Deeper Insights into the Effect of Humic Acid on Kitchen Waste Anaerobic Digestion: Enzyme Activities, Microbial Community Dynamics, and Key Metabolic Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrate and Inoculum
2.2. Design of Batch Anaerobic Digestion Experiments
2.3. Physical, Chemical, and Enzymatic Analysis
2.4. High-Throughput 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
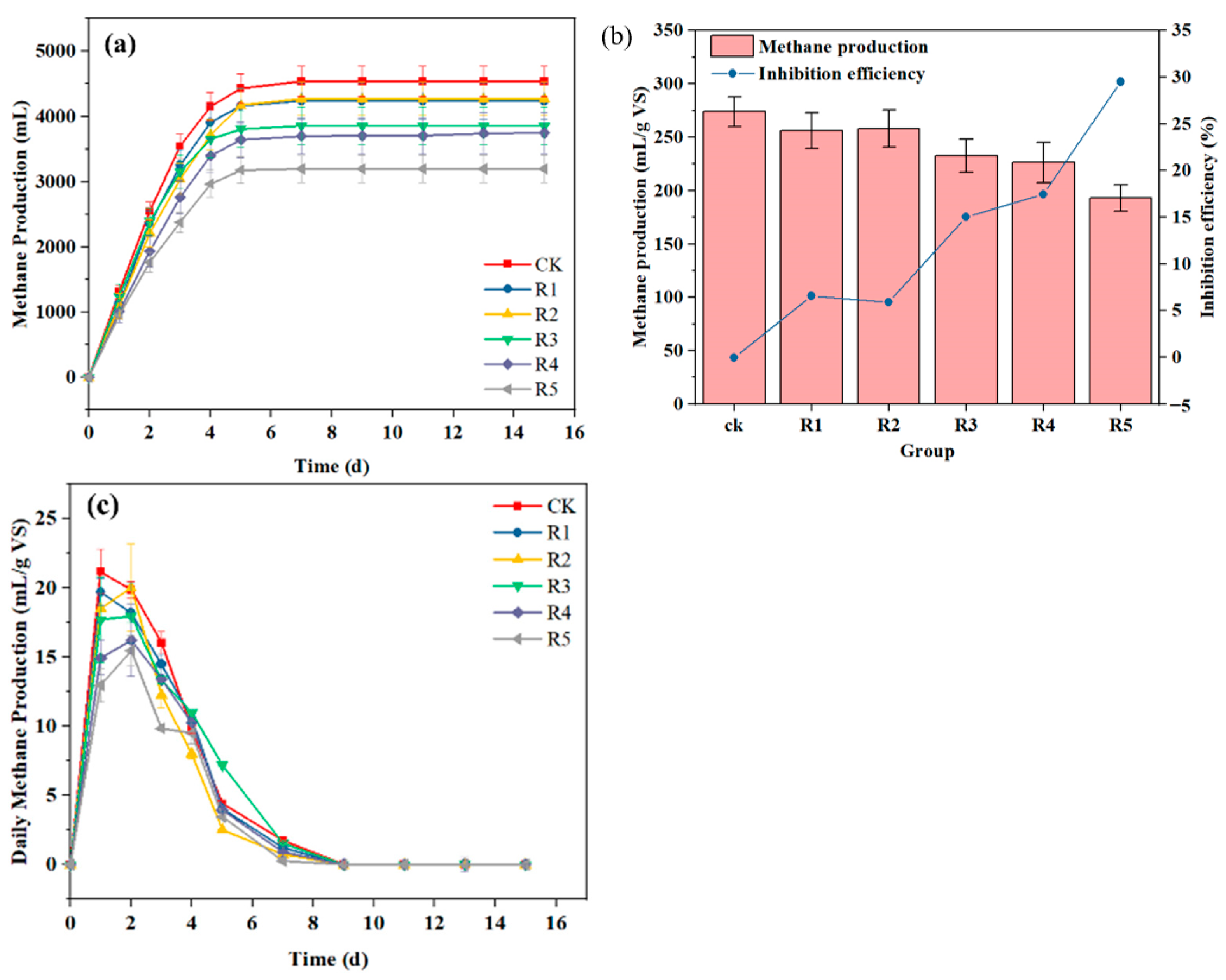
3.1. Impact of HA on KW Anaerobic Digestion Performance
3.1.1. Methanogenic Performance Analysis
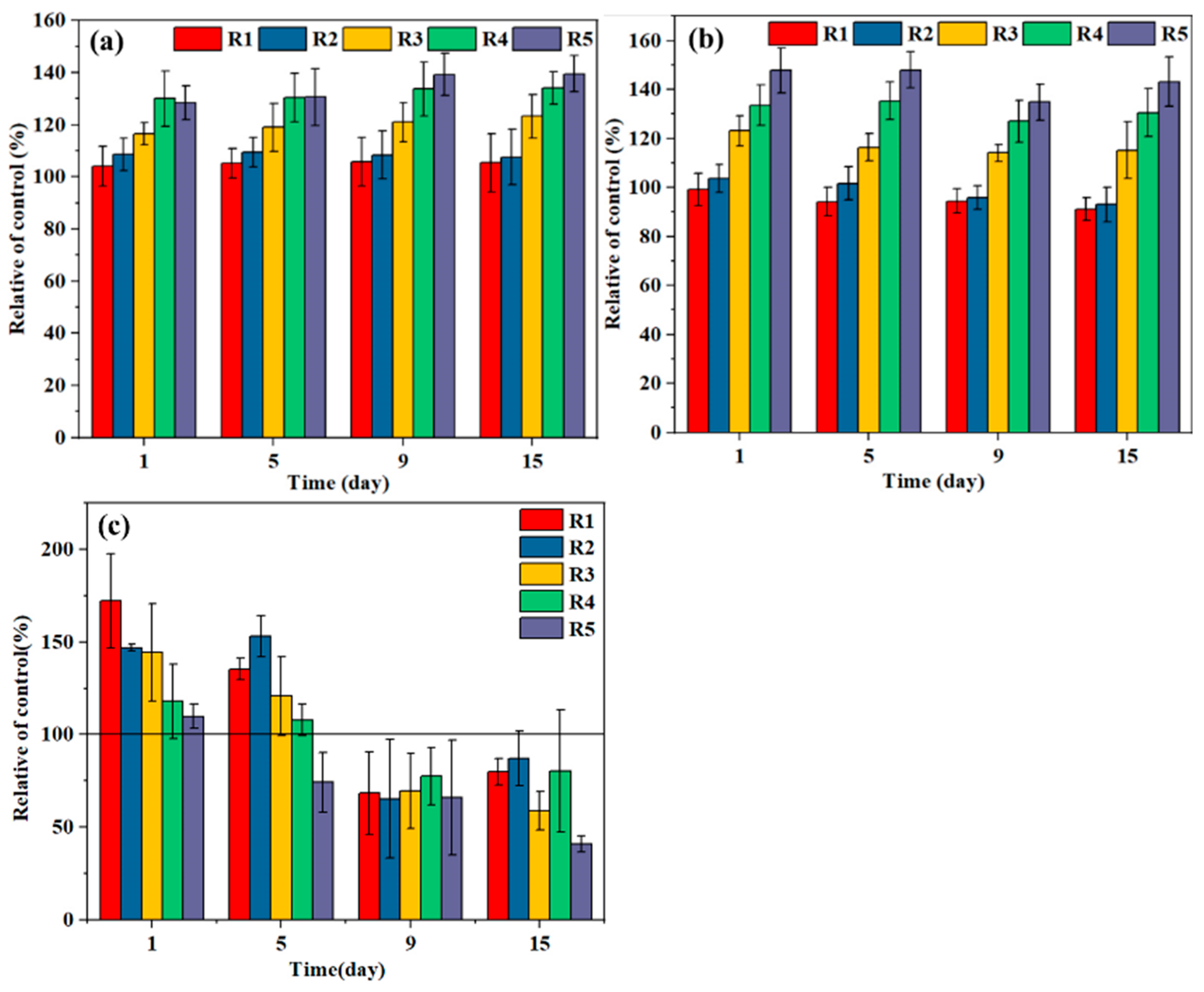
3.1.2. Activities of Key Enzymes and Production of VFAs in AD
3.2. ROS Production and Related Enzyme Activities
ROS Production and SOD Activities
3.3. Relationship between ETS Activity and SCOD
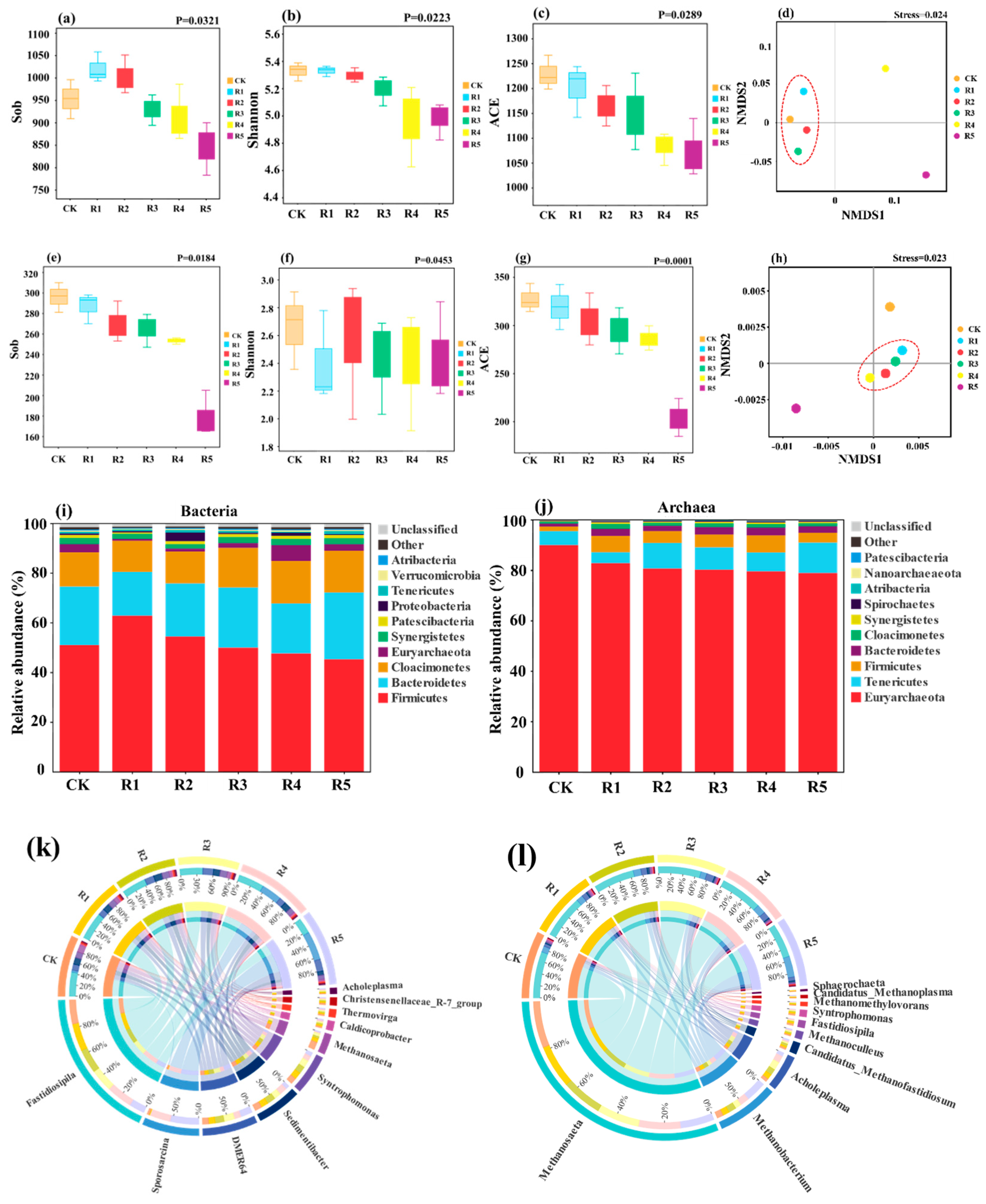
3.4. Microbial Community Structure Analysis
3.4.1. Composition and Variation of Bacterial Communities
3.4.2. Composition and Variation of Archaeal Communities
3.5. Analysis of the Key Metabolic Pathways under Different HA Levels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.Y.; Xiao, M.Y.; Liang, C.Y.; Chui, C.M.; Wang, N.; Shi, J.P.; Liu, L. Multivariate insights into enhanced biogas production in thermophilic dry anaerobic co-digestion of food waste with kitchen waste or garden waste: Process properties, microbial communities and metagenomic analyses. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.Z.; Peng, Y.Y.; Mironov, V.; Chen, J.X.; Jin, H.X.; Zhang, S.H. Feasibility of sewage sludge and food waste aerobic co-composting: Physicochemical properties, microbial community structures, and contradiction between microbial metabolic activity and safety risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hao, X.D.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Luo, Y.Q.; Cao, D.Q. Effect of humic acids on batch anaerobic digestion of excess sludge. Water Res. 2019, 155, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Lyu, T.; Dong, R.J.; Wu, S.B.A. Revealing the link between evolution of electron transfer capacity of humic acid and key enzyme activities during anaerobic digestion. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 301, 113914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Q.; Muhmood, A.; Lyu, T.; Dong, R.J.; Liu, H.T.; Wu, S.B. Mechanisms of genuine humic acid evolution and its dynamic interaction with methane production in anaerobic digestion processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efremenko, E.; Stepanov, N.; Senko, O.; Maslova, O.; Volikov, A.; Zhirkova, A.; Perminova, I. Strategies for variable regulation of methanogenesis efficiency and velocity. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2022, 106, 6833–6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Xu, L.; Zong, Y.; Pang, W.H.; Xie, L. Effect of anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) on anaerobic digestion under ammonia stress: Triggering mediated interspecies electron transfer (MIET). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, A.F.; Azman, S.; Plugge, C.M.; Zeeman, G.; van Lier, J.B.; Stams, A.J. Effect of humic acids on the activity of pure and mixed methanogenic cultures. Biomass Bioenergy 2017, 99, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degli Esposti, M.; McLennan, H. Mitochondria and cells produce reactive oxygen species in virtual anaerobiosis: Relevance to ceramide-induced apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 1998, 430, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennicke, C.; Cochemé, H.M. Redox metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling and function. Mol. Cell. 2021, 81, 3691–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.W.; Sun, H.Y.; Xing, R.Z.; Zhou, S.G. Degradation of microplastics by hydroxyl radicals generated during microbially driven humus redox transformation. Water Res. 2022, 221, 118731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Liu, Y.W.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, C.P.; Niu, Q.Y.; Cheng, J.J. Effects of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural on removal performance and microbial community structure of aerobic activated sludge treating digested swine wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.T.; Tan, W.B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Sun, Q.H.; Qi, H.S.; Xie, X.Y.; Wei, Z.M. Diversity in the Mechanisms of Humin Formation during Composting with Different Materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ye, C.; Zhang, S. Effects of antibiotics on hydrolase activity and structure of microbial community during aerobic co-composting of food waste with sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 321, 124506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Chen, Z.; Peng, Y.Y.; Huang, W.Z.; Liu, J.X.; Mironov, V.; Zhang, S.H. Deeper insights into the effects of substrate to inoculum ratio selection on the relationship of kinetic parameters, microbial communities, and key metabolic pathways during the anaerobic digestion of food waste. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Wei, W.; Huang, Q.S.; Sun, J.; Dai, X.H.; Ni, B.J. Revealing the Mechanisms of Polyethylene Microplastics Affecting Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 9604–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizama, A.C.; Figueiras, C.C.; Pedreguera, A.Z.; Espinoza, J.E.R. Enhancing the performance and stability of the anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge by zero valent iron nanoparticles dosage. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.G.; Xiao, N.D.; Zheng, X.; Li, M. Effect of Humic Acids with Different Characteristics on Fermentative Short-Chain Fatty Acids Production from Waste Activated Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4929–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A. The supramolecular structure of humic substances. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 810–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, L.G.A.; Jolly, M. Controlling and monitoring anaerobic digesters fed with thermally hydrolysed sludge. Water Environ. J. 2004, 18, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.; Starrenbury, D.; Tait, S.; Barr, K.; Batstone, D.J.; Lant, P. Decreasing activated sludge thermal hydrolysis temperature reduces product colour, without decreasing degradability. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4699–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezairliyan, B.; Ausubel, F.M. Investment in secreted enzymes during nutrient-limited growth is utility dependent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7796–E7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, S.D.; Astals, S.; Lu, Y.; Peces, M.; Jensen, P.D.; Batstone, D.J.; Tait, S. Humic acid inhibition of hydrolysis and methanogenesis with different anaerobic inocula. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parawira, W.; Murto, M.; Read, J.S.; Mattiasson, B. Profile of hydrolases and biogas production during two-stage mesophilic anaerobic digestion of solid potato waste. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 2945–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, P.; Vowell, B.J.; Hall, M.; Realff, M.J.; Lee, J.H.; Bommarius, A.S. Elucidation of cellulose accessibility, hydrolysability and reactivity as the major limitations in the enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.Y.; Cao, W.B.; Guo, W.; Fang, S.Y.; Huang, W.X.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.S.; Du, W.; Cao, J.S.; Feng, Q.; et al. Antagonistic effects of surfactants and CeO2 nanoparticles co-occurrence on the sludge fermentation process: Novel insights of interaction mechanisms and microbial networks. J. Hazard Mater. 2022, 438, 129556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, K. Evaluating the evidence for hormesis: A statistical perspective. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2001, 31, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.J.; Rose, A.L.; Lu, Z. Reactive oxygen species in the world ocean and their impacts on marine ecosystems. Redox Biol. 2022, 52, 102285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeyev, M.A.; Shatilina, Z.M.; Kolesnichenko, A.V.; Bedulina, D.S.; Kolesnichenko, V.V.; Pflugmacher, S.; Steinberg, C.E.W. Natural organic matter (NOM) induces oxidative stress in freshwater amphipods Gammarus lacustris Sars and Gammarus tigrinus (Sexton). Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.H.; Rehman, H.M.; Akhtar, T.; Alsamadany, H.; Hamooh, B.T.; Mujtaba, T.; Daur, I.; Al Zahrani, Y.; Alzahrani, H.A.; Ali, S. Humic substances: Determining potential molecular regulatory processes in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, H.; Ninomiya, M.; Sugiyama, H.; Itabashi, A.; Uno, K.; Tanaka, K.; Koketsu, M. Comparative analysis of p-terphenylquinone and seriniquinone derivatives as reactive oxygen species-modulating agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 76, 128992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, C.F.; Wang, J.M. Changes in superoxide dismutase activity postpartum from Laoshan goat milk and factors influencing its stability during processing. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 17, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhao, J.W.; Wang, D.B.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, Q.L.; Ni, B.J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.M.; Zeng, G.M.; et al. Free nitrous acid promotes hydrogen production from dark fermentation of waste activated sludge. Water Res. 2018, 145, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Role and potential of direct interspecies electron transfer in anaerobic digestion. Energies 2018, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Z.B. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thauer, R.K.; Jungermann, K.; Decker, K. Energy-conservation in chemotropic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol. Rev. 1977, 41, 100–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Wang, L.; Cui, E.Y.; Lu, H. Bioactivity kinetics of organic matter biodegradation and nitrification. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 35, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Huang, W.X.; Fang, S.Y.; Li, Z.Z.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, F.; Cheng, X.S.; Cao, J.S.; Feng, L.Y.; Luo, J.Y.; et al. Zinc pyrithione induced volatile fatty acids promotion derived from sludge anaerobic digestion: Interrelating the affected steps with microbial metabolic regulation and adaptive responses. Water Res. 2023, 234, 119816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, S.; Khadem, A.F.; Plugge, C.M.; Stams, A.J.M.; Bec, S.; Zeeman, G. Effect of humic acid on anaerobic digestion of cellulose and xylan in completely stirred tank reactors, inhibitory effect, mitigation of the inhibition and the dynamics of the microbial communities. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.J.; Huang, S.Y.; Wan, Y.Q.; Deng, F.; Cao, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, D. Power to biogas upgrading, Effects of different H2/CO2 ratios on products and microbial communities in anaerobic fermentation system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, S.V.; Meyer, B.H. The archaeal cell envelope. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanwonterghem, I.; Jensen, P.D.; Dennis, P.G.; Hugenholtz, P.; Rabaey, K.; Tyson, G.W. Deterministic processes guide long-term synchronised population dynamics in replicate anaerobic digesters. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2015–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovley, D.R.; Coates, J.D.; BluntHarris, E.L.; Phillips, E.J.P.; Woodward, J.C. Humic substances as electron acceptors for microbial respiration. Nature 1996, 382, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.W.; Huang, J.; Pan, F.K. Polychlorinated biphenyls affects anaerobic methane production from waste activated sludge through suppressing hydrolysis-acidification and methanation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| KW | BS | |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.66 ± 0.06 | 8.07 ± 0.01 |
| Salinity (‰) | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 17.94 ± 0.11 |
| EC (ms/cm) | 481.67 ± 12.58 | 30.30 ± 0.53 |
| VS (%) | 94.60 ± 1.07 | 35.48 ± 10.19 |
| Water content (%) | 80.40 ± 0.12 | 97.05 ± 0.4 |
| C (%) | 35.97 ± 0.14 | 18.84 ± 1.49 |
| N (%) | 4.85 ± 0.02 | 2.99 ± 0.35 |
| S (%) | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.04 |
| C/N | 7.42 ± 0.05 | 6.31 ± 0.24 |
| Lipid(mg/g) | 81.28 ± 0.13 | 1.88 ± 0.47 |
| Protein(mg/g) | 46.98 | Not determined |
| Starch(mg/g) | 372.21 | Not determined |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z. Deeper Insights into the Effect of Humic Acid on Kitchen Waste Anaerobic Digestion: Enzyme Activities, Microbial Community Dynamics, and Key Metabolic Pathways. Fermentation 2023, 9, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100881
Lyu L, Li Y, Zhang S, Chen Z. Deeper Insights into the Effect of Humic Acid on Kitchen Waste Anaerobic Digestion: Enzyme Activities, Microbial Community Dynamics, and Key Metabolic Pathways. Fermentation. 2023; 9(10):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100881
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyu, Lin, Yanzeng Li, Shenghua Zhang, and Zhou Chen. 2023. "Deeper Insights into the Effect of Humic Acid on Kitchen Waste Anaerobic Digestion: Enzyme Activities, Microbial Community Dynamics, and Key Metabolic Pathways" Fermentation 9, no. 10: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100881
APA StyleLyu, L., Li, Y., Zhang, S., & Chen, Z. (2023). Deeper Insights into the Effect of Humic Acid on Kitchen Waste Anaerobic Digestion: Enzyme Activities, Microbial Community Dynamics, and Key Metabolic Pathways. Fermentation, 9(10), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9100881





