Bioinformatic Modeling (In Silico) of Obtaining Bioactive Peptides from the Protein Matrix of Various Types of Milk Whey
Abstract
1. Introduction
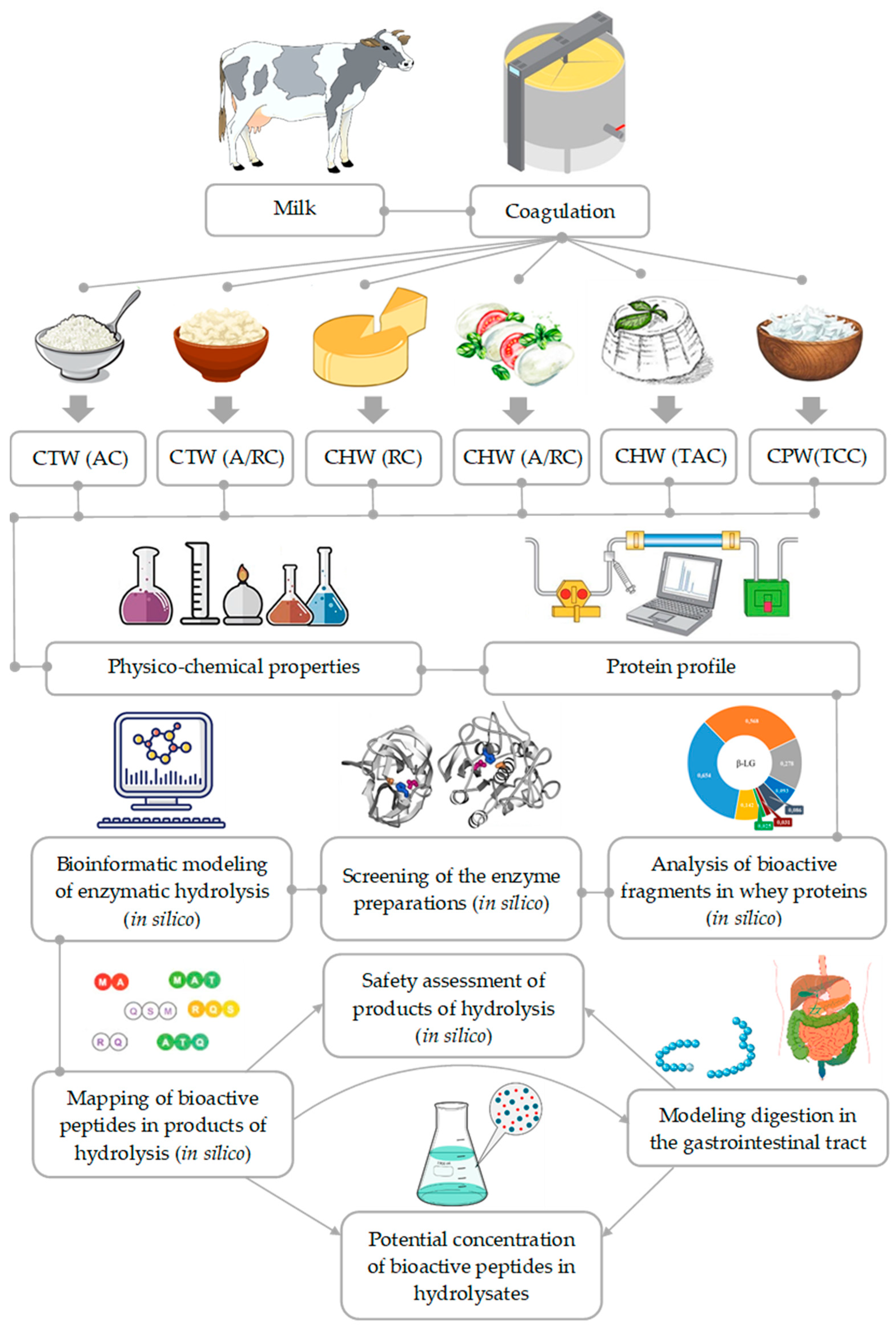
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Whey Samples
2.2. Determination of Physicochemical Properties of Whey
2.3. Method of Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Screening of Bioactive Sites in the Protein Structure and Release of Bioactive Peptides
- Theoretical degree of hydrolysis (DH)DH= d/D × 100,d—the number of hydrolyzed peptide bonds in the protein–peptide chain; D—total number of peptide bonds in the protein–peptide chain.
- Frequency of bioactive fragments in the protein sequence (A)A = a/N,a—the number of fragments with a target activity; N—the number of amino acid residues.
- Potential biological activity of protein fragments (B)B = [Σ(ai/IC50i)]/N,ai—the number of repeats of the i-th bioactive fragment in the protein sequence; IC50i—the concentration of the i-th bioactive peptide corresponding to half-maximum inhibition [μM]; N—the number of amino acid residues.
- Frequency of release of fragments with a target activity by selected enzymes (AE)AE = d/N,d—the number of peptides with a target activity (e.g., ACE inhibitors) released by selected enzymes; N—the number of amino acid residues in the protein.
- Relative frequency of release of fragments with a target activity by selected enzymes (W)W = AE/A,AE—the frequency of release of fragments with a target activity by selected enzymes; A—the frequency of occurrence of bioactive fragments in the protein sequence.
- Activity of fragments potentially released by proteolytic enzyme(s) (BE)BE = [Σ(dj/IC50j)]/N,dj—the number of repeats of the j-th bioactive fragment released by selected enzyme(s) from the protein sequence; EC50j—the concentration of the j-th bioactive peptide corresponding to its half-maximal activity [μM]; IC50j—the concentration of the j-th bioactive peptide corresponding to its half-maximal inhibition [μM]; N—the number of amino acid residues in the protein chain
- Relative activity of fragments potentially released by proteolytic enzyme(s) (V)V = BE/B,BE—the activity of the fragments potentially released by the proteolytic enzyme(s); B—the potential biological activity of the protein fragments
- The concentration of bioactive peptides was determined by the formulaA—the bioactive function of peptides; —the concentration of bioactive peptides with function A (mg/100 g); n—the number of proteins; protein, —bioactive peptides of the i-th protein with function A; Nj—the number of concrete peptide; Mj —the molecular mass of the concrete peptide.
- The content of free amino acids was determined by calculating individual amino acids in the obtained digestive models by a single enzyme or a combination of enzymes using Expasy Peptide Cutter tools (http://expasy.org (accessed on 16 March 2022)).
2.5. Simulations of Digestion in the Gastrointestinal Tract
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Protein Profile and Physico-Chemical Composition of Milk Whey
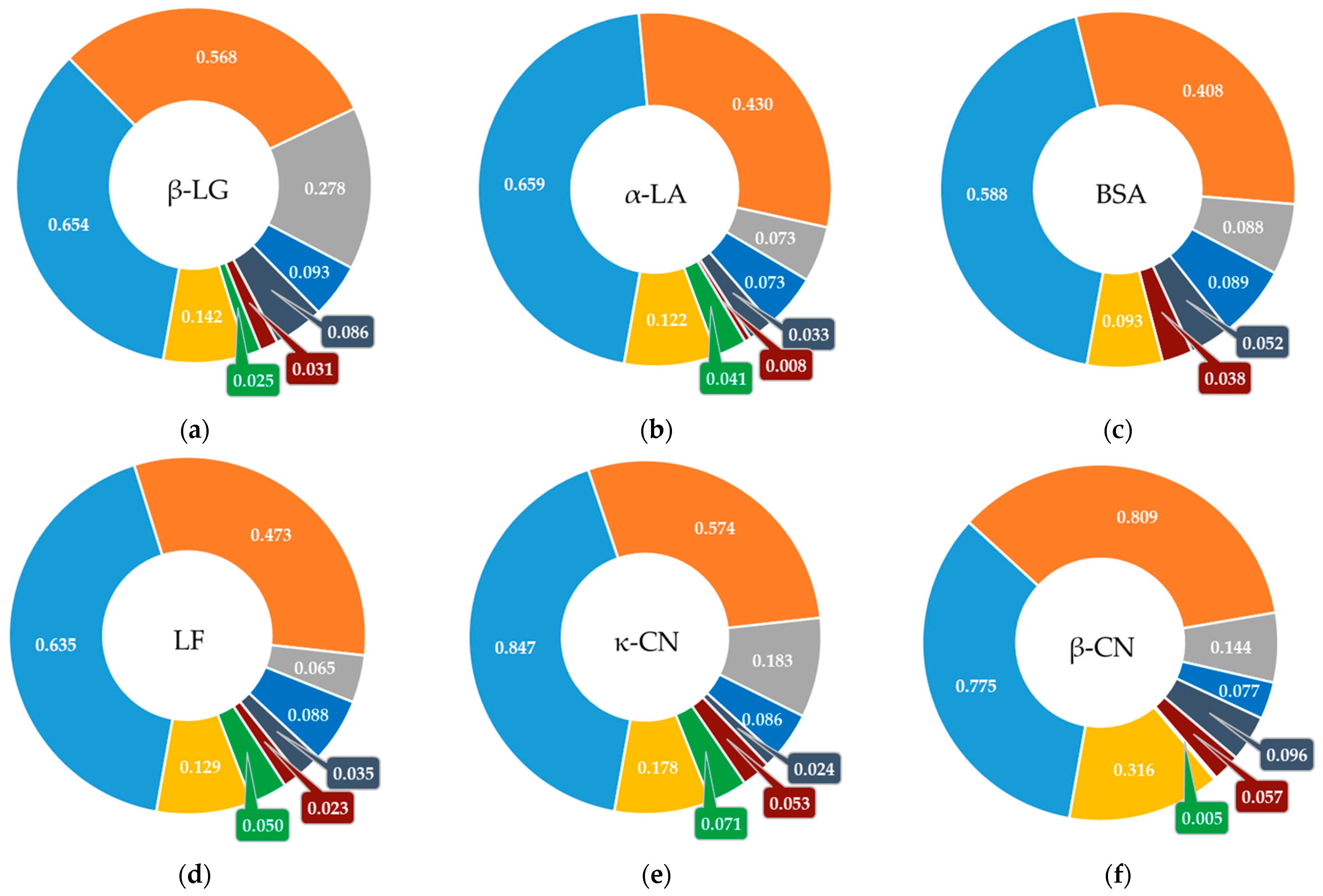
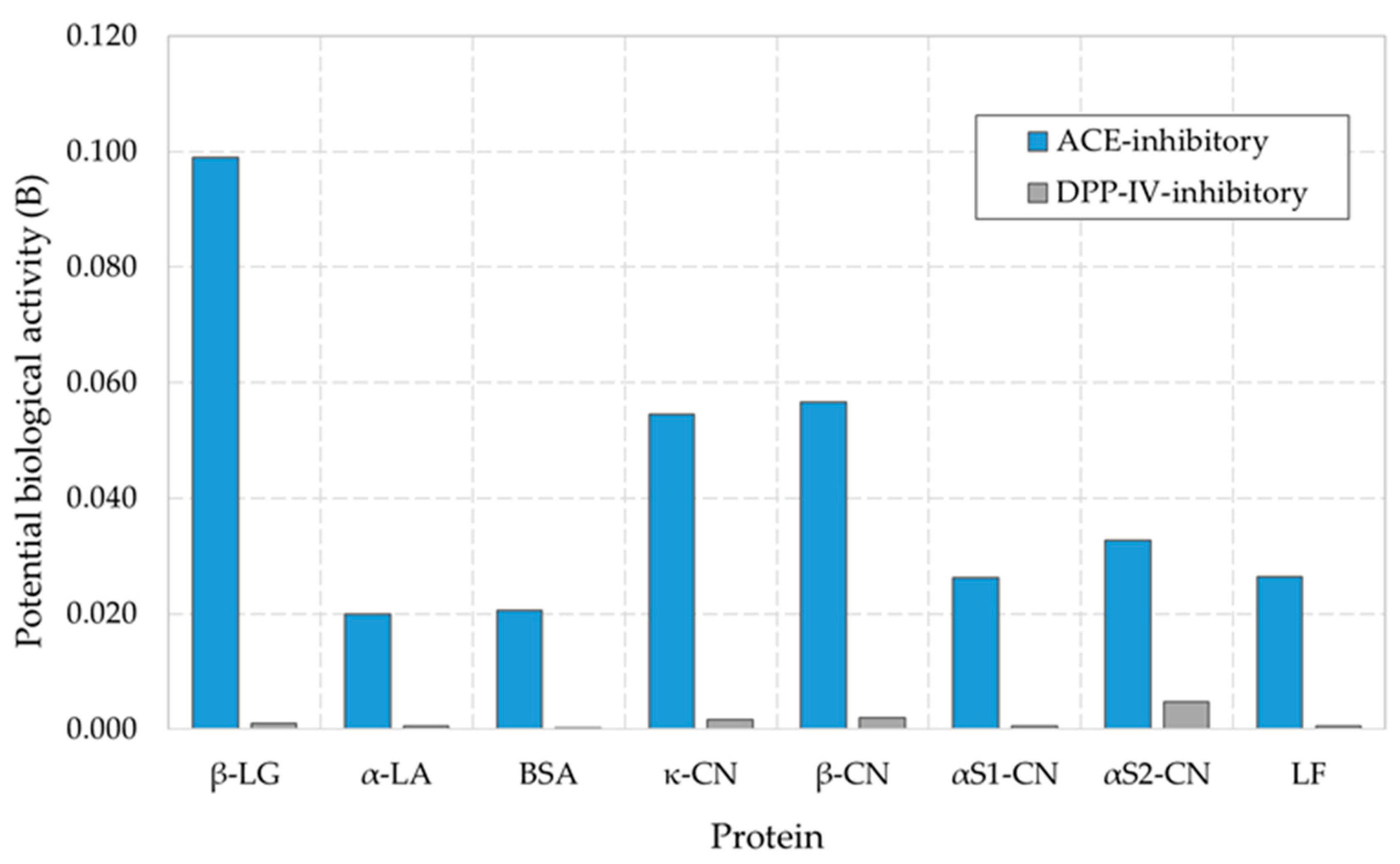
3.2. Screening Bioactive Sites in the Structure of Milk Whey Protein
3.3. Bioinformatic Modeling of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Milk Whey Proteins by Enzymatic Preparations
3.4. Bioinformatic Analysis of Products of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Milk Whey Proteins
3.5. Modeling (In Silico) of the Digestion of Enzymatic Hydrolysis Products from Milk Whey Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asunis, F.; De Gioannis, G.; Dessì, P.; Isipato, M.; Lens, P.N.L.; Muntoni, A.; Polettini, A.; Pomi, R.; Rossi, A.; Spiga, D. The dairy biorefinery: Integrating treatment processes for cheese whey valorisation. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 276, 111240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandona, E.; Blažić, M.; Režek Jambrak, A. Whey Utilization: Sustainable Uses and Environmental Approach. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 59, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, A.F.; Marnotes, N.G.; Rubio, O.D.; Garcia, A.C.; Pereira, C.D. Dairy By-Products: A Review on the Valorization of Whey and Second Cheese Whey. Foods 2021, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khramtsov, A.G.; Babenyshev, S.P.; Zhidkov, V.E.; Mamay, D.S.; Nurullo, M.; Mamay, A.V. Membrane purification of secondary milk raw materials: Intensification of processes. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 677, 032060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, T.M.M.M.; Rosa, D.; Comi, G.; Iacumin, L. Prospects for the use of whey for polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, H.M.; Jimenez-Flores, R.; Bleck, G.T.; Brown, E.M.; Butler, J.E.; Creamer, L.K.; Hick, C.L.; Hollar, C.M.; Ng-Kwai-Hang, K.F.; Swaisgood, H.E. Nomenclature of the Proteins of Cows’ Milk—Sixth Revision. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1641–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papademas, P.; Kotsaki, P. Technological utilization of whey towards sustainable exploitation. J. Adv. Dairy Res. 2019, 7, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, J.S.S.; Yan, S.; Pilli, S.; Kumar, L.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Cheese whey: A potential resource to transform into bioprotein, functional/nutritional proteins and bioactive peptides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Chand, R.; Kapila, S. Biofunctional Properties of Bioactive Peptides of Milk Origin. Food Rev. Int. 2008, 25, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, Z.; Cakir-Kiefer, C.; Roux, E.; Perrin, C.; Miclo, L.; Dary-Mourot, A. Strategies of producing bioactive peptides from milk proteins to functionalize fermented milk products. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, B.; Athira, S.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, R.; Sarkar, P. Bioactive Peptides from Whey Proteins. Whey Proteins Milk Med. 2019, 519–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, E.M.; Saavedra, L.; Ferranti, P. Bioactive Peptides Derived from Casein and Whey Proteins. Biotechnol. Lact. Acid Bact. 2010, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Ashaolu, T.J. Bioactivity and safety of whey peptides. LWT 2020, 134, 109935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Casas, D.E.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R.; Chávez-González, M.L.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C. Enzymatic hydrolysis and microbial fermentation: The most favorable biotechnological methods for the release of bioactive peptides. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worsztynowicz, P.; Białas, W.; Grajek, W. Integrated approach for obtaining bioactive peptides from whey proteins hydrolysed using a new proteolytic lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullius, A.; Goettert, M.I.; de Souza, C.F.V. Whey protein hydrolysates as a source of bioactive peptides for functional foods—Biotechnological facilitation of industrial scale-up. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 42, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchinin, A.G.; Bolshakova, E.I. Hybrid Strategy of Bioinformatics Modeling (in silico): Biologically Active Peptides of Milk Protein. Food Process. Tech. Technol. 2022, 52, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfatti, V.; Grigoletto, L.; Cecchinato, A.; Gallo, L.; Carnier, P. Validation of a new reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography method for separation and quantification of bovine milk protein genetic variants. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1195, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, M.; Gomes, D.; Pereira, C. Liquid Whey Protein Concentrates Produced by Ultrafiltration as Primary Raw Materials for Thermal Dairy Gels. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 55, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Database of Bioactive Peptides: Current Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Mooney, C.; Shields, D.C.; Fitzgerald, R.J. In silico approaches to predict the potential of milk protein-derived peptides as dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors. Peptides 2014, 57, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayd, T.; Dufour, C.; Chambon, C.; Buffière, C.; Remond, D.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Combined in vivo and in silico approaches for predicting the release of bioactive peptides from meat digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 249, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N.; Bhandari, B. Functional milk proteins: Production and utilization-whey-based ingredients. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Proteins: Applied Aspects; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1B, pp. 67–98. [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald, R.J.; Cermeño, M.; Khalesi, M.; Kleekayai, T.; Amigo-Benavent, M. Application of in silico approaches for the generation of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.; Chen, G.Q.; Freeman, B.; Suarez, F.; Freckleton, A.; Bathurst, K.; Kentish, S.E. Fouling and in-situ cleaning of ion-exchange membranes during the electrodialysis of fresh acid and sweet whey. J. Food Eng. 2018, 246, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, C.; Kleinschmidt, T. Synthesis of galactooligosaccharides using sweet and acid whey as a substrate. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 48, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persaud, D.R.; Barranco-Mendoza, A. Bovine serum albumin and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Is cow’s milk still a possible toxicological causative agent of diabetes? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkova, A.A.; Ryazantseva, K.A.; Agarkova, E.Y.; Kruchinin, A.G.; Tsentalovich, M.Y.; Fedorova, T.V. Rational design of enzyme compositions for the production of functional hydrolysates of cow milk whey proteins. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2017, 53, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazorra-Manzano, M.A.; Robles-Porchas, G.R.; González-Velázquez, D.A.; Torres-Llanez, M.J.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; García-Sifuentes, C.O.; González-Córdova, A.F.; Vallejo-Córdoba, B. Cheese Whey Fermentation by Its Native Microbiota: Proteolysis and Bioactive Peptides Release with ACE-Inhibitory Activity. Fermentation 2020, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Hernández Álvarez, A.J.; Maycock, J.; Murray, B.S.; Boesch, C. Comparison of alcalase- and pepsin-treated oilseed protein hydrolysates—Experimental validation of predicted antioxidant, antihypertensive and antidiabetic properties. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreira, R.L.; de Oliveira Afonso, W. Obtaining oligopeptides from whey: Use of subtilisin and pancreatin. Am. J. Food Technol. 2008, 3, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, H. Milk-derived bioactive peptides: From science to applications. J. Funct. Foods 2009, 1, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, A.P.F.; Bertolini, D.; Lopes, N.A.; Veras, F.F.; Gregory, G.; Brandelli, A. Characterization of nanoliposomes containing bioactive peptides obtained from sheep whey hydrolysates. LWT 2019, 101, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name of Parameter | CTW (AC) | CTW (A/RC) | CHW (RC) | CHW (A/RC) | CHW (TAC) | CPW (TCC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fat, % | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.14 ± 0.05 | 0.87 ± 0.05 | 0.74 ± 0.14 | 0.53 ± 0.17 | 0.11 ± 0.06 |
| Protein, % | 0.55 ± 0.05 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 0.92 ± 0.07 | 0.83 ± 0.09 | 0.30 ± 0.06 | 0.24 ± 0.02 |
| Casein, % | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.11 ± 0.03 |
| αS1-CN | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.04 ± 0.02 |
| αS2-CN | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| β-CN | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| κ-CN | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.01 |
| Whey protein, % | 0.51 ± 0.07 | 0.42 ± 0.04 | 0.84 ± 0.04 | 0.78 ± 0.06 | 0.15 ± 0.04 | 0.13 ± 0.02 |
| β-LG | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | 0.43 ± 0.04 | 0.45 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.02 |
| α-LA | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.03 |
| BSA | 0.021 ± 0.003 | 0.033 ± 0.005 | 0.027 ± 0.004 | 0.038 ± 0.005 | 0.007 ± 0.002 | 0.005 ± 0.001 |
| LF | 0.0026 ± 0.0002 | 0.0027 ± 0.0006 | 0.0016 ± 0.0002 | 0.0028 ± 0.0003 | 0.0010 ± 0.0005 | 0.0009 ± 0.0004 |
| Lactose, % | 3.71 ± 0.19 | 4.04 ± 0.18 | 5.03 ± 0.17 | 4.46 ± 0.15 | 5.21 ± 0.18 | 5.28 ± 0.12 |
| Ash, % | 0.67 ± 0.04 | 0.61 ± 0.02 | 0.51 ± 0.02 | 0.53 ± 0.04 | 0.64 ± 0.04 | 0.57 ± 0.05 |
| Calcium, mg/100 g | 90.98 ± 2.72 | 78.15 ± 2.92 | 54.32 ± 3.44 | 66.31 ± 2.36 | 85.36 ± 3.31 | 63.05 ± 2.91 |
| Total solids, % | 6.13 ± 0.16 | 6.19 ± 0.21 | 7.34 ± 0.15 | 6.69 ± 0.19 | 7.04 ± 0.22 | 6.65 ± 0.21 |
| Titratable acidity, °T | 66 ± 3 | 63 ± 2 | 17.1 ± 0.2 | 29 ± 2 | 47 ± 3 | 15 ± 2 |
| pH | 4.55 ± 0.05 | 5.14 ± 0.05 | 6.39 ± 0.05 | 5.81 ± 0.02 | 5.45 ± 0.06 | 6.82 ± 0.04 |
| Whey | β-LG | α-LA | BSA | LF | κ-CN | β-CN | αS1-CN | αS2-CN | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHt | FAA | DHt | FAA | DHt | FAA | DHt | FAA | DHt | FAA | DHt | FAA | DHt | FAA | DHt | FAA | |
| Pepsin (pH > 2) EC 3.4.23.1 | 73.3 | 86 | 68.3 | 64 | 68.5 | 288 | 66.9 | 229 | 61.2 | 66 | 63.1 | 81 | 67.7 | 96 | 71.2 | 110 |
| Proteinase P1 EC 3.4.21.96 | 49.1 | 51 | 39.7 | 31 | 41.7 | 157 | 43.8 | 135 | 54.1 | 68 | 67.3 | 116 | 50.0 | 67 | 45.8 | 58 |
| Chymotrypsin EC 3.4.21.2 | 42.4 | 33 | 34.9 | 20 | 34.7 | 74 | 32.9 | 67 | 43.6 | 33 | 52.3 | 55 | 47.6 | 50 | 44.3 | 50 |
| Pancreatic elastase EC 3.4.21.36 | 47.3 | 38 | 42.1 | 26 | 42.3 | 130 | 49.7 | 135 | 48.3 | 46 | 41.6 | 35 | 43.1 | 38 | 42.9 | 45 |
| Ficine EC 3.4.22.3 | 37.0 | 25 | 38.9 | 23 | 41.8 | 119 | 43.8 | 110 | 30.8 | 22 | 35.5 | 28 | 41.7 | 43 | 38.7 | 43 |
| Stem bromelain EC 3.4.22.32 | 43.6 | 36 | 36.5 | 21 | 45.0 | 143 | 52.5 | 148 | 41.3 | 39 | 41.1 | 38 | 39.7 | 36 | 37.7 | 33 |
| Proteinase K EC 3.4.21.67 | 37.6 | 23 | 32.5 | 13 | 32.0 | 68 | 32.7 | 63 | 38.4 | 26 | 49.1 | 63 | 39.2 | 37 | 33.5 | 27 |
| Thermolysin EC 3.4.24.27 | 38.2 | 28 | 30.2 | 9 | 34.2 | 82 | 34.1 | 70 | 33.7 | 24 | 32.2 | 22 | 32.3 | 23 | 30.2 | 24 |
| Papain EC 3.4.22.2 | 36.4 | 16 | 28.6 | 13 | 34.8 | 66 | 38.5 | 64 | 34.9 | 20 | 31.3 | 21 | 31.4 | 29 | 29.7 | 15 |
| Subtilisin EC 3.4.21.62 | 27.3 | 16 | 28.6 | 8 | 26.8 | 46 | 30.2 | 41 | 26.2 | 13 | 32.2 | 25 | 29.4 | 18 | 29.3 | 15 |
| Chymotrypsin EC 3.4.21.1 | 26.1 | 12 | 28.6 | 10 | 24.2 | 35 | 22.7 | 31 | 20.1 | 9 | 24.3 | 13 | 26.5 | 16 | 25.0 | 15 |
| Cocolysin EC 3.4.24.30 | 32.7 | 18 | 25.4 | 7 | 28.2 | 56 | 27.2 | 44 | 27.3 | 14 | 23.4 | 11 | 27.0 | 16 | 23.6 | 15 |
| Chimaza EC 3.4.21.39 | 19.4 | 8 | 19.1 | 6 | 18.3 | 23 | 17.4 | 18 | 12.8 | 4 | 16.8 | 6 | 17.6 | 13 | 15.1 | 7 |
| Trypsin EC 3.4.21.4 | 10.9 | 2 | 10.32 | 2 | 13.7 | 7 | 13.4 | 6 | 8.1 | 1 | 7.2 | 2 | 9.8 | 3 | 14.2 | 6 |
| V-8 protease (pH = 7.8) EC 3.4.21.19 | 15.8 | 4 | 15.9 | 6 | 16.5 | 20 | 9.9 | 4 | 9.3 | 2 | 10.7 | 6 | 15.7 | 7 | 13.2 | 9 |
| Pancreatic elastase II EC 3.4.21.71 | 18.2 | 5 | 13.5 | 3 | 15.3 | 13 | 13.0 | 9 | 8.1 | 3 | 17.3 | 6 | 14.7 | 6 | 10.4 | 1 |
| Whey | Bioactivity | β-LG | α-LA | BSA | LF | κ-CN | β-CN | αS1-CN | αS2-CN | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | V | W | V | W | V | W | V | W | V | W | V | W | V | W | V | ||
| Pepsin (pH > 2) EC 3.4.23.1 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.111 | 0.019 | 0.170 | 0.164 | 0.172 | 0.094 | 0.106 | 0.020 | 0.102 | 0.089 | 0.144 | 0.159 | 0.148 | 0.136 | 0.094 | 0.163 |
| Antioxidative | 0.047 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.131 | - | 0.047 | - | 0.154 | - | 0.059 | - | 0.097 | - | |
| Proteinase P1 EC 3.4.21.96 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.067 | 0.002 | - | - | 0.043 | 0.027 | 0.036 | 0.009 | 0.070 | 0.010 | 0.077 | 0.087 | 0.055 | 0.114 | 0.062 | 0.006 |
| Antioxidative | 0.024 | - | 0.111 | - | 0.036 | - | - | - | 0.023 | - | 0.077 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.032 | - | |
| Chymotrypsin EC 3.4.21.2 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.089 | 0.005 | 0.076 | 0.020 | 0.108 | 0.013 | 0.170 | 0.026 | 0.109 | 0.047 | 0.077 | 0.029 | 0.098 | 0.024 | 0.094 | 0.105 |
| Antioxidative | 0.143 | - | - | - | 0.072 | - | 0.131 | - | 0.070 | - | 0.116 | - | 0.059 | - | 0.129 | - | |
| Pancreatic elastase EC 3.4.21.36 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.089 | 0.004 | 0.076 | 0.140 | 0.065 | 0.022 | 0.057 | 0.001 | 0.055 | 0.008 | 0.048 | 0.018 | 0.093 | 0.094 | 0.098 | 0.038 |
| Antioxidative | 0.072 | - | - | - | 0.036 | - | 0.044 | - | 0.070 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.079 | - | 0.097 | - | |
| Ficine EC 3.4.22.3 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.067 | 0.012 | 0.094 | 0.014 | 0.043 | 0.010 | 0.036 | 0.020 | 0.047 | 0.011 | 0.096 | 0.026 | 0.114 | 0.230 | 0.067 | 0.055 |
| Antioxidative | 0.047 | - | 0.221 | - | - | - | 0.087 | - | 0.047 | - | - | - | 0.020 | - | 0.064 | - | |
| Stem bromelain EC 3.4.22.32 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.056 | 0.003 | 0.038 | 0.00032 | 0.043 | 0.001 | 0.050 | 0.003 | 0.047 | 0.004 | 0.067 | 0.008 | 0.098 | 0.056 | 0.107 | 0.047 |
| Antioxidative | 0.047 | - | 0.111 | - | - | - | 0.087 | - | 0.047 | - | - | - | 0.118 | - | 0.032 | - | |
| Proteinase K EC 3.4.21.67 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.078 | 0.004 | 0.076 | 0.010 | 0.097 | 0.038 | 0.064 | 0.008 | 0.086 | 0.016 | 0.067 | 0.071 | 0.093 | 0.150 | 0.080 | 0.011 |
| Antioxidative | 0.047 | - | - | - | 0.036 | - | 0.044 | - | 0.093 | - | 0.077 | - | 0.079 | - | 0.161 | - | |
| Thermolysin EC 3.4.24.27 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.067 | 0.002 | 0.094 | 0.038 | 0.075 | 0.002 | 0.099 | 0.157 | 0.070 | 0.027 | 0.096 | 0.016 | 0.059 | 0.019 | 0.072 | 0.170 |
| Antioxidative | 0.047 | - | 0.111 | - | - | - | 0.087 | - | 0.047 | - | 0.116 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.032 | - | |
| Papain EC 3.4.22.2 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.044 | 0.003 | 0.057 | 0.00036 | 0.075 | 0.056 | 0.050 | 0.001 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.087 | 0.068 | 0.098 | 0.131 | 0.130 | 0.047 |
| Antioxidative | 0.024 | - | 0.221 | - | 0.036 | - | 0.087 | - | 0.023 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.059 | - | 0.064 | - | |
| Subtilisin EC 3.4.21.62 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.033 | 0.016 | 0.076 | 0.037 | 0.032 | 0.014 | 0.036 | 0.014 | 0.055 | 0.034 | 0.058 | 0.050 | 0.076 | 0.064 | 0.076 | 0.145 |
| Antioxidative | 0.047 | - | - | - | 0.036 | - | 0.087 | - | 0.093 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.020 | - | 0.193 | - | |
| Chymotrypsin EC 3.4.21.1 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.022 | 0.001 | 0.057 | 0.00017 | 0.054 | 0.008 | 0.021 | 0.013 | 0.047 | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.00006 | 0.047 | 0.052 | 0.040 | 0.067 |
| Antioxidative | 0.024 | - | 0.111 | - | - | - | 0.044 | - | 0.116 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.161 | - | |
| Cocolysin EC 3.4.24.30 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.067 | 0.001 | 0.057 | 0.038 | 0.042 | 0.120 | 0.043 | 0.021 | 0.055 | 0.027 | 0.077 | 0.002 | 0.042 | 0.120 | 0.072 | 0.086 |
| Antioxidative | 0.047 | - | 0.111 | - | - | - | 0.044 | - | 0.047 | - | 0.116 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.032 | - | |
| Chimaza EC 3.4.21.39 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.022 | 0.001 | 0.038 | 0.004 | 0.043 | 0.011 | 0.028 | 0.013 | 0.039 | 0.013 | 0.019 | 0.003 | 0.034 | 0.044 | 0.031 | 0.058 |
| Antioxidative | 0.024 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.087 | - | 0.093 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.161 | - | |
| Trypsin EC 3.4.21.4 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.056 | 0.003 | 0.019 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.007 | 0.028 | 0.007 | 0.031 | 0.023 | 0.039 | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.006 | 0.022 | 0.002 |
| Antioxidative | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.044 | - | 0.023 | - | 0.039 | - | 0.059 | - | - | - | |
| V-8 protease (pH = 7.8) EC 3.4.21.19 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.011 | 0.000007 | 0.019 | 0.007 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.017 | 0.00013 | 0.004 | 0.000015 |
| Antioxidative | - | - | - | - | 0.036 | - | 0.036 | - | 0.023 | - | - | - | 0.039 | - | - | - | |
| Pancreatic elastase II EC 3.4.21.71 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.022 | 0.001 | 0.019 | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.001 | 0.028 | 0.012 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 0.026 | 0.013 | 0.022 | 0.011 |
| Antioxidative | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.044 | - | 0.047 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.032 | - | |
| Protein | DHt | FAA | Activity | AE | W | BE | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-LG | 52.12 | 47 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.072 | 0.133 | 0.0022 | 0.023 |
| Antioxidative | 0.036 | 0.143 | - | - | |||
| α-LA | 46.83 | 25 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.063 | 0.151 | 0.0035 | 0.146 |
| Antioxidative | - | - | - | - | |||
| BSA | 46.83 | 125 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.072 | 0.182 | 0.0029 | 0.143 |
| Antioxidative | 0.007 | 0.079 | - | - | |||
| LF | 47.26 | 113 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.071 | 0.156 | 0.0049 | 0.194 |
| Antioxidative | 0.014 | 0.226 | - | - | |||
| κ-CN | 56.98 | 55 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.087 | 0.161 | 0.0011 | 0.021 |
| Antioxidative | 0.017 | 0.107 | - | - | |||
| β-CN | 68.69 | 110 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.126 | 0.192 | 0.0016 | 0.031 |
| Antioxidative | 0.009 | 0.087 | - | - | |||
| αS1-CN | 62.25 | 81 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.102 | 0.164 | 0.0039 | 0.151 |
| Antioxidative | 0.015 | 0.070 | - | - | |||
| αS2-CN | 58.96 | 74 | ACE-inhibitory | 0.066 | 0.135 | 0.0025 | 0.080 |
| Antioxidative | 0.019 | 0.154 | - | - |
| Peptide | Bioactivity | Protein Precursor | Location | Bitterness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 67–68 | - |
| ACQ | Antioxidative | β-LG | 120–122 | - |
| AE | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 174–175; 319–320 | - |
| LF | 424–425 | - | ||
| αS1-CN | 64–65; 118–119 | - | ||
| β-LG | 113–114 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 64–65 | - | ||
| AF | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | β-CN | 195–196 | - |
| AI | ACE inhibitor | α-LA | 40–41 | - |
| AIP | ACE inhibitor | k-CN | 109–111 | - |
| AL | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 417–418; 505–506 | - |
| LF | 42–43; 314–315; 327–328 | - | ||
| β-LG | 136–137 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 179–180 | - | ||
| AP | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 154–155 | - |
| LF | 1–2 | - | ||
| β-CN | 105–106 | - | ||
| β-LG | 37–38 | - | ||
| AS | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 196–197 | - |
| LF | 159–160 | - | ||
| AY | Antioxidative; ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 169–170 | - |
| αS1-CN | 147–148 | - | ||
| CAQ | Antioxidative | β-LG | 68–70 | - |
| CF | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 103–104; 502–503 | - |
| CHI | Antioxidative | β-LG | 164–166 | - |
| DKIHP | ACE inhibitor | β-CN | 47–51 | - |
| DP | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 120–121 | - |
| DQ | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 109–110 | - |
| α-LA | 118–119 | - | ||
| αS1-CN | 51–52 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 112–113 | - | ||
| DY | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 464–465 | bitter |
| GA | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 151–152 | - |
| GE | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 15–16; 212–213; 410–411 | bitter |
| k-CN | 132–133 | bitter | ||
| LF | 181–182 | bitter | ||
| β-CN | 10–11 | bitter | ||
| β-LG | 66–67 | bitter | ||
| GF | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 413–414 | bitter |
| LF | 316–317 | bitter | ||
| GG | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | α-LA | 19–20 | - |
| GK | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 444–445 | - |
| GL | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 39–40 | bitter |
| LF | 459–460; 486–487 | bitter | ||
| α-LA | 51–52 | bitter | ||
| αS1-CN | 10–11 | bitter | ||
| GP | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 589–590 | bitter |
| β-CN | 66–67; 205–206 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 104–105 | bitter | ||
| GQ | ACE inhibitor | LF | 302–303; 378–379 | - |
| GS | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 337–338 | - |
| LF | 298–299; 331–332 | - | ||
| GY | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 197–198; 446–447 | bitter |
| α-LA | 35–36 | bitter | ||
| αS1-CN | 95–96 | bitter | ||
| HA | DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 261–262 | - |
| HE | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 477–478 | - |
| HF | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 18–19 | - |
| HIRL | ACE inhibitor | β-LG | 150–153 | - |
| HL | Antioxidative; ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 104–105 | - |
| β-CN | 138–139 | - | ||
| HP | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 102–103 | - |
| HS | DPP-IV inhibitor | α-LA | 70–71 | - |
| IAF | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 25–27 | - |
| IG | DPP-IV inhibitor | αS1-CN | 140–141 | - |
| II | DPP-IV inhibitor | β-CN | 213–214 | - |
| IL | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 469–470 | bitter |
| k-CN | 75–76 | bitter | ||
| β-LG | 56–57 | bitter | ||
| IN | DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 51–52; 163–164 | bitter |
| α-LA | 55–56 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 87–88 | - | ||
| IP | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 26–27; 121–122 | bitter |
| LF | 483–484 | bitter | ||
| β-CN | 68–69; 76–77 | bitter | ||
| IQ | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 208–209 | bitter |
| k-CN | 28–29 | bitter | ||
| β-CN | 193–194 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 200–201 | - | ||
| IW | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 275–276 | - |
| IY | Antioxidative; ACE inhibitor | LF | 83–84; 411–412 | - |
| KA | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | β-CN | 180–181 | - |
| KCL | Antioxidative | LF | 203–205 | - |
| KE | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 283–284 | - |
| LF | 251–252 | - | ||
| αS1-CN | 85–86; 128–129; 136–138 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 32–33 | - | ||
| KF | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 210–211; 227–228 | bitter |
| LF | 285–286 | bitter | ||
| β-CN | 32–33 | bitter | ||
| β-LG | 139–140 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 93–94; 177–178 | bitter | ||
| KKY | Antioxidative | β-LG | 102–104 | - |
| KL | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 116–117; 281–282; 408–409; 520–521; 591–592 | - |
| KL | ACE inhibitor | LF | 75–76 | - |
| α-LA | 116–117; 126–127 | - | ||
| KP | Antioxidative; ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 118–119 | bitter |
| k-CN | 46–47 | bitter | ||
| β-LG | 47–48 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 197–198 | bitter | ||
| KS | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 66–67; 293–294 | - |
| LF | 290–291 | - | ||
| KT | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 562–563 | - |
| KY | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 163–164 | - |
| β-CN | 115–116 | - | ||
| RF | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 16–17 | - |
| αS1-CN | 22–23 | - | ||
| RL | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 202–203; 357–358; 472–473 | bitter |
| αS1-CN | 102–103; 121–123 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 164–165 | bitter | ||
| RM | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 458–459 | - |
| LF | 25–26 | - | ||
| RN | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 100–101 | - |
| RP | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 77–78; 137–138; 442–443 | - |
| αS1-CN | 1–2 | - | ||
| RY | Antioxidative; ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 34–35 | - |
| LF | 333–334 | - | ||
| αS1-CN | 92–93 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 174–175 | - | ||
| TA | DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 171–172 | - |
| TD | DPP-IV inhibitor | β-CN | 132–133 | - |
| TE | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 47–48 | - |
| LF | 143–144; 444–445 | - | ||
| α-LA | 48–49 | - | ||
| αS1-CN | 49–50 | - | ||
| β-CN | 41–42 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 148–149; 158–159 | - | ||
| TF | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 523–524 | - |
| αS2-CN | 38–39 | - | ||
| TK | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 244–245 | - |
| TL | DPP-IV inhibitor | β-CN | 130–131 | - |
| αS2-CN | 126–127 | - | ||
| TM | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 189–190 | - |
| β-LG | 6–7 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 3–4 | - | ||
| TP | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 431–432; 507–508 | - |
| k-CN | 137–138 | - | ||
| β-CN | 82–83 | - | ||
| β-LG | 49–50 | - | ||
| TQ | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 596–597 | - |
| β-CN | 55–56; 80–81 | - | ||
| β-LG | 158–159 | - | ||
| TR | DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 353–354 | - |
| TS | DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 135–136 | - |
| αS2-CN | 134–135 | - | ||
| TT | DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 218–219 | - |
| TW | Antioxidative; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 461–462 | - |
| TY | Antioxidative; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 85–86; 511–512 | - |
| αS2-CN | 19–20 | - | ||
| VA | DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 97–98; 450–451 | - |
| VAF | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 569–571 | - |
| LF | 212–214 | - | ||
| VAGTW | ACE inhibitor | β-LG | 15–19 | - |
| VAP | DPP-IV inhibitor | αS1-CN | 25–27 | - |
| VE | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 234–235; 300–301; 437–438; 545–546; 587–588 | bitter |
| k-CN | 143–144 | bitter | ||
| αS1-CN | 78–79 | bitter | ||
| β-CN | 13–14; 118–119; 134–135 | bitter | ||
| β-LG | 43–44 | bitter | ||
| VF | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 167–168; 384–385 | bitter |
| LF | 66–67; 220–221 | bitter | ||
| α-LA | 8–9 | bitter | ||
| αS1-CN | 31–32 | bitter | ||
| β-LG | 83–84 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 150–151 | bitter | ||
| VGP | ACE inhibitor | LF | 360–362 | - |
| VKL | Antioxidative | BSA | 40–42 | - |
| VL | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 23–24; 194–195; 354–355; 475–476 | bitter |
| k-CN | 31–32; 80–81 | bitter | ||
| LF | 394–395; 396–397; 422–423; 440–441 | bitter | ||
| αS1-CN | 15–16 | bitter | ||
| β-CN | 166–167; 174–175; 203–204 | bitter | ||
| β-LG | 94–95; 96–97 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 107–108 | bitter | ||
| VM | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 564–565 | - |
| β-CN | 94–95; 159–160 | - | ||
| VN | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 43–44; 497–498 | - |
| LF | 489–490 | - | ||
| αS1-CN | 37–38 142–143 | - | ||
| VP | ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 426–427; 513–514 | - |
| k-CN | 85–86 | - | ||
| LF | 162–163; 258–259; 420–421 | - | ||
| αS1-CN | 74–75; 88–89; 108–109; 114–115; 171–172 | - | ||
| β-CN | 8–9; 86–87; 177–178; 182–183 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 119–120 | - | ||
| VQ | DPP-IV inhibitor | k-CN | 166–167 | - |
| α-LA | 42–43 | - | ||
| VRGP | ACE inhibitor | β-CN | 207–210 | - |
| VRY | ACE inhibitor | BSA | 420–422 | - |
| αS2-CN | 210–212 | - | ||
| VS | DPP-IV inhibitor | BSA | 352–353; 429–430; 439–440; 482–483; 594–595 | - |
| α-LA | 21–22 | - | ||
| β-CN | 97–98 | - | ||
| αS2-CN | 7–8 | - | ||
| VW | Antioxidative; ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | LF | 356–357 | - |
| VY | Antioxidative; ACE inhibitor; DPP-IV inhibitor | β-CN | 59–60 | bitter |
| β-LG | 41–42 | bitter | ||
| αS2-CN | 189–190 | bitter |
| Whey | Content of Bioactive Peptides in Hydrolysates of Different Types of Whey (in Terms of Standardized Whey with a Mass Fraction of Protein 1%), mg/100 g | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidative | ACE-Inhibitory | DPP-IV- Inhibitory | Bitter | Toxin | Allergen Epitopes | |
| CTW (AC) | 28.29 (50.08) | 76.54 (136.38) | 86.68 (154.04) | 47.20 (84.32) | 1.26 (1.89) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CTW (A/RC) | 23.42 (53.75) | 61.54 (141.53) | 71.40 (164.29) | 38.62 (88.80) | 1.89 (4.41) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CHW (RC) | 41.29 (45.97) | 115.24 (127.42) | 130.90 (145.10) | 71.94 (79.25) | 1.26 (1.89) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CHW (A/RC) | 43.23 (51.95) | 108.26 (130.05) | 124.14 (149.25) | 68.91 (82.75) | 1.89 (2.52) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CHW (TAC) | 7.43 (25.24) | 50.26 (171.30) | 55.05 (188.46) | 24.00 (100.52) | 0.34 (1.26) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CPW (TCC) | 6.79 (29.02) | 41.10 (177.04) | 45.53 (197.07) | 29.72 (103.09) | 0.35 (1.26) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| Peptide | Protein Precursor (Location) | Bioactivity | IC50, µM | Sensory Characteristics | Allergenicity | Toxicity | Hydropathicity | PI | Molecular Mass, Da |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF | BSA (516–517) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 2.30 | 5.88 | 236.26 |
| CF | BSA (384–385) | ACE inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 2.65 | 5.85 | 285.18 |
| GL | BSA (21–22) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 1.70 | 5.80 | 188.21 |
| DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | - | - | ||||||
| GR | LF (113–114) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | −2.45 | 10.11 | 231.24 |
| IA | β-LG (74–75) BSA (25–26; 297–298; 7–8;145–146) LF (49–50) κ-CN (22–23; 129–130) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 3.15 | 5.88 | 202.24 |
| IE | BSA (187–188) κ-CN (157–158) β-CN (30–31) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 0.50 | 4.00 | 260.31 |
| IG | αS1-CN (44–45; 140–141; 192–193) αS2-CN (54–55) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 2.05 | 5.88 | 188.21 |
| IH | β-CN (49–50) αS1-CN (131–132) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 0.65 | 7.10 | 268.30 |
| DPP-III inhibitor | NA | - | - | ||||||
| IL | β-LG (56–57) α-LA (97–98) BSA (469–470) LF (135–136) κ-CN (75–76) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 4.15 | 5.88 | 244.32 |
| IM | α-LA (91–92) | ACE inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 3.20 | 5.88 | 262.39 |
| IN | α-LA (55–56; 103–104) κ-CN (51–52; 163–164; 126–127) β-CN (26–27) αS2-CN (87–88) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 0.50 | 5.88 | 245.26 |
| IP | β-LG (80–81) BSA (305–306) LF (131–132; 320–321;483–484) κ-CN (110–111; 26–27; 121–122) β-CN (68–69; 76–77) αS1-CN (188–189) αS2-CN (207–208) | ACE inhibitor | 130.0 | bitter | - | - | 1.45 | 5.88 | 228.28 |
| DPP-IV inhibitor | 149.6 | ||||||||
| IQ | β-LG (12–13) BSA (208–209) κ-CN (28–29) β-CN (193–194) αS1-CN (83–84) αS2-CN (200–201) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 0.50 | 5.88 | 259.29 |
| IR | β-LG (151–152) LF (46–47) κ-CN (9–10) | ACE inhibitor | 695.0 | - | - | - | 0.00 | 10.11 | 287.35 |
| IW | α-LA (59–60) LF (275–276) | ACE inhibitor | 0.7 | bitter | - | - | 1.80 | 5.88 | 317.37 |
| IY | LF (83–84; 411–412) | ACE inhibitor | 2.1 | - | - | - | 1.60 | 5.88 | 294.33 |
| VA | β-LG (15–16) BSA (221–222; 54–55; 79–80; 569–570) LF (79–80; 97–98; 153–154; 212–213; 264–265; 450–451) κ-CN (48–49; 147–148) αS2-CN (66–67) | DPP-IV inhibitor | 168.2 | bitter | - | - | 3.00 | 5.88 | 188.21 |
| VD | β-LG (132–133) BSA (392–392; 572–573) LF (245–246; 268–269; 324–325; 475–476) αS2-CN (75–76; 143–144) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | umami, bitter, salty | - | - | 0.35 | 3.80 | 232.22 |
| VE | αS1-CN (78–79) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 0.35 | 4.00 | 246.25 |
| VF | β-LG (83–84) α-LA (8–9) BSA (167–168; 384–385) LF (66–67; 220–221) αS1-CN (31–32) αS2-CN (150–151) | ACE inhibitor | NA | bitter | - | - | 3.50 | 5.88 | 264.31 |
| VG | α-LA(101–102) BSA (446–447) LF (360–361) | ACE inhibitor | NA | umami, bitter | - | - | 1.90 | 5.88 | 174.19 |
| VH | BSA (246–247) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 0.50 | 7.10 | 254.28 |
| VK | α-LA (94–95) BSA (40–41) LF (215–216; 453–454;100–101) β-CN (100–101) αS2-CN (114–115) | ACE inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 0.15 | 9.11 | 245.31 |
| VL | β-LG (94–95; 96–97) BSA (23–24; 194–195; 354–355; 475–476) LF (394–395; 396–397; 422–423; 440–441) κ-CN (31–32; 80–81) β-CN (166–167; 174–175; 203–204) αS1-CN (15–16) αS2-CN (107–108) | DPP-IV inhibitor | 74.0 | bitter | - | - | 4.00 | 5.88 | 230.29 |
| VM | BSA (564–565) β-CN (94–95; 159–160) | ACE inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 3.05 | 5.88 | 248.33 |
| DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | ||||||||
| VN | BSA (43–44; 497–498] LF (489–490) αS1-CN (37–38; 142–143) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 0.35 | 5.88 | 231.24 |
| VP | BSA (426–427; 513–514) LF (162–163; 258–259; 420–421) κ-CN (85–86) β-CN (8–9; 86–87; 177–178; 182–183) αS1-CN (74–75; 88–89; 108–109; 114–115; 171–172) αS2-CN (119–120) | ACE inhibitor | 420.0 | sour | - | - | 1.30 | 5.88 | 214.25 |
| DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | ||||||||
| VQ | α-LA (42–43) κ-CN (85–86) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 0.35 | 5.88 | 245.26 |
| VR | β-LG (127–128) BSA (420–421) LF (6–7; 37–38) κ-CN (69–70) β-CN (207–208) αS2-CN (44–45; 210–211) | ACE inhibitor | 52.8 | salty | - | - | −0.15 | 10.11 | 273.32 |
| DPP-IV inhibitor | 826.1 | ||||||||
| VS | α-LA (21–22) BSA (352–353; 429–430; 439–440; 82–483; 594–595) β-CN (97–98) αS2-CN (7–8) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 1.70 | 5.88 | 204.21 |
| VT | β-LG (3–4) BSA (240–241; 486–487; 236–237) LF (57–58; 381–382) κ-CN (168–169) | DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 1.75 | 5.88 | 218.24 |
| VW | LF (356–357) | ACE inhibitor | NA | - | - | - | 1.65 | 5.88 | 303.34 |
| DPP-IV inhibitor | NA | ||||||||
| VY | β-LG (41–42) β-CN (59–60) αS2-CN (189–190) | ACE inhibitor | 7.1 | bitter | - | - | 1.45 | 5.88 | 280.13 |
| Whey | Content of Bioactive Peptides in Hydrolysates of Different Types of Whey (in Terms of Standardized Whey with a Mass Fraction of Protein 1%), mg/100 g | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidative | ACE-Inhibitory | DPP-IV- Inhibitory | Bitter | Toxin | Allergen Epitopes | |
| CTW (AC) | 0.00 (0.00) | 42.34 (75.40) | 44.92 (79.95) | 49.47 (88.16) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CTW (A/RC) | 0.00 (0.00) | 34.82 (80.07) | 38.29 (88.14) | 41.99 (96.53) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CHW (RC) | 0.00 (0.00) | 64.52 (71.18) | 68.60 (75.80) | 74.10 (81.98) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CHW (A/RC) | 0.00 (0.00) | 61.80 (74.04) | 66.99 (80.44) | 75.95 (91.40) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CHW (TAC) | 0.00 (0.00) | 25.46 (86.08) | 29.22 (99.35) | 24.64 (83.54) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
| CPW (TCC) | 0.00 (0.00) | 21.80 (93.15) | 25.11 (108.04) | 20.55 (88.52) | 0.00 (0.00) | 0.00 (0.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kruchinin, A.G.; Bolshakova, E.I.; Barkovskaya, I.A. Bioinformatic Modeling (In Silico) of Obtaining Bioactive Peptides from the Protein Matrix of Various Types of Milk Whey. Fermentation 2023, 9, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040380
Kruchinin AG, Bolshakova EI, Barkovskaya IA. Bioinformatic Modeling (In Silico) of Obtaining Bioactive Peptides from the Protein Matrix of Various Types of Milk Whey. Fermentation. 2023; 9(4):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040380
Chicago/Turabian StyleKruchinin, Aleksandr G., Ekaterina I. Bolshakova, and Irina A. Barkovskaya. 2023. "Bioinformatic Modeling (In Silico) of Obtaining Bioactive Peptides from the Protein Matrix of Various Types of Milk Whey" Fermentation 9, no. 4: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040380
APA StyleKruchinin, A. G., Bolshakova, E. I., & Barkovskaya, I. A. (2023). Bioinformatic Modeling (In Silico) of Obtaining Bioactive Peptides from the Protein Matrix of Various Types of Milk Whey. Fermentation, 9(4), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040380





