Abstract
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is shocked by various temperature processes in milk, which forces the organism to make proteins as a result of changes in the synthesis of enzymes that might give the strain special characteristics. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of the heat shock factor on changing the results of biochemical and molecular tests among E. coli strains obtained from ice cream and non-pasteurized milk when compared to a reference strain from the American-type culture collection (ATCC) in order to determine the phenotypic variation caused by the temperature conditions of the manufacturing process. Furthermore, isolates with characteristics similar to E. coli were discovered, but they were not E. coli and caused some ambiguity. To test the E. coli contamination of traditional and industrial ice cream, 82 samples were chosen at random. SDS-PAGE and 16S rDNA sequencing were carried out, as well as phenotypic testing. Isolated strains did not exactly match the reference strain. The results of biochemical testing and protein analysis revealed that the isolates were diverse. Samples E. coli phenons were classified. In the electrophoresis, the ice cream strain had two protein bands in the 20.75 and 23.59 kDa ranges that were distinct from the reference strain. These isolates appear to experience alterations in enzyme characteristics and structural proteins as a result of being exposed to various temperature conditions, such as pasteurization and frigidity. When compared to the reference strain, the calculated similarity percentage of the elicited isolate varied from 60 to 70%. The electrophoretic patterns of E. coli isolated elicited from milk samples differed from E. coli isolated obtained from the ice cream. The distinctions were in the intensity or position of the bands. The results also revealed that when isolates are subjected to thermal stresses, they exhibit a pattern similar to that of ice cream isolates. These considerations are made because a change in protein composition might result in a change in biochemical features, resulting in uncertainty in its identification. Sequences revealed that the sequences were related to E. coli 16S rDNA, despite differences in phenotypic and electrophoretic features between the isolated bacteria and the reference strain E. coli ATCC 25922. Our findings revealed that 16S rDNA could potentially be used to instantly implement an appropriate preventive measure for the purpose of identifying this type of bacteria and avoid some ambiguity.
1. Introduction
The first description of E. coli was provided by the German pediatrician, Theodor Escherichia. In 1885, he isolated the above bacteria from the stool of a child with enteritis, called Bacterium coli. It was called Bacterium colon due to its place in the large colon (bacterium means stretched and bacilliform) [1]. Escherichia demonstrated the presence of E. coli in all human feces, which is significant given its unique place among opportunistic bacteria due to its ability to cause intestinal infections. Its presence in the gut inhibits the growth of other proteolytic bacteria while also contributing to the synthesis of a number of B-group vitamins. Schardinger then proposed E. coli as a fecal contamination indicator. E. coli was identified as a food pathogen in 1971 [2]. Milk and its products derived from cows can harbor various microorganisms. These microorganisms play essential roles in facilitating dairy fermentations (e.g., Lactococcus, Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Propionibacterium, and fungal populations), causing spoilage (e.g., Pseudomonas, Clostridium, Bacillus, and other spore-forming or thermoduric microorganisms), promoting health (e.g., Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria), or causing disease (e.g., Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella, E. coli, Campylobacter, S. aureus, and mycotoxin-producing fungi) [3]. Dairy products, such as ice cream, may give important nutrients to a variety of microbes. Gram-negative bacteria make up more than 90% of the microbial community in cold raw milk [4]. Furthermore, food is a major source of contamination by chemical and biological agents. More than 70% of infectious diseases are transferred to humans through contaminated food [5]. Milk contamination can occur directly from dairy animals shedding pathogens into the milk or indirectly during the milking, collecting, and transportation processes [6]. To destroy the bacteria, milk can be pasteurized at a certain temperature. Thus, one of the most major causes of contamination is a lack of hygiene during production [7]. The presence of E. coli is the first sign of fecal contamination. E. coli identification is so important as a hygiene measure that it is used to assess contamination by other pathogenic microbes [8]. Bacteria are commonly found in the colon and feces of humans and other warm-blooded animals. Diarrhea is caused by oral contamination with feces. E. coli is a resistant bacterium that may survive in water and food for weeks or months under natural conditions [9,10].
When bacteria are subjected to pH and temperature stresses, sublethal stresses are likely to occur. This results in variances in their tolerance to the subsequent heat treatment. Bacteria may be able to adapt to non-optimal conditions and require a longer time to be destroyed, depending on the pH and temperature of the environment. In diverse conditions, E. coli O157:H7 strains demonstrate a wide variety of heat tolerances, impacting their resistance to certain following procedures [11].
In nature, bacteria are subjected to a variety of harmful and severe stresses, including nutrient deficiency, osmotic pressure, extremely high or low temperatures, acid, and antimicrobial compounds. Bacterial adaptation to these unfavorable environmental conditions is accomplished through the utilization of defensive mechanisms. Bacterial stress responses are controlled at three levels: transcription, translation, and post-translational. This results in alterations in gene expression, protein activity, and cell metabolism. These bacterial stress responses result in stress tolerance and cellular damage repair [12].
Heat and cold are two of the most common environmental stresses for bacteria. HSR (heat shock response) and CSR (cold shock response) are biochemical responses that bacteria exhibit in response to sudden and significant temperature increases and decreases, respectively [13]. Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are synthesized by HSR when bacteria are subjected to heat [14]. Heat shock proteins are beneficial in restoring the native structure of thermally unfolded proteins and preventing proteasomal protein destruction [15]. Cold shock proteins (CSPs) are produced in response to a rapid considerable reduction in temperature [16].
The CSP family has nine homologous proteins (CspA to CspI). These CSPs are thought to be nucleic acid chaperones that enhance the trigger of bacterial translation when exposed to cold stress [17,18]. ClpL (a major HSP) influences cell wall biosynthesis, which enhances β-lactam resistance [19]. A ClpXP protease is believed to be a protein quality control system. This system is created by thermal shock and other stresses, and it is accompanied with antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, HSR increases the rate of genetic recombination and HGT in class 1 integrons, which contributes to Gram-negative multidrug resistance. E. coli is a commensal bacterium present in animal guts [20,21]. Because of the buffer and temperature conditions, ice cream is susceptible to bacterial contamination. A high number of anaerobic microorganisms, such as Bacteroides, influence this foodstuff [22]. The most common cause of diarrhea is bacteria. Despite the availability of simple effective therapies, more than 1400 children die of diarrhea every day, or over 480,000 children each year. It appears to be a greater threat than malaria, measles, and HIV/AIDS combined [23]. Diarrhea is defined as having watery stools and excreting more than three times a day on average. Diarrhea affects children under the age of five in underdeveloped nations 3.3 times per year, or even 9 times per year in some areas. The prevalence of intestinal pathogens is influenced by a number of epidemiological parameters, including host, environmental factors, and health care facilities [24]. E. coli is a pathogen found in humans and other animals’ intestines [25]. The presence of food-borne pathogens in raw cow milk varies, although it has been demonstrated in several surveys. Campylobacter, Salmonella spp., and human pathogenic verocytotoxin-producing E. coli have all been related to food-borne diseases. Several toxin-producing strains, including Vero toxigenic E. coli (VTEC), have been discovered in milk-derived foods. Some of them are resistant to drugs [26]. Milk-borne and milk product-borne outbreaks account for 2–6% of bacterial food-borne illnesses in developed nations [27]. However, nothing is known about the distinct E. coli isoforms found in traditional and industrial ice creams.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the findings of biochemical and molecular tests performed on E. coli strains isolated from ice cream in order to determine the phenotypic variation caused by the temperature conditions of the manufacturing process. To identify and characterize various E. coli isoforms, we utilized biochemical assays in conjunction with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) of whole-bacteria proteins and sequenced 16S rDNA.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sampling
According to this research’s design, that of a descriptive cross-sectional study, three samples from each store were chosen at random and carried out in three steps. Without previous notification, ice cream was purchased as a regular customer from ice cream sale centers for sampling. The samples were put in the cool box at a temperature close to that maintained by the material suppliers and quickly transferred to the laboratory for microbiological tests. The presence of E. coli was then determined in all samples. To test E. coli contamination in ice creams, 82 samples were chosen at random from the province of Isfahan. The samples were kept at 10 °C. Microbial testing carried out in accordance with standard procedures [28].
2.2. Livestock Milk Sampling
A semi-mechanized livestock center was chosen to compare the isolates of ice cream derived from milk samples, and samples were analyzed for E. coli infection to determine the phenotypic variations in the isolates acquired from ice cream. Thirteen isolates were chosen, and their phenotypic and electrophoretic patterns were examined. The samples (10 mL) were diluted to 0.1 in a test tube containing 10 mL of double concentrated Fluorocult LMX Broth (LMX, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and a Durham microtube. The samples were then incubated for 8 h at 35 °C. The color change of the liquid medium to blue-green and the generation of gas were signs of E. coli in the medium. Subsequently, 0.5 mL of 5 M sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was added to each tube to induce blue fluorescence using a long-wave UV light source (366 nm). The presence of E. coli was confirmed by the appearance of a red ring with the addition of Kovac’s reagent (isoamyl alcohol, para-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde, concentrated hydrochloric acid). The sample was cultured on Chromocult coliform agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) for 24 h before being treated at 35 °C with indole reagent to separate the isolates. E. coli colonies ranged from dark blue to violet [29]. Meanwhile, coliform and microflora colonies were red and colorless, respectively. Blue and violet colonies were chosen, cultured on nutrient agar, kept at 35 °C for 24 h, and stored for supplementary testing at 4 °C. Each isolate’s fresh culture was transferred to a microtube containing sterile normal saline and kept at 4 °C. For long-term preservation, pure isolates were transferred to tubes containing nutritional agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) for 24 h at 37 °C. Following that, sterile liquid paraffin was added to the culture tubes, and the tubes were kept at 4 °C [28,30,31].
2.3. Heat Shock in Bacteria Isolated from Raw Milk
Each isolate experienced six repetitions of this step. The bacterial sediment was separated using a centrifuge set at 1200 rpm, rinsed multiple times with sterile physiological serum, and then centrifuged once more. Additionally, 4 °C was used for the centrifugation process. The bacterial sediment was maintained in 1 mL of fetal bovine serum at 4 °C after being washed three times. The isolates were electrophoresed in SDS-PAGE after 7 days.
2.4. Phenotypic Tests
Biochemical assays were used to compare each isolate to the reference strain of E. coli ATCC 25922. Further biochemical tests were performed on the isolates to provide a more precise diagnosis. Biochemical tests were performed for the identification of the E. coli species isolated from ice cream and unpasteurized milk with the help of Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology [28]. In EC (Escherichia coli) broth, LMX broth, and lauryl tryptose broth, gas was sometimes generated from the lactose by the production of acid from a variety of substrates. Numerical taxonomy analysis was used to describe the 48 strains. The Jaccard coefficient was used to calculate a distance matrix, and the UPGMA algorithm was utilized to perform cluster analysis. The dendrogram was created using the NTYSYSPC Ver 2.02e program [32] (Figure 1).
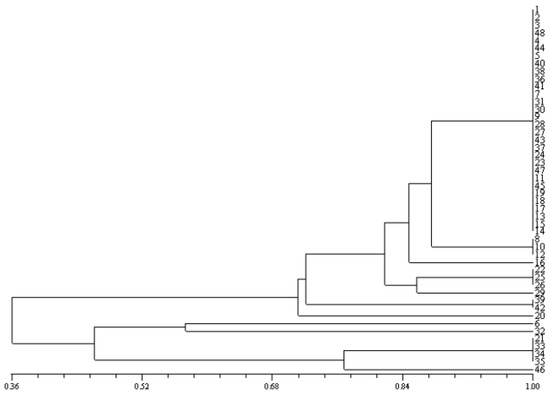
Figure 1.
Dendrogram for phenotypic characteristics of 48 isolates among ice cream samples based on the UPGMA algorithm of utilized carbon sources. Phenon 1 (1–16), Phenon 2 (22–29), Phenon 3 (39–42), Phenon 4 (2), Phenon 5 (6), Phenon 6 (32), Phenon 7 (21–35), and Phenon 8 (46).
2.5. Whole-Bacteria Protein Electrophoresis
SDS-PAGE in modified Laemmli method was used to process the vertical slab unit to compare whole-cell protein profiles [33]. The bacteria were incubated on nutrient agar at 35 °C for 24 h. The colonies were then suspended in sterile distilled water, and their OD was calibrated using a spectrophotometer at 2.8–3 units per 600 nm. SDS buffer was added to the samples. After the lysis of bacteria, 2-mercaptoethanol was added to the samples and left for 5 min at 95 °C. Proteins were extracted, and electrophoresis (Bio-rad, Hercules, CA, USA) was performed at 100 V in a 12% polyacrylamide gel. Finally, the molecular weight of proteins was evaluated using the LMW-SDS Marker Kit 14–97 kDa (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) as the molecular weight detection standard.
2.6. Calculating the Percentage of Similarity
The difference in the protein profile of the isolates produced from infected specimens was examined by the reference strain, and the degree of conformity between the isolates with the reference strain and with each other was calculated after determining the similarity. The presence of non-type specific isolates, showing the presence of variations between isolates and reference strains, may be determined using this approach. This might be due to environmental factors causing diversity. The percentage of similarity between isolates and standard subspecies was used to evaluate the similarity between isolates [34].
Nxy: Common protein bands between isolates x, y;
nx: Total number of protein x bands;
ny: Total number of protein y bands;
2.7. Investigating E. coli Strains via Sequencing of 16S rDNA
2.7.1. DNA Extraction
The DNA was extracted using bacterial suspension cultures. DNA was extracted and purified in this investigation using a QIAamp DNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The extraction was carried out in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, with each extraction containing 100 µL of sample. A NanoDrop 1000 spectrophotometer was used to measure the concentrations of DNA isolated from bacterial isolates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA). Based on DNA concentration, the equivalent of bacterial genomic DNA was estimated. Finally, by utilizing 16S rDNA reproduction with PCR, the acquired DNA was used to identify the bacteria.
2.7.2. PCR Method
PCR was performed using primer pairs 16s27f and 16s1492R [35]. The PCR program was conducted to reproduce 16S rDNA. The sequencing primers were (from 5′ to 3′): forward 16s27f, AGAGTTTGATCTTGGCTCAG, and reverse 16s1492R, TACGGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT, and Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). One reaction provided as an E. coli positive control (DNA generated using the standard procedure), while another acted as a negative control (distilled water). PCR was performed in 50 µL of the total volume containing 20–30 ng of genomic DNA, 2.5 mM magnesium chloride, 2 U of Taq DNA polymerase, 0.6 mM dNTP Mix, and 0.3 mM primers. PCR thermal cycling conditions were as follows: 95 °C for 5 min, 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 1 min, with a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min.
2.7.3. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis and PCR Product Purification
The reaction mixture (10 µL) was then electrophoretically separated using 1% agarose with ethidium bromide at a concentration of 10 µg/mL. The reaction product was visualized under the Gel doc/UV trans-illuminator. Finally, fragments accompanied by PCR products were detected using GeneRuler™ 100bp DNA Ladder Plus weight (ThermoScientific, Waltham, MA, USA) as a DNA ladder, and electrophoresis (BIO-RAD, Hercules, CA, USA) was performed at 100 V. The PCR product was purified by QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). The PCR amplified product of 16S rDNA (100 ng concentration) was used for sequencing with single 16S rDNA 27F. The forward primer was 5′-AGAGTTTGATCTTGGCTCAG-3′ by ABI (Applied Biosystem Inc., Seattle, WA, USA) DNA sequencer.
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Tests of Isolated Coliforms
From among the 82 tested samples, 48 isolates were obtained (Indole-positive). Isolates were classified due to the biochemical diversity of the isolates and the lack of a definite diagnosis. Important variables were used to classify clusters. Based on differences in biochemical tests, numerical analytical results revealed that isolates were transformed into eight phenons. The dendrogram illustrates the clustering patterns of 39 phenotypic traits (Figure 1). Using numerical analysis, the samples were transformed into eight phenons. These phenons resulted from the strains’ phenotypic differences and variation in acid production using different carbon sources.
Some isolates recorded in this test, however, were completely similar, close, or even different. Gram-negative bacteria, rod-shaped bacteria (with lengths of 2–6 µm and widths of 1–1.5 µm), movable bacteria, environmental flagella bacteria, non-spore forming, positive catalase and negative oxidase bacteria, nitrate reducing bacteria, and fermentation bacteria were all isolated from ice cream samples collected from various locations throughout Isfahan (Table 1). Furthermore, some mucoid colonies with capsules but mostly without capsules, resembling E. coli and capable of producing indole, were isolated. Table 2 shows the results of these tests used to identify the coliform phenons isolated from ice cream. In contrast to analyses using the proposed method, such as using media containing chromogenic substances, for example, LMX broth and Chromocult coliform agar, and long-wave 366 nm UV light, positive indole isolates, such as inactive E. coli, E. hermanii, Providencia rettgeri, K. oxytoca, and M. morganii, could interfere with the final result. Colorful ice creams, such as those containing saffron, cacao, strawberry, etc., may cause errors because they alter the color of the environment and interfere with the resulting fluorescence. As a result, vanilla ice cream was frequently used in the research. Other, more colorful, ice creams were also used, but due to the high dilution needed to resolve the problem of interference, the time to obtain results for the recommended method was extended. The results show that traditional ice cream contaminations conformed to Pourmahmoodi’s results [5].

Table 1.
Physiological properties of 48 isolates obtained from different regions for ice-cream.

Table 2.
Characteristics of coliform strains from ice cream compared with milk and reference strain of E. coli.
Phenon 1 isolates were able to form metallic green colonies on Eosin methylene blue (EMB) and violet colonies on Chromocult coliform agar, as well as fluorescence color against a 366 nm UV lamp and positive methyl red. The production of negative movable acetoin were not able to hydrolyze urea or consume citrate. They could, however, hydrolyze lysine and ferment glucose under anaerobic conditions. Only 9% of phenon 1 isolates were able to hydrolyze gelatin, which differed from the standard isolate.
The phenon 2 strain displayed a green metallic sheen on EMB agar, which was different from the standard isolate. On MacConkey agar, however, all cases produced a red colony. On LMX broth, all isolates were blue, but none fluoresced against 366 nm UV. All isolates were motile, unable to hydrolyze urea, and unable to consume citrate, despite being positive for methyl and negative for acetoin. Furthermore, the isolates were unable to hydrolyze gelatin, move, or react with acid/acid + gas, which was similar to the standard isolate and whole-bacteria protein profiles. Nonetheless, the isolates of phenon 2 were not excessively fermented.
Phenon 3 isolates were unable to produce a green metallic sheen on EMB agar or red colonies on MacConkey agar. On Chromocult coliform agar, 50% of the isolates formed violet colonies (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). All isolates produced a blue color in the LMX broth but did not fluoresce when exposed to a 366 nm UV lamp. On nutrient agar, all isolates had yellow pigment. They were unable to consume urea, produce acetoin, hydrolyze gelatin, or hydrolyze lysine. Furthermore, the acid/acid+gas reaction on triple sugar iron (TSI) agar, they produce a positive methyl-red test. These activities were very similar to E. heramanii.
Phenon 4 isolates did not have a green metallic sheen on EMB agar and could not form red colonies on MacConkey agar. These isolates did not hydrolyze urea and did not produce pigment. Furthermore, they were unable to consume citrate, were negative for methyl red, could not produce acetoin, and were immovable, all of which were similar to metabolically inactive E. coli strains based on biochemical tests, but were not E. coli. Phenon 5 isolates did not produce a green metallic sheen on EMB agar and did not form red colonies on MacConkey agar. Moreover, on Chromocult coliform agar, this strain was unable to form violet colonies and was unable to produce blue color and fluorescence in LMX broth. Besides that, in TSI agar, Phenon 5 hydrolyzed urea, consumed citrate, was positive methyl red, movable, and produced an alkaline/acid reaction.
In terms of urea hydrolysis, citrate consumption, the production of red colonies on MacConkey agar, and being negative for methyl red, the isolates of phenon 6 were comparable to the isolate of Klebsiella oxytoca. These isolates were immobile, produced acetoin, acid/acid + gas, and lysine hydrolysis.
The isolates of phenon 7 were very similar to the Morganella morganii isolate in terms of urea hydrolysis, a lack of citrate consumption, and a production of mixed acid (positive red methyl). However, these isolates were unable to produce acetoin, react with alkaline/acid in TSI agar, produce red colonies on MacConkey agar, exhibit metallic green on EMB agar, and emit blue color fluorescence LMX broth.
In the dendrogram of phenotypic characteristics, the isolates of phenon 8 had similar characteristics to M. morganii isolation in terms of the production of mixed acid (positive methyl red) and the alkaline/acid reaction. Urea hydrolysis was variable between the isolates, however. Because M. morganii lacked certain metabolic features and interacted with other Enterobacteriaceae family members, such as by sharing characteristics with E. coli that were metabolically inert, it was not classified as a recognized phenon.
3.2. Electrophoresis of Bacteria Proteins
The regression equation was used to determine the molecular weight of unknown bacterial proteins. The isolate proteins electrophoretically compared favorably to each other and to the standard E. coli ATCC 25922 isolate. However, some variations were also observed. Three isolates contained protein bands with sizes of 80.95, 24.35, 22.15, 17.75, and 12.15 kDa, which were not present in typical isolates. The 20.75 and 23.59 kDa bands were seen in isolate 42. These features differentiated the isolation from the standard. Protein bands measuring 16.66 kDa were present in isolates 5 and 8, which further identified them from the typical strain. Protein bands with a 9.73 kDa size were present in isolates 2, 4, 6, and 8, and they were unique from the reference strain (Figure 2). Protein electrophoresis revealed distinct protein bands for the isolates from traditional and commercial ice creams. Protein bands with sizes of 80.95, 24.35, 22.15, 17.75, and 12.15 kDa were seen in isolate 3, in contrast to the standard isolates. To compare the electrophoretic patterns of E. coli isolates with non-shock isolates, milk samples of E. coli that were directly isolated from livestock centers were utilized (Figure 3). After that, isolates of E. coli were found in milk following a thermal shock (Figure 4). The percentage of similarity could not be calculated precisely since the bands’ positions or severities varied.
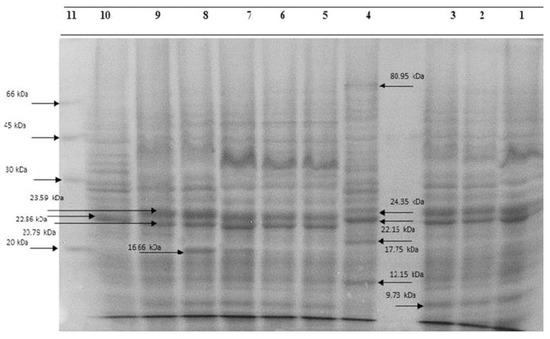
Figure 2.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis whole-bacteria protein profiles of E. coli strains from ice cream. Lane 1, 13 (phenon 1); Lane 2, 1 (phenon 1); Lane 3, 2 (phenon 1); Lane 4, 3 (phenon 1); Lane 5, 5 (phenon 1); Lane 6, 7 (phenon 1); Lane 7, 11 (phenon 1); Lane 8, 12 (phenon 1); Lane 9, 10 (phenon 1); and Lane 10 (reference strain) E. coli ATCC 25922.
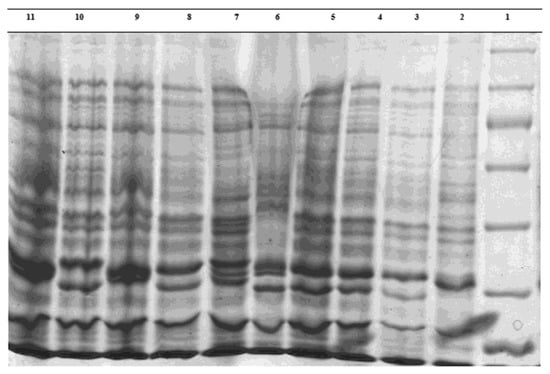
Figure 3.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis whole-bacteria protein profiles of E. coli strains from milk. Lane 1, marker; Lane 2, reference strain E. coli ATCC 25922; Lane 3, E. coli strain 126; Lane 4, E. coli strain 14; Lane 5, E. coli strain 121; Lane 6, E. coli strain 8; Lane 7, E. coli strain 153; Lane 8, E. coli strain 119; Lane 9, E. coli strain 11; Lane 10, E. coli strain 140; and Lane 11, E. coli strain 77.
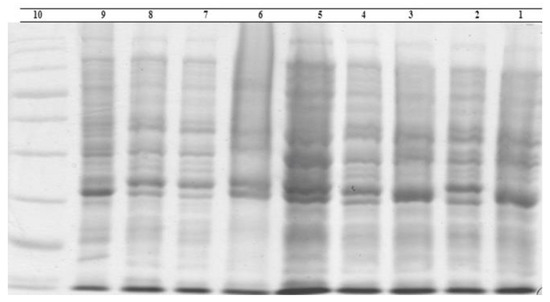
Figure 4.
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis whole-bacteria protein profiles of E. coli strains from milk after the thermal shock. Lane 1, E. coli strain 77; Lane 2, E. coli strain 140; Lane 3, E. coli strain 143; Lane 4, E. coli strain 119; Lane 5, E. coli strain 153; Lane 6, E. coli strain 8; Lane 7, E. coli strain 126; Lane 8, E. coli strain 14; Lane 9, reference strain E. coli ATCC 25922; and Lane 10, marker.
3.3. Sequencing of 16S rDNA
The PCR products were identified and analyzed using agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. After PCR amplification, the size of the amplified fragments (bp) was around 1500 bp (Supplementary Figure S1). The PCR product was first purified before sequencing. Sequencing was conducted using forward primer 27f, which corresponded with the Sanger method by the Macrogen Company (Seoul, South Korean). Therefore, the first 1000 nucleotides were preserved, and the last ones were eliminated. E. coli strain verified for all species. Despite the variations in biochemical testing and protein electrophoresis, all strains of E. coli can be said to be related based on the results of the multiple alignment program blast for the thousand base pair sequence of the 16S rRNA gene fragment (Supplementary Figure S2). The following Genbank accession codes for our nucleotide sequences make it possible to observe the strain-related sequences that were entered into the NCBI’s nucleotide database:
Seq1-KJ660333 (GI: 657085785), Seq2-KJ660334 (GI: 657085786), Seq3-KJ660335 (GI: 657085787), Seq4-KJ660336 (GI: 657085788), Seq5-KJ660337 (GI: 657085789), Seq6-KJ660338 (GI: 657085790), and Seq7-KJ660339 (GI: 657085791).
4. Discussion
The bacteria E. coli is typically detected in the intestines of animals. It is also pathogenic in addition to causing gastroenteritis, bacteremia, and urinary tract infections. Studies have shown that the bacteria is highly susceptible to selection pressure. It has also been shown that it is capable of picking up and transferring antibiotic resistance genes to and from other bacterial strains [36]. There are a number of ways in which bacteria can adapt to adverse or damaging conditions, such as acidic, heat-induced damage, cold-induced damage, starvation-induced damage, oxidative damage, envelope damage, and osmotic stress. The stress-triggered regulatory mechanisms have an impact on all aspects of bacterial survival, including adaptability, physiological alterations, virulence potential, and antibiotic resistance [12].
E. coli is shocked by the various temperature processes in milk, which forces it to make proteins as a result of changes in the production of the strain’s unique set of enzymes. Cells are visibly prompted to produce heat shock proteins (hsps) when they are exposed to greater temperatures. Almost all species have been identified to induce hsps in this way. In E. coli, about 20 hsps are known [37]. The induction of hsps in E. coli is accomplished by increasing hsp gene transcription, which is mediated by the rpoH, htpR, and hin regulatory gene products [38]. One of the issues in the world has always been the prevalence of infectious foodborne diseases, and treating these illnesses costs a great deal each year [37]. Due to its constituent ingredients and the conditions of its manufacturing and maintenance, ice cream has a significant potential for microbial contamination. This study was conducted to determine the phenotypic diversity of E. coli bacteria that commonly cause food contamination in the food production process. The level of microbial contamination in ice cream has been the subject of significant research, but phenotypic diversity and protein profiles, which were the subjects of this study, have received little attention to date. The majority of studies have approached food sample contamination from a health perspective, as shown by the examples in this paper; however, additional molecular studies are required at various points of different food samples. Nearly 60% of raw milk samples were found to be contaminated with E. coli, according to studies by Somur in Pakistan, and these isolates may have changed properties due to thermal processes, making it harder to identify in the final product [39]. It appears that some approaches take into account the design of impedance-based prediction models because of these diagnostic disparities [40]. A total of 90% of the E. coli isolated from raw milk has a typical form, and 10% of the strains are E. coli enterotoxigenic and enteroaggregative strains, according to molecular investigations conducted by Baniadian et al. [41]. As a result, while it is simpler to identify the typical form, and when food is contaminated by the typical form, there is also a possibility that it will be contaminated with potentially hazardous microorganisms.
The 39 physiological and biochemical tests, as well as protein profiles, revealed that the isolates were diverse. Using the numerical analysis of phenotypic characteristics, the samples were divided into eight phenons. Despite the variations in the findings of the biochemical and protein electrophoresis tests, the results of the blast and multiple alignments for the first 1000 bp of the 16S rDNA revealed that all strains were related to E. coli. Because identical conditions were utilized to conduct the PCR reaction in all stages and the use of appropriate primers, only one band, corresponding to 16S rDNA, was detectable in this investigation, and non-specific bands could not be obtained [42]. Thus, our findings showed that it is essential to provide a technique to identify the strain of E. coli in samples. When the number of bacteria in milk is minimal, it is important to detect pathogens early on in the development of an infection [43]. To prevent false negative results brought on by a lack of bacterial growth, PCR can be used to detect bacteria in milk that contain preservatives or residual therapeutic antibiotics [29]. To identify the E. coli strain, high sensitivity, specificity, and speed are also required. The findings of the current investigation show that isolated strains did not match the reference strain exactly. E. coli is an opportunistic pathogen that lives in both other animals and the human colon. Their fecal contamination is brought on by the presence of this bacterium in food and water. The protein profile of the isolates derived from ice cream differs from that of the milk, thus requiring further study, as evidenced by a comparison of electrophoretic patterns between samples of milk and ice cream. Future research is required to determine how much these conditions can alter the bacteria’s biochemical characteristics by using molecular methods to detect genetic alterations carried on by various heat treatments. Furthermore, it is essential to conduct additional analyses of the protein profiles using more accurate techniques, such as two-dimensional electrophoresis, and to learn about the protein sequencing and potential applications of it in the industry as natural antifreeze. In order to ascertain the extent to which various temperature processes are efficient in biochemical modifications, this investigation should be conducted on other pathogenic bacteria, and its acquired results should be compared with reference strain.
5. Conclusions
Considering that food is affected by different temperature processes. It seems that thermal shock causes changes in phenotypic characteristics, especially biochemical tests, and this causes problems in diagnosis. Therefore, diagnostic characteristics that receive the least impact from temperature shocks should be used. Considering that E. coli is the best indicator of fecal contamination and is usually checked in most foods, the characteristics of this bacterium that have less change compared to the reference strain can be used for more reliable diagnosis. Of course, depending on the type of stress, including acid-stress, heat- and cold-stress, starvation-stress, oxidative-stress, envelope-stress-mediated preservative resistance, osmotic-stress, etc., its characteristics may change, which should be considered. The results of the present study indicated that isolated strains did not completely match the reference strain. Results from biochemical tests and protein showed heterogeneous isolates. Our findings revealed that only one band related to 16S rDNA was identifiable and non-specific bands could not be observed. Sensitivity, specificity, and the high rapidity in achieving results are regarded as the advantages of PCR. Based on this, it could be possible to immediately make use of a suitable protective measure for the purpose of diagnosing this type of bacteria, especially in especial environments.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation8120730/s1, Figure S1: Gel electrophoresis of genomic DNA extraction of 7 isolates obtained from ice cream (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9 and 10) in 1% agarose gel in 1x TBE buffer at 100 V (a), PCR amplification pattern of 7 isolates obtained from ice cream amplified by primer pairs 16s27f and 16s1492R as well as molecular marker 100 bp (b). Agarose gel (1%) of purified PCR product from 7 isolates obtained from ice cream indicated (C). Figure S2: Alignment: 16S Aligned Seqs. of E. coli strains obtained from ice cream (1,2,3,4,5,9, 10) in comparison with E.coli (gi|537366568|gb| KF574803.1| Escherichia coli strain CRTY15 16S ribosomal RNA gene, partial sequence)from NCBI.fas.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R., M.G. and R.N.; data curation, M.R., M.G., R.N. and S.S.; formal analysis, M.G.; funding acquisition, M.G.; investigation, M.R., M.G. and R.N.; methodology, M.R., M.G. and R.N.; project administration, M.G. and R.N.; resources, M.R., M.G., R.N. and S.S.; software, M.R., M.G., R.N. and S.S.; supervision, M.G., R.N. and S.S.; validation, M.G.; visualization, M.R., M.G., R.N. and S.S.; visualization, M.R., M.G., R.N. and S.S.; writing—original draft, M.R., M.G. and R.N.; writing—review and editing, M.G., R.N. and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Isfahan (Khorasgan) Branch, Islamic Azad University and Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the Corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all those who helped us finish this work, for their scientific and crucial contributions, and for their participation in our project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Erjavec, M.S. Introductory Chapter: The versatile Escherichia coli. In The Universe of Escherichia coli; Intech Open: Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tortorello, M.L. Indicator organisms for safety and quality-uses and methods for detection: Mini review. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, L.; OSullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.A.; Motazzim-ul-Haque, H.M.; Noor, R. Isolation and identification of pathogenic Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp. and Staphylococcus spp. in raw milk samples collected from different areas of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Stamford J. Microbiol. 2011, 1, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmahmoodi, A.; Mohammadi, j.; Mirzai, A.; Momeni-Negad, M.; Afshar, R. Epidemiological study of traditional ice cream in Yasuj. Armaghan Danesh 2002, 8, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Motarjemi, Y.; Moy, G.G.; Jooste, P.J.; Anelich, L.E. Chapter 5—Milk and dairy products. In Food Safety Management; Motarjemi, Y., Lelieveld, H., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 83–117. [Google Scholar]
- Domenech, E.; Amoros, J.A.; Escriche, I. Effectiveness of prerequisites and the HACCP plan in the control of microbial contamination in ice cream and cheese companies. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jooste, P.J.; Anelich, L.; Motarjemi, Y. Safety of food and beverages: Milk and dairy products. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Motarjemi, Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014; p. 2304. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini-Jazani, N.; Hadizadeh, O.; Farzaneh, H.; Moloudizargari, M. Synergistic antibacterial effects of β-Chloro-L-alanine and phosphomycin on urinary tract isolates of E. coli. BJM 2013, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ori, E.; Takagi, E.; Andrade, T.; Miguel, B.; Cergole-Novella, M.; Guth, B.; Camargo, C. Diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli and Escherichia albertii in Brazil: Pathotypes and serotypes over a 6-year period of surveillance. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Bushlaibi, M.; Alrefaei, R.; Ndegwa, E.; Kaseloo, P.; Wynn, C. Influence of prior pH and thermal stresses on thermal tolerance of foodborne pathogens. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2033–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawan, J.; Juhee, A. Bacterial stress responses as potential targets in overcoming antibiotic resistance. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somero, G.N. The cellular stress response and temperature: Function, regulation, and evolution. J. Exp. Zool. 2020, 333, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, R.I.; Kline, M.P.; Bimston, D.N.; Cotto, J.J. The heat-shock response: Regulation and function of heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones. Essays Biochem. 1997, 32, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.J.; Fort, P.E. Heat shock proteins regulatory role in neurodevelopment. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gross, C.A. Cold shock response in bacteria. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2021, 55, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoza, E.; Singh, H.C. group-mediated antibiotic stress mimics the cold shock response. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3372–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keto-Timonen, R.; Hietala, N.; Palonen, E.; Hakakorpi, A.; Lindstrom, M.; Korkeala, H. Cold shock proteins: A minireview with special emphasis on Csp-family of enteropathogenic Yersinia. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.D.; Kwon, H.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, K.W.; Briles, D.E.; Pyo, S.; Rhee, D.K. Decrease in penicillin susceptibility due to heat shock protein ClpL in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2714–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, M.; Cui, L.; Iizuka, R.; Komoto, A.; Neoh, H.M.; Watanabe, Y.; Hishinuma, T.; Hiramatsu, K. walK and clpP mutations confer reduced vancomycin susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 3870–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.H.; Novak, J.T.; Knocke, W.R.; Pruden, A. Elevation of antibiotic resistance genes at cold temperatures: Implications for winter storage of sludge and biosolids. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Ghaemi, A.; Aslani, M.; Mozafari, N.; Livani, S.; Dadgar, T. The prevalence of enteroaggregative Escherichia coli in cases of diarrhea in Gorgan. J. Gorgan Univ. Med. Sci. 2008, 2, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pickbourn, L.; Ndikumana, L. Does Health Aid Reduce Infant and Child Mortality from Diarrhoea in Sub-Saharan Africa? J. Dev. Stud. 2019, 55, 2212–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Yoosefi, M. The study of effective factors on persisted diarrhea in under five year old children Gorgan and Agh-Ghala health center. J. Gorgan Univ. Med. Sci. 2002, 10, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Black, R.E.; Brown, K.H.; Becker, S.; Alim, A.R.M.A.; Merson, M.H. Contamination of weaning foods and transmission of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea in children in rural Bangladesh. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. 1982, 76, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Baz, A.H. Prevalence, molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Vero toxigenic E. Coli in fresh soft cheese, ice cream and yoghurt in Mansoura city. Alex. J. Vet. Sci. 2019, 62, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, W.L.; Cardoen, S.; Daube, G.; De Block, J.; Dewettinck, K.; Dierick, K. Raw or heated cow milk consumption: Review of risks and benefits. Food Control 2013, 31, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, B.A.; Sahm, D.F.; Weissfeld, A. Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology, 12th ed.; Mosby: London, UK, 2007; pp. 1, 56. [Google Scholar]
- Goli, M.; Ezzatpanah, H.; Ghavami, M.; Chamani, M.; Nedaeinia, R. Multiplex-polymerase chain reaction as a mastitis screening test for major pathogens in dairy cattle farms at different size scales and in several parities. J. Res. Agric. Sci. 2012, 8, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, F.E.G.; Wakelin, D.; Gillespie, S.H.; Despommier, D.D. Topley & Wilson’s Microbiology and Microbial Infections: Parasitology; Arnold, E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; 608p. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Jorgenson, J.H.; Pfaller, M.A.; Yolken, R.H. Manual of Clinical Microbiology; American Society for Microbiology Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 47, pp. 625–626. [Google Scholar]
- Sneath, P.H.A.; Sokal, R.R. Numerical Taxonomy: The Principles of Numerical Classification; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973; 573p. [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khakpour, M.; Garedaghi, Y. Molecular differentiation of sheep and cattle isolates of Fasciola hepatica using RAPD-PCR. Arch. Razi Inst. 2012, 67, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.X.; Zhou, Y.B.; Xiang, X.Z.; Zhu, Z.B.; Pen, L.; Luo, Y.W.; Lu, J. The molecular ecology analysis of microbial communities in waste water–based mud. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.H.; Wei, C.K.; Jing, Y.Q.; Zi, X.L.; Sathish, A.; Mahathir, H.; Cliff, C.; Kelyn, L.G.S.; Siyao, G.; Moon, Y.F.T.; et al. 2020. Occurrence and antimicrobial resistance traits of Escherichia coli from wild birds and rodents in singapore. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Ending Preventable Child Deaths from Pneumonia and Diarrhoea by 2025: The Integrated Global Action Plan for Pneumonia and Diarrhoea (GAPPD); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa, N.; Yura, T. Heat shock protein GroE of Escherichia coli: Key protective roles against thermal stress. Genes Dev. 1988, 2, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, A.H.; Arion, M.A.; Khaskheli, M.; Bhutto, B. Isolation of Escherichia coli from row milk productions in relation to public health sold under market conditions at Tandojam. Pak. J. Nutr. 2002, 1, 151–152. [Google Scholar]
- Fazlara, A.; Maktabi, S.; Norouzi, F. Comparative survey on predictive impediometric models for microbial load in vanilla and cocoa ice-creams produced with traditional and industrial methods. Int. Iran Congress Microbiol. 2016, 12, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bonyadian, M.; Moshtaghi, H.; Akhavan-Taheri, M. Molecular characterization and antibiotic resistance of enterotoxigenic and entero-aggregative Escherichia coli isolated from raw milk and unpasteurized cheeses. Vet Res. Forum. 2014, 5, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ko, K.S.; Hong, S.K.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, H.K.; Park, M.Y.; Miyamoto, H. Detection and identification of Legionella pneumophila by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the RNA polymerase gene (rpoB). J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 54, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negoro, E.; Iwasaki, H.; Tai, K.; Ikegaya, S.; Takagi, K.; Kishi, S. Utility of PCR amplification and DNA microarray hybridization of 16S rDNA for rapid diagnosis of bacteremia associated with hematological diseases. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).