Abstract
The development of novel antibacterial drugs needs urgent action due to the global emergence of antibiotic resistance. In this challenge, actinobacterial strains from arid ecosystems are proving to be promising sources of new bioactive metabolites. The identified Streptomyces rochei strain CMB47, isolated from coal mine Saharan soil, provided an ethyl acetate extract which tested against a series of pathogens. It displayed a minimum inhibitory concentration of <0.439 µg/mL against MRSA. A statistical experimental design using a response surface methodology (RSM) based on the second-order rotatable central composite design (RCCD) was planned to develop an efficient fermentation process able to improve the bioactive metabolite production. The optimal conditions were determined for starch and NaNO3 concentrations, incubation time and the initial pH value, reaching the inhibition zone diameter of 20 mm, close to the experimental value, after validation of the model. A bioassay-guided fractionation of the crude extract provided the most active fractions, which were analyzed by HPLC equipped with a photodiode array detector and coupled online with an electrospray mass spectrometer (HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS), obtaining preliminary indications on the molecular structures of the metabolites. These results support the potential interest in further investigations into the purification and full characterization of the metabolites responsible for the biological activity observed so far.
1. Introduction
Over several decades, the bacteria that are commonly involved in human pathologies have developed resistance mechanisms to any new antibiotics, including carbapenems and third-generation cephalosporins, the best available antibiotics for treating multidrug-resistant bacteria [1]. As recently reported [2], in 2019, S. aureus was involved in 40 million infections and caused more than one million deaths. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) belongs to the priority list of antibiotic-resistant pathogens published by the World Health Organization (WHO). The list, including the 12 families of bacteria most threatening to human health, was established in order to guide and promote the research and development of new antibiotics. The worldwide emergence of MRSA strains poses a serious public health problem because they are responsible for a wide variety of infections [3]. Moreover, there are limited therapeutic options still available [4,5,6] due to the small number of antibiotics that have been added to the clinician’s arsenal in the last few decades.
Secondary metabolites produced by microorganisms, specifically Actinobacteria, are regarded one of the major sources of antibacterial agents. Actinobacteria investigated so far include several genera, from the most common, such as Streptomyces and Nocardiopsis, to the rarest, such as Saccharothrix, Streptosporangium or Actinomadura. However, depending on their abundance in the soil, 99% of the actinobacteria species still remains unexplored [7]. These microorganisms are a source of wide structural and biological diversity, associated to a similarly wide chemodiversity, which is of interest for biotechnological, agricultural and medicinal applications. Moreover, the mechanisms of adaptation of actinobacteria to extreme environments allow them to synthesize novel and unusual metabolites.
Actinobacteria belonging to the genus Streptomyces are the major producers of antibiotics [8], and this genus has been regarded as containing the most prolific producers of therapeutic compounds [9].
Streptomyces rochei species are well known producers of metabolites that are active against a wide variety of bacterial and fungal pathogens and against tumor cell lines. Significant examples are the polyketide antibiotics lankacidin and lankamycin from S. rochei 7434AN4 [10,11], the new metabolites from the coculture of the marine-derived actinobacterium Streptomyces rochei MB037 and the fungus Rinocladiella similis 35 [12]. Furthermore, it was reported that the marine-derived S. rochei MHM13 and S. rochei MS-37 have the ability to synthesize silver nanoparticles, exhibiting a wide range of inhibition against both Gram-positive and -negative bacteria [13,14]. Additionally, enzymes with biotechnological interest [15,16] are produced by a new soil-derived Streptomyces rochei subsp. chromatogenes NEAE-K [17].
One of the potential approaches to the antibiotic resistance is the search for novel molecules derived from unexplored sources, including peculiar niche habitats [18]. This is confirmed by recent studies on the isolation and characterization of new actinobacteria strains from particular environments. The Algerian Saharan soil constitutes an ecosystem abundant in Actinobacteria, especially belonging to rare species, which have proven to be good producers of new and known antimicrobial molecules against a range of pathogens [19].
A challenge in the screening of Actinobacteria lies in the search for growth conditions favorable to the production of novel secondary metabolites and to the dereplication of known molecules [20]. The optimized conditions applied to the fermentation process (involving media composition and parameters such as pH, temperature, inoculum size and aeration) can affect not only the growth, but also the enhance the production and the nature of secondary metabolites [21,22]. By evaluating the interactions between the different variables, experimental designs are successfully applied in bioprocessing, finding advantages in reduced time, efforts and resources if compared with the conventional approach. By using this optimization approach, we have recently explored coil mining soil actinobacteria with the aim of finding preliminary new metabolites as potential drug candidates. This work allowed the selection and identification of the Streptomyces klenkii CMB51 strain, which exhibits antagonistic activity against the multiresistant uropathogenic germ E. coli ST31 [23].
Our continuous investigation for new active metabolites produced by actinobacteria derived from the extremobiosphere has allowed us to report here on the isolation of the CMB47 strain, identified as S. rochei, which shows broad inhibitions against S. aureus and MRSA. The modeling and optimization approach applied to the culture process enabled us to select the crucial parameters for the maximum production of anti-MRSA metabolites. Additionally, LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis on the most bioactive fractions from the crude extract gave preliminary indications for identifying the metabolites responsible for anti-MRSA activity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Actinobacterial Strain
The CMB47 strain belongs to the collection of the Laboratoire de Microbiologie Appliquée (LMA), University of Bejaia, Algeria. It was isolated in 2019 from the soil of an abandoned coal mine in the Bechar region in southwest Algeria (latitude 31°35′0.02″ N, longitude 2°13′54.68″ O). This site is a particular ecosystem, consisting of charcoal-rich soil and devoid of vegetation. The isolation of the actinobacteria was performed by a serial dilution on SCA medium [23,24]. The strain was selected based on its strong inhibition against MRSA ATCC 43300 and S. aureus ATCC 29213.
2.2. Characterization and Identification of the Actinobacteria Strain
The cultural features of the selected strain were studied according to the recommendations by Shirling et al. [25] based on macro- and micromorphological properties and physiological, biochemical and 16S rRNA gene sequence analyses. The cultural features include intensity of growth, color of aerial and substrate mycelia, growth pattern and production of soluble pigments on International Streptomyces Project (ISP) media. Moreover, various physiological and biochemical tests were performed, as reported by Williams et al. [26] and in Bergey’s manual [27], recording the results after 7 days of incubation at 28 °C. In addition, the strain was evaluated for its tolerance to a range of NaCl concentrations (0%, 0.2%, 0.4%, 1%, 2%, 4%, 6% and 8%) on glucose–yeast extract agar (GYEA) medium. The use of glucidic compounds (1% w/v) on ISP9 medium, resistance or sensitivity to some physical agents such as growth at different initial pH values (5, 7, 9 and 11) and temperatures (4 °C, 37 °C, 40 °C and 50 °C) were also achieved. Furthermore, the studied strain was tested for its resistance to heavy metals using five different metal ions: iron (Fe(NO3)3), chromium (K2Cr2O7), copper (CuSO4), cadmium (Cd(NO3)2) and zinc (ZnSO4), as well as their mixture (used at 50 mg/L concentration) in the agar nutrient (AN) medium [28]. Analytical profiling index (API) strip tests were carried out for the identification of the genus the strain belongs to. The API NE strips (bioMérieux, SA, Marcy-l’Etoile, France) were used to investigate the physiological and biochemical characteristics of the CMB47 strain, following the manufacturer’s instructions. The results were analyzed using APILAB Plus software (bioMérieux).
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction, Amplification, Sequencing of the 16S rRNA Gene and Phylogenetic Analysis
Genomic DNA extraction of the CMB47 isolate was performed according to standard procedure [29]. In detail, the amplification of 16S rRNA was carried out in a prime thermal cycler (Techne) using two universal primers (27F: 5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′ and 1525R: 5′-AAGGAGGTGATCCAAGCC-3′) [30].
The genomic DNA was purified using the Wizard® Genomic DNA purification kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and then used as a template for PCR. DNA electrophoresis, DNA purification, restriction, ligation and transformation were all performed according to the methods previously described [29].
The nucleotide sequence of the cloned 16S rRNA gene was determined using BigDye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction kits and the automated DNA sequencer ABI PRISM® 3100-Avant Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The obtained sequence was compared with the ones available in the sequence databases and with the EzTaxon-e server [31], a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S rRNA gene sequences from type strains. Phylogenetic and molecular evolutionary genetic analyses were performed using MEGA software (version 4.1). Distances and clustering were calculated using the neighbor-joining method. The tree topology of the neighbor-joining data was evaluated by bootstrap analysis with 100 resamplings. Multiple-nucleotide sequence alignment was performed using the BioEdit version 7.0.2 software program and the ClustalW2 program, available at the European Bioinformatics Institute server [32]. The nucleotide sequence data of the 16S rRNA (1501 bp) genes reported in this paper have been submitted to the GenBank database under accession number MW131348.
2.4. Extracellular Enzyme Production Potential Evaluation
In order to detect the amylase activity, the CMB47 strain was seeded on the Gauss medium and incubated at 28 °C for 7 days [33]. The amylolytic potential was detected by submerging the agar plates with Gram’s iodine solution (2.0%). The change in color to clear zones around the growing colonies to dark blue was considered positive. To observe cellulase production of CMB47, it was grown in agar plates, supplemented with carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) (0.5%) as the only carbon substrate and incubated at 28 °C for 7 days. The experiment was carried out in triplicate. The plates were then flooded with Congo red and NaCl. The clear zones around colonies indicated positive cellulase activity [34]. Lipase production was carried out on Sierra medium in which Tween 20 and Tween 80 (0.5%) were supplemented. Agar plates were inoculated and incubated at 28 °C for 7 days. The production of lipases is reflected by the formation of opaque zones around colonies—evidence of Tween 20 and 80 hydrolysis [35]. Tyrosinase activity was assessed in medium containing L-tyrosine [36]. The appearance of black or brown color around the colonies and diffused into the medium, after incubation at 28 °C for 7 days, indicated tyrosinase activity. Protease production was detected for the CMB47 strain on a milk agar plate, containing basal medium amended with 5% of skimmed milk [37]. After 7 days of incubation at 28 °C, zones of casein hydrolysis (clear zones) indicated positive results. Analytical profiling index (API) strip tests were also carried out. The API NE strips (bioMérieux, SA, Marcy-l’Etoile, France) were used to investigate the physiological and biochemical characteristics of CMB47, following the manufacturer’s instructions. The results were analyzed with APILAB Plus software (bioMérieux).
2.5. Screening the Culture Medium and Kinetics Study for the Anti-MRSA Metabolite Production
In order to obtain high bioactivity from the designated performing strain, it is essential to select an appropriate production medium for an efficient fermentation process.
The following media were used: SCA (starch, 10 g; casein, 0.3 g; NaCl, 2 g; K2HPO4, 2 g; KNO3, 2 g; MgSO4·7H2O, 0.05 g; CaCO3, 0.02 g; FeSO4·7H2O, 0.01 g; agar, 18 g; pH 7.2; 1 L distilled water), Czapeck (starch, 10 g; NaNO3, 3 g; K2HPO4, 1 g; MgSO4·7H2O, 0.5 g; KCl, 0.5 g; FeSO4·7H2O, 0.01 g; agar, 18 g; pH 7.0; 1 L distilled water), Gauss (starch, 20 g; K2HPO4, 0.5 g; KNO3, 1 g; MgSO4·7H2O, 0.5 g; agar, 18 g; pH 7.2; 1 L distilled water), ISP2 (glucose, 4 g; yeast extract, 4 g; malt extract, 10 g; agar, 20 g; pH 7.2; 1 L distilled water). The pure strain was inoculated at 107 spores/mL, in Petri plates containing the synthetic production media and incubated at 28 °C for 7 days. The antimicrobial activity was evaluated against MRSA using the agar cylinders method. The medium giving the greatest inhibition, expressed in diameters of the inhibition zones, was selected as the basic production medium for the study of the kinetics and production optimization.
The kinetics of the active metabolite production of the CMB47 strain was carried out for 10 days on the previously selected medium. The evaluation of the anti-MRSA activity was determined after two days of incubation by estimating the diameter of the inhibition zones around the plug according to the agar cylinders method.
2.6. Strain Cultivation and Secondary Metabolite Extraction
2.6.1. Spore Suspension and Strain Cultivation
The pure CMB47 strain was cultured on the Czapeck medium at 28 °C for 7 days. The spore suspension was prepared in 10 mL of distilled water and the inoculum adjusted to 107 spores/mL by measuring the optical density (OD) at 600 nm for OD = 1 [38].
2.6.2. Crude Extract
Active metabolites were extracted twice by an overnight maceration of culture medium together with mycelial mass using a sufficient volume of ethyl acetate. After combination of the filtrates, the organic phase was evaporated to dryness using a rotavapor, giving 427.3 mg of crude extract, which was suspended in 5 mL of methanol before the biological screening.
2.7. Anti-MRSA Susceptibility Test of the Crude Extract
2.7.1. Well Diffusion Assay
Antimicrobial susceptibility assay was carried out using the well diffusion method against MRSA (ATCC 43400). Wells of 6 mm in diameter are formed on Mueller–Hinton, previously inoculated with 107 UFC/mL of MRSA, and volumes of 100 μL of extract were then introduced. Methanol and vancomycin were used as negative and positive controls. The plates were placed at 4 °C for 2 h to allow the diffusion of the active substances and then incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The clear zones of inhibition observed around the wells suggested antagonistic activity, and diameters of inhibition zones were subsequently measured. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
2.7.2. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Values
The lowest concentration of crude extract that completely inhibited the bacterial growth was considered to be the MIC value. It was determined using the microbroth dilution method, as defined in the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines [39]. The serially diluted fraction of crude extract (450 µg/mL) with sterile Mueller–Hinton broth was added to precoated microbial cultures in 96-well microtiter plates to give a final concentration of 0.225–4.29 µg/L. A sample control (CMB47 extract alone) and a blank (media only) were included in each assay. Vancomycin (30 μg/disc) was used as positive control. The titer plate was incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Each experiment was carried out in triplicate.
2.8. Experimental Design and Optimization of Anti-MRSA Activity
In order to improve the production of active metabolites by the CMB47 strain cultured on the selected medium, optimization trials were carried out with response surface methodology (RSM) using the rotatable central composite design (RCCD). The influence of four parameters were evaluated: starch and NaNO3 concentrations, incubation time and initial pH at extreme values, as reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Coded and actual values of the variables for central composite experimental design.
Overall, thirty experiments were carried out and the design was composed of 24 factorial designs (1–16 trials). Six replicates (17–22 trials) in the center domain condition and at star points (23–30 trials) were added to estimate the model curvature and allow the evaluation of the experimental error (Table S1).
Excel software was used in this study to construct the experimental design and statistically analyze the experimental data. In detail, the regression analysis was performed to estimate the response function as a second-order polynomial equation, as presented below.
where represents the predicted anti-MRSA activity, expressed as diameter of inhibition zones; xj and xu represent the independent factors (medium component) in the form of coded values; b0 is the intercept term; and bj, buj and bjj are the linear, interaction and quadratic terms, respectively [40,41,42]. The coefficients of the fitted equation were obtained from Equation (2), as follows [40,41,42]:
where B is the column matrix of estimated coefficients; the dispersion matrix; the transpose matrix of experiments matrix [X]; and Y is the column matrix of observations.
In order to determine the validity of the mathematical model equation so developed, experiments were performed in triplicate under the optimal conditions, as predicted by the model. The average values of the experimental data were compared with the predicted values to determine the accuracy and suitability of this model.
2.9. Fractionation of the Bioactive Crude Extract and Its Metabolite Profile by HPLC-DAD and LC–ESIMS Analyses
Ethyl acetate crude extract of strain CMB47 (124.6 mg) was investigated for the study of its metabolites. The extract was analyzed through TLC (silica gel 60 F254, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), using dichloromethane–methanol (9:1, v/v) as mobile phase, and then subjected to fractionation on a chromatographic silica gel column, using dichloromethane–methanol at gradient elution, collecting 12 fractions (25 mL each). The bioactivity-guided evaluation conducted for the 12 fractions was performed against MRSA based on the well diffusion method, testing 100 µL each. Fraction 11 eluted with 100% methanol showed relevant bioactivity. It was subjected to a flash chromatography, using a reversed-phase RP-18 column and a gradient of methanol–water as mobile phase, to yield 6 fractions (A-F). The purity of the fractions was verified through analytical reversed-phase C18 HPLC-DAD analysis at 254 nm, using isocratic condition of methanol–water (8:2, v/v). The presence of three compounds was detected in the chromatograms of both fractions 11B (6.1 mg, 4.89%; tR1 = 6.9 min, tR2 = 8.2 min, tR3 = 10.4 min) and 11D (5.4 mg, 4.33%; tR1 = 8.2 min, tR2 = 9.6 min, tR3 = 10.7 min), after confirming their anti-MRSA activity.
LC-ESI–MS analysis of ethyl acetate extract was carried out on a Hewlett–Packard HP1100 HPLC-UV diode array detector (DAD), coupled online with an Esquire–Bruker–Daltonics mass spectrometer.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Screening of Active Actinobacteria Strains
In this study, from the coal mine soil from the Bechar region in southwest Algeria, we targeted the isolation of different genera of actinobacteria, looking for new natural products.
Several actinobacteria-like colonies with similar and different morphologies were obtained. The development of isolates was monitored through regular counts after 3, 7, 14, 21 and 30 days of incubation at 28 °C, giving 271 isolates. They were screened for their activity against Gram-positive and -negative bacteria, as well as a pathogenic yeast. Of 119 tested strains, 82 showed the ability to inhibit the growth of at least one target germ. It was noticed that the antagonism varied according to the tested and the target strains, showing significant antagonistic effect and bacteriostatic activities. Altogether, 54 and 50 strains inhibited the growth of S. aureus and MRSA, respectively. The growth of E. coli ST131 and C. albicans was inhibited by 42 and 22 strains, respectively. Only five isolates exhibited broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against all of the tested germs [23]. The potential of the isolates against Gram-positive bacteria was observed more often than that against Gram-negative bacteria. This frequency of soil actinobacteria was similar to those reported by numerous authors [43]. In order to obtain a better representation of the different isolates and to define the strain classification categories, statistical analyses of hierarchical ascending classification (CAH) and PCA were carried out [23].
In this screening, strains CMB47 and CMB51 displayed significant inhibitory effects worthy of further investigation. CMB47 has shown a spectrum of activity exclusively directed against Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus and MRSA, with inhibition diameters recorded at 20 and 18 mm, respectively. Based on this evidence, strain CMB47 was selected and subjected to subsequent studies regarding its metabolism potential.
3.2. Polyphasic and Molecular Characterization of the Selected Active CMB47 Strain
The CMB47 isolate was characterized using the methods recommended by the ISP. Cultural properties on different ISP culture media (ISP2, ISP3, ISP4, ISP5 and ISP6), as well as on SCA, Czapeck and Gauss media, were examined after 21 days of incubation at 28 °C. The colonies of the strain revealed diverse morphological appearances, with varied spore color, aerial and substrate mycelium and colony morphology. The growth of the isolate on different media is given in Table S2.
CMB47 grew abundantly on ISP2, ISP3, ISP4, ISP5, Gauss, SCA and Czapeck media, whereas good-to-moderate growth was observed when grown on ISP6. Weak growth was observed on the ISP1 medium. The strain produced a purple substrate mycelium on all tested media, while the aerial mycelium varied according to culture medium, from white to gray and from pink to purple. Diffusible yellow-to-purple-brown pigments were also observed in all tested media. Prominent differences in the extent of growth, structure and pigmentation of the colonies on different media were in line with the earlier reports [44,45].
A detailed view of the morphology was obtained through the study of single colonies (Figure 1a). The microscopic observations showed a branched flexuous mycelium and the arrangement of spores in a chain inside the mycelium, as shown in Figure 1b.
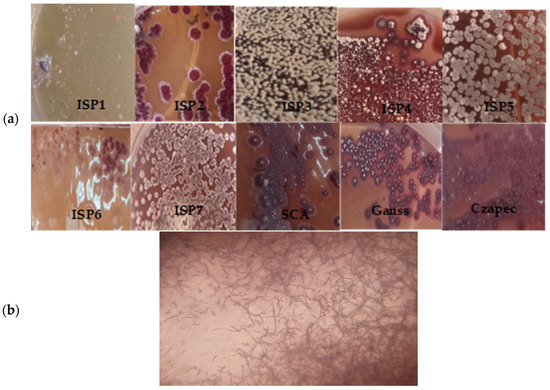
Figure 1.
(a) Morphological characterization of CMB47 colony observations made on different ISP and some culture media. (b) Microscopic observation of the mycelial network of branched hyphae of CMB47.
According to the methods described in Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology [27], the morphological, biochemical and physiological characteristics showed that the CMB47 isolate appeared to be endospore-forming, catalase and oxidase positive. The optimal culture conditions for the growth of the isolate were investigated. It was found that the strain grew in the temperature range from 28 to 40 °C, with a pH from 3 to 11 and a NaCl tolerance from 0% to 1% (with moderate growth in 4% NaCl). CMB47 cultivated on ISP9 for carbohydrate utilization showed excellent growth in the presence of galactose, mannose, mannitol, cellulose, sucrose, starch and glucose; moderate development was observed with fructose and xylose. The outcome from the API ZYM tests revealed that, while the activities exhibited by CMB47 for alkaline phosphatase, esterase lipase (C8), leucine arylamidase and valine arylamidase were positive, those exhibited for lipase (C14), trypsin, α-chymotrypsin, N-acetyl-β-lucosamidase, β-glucuronidase, α-mannosidase and α-fucosidase were negative. Moreover, the isolate tolerated the presence of Fe, Cr and Cu metal ions with a moderate growth; no development was observed with Zn, Cd and mixture metal ions. The physiological and biochemical properties of the strain are given in Table S3. Combining all the obtained morphological, microscopic, physiological and biochemical properties, they clearly confirmed that the CMB47 strain belongs to the Streptomyces genus.
Amplification of the 16S rRNA gene from the genome of CMB47 produced a sequence of 1501 nucleotides. The 16S rRNA gene sequence from strain CMB47 was 99% similar to those of the Streptomyces rochei strain. A phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene (Figure 2) showed that the novel CMB47 isolate clustered with members of the genus Streptomyces, the nearest neighbor being the Streptomyces rochei strain A-1T (GenBank accession no. GQ392058), which had a sequence similarity of 99.47. The nearest Streptomyces strains identified by BLAST were imported into the ARB software package and aligned. The phylogenetic tree was then constructed using neighbor-joining methods and Jukes–Cantor distance matrices. Based on the results obtained in the course of the present study, we suggest the assignment of the CMB47 isolate (GenBank accession no. MW131348) as Streptomyces rochei CMB47.
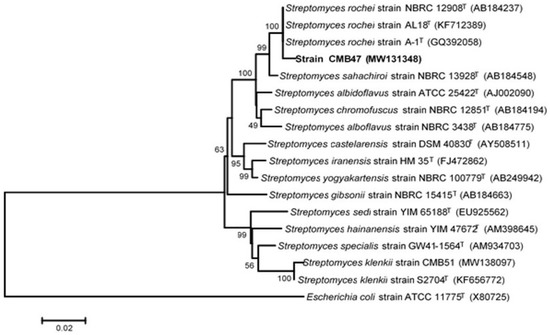
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences, showing the position of strain CMB47 (GenBank accession no. MW131348) within the radiation of the genus Streptomyces. The sequence of E. coli strain ATCC 11775T (accession no. X80725) was chosen as an outgroup. Numbers at the nodes indicate the level of bootstrap support (%); only values > 50% are shown. GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. Bar, 0.02 nt substitutions per base.
3.3. Kinetic Study on the Production of Anti-MRSA Metabolites by Strain CMB47
This analysis was carried out after determining the best production medium. Numerous studies indicate that the nature of the carbon, nitrogen and mineral sources entering into the culture media composition greatly influences the production capacity of antibiotics in actinobacteria [21,46]. For this reason, the antimicrobial activity of the isolate was evaluated on four culture media: SCA, Czapeck, Gauss and ISP2, using the agar plugs method after 7 days of incubation at 28 °C. The medium on which the strain exhibited the most significant antimicrobial activity was selected.
From the obtained results depicted in Figure 3a, it is evident that CMB47 presents close and significant activities against MRSA on all of the tested culture media. The diameters of the inhibition zones ranged between 16.5 and 20.16 mm. The most important activity was recorded using the Czapeck medium (20.16 mm) compared to the Gauss and ISP2 media. Thus, the Czapeck agar medium was selected for further studies. According to the kinetics profile reported in Figure 3b, the anti-MRSA activity of CMB47 was detected from the second day of incubation, and the production increased to reach its optimum after the third day. It was clearly noticed that the antagonistic effect is persistent, and the anti-MRSA activity is practically constant throughout the whole incubation period.
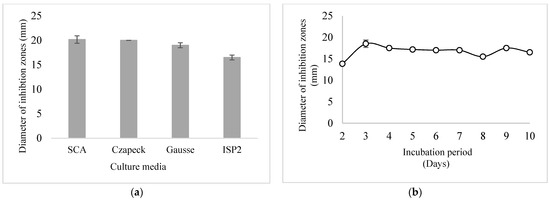
Figure 3.
Anti-MRSA activity variation (a). Kinetics of anti-MRSA compounds production (b).
3.4. Anti-MRSA Activity Evaluation of Crude Extracts
Extraction of the bioactive secondary metabolites produced by the CMB47 isolate was carried out by maceration, obtaining 1 mg/mL of crude extract recovered in methanol and 0.45 mg/mL recovered in ethyl acetate.
The antagonistic activity against MRSA demonstrated by the wells technique allowed us to highlight the potency of both crude extracts, which displayed significant inhibitory effects, estimated at 38 and 34 mm of diameter for the methanol and ethyl acetate extracts, respectively. The MIC evaluation of the two extracts was carried out using the microdilution method. After 24 h of incubation, the results were assessed by a visual evaluation of the turbidity in the various wells, and the MIC corresponded to the concentration of the first well from which no visible culture was observed. The investigated extracts exhibited potent anti-MRSA activity with the minimum concentration of extract, which allows the inhibition of the MRSA growth, estimated at 1.95 µg/mL for methanol extract and 0.439 µg/mL for ethyl acetate extract. The date obtained, proving in line with the wells method data, can be considered as significant since it performed better than the standard drug vancomycin (0.5 to 2 µg/mL) for MRSA strains [47]. In summary, these results for the anti-MRSA activity of the CMB47 metabolites strengthen the role of Saharan actinobacterial species as being promising sources of molecules that act against a range of pathogenic bacteria and fungi, particularly MRSA [19].
3.5. Central Composite Experimental Design Analysis
In this study, the rotatable central composite experimental design, with four factors at five levels (−2, −1, 0, +1 and +2), was employed to investigate and optimize the influence of the process variables on the anti-MRSA activity of CMB47 isolate. The RCCD was selected for modeling and optimizing the effects of influencing factors on the response, in order to predict the linear and quadratic interaction effects of the parameters.
The medium composition and the operating parameters are important factors affecting the antibacterial activity in microorganisms [48]. The concentration of carbon and nitrogen sources, starch and NaNO3, as well as the initial pH value and incubation period, are the most important cultural parameters influencing the response.
The results are listed in Table S1. The model coefficients (Equation (2)) are estimated using the standard least-square regression technique using “EXCEL” software. From a statistical point of view, three tests are required to evaluate the adequacy of the model: Student’s t-test, which is about the significance of factors, the R-square test and Fisher’s test [40,41,42].
The estimated t values for particular process parameters can be calculated as follows:
with
where is the coefficient variance; is the diagonal term of the matrix; is the replication variance; is the observed value of the anti-MRSA activity for ith central point; is the average value of the strain activity at a center trial; and n0 is the repetition number of experiments at the center domain condition (in this design, n0 = 6).
The tabulated t value [40,41,42] for a 5% level of significance and five degrees of freedom (f = 6 − 1 = 5) is t0.05 (5) = 2.57. It was found that the coefficients b1, b4, b12, b13, b23, b24, b11 and b44 are not significant; therefore, they are excluded from the regression equation.
The test of regression significance has been carried out via Fisher’s variance ratio test, known as the F-test. The F-ratio is given by the following form:
where and are the regression and residual variances, respectively; N is the total number of observations (N = 30); is the number of significant coefficients ( = 7); yi is the experimental value of anti-MRSA activity for ith observation; and is the predicted value of the response for ith observation.
Table 2 reports the values of , and F that were calculated for the regression equation. The test of significance of regression confirms that the established predicting equation gives an excellent fitting to the observed data (estimated F value > tabulated F value). Finally, the R2 value, which shows the fit between the experimental and the predicted data, was found to be 85%. All these results indicate that the model equation can adequately represent the data.

Table 2.
Fisher’s test results for regression significance.
The obtained model for anti-MRSA activity, after discarding the insignificant coefficients, is as follows:
According to the regression model and ANOVA results, it is clearly observed that the most significant factors are NaNO3 concentration (X2) and incubation time (X3), while starch (X1) and pH (X4) affect the response in interaction with other factors ((X1X4) and (X3X4)).
Additionally, the NaNO3 concentration had the highest impact on the anti-MRSA activity, considering the highest linear coefficient (0.41), followed by the incubation time (0.27). Otherwise, the NaNO3 concentration had a significant negative effect, indicating that the anti-MRSA activity decreased as the level of this parameter increased. The positive coefficient for incubation time showed that the antibacterial activity increased with this parameter.
The contour plots and their corresponding response surface plots of the quadratic model, obtained using MATLAB 7.0 software, are shown in Figure 4. The figures are drawn in a starch (X1)–pH (X4) plan for various levels of NaNO3 (X2) and incubation times (X3) (−1, 0 and +1).
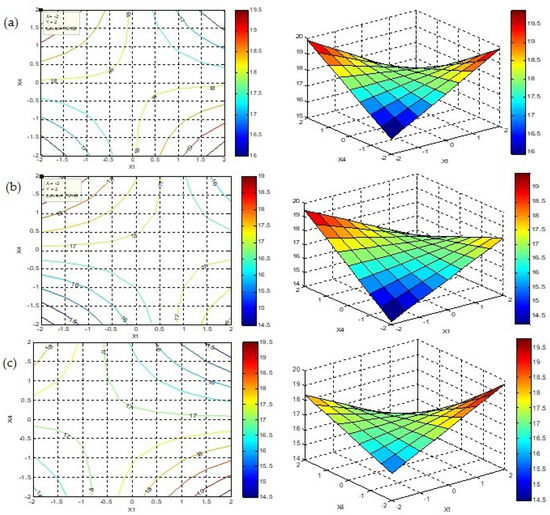
Figure 4.
Contour plots and response surface plots for different conditions. (a) X2 = 0, X3 = 0; (b) X2 = +1, X3 = +1; (c) X2 = −1, X3 = −1.
Analyzing the results, it is evident that the anti-MRSA activity ranged from 19.5 mm to 20 mm for different operating parameter conditions (Figure 4). The optimum antibacterial activity of 20 mm was selected due to the most economical and favorable conditions for the strain, which are 2 g/L of starch concentration (X1 = −2), 3 g/L of NaNO3 concentration (X2 = 0), 7 days of incubation time (X3 = 0) and a media pH of 11 (X4 = +2).
In order to determine the model adequacy, the optimized predicted levels of starch and NaNO3 concentrations, incubation time and pH value were considered for experimental anti-MRSA activity to be compared with the predictive data. The experiment was run in triplicate. The measured anti-MRSA activity of 18.5 mm, close to the predicted 20 mm value, proves a high degree of accuracy of the developed model.
3.6. Secondary Metabolite Profiling by DAD-HPLC/ESI-MS Analysis
HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS analysis of CMB47 ethyl acetate crude extract was undertaken to evaluate the chemical profile, including the bioactive metabolite.
Interestingly, the analysis was later carried out on the active fractions 11B and 11D, showing the highest activity against MRSA, with inhibitory zones of 35 mm and 15 mm, respectively, in comparison to the 19 mm zone of vancomycin (30 µg/disc).
The HPLC-MS analysis showed three signals at the retention times of 6.9, 8.2 and 10.4 min, associated with the MS signals recorded in the positive ion mode at m/z 207, 221 and 235. They could be assigned to the corresponding [M + H]+ ions, supported by the experiment acquired in the negative ion mode, giving signals at m/z 205, 219 and 233, which correspond to the [M-H]− ions matching the same chromatographic peaks (Figure S1). The respective compounds displayed the same UV chromatogram, and the chromatogram recorded at 296 nm showed the prevailing abundance of the components at 8.2 min, which are associated with [M + H]+ at m/z 221 (Figure S2).
These data indicate that the bioactivity observed for fraction 11B is related to the presence of three metabolites with molecular mass values of 206, 220 and 234 Da, which differ by 14 units, attributable tentatively to homologous series (different in the number of CH2 unit), or in the presence of one/two OMe replacing OH groups or NMe replacing NH units. The same analysis of the fraction 11D displayed a more complex, but similar, pattern as fraction 11B. No correlations were found in the comparison of the molecular masses of the three metabolites produced by S. rochei CMB47 with all the known antibiotics produced by S. rochei, supporting the potential novelty of their molecular structures.
4. Conclusions
The present study was successful in determining the biological relevance of actinobacterial isolates from a coal mining soil in the Bechar region of southwestern Algeria. A novel strain, Streptomyces rochei CMB47, showed significant activity against MRSA.
The study on the variation of the nutrient conditions in the culture medium was provided by applying the central composite design and RSM modeling targeting, with the aim of enhancing the anti-MRSA activity. Thus, the statistical trial using RSM for maximizing the bioactivity of S. rochei CMB47 was validated as a potent and useful tool.
The relevant anti-MRSA activity of the ethyl acetate crude extract prompted us to analyze the metabolic profile. After a bioassay-guided fractionation, the DAD-HPLC/ESI-MS analysis of the two most bioactive fractions provided preliminary structural indications of the compounds responsible for MRSA inhibition.
These results warrant further investigation into the structural elucidation of the bioactive metabolites, the molecular mass values of which, to the best of our knowledge, have not found any correspondence with those of antibiotic metabolites isolated so far from S. rochei. Additionally, the physiological and enzymatic potential of the isolate provides interesting prospects for possible indications in the biotechnological field through future targeted survey.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation9040381/s1, Table S1: Composite design matrix and results of anti-MRSA compound production; Table S2: Cultural characteristics of the isolate CMB47 on international Streptomyces project (ISP) and some media; Table S3: Physiological properties of strain CMB47. Figure S1: HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS analysis of the bioactive fraction 11B from ethyl acetate crude extract of S. rochei CMB47 strain. Figure S2: HPLC-DAD/ESI-MS analysis of the bioactive fraction 11B from ethyl acetate crude extract of S. rochei CMB47 strain.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.D. and I.M.; methodology, I.D., I.M., C.B. and H.B.; results evaluation, I.D., W.D., S.S. and I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, I.D., W.D. and I.M.; writing—review and editing, I.D., M.K. and I.M.; supervision, I.D. and I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Algerian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research in the frame of PRFU research project N° D01N01UN060120190002.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Adriano Sterni, from the Laboratory of Bioorganic Chemistry at the university of Trento, for recording the MS spectra.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organisation Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics are Urgently Needed. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/bacteria-antibiotics-needed/en/ (accessed on 27 February 2022).
- GDB 2019 Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2022, 400, 2221–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S.; De Lencastre, H.; Garau, J.; Kluytmans, J.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Peschel, A.; Harbarth, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18033–18045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.Y.; Caffrey, A. Thrombocytopenia with tedizolid and linezolid. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 62, e01453-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankenfeld, C.; Mittal, S.; Melendez, Y.; Mendez-Vigo, L.; Lamp, K.C.; Keller, K.N.; Bertolami, S.R. Daptomycin: A comparison of two intravenous formulations. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.W.; Olsen, R.J.; Mehta, S.C.; Palzkill, T.; Cernoch, P.L.; Perez, K.K.; Musick, W.L.; Rosato, A.E.; Musser, J.M. PBP2a mutations causing high-level ceftaroline resistance in clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6668–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J. Millennium bugs. Trends Cell Biol. 1999, 9, 2e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watve, M.G.; Tickoo, R.; Jog, M.M.; Bhole, B.D. How many antibiotics are produced by the genus Streptomyces? Arch. Microbiol. 2001, 176, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdy, J. Thoughts and facts about antibiotics: Where we are now and where we are heading. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinashi, H.; Mori, E.; Hatani, A. Isolation and characterization of linear plasmids from lankacidin-producing Streptomyces species. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindita, Y.; Cao, Z.; Fauzi, A.A.; Teshima, A.; Misaki, Y.; Muslimin, R.; Yang, Y.; Shiwa, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Tagami, M.; et al. The genome sequence of Streptomyces rochei 7434AN4, which carries a linear chromosome and three characteristic linear plasmids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10973–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Banakar, S.P.; Liu, L.; Shao, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, C. New metabolites from the co-culture of marine-derived actinomycete Streptomyces rochei MB037 and fungus Rhinocladiella similis 35. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Elnaby, H.M.; Abo-Elala, G.M.; Abdel-Raouf, U.M.; Hamed, M.M. Antibacterial and anticancer activity of extracellular synthesized silver nanoparticles from marine Streptomyces rochei MHM13. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2016, 42, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsilk, S.E.; Khalil, M.A.; Aboshady, T.A.; Alsalmi, F.A.; Ali, S.S. Streptomyces rochei MS-37 as a novel marine actinobacterium for green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Molecules 2022, 27, 7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maibeche, R.; Boucherba, N.; Bendjeddou, K.; Prins, A.; Bouiche, C.; Hamma, S.; Benhoula, M.; Azzouz, Z.; Bettache, A.; Benallaoua, S.; et al. Peroxidase-producing actinobacteria from Algerian environments and insights from the genome sequence of peroxidase-producing Streptomyces sp. S19. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irdani, T.; Perito, B.; Mastromei, G. Characterization of a Streptomyces rochei endoglucanase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 782, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Naggar, N.E.; El-Shweihy, N.M. Bioprocess development for L-asparaginase production by Streptomyces rochei, purification and in-vitro efficacy against various human carcinoma cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7942–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fielder, H.P.; Bruntner, C.; Bull, A.T. Marine actinomycetes as a source of novel secondary metabolites. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2004, 87, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djinni, I.; Defant, A.; Kecha, M.; Mancini, I. Actinobacteria derived from Algerian ecosystems as a prominent source of antimicrobial molecules. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machushynets, N.V.; Wu, C.; Elsayed, S.S.; Hankemeier, T.; Van Wezel, G.P. Discovery of novel glycerolated quinazolinones from Streptomyces sp. MBT27. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djinni, I.; Defant, A.; Djoudi, W.; Chaabane Chaouch, F.; Souagui, S.; Kecha, M.; Mancini, I. Modeling improved production of the chemotherapeutic polypeptide actinomycin D by a novel Streptomyces sp. strain from a Saharan soil. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djinni, I.; Djoudi, W. Streptomyces sp. WR1L1S8 a potent endophytic marine strain for heavy metal resistance and copper removal enhanced by RSM modeling. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djinni, I.; Djoudi, W.; Harfi, N.; Stambouli, I.; Khamtache, S.; Makhlouf, D.; Yanat, B.; Souagui, S.; Kecha, M. Enhanced anti-E. coli ST131 metabolites production by a novel Streptomyces sp. CMB51 strain isolated from a coal mininig soil using statistical optimization. Geomicrobiol. J. 2022, 39, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuster, E.; Williams, S.T. Selection of Media for Isolation of Streptomycetes. Nature 1964, 202, 928–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirling, E.B.; Gottlieb, D. Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1966, 16, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.T.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G. Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Williams, S.T., Sharpe, M.E., Holt, J.P., Eds.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1989; Volume 4, pp. 2452–2492. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, J.G.; Krieg, N.R.; Sneath, P.H.A.; Stanley, J.T.; Williams, S.T. Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 9th ed.; Williams and Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Daboor, S.M.; Haroon, A.M.; Neven, A.E.; Hanona, S.I. Heavy metal adsorption of Streptomyces chromofuscus. J. Clin. Med. 2014, 2, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Gurtler, V.; Stanisich, V.A. New approches to typing and identification of bacteria using the 16S-23S rDNA spacer region. Microbiology 1996, 142, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EzTaxon-e Server. Available online: http://eztaxon-e.ezbiocloud.net/ (accessed on 9 June 2019).
- European Bioinformatics Institute Server. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/ (accessed on 9 June 2019).
- Haritha, R.; Siva Kumar, K.; Jagan Mohan, Y.S.Y.V.; Romana, T. Amylolytic and proteolytic Actinobacteria isolated from marine sediments of Bay of Bengal. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 1, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rathnan, R.K.; Ambili, M. Cellulase enzyme production by Streptomyces sp. using fruit waste as substrate. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 1114–1118. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of microorganisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 1957, 23, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasiva Rao, K.R.S.; Tripathy, N.K.; Mahalaxmi, Y.; Prakasham, R.S. Laccase and peroxidase free tyrosinase production by isolated microbial strain. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVos, P.; Garrity, G.M.; Jones, D.; Krieg, N.R.; Ludwig, W.; Rainey, F.A.; Schleifer, K.H.; Whitman, W.B. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, 2nd ed.; The Firmicute; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Kieser, T.; Bibb, M.J.; Buttner, M.J.; Chater, K.F.; Hopwood, D.A. Practical Streptomyces Genetics, 2nd ed.; John Innes Foundation: Norwich, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, Approved Standard, 9th ed.; CLSI Document M07-A9; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, CLSI: Louis, MS, USA, 2012; Volume 32, pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Hunter, W.G.; Hunter, J.S. Statistics for Experimenters; Edition Wiley Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Sado, G.; Sado, M.C. Les Plans D’expériences de L’expérimentation à L’assurance Qualités; AFNOR Technique: Paris, France, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Goupy, J. Plans d’expériences Pour Surfaces de Réponse; Dunod: Paris, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Basilio, A.; Gonzalez, I.; Vicente, M.; Gorrochategui, J.; Cabello, A.; Gonzalez, A.; Genilloud, O. Patterns of antimicrobial activities from soil actinomycetes isolated under different conditions of pH and salinity. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, T.A.; Bharat, B.; Bhasin, S.; Modi, H.A. Approach towards different fermentative techniques for the production of bioactive actinobacterial melanin. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Dubey, A.K. Isolation and characterization of a new endophytic Actinobacterium Streptomyces californicus strain ADR1 as a promising source of anti-bacterial, anti-biofilm and antioxidant metabolites. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djinni, I.; Djoudi, W.; Souagui, S.; Rabia, F.; Rahmouni, S.; Mancini, I.; Kecha, M. Streptomyces thermoviolaceus SRC3 strain as a novel source of the antibiotic adjuvant streptazolin: A statistical approach toward the optimized production. J. Microbiol. Meth. 2018, 148, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, C.N.; Tandel, K.; Grover, N.; Bhatt, P.; Sahni, A.K.; Sen, S.; Prahraj, A.K. In vitro vancomycin susceptibility amongst methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Med. J. Armed Forces India. 2014, 70, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Tomoda, H.; Omura, S. Phenatic acids A and B, new potentiators of antifungal miconazole activity produced by Streptomyces sp. K03-0132. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).