Abstract
Chenopodium album L. (CAL) is an excellent vegetable crop that is rich in nutrients and possesses potential pharmaceutical value. However, the research on the secondary metabolites and the processing utilization of CAL has been rarely reported. In this study, the polyphenol content, microstructure and secondary metabolite composition of aerial parts of CAL (AC), including stems, leaves, inflorescence and grain, before and after fermentation were investigated. The results showed that the polyphenol content of fermented AC (FAC) was significantly higher than that of AC (increased by 38.62%). The AC had a compact surface, while FAC had a loose and cracked surface with large holes. A total of 545 secondary metabolites, including 89 alkaloids, 179 flavonoids, 25 lignans and coumarins, 163 phenolic acids, 35 terpenoids, 9 quinones, 6 tannins and 39 others, were identified in the AC and FAC by UHPLC-QQQ-MS metabolomics. Differential metabolites analysis reviewed 285 differential metabolites (117 upregulated and 168 downregulated) between AC and FAC. The decrease in parts of toxic alkaloids accompanied with the increase in some biologically active substances with small molecules, such as quercetin, kaempferol, p-coumaric acid and protocatechuic acid, indicated that fermentation is beneficial to enhance the bioavailability of AC. This study provides a reference value for the identification of secondary metabolites from AC and the application of fermentation in the deepness development of AC.
1. Introduction
Chenopodium is a species considered to be an excellent vegetable crop [1] because it can provide proteins, dietary fiber, minerals, vitamins and essential fatty acids [2]. Chenopodium album L. (CAL), also known as lamb’s quarter, is a natural plant which withstands harsh soil and climatic conditions, distributed around the world, including in semi-arid and light-saline environments of China [1,3]. The potential pharmaceutical value of this plant, such as antiscorbutic, diuretic, anthelmintic and cardiotonic, has been demonstrated [4]. It can also be used for the treatment of peptic ulcer, flatulence, hepatic disorders, spleen enlargement and burns [5]. CAL contains many secondary metabolites, including polyphenols, flavonoids and alkaloids, which exhibit strong antioxidant, antibacterial, anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity [1,2]. Laghari et al. (2011) [6] confirmed that the extract of CAL leaves had a high level of total phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity and revealed that the extract of CAL leaves has great potential as a source for natural health products.
A scanning of the literature has revealed that the CAL also contain some antinutritional factors such as saponins, tannins and phytic acid, which limits the digestion and utilization of proteins and carbohydrates by animals [7]. Fermentation is a traditional technique for food quality modification, which transforms complex organic substances into a simpler form, increases the nutritional value of raw material(s) and enhances specific biological functionalities due to the created secondary metabolites [8]. It has been proven that fermentation decreases the phytic acid level of wheat bran [9], and total tannin, oxalic acid, phytic acid and saponin of paper mulberry [10]. Therefore, it is worth trying to use fermentation technology for the depth development of CAL. The previous study in our lab established the fermentation conditions for aerial parts of CAL (AC) and found that fermented AC (FAC) had positive effects on growth, nutrient digestibility, immunity, carcass characteristics and meat quality of broilers [3]. However, the investigation on secondary metabolites analysis of CAL was limited, and no work about the effects of fermentation on secondary metabolites of CAL has been reported.
In recent years, widely targeted metabolomics analysis, mostly based on ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QQQ-MS), has been increasingly applied in the field of analysis and identification of secondary metabolites in plants, due to its advantages of high throughput, fast separation, high sensitivity and wide coverage [11,12,13]. It integrates the advantages of nontargeted and targeted metabolite detection technologies and provides an effective qualitative and quantitative method to identify secondary metabolites [14]. Therefore, the polyphenol content and microstructure of aerial parts of CAL (including stems, leaves, inflorescence and grain) before and after fermentation were compared. Then, the UHPLC-QQQ-MS metabolomics approach was employed to analyze the types and relative contents of secondary metabolites. These results enrich our understanding of the chemical components of AC and provide a reference for the application of fermentation in the deepness development of AC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The CAL used in this work was collected from April to November in Hohhot (Inner Mongolia, Hohhot, China) and identified by Professor Zhaozhe Li of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. The aerial parts of CAL, including stems, leaves, inflorescence and grain, were obtained, dried at 25 °C in the shade, ground to a fine powder and then combined for further fermentation. Bacillus subtilis (CGMCC 1.0892), Lactobacillus plantarum (CGMCC No.1.12934) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (CGMCC No. 2.1190) were purchased from the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre (Beijing, China). Pectinase was obtained commercially (Beijing Solarbio Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). Maize meal and ground cinnamon were obtained from a local market. All other chemicals were of analytical grade.
2.2. Fermentation of AC and Sample Preparation
The fermentation of AC was conducted based on previous study [3]. Briefly, AC was mixed with corn meal, ground cinnamon and pectinase at a ratio of 16.5:3.0:0.1:0.4 (4 kg in total), blended with 50% distilled water (w/v), and inoculated with 0.1% compound probiotics. The compound probiotics were prepared by mixing S. cerevisiae, B. subtilis and L. plantarum at a ratio of 1:1:1. Fermentation was conducted with multi-layer polythene bags (5 kg capacity) equipped with a gas pressure opening valve in an incubator for 24 h at 30 °C. The substrate before and after fermentation, the AC and FAC, were collected, allowed to dry (45 °C, 24 h) and used for further analysis.
2.3. Determination of Polyphenol Content
Extractions of AC and FAC were performed using the hot water extraction method. The sample was extracted at 85 °C with distilled water at a ratio of 1:40 (g/mL) for 90 min. The extracts were lyophilized and kept at 4 °C. The polyphenol content of the AC and FAC extracts was determined by the Folin–Ciocalteu method according to Liu et al. (2022) [15], and gallic acid was used as a standard. An appropriate concentration of the sample solution (0.5 mL) was mixed with 10% Folin–Ciocalteu reagent (2.5 mL) and shaken. After 5 min, 2.0 mL of the 7.5% Na2CO3 solution was added to the mixture. The reaction mixture was kept in the dark for 60 min, after which the absorbance was measured at 756 nm. All the determinations were carried out in triplicate.
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
Microscopic images of the AC and FAC were recorded using a JSM-6390 LV scanning electron microscope. The AC and FAC samples were sputter-coated with gold under vacuum, and their images were viewed at an accelerating voltage of 20 kV.
2.5. Secondary Metabolites Analysis
2.5.1. Sample Preparation and Extraction Process
The AC and FAC samples are freeze-dried by vacuum freeze-dryer (Scientz-100F). The freeze-dried sample was crushed using a mixer mill (MM 400, Retsch) with a zirconia bead for 1.5 min at 30 Hz. Dissolve 100 mg of lyophilized powder with 1.2 mL 70% methanol solution, vortex 30 s every 30 min for 6 times in total, place the sample in a refrigerator at 4 °C overnight. Following centrifugation at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, the extracts were filtrated (SCAA-104, 0.22μm pore size; ANPEL, Shanghai, China) before UPLC-MS/MS analysis.
2.5.2. UPLC Conditions
The sample extracts were analyzed using an UPLC-ESI-MS/MS system (UPLC, SHIMADZU Nexera X2 system, Kyoto, Japan; MS, Applied Biosystems 4500 Q TRAP, Foster City, CA, USA). The analytical conditions were as follows. UPLC: column, Agilent SB-C18 (1.8 µm, 2.1 mm × 100 mm). The mobile phase consisted of solvent A, pure water with 0.1% formic acid, and solvent B, acetonitrile with 0.1% formic acid. Sample measurements were performed with a gradient program that employed the starting conditions of 95% A, 5% B. Within 9 min, a linear gradient to 5% A, 95% B was programmed, and a composition of 5% A, 95% B was kept for 1 min. Subsequently, a composition of 95% A, 5.0% B was adjusted within 1.1 min and kept for 2.9 min. The flow velocity was set as 0.35 mL per minute. The column oven was set to 40 °C. The injection volume was 4 μL. The effluent was alternatively connected to an ESI triple quadrupole linear ion trap (QTRAP)-MS.
2.5.3. ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS
Linear ion trap (LIT) and triple quadrupole (QQQ) scans were acquired on a triple quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometer (QTRAP, Applied AB4500 QTRAP UPLC/MS/MS System, Foster City, CA, USA), equipped with an ESI Turbo Ion Spray interface, operating in positive and negative ion mode and controlled by Analyst 1.6.3 software (AB Sciex, Framingham, MA, USA). The ESI source operation parameters were as follows: ion source, turbo spray; source temperature 550 °C; ion spray voltage (IS) 5500 V (positive ion mode)/−4500 V (negative ion mode); ion source gas I (GSI), gas II(GSII), curtain gas (CUR) was set at 50, 60 and 25.0 psi, respectively; the collision-activated dissociation (CAD) was set to high. Instrument tuning and mass calibration were performed with 10 and 100 μmoL/L polypropylene glycol solutions in QQQ and LIT modes, respectively. QQQ scans were acquired as multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) experiments with collision gas (nitrogen) set to medium. DP and CE for individual MRM transitions were carried out with further DP and CE optimization. A specific set of MRM transitions were monitored for each period according to the metabolites eluted within this period [16].
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The polyphenol content data for the AC and FAC were sorted in Excel 2020 for Windows and analyzed in triplicate, and the results were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) using SAS 9.3 for Windows. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple range tests were used to determine the significance of the differences among samples, with a significance level of 0.05.
Metabolite data were log2-transformed for statistical analysis to improve normality and were normalized. Hierarchical clustering analysis (HCA), principal component analysis (PCA), and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) have been used to analyze the multivariate and differences of metabolites by R software. Based on OPLS-DA analysis, the differential metabolites were screened by the following criteria: (1) if the difference of metabolites content between the control group and the experimental group is more than 2 times or less than 0.5, the difference is considered to be significant; (2) on the basis of the above, the metabolites with VIP ≥1 are selected. The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database was used to annotate the differential metabolites and analyze metabolic pathways. All data were graphed using GraphPad Prism v6.01 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Polyphenol Content
Polyphenols constitute a large group of plant secondary metabolites widely distributed throughout the plant-derived foods [17]. They exhibit several biological activities, for instance, functioning as antioxidant, antiaging, anti-inflammation properties, and have positive effects on human microbiota composition and functionality [18]. The levels of polyphenols of the AC and FAC are shown in Figure 1. The polyphenol content of the FAC increased to 18.59 ± 1.49 mg/g, which was a 38.62% increase compared to that of the AC (13.41 ± 1.40 mg/g). The result clearly indicated that the fermentation significantly improved the polyphenol content of AC (p < 0.05). Gan et al. (2016) [19] investigated the influences of fermentation on the polyphenols of eight common edible legumes, they found that both natural and LAB-mediated fermentation significantly enhanced polyphenol in the soluble fraction of all selected edible legumes compared to nonfermented. It coincides with the experimental results. An improvement in polyphenol content may be caused via secondary metabolic pathways in the fermentation process or released from the substrate by enzymes produced by the microorganisms [20].
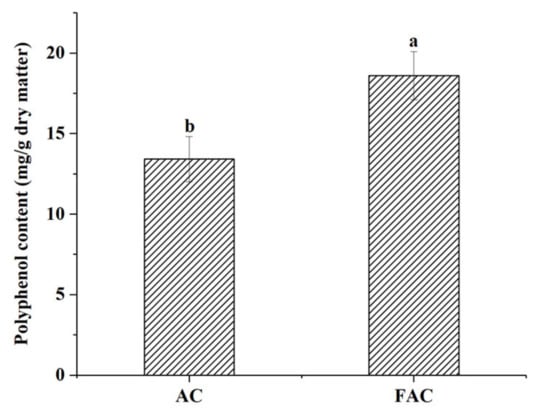
Figure 1.
The polyphenol content of AC before and after fermentation. ab p < 0.05 compared between AC and FAC.
3.2. SEM Analysis
SEM is a qualitative method for characterizing plant surface microstructure. Figure 2 shows the surface images of the AC and FAC at a magnification factor of 1000-fold. The two observations showed that both the AC and FAC had many discontinuous fragments. However, the AC had a compact surface structure and did not show obvious holes on the surface. In contrast, FAC had loose and cracked surface structure with large holes. It is reported that during the fermentation process, the micro-structure of substrate materials is altered, which further influences the retention and release of the bioactive substances in the substrate material [8]. Chen et al. (2019) compared SEM images of rice bran before and after fermentation, they found fermentation changed the microstructure of rice bran from being compact to loose and porous, and increased the extractability of bound phenolics [21]. It is suggested that fermentation treatment broke down the cell wall structure of rice bran and made the alkali ions more accessible to the covalent bonds between phenolics and fiber. Similarly, in this experiment, the polyphenol content of the AC was increased by 38.63% by fermentation, which confirmed that fermentation promoted the release of the polyphenols through changing the structure of substrate.
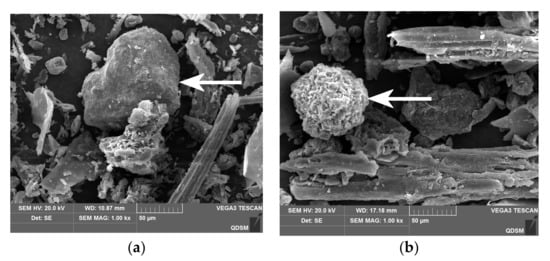
Figure 2.
SEM images of (a) AC and (b) FAC.
3.3. Data Quality Assessment and Metabolites Identified
In order to have a clearer understanding of the changes in the secondary metabolites of AC before and after fermentation, the UPLC-MS platform was adopted. The total ion current (TIC) map of the mixed sample quality control (QC) is shown in Figure S1a and shows the summed intensity of all ions in the mass spectrum at different time points [16]. Based on the local metabolic database, the metabolites of the samples were qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by mass spectrometry. The multipeak detection plot (XIC) of the metabolites in multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode is illustrated in Figure S1b, and the figure shows the substances that can be detected in the sample, and each mass peak of a different color represents a detected metabolite [22]. Through the overlap display analysis of the TIC map of different quality control QC samples (Figure S1c), the results showed the high overlap ratio of total ion current (TIC) curves of the QC samples, indicating that the signal stability was good and the test results were reliable.
A total number of 545 secondary metabolites were target identified in AC and FAC, including 89 alkaloids, 179 flavonoids, 25 lignans and coumarins, 163 phenolic acids, 35 terpenoids, 9 quinones, 6 tannins, and 39 others (Figure 3a). The accumulation pattern of secondary metabolites among AC and FAC could be visualized through a heatmap hierarchical cluster analysis (Figure 3b). The heatmap showed that the three biological replicates of each group were clustered together, indicating the good homogeneity between replicates and the high reliability of the data. Principal component analysis (PCA) is a multidimensional data statistical analysis method of unsupervised pattern recognition [22]. The PCA result showed that there are significant differences among AC and FAC groups, and no significant difference within groups (Figure 3c).
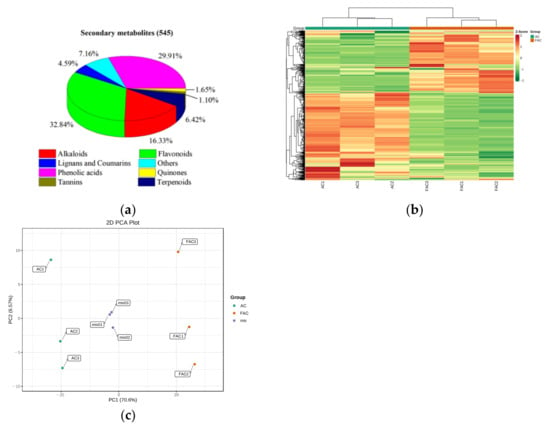
Figure 3.
Secondary metabolites identified. (a) Classification of the 545 secondary metabolites of AC and FAC; (b) hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA); (c) principal component analysis (PCA).
3.4. Identification of Differential Metabolites
Orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) is a multivariate statistical analysis method with supervised pattern recognition which can maximize group differentiation between groups and help to find differential metabolites [13]. The score plots between AC and FAC in OPLS-DA are shown in Figure 4a. In the OPLS-DA model, R2X and R2Y were used to represent the interpretation rate to the X and Y matrices, respectively, and Q2 represented the prediction ability. A Q2 value greater than 0.9 indicates that the model is excellent. According to the results (R2Y = 1, Q2 = 0.986) in Figure 4b, the models are stable and reliable and could be applied to further screen for differential metabolites. In addition, the OPLS-DA mode was verified through 200 alignment experiments, and the result confirmed that the model was meaningful (Figure 4b).
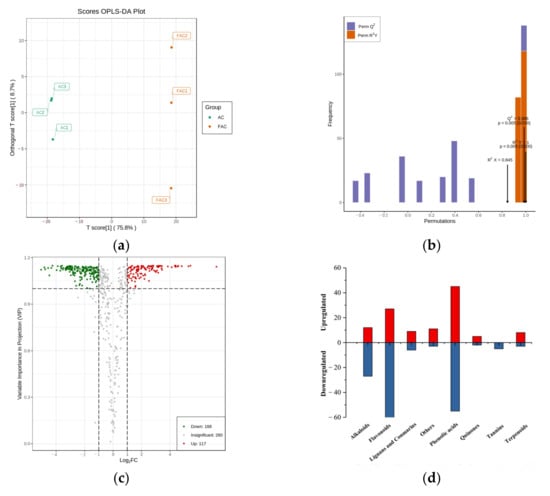
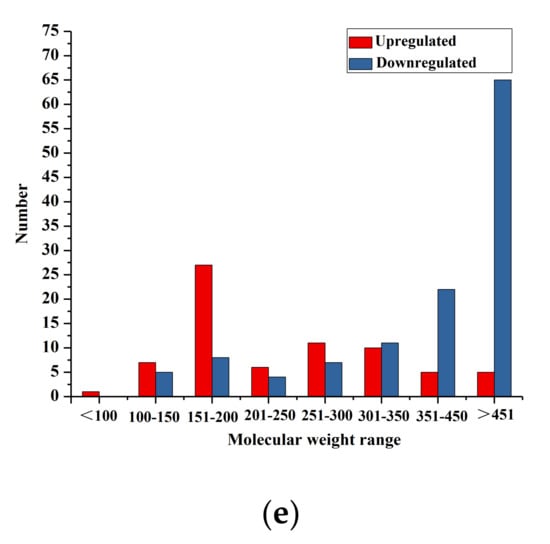
Figure 4.
Differentially accumulated metabolites between AC and FAC. (a) Score scatter plot of the OPLS-DA model; (b) permutation test of the OPLS-DA model; (c) volcano plot of the differential metabolites; (d) classification of differentially expressed metabolites; (e) molecular weight range of differential phenolic acids and flavonoids.
The differential metabolites between two sample groups could be visualized through a volcano plot (Figure 4c). The criteria for significant differences included a fold change of ≥2 or ≤0.5 and a VIP score of ≥1. A total of 285 differential metabolites were identified (Table S1) between AC and FAC. Compared with AC, 117 metabolites in FAC were upregulated, while 168 metabolites were downregulated. The differential metabolites produced during fermentation were further classified and compared. Among all these differential metabolites, there were 39 alkaloids, 94 flavonoids, 100 phenolic acids, 15 lignans and coumarins, 7 quinones, 5 tannins, 11 terpenoids and 14 others (Table S1). The major categories were alkaloids, phenolic acids and flavonoids, accounting for more than 80% of the total detected differential substances (Figure 4d).
Alkaloids is one of the largest groups of naturally occurring plant defense compounds that have been used by humans as poisons, stimulants, sedatives and medicinal substances for thousands of years [23]. Although possessing significant benefits to humans and pharmaceutical industries, some of the plant alkaloids are categorized as main plant toxins due to their enormous structural diversity [24]. Natural toxins in the plants are often not popular due to their potential hazard for human health related to their presence as contaminants in food [25]. In this study, parts of toxic alkaloid content such as serotonin, cadaverine, spermine were significantly downregulated (Table S1) after fermentation. It was demonstrated that fermentation successfully degraded the parts of the toxic compound in the AC. Similar results were observed by Deus et al. (2021) who performed fermentation of cocoa [26]. Six amines were detected during cocoa on-farm fermentation, and the total levels of most amines decreased, in which the levels of serotonin decreased continuously and could not be detected [26]. We speculated that the reason why parts of toxic alkaloids declined in this study was the degradation caused by enzymes produced by microorganisms during the fermentation process.
Flavonoids are an important class of natural products and belong to phenolic compounds. Flavonoids are synthesized by plants via primary or secondary metabolisms. Flavonoids are also an integral part of diets for humans because they cannot be synthesized by humans [27,28]. Flavonoids are associated with a broad spectrum of health-promoting effects, such as anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, anti-mutagenic and anti-carcinogenic properties coupled with their capacity to modulate key cellular enzyme function [29]. Phenolic acids, as another important class of phenolic compounds, have one carboxylic acid group and are acknowledged as strong natural antioxidants. Additionally, phenolic acids exhibit a wide range of biological and pharmacological properties including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antimicrobial, antiallergic, antiviral, antithrombotic, hepatoprotective and act as signaling molecules [30]. In comparation of differential phenolic acids and flavonoids before and after fermentation in this study, we found that the relative contents of compounds with high molecular weight were dramatically downregulated, while active substances with small molecular weight were significantly increased (Figure 4e). For instance, the relative contents of quercetin, kaempferol, p-Coumaric acid, protocatechuic acid, protocatechualdehyde and 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid of FAC were significantly higher than that of AC (Table S1). Quercetin and kaempferol are the major representative flavanols of flavonoids. Quercetin has been recognized for its multiple biological activities such as anti-oxidation, anti-inflammatory and anticancer [31]. Kenan Kinaci et al. (2012) found that quercetin increased GSH levels and decreased the eNOS and NF-κB expression levels in renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in rats [32]. In a study performed by Yuan et al. (2020), the therapeutic mechanism of quercetin for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was by inhibiting neutrophil activities [33]. Yousuf and colleagues (2020) have investigated the anticancer activity of quercetin by establishing Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6) as a target. They found that quercetin could decrease the expression of CDK6 and inhibit the viability and colony formation potential of selected cancer cells [34]. Kaempferol displays several pharmacological properties, such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer and anti-tumor activities [35]. Rho et al. (2011) isolated kaempferol from kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) leaves and evaluated its anti-inflammatory activity. They found that kaempferol showed potent NO inhibitory activity by suppressing the expression of iNOS mRNA in a dose-dependent manner without cytotoxicity [36]. Wang et al. (2021) explored the underlying molecular mechanism of kaempferol in suppressing pancreatic cancer inducing ROS-dependent apoptosis via tissue transglutaminase (TGM2)-mediated Akt/mTOR signaling [37]. P-coumaric acid is one of the most important phenolic acids, shows antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer activity and plays an important role in human health [38]. One study found that p-coumaric acid decreased basal oxidative stress more effectively than vitamin E according to DNA damages in rat colonic mucosa [39]. Lou et al. (2012) specified that p-coumaric acid exhibits an antimicrobial effect against Salmonella typhimurium, Shigella dysenteriae and Escherichia coli [40]. A study performed by Sharma et al. (2017) revealed that p-coumaric acid induces a significant dose-dependent reduction of polyp incidence in the colon of rats exposed to the procarcinogen DMH and suppresses the formation of preneoplastic lesions [41]. Protocatechuic acid is a main anthocyanin metabolite and is reported to have antioxidant activities by decreasing lipid peroxidation and increasing the scavenging of free radical scavenging such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and diphenylpicrylhydrazyl (DPPH) [42]. Protocatechuic aldehyde is the primary metabolites of proanthocyanidins and is demonstrated to have antiadipogenic, anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties both in vivo and in vitro [43]. Wei et al. (2013) investigated the anti-inflammatory effect of protocatechuic aldehyde on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (MI/R) injury. It was suggested that the levels of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, intracellular adhesion molecule-1, phosphorylated IκB-α and the nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) were all evidently decreased by protocatechuic aldehyde both in vivo and in vitro. Furthermore, protocatechuic aldehyde could exert great protective effects against MI/R injury in rats and ischemia/reperfusion (SI/R) injury in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes [44]. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a valuable intermediate for the synthesis of several bioproducts with potential applications in food, cosmetics, pharmacy, fungicides, etc. [45]. In this study, fermentation processes increased the relative contents of these active substances with small molecular weight mentioned above. The increase in active substances with small molecular weight in FAC is partially attributed to the liberation of polyphenols induced by enzymes degradation during fermentation. It is confirmed by the looser surface structure of FAC, which makes enzymes more easily able to access the interior structure of AC [21]. The results of differential metabolites of AC and FAC indicated that fermentation is beneficial to the partial degradation of toxic alkaloids and increases in biologically active substances with small molecules in aerial parts of CAL.
3.5. KEGG Annotation and Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
According to the KEGG annotation and enrichment results, the major pathways are presented in bubble plots in Figure 5. On the basis of metabolic pathway analysis, the results indicated that a total of 134 differential metabolites were annotated to metabolic pathways; the top five metabolic pathways, ranked in terms of the p-value, were “biosynthesis of secondary metabolites”, “metabolic pathways”, “ubiquinone and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis”, “biosynthesis of various secondary metabolites—part 2” and “phenylpropanoid biosynthesis” in AC versus FAC. The pathway of the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites changed dramatically before and after fermentation, which explained that the synthesis and accumulation of secondary metabolites was influenced by fermentation.
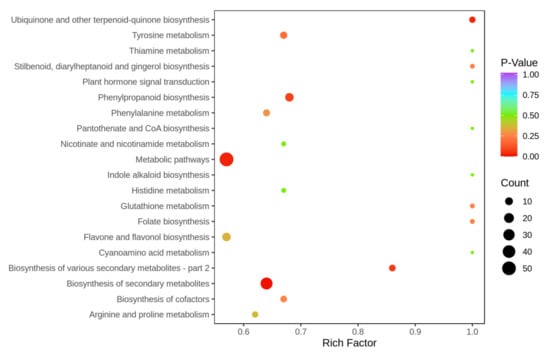
Figure 5.
Top 20 enriched KEGG pathways for differential metabolites of AC and FACL.
We focused on the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites to uncover metabolite changes. According to the biosynthesis of the secondary metabolites pathway, the relative contents of many valuable compounds were obviously increased after fermentation, for example, coumarin, scopoletin and cinnamic acid. Coumarins are a broad family of secondary metabolites found in plants [46]. Due to their physiological, bacteriostatic and anti-tumor activity, they have attracted much attention for further backbone derivatization and screening as novel therapeutic agents [47]. The coumarin nucleus has proved to be easily decorated, giving the possibility of designing new coumarin-based compounds and investigating their potential in the treatment of various diseases [46]. Scopoletin is a derivative of coumarin; one of the most widespread coumarins in nature, it has been reported to exhibit pharmacological activity, including anti-hypertensive, anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic properties [48]. Armenia et al. (2019) investigated the blood pressure lowering effect of scopoletin in oxidative stress-associated hypertensive rats, and found that scopoletin significantly decreased the systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) of the rats [49]. Cinnamic acid is a natural aromatic carboxylic acid found in plants, and has been studied in antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic properties [50]. A study conducted by Balli et al. (2020) showed that fermented millet had an approximate 30% higher cinnamic acid content and played higher antioxidant protection effects on human erythrocytes [51]. In sum, the enhancement of valuable compounds proved that fermentation improved the bioavailability of aerial parts of CAL.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the surface structure, polyphenol content and secondary metabolites of the aerial parts of CAL were considerably altered by fermentation. A total of 545 secondary metabolites, including 89 alkaloids, 179 flavonoids, 25 lignans and coumarins, 163 phenolic acids, 35 terpenoids, 9 quinones, 6 tannins and 39 others, were identified by the liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach, which is used to given us a better understanding of secondary metabolites in the aerial parts of CAL. There are 285 differential metabolites that were identified (117 upregulated and 168 downregulated), mainly concentrating on alkaloids, phenolic acids and flavonoids. After fermentation, the relative amount of biologically active substance such as quercetin, kaempferol, protocatechuic acid, protocatechualdehyde and coumarin were significantly increased, while parts of toxic alkaloids such as serotonin, cadaverine and spermine were significantly decreased. The present work lays the foundation for the application of fermentation technology for deep exploitation of the aerial parts of CAL.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation9020100/s1, Figure S1: (a) Total ion current of one quality control sample by mass spectrometry; (b) Multi-peak detection plot of metabolites in the multiple reaction monitoring mode; (c) Total ion current overlaps of the quality control sample by mass spectrometry detection. Table S1: Differential metabolites of AC and FAC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.A.; methodology, N.L.; software, N.L.; validation, Y.W.; formal analysis, N.L.; investigation, Y.W.; resources, J.Q; data curation, X.A.; writing—original draft preparation, N.L.; writing—review and editing, N.L.; supervision, X.A.; project administration, J.Q.; funding acquisition, J.Q. and X.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Major Science and Technology Program of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (grant number 2020ZD0004); Major Science and Technology Program of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (grant number 2021ZD0023-3) and Symbolic Achievements Special Fund Project of College of Animal Science of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University(grant number BZCG202110).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Choudhary, S.P.; Sharma, D.K. Bioactive constituents, phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Chenopodium album: A miracle weed. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 2014, 1, 545–552. [Google Scholar]
- Poonia, A.; Upadhayay, A. Chenopodium album Linn: Review of nutritive value and biological properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. Mysore 2015, 52, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Qi, J. Effects of dietary supplementation with fermented Chenopodium album L. on growth, nutrient digestibility, immunity, carcase characteristics and meat quality of broilers. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Asrar, M.; Rasul, A.; Sultana, S.; Saleem, U. Chenopodium album extract ameliorates carbon tetrachloride induced hepatotoxicity in rat model. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 3408–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleman, M.; Faiz, A.U.H.; Abbas, F.I. Antibacterial, antiparasitic and phytochemical activities of Chenopodium album (Bathua) plant extract. Bangladesh J. Bot. 2021, 50, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghari, A.H.; Memon, S.; Nelofar, A.; Yasmin, K.M. Determination of free phenolic acids and anti-oxidant activity of methanolic extracts obtained from fruits and leaves of Chenopodium album. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, R.; Saxena, D.C.; Singh, S. Analyzing the effect of optimization conditions of germination on the antioxidant activity, total phenolics, and antinutritional factors of Chenopodium (Chenopodium album). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Cui, C.; Ruan, Z. Fermentation-enabled wellness foods: A fresh perspective. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 203–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasković, S.J.; Šekuljica, N.; Jovanović, J.; Gazikalović, I.; Grbavčić, S.; Đorđević, N.; Luković, N.; Hao, J.; Vukašinović Sekulić, M.; Knežević-Jugović, Z. Upgrading of valuable food component contents and anti-nutritional factors depletion by solid-state fermentation: A way to valorize wheat bran for nutrition. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 99, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Lin, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Effects of Lacto bacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Paper Mulberry Silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wen, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Pang, X.; Deng, Z.; Liu, T.; Guo, Y. Study on metabolic variation in whole grains of four proso millet varieties reveals metabolites important for antioxidant properties and quality traits. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y. Analysis of flavonoid metabolites in citrus peels (Citrus reticulata “Dahongpao”) using UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Gu, C.; He, S.; Zhu, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Q. Widely targeted metabolomics analysis reveals new biomarkers and mechanistic insights on chestnut (Castanea mollissima Bl.) calcification process. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.C.; Liu, Y.J.; He, G.R.; Cao, Y.W.; Bi, M.M.; Song, M.; Yang, P.P.; Xu, L.F.; Ming, J. Comprehensive analysis of secondary metabolites in the extracts from different lily bulbs and their antioxidant ability. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, Y.; An, X.; Qi, J. Study on the Enhancement of Antioxidant Properties of Rice Bran Using Mixed-Bacteria Solid-State Fermentation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, J.; Zeng, J. Metabolomics analysis of the peels of different colored citrus fruits (Citrus reticulata cv. ‘Shatangju’) during the maturation period based on UHPLC-QQQ-MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condezo-Hoyos, L.; Gazi, C.; Pérez-Jiménez, J. Design of polyphenol-rich diets in clinical trials: A systematic review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 149, 110655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Escobar, R.; Aliaño-González, M.J.; Cantos-Villar, E. Wine polyphenol content and its influence on wine quality and properties: A review. Molecules 2021, 26, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.Y.; Shah, N.P.; Wang, M.F.; Lui, W.Y.; Corke, H. Fermentation alters antioxidant capacity and polyphenol distribution in selected edible legumes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, C.L.; de Lima, F.S.; Guelfi, M.F.G.; da Silva Fernandes, M.; Georgetti, S.R.; Ida, E.I. Parameters of the fermentation of soybean flour by Monascus purpureus or Aspergillus oryzae on the production of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dong, L.; Jia, X.; Liu, L.; Huang, F.; Chi, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R. Extrusion and fungal fermentation change the profile and antioxidant activity of free and bound phenolics in rice bran together with the phenolic bioaccessibility. LWT 2019, 115, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Ren, R.; Wei, Y.; Jin, J.; Ahmad, S.; Lu, C.; Wu, J.; Zheng, C.; Yang, F.; Zhu, G. Comparative metabolomic analysis reveals distinct flavonoid biosynthesis regulation for leaf color development of Cymbidium sinense ‘Red Sun’. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershenzon, J. Alkaloids: Biochemistry, Ecology, and Medicinal Applications; Crop Science Society of America: New York, NY, USA, 1999; p. 486. [Google Scholar]
- Adibah, K.Z.M.; Azzreena, M.A. Plant toxins: Alkaloids and their toxicities. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 6, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Qie, M.; Li, S.; Guo, C.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y. Study of the occurrence of toxic alkaloids in forage grass by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1654, 462463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, V.L.; Bispo, E.S.; Franca, A.S.; Gloria, M.B.A. Understanding amino acids and bioactive amines changes during on-farm cocoa fermentation. J Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 97, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addi, M.; Elbouzidi, A.; Abid, M.; Tungmunnithum, D.; Elamrani, A.; Hano, C. An overview of bioactive flavonoids from Citrus fruits. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Song, M.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; An, X.; Qi, J. The effects of solid-state fermentation on the content, composition and in vitro antioxidant activity of flavonoids from dandelion. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Ye, H.; Kamaraj, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Pavek, P. A review on pharmacological activities and synergistic effect of quercetin with small molecule agents. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenan Kinaci, M.; Erkasap, N.; Kucuk, A.; Koken, T.; Tosun, M. Effects of quercetin on apoptosis, NF-κB and NOS gene expression in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 3, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Huang, G.; Xu, A. Quercetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting neutrophil inflammatory activities. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 84, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, M.; Khan, P.; Shamsi, A.; Shahbaaz, M.; Hasan, G.M.; Haque, Q.M.R.; Christoffels, A.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Inhibiting CDK6 activity by quercetin is an attractive strategy for cancer therapy. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27480–27491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Saeed, F.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Fokou, P.; Arshad, M.; Khan, H.; et al. Kaempferol: A key emphasis to its anticancer potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, H.S.; Ghimeray, A.K.; Yoo, D.S.; Ahn, S.M.; Kwon, S.S.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, D.H.; Cho, J.Y. Kaempferol and kaempferol rhamnosides with depigmenting and anti-inflammatory properties. Molecules 2011, 16, 3338–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Qu, C.; Chen, L.; Geng, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yu, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Meng, Z.; et al. Kaempferol induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via TGM2-mediated Akt/mTOR signaling. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boz, H. p-Coumaric acid in cereals: Presence, antioxidant and antimicrobial effects. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 2323–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, F.; Luceri, C.; Giovannelli, L.; Dolara, P.; Lodovici, M. Effect of 4-coumaric and 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid on oxidative DNA damage in rat colonic mucosa. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 89, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Wang, H.; Rao, S.; Sun, J.; Ma, C.; Li, J. p-Coumaric acid kills bacteria through dual damage mechanisms. Food Control 2012, 25, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.H.; Chellappan, D.R.; Chinnaswamy, P.; Nagarajan, S. Protective effect of p-coumaric acid against 1, 2 dimethylhydrazine induced colonic preneoplastic lesions in experimental rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sroka, Z.; Cisowski, W. Hydrogen peroxide scavenging, antioxidant and anti-radical activity of some phenolic acids. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gai, Z.; Gui, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y. Antioxidant Effects of Protocatechuic Acid and Protocatechuic Aldehyde: Old Wine in a New Bottle. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. 2021, 2021, 6139308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.; Guan, Y.; Yin, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, Y.; Quan, W.; Xi, M.; Wen, A. Anti-inflammatory effect of protocatechuic aldehyde on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Inflammation 2013, 36, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Bilal, M.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid—A versatile platform intermediate for value-added compounds. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 3561–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, F.; Pinna, C.; Dallavalle, S.; Tamborini, L.; Pinto, A. An overview of coumarin as a versatile and readily accessible scaffold with broad-ranging biological activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.K.; Joshi, H. Coumarin: Chemical and pharmacological profile. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 6, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- He, B.T.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, B.Z.; Yuan, Y.J. Advances in biosynthesis of scopoletin. Microb. Cell Factories 2022, 21, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenia, A.; Hidayat, R.; Meiliani, M.; Yuliandra, Y. Blood pressure lowering effect of scopoletin on oxidative stress-associated hypertensive rats. J. Res. Pharm. 2019, 23, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruwizhi, N.; Aderibigbe, B.A. Cinnamic acid derivatives and their biological efficacy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balli, D.; Bellumori, M.; Pucci, L.; Gabriele, M.; Longo, V.; Paoli, P.; Melani, F.; Mulinacci, N.; Innocenti, M. Does fermentation really increase the phenolic content in cereals? A study on millet. Foods 2020, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).