Valorisation through Lactic Fermentation of Industrial Wastewaters from a Bean Blanching Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain and Feedstock
2.2. Fermentation Apparatus
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Bacterial Count and Organic Acid Determination
2.4.2. Total Protein Evaluation
2.4.3. Total Starch and Glucose Estimation
2.4.4. Total Polyphenol and Flavonoid Determination
2.4.5. Total Saponin Determination
2.4.6. Antioxidant Activity
2.4.7. Foaming Capacity (FC) and Foaming Stability (FS) Estimation
2.4.8. Emulsifying Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsifying Stability Index (ESI) Determination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fermentation Results
3.2. Functional Characterisation of Fermented Blanching Water
3.3. Economic Considerations and Challenges
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. Global Food Losses and Food Waste. Extent, Causes, and Prevention; Food and Agricultural Organisation of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lobova, S.V.; Tyryshkin, V.V. Is It Possible to Change to a Circular Economy Based on Waste Recycling? An Overview of the Situation, Opportunities, and Barriers for the Altai Krai. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 670, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, V.M.; Chiriac, M.; Deak, G.; Pipirigeanu, M.; Izhar, T.N.T. Strategic actions for packaging waste management and reduction. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 616, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariatli, F. Linear Economy Versus Circular Economy: A Comparative and Analyzer Study for Optimization of Economy for Sustainability. J. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 6, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, S.; Linnenluecke, M. Circular economy and resilience: A research agenda Circular economy and resilience: A research agenda. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 2754–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimmalu, A.; Ramasamy, R. Food Processing Industry Waste and Circular Economy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 955, 012089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropea, A. Food Waste Valorisation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, Y.; Lin, K.Y.; Hong, E.; Kwon, E.; Lee, J. The Valorisation of Food Waste via Pyrolysis: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. Recovery of biomolecules from food wastes—A review. Molecules 2014, 19, 14821–14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Prisco, I.; Garella, I.; Gallo, M.; Nigro, R. Extracting the lipid fraction from waste bilberry seeds with a hydrofluorocarbon solvent. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 157, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Gallo, M.; Varriale, L.; Garella, I.; Nigro, R. Recovery of Carotenoids from Tomato Pomace Using a Hydrofluorocarbon Solvent in Sub-Critical Condition. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fia, R.L.; Matos, A.T.; Borges, A.C.; Fia, R.; Cecon, P.R. Treatment of wastewater from coffee bean processing in anaerobic fixed bed reactors with different support materials: Performance and kinetic modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 108, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, R.; Rajagopal, R.; Torrijos, M.; Thanikal, J.M.; Ramanujam, R. Anaerobic treatment of winery wastewater in fixed bed reactors. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2010, 33, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meksi, N.; Haddar, W.; Hammami, S.; Mhenni, M.F. Olive mill wastewater: A potential source of natural dyes for textile dyeing. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 40, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Saady, N.M.C.; Torrijos, M.; Thanikal, J.V.; Hung, Y.-T. Sustainable Agro-Food Industrial Wastewater Treatment Using High-Rate Anaerobic Process. Water 2013, 5, 292–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyei, D.; Shanbhag, B.K.; He, L. Enzymes for food waste remediation and valorisation. In Improving and Tailoring Enzymes for Food Quality and Functionality; Yada, R.Y., Ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2015; pp. 123–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallh, M.N.; Abdelhalim, W.S.; Abdelhalim, H.S. Industrial wastewater treatment of food industry using best techniques. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Invent. 2016, 5, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Economou, C.N.; Tatoulis, T.I. Wastewater treatment and water reuse in the food industry. In The Interaction of Food Industry and Environment; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 245–280. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, A.I.; Laca, A.; Díaz, M. Fungal treatment of an effluent from sewage sludge digestion to remove recalcitrant organic matter. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021, 172, 108056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Yamamoto-Ikemoto, R. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal from wastewater treatment plant effluent via bacterial sulfate reduction in an anoxic bioreactor packed with wood and iron. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 9835–9853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Shobana, S.; Nagarajan, D.; Lee, D.J.; Lee, K.S.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, J.S. Biomass based hydrogen production by dark fermentation—Recent trends and opportunities for greener processes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 50, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, V.T.; Ferraz-Júnior, A.D.N.; Trably, E.; Zaiat., M. Biohydrogen production at pH below 3.0: Is it possible? Water Res. 2018, 128, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Behera, S.; Park, H. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste leachate and piggery wastewater for methane production: Statistical optimization of key process parameters. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, Z.; Sharma, M.; Gaffey, J.; Sharma, M.; Dewhurst, R.J.; Moreau, B.; Newbold, J.; Clark, W.; Thakur, V.K.; Gupta, V.K. Valorization of dairy waste and by-products through microbial bioprocesses. Bioresour Technol. 2022, 346, 126444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Chiang, L.M. Methane Potential of Sewage Sludge to Increase Biogas Production. Master’s Thesis, Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cintas, L.M.; Casaus, M.P.; Herranz, C.; Nes, I.F.; Hernández, P.E. Review: Bacteriocins of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 7, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juodeikiene, G.; Cizeikiene, D.; Glasner, C.; Bartkiene, E.; Dikiy, A.; Shumilina, E.; Ilić, N.; Di Berardino, S.; Foncesa, C. Evaluation of the potential of utilizing lactic acid bacteria and dairy wastewaters for methane production. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2017, 35, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, H.; Reim, V.; Rohn, S. Stability of saponins from chickpea, soy, and faba beans in vegetarian, broccoli-based bars subjected to different cooking techniques. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Singh, N.; Kaur, A. Saponins in pulses and their health promoting activities: A review. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlü-Üstündağ, Ö.; Mazza, G. Saponins: Properties, applications, and processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2007, 47, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, J.J.; Huo, S.; Serventi, L. Phytochemical content and emulsifying ability of pulses cooking water. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, D.; Nigro, F.; Colucci Cante, R.; Passannanti, F.; Gallo, M.; Budelli, A.; Marzocchella, A.; Nigro, R. Fermentation of Rice Flour Supernatant Using Lactobacillus Paracasei Cba L74. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2019, 75, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, P.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Schiattarella, P.; Zappulla, S.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Lactic fermentation of cereals aqueous mixture of oat and rice flours with and without glucose addition. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, F.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Salameh, D.; Schiattarella, P.; Schioppa, C.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Effect of the glucose addition during lactic fermentation of rice, oat, and wheat flours. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2020, 7, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, F.; Schiattarella, P.; Esposito, A.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Banana Puree Lactic Fermentation: The Role of Ripeness, Heat Treatment, and Ascorbic Acid. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Passannanti, F.; Schioppa, C.; Montella, S.; Colucci Cante, R.; Nigro, F.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Enzymatic pre-treatment and lactic fermentation of wheat flour suspension at a high solid content. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Salameh, D.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Lactic fermentation of cooked navy beans by Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 aimed at a potential production of functional legume-based foods. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 98, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Budelli, A.; Nigro, R. Mathematical modelling of Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 growth during rice flour fermentation performed with and without pH control. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, G.; Nigro, F.; Colucci Cante, R.; Passannanti, F.; Gallo, M.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R. Functional Properties of an Oat-Based Postbiotic Aimed at a Potential Cosmetic Formulation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Nanayakkara, M.; Lania, G.; Parisi, F.; Salameh, D.; Budelli, A.; Barone, M.V.; Nigro, R. Effect of pH control during rice fermentation in preventing a gliadin P31-43 entrance in epithelial cells. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labruna, G.; Nanayakkara, M.; Pagliuca, C.; Nunziato, M.; Iaffaldano, L.; D’Argenio, V.; Colicchio, R.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R.; Salvatore, P.; et al. Celiac disease-associated Neisseria flavescens decreases mitochondrial respiration in CaCo-2 epithelial cells: Impact of Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 on bacterial-induced cellular imbalance. Cell Microbiol. 2019, 21, e13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, M.; Lania, G.; Cuomo, M.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Budelli, A.; Fasano, F.; Troncone, R.; Auricchio, S.; Barone, M.V.; et al. Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 interferes with gliadin peptides entrance in Caco-2 cells. Int. J. Food Sci. 2014, 65, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, E.R. Aseptic laboratory techniques: Plating methods. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, e3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aikpokpodion, P.E.; Dongo, L.N. Effects of fermentation intensity on polyphenols and antioxidant capacity of cocoa beans. Int. J. Sustain. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, H.F.; Hashim, Z.; Soon, W.T.; Rahman, N.S.A.; Zainudin, A.N.; Majid, F.A.A. Comparative study of herbal plants on the phenolic and flavonoid content, antioxidant activities and toxicity on cells and zebrafish embryo. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiai, S.; Oura, H.; Nakajima, T. Color reaction of some sapogenins and saponins with vanillin and sulfuric acid. Planta Med. 1976, 29, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzie, I.F.; Devaki, M. The ferric reducing/antioxidant power (FRAP) assay for non-enzymatic antioxidant capacity: Concepts, procedures, limitations, and applications. In Measurement of Antioxidant Activity & Capacity; Apak, R., Capanoglu, E., Shahidi, F., Eds.; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai-Ut, S.; Ketnawa, S.; Chaiwut, P.; Rawdkuen, S. Biochemical and functional properties of protein from red kidney, navy, and adzuki beans. Asian J. Food Agro-Ind. 2009, 2, 493–504. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, L.; Wanasundara, J.; Nickerson, M.T. The effect of pH and NaCl levels on the physicochemical and emulsifying properties of a cruciferin protein isolate. Food Biophys. 2014, 9, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: “Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 16–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colucci Cante, R.; Gallo, M.; Nigro, F.; Vitelli, C.; Passannanti, F.; Budelli, A.L.; Nigro, R. Optimization of Mixing Conditions for Improving Lactobacillus Paracasei Cba L74′ S Growth During Lactic Fermentation of Cooked Navy Beans and Functional Characterization of the Fermented Products. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 93, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, S.E.; Axelsson, L.T.; McFeeters, R.F. Anaerobic L-lactate degradation by Lactobacillus plantarum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 66, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorquet, F.; Goffin, P.; Muscariello, L.; Baudry, J.B.; Ladero, V.; Sacco, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; Hols, P. Characterization and functional analysis of the poxB gene, which encodes pyruvate oxidase in Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 3749–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quatravaux, S.; Remize, F.; Bryckaert, E.; Colavizza, D.; Guzzo, J. Examination of Lactobacillus plantarum lactate metabolism side effects in relation to the modulation of aeration parameters. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouroozi, R.V.; Noroozi, M.V.; Ahmadizadeh, M. Determination of protein concentration using Bradford microplate protein quantification assay. Dis. Diagn. 2015, 4, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, L.; Garro, M.S.; De Giori, G.S. Enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean protein using lactic acid bacteria. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Cano, I.; Rocha-Mendoza, D.; Ortega-Anaya, J.; Wang, K.; Kosmerl, E.; Jiménez-Flores, R. Lactic acid bacteria isolated from dairy products as potential producers of lipolytic, proteolytic and antibacterial proteins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 5243–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klupsaite, D.; Juodeikiene, G.; Zadeike, D.; Bartkiene, E.; Maknickiene, Z.; Liutkute, G. The influence of lactic acid fermentation on functional properties of narrow-leaved lupine protein as functional additive for higher value wheat bread. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Li, L. Effects of extracellular proteases and its inhibitors on the gel characteristics of soy protein induced by lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emkani, M.; Oliete, B.; Saurel, R. Effect of Lactic Acid Fermentation on Legume Protein Properties, a Review. Fermentation 2022, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, M.J.; Sánchez, L.A.; Saguir, F.M.; de Nadra, M.C. Lactic acid bacteria isolated from apples are able to catabolise arginine. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1003–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Páez, E.; Alanis-Guzmán, M.G.; Hernández-Luna, C.E.; Báez-González, J.G.; Amaya-Guerra, C.A.; Andrés-Grau, A.M. Increasing antioxidant activity and protein digestibility in Phaseolus vulgaris and avena sativa by fermentation with the Pleurotusostreatus fungus. Molecules 2017, 22, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, B.; Yin, L.; Yao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Gui, J.; Lu, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J. Effects of fermentation on the haemolytic activity and degradation of Camellia oleifera saponins by Lactobacillus crustorum and Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Hsieh, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Chou, C.C. Effect of lactic fermentation on the total phenolic, saponin and phytic acid contents as well as anti-colon cancer cell proliferation activity of soymilk. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 115, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolívar-Monsalve, J.; Ceballos-González, C.F.; Ramírez-Toro, C.; Bolívar, G.A. Reduction in saponin content and production of gluten-free cream soup base using quinoa fermented with Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.M.; Linh, N.T.T.; Hoa, N.T.; Thuy, D.T.K.; Giap, D.D. Effect of Lactic Fermentation and Spray Drying Process on Bioactive Compounds from Ngoc Linh Ginseng Callus and Lactobacillus plantarum Viability. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 49, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Su, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, G.; Huang, D.; Terry, N.; Wang, F. Increased Extracellular Saponin Production after the Addition of Rutin in Truffle Liquid Fermentation and Its Antioxidant Activities. Fermentation 2021, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Dekker, S.; Kyriakopoulou, K.; Boom, R.M.; Smid, E.J.; Schutyser, M.A.I. Enhanced nutritional value of chickpea protein concentrate by dry separation and solid-state fermentation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuchi, C.; Victory, I.; Echeta, C. The functional properties of foods and flours. Int. J. Adv. Acad. Res. 2019, 5, 139–160. [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher, S.; Drusch, S. Interfacial Properties of Saponin Extracts and Their Impact on Foam Characteristics. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Dale, K.J.; Liu, S.; Zhu, J.; Serventi, L. Composition of legume soaking water and emulsifying properties in gluten-free bread. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2018, 24, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Yoshida, R.; Maeda, H.; Furuta, H.; Corredig, M. Study of the role of the carbohydrate and protein moieties of soy soluble polysaccharides in their emulsifying properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5506–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakauma, M.; Funami, T.; Noda, S.; Ishihara, S.; Al-Assaf, S.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O. Comparison of sugar beet pectin, soybean soluble polysaccharide, and gum Arabic as food emulsifiers. Effect of concentration, pH, and salts on the emulsifying properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzębski, M.; Siejak, P.; Smułek, W.; Fathordoobady, F.; Guo, Y.; Pawlicz, J.; Trzeciak, T.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Kitts, D.D.; Singh, A.; et al. Plant Extracts Containing Saponins Affects the Stability and Biological Activity of Hempseed Oil Emulsion System. Molecules 2020, 25, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


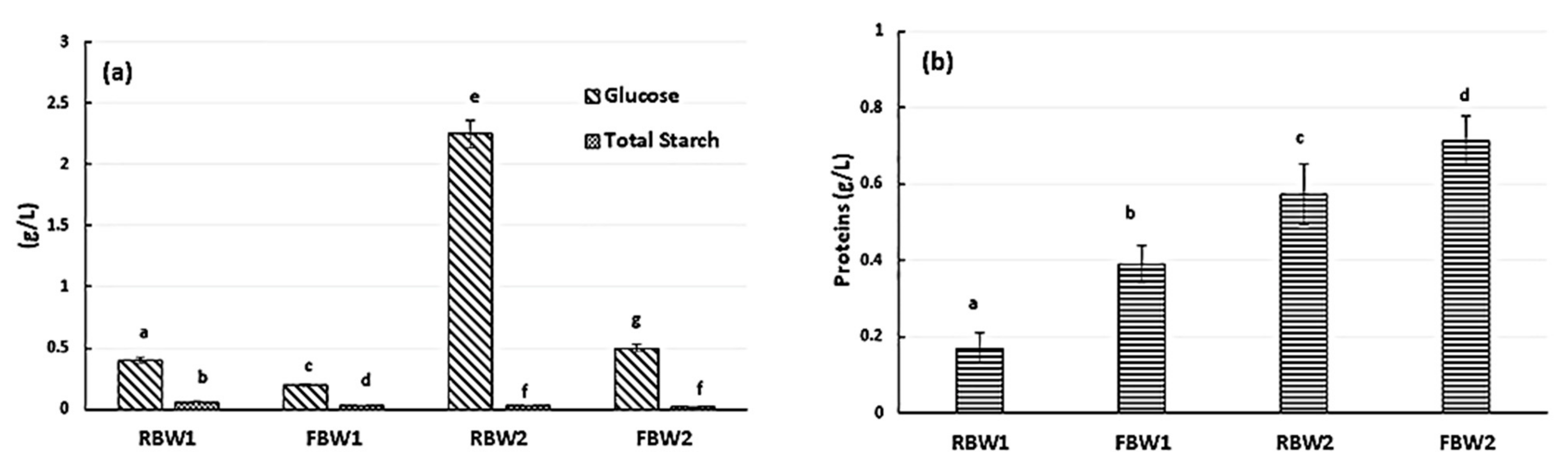
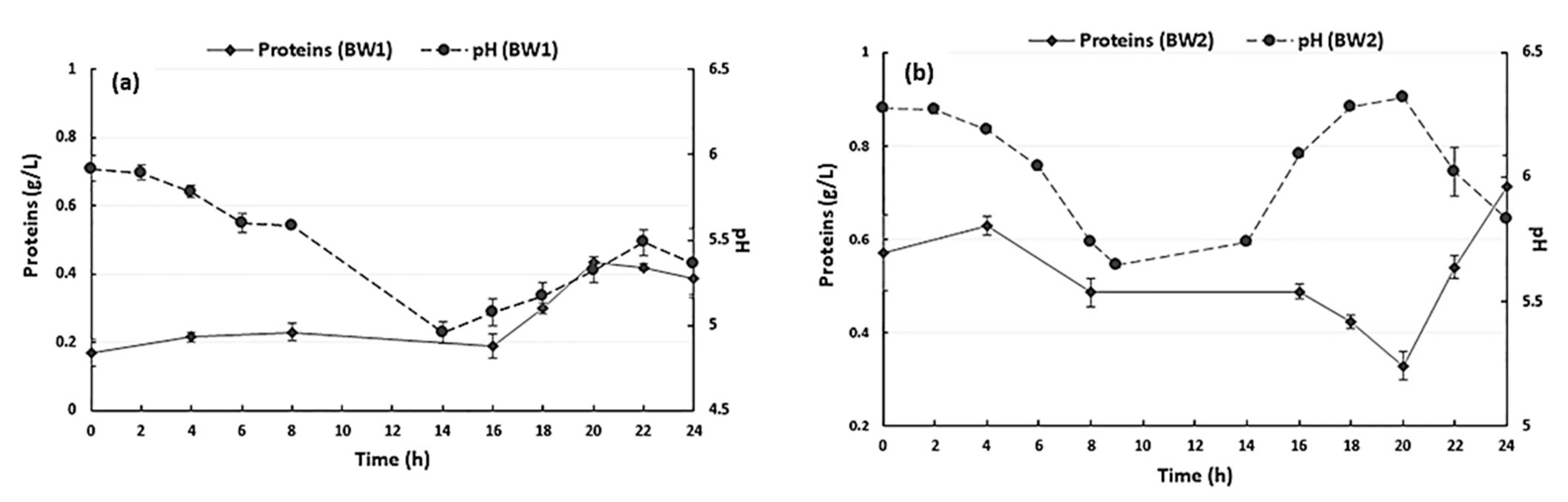

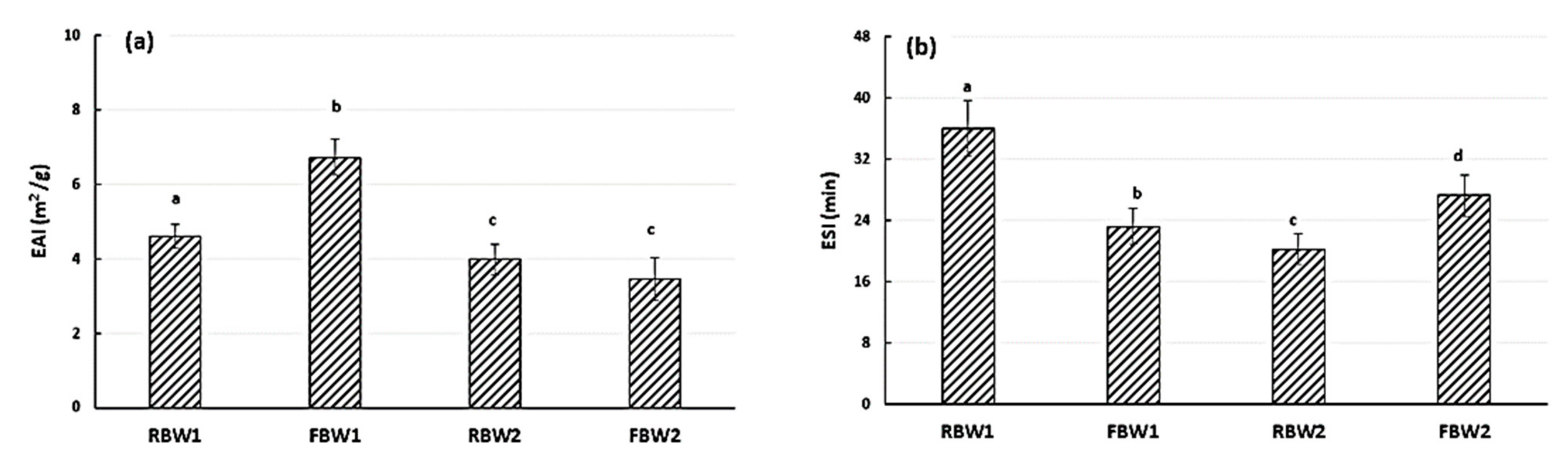
| Samples | °Bx | Dry Matter (%) | pH | Proteins (%) | Glucose (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBW1 | 0.75 | 1.068 | 5.92 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| RBW2 | 1.25 | 1.701 | 6.27 | 0.05 | 0.22 |
| RBW1 | FBW1 | RBW2 | FBW2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC (mgGAE/mL) | 0.086 ± 0.001 a | 0.115 ± 0.040 b | 0.245 ± 0.0025 c | 0.302 ± 0.0085 d |
| TFC (mgQE/mL) | 0.0026 ± 0.0061 a | 0.0037 ± 0.0067 b | 0.005 ± 0.0001 c | 0.0076 ± 0.0021 d |
| AA (mmolTE/mL) | 0.387 ± 0.158 a | 0.485 ± 0.1202 b | 1.052 ± 0.229 c | 1.449 ± 0.659 d |
| TSC (mgOAE/mL) | 1.541 ± 0.025 a | 1.590 ± 0.057 a | 2.868 ± 0.289 c | 6.682 ± 0.689 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colucci Cante, R.; Recupero, A.; Prata, T.; Nigro, F.; Passannanti, F.; Gallo, M.; Lentini, G.; Nigro, R.; Budelli, A.L. Valorisation through Lactic Fermentation of Industrial Wastewaters from a Bean Blanching Treatment. Fermentation 2023, 9, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040350
Colucci Cante R, Recupero A, Prata T, Nigro F, Passannanti F, Gallo M, Lentini G, Nigro R, Budelli AL. Valorisation through Lactic Fermentation of Industrial Wastewaters from a Bean Blanching Treatment. Fermentation. 2023; 9(4):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040350
Chicago/Turabian StyleColucci Cante, Rosa, Angelica Recupero, Tommaso Prata, Federica Nigro, Francesca Passannanti, Marianna Gallo, Giulia Lentini, Roberto Nigro, and Andrea Luigi Budelli. 2023. "Valorisation through Lactic Fermentation of Industrial Wastewaters from a Bean Blanching Treatment" Fermentation 9, no. 4: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040350
APA StyleColucci Cante, R., Recupero, A., Prata, T., Nigro, F., Passannanti, F., Gallo, M., Lentini, G., Nigro, R., & Budelli, A. L. (2023). Valorisation through Lactic Fermentation of Industrial Wastewaters from a Bean Blanching Treatment. Fermentation, 9(4), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040350










