at 24 h, with only 14.4 g/L GA as a remnant.
The kinetics of G. oxydans in the enzymatic hydrolysate medium are shown in Figure 2b. Glucose was completely consumed at 12 h, producing 98.7 g/L GA with a yield of 92.4%. As with the earlier results, the xylose was not metabolized until the glucose was depleted. Finally, 25.4 g/L XA was produced at 24 h with a yield of 90.4%. Meanwhile, GA was partially further oxidized to the by-product 2-KGA, with a corresponding content of 19.8 g/L at 24 h. In comparison, the fermentation performance of the simulation medium was better than that of the enzymatic hydrolysate, suggesting that the enzymatic hydrolysate contained some inhibitors. However, in general, the fermentation process profile of G. oxydans was very similar in both mediums. Also, the glucose conversion followed the same pattern: the fermentation was divided into two stages, including the conversion of glucose to GA and further metabolism of xylose and GA, where xylose was bio-oxidized into XA and GA was partly converted to 2-KGA [39]. This phenomenon suggested that it is feasible to manually stop the reaction when the glucose is consumed by G. oxydans, thus retaining GA and xylose in the fermentation broth. Meanwhile, xylose can be removed by downstream organisms by converting it into other products such as ethanol or SCP.
3.3. The Effects of G. oxydans and GA on C. tropicalis
GA can be further oxidized to 2-KGA, which complicates the co-production of GA and XA [40]. A higher yield of GA can be achieved by preventing the further oxidation or metabolism of GA and xylose. Therefore, to reduce by-product production and improve the purity of GA in the fermentation broth, C. tropicalis was introduced into the synthetic medium for the production of SCP or ethanol for indirectly removing xylose.
First, we evaluated the effect on the fermentability of glucose and xylose when G. oxydans and C. tropicalis were present simultaneously. G. oxydans and C. tropicalis were added to the simulation medium (100 g/L glucose and 25 g/L xylose) at 2 OD600 units as initial inoculum, and the results are shown in Figure 3a.
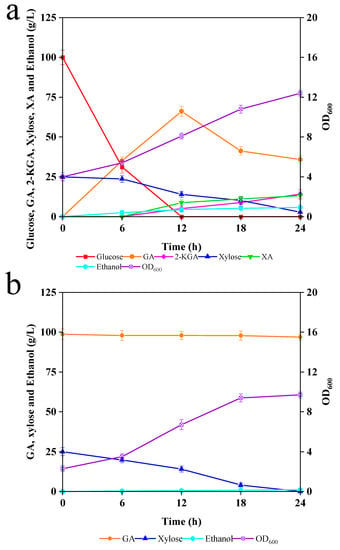
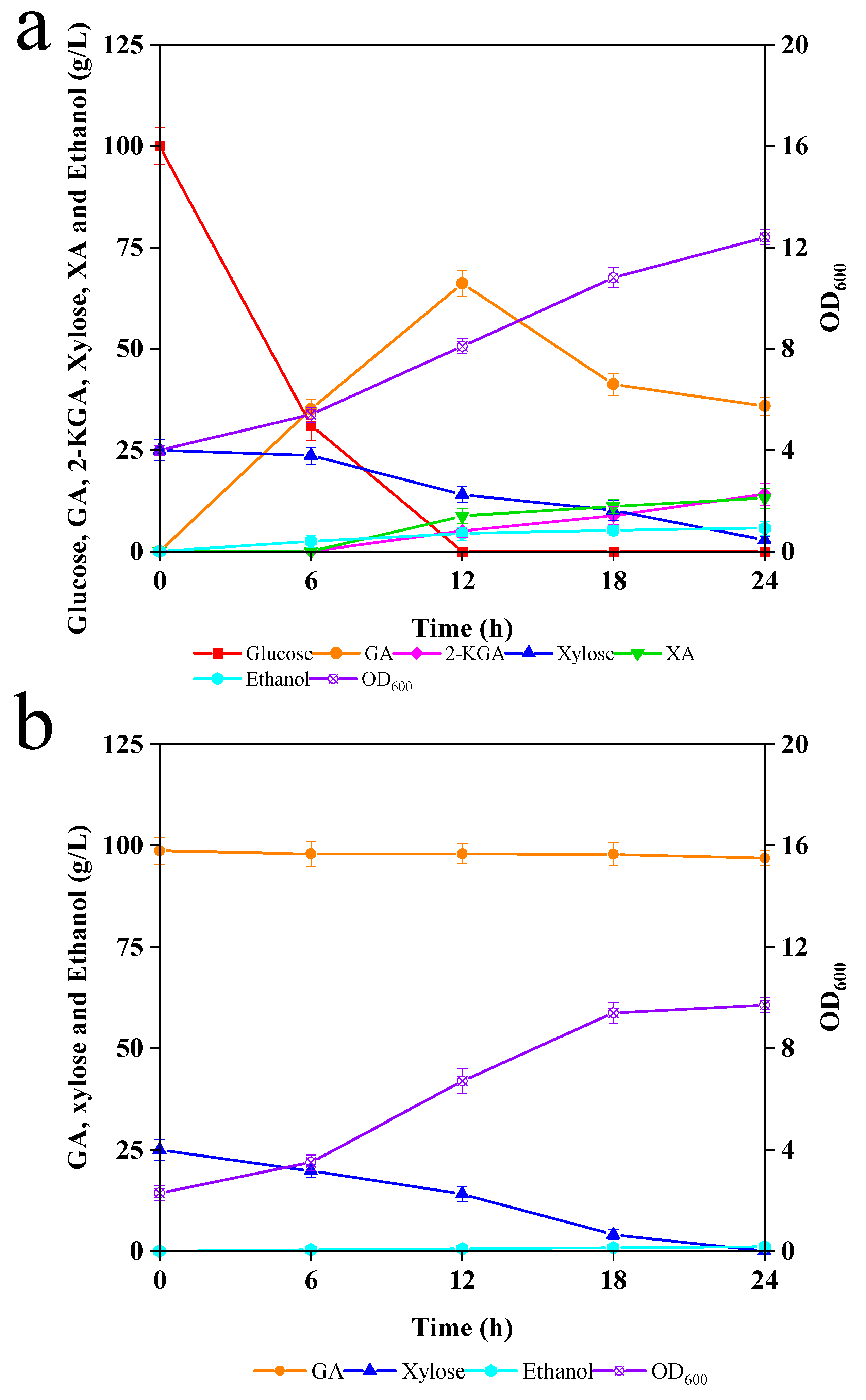
Figure 3.
(a) Co-fermentation of simulation medium with G. oxydans and C. tropicalis; and (b) the effect of GA on the xylose fermentation of C. tropicalis.
G. oxydans and C. tropicalis preferentially utilized glucose in the medium over xylose; glucose was found to be rapidly and completely consumed within 6–12 h. Meanwhile, xylose was also utilized within 24 h. It could be seen that 66.1 g/L GA, 5.1 g/L 2-KGA, 4.4 g/L ethanol, and 8.7 g/L XA were accumulated at 12 h. As the catalytic conversion continued, the xylose was largely consumed, and the GA content decreased significantly, eventually producing 35.8 g/L GA, 14.1 g/L 2-KGA, 5.7 g/L ethanol, and 13.1 g/L XA with yields of 32.9, 13.1, 8.9, and 47.3%, respectively.
Notably, both G. oxydans and C. tropicalis grew normally in the co-fermentation broth, and their total biomass increased from 4 OD600 to 12.4 OD600 after 24 h. Obviously, in the case of the same initial inoculum, there was some competition between G. oxydans and C. tropicalis, where G. oxydans dominated the synthetic medium, converting most of the glucose and xylose to GA and XA. Moreover, the co-fermentation produced significantly lower GA content compared to the single G. oxydans fermentation. In addition, the complex composition of the fermentation broth caused difficulties in the separation and purification processes, which suggested that co-fermentation with G. oxydans and C. tropicalis is not suitable for producing chemicals from glucose and xylose.
As shown in Figure 2b, G. oxydans in the simulation medium produced approximately 98.7 g/L of GA and 25 g/L of xylose in the fermentation broth. Therefore, we used a medium containing 98.7 g/L GA and 25 g/L xylose to mimic the effect of G. oxydans on C. tropicalis fermentation for the production of SCP. The medium initial pH was adjusted to neutral with NaOH. As shown in Figure 3b, the GA content was relatively constant throughout the fermentation process; meanwhile, 25 g/L xylose was completely used up at 24 h. This suggested that GA was not metabolized by C. tropicalis, and therefore the strain was suitable for removing xylose. In addition, the maximum ethanol production was only 1.1 g/L, indicating that most of the xylose was used for the proliferation of C. tropicalis. Eventually, its OD600 increased from 2.3 to 9.7. Although the presence of GA could have an inhibitory effect on the performance of C. tropicalis in catabolically metabolizing xylose, the xylose was still completely metabolized into ethanol and SCP, which can be easily separated from the fermentation broth by centrifugation or spray-drying. Overall, it was found to be more economical to use C. tropicalis to remove xylose and extract SCP.
As shown in Figure 3a, during the co-fermentation with G. oxydans and C. tropicalis, the presence of G. oxydans reduced the xylose conversion rate. Therefore, we used a two-step fermentation method to utilize glucose and xylose from the lignocellulosic hydrolysate. Notably, G. oxydans can further oxidize GA to 2-KGA, and therefore, for a high yield of GA, the reaction must be stopped at the point when the glucose was consumed to avoid a reduction in GA production. Accordingly, GA fermentation was first performed using G. oxydans, and the cells were subsequently removed by centrifugation from the medium, thus retaining only GA and xylose. Second, the medium pH was adjusted to neutral, and SCP was prepared using C. tropicalis. This fermentation broth contained relatively pure GA, which can be obtained by centrifugation. The large amount of SCP obtained at the end of fermentation could be added to the feed to improve the utilization of the lignocellulosic hydrolysate.
3.4. Sequential Bioprocess for Converting Enzymatic Hydrolysates into GA and Single-Cell Protein
Based on our previous findings showing that G. oxydans can effectively bio-oxidize glucose to GA and C. tropicalis can transform 90% xylose into biomass, a two-step fermentation was designed with enzymatic hydrolysate from corncob as feedstock using G. oxydans and C. tropicalis. The enzymatic hydrolysate contained 98.1 g/L glucose and 25.4 g/L xylose, and the results are shown in Figure 4.
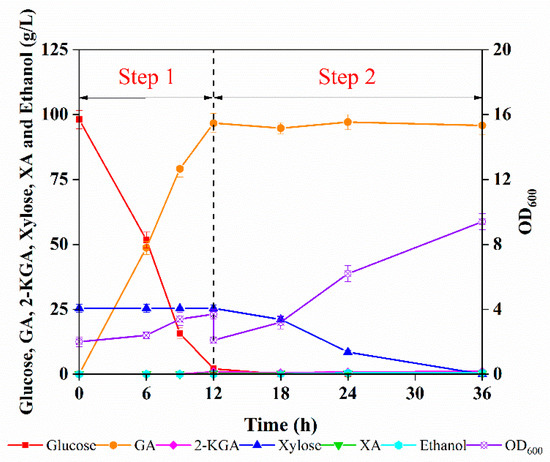
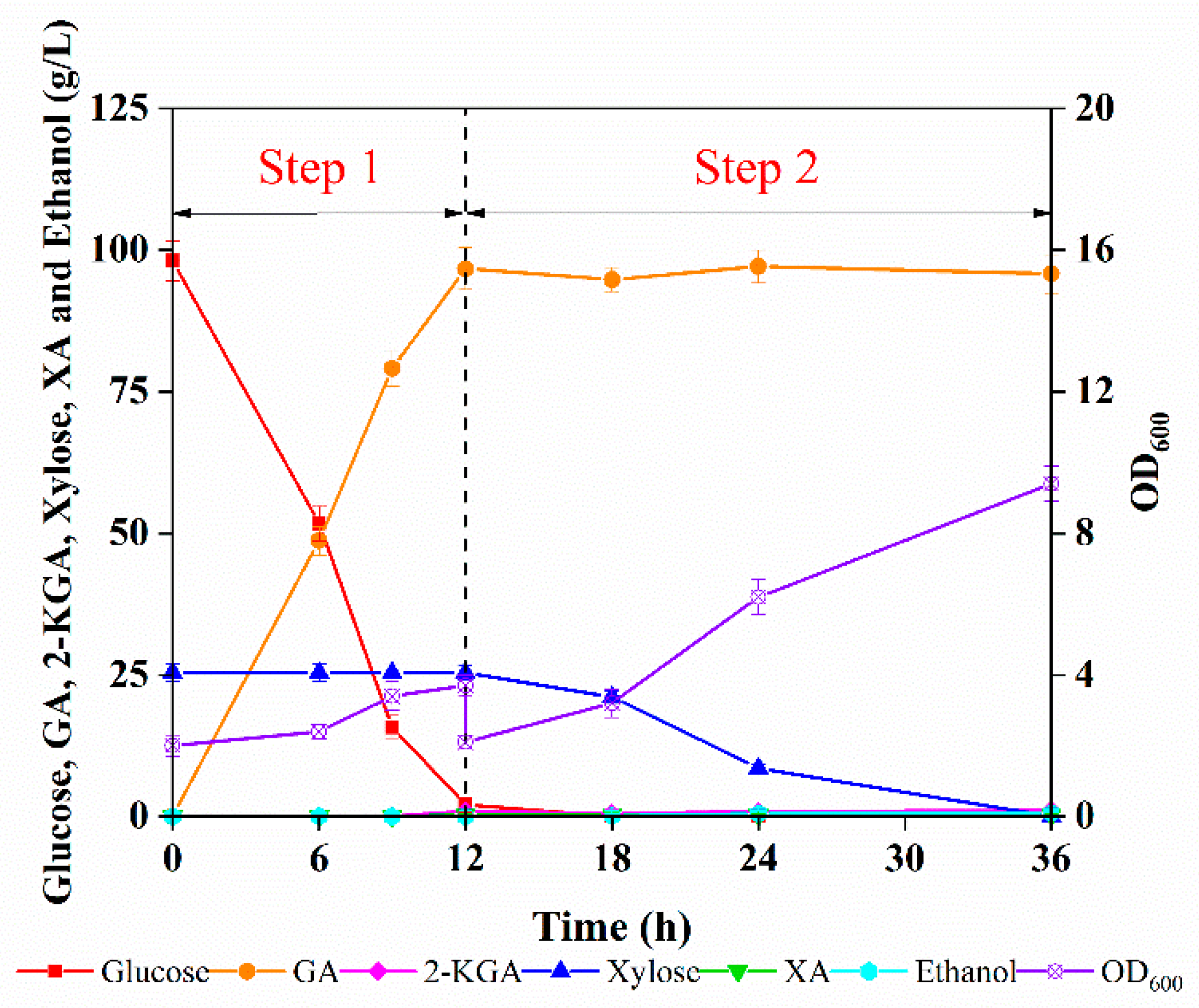
Figure 4.
The two-step fermentation of enzymatic hydrolysate containing glucose and xylose by G. oxydans and C. tropicalis for the production of GA and SCP.
Glucose was converted into 96.7 g/L GA by G. oxydans with a yield of 90.5% in 12 h. The OD600 increased from 2 to 3.7, i.e., approximately 2.5 g/L G. oxydans cells were obtained. Notably, the glucose utilization rate was slightly lower than that of the synthetic medium, which can be attributed to inhibitors in the enzymatic digestor. After 12 h of fermentation, G. oxydans cells in the hydrolysate broth were separated by centrifugation to avoid its effect on the fermentation of C. tropicalis (Section 3.3). Subsequently, 96.7 g/L GA and 25 g/L xylose were left for SCP production by C. tropicalis.
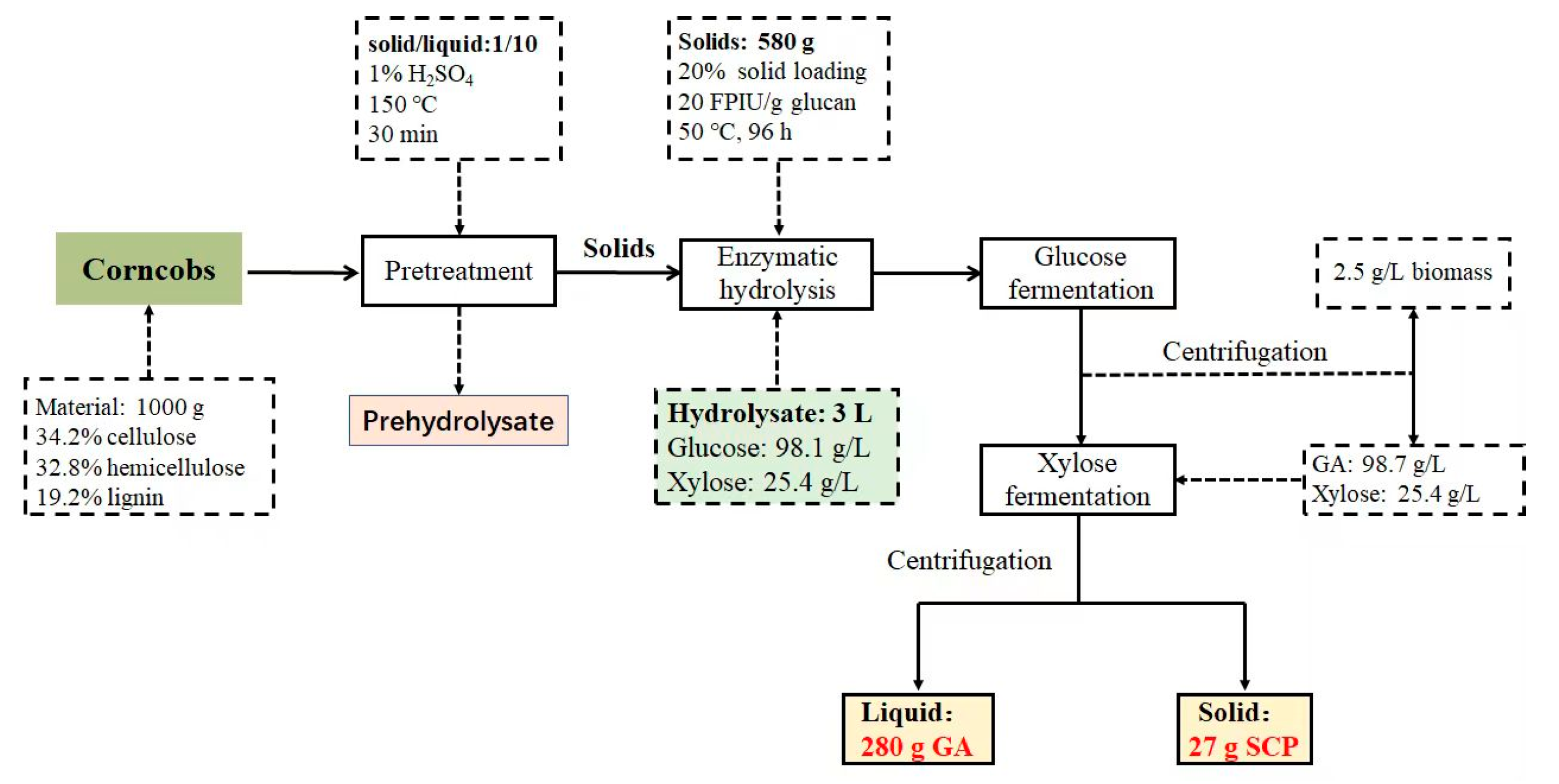
Finally, the fermentation process was terminated after 36 h, when the xylose was completely consumed with almost no ethanol. Although there was a slight downregulation compared to that in the GA medium, the OD600 of C. tropicalis still increased from 2.1 to 9.4. After C. tropicalis fermentation, 95.8 g/L GA and 9.0 g/L SCP were collected from 1 L of enzymatic hydrolysate that initially contained 98.1 g/L glucose and 25.4 g/L xylose, highlighting that the fermentable sugars from the lignocellulosic feedstock, both the glucose and xylose, were fully utilized. Furthermore, the material balance, calculated to obtain the relevant products derived from 1000 g of corncob, is depicted in Figure 5. In total, approximately 280 g GA and 27 g SCP were harvested from 1000 g of the corncob feedstock, which contained 34.2% cellulose and 32.8% hemicellulose. In addition, the acid-pretreated hemicellulosic hydrolysate that contained a large amount of xylose was converted into XA by G. oxydans. Meanwhile, G. oxydans cells were removed after GA fermentation to improve the utilization of the corncob feedstock. Taken together, the two-step fermentation method provides a relatively simple and efficient method for obtaining high-concentration GA as a concrete additive from corncob enzymatic hydrolysates with additional access to SCP, thus opening up broad prospects for the development of an industrial lignocellulosic biorefinery.
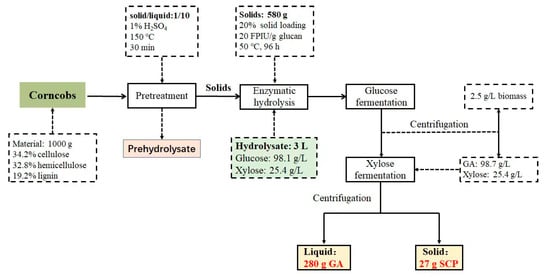
Figure 5.
The main steps in the combined process of pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, and fermentation, as well as the mass balance of GA and SCP.
4. Conclusions
A two-step sequential fermentation method for converting glucose and xylose from corncob hydrolysate into GA and SCP was successfully established. The glucose in the enzymatic hydrolysate can be preferentially and rapidly bio-oxidized into GA within 12 h by G. oxydans. Subsequently, the remained xylose could be selectively converted into SCP using C. tropicalis. This strategy offers an alternative for utilizing lignocellulosic hydrolysates to produce value-added products, which can help in the development of the lignocellulosic biorefinery industry. The started sugar concentration is still too low and cannot satisfy the requirements for industrialization; therefore, in the future, high-concentration enzymatic hydrolysate fermentation needs further study to reduce energy consumption and improve the utilization rate of equipment.
Author Contributions
Methodology, formal analysis, investigation, L.C.; formal analysis, writing-original draft, R.H.; validation, data curation, J.Y. and Y.F.; resources, data curation, conceptualization, writing—review & editing, K.J. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31901270), Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (SJCX22_0324), Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province, China, the start-up funds of Nanjing Forestry University for scientific research (163030163), and Basic Scientific Research Funds of Hangzhou Medical College (KYYB202209).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Advanced Analysis and Testing Center of Nanjing Forestry University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest for this article.
References
- Saravanan, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Jeevanantham, S.; Karishma, S.; Vo, D.N. Recent advances and sustainable development of biofuels production from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, B.; Hou, Y.; Wang, F.; Bao, Y.; Zeng, F.; Qin, C.; Liang, C.; Huang, C.; Ma, J.; Yao, S. Highly selective separation of eucalyptus hemicellulose by salicylic acid treatment with both aromatic and hydroxy acids. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 355, 127304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Pawar, K.D.; Rajput, B.P.; Rahi, P.; Pandit, R.S. Purification of a cellulase from cellulolytic gut bacterium, Bacillus tequilensis G9 and its evaluation for valorization of agro-wastes into added value byproducts. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 101219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Duan, X.; Wei, W.; Wang, S.; Ni, B. Photocatalytic conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to valuable products. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 4266–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nie, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; He, H.; Pan, F.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Ji, X.; Zhang, S. Cascade utilization of lignocellulosic biomass to high-value products. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 3499–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K.; Jia, Y.; Yang, C.; Shen, B.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q. In-situ lignin modification with polyethylene glycol-epoxides to boost enzymatic hydrolysis of combined-pretreated masson pine. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Dhole, N.P.; Xie, R.; Pawar, K.D.; Ullah, K.; Rahi, P.; Pandit, R.S.; Sun, J. Valorization potential of a novel bacterial strain, Bacillus altitudinis RSP75, towards lignocellulose bioconversion: An assessment of symbiotic bacteria from the stored grain pest, Tribolium castaneum. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.A.; Shaikh, A.A.; Pawar, K.D.; Pandit, R.S. Exploring the gut of Helicoverpa armigera for cellulose degrading bacteria and evaluation of a potential strain for lignocellulosic biomass deconstruction. Process Biochem. 2018, 73, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, W.; Lai, C.; Yong, Q.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Meng, X. Revealing the mechanism of surfactant-promoted enzymatic hydrolysis of dilute acid pretreated bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursachi, V.; Gutt, G. Production of cellulosic ethanol from enzymatically hydrolysed wheat straws. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Vadlani, P.V. Biosynthesis of d-lactic acid from lignocellulosic biomass. Biotechnol. Lett. 2018, 40, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Bao, J. Simultaneous saccharification and aerobic fermentation of high titer cellulosic citric acid by filamentous fungus Aspergillus niger. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, Y. Integrative process for sugarcane bagasse biorefinery to co-produce xylooligosaccharides and gluconic acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañete-Rodríguez, A.M.; Santos-Dueñas, I.M.; Jiménez-Hornero, J.E.; Ehrenreich, A.; Liebl, W.; García-García, I. Gluconic acid: Properties, production methods and applications—An excellent opportunity for agro-industrial by-products and waste bio-valorization. Process Biochem. 2016, 51, 1891–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, C.; Wang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hao, Y. Comparative investigation of effect of borax and sodium gluconate retarders on properties of magnesium phosphate cement. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 13187–13198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Ge, D.; Yu, J.; Shen, X. Influence of sodium gluconate on the performance and hydration of portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Han, Y.; Liu, T.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, S.Q. Magnesium oxychloride cement reinforced via d-gluconic acid sodium salt for slow-curing, with enhanced compressive strength and water resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Bao, J. High titer gluconic acid fermentation by Aspergillus niger from dry dilute acid pretreated corn stover without detoxification. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, V.K.; Qazi, G.N.; Kumar, A. Gluconobacter oxydans: Its biotechnological applications. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 3, 445–456. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Bao, J. Fermentative production of high titer gluconic and xylonic acids from corn stover feedstock by Gluconobacter oxydans and techno-economic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzanaeva, L.; Kruk, B.; Ruchala, J.; Nielsen, J.; Sibirny, A.; Dmytruk, K. The role of peroxisomes in xylose alcoholic fermentation in the engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell Biol. Int. 2020, 44, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, F.; Zacchi, G.; Galbe, M.; Wallberg, O. Sequential targeting of xylose and glucose conversion in fed-batch simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation of steam-pretreated wheat straw for improved xylose conversion to ethanol. BioEnergy Res. 2017, 10, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finneran, K.T.; Popovic, J. Solvent production from xylose. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8707–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Xie, C.; Xia, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Tang, Y. The effect of xylose reductase genes on xylitol production by industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae in fermentation of glucose and xylose. Process Biochem. 2020, 95, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lü, S.; Xu, Y.; Mo, Y.; Yu, S. Improving the performance of cell biocatalysis and the productivity of xylonic acid using a compressed oxygen supply. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 93, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochova, K.; Schollbach, K.; Gauvin, F.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Effect of saccharides on the hydration of ordinary portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, M.; Deng, Y.; Suo, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, H. Bioconversion of apple pomace into microbial protein feed based on extrusion pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 1496–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, S.; Bravo, V.; García, J.F.; Cruz, N.; Cuevas, M. Fermentation of d-glucose and d-xylose mixtures by Candida tropicalis NBRC 0618 for xylitol production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, G.; Joshua, C.; He, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, R.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Q. Furfural tolerance and detoxification mechanism in Candida tropicalis. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2016, 9, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Zheng, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, R.; Sun, W. Xylitol production by Candida tropicalis 31949 from sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Sugar Tech 2019, 21, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S. Simultaneous bioconversion of xylose and glycerol to xylonic acid and 1,3-dihydroxyacetone from the mixture of pre-hydrolysates and ethanol-fermented waste liquid by Gluconobacter oxydans. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvira, P.; Tomás-Pejó, E.; Ballesteros, M.; Negro, M.J. Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4851–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Kadhum, H.J.; Murthy, G.S.; Dien, B.S.; Singh, V. High solids loading biorefinery for the production of cellulosic sugars from bioenergy sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 318, 124051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyaso, T.; Manowattana, A.; Techapun, C.; Watanabe, M. Efficient bioconversion of enzymatic corncob hydrolysate into biomass and lipids by oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium paludigenum KM281510. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Guo, X.; Feng, X.; Li, C. An environment friendly and efficient process for xylitol bioconversion from enzymatic corncob hydrolysate by adapted Candida tropicalis. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 263, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Luo, J.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y. Efficient high-solids enzymatic hydrolysis of corncobs by an acidic pretreatment and a fed-batch feeding mode. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 326, 124768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommarius, A.S.; Katona, A.; Cheben, S.E.; Patel, A.S.; Ragauskas, A.J.; Knudson, K.; Pu, Y. Cellulase kinetics as a function of cellulose pretreatment. Metab. Eng. 2008, 10, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, K. Biorefinery cascade processing for converting corncob to xylooligosaccharides and glucose by maleic acid pretreatment. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 4946–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Cao, R.; Tao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S. Characteristics and kinetics of the aldonic acids production using whole-cell catalysis of Gluconobacter oxydans. BioResources 2015, 10, 4277–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Huang, L.; Cao, R.; Xu, Y. Efficient coproduction of gluconic acid and xylonic acid from lignocellulosic hydrolysate by Zn(ii)-selective inhibition on whole-cell catalysis by Gluconobacter oxydans. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).