Functional, Physicochemical, Rheological, Microbiological, and Organoleptic Properties of Synbiotic Ice Cream Produced from Camel Milk Using Black Rice Powder and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Basic Ice Cream Mixtures
2.3. Chemical Analysis of Black Rice Powder (BRP)
2.3.1. Proximate Analysis
2.3.2. Determination of Total Phenolic Compounds (TPCs) and Antioxidant Scavenging Activity (AA)
2.3.3. Determination of Total Anthocyanins
2.4. Chemical Composition Analysis of the Synbiotic Ice Cream
2.4.1. Proximate Composition
2.4.2. Determination of the Physicochemical and Rheological Properties of Synbiotic Ice Cream
2.4.3. Microbial Analysis of the Synbiotic Ice Cream
2.4.4. Sensory Evaluation
2.4.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition and Bioactive Components of Black Rice Powder (BRP)
3.2. Physicochemical Properties of the Synbiotic Ice Cream
3.2.1. Chemical Properties
3.2.2. Physical Properties of the Synbiotic Ice Cream
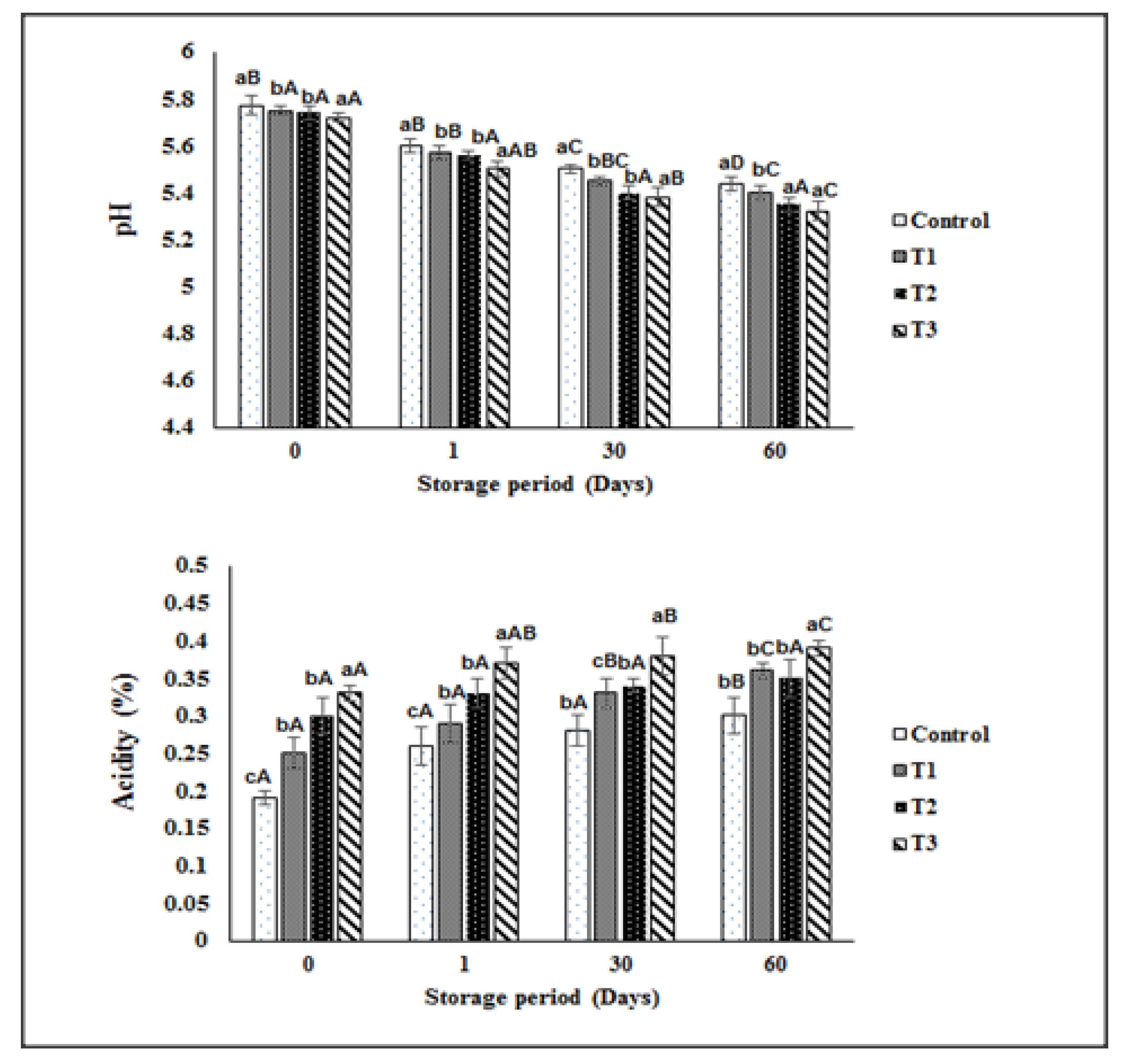
3.2.3. The Acidity and pH Levels of Synbiotic Ice Cream Samples
3.2.4. Microbiological Properties of Synbiotic Ice Cream (Survival of Probiotic Bacteria)
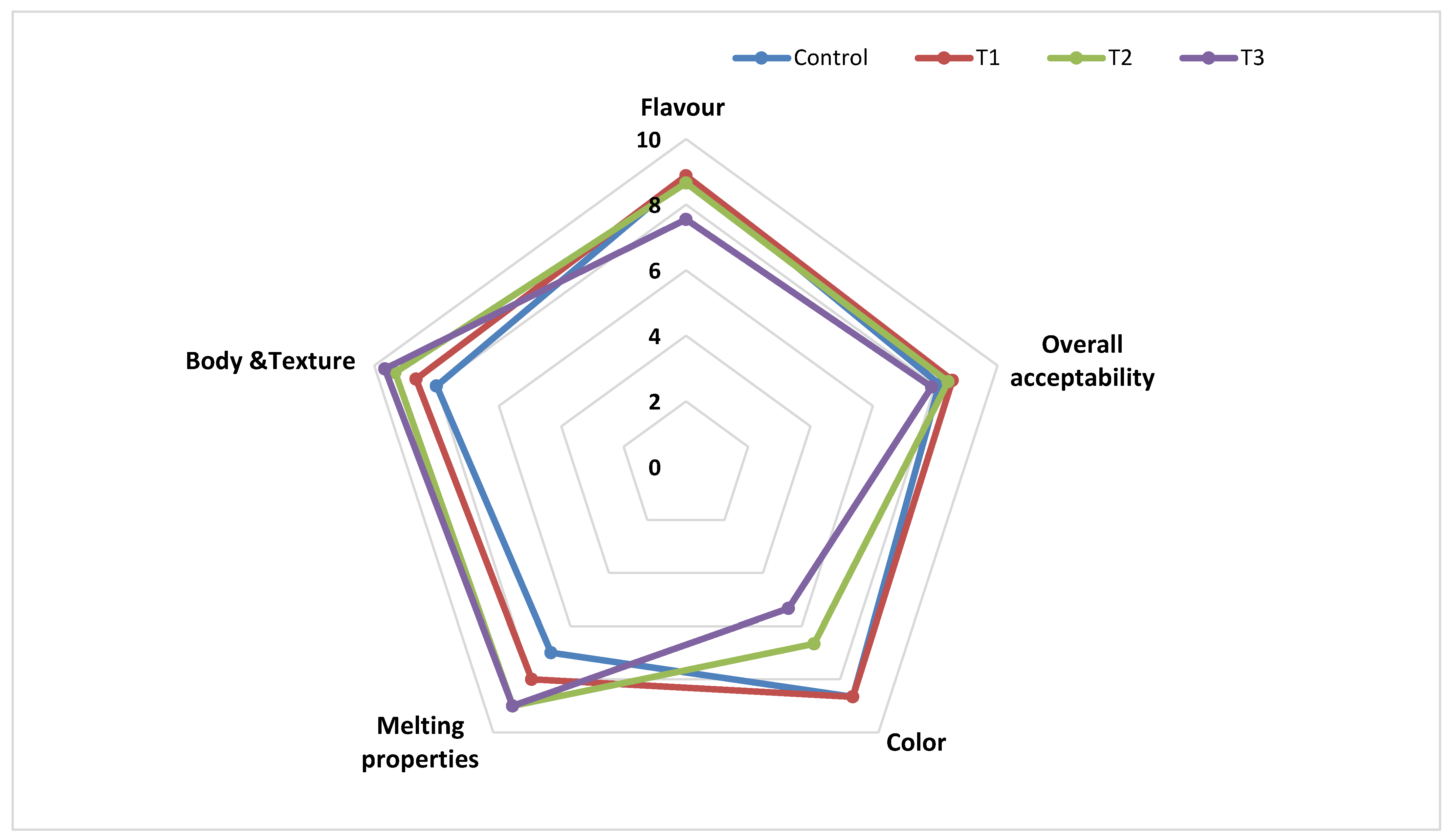
3.2.5. Sensory Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdullahi, A. Camel Milk-A Review. J. Anim. Sci. Livest. Prod. 2019, 3, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dowelmadina, I.; El Zubeir, I.; Arabi, O.; Abakar, A. Omega-3 fatty acids in milk fat of some Sudanese camels. J. Dairy Res. Technol. 2019, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mada, S.B.; Ugwu, C.P.; Abarshi, M.M. Health promoting effects of food-derived bioactive peptides: A review. Int. J. Pept. Res. Therapeut. 2020, 26, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberfroid, M.B. Prebiotics and probiotics: Are they functional foods? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 1682S–1687S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corvitto, A. The Secrets of Ice Cream: Ice Cream without Secrets; Grupo Vilbo: Barcelona, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sayar, E.; Şengül, M.; Ürkek, B. Antioxidant capacity and rheological, textural properties of ice cream produced from camel’s milk with blueberry. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, S.; Fardous, M.; El-Rashody, M.G. Effect of Camel Milk Fortified with Dates in Ice Cream Manufacture on Viscosity, Overrun, and Rheological Properties during Storage Period. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Atwaa, E.S.H.; Shahein, M.R.; El-Sattar, E.S.A.; Hijazy, H.H.A.; Albrakati, A.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Bioactivity, Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Probiotic Yoghurt Made from Whole Milk Powder Reconstituted in Aqueous Fennel Extract. Fermentation 2022, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahein, M.R.; Atwaa, E.S.H.; El-Zahar, K.M.; Elmaadawy, A.A.; Hijazy, H.H.A.; Sitohy, M.Z.; Albrakati, A.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Remedial Action of Yoghurt Enriched with Watermelon Seed Milk on Renal Injured Hyperuricemic Rats. Fermentation 2022, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swelam, S.; Zommara, M.A.; Abd El-Aziz, A.E.-A.M.; Elgammal, N.A.; Baty, R.S.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Insights into Chufa Milk Frozen Yoghurt as Cheap Functional Frozen Yoghurt with High Nutritional Value. Fermentation 2021, 7, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán-Barrientos, L.; Hernández-Mendoza, A.; Torres-Llanez, M.; González-Córdova, A.; Vallejo-Córdoba, B. Invited review: Fermented milk as antihypertensive functional food. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4099–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahein, M.R.; Atwaa, E.S.H.; Radwan, H.A.; Elmeligy, A.A.; Hafiz, A.A.; Albrakati, A.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Production of a Yogurt Drink Enriched with Golden Berry (Physalispubescens L.) Juice and Its Therapeutic Effect on Hepatitis in Rats. Fermentation 2022, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linn, Y.H.; Thu, K.K.; Win, N.H.H. Effect of probiotics for the prevention of acute radiation-induced diarrhoea among cervical cancer patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, A.; Milani, E.; Madadlou, A.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Mokarram, R.R.; Salarbashi, D. Synbiotic yogurt-ice cream produced via incorporation of microencapsulated lactobacillus acidophilus (la-5) and fructooligosaccharide. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranadheera, C.S.; Evans, C.; Adams, M.; Baines, S. Production of probiotic ice cream from goat’s milk and effect of packaging materials on product quality. Small Rumin. Res. 2013, 112, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.; Misra, S.; Mohapatra, S.; Sahu, P.S. Prebiotics and synbiotics: Recent concepts in nutrition. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Young, J.C.; Rabalski, I. Anthocyanin composition in black, blue, pink, purple, and red cereal grains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4696–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, H.; Shehzad, M.; Rabail, R.; Kowalczewski, P.Ł.; Kidoń, M.; Jeżowski, P.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Rakha, A.; Din, A.; Aadil, R.M. Delving into the Nutraceutical Benefits of Purple Carrot against Metabolic Syndrome and Cancer: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.A.M.; Elkot, W.F. Functional Properties and Nutritional Quality of Processed Cheese Spreads Enriched with Black Rice Powder. Egypt. J. Food Sci. 2020, 48, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, H.; He, S.; Lou, Q.; Yu, M.; Tang, M.; Tu, L. Metabolism and prebiotics activity of anthocyanins from black rice (Oryza sativa L.) in vitro. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195754. [Google Scholar]
- Thanuja, B.; Parimalavalli, R. Comparison of antioxidant compounds and antioxidant activity of native and dual modified rice flour. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2020, 11, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N.; Murali, R. Black Rice: A novel ingredient in food processing. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 10, 771. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, A.; Ranadheera, C.; Prasanna, P.; Senevirathne, N.; Vidanarachchi, J. Development of a rice incorporated synbiotic yogurt with low retrogradation properties. Int. Food Res. J. 2015, 22, 2032. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, A.M.; Elkot, W.F.; Mohamed, O.R. Functional properties and nutritional quality of ice cream enriched with Jerusalem artichoke flour. J. Agroa. Process. Technol. 2016, 22, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- El-Samahy, S.; Gaballah, A.; Embaby, H.; Hamed, Y.; Khalil, R. A novel low fat ice cream based on the use of preparation of cactus pear (Opuntia dillenii) pulp. Egypt. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 43, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Elkot, W.F.; Ismail, H.A.; Rayan, A.M. Enhancing The Functional Properties and Nutritional Quality of Ice Milk with Sebesten Fruits (Cordia myxa L.). Egypt. J. Food Sci. 2017, 45, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 18th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, A.; Marjan, Z.M.; Foong, C.W. Total antioxidant activity and phenolic content in selected vegetables. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burits, M.; Bucar, F. Antioxidant activity of Nigella sativa essential oil. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrolstad, R.E.; Durst, R.W.; Lee, J. Tracking color and pigment changes in anthocyanin products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.T.; Goff, H.D.; Hartel, R.W. Ice Cream, 6th ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Baú, T.R.; Garcia, S.; Ida, E.I. Evaluation of a functional soy product with addition of soy fiber and fermented with probiotic kefir culture. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2014, 57, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalın, A.; Kesenkas, H.; Dinkci, N.; Unal, G.; Ozer, E.; Kınık, O. Enrichment of probiotic ice cream with different dietary fibers: Structural characteristics and culture viability. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B.A.M.; US Food and Drug Administration; Center for Safety and Applied Nutrition. Bacteriological Analytical Manual (BAM); US Food and Drug Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sompong, R.; Siebenhandl-Ehn, S.; Linsberger-Martin, G.; Berghofer, E. Physicochemical and antioxidative properties of red and black rice varieties from Thailand, China and Sri Lanka. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Mou, R.; Zhu, Z.; Beta, T. Phenolic acids, anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, antioxidant activity, minerals and their correlations in non-pigmented, red, and black rice. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolea, C.-A.; Vizireanu, C. Polyphenolic content and antioxidant properties of black rice flour. Ann. Univ. Dunarea Jos Galati Fascicle VI Food Technol. 2017, 41, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, M.A.; Huma, N.; Mueen-Ud-Din, G.; Shabbir, M.A.; Mahmood, S. Effect of fat replacement by fig addition on ice cream quality. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2004, 6, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Rabo, F.; Dewidar, O. Broken rice for production of functional ice cream. Ismailia J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2017, 5, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet-Sarvestani, N.; Eskandari, M.H.; Hosseini, S.M.H.; Niakousari, M.; Hashemi Gahruie, H.; Khalesi, M. Production of synbiotic ice cream using Lactobacillus casei/Lactobacillus plantarum and fructooligosaccharides. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.N.; Kamaruding, N.A.; Ismail, N.; Shaharuddin, S. Value addition to ice cream by fortification with okara and probiotic. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 46, e16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, M.; Znamirowska, A.; Buniowska, M. Probiotic Sheep Milk Ice Cream with Inulin and Apple Fiber. Foods 2021, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobab, U.; Batool, Z.; Manzoor, M.F.; Shabbir, M.A.; Khan, M.R.; Aadil, R.M. Sources, formulations, advanced delivery and health benefits of probiotics. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2020, 32, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Criscio, T.; Fratianni, A.; Mignogna, R.; Cinquanta, L.; Coppola, R.; Sorrentino, E.; Panfili, G. Production of functional probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic ice creams. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 4555–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akalın, A.; Erişir, D. Effects of inulin and oligofructose on the rheological characteristics and probiotic culture survival in low-fat probiotic ice cream. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, M184–M188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampopoulos, D.; Pandiella, S.; Webb, C. Growth studies of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria in cereal-based substrates. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Espírito Santo, A.P.; Cartolano, N.S.; Silva, T.F.; Soares, F.A.; Gioielli, L.A.; Perego, P.; Converti, A.; Oliveira, M.N. Fibers from fruit by-products enhance probiotic viability and fatty acid profile and increase CLA content in yoghurts. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 154, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Góral, M.; Kozłowicz, K.; Pankiewicz, U.; Góral, D. Magnesium enriched lactic acid bacteria as a carrier for probiotic ice cream production. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, U.K.S. Black Rice. In Research, History and Development Book; Ujjawal, K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]

| Ingredients | Amount/100 kg | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Whole camel milk | 46 | 46 | 46 | 46 |
| Cream | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 |
| Skim milk powder | 5.9 | 4.43 | 2.95 | 1.48 |
| Sucrose | 15 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Vanilla flavor | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Gelatin | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| BR powder | 0 | 1.47 | 2.95 | 4.42 |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Ingredient | Concentration |
|---|---|
| Moisture (%) | 10.85 ± 0.21 |
| Total carbohydrates (%) | 74.34 ± 0.41 |
| Crude protein (%) | 8.47 ± 0.05 |
| Crude fat (%) | 2.49 ± 0.16 |
| Total dietary fiber (%) | 1.26 ± 0.02 |
| Ash content (%) | 2.59 ± 0.03 |
| Zinc content (mg/100 g) | 3.53 ± 0.01 |
| Iron content (mg/100 g) | 1.42 ± 0.00 |
| Manganese content (mg/100 g) | 2.73 ± 0.02 |
| Total phenolic compounds (mg GAE/100 g) | 473.6 ± 3.17 |
| Total Scavenging activity (DPPH, %) | 56.15 ± 0.06 |
| Total anthocyanins (mg cyanide 3-glucoside/100 g) | 132.2 ± 1.21 |
| Color readings | |
| L * | 63.33 ± 0.00 |
| a * | 8.41 ± 0.05 |
| b | 6.41 ± 0.01 |
| Chemical Properties | Total Solids | Protein | Fat | Carbohydrates | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 34.65 ± 0.34 b | 3.51 ± 0.50 a | 8.70 ± 0.11 a | 16.15 ± 0.20 c | 0.74 ± 0.00 c |
| T1 | 36.55 ± 0.60 a | 3.50 ± 0.10 a | 8.75 ± 0.07 a | 17.18 ± 0.15 b | 0.82 ± 0.00 b |
| T2 | 37.16 ± 0.33 a | 3.25 ± 0.08 a | 8.80 ± 0.10 a | 17.90 ± 0.05 a | 0.89 ± 0.00 a |
| T3 | 37.40 ± 0.35 a | 3.10 ± 0.10 a | 8.80 ± 0.15 a | 18.20 ± 0.05 a | 0.98 ± 0.00 a |
| Physicochemical and Rheological Properties | |||||
| Ice cream treatments | Freezing point (°C) | Overrun% | Viscosity (cP) | First drip time (min) | Complete melting times (min) |
| Control | −2.34 ± 0.01 d | 38.55 ± 0.27 c | 324 ± 2.00 d | 4.15 ± 0.00 d | 43.45 ± 0.28 d |
| T1 | −2.42 ± 0.00 c | 39.88 ± 0.01 b | 392 ± 2.51 c | 5.70 ± 0.02 c | 47.16 ± 0.14 c |
| T2 | −2.47 ± 0.02 b | 41.90 ± 0.10 a | 421 ± 1.15 b | 5.80 ± 0.00 b | 49.76 ± 0.57 b |
| T3 | −2.51 ± 0.00 a | 41.80 ± 0.40 a | 440 ± 1.79 a | 6.10 ± 0.00 a | 53.20 ± 0.20 a |
| Storage Periods (Days) | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Total Bacteria Count (log cfu/g) | ||||
| Ice cream Mix | 8.35 ± 0.10 aC | 8.41 ± 0.09 aB | 8.41 ± 0.10 aB | 8.66 ± 0.06 aA |
| 1 | 8.21 ± 0.09 bC | 8.23 ± 0.09 bC | 8.40 ± 0.09 abB | 8.50 ± 0.16 bA |
| 30 | 8.05 ± 0.18 cD | 8.08 ± 0.20 cC | 8.19 ± 0.12 bB | 8.30 ± 0.09 cA |
| 60 | 7.35 ± 0.16 dC | 7.70 ± 0.21 dB | 8.00 ± 0.13 cA | 8.00 ± 0.13 dA |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 (log cfu/g) | ||||
| Ice cream Mix | 8.20 ± 0.06 aB | 8.23 ± 0.11 aB | 8.40 ± 0.05 aAB | 8.50 ± 0.08 aA |
| 1 | 8.10 ± 0.17 bC | 8.17 ± 0.14 bB | 8.11 ± 0.12 bC | 8.31 ± 0.08 bA |
| 30 | 8.00 ± 0.10 bcC | 8.06 ± 0.15 cB | 8.13 ± 0.13 bA | 8.13 ± 0.09 cA |
| 60 | 7.25 ± 0.13 cC | 7.44 ± 0.11 cdB | 7.62 ± 0.11 cA | 7.66 ± 0.07 dA |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elkot, W.F.; Ateteallah, A.H.; Al-Moalem, M.H.; Shahein, M.R.; Alblihed, M.A.; Abdo, W.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Functional, Physicochemical, Rheological, Microbiological, and Organoleptic Properties of Synbiotic Ice Cream Produced from Camel Milk Using Black Rice Powder and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5. Fermentation 2022, 8, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040187
Elkot WF, Ateteallah AH, Al-Moalem MH, Shahein MR, Alblihed MA, Abdo W, Elmahallawy EK. Functional, Physicochemical, Rheological, Microbiological, and Organoleptic Properties of Synbiotic Ice Cream Produced from Camel Milk Using Black Rice Powder and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5. Fermentation. 2022; 8(4):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040187
Chicago/Turabian StyleElkot, Wael F., Ateteallah H. Ateteallah, Maalem H. Al-Moalem, Magdy Ramadan Shahein, Mohamed A. Alblihed, Walied Abdo, and Ehab Kotb Elmahallawy. 2022. "Functional, Physicochemical, Rheological, Microbiological, and Organoleptic Properties of Synbiotic Ice Cream Produced from Camel Milk Using Black Rice Powder and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5" Fermentation 8, no. 4: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040187
APA StyleElkot, W. F., Ateteallah, A. H., Al-Moalem, M. H., Shahein, M. R., Alblihed, M. A., Abdo, W., & Elmahallawy, E. K. (2022). Functional, Physicochemical, Rheological, Microbiological, and Organoleptic Properties of Synbiotic Ice Cream Produced from Camel Milk Using Black Rice Powder and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5. Fermentation, 8(4), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040187







