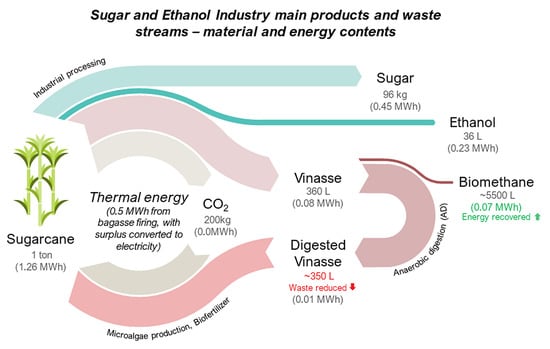
Biomethane Production from Sugarcane Vinasse in a Circular Economy: Developments and Innovations
Abstract
1. Introduction
The Importance of Biohydrogen Production
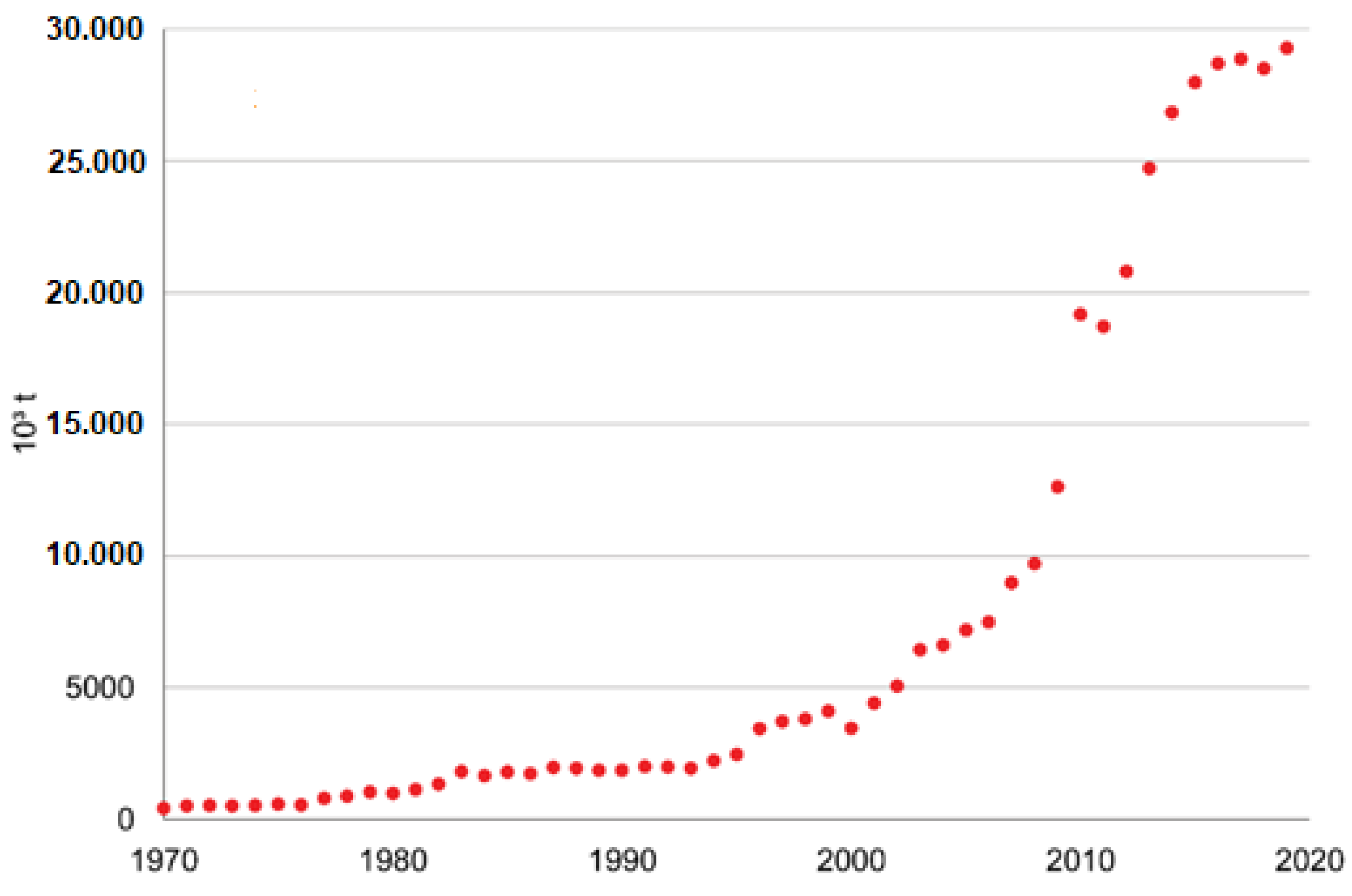
2. Sugarcane Vinasse
| Reference/ Components | [37] | [38] | [25] | [39] | [40] | [26] | [41] | [42] | Average (1st Generation) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.4 | 4.2 | nd | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.6 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 5.25 | 4.4 | 4.6 |
| COD (g O2/L) | 103 | 28.5 | nd | 36.0 | 39 | 49.0 | 31.7 | 25.2 | 33 | 67.3 | 45.8 |
| BOD (g O2/L) | 57.4 | 16.5 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 13.4 | 7.9 | 15 | 21.0 | 21.87 |
| Ca (mg/L) | 719 | 515.2 | 3160 | 741 | 1502 | 1304 | 828 | 671 | 1180 | nd | 1180 |
| Cl (mg/L) | nd | 1218.9 | 59.4 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 2161 | nd | 1146 |
| P (mg/L) | 190 | 120.8 | 560 | 111 | 35 | 64 | 5518 | 207 | 135 | nd | 852.5 |
| Mg (mg/L) | 237 | 244.7 | 162.4 | 354 | 428 | 543 | 321.3 | 264 | 523.5 | nd | 319.3 |
| N (mg/L) | 1190 | 356.6 | nd | 1603 | 570 | 762 | 234 | 171 | 329.5 | 1100 | 698.09 |
| K (mg/L) | 2056 | 1750.9 | 1620 | 3147 | 2334 | 2827 | 3276 | 3401 | 2557.9 | nd | 2551.5 |
| SO4 (mg/L) | 710 | 1537.6 | 1680 | 2300 | 2700 | 2900 | 340.3 | 2993 | 2264 | nd | 1936.1 |
2.1. Current Pretreatments, Treatments, Disposal, and Usage
2.2. Energetic Potential in Vinasse
3. Vinasse Anaerobic Digestion
3.1. Microbial Community Diversity in Vinasse AD
3.2. Vinasse Methanogenic Potential and Digestion
3.3. Vinasse Composition Effects on Methanogenesis
3.4. Improving Vinasse Biodigestion with Co-Substrates
3.5. Early Implementations of Industrial Processes
4. Current Trends and Technologies
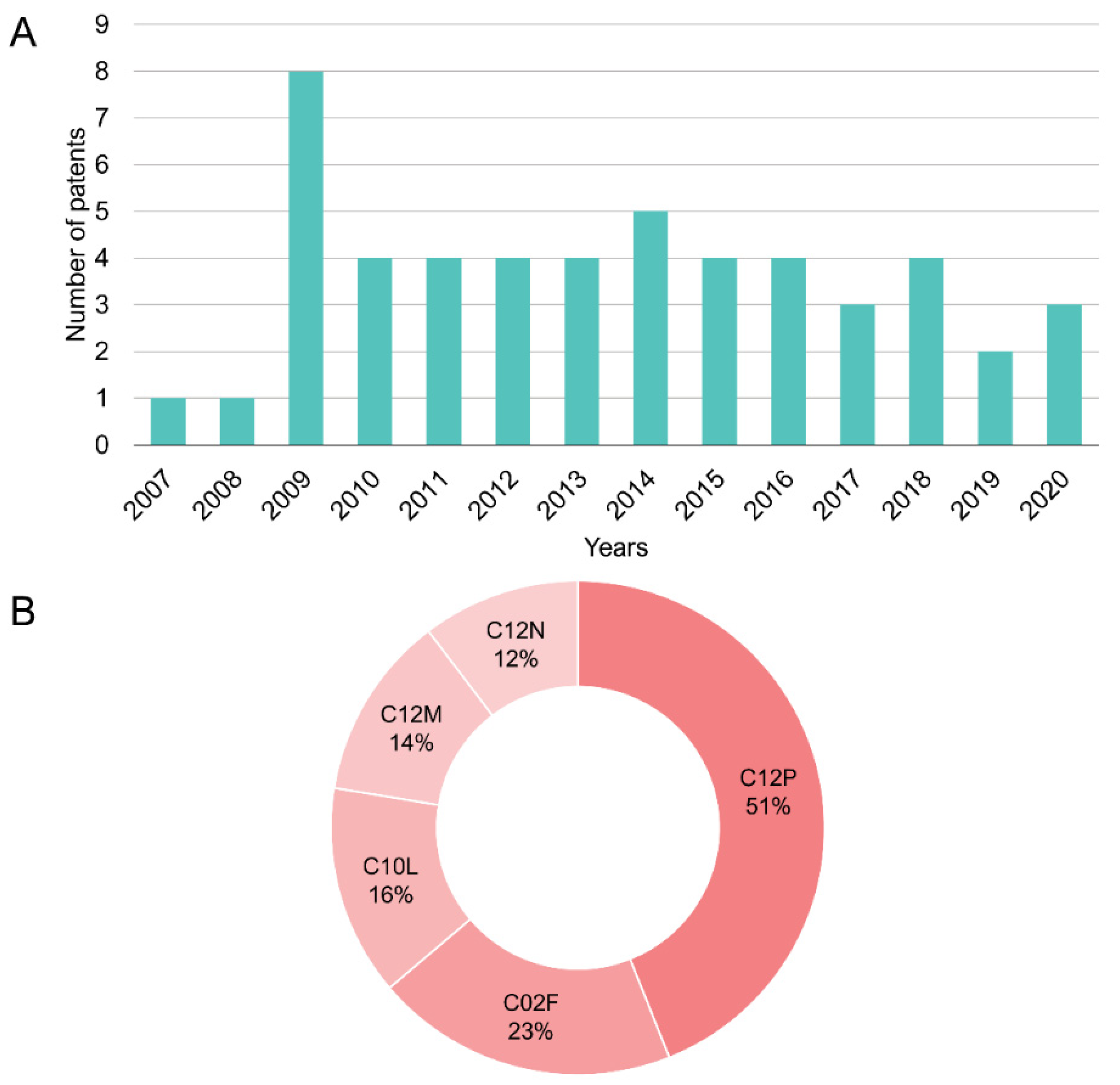
4.1. Patents in Vinasse Biodigestion
4.2. Recent and Announced Projects
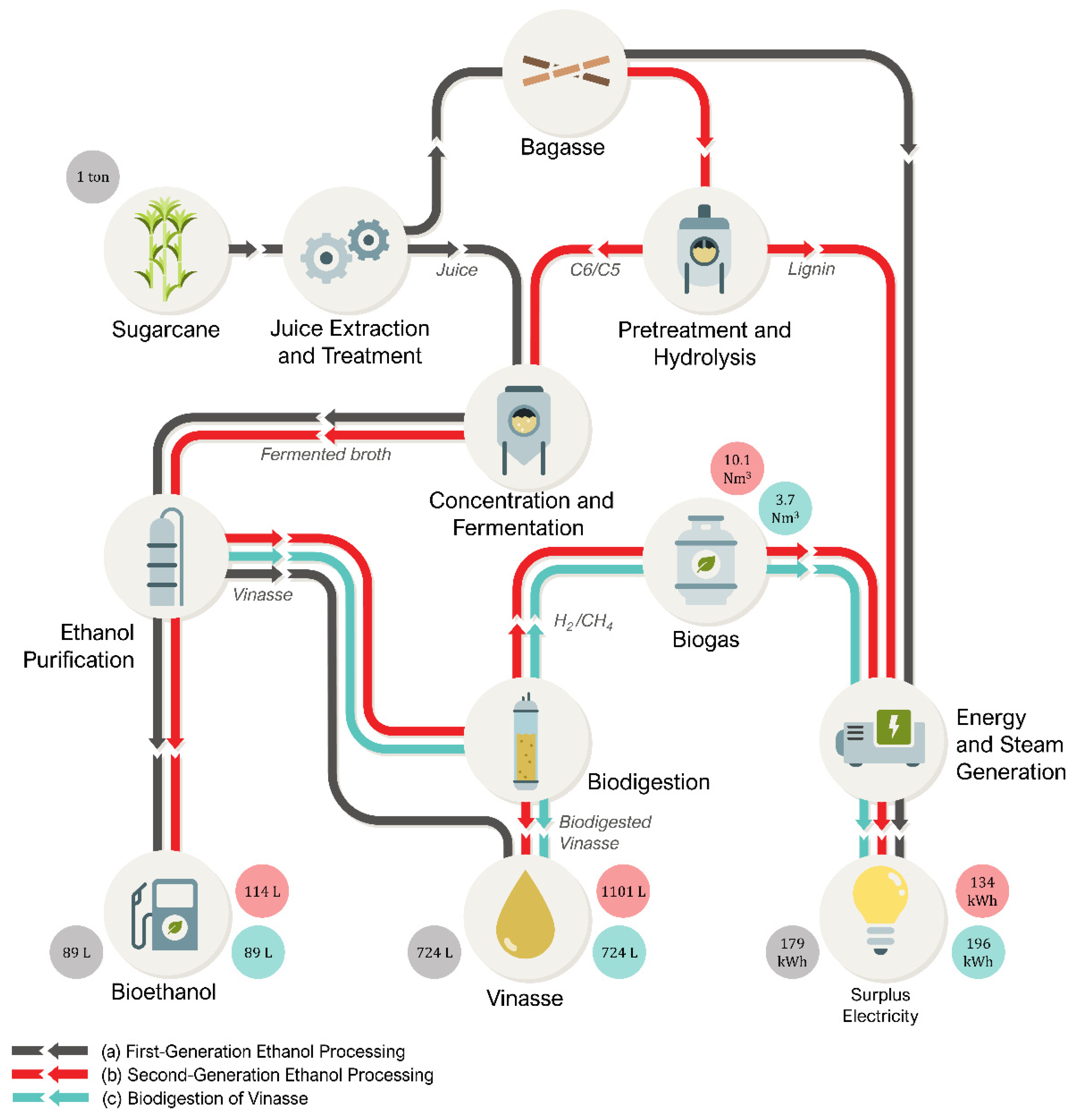
5. Vinasse Treatment and the Circular Economy
5.1. Current Practices of Circular Economy in the Sugarcane Industry
5.2. The Next Challenge: Valorization of Liquid Residues
5.3. The Ideal Sugarcane Biorefinery
6. Perspectives and Challenges in Vinasse Anaerobic Digestion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, Y.K. Performance of a Two-Stage Methane Digestor for Alcohol Stillage Derived from Sugarcane Molasses. Biotechnol. Lett. 1983, 5, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laluce, C. Current Aspects of Fuel Ethanol Production in Brazil. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 1991, 11, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín, E.J.; Doelel, H.W.; Mercado, G. Resource Recovery through Recycling of Sugar Processing By-Products and Residuals. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 1995, 15, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarte-Toro, J.C.; Cardona Alzate, C.A. Biorefineries as the Base for Accomplishing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Transition to Bioeconomy: Technical Aspects, Challenges and Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaideen, K.; Abdelkareem, M.A.; Wilberforce, T.; Elsaid, K.; Sayed, E.T.; Maghrabie, H.M.; Olabi, A.G. Biogas Role in Achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals: Evaluation, Challenges, and Guidelines. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 131, 104207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.C.; Chagas, M.F.; Watanabe, M.D.B.; Bonomi, A.; Maciel Filho, R. Low Carbon Biofuels and the New Brazilian National Biofuel Policy (RenovaBio): A Case Study for Sugarcane Mills and Integrated Sugarcane-Microalgae Biorefineries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 115, 109365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, M.H.; Mendes, F.M.; Ramos, L.; Dias, M.O.S.; Bonomi, A.; Jesus, C.D.F.; Watanabe, M.D.B.; Junqueira, T.L.; Milagres, A.M.F.; Ferraz, A. Techno-Economic Assessment of Bioenergy and Biofuel Production in Integrated Sugarcane Biorefinery: Identification of Technological Bottlenecks and Economic Feasibility of Dilute Acid Pretreatment. Energy 2020, 125, 117422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, E.B.; Letti, L.A.J.; Karp, S.G.; Sydney, A.C.N.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Woiciechowski, A.L.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R. Current Analysis and Future Perspective of Reduction in Worldwide Greenhouse Gases Emissions by Using First and Second Generation Bioethanol in the Transportation Sector. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.-P. New Bioproduction Systems for Chemicals and Fuels: Needs and New Development. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuess, L.T.; Garcia, M.L. Anaerobic Biodigestion for Enhanced Bioenergy Generation in Ethanol Biorefineries: Understanding the Potentials of Vinasse as a Biofuel. In Bioenergy Systems for the Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 149–183. [Google Scholar]
- Fuess, L.T.; Rodrigues, I.J.; Garcia, M.L. Fertirrigation with Sugarcane Vinasse: Foreseeing Potential Impacts on Soil and Water Resources through Vinasse Characterization. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT-Database Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 3 March 2023).
- Sakthivel, P.; Subramanian, K.A.; Mathai, R. Indian Scenario of Ethanol Fuel and Its Utilization in Automotive Transportation Sector. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 132, 102–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Valladares-Diestra, K.K.; Bittencourt, G.A.; Zevallos Torres, L.A.; Vieira, S.; Karp, S.G.; Sydney, E.B.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Thomaz Soccol, V.; Soccol, C.R. Beyond Sugar and Ethanol: The Future of Sugarcane Biorefineries in Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Produção de Cana-de-Açúcar No Brasil. IBGE. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/explica/producao-agropecuaria/cana-de-acucar/br (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- de Souza Dias, M.O.; Maciel Filho, R.; Mantelatto, P.E.; Cavalett, O.; Rossell, C.E.V.; Bonomi, A.; Leal, M.R.L.V. Sugarcane Processing for Ethanol and Sugar in Brazil. Environ. Dev. 2015, 15, 35–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formann, S.; Hahn, A.; Janke, L.; Stinner, W.; Sträuber, H.; Logroño, W.; Nikolausz, M. Beyond Sugar and Ethanol Production: Value Generation Opportunities through Sugarcane Residues. Front. Energy Res. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofoletti, C.A.; Escher, J.P.; Correia, J.E.; Marinho, J.F.U.; Fontanetti, C.S. Sugarcane Vinasse: Environmental Implications of Its Use. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 2752–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, E.B.; Larroche, C.; Novak, A.C.; Nouaille, R.; Sarma, S.J.; Brar, S.K.; Letti, L.A.J.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R. Economic Process to Produce Biohydrogen and Volatile Fatty Acids by a Mixed Culture Using Vinasse from Sugarcane Ethanol Industry as Nutrient Source. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydney, E.B.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Letti, L.A.J.; Magalhaes, A.I., Jr.; Karp, S.G.; Martinez-Burgos, W.J.; de Souza Candeo, E.; Rodrigues, C.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Neto, C.J.D.; et al. Current Developments and Challenges of Green Technologies for the Valorization of Liquid, Solid, and Gaseous Wastes from Sugarcane Ethanol Production. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 404, 124059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues Reis, C.E.; Hu, B. Vinasse from Sugarcane Ethanol Production: Better Treatment or Better Utilization? Front. Energy Res. 2017, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N.; Rai, V. Melanoidins as Major Colourant in Sugarcane Molasses Based Distillery Effluent and Its Degradation. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4648–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoarau, J.; Caro, Y.; Grondin, I.; Petit, T. Sugarcane Vinasse Processing: Toward a Status Shift from Waste to Valuable Resource. A Review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2018, 24, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Burgos, W.J.; Sydney, E.B.; de Paula, D.R.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Molina, D.; Soccol, C.R. Hydrogen Production by Dark Fermentation Using a New Low-Cost Culture Medium Composed of Corn Steep Liquor and Cassava Processing Water: Process Optimization and Scale-Up. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.D.; Lopes da Silva, A.L.; da Luz Costa, J.; Scheidt, G.N.; Novak, A.C.; Sydney, E.B.; Soccol, C.R. Development of a Vinasse Nutritive Solution for Hydroponics. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 114, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, J.E.; Christofoletti, C.A.; Marcato, A.C.C.; Marinho, J.F.U.; Fontanetti, C.S. Histopathological Analysis of Tilapia Gills (Oreochromis Niloticus Linnaeus, 1758) Exposed to Sugarcane Vinasse. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 135, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsaee, M.; Kiani Deh Kiani, M.; Karimi, K. A Review of Biogas Production from Sugarcane Vinasse. Biomass. Bioenergy 2019, 122, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpanez, T.G.; Moreira, V.R.; Assis, I.R.; Amaral, M.C.S. Sugarcane vinasse as organo-mineral fertilizers feedstock: Opportunities and environmental risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 154998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuess, L.T.; Garcia, M.L.; Zaiat, M. Seasonal Characterization of Sugarcane Vinasse: Assessing Environmental Impacts from Fertirrigation and the Bioenergy Recovery Potential through Biodigestion. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 634, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubin, M.R.; Carvalho, J.L.N.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Nogueira, L.A.H.; Souza, G.M.; Cantarella, H. Land Use and Management Effects on Sustainable Sugarcane-Derived Bioenergy. Land 2021, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Carmo, J.B.; Filoso, S.; Zotelli, L.C.; De Sousa Neto, E.R.; Pitombo, L.M.; Duarte-Neto, P.J.; Vargas, V.P.; Andrade, C.A.; Gava, G.J.C.; Rossetto, R.; et al. Infield Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Sugarcane Soils in Brazil: Effects from Synthetic and Organic Fertilizer Application and Crop Trash Accumulation. GCB Bioenergy 2013, 5, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, B.G.; Carvalho, J.L.N.; Cerri, C.E.P.; Cerri, C.C.; Feigl, B.J. Soil Greenhouse Gas Fluxes from Vinasse Application in Brazilian Sugarcane Areas. Geoderma 2013, 200–201, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.E.R.; Bento, H.B.S.; Alves, T.M.; Carvalho, A.K.F.; De Castro, H.F. Vinasse Treatment within the Sugarcane-Ethanol Industry Using Ozone Combined with Anaerobic and Aerobic Microbial Processes. Environments 2019, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarme, O.F.H.; Baêta, B.E.L.; Filho, J.B.G.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; de Aquino, S.F. Use of Anaerobic Co-Digestion as an Alternative to Add Value to Sugarcane Biorefinery Wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 287, 121443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Wang, Q. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewaters: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Deng, C.-B.; Wang, X.-F.; Chen, G.; Mihucz, V.G.; Xu, G.-P.; Deng, Q.-C. Effects of Long-Term Application of Vinasse on Physicochemical Properties, Heavy Metals Content and Microbial Diversity in Sugarcane Field Soil. Sugar Tech. 2019, 21, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertiello, A. Upgrading of Agricultural and Agro-Industrial Wastes: The Treatment of Distillery Effluents (Vinasses) in Italy. Agric. Wastes 1982, 4, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, E. Valorization of Vinasse as Broth for Biological Hydrogen and Volatile Fatty Acids Production by Means of Anaerobic Bacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Paraná—UFPR, Curitiba, Brazil, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Siqueira, L.M.; Damiano, E.S.G.; Silva, E.L. Influence of Organic Loading Rate on the Anaerobic Treatment of Sugarcane Vinasse and Biogás Production in Fluidized Bed Reactor. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2013, 48, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.F.H.; de Souza, R.B.; Souza, C.P.; Christofoletti, C.A.; Fontanetti, C.S. Toxicity of Two Effluents from Agricultural Activity: Comparing the Genotoxicity of Sugar Cane and Orange Vinasse. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Godoi, L.A.G.; Camiloti, P.R.; Bernardes, A.N.; Sanchez, B.L.S.; Torres, A.P.R.; da Conceição Gomes, A.; Botta, L.S. Seasonal Variation of the Organic and Inorganic Composition of Sugarcane Vinasse: Main Implications for Its Environmental Uses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29267–29282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulli, M.M.; Villegas, L.B.; Colin, V.L. Treatment of Sugarcane Vinasse Using an Autochthonous Fungus from the Northwest of Argentina and Its Potential Application in Fertigation Practices. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Rodríguez, E.F.; Fukushima, N.A.; Palacios-Bereche, R.; Ensinas, A.V.; Nebra, S.A. Vinasse Concentration and Juice Evaporation System Integrated to the Conventional Ethanol Production Process from Sugarcane—Heat Integration and Impacts in Cogeneration System. Renew. Energy 2018, 115, 474–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortegón, G.P.; Arboleda, F.M.; Candela, L.; Tamoh, K.; Valdes-Abellan, J. Vinasse Application to Sugar Cane Fields. Effect on the Unsaturated Zone and Groundwater at Valle Del Cauca (Colombia). Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buller, L.S.; Romero, C.W.; da, S.; Lamparelli, R.A.C.; Ferreira, S.F.; Bortoleto, A.P.; Mussatto, S.I.; Forster-Carneiro, T. A Spatially Explicit Assessment of Sugarcane Vinasse as a Sustainable By-Product. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 765, 142717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuess, L.T.; Garcia, M.L. Implications of Stillage Land Disposal: A Critical Review on the Impacts of Fertigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 145, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, B.S.; Vieira, J.P.F.; Contesini, F.J.; Mantelatto, P.E.; Zaiat, M.; Pradella, J.G.D.C. High Value Added Lipids Produced by Microorganisms: A Potential Use of Sugarcane Vinasse. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- España-Gamboa, E.; Vicent, T.; Font, X.; Dominguez-Maldonado, J.; Canto-Canché, B.; Alzate-Gaviria, L. Pretreatment of Vinasse from the Sugar Refinery Industry under Non-Sterile Conditions by Trametes Versicolor in a Fluidized Bed Bioreactor and Its Effect When Coupled to an UASB Reactor. J. Biol. Eng. 2017, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-González, V.; Galíndez-Mayer, J.; Rinderknecht-Seijas, N.; Poggi-Varaldo, H.M. Treatment of Mezcal Vinasses: A Review. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 157, 524–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, P.; De Figueroa, L.I.C.; Pajot, H.F. Dual Purpose of Ligninolytic- Basidiomycetes: Mycoremediation of Bioethanol Distillation Vinasse Coupled to Sustainable Bio-Based Compounds Production. Fungal. Biol. Rev. 2020, 34, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney, E.B.; Duarte, E.R.; Martinez Burgos, W.J.; de Carvalho, J.C.; Larroche, C.; Soccol, C.R. Development of Short Chain Fatty Acid-Based Artificial Neuron Network Tools Applied to Biohydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 5175–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, N.A.; Palacios-Bereche, M.C.; Palacios-Bereche, R.; Nebra, S.A. Energy Analysis of the Ethanol Industry Considering Vinasse Concentration and Incineration. Renew. Energy 2019, 142, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, V.G.; Duda, R.M.; da Silva Vantini, J.; Omori, W.P.; Ferro, M.I.T.; de Oliveira, R.A. Improved Methane Production from Sugarcane Vinasse with Filter Cake in Thermophilic UASB Reactors, with Predominance of Methanothermobacter and Methanosarcina Archaea and Thermotogae Bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyuna, L.S.M.; Fuess, L.T.; Zaiat, M. Unraveling the Influence of the COD/Sulfate Ratio on Organic Matter Removal and Methane Production from the Biodigestion of Sugarcane Vinasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 232, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, A.M.; De Souza, R.R. Use of Sugar Cane Vinasse as Substrate for Biosurfactant Production Using Bacillus Subtilis Pc. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2014, 37, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.E.R.; Valle, G.F.; Bento, H.B.S.; Carvalho, A.K.F.; Alves, T.M.; de Castro, H.F. Sugarcane By-Products within the Biodiesel Production Chain: Vinasse and Molasses as Feedstock for Oleaginous Fungi and Conversion to Ethyl Esters. Fuel 2020, 277, 118064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, F.; Tadeu Fuess, L.; Soares Cavalcante, G.; Ângela Talarico Adorno, M.; Zaiat, M. Value-Added Soluble Metabolite Production from Sugarcane Vinasse within the Carboxylate Platform: An Application of the Anaerobic Biorefinery beyond Biogas Production. Fuel 2021, 286, 119378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, S.C.; Moravia, M.C.S.A.; Couto, C.F. Combined Process of Ultrafiltration and Nanofiltration for Vinasse Treatment With and Without Pre-Coagulation. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Díaz, A.; Pereda-Reyes, I.; Dueñas-Moreno, J.; Véliz-Lorenzo, E.; Díaz-Marrero, M.A.; Menéndez-Gutiérrez, C.L.; Oliva-Merencio, D.; Zaiat, M. Combined Treatment of Vinasse by an Upflow Anaerobic Filter-Reactor and Ozonation Process. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siles, J.A.; García-García, I.; Martín, A.; Martín, M.A. Integrated Ozonation and Biomethanization Treatments of Vinasse Derived from Ethanol Manufacturing. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 188, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavifar, M.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Younesi, H.; Galehdar, M. Fenton and Photo-Fenton Treatment of Distillery Effluent and Optimization of Treatment Conditions with Response Surface Methodology. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 5, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Şenol, H.; Papirio, S. Enhanced Lignocellulosic Component Removal and Biomethane Potential from Chestnut Shell by a Combined Hydrothermal–Alkaline Pretreatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietzler, J. Process for the Production of Methane from Process Waters and Biogenic Material. BR Patent PI0915815B1, 4 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Adrianus, C.; Claudia, R. Process and System for Producing Biogas from Anaerobic Digestion of Plant Biomass in Solid Phase. WO2012/153189A2, 17 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Huandong, Z.; Yuancheng, Z.; Mengmeng, Y.; Zhifeng, L.; Kaiyan, T. A Method of Biogas Is Produced Using Vinasse for Raw Material High-Temperature Anaerobic Fermentation. CN Patent 105039422B, 27 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, V.G.d.; Duda, R.M.; Oliveira, R.A.d. Biomethane Production from Vinasse in Upflow Anaerobic Sludge Blanket Reactors Inoculated with Granular Sludge. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.E.d.F.; Abud, A.K.d.S. Anaerobic Biodigestion of Sugarcane Vinasse under Mesophilic Conditions Using Manure as Inoculum. Rev. Ambiente Água 2016, 11, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chingono, K.E.; Sanganyado, E.; Bere, E.; Yalala, B. Adsorption of Sugarcane Vinasse Effluent on Bagasse Fly Ash: A Parametric and Kinetic Study. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Yu, S.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Yao, T.; Qin, J. Modeling and Optimization of Sugarcane Juice Clarification Process. J. Food Eng. 2021, 291, 110223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaba, O.R.; Lahiri, S.K.; T’Jonck, S.; Dutta, A. Experimental and Artificial Neural Network Modeling of a Upflow Anaerobic Contactor (UAC) for Biogas Production from Vinasse. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2016, 14, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, M.; Perez, M.; Solera, R. Benefits in the Valorization of Sewage Sludge and Wine Vinasse via a Two-Stage Acidogenic-Thermophilic and Methanogenic-Mesophilic System Based on the Circular Economy Concept. Fuel 2021, 296, 120654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, V.; Shafiei, M.; Karimi, K. Techno-Economic Study of Castor Oil Crop Biorefinery: Production of Biodiesel without Fossil-Based Methanol and Lignoethanol Improved by Alkali Pretreatment. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Giwa, A.; Mohammed, E.O.; Mohammed, O.; Al Hajaj, A.; Abu-Zahra, M.R.M. CO2 Utilization from Power Plant: A Comparative Techno-Economic Assessment of Soda Ash Production and Scrubbing by Monoethanolamine. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S.; Zaiat, M.; Oller do Nascimento, C.A.; Fuess, L.T. Does Sugarcane Vinasse Composition Variability Affect the Bioenergy Yield in Anaerobic Systems? A Dual Kinetic-Energetic Assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAB, (Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento) Acompanhamento Da Safra Brasileira. Available online: https://www.conab.gov.br/info-agro/safras/cana (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Bernal, A.P.; dos Santos, I.F.S.; Moni Silva, A.P.; Barros, R.M.; Ribeiro, E.M. Vinasse Biogas for Energy Generation in Brazil—An Assessment of Economic Feasibility, Energy Potential and Avoided CO2 Emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, R.; Lunelli, B.H. Exergy Analysis of Biogas Production from Sugarcane Vinasse. BioEnergy Res. 2023, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPE (Empresa de Pesquisa Energética). Cenários de Oferta de Etanol e Demanda de Ciclo Otto 2021–2030; EPE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2020; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Van, D.P.; Fujiwara, T.; Tho, B.L.; Toan, P.P.S.; Minh, G.H. A Review of Anaerobic Digestion Systems for Biodegradable Waste: Configurations, Operating Parameters, and Current Trends. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Shome, A.; Banerjee, S.N.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Mathew, A.K.; Chaudhury, S. An Overview of Physico-Chemical Mechanisms of Biogas Production by Microbial Communities: A Step towards Sustainable Waste Management. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Zaghloul, M.S.; Hamza, R.A.; Elbeshbishy, E. Comparing VFA Composition, Biomethane Potential, and Methane Production Kinetics of Different Substrates for Anaerobic Fermentation and Digestion. Fermentation 2023, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Wang, X.; Xi, J.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Linkage of Kinetic Parameters with Process Parameters and Operational Conditions during Anaerobic Digestion. Energy 2017, 135, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainthola, J.; Kalamdhad, A.S.; Goud, V. V Optimization of Process Parameters for Accelerated Methane Yield from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Rice Straw and Food Waste. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlinar, S.; Weig, A.R.; Freitag, R. Influence of Mixing and Sludge Volume on Stability, Reproducibility, and Productivity of Laboratory-Scale Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vrieze, J. The next Frontier of the Anaerobic Digestion Microbiome: From Ecology to Process Control. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Zhou, J.; Zuo, J.; Yang, Y. High Variations of Methanogenic Microorganisms Drive Full-Scale Anaerobic Digestion Process. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Xu, F.; Yang, T.; Wang, X.; Lyu, T.; Huang, Z. Microbial Behavior and Influencing Factors in the Anaerobic Digestion of Distiller: A Comprehensive Review. Fermentation 2023, 9, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Yan, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Jha, A.K. Specific Quorum Sensing Signal Molecules Inducing the Social Behaviors of Microbial Populations in Anaerobic Digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Sabidi, S.; Sanchez-Torres, V.; Hoshiko, Y.; Toya, S. Engineering Anaerobic Digestion via Optimizing Microbial Community: Effects of Bactericidal Agents, Quorum Sensing Inhibitors, and Inorganic Materials. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 7607–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Role and Potential of Direct Interspecies Electron Transfer in Anaerobic Digestion. Energies 2018, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordaz-Diaz, L.A.; Bailón-Salas, A.M. Molecular Identification of Microbial Communities in the Methane Production from Vinasse: A Review. Bioresources 2020, 15, 4528–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanaro, S.; Treu, L.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Kovalovszki, A.; Ziels, R.M.; Maus, I.; Zhu, X.; Kougias, P.G.; Basile, A.; Luo, G.; et al. New Insights from the Biogas Microbiome by Comprehensive Genome-Resolved Metagenomics of Nearly 1600 Species Originating from Multiple Anaerobic Digesters. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlin Christy, P.; Gopinath, L.R.; Divya, D. A Review on Anaerobic Decomposition and Enhancement of Biogas Production through Enzymes and Microorganisms. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 34, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, N.; Hintersonnleitner, A.; Wagner, A.O.; Illmer, P. Hydrogenotrophic Methanogenesis and Autotrophic Growth of Methanosarcina Thermophila. Archaea 2018, 2018, 4712608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, B. Syntrophic Associations in Methanogenic Degradation. In Molecular Basis of Symbiosis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Iltchenco, J.; Almeida, L.G.; Beal, L.L.; Marconatto, L.; dos Anjos Borges, L.G.; Giongo, A.; Paesi, S. Microbial Consortia Composition on the Production of Methane from Sugarcane Vinasse. Biomass. Convers. Biorefin. 2020, 10, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anukam, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Naqvi, M.; Granström, K. A Review of the Chemistry of Anaerobic Digestion: Methods of Accelerating and Optimizing Process Efficiency. Processes 2019, 7, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, A.F.; Janke, L.; Harms, H.; Zang, J.W.; Fonseca-Zang, W.A.; Stinner, W.; Nikolausz, M. Assessment of the Variations in Characteristics and Methane Potential of Major Waste Products from the Brazilian Bioethanol Industry along an Operating Season. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 4022–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, L.; Leite, A.; Nikolausz, M.; Schmidt, T.; Liebetrau, J.; Nelles, M.; Stinner, W. Biogas Production from Sugarcane Waste: Assessment on Kinetic Challenges for Process Designing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20685–20703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Lebon, E.; Akinlabi, E.; Madyira, D.; Adelard, L. Influence of Inoculum to Substrate Ratio on Methane Production in Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) Tests of Sugarcane Distillery Waste Water. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 35, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillet, H.; Adelard, L. Start-Up Strategy and Process Performance of Semi-Continuous Anaerobic Digestion of Raw Sugarcane Vinasse. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2021, 12, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquerizo, F.R.; Cruz-Salomon, A.; Valdovinos, E.R.; Pola- Albores, F.; Lagunas- Rivera, S.; Meza- Gordillo, R.; Ruiz Valdiviezo, V.M.; Simuta Champo, R.; Moreira- Acosta, J. Anaerobic Treatment of Vinasse from Sugarcane Ethanol Production in Expanded Granular Sludge Bed Bioreactor. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2017, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, M.P.C.; Brenelli, L.B.; Mockaitis, G.; Rabelo, S.C.; Franco, T.T.; Moraes, B.S. Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) from Sugarcane Biorefinery Residues: Maximizing Their Use by Co-Digestion. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiochet Pinto, L.; Pinheiro Neto, D.; de Leles Ferreira Filho, A.; Domingues, E.G. An Alternative Methodology for Analyzing the Risk and Sensitivity of the Economic Viability for Generating Electrical Energy with Biogas from the Anaerobic Bio-Digestion of Vinasse. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, I.Z.; dos Santos, I.F.S.; Barros, R.M.; de Castro e Silva, H.L.; Tiago Filho, G.L.; Moni e Silva, A.P. Vinasse Biogas Energy and Economic Analysis in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanez, R.; Chiaranda, B.C.; Ferreira, R.G.; França, A.L.P.; Honório, C.D.; Rodrigues, J.A.D.; Ratusznei, S.M.; Zaiat, M. Anaerobic Biological Treatment of Vinasse for Environmental Compliance and Methane Production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.S.; Ricci, B.C.; França Neta, L.S.; Amaral, M.C.S. Sugarcane Vinasse Treatment by Two-Stage Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor: Effect of Hydraulic Retention Time on Changes in Efficiency, Biogas Production and Membrane Fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, V.T.; Santos, F.S.; Amaral, M.C.S. Two-Stage Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor for the Treatment of Sugarcane Vinasse: Assessment on Biological Activity and Filtration Performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verona Peruzzo, V.; Sachet, F.H.; R Torres, A.P.; de Souza, M.P.; Beal, L.L. Influence of Sulfide on the Evaluation of Methane Production through the Degradation of Sugarcane Vinasse. Sci. Cum. Ind. 2018, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyberatos, G.; Pullammanappallil, P.C. Anaerobic Digestion in Suspended Growth Bioreactors. In Environmental Biotechnology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 395–438. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, J.J.; da Silva, B.F.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Stradiotto, N.R. Sample preparation and antibiotic quantification in vinasse generated from sugarcane ethanol fuel production. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1666, 462833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, L.; Leite, A.F.; Batista, K.; Silva, W.; Nikolausz, M.; Nelles, M.; Stinner, W. Enhancing Biogas Production from Vinasse in Sugarcane Biorefineries: Effects of Urea and Trace Elements Supplementation on Process Performance and Stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 217, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetten, M.S.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Methanogenesis from Acetate: A Comparison of the Acetate Metabolism in Methanothrix soehngenii and Methanosarcina Spp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1992, 88, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintsche, B.; Glaser, K.; Sträuber, H.; Centler, F.; Liebetrau, J.; Harms, H.; Kleinsteuber, S. Trace Elements Induce Predominance among Methanogenic Activity in Anaerobic Digestion. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- España-Gamboa, E.; Mijangos-Cortes, J.; Barahona-Perez, L.; Dominguez-Maldonado, J.; Hernández-Zarate, G.; Alzate-Gaviria, L. Vinasses: Characterization and Treatments. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 1235–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.P.; Lovato, G.; Albanez, R.; Ratusznei, S.M.; Rodrigues, J.A.D. Improvement of Sugarcane Stillage (Vinasse) Anaerobic Digestion with Cheese Whey as Its Co-Substrate: Achieving High Methane Productivity and Yield. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 189, 987–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López González, L.M.; Pereda Reyes, I.; Romero Romero, O. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sugarcane Press Mud with Vinasse on Methane Yield. Waste Manag. 2017, 68, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovato, G.; Batista, L.P.P.; Preite, M.B.; Yamashiro, J.N.; Becker, A.L.S.; Vidal, M.F.G.; Pezini, N.; Albanez, R.; Ratusznei, S.M.; Rodrigues, J.A.D. Viability of Using Glycerin as a Co-Substrate in Anaerobic Digestion of Sugarcane Stillage (Vinasse): Effect of Diversified Operational Strategies. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 720–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syaichurrozi, I.; Rusdi, R.; Dwicahyanto, S.; Toron, Y.S. Biogas Production from Co-Digestion Vinasse Waste and Tofu-Processing Wastewater and Kinetics. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2016, 6, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Tripathi, S.; Balomajumder, C. Characterization of Pressmud: A Sugar Industry Waste. Fuel 2011, 90, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangavati, P.B.; Safi, M.J.; Singh, A.; Prasad, B.; Mishra, I.M. Pyrolysis and Thermal Oxidation Kinetics of Sugar Mill Press Mud. Acta 2005, 428, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Martínez, R.D.; Sanches-Pereira, A.; Ortiz, W.; Galindo, M.F.G.; Coelho, S.T. The State-of-the-Art of Organic Waste to Energy in Latin America and the Caribbean: Challenges and Opportunities. Renew Energy 2020, 156, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA Outlook for Biogas and Biomethane: Prospects for Organic Growth; IEA: Paris, France, 2020.
- Li, Y.-R.; Song, X.-P.; Wu, J.-M.; Li, C.-N.; Liang, Q.; Liu, X.-H.; Wang, W.-Z.; Tan, H.-W.; Yang, L.-T. Sugar Industry and Improved Sugarcane Farming Technologies in China. Sugar Technol. 2016, 18, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundhoo, Z.M.A.; Mauthoor, S.; Mohee, R. Potential of Biogas Production from Biomass and Waste Materials in the Small Island Developing State of Mauritius. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 1087–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López González, L.M.; Pereda Reyes, I.; Pedraza Garciga, J.; Barrera, E.L.; Romero Romero, O. Energetic, Economic and Environmental Assessment for the Anaerobic Digestion of Pretreated and Codigested Press Mud. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Melchor, D.J.; Cañizares-Villanueva, R.O.; Terán-Toledo, J.R.; López-Pérez, P.A.; Cristiani-Urbina, E. Hydrodynamic and Mass Transfer Characterization of Flat-Panel Airlift Photobioreactors for the Cultivation of a Photosynthetic Microbial Consortium. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 128, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Arroyave, C.; Peláez, C. Effect of Using Effluent from Anaerobic Digestion of Vinasse as Water Reuse on Ethanol Production from Sugarcane-Molasses. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriroth, K.; Vanichsriratana, W.; Sunthornvarabhas, J. The Current Status of Sugar Industry and By-Products in Thailand. Sugar Technol. 2016, 18, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harihastuti, N.; Yuliasni, R.; Djayanti, S.; Handayani, N.I.; Rame, R.; Prasetio, A.; Kadier, A. Full-Scale Application of Up-Flow High Rate Anaerobic Reactor with Substrate Modification and Effluent Recirculation for Sugarcane Vinasse Degradation and Biogas Generation. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Neto, J.V.; Gallo, W.L.R.; Nour, E.A.A. Production and Use of Biogas from Vinasse: Implications for the Energy Balance and GHG Emissions of Sugar Cane Ethanol in the Brazilian Context. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2020, 39, 13226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, L.A.B.; Rossell, C.E.V.; Jordan, R.A.; Leal, M.R.L.V.; Lora, E.E.S. R&D Needs in the Industrial Production of Vinasse. In Sugarcane Bioethanol—R&D for Productivity and Sustainability; ditora Edgard Blücher: São Paulo, Brazil, 2014; pp. 619–636. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva Neto, J.V.; Elaiuy, M.L.C.; Nour, E.A.A. ADM1 Approach to the Performance Optimisation and Biogas H2S Prediction of a Large-Scale Anaerobic Reactor Fed on Sugarcane Vinasse. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, I.; Borzacconi, L.; Passeggi, M. Anaerobic Treatment of Sugar Cane Vinasse: Treatability and Real-Scale Operation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, I.; Redjeki, S.; Astuti, D.H. Biogas Production and Removal COD—BOD and TSS from Wastewater Industrial Alcohol (Vinasse) by Modified UASB Bioreactor. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 58, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.E.; Fuzaro, G.; Polegato, A.R. Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Vinasse in Pilot Plant UASB Reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Nery, V.; Alves, I.; Zamariolli Damianovic, M.H.R.; Pires, E.C. Hydraulic and Organic Rates Applied to Pilot Scale UASB Reactor for Sugar Cane Vinasse Degradation and Biogas Generation. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 119, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- España-Gamboa, E.I.; Mijangos-Cortés, J.O.; Hernández-Zárate, G.; Maldonado, J.A.D.; Alzate-Gaviria, L.M. Methane Production by Treating Vinasses from Hydrous Ethanol Using a Modified UASB Reactor. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Díaz, A.; Pereda-Reyes, I.; Oliva-Merencio, D.; Lebrero, R.; Zaiat, M. Anaerobic Digestion of Sugarcane Vinasse Through a Methanogenic UASB Reactor Followed by a Packed Bed Reactor. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, R.M.; Seabra, J.E.A. Technical-Economic Assessment of Different Biogas Upgrading Routes from Vinasse Anaerobic Digestion in the Brazilian Bioethanol Industry. Energy 2017, 119, 754–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuess, L.T.; Zaiat, M. Economics of Anaerobic Digestion for Processing Sugarcane Vinasse: Applying Sensitivity Analysis to Increase Process Profitability in Diversified Biogas Applications. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 115, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Neto, J.V.; Gallo, W.L.R. Potential Impacts of Vinasse Biogas Replacing Fossil Oil for Power Generation, Natural Gas, and Increasing Sugarcane Energy in Brazil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontam, G.; Cambon, J.-L. Method and Device for Manufacturing Combustible Gases by Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Residues. EP Patent 79832-A, 16 November 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Olivo, C.; Lebedeva, I.; Chu, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Wu, S.Y. A Patent Analysis on Advanced Biohydrogen Technology Development and Commercialisation: Scope and Competitiveness. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 14103–14110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirnev, P.C.S.; Carvalho, J.C.; Vandenberghe, L.P.S.; Karp, S.G.; Soccol, C.R. Technological Mapping and Trends in Photobioreactors for the Production of Microalgae. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.C.; Braga, M.Q.; Ázara, M.S.; Garcia, K.J.; Alencar, S.N.M.; Ramos, T.S.; Siniscalchi, L.A.B.; Assemany, P.P.; Ensinas, A.V. Recovery of vinasse with combined microalgae cultivation in a conceptual energy-efficient industrial plant: Analysis of related process considerations. Renew. Sustain. EnergyRev. 2022, 155, 111904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, P.; Andersen, M.; Lübeck, M. Method for Providing Proteins and Fermentation Products from a Plant Material. WO2015197078A1, 25 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hans-Joachim, A. Method for Exploitation of Material and Energy from Wastes from/ /Sugar Cane Processing and Arrangement for Carrying out the Method. BR Patent 1120190097686A2, 13 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, R.G.; Goldenberg, S.; Cherix, J.; Mattos, L.F.A. Effuent Valuation Process of the Sucro Energy Sector. BR Patent 102016023277-5A2, 06 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Godoy, A.; Lorenzi, M.S.; Paulillo, S.C.L.; Machado, S.C.V.; Lucas, C.M.R.S.; Lopes, M.L. Integrated Process of Oil and Biogas Production from Vinasse. BR Patent 1020150310110A8, 10 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, J.; Coelho, R.S. Process for Production of Bioenergy and Biofertilizers through Anaerobic Digestion and Algae Cultivation Using Agro-Industrial by-Products. BR Patent 132014025044, 07 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, E.M.; Gardemann, A.A. Equipment and Process for Anaerobic Digestion of Vinasse and Biogas Production. BR Patent 1020140247572A2, 03 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger, G.; Dunaev, T. Ethanol and Biogas Production Method, and Ethanol Installation for Ethanol and Biogas Production. BR Patent 1020130219029A2, 27 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Florindo, E.; Marcello, A. Biological Purification Plant for Recycling of Vegetable Vegetable Waste. BR Patent 1020120203359A2, 14 August 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Frohlich, S. Vinasse Treatment System with Power Generation, Reuse Water Generation and Concentrated Organic Fertilization. BR Patent 1100736-2 B1, 21 January 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Goldemberg, S.; Ambrogi, V.S. Method of Sequential Treatment of Wastes from the Sugar and Alcohol Sector with Production of Microalgal Biomass and Production of Renewable Fuels. BR Patent 09039848A2, 14 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Giannetti, B.W. Incentivized Methanization of the Concentrated Organic Matter of the Effluent from Ethyl Alcohol Distillation. BR Patent 0704885A2, 18 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Audi, R. Processes for Obtaining CO + H2O through the Reform of CH4 from Biogas in an Aluminum / Nickel and Water Vapor Mixed-Bed Gasifier, as Well as CO2 / Hydrocarbon Reform through the Integral Biogas Passage into the Fixed-Bed Reformer to Obtain CO. BR Patent PI 0002731-6, 13 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Audi, R. Process for Obtaining Methanol from Waste and Waste Left by the Production of Ethanol and Sugar. BR Patent 97043826A, 15 December 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, E. Vinasse to Generate Energy. Pesquisa FAPESP. Available online: www.revistapesquisa.fapesp.br (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- COGEN, (Associação da Indústria de Cogeração de Energia) ABiogás Divulga Novo Potencial Do Biogás Para o Mercado Brasileiro Durante Fórum Em São Paulo. 2022. Available online: https://www.cogen.com.br (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- FINEP Brasil Domina Tecnologia Que Transforma Vinhaça Em Biogás. Available online: www.finep.gov.br (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Bioenergia Produção de Biogás e o Setor Sucroenergético. Available online: www.canalbioenergia.com.br (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Buosi, G. Projeto Pioneiro Em Distribuição de Biometano Segue Em Expansão. 2022. Available online: www.imparcial.com.br (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- UNICA Usina de Biogás Da Raízen Entra Em Operação Comercial. 2022. Available online: www.unica.com.br (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Zaparolli, D. O Impulso Que Vem Do Canavia. Available online: https://revistapesquisa.fapesp.br/o-impulso-que-vem-do-canavial/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Khasreen, M.M.; Banfill, P.F.G.; Menzies, G.F. Life-Cycle Assessment and the Environmental Impact of Buildings: A Review. Sustainability 2009, 1, 674–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizen. 2020 Circular Economy. Available online: www.raizen.com.br/en/sustainability/circular-economy (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- EPE, (Empresa de Pesquisa Energética) Balanço Energético Nacional (BEN)—Séries Históricas Completas. Available online: www.epe.gov.br (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Maga, D.; Thonemann, N.; Hiebel, M.; Sebastião, D.; Lopes, T.F.; Fonseca, C.; Gírio, F. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of First- and Second-Generation Ethanol from Sugarcane in Brazil. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2019, 24, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longati, A.A.; Lino, A.R.A.; Giordano, R.C.; Furlan, F.F.; Cruz, A.J.G. Biogas Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Vinasse in Sugarcane Biorefinery: A Techno-Economic and Environmental Analysis. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2020, 11, 4573–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, B.S.; Junqueira, T.L.; Pavanello, L.G.; Cavalett, O.; Mantelatto, P.E.; Bonomi, A.; Zaiat, M. Anaerobic Digestion of Vinasse from Sugarcane Biorefineries in Brazil from Energy, Environmental, and Economic Perspectives: Profit or Expense? Appl. Energy 2014, 113, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuess, L.T.; Klein, B.C.; Chagas, M.F.; Alves Ferreira Rezende, M.C.; Garcia, M.L.; Bonomi, A.; Zaiat, M. Diversifying the Technological Strategies for Recovering Bioenergy from the Two-Phase Anaerobic Digestion of Sugarcane Vinasse: An Integrated Techno-Economic and Environmental Approach. Renew. Energy 2018, 122, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira, T.L.; Chagas, M.F.; Gouveia, V.L.R.; Rezende, M.C.A.F.; Watanabe, M.D.B.; Jesus, C.D.F.; Cavalett, O.; Milanez, A.Y.; Bonomi, A. Biotechnology for Biofuels Techno—Economic Analysis and Climate Change Impacts of Sugarcane Biorefineries Considering Different Time Horizons. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán-Escandón, A.; Ruiz, J.M.O.; Tigre, J.D.C.; Zalamea-León, E.F. Assessment of Power Generation Using Biogas from Landfills in an Equatorial Tropical Context. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, E.L.; Rosa, E.; Spanjers, H.; Romero, O.; De Meester, S.; Dewulf, J. A Comparative Assessment of Anaerobic Digestion Power Plants as Alternative to Lagoons for Vinasse Treatment: Life Cycle Assessment and Exergy Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, I.C.; Seabra, J.E.A.; Silva, E.A.R. Green House Gases Emissions in the Production and Use of Ethanol from Sugarcane in Brazil: The 2005 / 2006 Averages and a Prediction for 2020. Biomass. Bioenergy 2020, 32, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, T.D.F.; Cavalett, O.; Chagas, M.F.; De Morais, E.R.; Nunes, J.L.; Franco, H.C.J.; Galdos, M.V.; Scarpare, F.V.; Braunbeck, O.A.; Cortez, L.A.B.; et al. Technical and Economic Assessment of Trash Recovery in the Sugarcane Bioenergy. Sci. Agric. 2013, 62, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Novacana Sugarcane and Ethanol Production Costs and the New Technologies of the Plants. Available online: www.novacana.com (accessed on 26 December 2022).
- Longati, A.A.; Cavalett, O.; Cruz, A.J.G. Life Cycle Assessment of Vinasse Biogas Production in Sugarcane Biorefineries; Elsevier Masson SAS: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 40, ISBN 9780444639653. [Google Scholar]
- Boontian, N.; Phorndon, T.; Piasai, C.; Padri, M. Combination of Alkaline and Heat Pretreatments with Zero-Valent Iron Application in Cassava Pulp and Wastewater for Methane Generation: Development from Batch to Continuous Systems. Fermentation 2023, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel-Rosales, A.; Montalvo-Romero, N.; García-Santamaría, L.E.; Sandoval-Herazo, L.C.; Bautista-Santos, H.; Fernández-Lambert, G. Post-Industrial Use of Sugarcane Ethanol Vinasse: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bkoor Alrawashdeh, K.A.; Al-Zboon, K.K.; Al-Tabbal, J.A.; AL-Samrraie, L.A.; Al Bsoul, A.; Damseh, R.A.; Khasawneh, A.; Dessouky, Y.; Tonbol, K.; Ali, B.M.; et al. The Effects of Nanoparticles- Zerovalent Iron on Sustainable Biomethane Production through Co-Digestion of Olive Mill Wastewater and Chicken Manure. Fermentation 2023, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, J.C.; Molina-Aulestia, D.T.; Martinez-Burgos, W.J.; Karp, S.G.; Manzoki, M.C.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; Rodrigues, C.; Scapini, T.; Vandenberghe, L.P.d.S.; Vieira, S.; et al. Agro-Industrial Wastewaters for Algal Biomass Production, Bio-Based Products, and Biofuels in a Circular Bioeconomy. Fermentation 2022, 8, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hao, Y.; Yang, T.; Xiao, W.; Pan, M.; Huo, S.; Lyu, T. Enhancing Bioenergy Production from the Raw and Defatted Microalgal Biomass Using Wastewater as the Cultivation Medium. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, B.B.; Overmans, S.; Medina, J.S.; Hong, P.Y.; Lauersen, K.J. Biomass Generation and Heterologous Isoprenoid Milking from Engineered Microalgae Grown in Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor Effluent. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, J.C.; Magalhães, A.I.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; Sydney, E.B.; Rodrigues, C.; Aulestia, D.T.M.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Soccol, V.T.; Soccol, C.R.; et al. Microalgal Biomass Pretreatment for Integrated Processing into Biofuels, Food, and Feed. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, J.C.; Goyzueta-Mamani, L.D.; Molina-Aulestia, D.T.; Magalhães Júnior, A.I.; Iwamoto, H.; Ambati, R.R.; Ravishankar, G.A.; Soccol, C.R. Microbial Astaxanthin Production from Agro-Industrial Wastes—Raw Materials, Processes, and Quality. Fermentation 2022, 8, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverio, M.S.; Calegari, R.P.; Leite, G.M.F.L.; Martins, B.C.; da Silva, E.A.; Neto, J.P.; Cusatis, M.W.; Calegari, R.P.; Gomig, A.; Baptista, A.S. Biogas Production from Second Generation Ethanol Vinasse. In Agronomia: Elo da Cadeia Produtiva; Silva, D.A.S., Ed.; Atena Editora: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2019; Volume 6, pp. 174–184. ISBN 978-85-7247-825-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sydney, E.B.; Novak, A.C.; Rosa, D.; Pedroni Medeiros, A.B.; Brar, S.K.; Larroche, C.; Soccol, C.R. Screening and Bioprospecting of Anaerobic Consortia for Biohydrogen and Volatile Fatty Acid Production in a Vinasse Based Medium through Dark Fermentation. Process Biochem. 2018, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raízen, S.A. Notice to the Market. Available online: https://api.mziq.com/mzfilemanager/v2/d/c016735f-1711-48ce-919f-a8c701b83c19/b3aeaa8b-be9d-c547-ce73-10dc4c750e5b?origin=1 (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Arif, S.; Batool, A.; Nazir, W.; Khan, R.S.; Khalid, N. Physiochemical Characteristics Nutritional Properties and Health Benefits of Sugarcane Juice. In Non-Alcoholic Beverages; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 227–257. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhu, R.; Gnansounou, E.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Bioconversion of Sugarcane Crop Residue for Value Added Products–An Overview. Renew. Energy 2016, 98, 203–215. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Arriaga, E.B.; Reynoso-Deloya, M.G.; Guillén-Garcés, R.A.; Falcón-Rojas, A.; García-Sánchez, L. Enhanced Methane Production and Organic Matter Removal from Tequila Vinasses by Anaerobic Digestion Assisted via Bioelectrochemical Power-to-Gas. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 320, 124344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Co-Substrate | Proportion (Vinasse: Co-Substrate) | Solids Content | BMP, as Reported | BMP, Recalculated, NL CH4 kg−1 COD | HRT or Batch Duration, Days | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Press mud (filter cake) | 75:25, VS% basis | 7.1% | 365 L CH4 kg−1 VS | 268.1 NL CH4 kg−1 COD | 24.1 | [117] |
| Hemicellulose hydrolysate | 75:25 Plus 1 g/L yeast extract and 15 g/L ash | 5% | 279 CH4 kg−1 COD | 279 NL CH4 kg−1 COD | 34 | [34] |
| Glycerin | 50:50, COD-basis | 0.5% | 15.25 mol CH4 kg COD applied | 341.6 NL CH4 kg−1 COD | 15 | [118] |
| Tofu wastewater | 20:80 by volume (74:26 by COD) | 2.1% | 159 NL CH4 kg−1 COD | 159 NL CH4 kg−1 COD | 20 | [119] |
| Cheese whey | 75:25 | 2.4% | 15.76 mmol CH4 gCOD−1 | 353 NL CH4 kg−1 COD | 20 | [116] |
| Document Number and Year | Assignee | Translated Title | IPC | Technology | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR 11 2019 009768 6 A2/WO 2018/091004 (2017) | Christine Apelt (Germany) | Process for material and energy recovery of residues from sugar cane processing and arrangement for performing the process | C12P 7/06; C12P 5/02; C02F 1/24; C02F 1/40; C02F 11/04; C02F 3/28; C02F 9/00; C05F 11/00; C05F 17/00; C05F 5/00 | Liquid and solid (ground) residues are hydrolyzed and fermented in continuous multi-stage cultures | Filed, active | [149] |
| BR 10 2016 023277 5 A2 (2016) | Federal University of Sao Carlos (Brazil) | Valorization process of effluents from the sucroenergetic sector | C02F 11/04; C02F 103/32; C05F 5/00 | The vinasse is pretreated to separate solid and liquid fractions; the liquid is used for microalgae cultivation, and the solid is used as a fertilizer, animal feed, or as a substrate in composting and biodigestion processes | Filed, active | [150] |
| BR 10 2015 031011 0 A8 (2015) | Fermentec—Tecnologias em Açúcar e Álcool Ltda. (Brazil) | Integrated process for the production of oil and biogas from vinasse | C10L 1/08; C10L 9/08; C12P 7/62 | Oleaginous yeasts are cultivated in the vinasse, and the residual broth is used for biogas production in a UASB reactor | Filed, active | [151] |
| BR 13 2014 025044 0 E2 and BR 10 2014 009156 4 A2 (2014) | Jorge Vinicius da Silva Neto (Brazil) | Process for the production of bioenergy and biofertilizers through anaerobic digestion and algae cultivation using agro-industrial by-products | C02F 9/14; C02F 3/28; C02F 3/32; C05F 5/00; C02F 103/20; C02F 103/32; C02F 11/04 | Vinasse is used for biogas production in an anaerobic reactor, and the digested broth is used for microalgae cultivation; CO2 from biogas combustion feeds the algal culture, and algal biomass feeds the biodigester | Abandoned | [152] |
| BR 10 2014 024757 2 A2 (2014) | Geo Energética Participações S.A. (Brazil) | Equipment and process for anaerobic vinasse biodigestion and biogas production | C02F 11/04; C12M 1/107 | Bioreactor of high vertical dimension with temperature control and continuous biodigestion process with biomass recirculation and O2 injection for biological consumption of H2S | Filed, active | [153] |
| BR 10 2013 021902 9 A2 (2013) | Veolia Water Solutions & Technologies Support (USA) | Method of ethanol and biogas production, and ethanol facility for the production of ethanol and biogas | C12P 7/06; C12P 7/14; C02F 9/02; C12M 1/107 | Biogas is produced from “distilled beer” vinasse in a membrane anaerobic bioreactor | Abandoned | [154] |
| BR 10 2012 020335 9 A2 (2012) | Geo Energética Participações S.A. (Brazil) | Biological purification production plant for recycling vegetable waste from sugar and alcohol production | C02F 103/32; C02F 9/14; C02F 9/08 | Two tank bioreactors and one lagoon to process solid and liquid wastes from distilleries producing biogas and an organic fertilizer | Filed, active | [155] |
| PI 1100736-2 B1 (2011) | Arka Ambiental Ltd.a. (Brazil) | Vinasse treatment system with power generation, reuse water generation, and concentrated organic fertilization | C12F 3/00; F03G 7/00; C05F 5/00 | Anaerobic reactor of internal circulation; system of biogas washing and drying for use in electric energy generation; system of ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis to separate reuse water and fertilizer | Granted, active | [156] |
| PI 0903984-8 A2 (2009) | Algae Biotecnologia Ltd.a. (Brazil) | Method of sequential treatment of wastes from the sugar and alcohol sector with production of microalgal biomass and production of renewable fuels | C12S 3/10; C12S 3/02; C12R 1/865; C12R 1/89 | Cultivation of microalgae in clarified vinasse, while the removed solids are destined for biogas and biofertilizer production; the residual liquid can alternatively be used for microalgae cultivation, and microalgal biomass can be alternatively biodigested; microalgae can biologically purify biogas | Abandoned | [157] |
| PI 0915815-4 B1/WO 2010/003397 (2009) | Johann Rietzler (Germany) | Process for the production of methane from process waters and biogenic material | C12P 5/02; C02F 3/28; C02F 3/30; C12M 1/113 | Process water containing biogenic material is converted to methane by immobilized or free bacteria, with biogas recirculation inside the bioreactor | Granted, active | [63] |
| PI 0704885-8 A2 (2007) | Bruce Wilson Giannetti (Brazil) | Incentivized methanization of the concentrated organic matter of the effluent from ethyl alcohol distillation | C07C 9/04; C02F 11/04 | The process comprises a reactor containing a membrane of expanded clay spheres serving as support for methanogenic bacteria; the effluent is pumped through sprayers inside the membrane; part of the biogas is reinjected inside the membrane to force the release of gas bubbles | Abandoned | [158] |
| PI 0002731-6 A2 (2000) | Ricardo Audi (Brazil) | Processes for obtaining CO + H2O through the reform of CH4 from biogas in an aluminum/nickel and water vapor mixed-bed gasifier, as well as CO2/hydrocarbon reform through the integral biogas passage into the fixed-bed reformer to obtain CO | C01B 3/40; C01B 3/44; C01B 32/40 | A process that involves biogas production from vinasse anaerobic digestion, separation of CO2 by monoethanolamine absorption, and CH4 reform in a fluidized bed gasifier to produce CO and H2; also, the biogas passes through a fixed-bed tubular reactor with catalyzers and is converted to CO | Denied | [159] |
| PI 0002730-8 A2 PI 9905239-3 A2 PI 9905240-7 A2 PI 9706185-9 A2 PI 9704382-6 A2 (1997-2000) | Ricardo Audi (Brazil) | Various | Various | Technologies involving the catalytic reform of CH4 obtained from vinasse anaerobic digestion, resulting in syngas for the synthesis of organic molecules | Abandoned or denied | [160] |
| Biorefinery Products | Climate Change Impacts (gCO2eq/ MJethanol) | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First-Generation Ethanol | Second-Generation Ethanol | Sugar | Vinasse | Energy | ||
| X | - | - | - | X | 17.2 | [172] |
| X | - | - | X | X | 16.8 | |
| X | X | - | - | X | 15.5 | |
| X | X | - | X | X | 15.2 | |
| X | X a | - | X b | X | 15.9 | |
| X | X a | - | X c | X | 15.6 | |
| X | - | - | - | - | 23.7 | [175] |
| X | - | - | X | X | 13.5 | |
| X | X | - | X | X | 10.9 | |
| - | - | - | X | X | 11.3 e | [76] |
| X | - | X | - | X | 23.0 f | [174] |
| X | - | X | X | X | 22.6 f | |
| X | X | X d | X | 22.8 f | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Carvalho, J.C.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Sydney, E.B.; Karp, S.G.; Magalhães, A.I., Jr.; Martinez-Burgos, W.J.; Medeiros, A.B.P.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Vieira, S.; Letti, L.A.J.; et al. Biomethane Production from Sugarcane Vinasse in a Circular Economy: Developments and Innovations. Fermentation 2023, 9, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040349
de Carvalho JC, de Souza Vandenberghe LP, Sydney EB, Karp SG, Magalhães AI Jr., Martinez-Burgos WJ, Medeiros ABP, Thomaz-Soccol V, Vieira S, Letti LAJ, et al. Biomethane Production from Sugarcane Vinasse in a Circular Economy: Developments and Innovations. Fermentation. 2023; 9(4):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040349
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Carvalho, Júlio Cesar, Luciana Porto de Souza Vandenberghe, Eduardo Bittencourt Sydney, Susan Grace Karp, Antonio Irineudo Magalhães, Jr., Walter José Martinez-Burgos, Adriane Bianchi Pedroni Medeiros, Vanete Thomaz-Soccol, Sabrina Vieira, Luiz Alberto Junior Letti, and et al. 2023. "Biomethane Production from Sugarcane Vinasse in a Circular Economy: Developments and Innovations" Fermentation 9, no. 4: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040349
APA Stylede Carvalho, J. C., de Souza Vandenberghe, L. P., Sydney, E. B., Karp, S. G., Magalhães, A. I., Jr., Martinez-Burgos, W. J., Medeiros, A. B. P., Thomaz-Soccol, V., Vieira, S., Letti, L. A. J., Rodrigues, C., Woiciechowski, A. L., & Soccol, C. R. (2023). Biomethane Production from Sugarcane Vinasse in a Circular Economy: Developments and Innovations. Fermentation, 9(4), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9040349